1 Introduction
The analysis of various elements relating to the spatial and temporal structure, composition, functioning ecosystems or to the biology of populations, are trend indicators that highlight the causes of regression or development of some taxa in forest ecosystems [1,2]. The interactions between biotic and abiotic factors and their influence on the diversity of insects, the coexistence of species and their distribution in forest have been well documented by Pesson [3].
As for the genus Populus, the etho-bio-ecological context of entomocenosis was approached by several authors [4–6] in terms of annual cycle and phenology. Other scientists have tried to characterize the succession of Aphid generations that occur in galls [7]. Later, Hammond et al. [8] have focused on the spatial and temporal variation of beetle assemblages on poplar. The synchronization of insect pests with the development of the host tree has been particularly studied in the case of poplar [9–11], as it plays a key role on their survival and population dynamics [12]. The influence of nutritional quality on this synchronization goes beyond its availability. In general, in the canopy, the quality of the resource decreases during the growing period [13–16], resulting in the large number of spring species, and especially primary consumer ones, taking advantage of the highest quality for their fitness [15–17]. In addition, physiological changes in the bark affect the development of many species of insects, since Kozlowski et al. [18] and Redmer et al. [19] argue that the degree of lignification, the quantity of water, sugar, protein and secondary compounds vary during the season and could increase or decrease the use of bark as foster substrate. Otherwise, Chararas [1] and Djazouli [20] showed the influence of abiotic factors such as temperature and light intensity on the performance of insects. Moreover, the mechanisms of defense against pests and diseases were assessed by comparing clonal variability of poplar stands [21–23]. Thus, the impact of temporal variations of secondary metabolites on the primary settlement of insects has been particularly studied in connection with the leaf development of their hosts [24–26].
However, few studies have addressed the overall relationships between each of the aerial poplar compartments (leaves, twigs, trunks and galls) and the consequences of physiological changes of host tree on the distribution and composition of communities, or trophic groups. For the sake of objectivity for long-term monitoring and for assessing the conservation state of natural ecosystems, the goal of our approach was to describe the taxonomic composition and the trophic structure of the entomocenosis present in each compartment of Populus nigra, and to evaluate the functioning of trophic groups or communities in relation to phenological characters of the host plant. Preliminary evidence suggests evaluating the following issues: (i) do the communities living on leaves, twigs, trunk and galls share structural and functional similarities? (ii) Do the physiological and seasonal variations of these compartments have an effect on the succession of insect communities and on their temporal abundance variations? (iii) What are the relationships between the trophic groups within each community, and between the different communities themselves?
2 Material and methods
2.1 Presentation of the study sites
The study was conducted on a natural monoclonal poplar stand in the plain of Mitidja (northern Algeria). It is the largest sub-coastal plain of Algeria, with a surface of approximately 140 000 hectares, about 100 km length, and a width varying between 5 and 20 km. On the Northern side, the plain is separated from the Mediterranean sea by the Sahel ride, and on the South, by the Blida Atlas mountain [27].
Two stations have been identified: the Soumàa station, on the foothills of the Blida Atlas is at an altitude of 200 m A.S.L. and south-exposed. It spreads on 4 hectares, and the vegetation is semi-open to open where a shrub layer prevails. The main noticeable tree species are Acacia mimosa, Eucalyptus globulus, Pinus halepensis and Ceratonia siliqua. We also note herbaceous species, as Avena alba, Calendula arvensis, Torilis nodosa, Biscutella didyma, Sinapis alba, Euphorbia helioscopia, Heliotropium europaeum and Borrago officinalis. The Koléa station is located on a surface covering about 6 ha, on the south side of the Sahel at an altitude of 250 m A.S.L. and south-exposed. It has an open vegetation, with an herbaceous layer characterized by the following species: Cyperus rotundus, Centaurea calcitrapa, Dittrichia viscosa, Oenanthe fistulosa, Andryala integrifolia and Sonchus oleraceus.
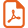
The climate of both stations is Mediterranean with a continental trend (humid stage with cool winter). The precipitation, mostly observed in winter and spring, is characterized by a great inter-annual and inter-monthly irregularity. The coldest month is January (mean minimum temperature of 4 °C and 5.1 °C, and mean maximum temperature of 8.92 °C and 6.66 °C at Soumàa and Koléa, respectively). The warmest months are July and August with mean minimum temperatures of 26.5 °C and 24.8 °C and mean maximum temperatures of 34.8 °C and 32.3 °C, respectively at Soumàa and Koléa (Fig. 1).
Ombrothermic diagram of BAGNOULS and GAUSSEN in the study sites, established from a 10 years period (1993–2003).
The campaign study (2002–2003) was characterized by an annual rainfall of 806.2 mm at Soumàa and 764.4 mm at Koléa, exceeding by almost 120 mm and 102 mm respectively the means observed in the last 10 years. Moreover, the distribution of these rainfalls was irregular, since more than 79% of rain fell between November 2002 and February 2003. The low rainfall recorded between June and October, together with rising temperatures and radiation, result in a strong evaporative demand [28].
2.2 Phenology of poplar
Black poplar is a pioneer species able to settle on fresh environments. The trees are found as spontaneous in alluvial plains, and their growth needs a long favourable period with warm and sunny summers. When these climatic conditions are fulfilled, the budding is precocious and the vegetation growth is sustained until the end of summer [29].
2.3 Sampling
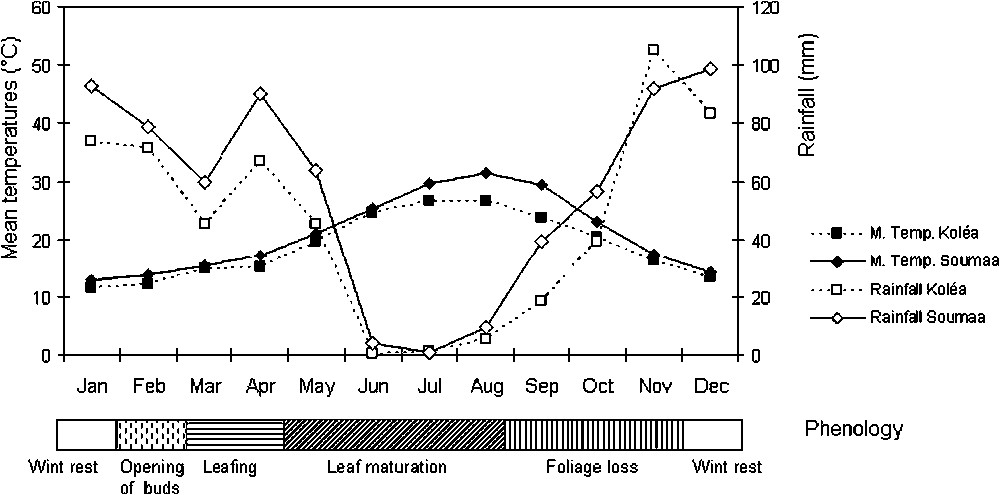
The sampling of entomofauna living on the unit areas defined by the poplar stands began in September 2002 until August 2003, covering a twelve months period. Every 15 days, we carefully examined the aerial compartments of poplar trees (trunk bark, twigs, leaves and galls). Due to a collection orderly and fairly comprehensive in space and time, we have defined for each station 3 transects of 100 m in length (disposition of trees given in Fig. 2), separated by 10 m [30]. In order to get accurate data of community structures, we followed the sampling stratification method described by Atger [31] who showed the good representation of the obtained data. At the level of leaves and twigs of each sampled tree, destructive samplings of 20 cm-long branches bearing about 20 leaves were done in each cardinal directions, at 1.80 m above the ground, so 4 sub-samplings were considered per tree. All the encountered specimens (insects, spiders and galls developed on leaves) were recorded. Fourteen yellow water traps were also placed per station (one yellow plate per tree at 1.50 m above the ground), and renewed every fortnight for counting. The assignation of each collected species to the different compartments were decided according the specific habitat determined by visual samplings. For example, Tapinoma nigerrimum specimens were added to the leave compartment as this ant is mobile on the trunks but stationary at the level of leaves. We completed these collections by the use of a sweeping net at about 2 m above the ground (5 min as unit of effort per tree, i.e. nearly 4 hours of investigation in all).
Experimental disposition of sampled trees within each study sites (a: Soumàa, b: Koléa) : Populus nigra; •: sampling position; Tr: transects.
All the specimens collected were put into jars containing formalin at 33%, and then kept in the laboratory to be identified and quantified. The Diptera were not taken into account due to identification difficulties.
2.4 Data analyses
We used the Michaelis–Menten curve as asymptotic function to estimate the richness of each compartment, following the procedure explained in EstimateS 8.0 manual [32].
The correlation between the abundance of species and the phenological variations in Populus nigra stands was analysed by a detrended correspondence analysis (DCA), followed by a hierarchical classification from Euclidean distances calculated on the coordinates of the first 3 axes of the DCA. It helps to consider the differences in composition and assembly of a sample [33]. The analysis was conducted with the software PAST. vers.1.81 [34], on a matrix based on the abundance (direct and indirect samplings) and periods of investigations in the study areas.
To explore the structure of communities living in the different compartments of Populus nigra, rank-abundance data were plotted and compared to the Motomura model: , where N is the total abundance for a species and R the rank [35]. Slope between communities was compared using the procedure described in PAST vers.1.81 [34]. Briefly, an analysis of covariance was conducted considering the slopes as means and squares of standard errors of x as the variances. The probability was calculated with corresponding Barlett's test.
The significance of temporal variations of logtransformed abundances for each community or trophic group was tested by Kruskal–Wallis tests considering all the species belonging to a community or a trophic group.
The adjustment of time variation abundances (log-transformed) to a normal distribution was assessed by calculating mean and variance. The mean was obtained by calculating the barycentre of the data, using the formula: , where Mi is the number of the ith month, from 1 to 12. The variance was estimated by successive approximation using a least square method. The significance of the lag between temporal distributions of functional groups was assessed by calculating cross-correlation using PAST vers.1.81.
The significance of Jaccard index between 2 communities was assessed by a double resampling method (Permutjac.exe program running on DOS, available on request). Briefly, the Jaccard index between 2 columns is compared to the sorted 1000 ones resulting from resamplings. In each resampling, 100 independent permutations affecting each column are conducted.
3 Results
3.1 Taxonomic composition
A total of 6707 individuals, distributed in 73 species belonging to 35 families were collected in the two study sites. The class of Hexapoda dominated the class of Arachnida with 55 and 18 species respectively. The main orders revealed by this investigation are the Homoptera, Hymenoptera, Coleoptera, and Araneae. Based on the knowledge of their diet and therefore their trophic position, the species fall within primary, secondary, tertiary consumers and trophobionts, in the 4 compartments previously defined (Table 1 and Appendix A). The secondary consumers appeared to harbour the greatest richness with an amount of 35 species. The percentage of primary consumers is relatively similar in the different compartments, often exceeding 80%. Although they belong to different families, they are all specific to Populus genus. Fifty five percent species are opophagous Hemiptera, followed by about 25% of folivorous Lepidoptera, and then folivorous and xylophagous beetles with an abundance of 20%. The Coccinellidae and the Araneae are by far the dominant group among secondary consumers, whereas species belonging to orders Mantidae and Hymenoptera are the most abundant tertiary consumers. These generalist auxiliary species can be found in tree and shrub layers. Finally, trophobionts, especially the families of Formicidae and Apidae, are most of the time confined to Aphididae populations.
Specific richness of entomocenosis in the four compartments.
| I Cons. | II Cons. | III Cons. | Trophob. | Total | |
| Trunk | 3 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 11 |
| Twigs | 8 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 14 |
| Leaves | 13 | 20 | 4 | 5 | 42 |
| Gall | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
3.2 Temporal global analysis of communities
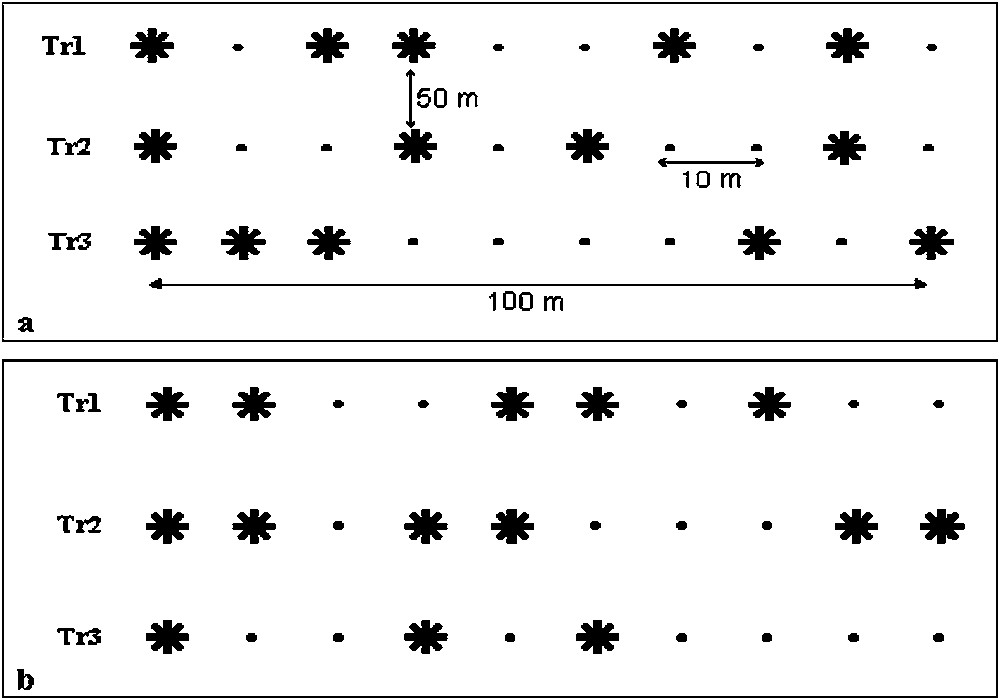
In a first time, the table of samplings including the 4 compartments was submitted to a DCA. In the factorial plan defined by Axis 1 × Axis 2, the distribution of species is dispersed (Fig. 3), indicating that the different components of Poplar entomocenosis seem to react differently to seasonal constraints. The ordination plan and the hierarchical classification based on the first 3 axes of DCA (data not shown) show a non-seasonal assemblage, distributed at the centre of the projection, and four well separated seasonal ones, named “early spring”, “spring-summer”, “late summer” and “autumn” on the base of the concerned months. Among the latter assemblages, the autumn one is situated at the right side of axis 1. At the opposite, the summer assemblage is projected toward the negative values of axis 2, whereas early-spring and spring summer ones on the positive values.
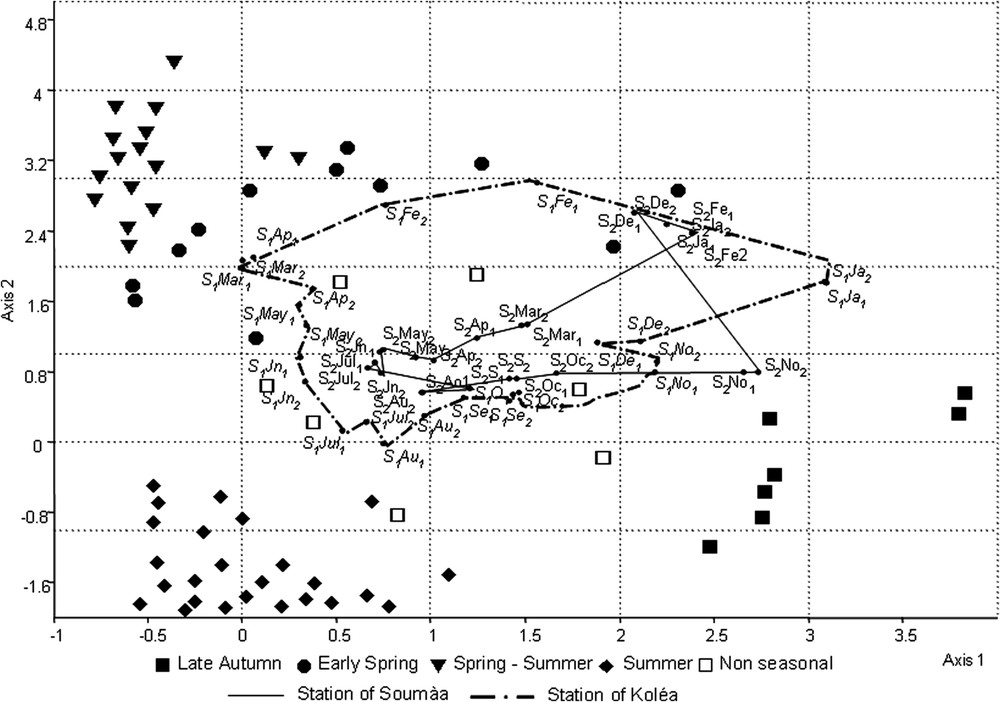
Detrended correspondence analysis (DCA) of assemblages living on Populus nigra from Soumàa and Koléa sites.
The same ordination plan shows a superposition of projections stations of Koléa and Soumàa between May and November, a period during which we observe the highest diversity and densities, reflecting the overall composition consistency of both stations (Table 2). This uniformity has led us to consider the mean abundances of all species for each group over the 2 stations. The estimated richness of each compartment during the May–November period (Table 3) is very close to the corresponding observed numbers of species, providing a good confidence in our samplings.
Monthly variations of Euclidean distances (calculated from the first 3 axes) between the projections of both stations.
| January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December | |
| Euclidean Distances | 0.677 | 0.759 | 0.942 | 0.741 | 0.215 | 0.276 | 0.572 |
Distribution of species and individuals in the 4 compartments between May to November in both stations.
| Leaves | Twigs | Trunk | Galls | |
| Observed number of species | 34 | 14 | 6 | 5 |
| Estimated number of speciesa | 38 | 17 | 7 | 5 |
| Individual total count | 2191 | 284 | 42 | 322 |
a From Michaelis–Menten richness estimator.
3.3 Community structures
For each compartment, the adjustment of rank-abundance (log-transformed abundances) diagrams to the geometric series of Motomura was assessed by calculating Pearson coefficients. Unexpectedly, two communities are identified in the leaves compartment, significantly differing by their respective slopes (∗∗∗). In contrast, the other three compartments contain only one community, as proved by homogeneous rank-abundance profiles. It appears that the 5 communities (Leaves 1, Leaves 2, Twigs, Galls and Trunk, named respectively L1C, L2C, TwC, GC and TrC in the following) are well modelled by the series of Motomura (Table 4).
Slope comparisons between the different communities.
| Leaves 1 | Leaves 2 | Twigs | Galls | Trunk | |
| Slopes | −0.61835 | −0.10911 | −0.311412 | −0.63901 | −0.44611 |
| Adjustment to Motomura model (P) | 5.34 × 10−3⁎⁎ | 8.81 × 10−31⁎⁎⁎ | 7.58 × 10−9⁎⁎⁎ | 2.01 × 10−3⁎⁎ | 6.15 × 10−16⁎⁎⁎ |
| Leaves 1 | – | ||||
| Leaves 2 | 3.81 × 10−36⁎⁎⁎ | – | |||
| Twigs | 3.62 × 10−10⁎⁎⁎ | 3.64 × 10−21⁎⁎⁎ | – | ||
| Galls | 0.9495NS | 3.99 × 10−38⁎⁎⁎ | 7.05 × 10−5⁎⁎⁎ | – | |
| Trunk | 8.08 × 10−3⁎⁎ | 1.35 × 10−29⁎⁎ | 3.2710−2⁎ | 0.0541 | – |
⁎ ;
⁎⁎ ;
⁎⁎⁎ .
The slope comparisons establish significant differences between the structures of the different communities, except for L1C compared to GC, and marginally for GC and TrC (Table 4 and Fig. 4). The richest and most balanced community is L2C, comprising 37 species, while the poorest one is L1C with only 5 (Chaitophorus leucomelas, C. populi-albae, Monosteira unicostata, Tapinoma nigerrimum and Crematogaster scutellaris). In L2C, the abundance ranks of primary consumers are lower than those of tertiary consumers, indicative of a significantly higher average abundance (Kruskal–Wallis test, ). In the same community, the trophobionts have marginally significant lower abundance ranks than tertiary consumers (). As for TwC, no significant difference was recorded in the average abundance ranks between trophic groups.
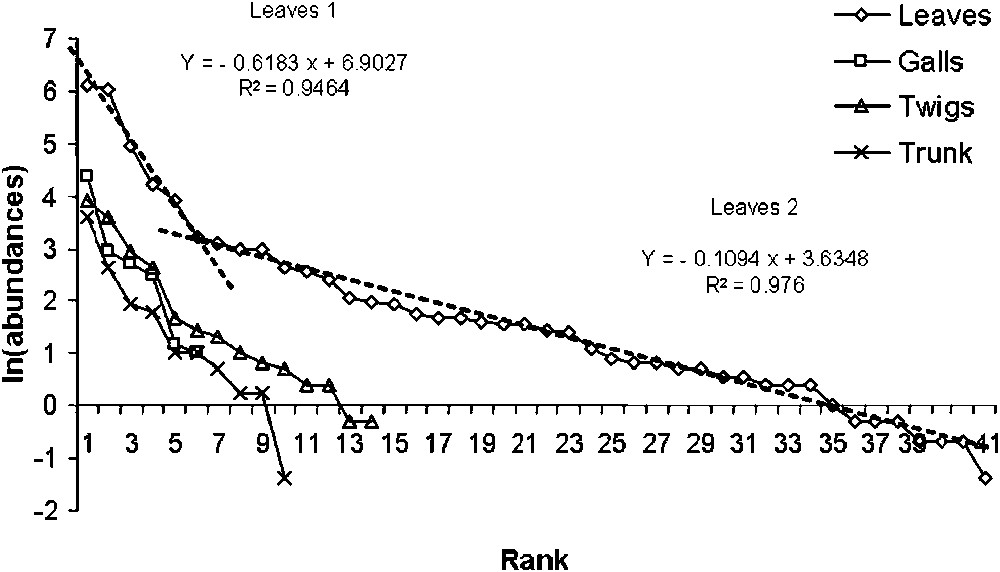
Adjustment of communities to the geometric series of MOTOMURA (ranks and logarithm of species abundances).
3.4 Faunal comparisons between communities
The calculation of Jaccard similarity indices (Table 5) shows that the faunal compositions differ highly significantly between communities. Indeed, only three species are shared by 2 compartments: Sphodromantis viridis (tertiary consumer) is common to TwC and L2C, Oenopia doublieri (secondary consumer) to TwC and GC and Crematogaster scutellaris (trophobiont) to L2C and GC.
3.5 Successions within Leaves, Twigs and Galls compartments
The position of abundance–time curves, their forms and their limits illustrate how species choose the compartment in which they specialize; this adjustment ensures succession meaning and the speed of their dynamics. In each community, we have separated the different functional groups in order to better visualize their temporal variation, using a synthetic curve (average abundances of different species).
The L1C comprises three opophagous Hemiptera (Chaitophorus leucomelas, C. populi-alba and Monosteira unicostata) and two trophobiont ants (Tapinoma nigerrimum and Crematogaster scutellaris). Their density are maintained at a high level throughout the season, and show no significant temporal variation (Kruskal–Wallis test, ).
In L2C, the primary consumers are organized into two groups, significantly different by their temporal abundance variations (Kruskal–Wallis, ). The early group, peaking in April (Fig. 5a), includes mostly opophagous species leaving on galls (Pemphigus versicarius, P. bursarius and P. protospirae). The following group culminates in July and comprises mainly folivorous species (Coleoptera Chrysomelidae; Lepidoptera Lyonetiidae, Lymantridae, Lithocolletidae, Stigmellidae and Notodontidae). The secondary consumers also show significant temporal variations, but with a unimodal distribution (), peaking in June (Fig. 5b), where 3 groups follow each other with a significant time lag (Table 6): Araneae, Anthocoridae–Coccinellidae and Hymenoptera (cross-correlation tests, and respectively). Tertiary consumers (mostly Mantidae) and trophobionts do not show significant variations over time (Kruskal–Wallis test, and respectively).
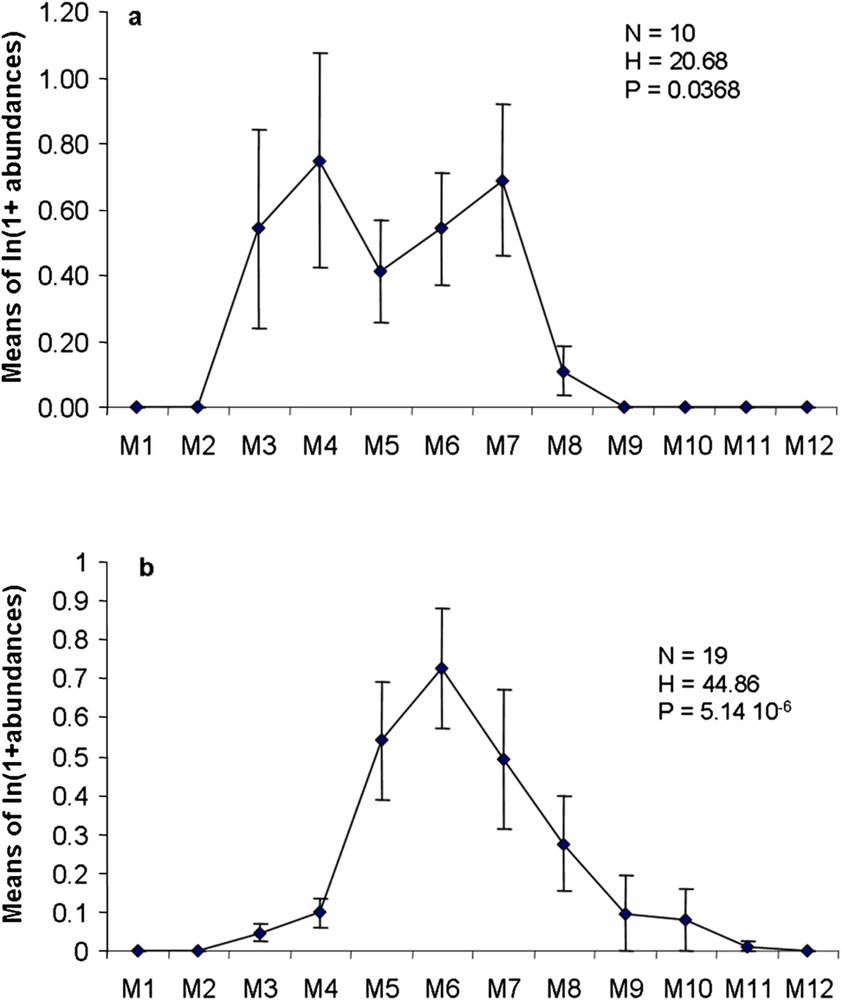
Succession of functional groups in the Leaves 2 compartment of Populus nigra; a: primary consumers; b: secondary consumers.
Temporal lag between trophic groups.
| Compartments | Functional groups | Cross-correlation test | |||
| Barycentrea | Lag. | P | |||
| Leaves 1 | CI | Chaitophorus leucomelas | 7.40 | 1 | 5.91 × 10−3⁎⁎ |
| Troph. | Tapinoma nigerrimum | 6.57 | |||
| CI | Chaitophorus leucomelas | 7.40 | 2 | 1.58 × 10−2⁎ | |
| Troph. | Crematogaster scutellaris | 4.59 | |||
| Leaves 2 | CI | Spring opophagous group | 3.82 | 3 | 1.9 × 10−4⁎⁎⁎ |
| Summer phyllophagous group | 6.30 | ||||
| CII | Araneae group | 4.94 | 1 | 5.15 × 10−4⁎⁎⁎ | |
| Anthocoridae–Coccinellidae group | 6.34 | ||||
| CII | Anthocoridae–Coccinellidae group | 6.34 | 1 | 2.24 × 10−2⁎ | |
| Hymenoptera group | 7.54 | ||||
| Twigs | CI | Spring-summer group | 4.92 | 4 | 6.7 × 10−35⁎⁎⁎ |
| Automnal group | 10.02 | ||||
| CII | Spring-summer group | 3.09 | 6 | 6 × 10−24⁎⁎⁎ | |
| Automnal group | 11.64 |
⁎ ;
⁎⁎ ;
⁎⁎⁎ .
a A barycentre at 7.40 means that the maximum Esperance to find the species is between the 7th and the 8th months, i.e. July and August.
At the level of TwC, the primary and secondary consumers are recorded throughout the year, without significant temporal variation (Kruskal–Wallis test, and respectively). However, within each type consumers in TwC, 2 groups can be identified and well separated, the first in spring-summer and the other in autumn (Table 6). In contrast, GC contains mainly secondary consumers where no subgroup can be defined, and no temporal variation observed (Kruskal–Wallis, ).
4 Discussion
One of the innovative characters of our work, identified by rank-abundance diagrams and comparisons of fauna, is that: (i) the structures of the communities in compartments of leaves, twigs, galls and trunk are significantly different; and (ii) the L2C houses 2 communities structurally and functionally different in terms of temporal variation and overall abundance. Compared to the questions mentioned in the introduction, we thus show a strong specialization of different communities or trophic groups compared to the quality of the substrate. The study of the temporal variation of each of these communities helps to interpret their determinism.
The L1C is characterized by a high density and a spectrum of activity spreading over the entire year. Although the species forming this group are mostly trophic specialists, their temporal abundance did not significantly differ. The pivotal point of this plant–insect relationship is the pioneer species Chaitophorus leucomelas whose founders show an affinity for newly developed leaves. While the young leaves of the Populus are known by their high concentration of phenolic compounds [36], and by flavonoids up to 8.1% of dry matter [37], this has not prevented the continuity of the consumption for all the remaining phenological phases. The work of Chararas [1] supports this idea by the fact that a numerous opophagous insects, through symbiotic micro-organisms or by the action of enzymes individuals, cope with toxic substances, often acting as phagostimulants. Meanwhile, it appears that the first colonies of C. leucomelas can recruit Crematogaster scutellaris workers which keep their brood already installed on the galls of P. lichtensteini. This trophobiont relationship will disappear once the colonies of Tapinoma nigerrimum have entered activity. The present association during the expansion phase of leaves is linked to the ants seeking of a major source of sugars in the form of honeydew [38,39]. After the leaf expansion phase, we observe the settlement of generalist opophagous immigrants represented by Chaitophorus populialbae and Monosteira unicostata which will run until the end of the cycle, taking advantage of the high rate of amino acids present in the sap during the growth and senescence of leaves [2].
In L2C, the temporal abundance variations of taxa differ very significantly between early spring and late summer, indicative of some specificity related to phenological characters of the leaves. The recruitment of spring group is due to the installation of opophagous gall species, specifically on petioles (P. bursarius and P. protospirae) and on leaf blades (Pemphigus versicarius), where their abundance coincides with the leaf expansion phase, at a required period for the development of the galls that can receive their progeny. Urban [40] reports a similar observation on the gall aphids leaving on the leaves of P. nigra, and shows that during the expansion phase, the leaf surface is proportional to the size of galls, and as a result of salivary secretions, young leaf tissues react by forming a hypertrophy that Pautov [41], considered as a stimulation of the subepidermic layer, homologous to a leaf at an early stage. Through the maturation phase of leaves that begins in June, we observe the installation of the late L2C, which is specifically enriched by the recruitment of leafminers (Stigmella trimaculella, Phyllocnistis suffusella and Paraleucoptera sinuella) and folivores (Dicranura vinulla, Stilpnotia salicis and Lymantria dispar). During this phase, the foliar concentrations of water, nitrogen and amino acids linked to proteins are relatively weak whereas there is a higher availability of soluble carbohydrate and more stable amounts of glucose, fructose and sucrose, which would correspond to an optimum quality for the fitness of the folivorous species. In contrast, Gruppe et al. [24] and Osier et al. [42] showed that there is an overall high level of condensed tannins and phenolic glycosides, although irregular over time and not susceptible to environmental factors. Due to a clear majority of specialist species, it is likely that this summer community has a trophic adaptation to toxic compounds, and as a result can acquire reproductive performance through the maintenance of the energy resource.
It appears a parallel with the community composition of saproxylic beetles that depends on the stocks of dead wood (softwood and hardwood). In particular, several works point out that the structural differences between communities depend on the state of wood decomposition [43,44]. In the same context, two studies [45,46] show that the availability of faunal communities living on four species of Pinus sp. varies significantly over time depending on their weakness degree.
The secondary consumers show a significant temporal variation of abundance, with a summer peak of richness and diversity. The succession of spiders, ladybugs-anthocorids and hymenoptera would therefore partly explain the decrease of preys observed during May and June. Information on the relative partition of preys is lacking and it is therefore impossible to estimate the impact of each trophic group. However, the relatively large number of opophages indicates that the partition of energy flow is moderate, mainly due to the activity of Coccinelidae compared to other groups. The unimodal abundance distribution of secondary consumers is essentially due to this last family, since Burgio et al. [47,48] stated that the period between late May and early July is critical for maintenance of these predator populations that are in breeding season.
Temporal analysis of composition fauna among tertiary consumers shows a stability of the ecological integrity of the leaves compartment. Through their spectrum of abundance over time behind the secondary consumers, the Mantidae participate to maintain a mutual pressure on secondary consumers in May, but at a higher level in August and November, probably related to the recruitment of Pemphigidae exiles [40], and the availability of alternative foods to reach sexual maturity [40,49].
The distribution of the temporal abundance of trophobionts is characterized by a stability which is justified by mutualism (trophobiosis) with Homoptera. The association of Formicidae populations to C. leucomelas and C. populialbae during the spring-summer period assumes that the aphids provide a source of energy known by many ants [39,50], and that the ants have a permanent access to a source of honeydew, thus avoiding the problems linked to the seasonal variation of nectar production by the host plant [51,52].
In the TwC, the primary consumers do not show temporal variation of abundance within a year, but their choice performance of foster supply varies depending on the physiological stage of the poplar. The lag time between the spring-summer and the autumn groups is attributed to seasonal variation in the quality of reserves carried by the sap flow in the twigs of the year and in the lignified ones. It is assumed that the installation of early spring-summer trophic group on the twigs of the year would give the larvae of opophages (Aphididae, Issidae and Asterolecaniidae) and xylophagous beetles (Cerambycidae) more chance to survive until adulthood. Later in autumn, with the lignification of twigs, the bark enhances their defense resources [36]. Although their nutritional value is lower [53], populations of Pterocomma populeum and Phloeomyzus passerinii recover [54,55] and complete their development, probably explaining the high abundance observed in autumn.
Among secondary consumers, the lag time between the spring-summer and autumn groups seems to be mainly influenced by the availability of prey. Because they build up strong relationships with Aphididae, secondary consumers (mostly Coccinellidae) respond to outbreaks of P. populeum and P. passerinii during spring-summer and autumn [54]. The canopy Coccinellidae, with sufficiently distinct ecological niches and using different resources, avoid direct competition that would cause local extinction of a species (competitive exclusion, see [56]).
The galls resulting from Pemphigidae founders get dried and fall during the defoliation of the host plant, except those of P. lichtensteini which are already constructed on twigs at the beginning of winter, get lignified and dry completely to form a shelter for species characteristic of the canopy, as Oenopia doublieri and Crematogaster scutellaris.
The high density of the different larvae stages of Phloeomyzus passerinii on lignified parenchymatous tissues of the trunk [55] during spring-summer and especially autumn is responsible of the harmful character of this opophagous insect to Populus. Its timing with the sap in the senescence phase allows it to acquire its energetic needs to overcome dormancy phase of his host, since Kozlowski et al. [18] demonstrated that the biochemical conditions prevailing in favourable season in terms of carbon and nitrogen amounts are still stored in the wood. Although the bark of the trunk can be compared to the twig's one, with significantly lower level and more diversified defense resources [36,57], the females of P. passerinii survive until the following season.
In the present analysis, the particular individualization of primary consumers can obviously be explained by their residential character on each compartment. In addition, the amplitude of phytochemical and histo-physiological changes in leaves compared to other compartments, throughout the growing season, modulates the recruitment of a large variety of taxa. It follows a succession of communities affected by the seasonal variation in leaf, and the requirements of reproductive trophic groups. However, it appears that the fitness of trophic groups takes advantage of adopting a temporal lag of abundance on sufficiently distinct ecological niches and using different resources.
Acknowledgements
This study, belonging to “Globalbiodiv” program, was financially supported by Tassili 08MDU726, in a PAI/CMEP cooperation. The technical assistance of Florence Vallet was highly appreciated.
Appendix A
| Comp. | Order | Family | Species | Funct. gr. | N |
| Trunk | Arachnida | Zodariidae | Zodarion algiricum | CII | 24 |
| Linyphiidae | Lepthyphantes djazairi | CII | 5 | ||
| Philodromidae | Philodromus cespitus | CII | 8 | ||
| Philodromus sp | CII | 12 | |||
| Gnaphosidae | Nomisia castanae | CII | 9 | ||
| Theridiidae | Enoplognatha sp | CII | 28 | ||
| Orthoptera | Acrididae | Anacridium aegyptium | CI | 5 | |
| Ochrilidia filicornis | CI | 1 | |||
| Hymenoptera | Formicidae | Aphaenogaster testaceo-pilosa | Troph | 55 | |
| Heteroptera | Nabidae | Himacerus apterus | CII | 11 | |
| Hemiptera | Aphididae | Phloeomesus passerini | CI | 356 | |
| Twigs | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Pemphigus lichtensteini | CI | 198 |
| Phloeomyzus passerini | CI | 146 | |||
| Pterocomma populeum | CI | 56 | |||
| Issidae | Hysteropterum grylloides | CI | 9 | ||
| Asterolecaniidae | Asterolecanium muni | CI | 15 | ||
| Coleoptera | Coccinellidae | Psyllobora vingintiduopunctata | CII | 17 | |
| Oenopia doublieri | CII | 14 | |||
| Coccinella algerica | CII | 8 | |||
| Buprestidae | Capnodis miliaris | CI | 3 | ||
| Melanophila picta | CI | 5 | |||
| Cerambycidae | Saperda carcharias | CI | 11 | ||
| Carabidae | Calathus melanocephalus | CII | 6 | ||
| Calathus fuscipes | CII | 3 | |||
| Mantoptera | Mantidae | Sphodromantis viridis | CIII | 5 | |
| Galls | Arachnida | Salticidae | Salticus sp5 | CII | 60 |
| Gnaphosidae | Zelotes bernardi | CII | 13 | ||
| Psocoptera | Sphaeropsocidae | Troctes divinatorius | Succ | 106 | |
| Coleoptera | Coccinellidae | Oenopia doublieri | CII | 63 | |
| Curculionidae | Rhynchites sp | CI | 48 | ||
| Hymenoptera | Formicidae | Crematogaster scutellaris | Troph | 39 | |
| Chalcidoidea | ? | CIII | 11 | ||
| Leaves | Hemiptera | Aphididae | Chaitophorus leucomelas | CI | 1829 |
| Chaitophorus populialbae | CI | 556 | |||
| Pemphigus prostospirae | CI | 78 | |||
| Pemphigus bursarirus | CI | 90 | |||
| Pemphigus versicarius | CI | 19 | |||
| Tingidae | Monosteira unicostata | CI | 201 | ||
| Coleoptera | Coccinellidae | Platynaspis luteorubra | CII | 56 | |
| Hyperaspis algerica | CII | 76 | |||
| Adalia decempunctata | CII | 44 | |||
| Scymnus mimulus | CII | 9 | |||
| Scymnus subvillosus | CII | 12 | |||
| Chrysomelidae | Syntomus fascomacielatus | CI | 32 | ||
| Mantoptera | Mantidae | Sphodromantis viridis | CIII | 18 | |
| Iris oratoria | CIII | 8 | |||
| Ameles abjecta | CIII | 7 | |||
| Ameles africana | CIII | 3 | |||
| Lepidoptera | Lyonetiidae | Paraleucoptera sinuella | CI | 19 | |
| Lymantriidae | Lymantria dispar | CI | 7 | ||
| Stilpnotia salicis | CI | 1 | |||
| Lithocolletidae | Phyllocnistis suffusella | CI | 28 | ||
| Stigmellidae | Stigmella trimaculella | CI | 24 | ||
| Notodontidae | Dicranura vinulla | CI | 17 | ||
| Hymenoptera | Formicidae | Crematogaster scutellaris | Troph | 277 | |
| Tapinoma nigerrimum | Troph | 1652 | |||
| Cataglyphis bicolor | CII | 99 | |||
| Messor barbara | Troph | 9 | |||
| Pheidole pallidula | Troph | 51 | |||
| Apidae | Apis mellifera | Troph | 21 | ||
| Vespidae | Polistes gallicus | CII | 3 | ||
| Chrysidae | Chrysis ignita | CIII | 6 | ||
| Arachnida | Salticidae | Salticus sp2 | CII | 6 | |
| Salticus sp3 | CII | 8 | |||
| Salticus sp4 | CII | 4 | |||
| Salticus sp1 | CII | 6 | |||
| Oonopidae | Gasamorpha loricatula | CII | 2 | ||
| Lycosidae | Trabaea paradoxa | CII | 2 | ||
| Clubionidae | Mesiotelus mauritanicus | CII | 3 | ||
| Scotina celans | CII | 10 | |||
| Gnaphosidae | Zelotes poecilochroaeformis | CII | 2 | ||
| Palpimanidae | Palpimanus sp1 | CII | 2 | ||
| Heteroptera | Anthocoridae | Anthocoris nemorum | CII | 29 | |
| Pentatomidae | Zicrona coerulea | CII | 12 | ||
| Nabidae | Himacerus mirmicoides | CII | 19 |