Version abrégée
1 Introduction
Au sein des profils latéritiques typiques en Afrique, Australie et Inde, l'horizon tacheté constitue la transition entre les horizons d'altération et les horizons ferrugineux cuirassés et nodulaires superficiels [1,4,9–12,18]. L'altération fournit des volumes riches en kaolinite néoformée et d'autres riches en quartz hérité [17,18]. Dans les volumes riches en kaolinite, au sein de l'horizon tacheté, le quartz est dissous [11] et la kaolinite substituée par de l'hématite [2]. Ainsi s'individualisent des taches rouges ou violacées. Localement, en présence de gœ thite, se forment des taches jaunes. Dans les volumes riches en quartz, un lessivage différencie des taches grises [3]. Vers le haut des profils, les taches rouges ou violacées se concentrent et s'indurent pour former successivement la carapace, la cuirasse et les horizons nodulaires. L'horizon tacheté évolue en cuirasse ferrugineuse (pétroplinthite) par concentration du fer et induration. L'absence d'horizon cuirassé ou nodulaire au-dessus d'un horizon tacheté, décrite en Afrique, est le résultat d'une ablation de la cuirasse [5,8]. Contrairement au cas de l'Afrique, de vastes étendues au Brésil présentent un horizon tacheté peu profond (plinthite ou paraplinthite) et peu d'affleurements de cuirasse ferrugineuse [13,14,16]. La cuirasse a-t-elle disparu ou ne s'est-elle pas formée ? En contribuant à la connaissance des couvertures à latérite d'Amazonie, l'objectif est de montrer qu'un horizon tacheté peut aussi se former du fait d'une perte en fer.
2 Site et méthodes d'étude
Le site est localisé dans le Bassin amazonien, entre Porto Velho (État du Rondonia) et Humaitá (État d'Amazonas) au Brésil. La pluviosité annuelle est de 2250 mm et l'évapotranspiration annuelle de 1500 mm, avec une saison sèche de juin à juillet (précipitation mensuelle inférieure à 40 mm). Des plateaux peu ondulés supportent une végétation de forêt ou savane. Des cambisols plinthiques [6] prédominent au sein de la couverture à latérite développée à partir de sédiments terrigènes (Pliocène moyen à supérieur) [14]. Une nappe est présente à faible profondeur (1 m), excepté durant la saison sèche (3 m). L'observation du sol et les prélèvements ont été faits dans une tranchée (profonde de 3,5 m) localisée sur une partie haute de plateau [15]. Des lames minces ont été observées en microscopie optique et en microscopie électronique à balayage (MEB) avec un détecteur d'électrons rétrodiffusés, puis des analyses chimiques quantitatives ont été réalisées à l'aide d'une microsonde [7]. Sur des aires de 20×20 μm, des cartes de la composition chimique ont été obtenues en dosant les principaux éléments (Si, Al, Fe, Ti et K) selon un espacement de 1 μm entre les points de mesure, puis en interpolant les données par krigeage linéaire.
3 Résultats
1. Le sol présente, de bas en haut, un horizon tacheté, un horizon de transition, un horizon subsuperficiel rouge, puis un horizon superficiel humifère. Au sein de l'horizon tacheté, épais de 2,5 m, se distinguent nettement des taches rouge vif (RV) 10R 4/8 à 2,5YR 4/6 (teinte Munsell à l'état humide), rouge sombre (RS) 10R 3/6, gris clair (GC) 10YR 7/2 et jaune vif (JV) 10YR 7/8. Les taches rouges forment un réseau tridimensionnel (1 à 3 cm de large) à allongement préférentiellement vertical, tandis que les taches GC forment un réseau imbriqué dans le précédent. La porosité est faible, principalement localisée dans GC. Dans l'horizon de transition (1,1–0,6 m de profondeur), les taches diminuent de taille et de proportion, alors que leurs teintes sont progressivement moins vives. Au-dessus, l'horizon subsuperficiel est rouge 2,5YR 5/6, puis l'horizon humifère est brun 5YR 4/4 à 10YR 3,5/2. L'importante fraction argileuse (Tableau 1) est constituée de kaolinite et d'illite, avec, en plus, de la vermiculite alumineuse dans l'horizon rouge [15]. La teneur totale en SiO2, Al2O3 et Fe2O3 varie sensiblement au sein de l'horizon tacheté et faiblement au contact de l'horizon subsuperficiel (Tableau 1).
Granulometrical and chemical composition (g per 100 g) of the mottled horizon (H1), the intermediate horizon (H2), the homogeneous red and subsuperficial horizon (H3) and the upper brown humus horizon (H4).
Composition granulométrique et chimique (g pour 100 g) de l'horizon tacheté (H1), de l'horizon de transition (H2), de l'horizon subsuperficiel rouge (H3) et de l'horizon superficiel humifère et brun (H4).
| Horizon | Depth (cm) | Clay | Silt | Sand | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | K2O | Organic carbon |
| H4 | 15 | 41 | 42 | 17 | 79 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2.0 |
| H3 | 45 | 45 | 39 | 16 | 68 | 18 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 0.8 |
| H2 | 95 | 57 | 31 | 12 | 63 | 22 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 0.3 |
| H1 | 155 | 54 | 31 | 15 | 67 | 21 | 9 | 1 | 2 | 0.1 |
| H1 | 275 | 43 | 28 | 29 | 76 | 15 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 0.1 |
2. L'horizon tacheté a été observé en microscopie optique à différentes profondeurs. Les pores sont des fissures délimitant des polyèdres (Fig. 1A) et des chenaux. Les taches rouges sont localisées préférentiellement au centre des polyèdres. Les taches RS sont constituées d'un plasma ferrugineux isotrope. Les taches RV sont constituées de particules ferrugineuses (2 à 3 μm), distribuées au sein d'un plasma gris massépique entre des grains quartzeux (Fig. 1B). Les taches GC se localisent entre les taches rouges et la paroi des pores (Fig. 1A). Elles sont composées d'un plasma et de grains identiques aux précédents. Enfin, les taches JV sans extinction sont en imprégnation sur la paroi des pores et, plus rarement, sur le bord des taches rouges. De rares argilanes gris sont observés au sein des taches GC. Aucun ferrane n'est présent et les ferriargilanes sont très rares.
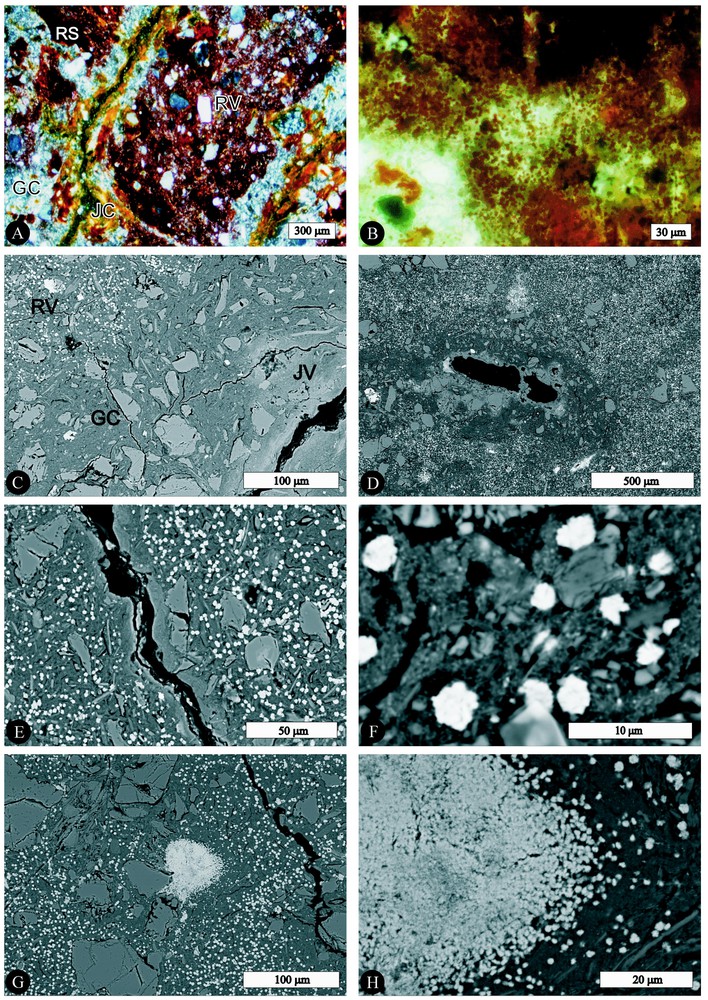
Spots: RS, dark red; RV, light red; GC, light gray; JV, yellow. A. Blocky microstructure (optical microscopy image under crossed polarizers). B. Fe-rich particles in RV spot (detail of Fig. 1A in plain light). C. Border of a planar void (black): spots RV, white Fe-rich particles, dark gray plasma and skeleton grains; GC, dark gray plasma and skeleton grains; JV, light gray plasma and skeleton grains. Image of Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). D. Border of channel biological void (SEM). E and F. RV spot composed of Fe-rich white particles, dark gray plasma and skeleton grains (SEM). G. RV spot (white and well-differentiated Fe-rich particles, dark gray plasma and skeleton grains) and RS spot (concentration of white and dense Fe-rich components) in the centre of the SEM image. H. Detail (SEM) of Fig. 1G. Centre and border of RS spot (concentration of undifferentiated and differentiated Fe-rich particles).
Taches : RS, rouge sombre ; RV, rouge vif ; GC, gris clair et JV, jaune vif. A. Microstructure polyédrique (image de microscopie optique en lumière polarisée). B. Détail d'une tache RV montrant les particules ferrugineuses (détail de la Fig. 1A en lumière naturelle). C. Bordure d'un pore fissural (en noir) : taches RV, particules ferrugineuses en blanc, plasma gris sombre et grains de squelette ; GC, plasma gris sombre et grain de squelette ; JV, plasma gris clair et grains de squelette. Image obtenue en microscopie électronique à balayage (MEB). D. Bordure d'un canal d'origine biologique. E et F. Tache RV composée de particules ferrugineuses en blanc, d'un plasma gris sombre et de grains de squelette (MEB). G. Tache RV (particules ferrugineuses bien différenciées en blanc, plasma gris sombre et grains de squelette) et tache RS (concentration de composés ferrugineux en blanc) au centre de l'image MEB. H. Détail (MEB) de la Fig. 1G. Centre et bordure d'une tache RS (amas de particules ferrugineuses individualisées ou non).
3. Au MEB, les taches RV apparaissent comme constituées de particules ferrugineuses blanches et denses, de 2 à 3 μm de diamètre, arrondies ou anguleuses, parfois jointives, mais le plus souvent espacées de 3 à 10 μm (Figs. 1C–1F). Elles sont nettement contrastées par rapport au plasma environnant gris sombre (sans constituant ferrugineux figuré), au sein duquel se distinguent des constituants fins individualisés (vraisemblablement kaolinite et illite) ou non individualisés (Figs. 1C et 1F). Les taches RS se présentent sous forme d'amas ferrugineux, blancs, avec ou sans particules ferrugineuses individualisées, avec des pores polyconcaves (assemblage de particules ferrugineuses), sans plasma gris sombre et sans squelette (Figs. 1G et 1H). Sur le bord des taches RS, des particules ferrugineuses (0,5 à 1 μm) sont individualisées au sein du plasma gris sombre. Les pores sont associés à des taches GC ou JV (Figs. 1C et 1D). Les taches GC et JV sont constituées du même plasma sans particule ferrugineuse, mais le plasma des taches JV apparaı̂t en gris clair.
4. Les caractéristiques micromorphologiques étant semblables au sein de l'horizon tacheté, une lame mince représentative a été sélectionnée pour des analyses chimiques. Les principales variations concernent la teneur en Fe2O3 (3 à 90 %) et, corrélativement, la teneur en SiO2 + Al2O3 (Tableau 2). Dans les taches RV (Figs. 2A et 2B), les particules ferrugineuses sont constituées de 55 à 70 % de Fe2O3, alors que le plasma gris sombre en contient 3 % au plus. Les taches RS sont composées de 70 à 90 % de Fe2O3 (Figs. 2A et 2D). Le plasma gris sombre des taches GC en comporte environ 2 % (Figs. 2E et 2F) et le plasma gris clair des taches JV de 15 à 25 %. Le rapport Si/Al varie de 1,1 à 1,3 et la teneur en K2O de 1 à 3 %. Ces caractéristiques sont conformes à la minéralogie (kaolinite et illite). Le caractère circonscrit des particules ferrugineuses, très net au MEB, n'est pas rendu par les cartes en isovaleurs de Fe2O3 (Figs. 2A et 2B). Ceci est dû au fait que les volumes analysés pour les points contigus se chevauchent, car la maille est de 1 μm entre chaque point.
Chemical composition of the spots: RV, light red; RS, dark red; GC, light gray; JV, yellow (measurements obtained by quantitative microprobe on thin section).
Composition chimique des taches rouge vif (RV), rouge sombre (RS), gris clair (GC) et jaune vif (JV). Analyses obtenues par microsonde quantitative sur lames minces.
| Spot | Fe2O3 | SiO2 + Al2O3 | Si/Al | K2O |
| g per 100 g | g per 100 g | g per 100 g | ||
| RV | ||||
| – Fe-rich particles | 55–70 | 30–45 | 1.1 | 1 |
| – Dark gray plasma | 3 | 95 | 1.1 | 2 |
| RS | 70–90 | 10–30 | 1.3 | 1 |
| GC | 2 | 95 | 1.2 | 3 |
| JV | 15–25 | 75–85 | 1.1 | 2 |
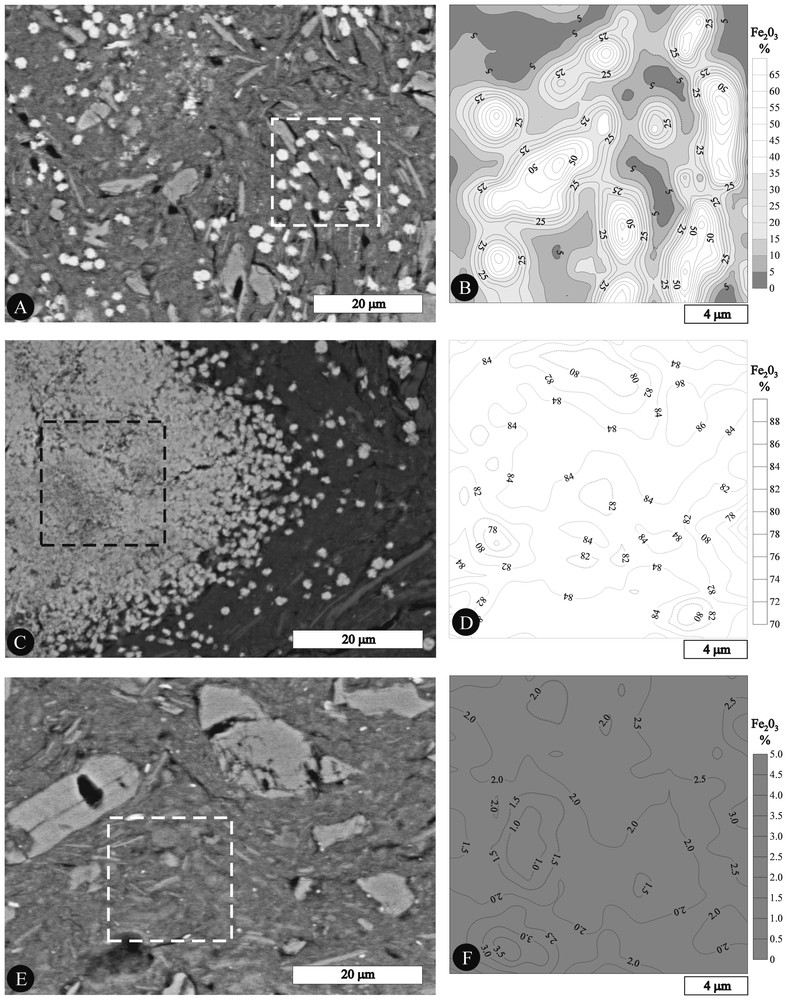
A, C and E. SEM images of RV, RS and GC spots and selected area for quantitative chemical measurements (RV, A; RS, C; GC, E). B, D and F. Maps of the Fe2O3 content in RV, RS and GC spots (selected areas of Figs. 2A, 2C and 2E, respectively).
A, C et E. Images (MEB) de taches RV, RS et GC avec les aires sélectionnées pour les analyses chimiques quantitatives (RV, A ; RS, C ; GC, E). B, D et F. Cartes de la teneur en Fe2O3 au sein de taches RV, RS and GC (aires sélectionnées sur les Figs. 2A, 2C et 2E, respectivement).
4 Discussion
Dans les profils latéritiques typiques, l'horizon tacheté est le siège d'une accumulation de fer. Schématiquement, les taches rouges ou jaunes se différencient, du fait d'une substitution de la kaolinite par des sesquioxydes de fer et d'une dissolution du quartz dans des volumes argileux hérités de l'altération. Les taches grises résultent d'un lessivage d'argile dans des volumes quartzeux également hérités. Ici, au sein de l'horizon tacheté, les taches grises ou jaunes sont situées près des fissures ou tubules, alors que les taches rouges en sont éloignées. Les taches grises ou jaunes sont constituées d'un plasma argileux (kaolinite et illite) associé à un squelette quartzeux. Le fer y est peu abondant. Les taches rouge vif sont constituées d'un plasma argileux semblable, pauvre en fer, dans lequel sont enchâssées des particules, circonscrites et très riches en fer. Les taches rouge sombre sont constituées d'amas denses de particules analogues. Les processus invoqués précédemment dans la différenciation en taches n'expliquent, ni la ségrégation du fer en particules isolées ou en amas dans les taches rouges loin des pores, ni l'absence de telles particules et la relative pauvreté en fer dans les taches grises ou jaunes proches des pores. Ici, un plasma argileux, un squelette quartzeux et des particules ferrugineuses isolées ou en amas constituaient une matrice initiale. Les pores actuels sont postérieurs. Les taches grises ou jaunes qui leurs sont associées témoignent respectivement d'une déferruginisation et d'une migration du fer. La saturation hydrique est sûrement responsable de la dissolution des particules ferrugineuses de la matrice initiale en bordure des pores. La majeure partie du fer dissous a probablement été exportée au travers des pores, lors de la saturation de l'horizon tacheté par la nappe. Ceci explique l'absence d'accumulation de fer dans les pores.
5 Conclusion
L'horizon tacheté est ici présent au sein d'un profil sans cuirasse et relativement peu altéré (la présence d'illite et vermiculite en témoigne). La différenciation tachetée résulte de la déferruginisation d'une matrice antérieure dans laquelle le fer était ségrégé. En relation avec les conditions actuelles, la déferruginisation prédomine et explique que l'évolution n'ait pas abouti à un cuirassement.
1 Introduction
Within the lateritic profiles that are typically thick and continuous in Africa, Australia and India, the mottled horizon constitutes the transition from weathered bedrock up to the lateritic duricrust and lateritic gravel [1,4,9–12,18]. The weathering process supplies kaolinite-rich volumes (in situ neoformation of kaolinite) and the other quartz-rich volumes (inherited from the bedrock) [17,18]. Two processes mix to form the mottled horizon. On the one hand, quartz is dissolved [11] in the kaolinite-rich volumes and kaolinite is substituted by iron sesquioxides, mainly hematite [2]. Iron enrichment occurs and forms red or purplish spots. Locally, the association of kaolinite and goethite causes yellow spots. On the other hand, a leaching in the quartz-rich volumes creates gray-coloured spots [3]. Towards the top of the lateritic profiles, the red or purplish spots concentrate to form successively the lateritic duricrust. The lateritic gravel results from the superficial weathering of the crust. The lateritic duricrust (petroplinthite) is considered as derived from the mottled horizon by iron enrichment and hardening. In Africa, the absence of lateritic duricrust or lateritic gravel over a mottled horizon is interpreted as the result of a dismantling of the duricrust and gravel [5,8]. Contrary to those in Africa, the laterite covers in Brazil exhibit large areas with mottled horizon at shallow depth (plinthite or paraplinthite) and few areas with superficial lateritic duricrust or lateritic gravel [13,14,16]. Did the duricrust and gravel disappear or did they not form there? The objective is to contribute to the knowledge of the laterite covers in the Amazon Basin and to show that mottled horizon can also form because of iron depletion.
2 Study site
The site [15] is located in the southern part of the Amazon Basin (8°18′S, 63°48′W, altitude 100 m), between the localities of Porto Velho (State of Rondonia) and Humaita (State of Amazonas) in Brazil. The climate is characterised by mean annual precipitation of 2250 mm and mean annual evapotranspiration of 1500 mm, with a dry season from June to July (monthly precipitation lower than 40 mm). The relief is dominated by undulated plateaus. The original vegetation consists of alternating savannah and open forest large areas [14]. Within the laterite cover, which developed from sediments of the Solimões group (Middle Pliocene–Upper Pleistocene), the predominant soil is considered to be a Plinthic Cambisol [6]. The groundwater table is close to the surface (1 m), except during the dry season (3 m).
3 Method of study
The macroscopic observation of the soil [15] was carried out in a trench (3.5 m depth), situated on a high part of plateau. Undisturbed and disturbed samples were collected. The granulometrical, mineralogical and chemical compositions were determined [15]. Thin sections of the mottled horizon were observed using an optical microscope and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) in the backscattered electron mode. The images reveal the chemical composition of the groundmass on a gray scale. Small areas were selected for quantitative chemical measurement of the major components (Si, Al, Fe, Ti and K) by electron probe microanalysis [7]. For each area (20×20 μm), maps of the chemical composition were obtained by measuring the elements with a spacing of 1 μm between the points of measurement. The data acquired were interpolated by linear kriging.
4 Soil macromorphology and composition
Four horizons were identified from the bottom to the top of the profile: mottled horizon, intermediate horizon, subsuperficial red horizon and upper humus horizon. All the horizons exhibit silty–clayey texture. The mottled horizon is 2.5 m thick and exhibits contrasting spots, light red (RV) 10R 4/8 to 2.5YR 4/6 (all Munsell colours referred to moist soil), dark red (RS) 10R 3/6, light gray (GC) 10YR 7/2 and yellow (JV) 10YR 7/8. Red RV and RS spots formed a three-dimensional network (1–3 cm thick), usually with vertical elongation. GC spots also form a three-dimensional network, similar in size and imbricated with the red network. The red spots predominated between 3.5 and 1.1 m depth (RV + RS ≈60%, GC ≈30% and JV ≈10%), while the gray spots predominated between 1.5 and 1.1 m (GC ≈60%, RV + RS ≈30% and JV ≈10%). The weak porosity consisted of fissural and tubular voids (diameter 0.5–1 mm) and was located within GC spots. The transition, between 1.1 and 0.6 m depth, from the mottled horizon to the upper horizon was characterised by the gradual disappearance of the mottled facies. The intermediate horizon was composed of a light yellowish–brown 10YR 6/4 matrix, in which abundant red 2.5YR 4/8 spots (soft, diffuse limit and millimetric to centimetric size) and ferruginous nodules (10R 4/6, 2 mm in diameter, soft, contrasted limit) were present. The spots decreased gradually in size and in proportion closer to the surface, and their colour became less lively and their outlines less defined than in the mottled horizon. The subsuperficial horizon (30 cm thick) was homogeneous red 2.5YR 5/6 and contained ferruginous nodules (similar to those of the underlying horizon). The upper humus horizon (30 cm thick) exhibited a brown colour varying from the bottom (5YR 4/4) to the top (10YR 3.5/2).
The granulometrical study indicated a large clay fraction (Table 1). In the area, clay fraction was composed of kaolinite and illite; the subsuperficial red horizon differed from the others by the additional presence of Al-vermiculite [15]. The chemical composition was variable within the mottled horizon. The SiO2 content ranged from 76 to 63%, the Al2O3 content from 15 to 22% and the Fe2O3 content from 7 to 12%. However, there was little variation between the top of the mottled horizon and the upper red horizon (Table 1).
5 Microscopy
Thin sections of the mottled horizon (250, 200 and 150 cm depth) were observed by optical microscopy. The pores were composed of planar voids, which delimited blocks (2–4 mm in size) and channels (millimetric diameter) resulting from biological activity. The skeleton (essentially quartz) was randomly distributed within the RV, GC and JV spots. Red spots were mostly located in the centre of the blocks (Fig. 1A). RS spots (continuous on surfaces from 70 to 700 μm) consisted of undifferentiated isotropic ferruginous plasma. RV spots (tens or hundreds of microns) consisted of well-differentiated ferruginous particles (2–3 μm in diameter), which were randomly distributed within gray masepic plasma between the skeleton grains (Fig. 1B). GC spots were located between red spots and the walls of the voids (Fig. 1A). They consisted of a gray masepic plasma and skeleton grains identical to those described above. JV spots impregnated the walls of planar or biologic voids and more rarely the border of RS or RV spots. Gray argillans within GC spots and ferri-argillans were rarely observed. No ferran was present.
The SEM observations showed that the RV spots consisted of white and dense ferruginous particles, 2–3 μm in diameter, rounded or subangular, mostly isolated and spaced 3–10 μm apart (Figs. 1C–1F). They contrasted with the dark gray surrounding plasma, which consisted of undifferentiated components (×3000) and well-differentiated clay particles (probably of kaolinite and illite), without differentiated ferruginous components (Figs. 1C and 1E). The centre of RS spots consisted of white and very dense ferruginous components, with or without individualization of ferruginous particles, without dark gray plasma and without skeleton grains (Figs. 1G and 1H). On the border of RS spots, ferruginous particles (0.5–1 μm) occurred within dark gray plasma. They became less dense with distance from the centre of the spots. GC spots and JV spots were systematically associated with the voids (Figs. 1C and 1D). They consisted of gray plasma, without differentiated ferruginous components, but appearing lighter in JV spots than in the GC and RV spots (Figs. 1C and 1D).
6 Chemical microanalysis
The micromorphological characteristics being similar within the mottled horizon, a representative thin section was selected for chemical microanalysis. The main variations were related to the content of Fe2O3 (3–90%) and the correlated content of SiO2 + Al2O3 (Table 2). The iron content varied in proportion to the redness of the various spots. In RV spots (Figs. 2A and 2B), the ferruginous particles consisted of 55 to 70% Fe2O3, while the gray dark plasma contained at most 3% Fe2O3. In RS spots the Fe2O3 content ranged from 70 to 90% (Figs. 2C and 2D). The gray dark plasma in the GC spots contained about 2% Fe2O3 (Figs. 2E and 2F) and the light gray plasma of JV spots from 15 to 25% Fe2O3. The Si/Al atomic ratio ranged from 1.1 to 1.3 and the content of K2O from 1 to 3%. These characteristics are consistent with the kaolinite and illite composition of the plasma. The predominantly isolated character of the ferruginous particles that appears in the SEM images was not reflected in the maps of the Fe2O3 contents. This is because the distance between the points of analysis was 1 μm and the volumes analysed for adjoining points overlapped one another.
7 Discussion
The mottled horizon within typical lateritic profiles constitutes the transition from the weathered bedrock up to the lateritic duricrust. Schematically, red spots and yellow spots differentiated because of the dissolution of quartz and the substitution of kaolinite by iron sesquioxides in kaolinite-rich volumes (inherited from the weathering) and gray spots resulted from the leaching of clay in quartz-rich volumes (also inherited). The lateritic duricrusts are considered as derived from mottled horizon by iron concentration and hardening.
In the case studied, gray and yellow spots were located near the fissures and the channels, while red spots were systematically away from the voids. Gray spots and yellow spots consisted of a clayey plasma (kaolinite and illite) associated with skeleton grains (quartz). The plasma of gray spots appeared by SEM dark gray, without distinctive iron component, whereas the iron content was very low (2%). The plasma of yellow spots that appeared also without distinctive iron component was lighter gray, with a higher iron content (15–25%) than in gray spots. The light red spots consisted of clayey plasma and skeleton grains similar to those of gray spots. Nevertheless, mainly contrasted and isolated Fe-rich particles were set in the clayey plasma. The iron content was very low (2%) in the clayey plasma and very high (55–70%) in the Fe-rich particles. The dark red spots consisted of dense concentration of Fe-rich particles, the clayey plasma being present only in the border where the Fe-rich particles were separated.
The processes generally involved in the spot differentiation did not explain the iron segregation (isolated or concentrated Fe-rich particles) in the red spots away from the voids and the relatively low iron content (absence of such Fe-rich particles) in the gray spots or yellow spots closed to the voids. This pattern does not result from iron concentration or depletion process according to the present pedological conditions. Therefore, we assume that it results from previous conditions. In the case studied, an initial horizon was uniformly composed of clayey plasma, skeleton grains and Fe-rich particles (isolated or concentrated). The current fissures and channels developed later. Currently, the red spots correspond to relict feature of the initial horizon. The transition from the red spots to the gray spots corresponds to the disappearance of the Fe-rich particles and the preservation of the clayey plasma with skeleton grains. The planar voids and the channel voids are systematically associated with gray spots or yellow spots, which result from depletion and transport of iron, respectively. The features of Fe-accumulation were absent in porosity (only argillans were rarely present in gray spots). Probably, the most of the dissolved iron was exported through pores during the periods of saturation of the mottled horizon by the groundwater table.
8 Conclusion
The mottled horizon has been developed within a profile less weathered (presence of illite and vermiculite) than the typical lateritic profiles and without duricrust. The evolution of the mottled horizon is complex. The light red spots consisted of clayey plasma in which isolated Fe-rich particles were set and the dark red spots consisted of concentrations of Fe-rich particles. This pattern is inherited from previous evolution, characterised by iron segregation. Gray and yellow spots, which are systematically associated with the present porosity, correspond to the disappearance of Fe-rich particles. We assume that the predominant process responsible for the mottled differentiation implies iron depletion. Therefore, the absence of Fe-accumulation explains why the evolution of the mottled horizon has not resulted in a lateritic duricrust.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the USP/Nupegel (Brazil) and the IRD (France). It was carried out thanks to the financial support of the FAPESP (Proc. 96/1447-1 & 97/01550-0) and CNPq (PRONEX 318). We are very grateful to the INRA–‘Science du sol’ (Orléans), and particularly to I. Cousin and C. LeLay for their support.



