1 Introduction
The Derraman granites intrude the Bulautad gneisses of the Archean domain of the East of the Oulad Dlim Massif, thrust onto the Reguibat Rise of the West African Craton (Fig. 1; Bea et al., 2016). They have been dated from the Cambrian (525 ± 3 Ma; Bea et al., 2016) and interpreted as linked to the rifting of NW Gondwana. The Derraman granites are aegirine–riebeckite A-type granites (Loiselle and Wones, 1979), a volumetrically minor group of the granitoid rocks worldwide, which has attracted attention because of their peculiar geochemical characteristics (elevated HFSE, REE and F contents with high Fe/Mg and Ga/Al ratios) and of their specific geotectonic setting (non-orogenic setting, e.g., Bonin, 2007 and references therein; Eby, 1990, 1992). The nature of the magmatic sources and the relative contributions of the crust and mantle in the A-type granite petrogenesis remain a hotly debated subject at the present time (e.g., Bonin, 2007; Martin, 2006). A significant step to understand these issues has arisen from the combinations of U–Th–Pb, Lu–Hf and oxygen isotopic records in zircons contained in these granites (e.g., Hawkesworth and Kemp, 2006). The nearly identical ionic radii of Zr4+ and Hf4+ and the larger abundance of Zr make that Hf does not form minerals of its own, but is instead always incorporated in Zr minerals. As a consequence, zircon often contains between 0.5 and 1.5 wt. % Hf (Bea et al., 2006; Claiborne et al., 2006) and shows Lu/Hf of ≈ 0.06–0.08, the lowest ration among the minerals that contain Lu and Hf (Bea et al., 2017). Therefore, zircons preserve the original hafnium isotope composition of the magmatic source that formed the rocks they belong to. This allows using the 176Hf/177Hf ratio measured in zircon as an indicator of the contribution of crustal and mantle sources to granite genesis. However, the Hf isotopic system cannot constrain alone, generally, the contribution of mantle magmas in the granite sources. To elucidate this issue properly, Hf measurements must be combined with the oxygen isotope content (e.g., Hawkesworth and Kemp, 2006; Kemp et al., 2005, 2009), which is a robust discriminator of the mantle vs. crust contribution to the granite genesis (Valley et al., 2005).
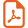
A. Location of studied zone. B. Location of Derraman granites in the Archean domain of the East Oulad Dlim Massif ina new geological map from Bea et al. (2017) and Montero et al. (2017). C. Schematic geological map of the Derraman-Laglat area (Bea et al., 2016).
Bea et al. (2016) have already studied the petrography, whole-rock major element, trace element, Sr and Nd isotope content, and determined the SHRIMP zircon U–Th–Pb age of the Derraman granites. The nature of the magmatic sources remains, however, problematic because of the discrepancy between the zircon U–Th–Pb crystallization age of 525 Ma, and the Nd model age of 1.8 Ga. Here, we report for the first time the zircon Hf-O isotopic compositions of the Derraman granites (20 zircons analyzed in one sample, Reg-122), to understand the discrepancy in the available ages. Based on the new data, we discuss the nature of the magma sources of the Derraman granites, the relative contribution of mantle and crust, and the relationship between the Cambrian A-type granite magmatism and the Paleoproterozoic carbonatitic magmatism in the framework of the West Reguibat Alkaline Province (WRAP, Bea et al., 2016; Montero et al., 2016).
2 Geological setting
The Derraman granites are intruding the Archean gneisses and metapelites of the easternmost part of the Oulad Dlim Massif (Fig. 1A). This massif is adjacent to the Archean TTG (tonalite–trondhjemite–granodiorite) rocks of the Reguibat Shield of the West African Craton (Bea et al., 2016; Montero et al., 2014).
The Oulad Dlim Massif is a crystalline domain formed of strongly and metamorphic deformed rocks (e.g., Michard et al., 2010). It is located west of the Archean Reguibat shield, and separated from it by a thin Paleozoic cover forming the Doloo Esder–Tiznagaten unit (also spelled Dhlou–Sdar–Tiznigated unit, Fig. 1B). This unit disappears to the south, putting the massif directly in contact with the Reguibat shield rocks (Fig. 1B). For Sougy (1962), the Oulad Dlim Massif is “the northern part of the Mauritanide belt” and therefore, a part of the Variscan orogen. Sougy and Bronner (1969) identified a number of nappes in this massif, as shown on the Geological Map of Morocco 1:1,000,000 (Hollard et al., 1985). On this map, the Mauritanide units are featured as a nappe synform preserved on top of the Reguibat shield. However, Villeneuve et al. (2006) discard this interpretation and, based on K–Ar radiometric data, they define four main west-dipping nappes, labeled from west to east: the Oued Togba; Sebkha Gezmayet, Dayat Lawda and Sebkha Matallah Units. Based on a large number of radiometric and isotopic data, Gärtner et al. (2013, 2015, 2016) adopt the same structural interpretation. In the frontal (eastern) part of the latter unit, Rjimati and Zemmouri (2002) individualized the Tiznigaten (sub-) unit made of greenschist-facies quartzite of supposedly Neoproterozoic age. Recent geochronological data, however, have shown that these quartzites are Cambrian–Ordovician (Villeneuve et al., 2015). Montero et al. (2017) found that the western part of the massif, corresponding to the eastern Oued Togba and the western Sebkha Gezmayet units, contains deformed Archean granites similar in age and geochemistry to those found in the Archean Reguibat shield. Accordingly, these authors consider the Oulad Dlim massif as a large synform affecting allochthonous units emplaced over the autochthonous Reguibat Shield, and recognize the following domains from east to west (Fig. 1B):
- • the Archean domain of the East or Bulautad Unit (Montero et al., 2017), mainly formed of deformed leptinitic gneisses (the Bulautad gneisses) covered by the Leglat metapelites, dated to ca. 3.1 Ga and ca. 2.8 Ga, respectively (Bea et al., 2016; Montero et al., 2014). These rock materials host the Cambrian Derraman granites and the Paleoproterozoic Gleibat Lafhouda carbonatites;
- • a Pan-African domain composed of two units: to the east, the Adrar–Sutuf metamafic complex consisting of ca. 605-Ma to ca. 585-Ma (Montero et al., 2017) gabbros, anorthosites and charnokites with scarce granitic gneisses, all of them strongly metamorphosed in the granulite or amphibole facies. To the west, a leucogranitic complex with SHRIMP zircon U–Th–Pb ages between ca. 590 to ca. 570 Ma (Montero et al., 2017);
- • the Archean domain of the West mostly formed of the Gareg syeno-granites and monzogranites with SHRIMP zircon U–Th–Pb ages between 2.90 ± 0.1 and 2.95 ± 0.1 Ga (Montero et al., 2017);
- • a narrow band of strongly deformed ca. 603-Ma to ca. 595-Ma Pan-African granites (Montero et al., 2017);
- • a Devono-Silurian domain comprising strongly deformed granitoids with SHRIMP zircon U–Th–Pb ages of 420–415 Ma (Montero et al., 2016), intruded by ca. 408-Ma undeformed granites (Montero et al., 2017).
3 The Derraman granites
The Derraman granites intrude the Archean Bulautad Unit between latitudes N 22° 36′ 14″ and N 22° 40′ 42″ (Fig. 1B). They form two kilometer-sized distinct bodies, North Derraman and Derraman Highs, and a few small satellites around the latter (Fig. 1C). The North Derraman body is emplaced in the Bulautad leucocratic gneisses, while the Derraman Highs forms a 200-m sheet-like body emplaced within the quartz-muscovite-chlorite Leglat schists. Towards the south, the Gleibat Lafhouda carbonatites that have been dated to ca. 1.85 Ga (Montero et al., 2016) crop out and intrude the Bulautad gneisses (Fig. 1B).
The Derraman granites are variably deformed, medium- to coarse-grained leucocratic rocks comprising a gray groundmass of quartz and alkali feldspar, in which dark clots of mafic minerals define a deformational planar to plano-linear mylonitic foliation associated with top-to-the-east sense of shear (Montero et al., 2017). This penetrative structure is conspicuous at the outcrop scale and compares with that of the Laglat schists; it has been referred to the Variscan thrust tectonics (Michard et al., 2010). Most granites are hypersolvus or transolvus, frequently displaying agpaitic textures. The groundmass consists of mesoperthitic alkali feldspar (average composition Ab60Or40) and quartz. The dark clots are formed of variable proportions of blue amphibole (Ca-rich riebeckite to Na-rich ferrorichterite), green aegirine-augite and annitic biotite, locally muscovitized. The Derraman granites contain abundant accessory minerals such as ilmenite, magnetite, fibrous stilpnomelane, muscovite, fluorite, zircon, apatite and calcite, monazite, fergusonite, aeschynite, samarskite, etc.
The chemical composition is highly silicic, subaluminous, with low Al2O3 and MgO, moderately high Na2O and K2O, and elevated FeOT/(FeOT + MgO). The agpaitic index ranges from 0.94 to 1.12 and about 40% of the analyzed samples are peralkaline. In the high-silica granite classification of Bea et al. (2000), all samples (23 samples from the two bodies of Derraman granites) plot in the A-type granites field. The trace element composition of the Derraman granites is also consistent with the A-type filiation. They have low concentrations of trace alkaline and alkaline-earth elements, but moderate to high concentrations of HFSE, especially Nb and Zr. The REE concentrations are, in general, moderately high, with LaN ≈ 200 and SmN ≈ 100, Eu/Eu* between 0.17 and 0.40, and variable HREE, which, when abundant, either decrease smoothly from Gd to Lu or are slightly concave upwards with a minimum in Er. However, some samples from the Derraman Highs granites are heavily enriched, with LaN ≈ 800 and a small positive Ce anomaly. The samples from the dikes show no significant differences with those from the main Derraman Highs body. According to Bea et al. (2016), all Derraman granites can be classified as A1-type (Anorogenic with Oceanic Island Basalts OIB-like geochemical signature) in the sense of Eby (1990, 1992).
The Sr isotope composition of the Derraman granites is highly variable because the Rb–Sr system was disturbed by post-magmatic events, as it often happens in this type of granites (Montero et al., 1998). In contrast, the 143Nd/144Nd525 Ma ratios are fairly constant in the range of 0.511612–0.511696, with negative values of ɛNd525Ma between–5.2 to–6.8 and an Nd model age of ca. 1.8 Ga. Bea et al. (2016) extracted zircons from four samples and found U–Th–Pb SHRIMP ages between ca. 527 Ma and ca. 525 Ma, except in a younger dyke dated at 514 ± 4 Ma.
4 Material and methods
In the present work, we studied zircons from one sample, REG-122 (long.: –14.5301, lat.: 22.6708), which represents the most abundant type of the homogeneous Derraman granites. This sample, collected from the North Derraman body, is a coarse-grained aegirine–riebeckite granite with 534 ppm of Zr. It contains abundant zircons crystals, mostly 100 to 300 μm euhedral to subhedral short bipyramids or, rarely, short bipyramidal prims (Fig. 2). These crystals are invariably opaque, dark brown or yellow, and show a well-defined oscillatory zoning (Fig. 2). Twenty-two grains were previously analyzed with SHRIMP, yielding a U–Th–Pb crystallization age of 527 ± 3 Ma (Bea et al., 2016).

Cathodoluminescence images ages and O–Hf isotopic values of representative analyzed zircons from REG-122 Derraman granites sampled in the North Derraman body. U–Th–Pb SHRIMP zircon ages from Bea et al. (2016).
Nineteen zircons from the population dated here were analyzed for oxygen isotopes at IBERSIMS laboratory (Granada University, Spain) following the method described by Ickeert et al. (2008). The mounts were slightly repolished and recoated with a 12 nm thick gold layer. The primary beam consisted of a 15-kV and 3- to 3.5-nA Cs ion beam focused to produce a 17 × 20-μm elliptical spot on the sample. The electrical charge of the non-conductive zircons caused by the primary beam was neutralized with an electron beam that impacted the sample in a ∼ 200-μm-diameter spot concentric with the Cs beam. The source slit was fixed at 150 μm, and secondary 18O and 16O were measured simultaneously in static mode on two Faraday cups with entry slits of 300 μm. The sample was pre-sputtered for 180 s prior to analysis. During the last 90 s of the pre-sputtering time, the secondary beam and the electron beam were focused to obtain the maximum signal on the Faraday cups. The measurement consisted of two sets of six scans, each scan lasting 10 s. The mass fractionation caused by the Earth's magnetic field was compensated with Helmholtz coils operated at –309 mA. This compensation also eliminated the mass fractionation related to the horizontal steering of the secondary beam. Electron-induced secondary-ion emission (EISI) was measured for 10 s both at the beginning of each scan and at the end of the measurement; it was then subtracted accordingly. Data reduction was performed using the POXI software developed by Peter Lanc and Peter Holden at the ANU. The zircon standard TEMORA-2 (δ18O = 8.2 ± 0.3 ‰, Black et al., 2004) was measured several times at the beginning of the session and every four unknowns it was cross-checked against the 91500 zircon standard δ18O = 9.86 ± 0.11 ‰, (Wiedenbeck et al., 2004), ten to fifteen replicates of which were measured as unknown interspersed throughout the analytical session.
Zircon Hf isotopes measurements were performed at the Geochronology and Isotope Geochemistry-SGIker facility of the University of the Basque Country (Spain, www.ibercron.es), with a Thermal-Fisher Scientific Nepture MC-ICP-MS device coupled with a New Wave Research UP-213 laser system equipped with a SuperCell laser. The data were collected in static mode during 50 s of ablation with a spot size of 40 μm. The isotopes 171Yb, 175Yb and 175Lu were simultaneously monitored during each analysis step to allow the correction of isobaric interferences between Lu and Yb isotopes on mass 176. The 176Yb and 176Lu were calculated using a 176Yb/175Yb of 0.7964 (Amelia and Davis, 2005) and 176Lu/175Lu of 0.02656 (Patchett and Tatsumoto, 1980), and by taking the instrumental mass fractionation of each individual analysis into account. For instrumental mass bias correction, Yb isotope ratios were normalized to 173Yb/171Yb of 1.13255 (Amelin and Davis, 2005) and Hf isotope ratios to 179Hf/177Hf of 0.7325 (Patchett and Tatsumoto, 1980) using an exponential law. The mass bias behavior of Lu was assumed to follow that of Yb. Data reduction was performed using the Iolite 2.5 software package for deconvolution of time-resolved data (Paton et al., 2011).
To calculate the Hf isotope parameters, we used the following CHUR values 176Lu/177Hf = 0.0336; 176Hf/177Hf = 0.282785 (Bouvier et al., 2008), and λ 176Lu = 1.867·10−11 y−1 (Scherer et al., 2001; Söderlund et al., 2004). We also assumed the mantle source was depleted and changed from chondritic (ɛHf = 0 at 4.56 Ga) to ɛHf0 Ga = +16 at the present time (Vervoort and Kemp, 2016). To calculate the zircon Hf model ages, we used Lu/Hf = 0.092, appropriate for the most felsic A-type granitoids like our analyzed sample (Bea et al., 2017).
5 Results
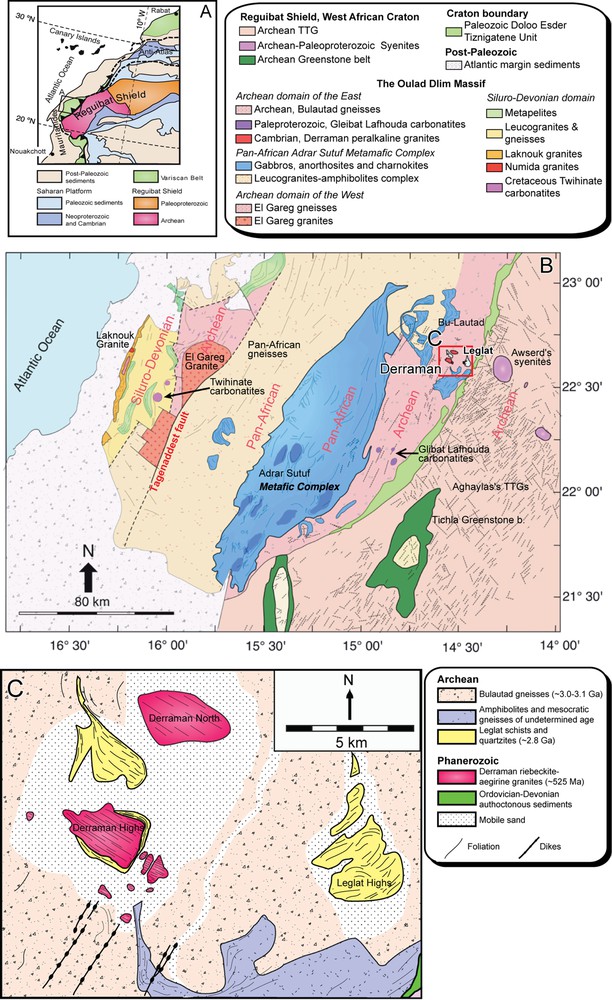
The SHRIMP Oxygen data are summarized in Table S1 in the Supplementary Material. Nineteen O isotopes measurements on 19 zircons (the same zircons dated with the SHRIMP method in Bea et al., 2016) yielded δ18O varying from 4.51 ± 0.35 ‰ to 6.04 ± 0.38 ‰, with an average value of 5.26 ± 0.22 ‰ (Fig. 3A and B), which is identical to the average value in mantle zircons (5.3 ± 0.3 ‰, Valley, 2003 and references therein; Fig. 3B). No relationship between the zircon form or age, on the one hand, and δ18O, on the other hand, was detected (Fig. 2).
A. Zircon O SHRIMP compositions for Derraman granites. B. Frequency and density distribution of the O compositions. C. Zircon Hf compositions for Derraman granites. D. Frequency and density distribution of the O compositions.
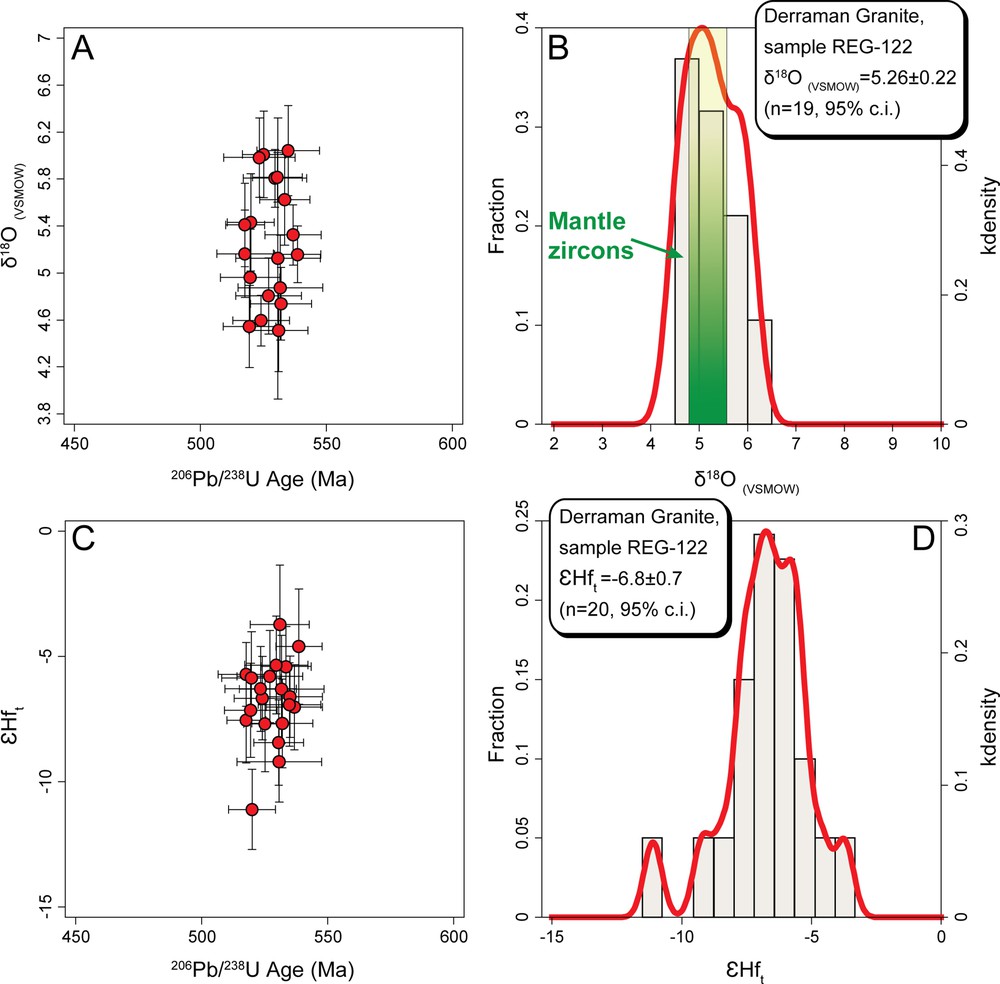
The Hf isotopic compositions were obtained in 20 zircons (the same zircons dated with SHRIMP method in Bea et al., 2016 and analyzed for O isotopes, Table S2 in the Supplementary Material). They are slightly more heterogeneous compared to oxygen isotopic compositions, with negative values of ɛHft Maranging from –3.8 to –10.9 and an average value of –6.8 ± 0.7 (Fig. 3C and D). This ɛHft Ma average value is far different from the Hf isotopic composition of the depleted mantle composition at 525 Ma (the SHRIMP U–Th–Pb age of Derraman granites). The zircon Hf model ages range from 1.6 Ga to 2.0 Ga and average at ca. 1.8 Ga (Fig. 4A), within the error of the whole-rock ca. 1.8 Nd model age (Fig. 4B; Bea et al., 2016).
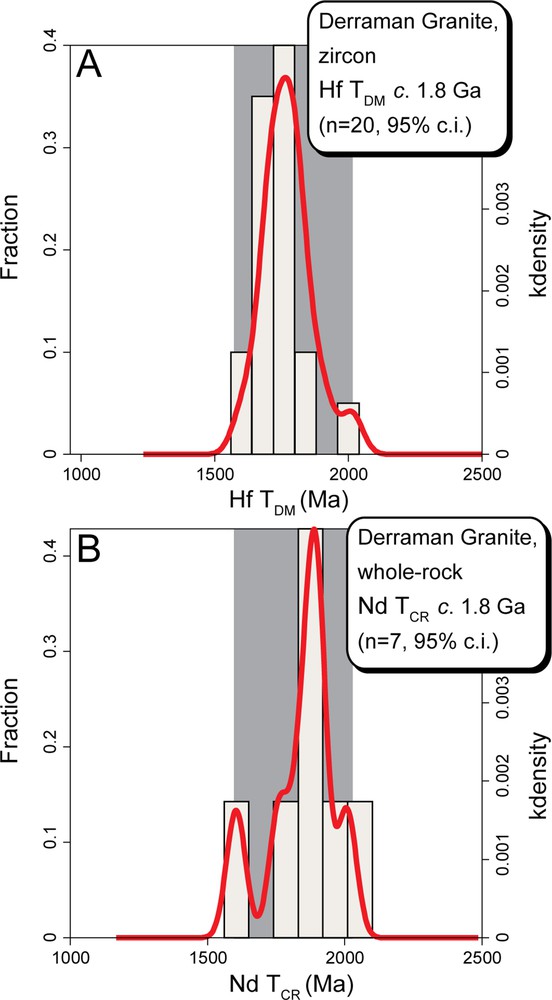
Frequency and density distribution of Hf TDM (A) and of Nd TCR (B) of Derraman granites. Note the similarity between the model age values of Hf and Nd of these granites, which are very far from the zircon crystallization age of ca. 525 Ma.
6 Discussion
Bea et al. (2016), in accordance with Martin's (2006) hypothesis for the genesis of A-type granites, concluded that the Derraman magmas were derived from the melting of crustal fenites, rather than being differentiated from mafic alkaline magmas. However, these authors could not decide whether the “old” Nd isotope signature of the Derraman granites had resulted from the melting of an old (Paleoproterozoic) fenite source, or would rather reflect the mixture of juvenile, 525-Ma magmas with their Archean host rocks.
The coincidental zircon Hf and whole-rock Nd model ages (Fig. 4) and the mantle-like oxygen isotope composition (Fig. 3B) of the Derraman zircons give us the key to understand the nature of the magmatic source.
The δ18O ≈ 5.3 value indicates that the Derraman magmas were not contaminated by their host rocks (Archean leucogneisses and metapelites), since the latter have an oxygen isotope composition markedly richer in the heaviest isotope (unpublished data of the authors). We must thus admit that the contribution of crustal materials was negligible in the granite genesis, and therefore that the ca. 1.8 Ga whole-rock Nd and zircon Hf model ages are related to mantle components. If so, we have to discriminate between two alternatives for the mid-Cambrian magmatism: (i) either melting of old fenites developed at the basis of the crust at ca. 1.8 Ga, with no external income of metasomatic fluids, or (ii) melting of lower crust granulites induced by metasomatic fluids released at ca. 525 from an old lithospheric metasome (e.g., Haggerty, 1999). In the latter case, the external income of metasomatic fluids was able to modify the isotopic composition of the melts. The two mechanisms might equally explain the geochemical characteristics of the Derraman magmas. However, the first mechanism explains better the geochemical signature of the Derraman granites: A-type granites are indeed water-poor (see Bonin, 2007; and references therein), and the Paleoproterozoic fenitization can be related to the 1.8 Ga carbonatitic magmatism that generated the neighboring ca. 1.85 Ga Gleibat Lahfouda carbonatites (Montero et al., 2016) and, probably, the Agracha carbonatites (still undated but with a geological position equivalent to that of Gleibat Lafhouda).
Accordingly, we suggest that the Derraman magmas were derived from the melting of 1.85 Ga crustal fenites during the ubiquitous Cambrian rifting event that affected this part of northern Gondwana (e.g., Stampfli et al., 2013; Torsvik and Cocks, 2013). This event has been well documented in other part of the West African Craton margins, including the Anti-Atlas and southern High Atlas (Álvaro et al., 2014 and references therein) and the Iberian Massif (e.g., Cambeses et al., 2017; Montero et al., 2009a, 2009b), and for the first time in this region of Morocco by Bea et al. (2016).
7 Conclusions
The Derraman aegirine–riebeckite hypersolvus granites, which are intruded in the deformed Archean gneisses of the East Oulad Dlim massif, have whole-rock Nd model ages close to ca. 1.8 Ga but a SHRIMP U–Th–Pb zircon age of ca. 525 Ma, while no inherited older zircon components are observed (Bea et al., 2016).
The new data presented here reveal that the mid-Cambrian zircons in the Derraman granites have Hf model ages around to ca. 1.8 Ga, that is, within error of the whole-rock Nd model age. They also have a mantle-like oxygen isotope composition averaging 5.26 ± 0.22 ‰. All together, these findings indicate that the Derraman magmas were not contaminated by the host Archean leucogneisses and metapelites and, hence, that the contribution of crustal materials to the Derraman magmatic sources was negligible.
We thus conclude that the ca. 1.8 Ga whole-rock Nd and zircon Hf model ages do not represent “mixed” ages (see Arndt and Goldstein, 1987) that would result from the assimilation of the host Archean gneisses and the metasediments, but instead indicate that the Derraman magmatic sources contained old mantle components.
The geochemical characteristics of the Derraman granites are consistent with these granites originating from the melting of fenites (Bea et al., 2016). Given the existence of ca. 1.8 Ga carbonatites in the unit that hosts the Derraman granites, we suggest that the fenites were produced from the interaction between lower crustal materials and alkaline metasomatic fluids released from a lithospheric metasome during the event dated to 1.85 Ga that generated the neighboring carbonatites of Glibat Lafhouda. The so-generated 1.85 Ga fenites likely remained undisturbed in the crust until the Middle Cambrian, when they remelted during the rifting event that affected the northern Gondwana at that time. The remelting then produced the Derraman granites.
Remarkably, the Archean materials of the East Oulad Dlim Massif and the West Reguibat Shield are the locus of a sustained alkaline magmatism that includes (i) the ca. 2.5 Ga kalsilite–nepheline syenites of Awsard–Tadardort, (ii) the ca. 1.8 Ga carbonatites of Gleibat Lafhouda and, probably, Agracha, (iii) the ca. 525 Ma peralkaline granites of Derraman. This paper represents the first step towards the understanding of the link among them.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Prof. Ricardo Arenas, Prof. Youssef Driouch and the editors of this special issue, A. Michard, O. Saddiqi, and I. Manighetti, for their helpful comments and constructive criticisms that greatly improved the manuscript. This paper has been financed by the Spanish grants CGL2013-40785-P and CGL2008-02864, and the Andalusian grant RNM2163. This is IBERSIMS publication No. 54.