Version française abrégée
L'étude des dépôts lacustres tardiglaciaires et holocènes du marais de Sarliève, ancien lac (5 km2) asséché au XVIIe siècle, situé dans un bassin versant marno-calcaire (29 km2), au sud-est de Clermont-Ferrand en Limagne (Fig. 1), a mis en évidence la présence de deux retombées de téphras. Le remplissage du marais est constitué de deux principaux types de dépôts (Fig. 1). On rencontre, d'une part, des sédiments de « bassins distaux » (type B) dans les lobes nord et sud du marais, constitués de l'empilement d'unités de sédiments silteux à silto-argileux, pour l'essentiel carbonatés (unités B1 à B6, Fig. 2), et, d'autre part, des sédiments de « delta » (type D : unités D1 à D7), rencontrés en partie médiane de la dépression et comprenant un épais corps sableux d'abord deltaïque, puis colluvial (Fig. 2). Des niveaux de téphra (unités T1 et T2), et de téphra remanié (D2) ont été rencontrés, mais uniquement dans les sédiments de bassins proximaux du marais de Sarliève (Fig. 2) ; les dépôts de bassins distaux en sont systématiquement dépourvus. Ces observations soulèvent deux principales questions relatives à l'âge et à l'occurrence des retombées volcaniques : (1) comment se placent les téphras rencontrés à Sarliève parmi les nombreux téphras issus de la chaîne des Puys toute proche [7] et dont certains ont atteint la Limagne du Dryas ancien à l'Atlantique [30,33], la retombée la plus récente identifiée étant celle du Pavin, vers 6,6/6,7 ka (5800/5900 BP) [16] ? (Précisons qu'à l'exception des âges notés BP, les âges sont donnés au sens habituel du terme.) (2) Pourquoi les téphras sont-ils présents dans les zones proximales et absents en zones distales dans le bassin sédimentaire ?
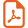
Sarliève marsh location, studied section pits and drilling cores position with deltaic and lacustrine facies distribution, and position of CF1 tephra (unreworked and reworked).
Localisation du marais de Sarliève, position des coupes et forages étudiés et distribution des faciès deltaïques et lacustres, et position du tephra CF1 (en place et remanié).
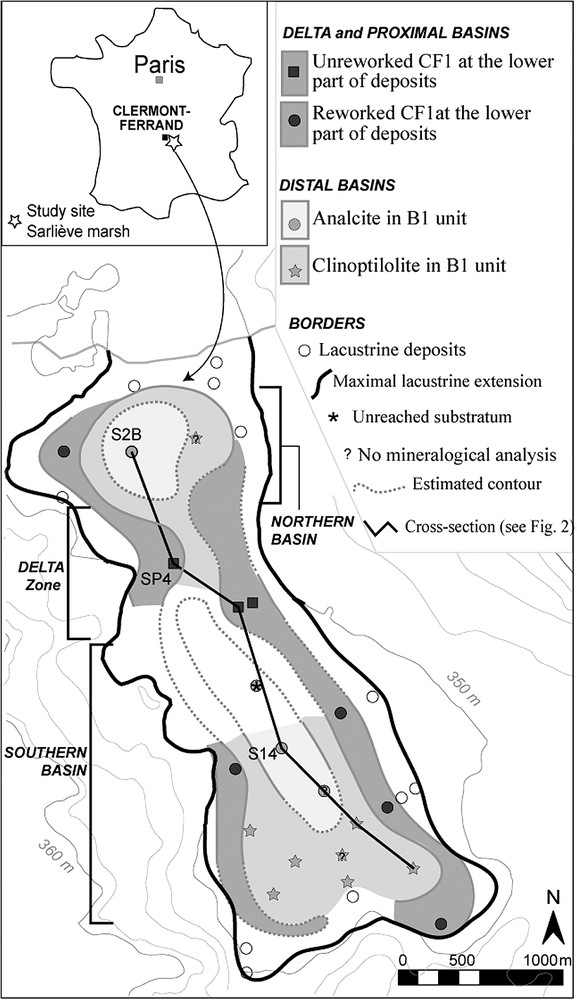
North–south cross-section through the Sarliève marsh deposits (see location in Fig. 1).
Coupe nord–sud dans les dépôts du marais de Sarliève (localisation : voir Fig. 1).
L'unité de téphra T1, la plus ancienne dans la série lacustre, a été identifiée sur des critères minéralogiques et géochimiques comme correspondant à une retombée en place de la partie basale du tephra CF1 (CF1a), a composition de magma trachyandésitique basaltique, issu du puy de la Nugère [30–34]. Ce téphra, présent en de nombreux points de la Grande Limagne, est un marqueur chronostratigraphique daté à environ () (environ 12 000 BP, moyenne de trois datations précisées dans [33]). D'autres lits de téphras âgés d'environ 12 000 BP et attribués à la Nugère ont préalablement été trouvés en Limagne [17] ; la similitude des âges soulève la possibilité d'une équivalence entre ces deux occurrences. La présence à Sarliève de CF1a permet de dater le début du comblement de la cuvette lacustre du Dryas ancien ou du Bölling.
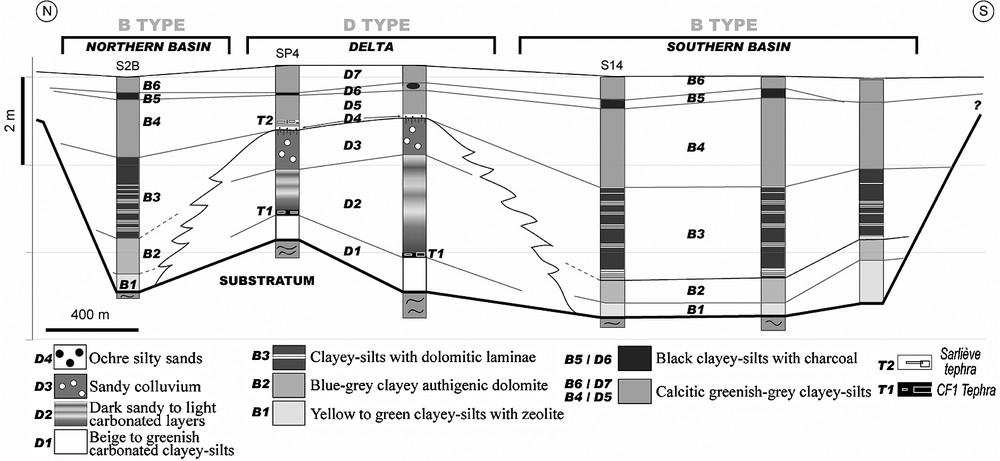
L'unité T2, fine couche de téphra située dans la partie inférieure de D5, correspond au « téphra de Sarliève » à composition de trachyte [20] et se distingue de toutes les autres retombées des volcans connus de la chaîne des Puys : il a été daté par méthode TL à () et son origine est jusqu'à ce jour inconnue [20]. Des conditions hydrochimiques particulières dans la dépression lacustre [8,9] au cours du dépôt du téphra et après celui-ci pourraient expliquer l'âge « trop vieux » donné par la méthode TL. En effet, un âge nettement plus récent peut être proposé pour ce téphra sur la base de données palynologiques acquises sur les sédiments de bassin (forage S2B) et de delta (coupe SP4) (Figs. 1 et 3). Dans l'unité B3 (Fig. 3), les pollens indiquent un riche milieu forestier typique de l'Atlantique, d'après les données du Massif central « montagnard » [3–6,12,21]. L'assemblage pollinique de l'unité D5, qui comprend le téphra T2, est marqué par l'expansion du Fagus et celle plus limitée d'Abies : généralement, dans le Massif central, le début d'expansion de Fagus se situe aux alentours de 5,3/5,4 ka (4700 BP) [22], à quelques siècles près [18] ; en outre, Argant et Cubizolle [2] ont proposé un âge moyen de 5,39 ka (environ 4700 BP) pour l'expansion de Fagus, à partir de datations concernant des sites à environ 20 km de Sarliève, dans le Massif central oriental. La régression brutale de tous les taxons forestiers dans les dépôts de delta D6, D7 et les dépôts distaux B5 et B6, suivie de leur quasi-disparition laissant place à un milieu très ouvert livré aux cultures, marque le Subatlantique. La position dans les chronozones du niveau T2, « téphra de Sarliève », non encore rapporté géochimiquement à un appareil volcanique connu, permet de poser l'hypothèse qu'il est un peu postérieur au début du Subboréal, vers 5,3/5,5 ka (4700 BP), soit un âge un peu plus récent que celui du « téphra de Beaunit » [15], daté à environ 5,6/5,8 ka . D'âges proches, ces tephras diffèrent de par leur composition minéralogique [15,20]. Les deux occurrences (téphra de Sarliève et Beaunit) soulignent la possibilité d'éruption(s) volcanique(s) de plus de 1000 ans, postérieure(s) à la dernière éruption volcanique connue de la chaîne des Puys. Ces occurrences soulèvent la question de leur origine, peut-être à rechercher plutôt au niveau du Cézallier volcanique que de la chaîne des Puys sensu stricto, dont la séquence de recouvrement téphrique récent commence à être bien connue.
Lithology and palynology of D-type deposits (SP4, pollen analysis by B. Prat) and B-type deposits (S2B, pollen analysis by J. Argant), and their chronostratigraphical relations. Lithological legend, see Fig. 2.
Lithologie et palynologie des dépôts de type D (SP4, analyse pollinique : B. Prat) et type B (S2B, analyse pollinique : J. Argant) et leurs relations chronostratigraphiques. Légende lithologique, voir Fig. 2.
Ces téphras, bien conservés dans les dépôts de deltas, s'estompent dans les dépôts de bassins. En particulier, CF1, bien visible à la base de D2 est absent de B1, unité pourtant mise en place entre la mise en eau du lac avant la retombée du téphra à () (ca. 12 000 BP), et la fin du Préboréal [avant environ ou ; Lyon-2435(GrA)] (Figs. 2 et 3). Cependant, l'unité B1 est caractérisée par la présence systématique de zéolites (analcite, souvent abondante dans les dépôts les plus distaux, et clinoptilolite dans les dépôts distaux plus périphériques) et est fortement enrichie en silicates, quartz microcristallin notamment. L'analcite, abondante dans la partie moyenne de l'unité B1 en partie centrale du bassin sud, se présente sous forme de groupes de cristaux automorphes de la taille des silts, développés sur des particules de l'encaissant (Fig. 4). Ces caractéristiques semblent attester l'origine authigène de ces analcites. À Sarliève, comme décrit dans différents dépôts lacustres anciens à actuels [13,23–25,27–29], la concentration élevée d'analcite authigène dans B1 pourrait résulter de réactions entre des pyroclastes, le téphra CF1, et les eaux saumâtres à salées et/ou alcalines des bassins nord et sud, alors endoréiques (conditions par ailleurs maintenues jusqu'à l'Atlantique [8,9]). Cette hypothèse de dissolution de CF1 et d'authigenèse subséquente de zéolites est confortée par : (1) la zonation de la distribution des matériaux volcaniques observée dans les dépôts de Sarliève (niveaux de téphra CF1 et/ou de cendres/sables noirs remaniés en partie proximale, clinoptilolite en périphérie des bassins et analcite en position centrale (Fig. 1), qui rappelle celle décrite dans le lac Tecopa [23], et (2) par la présence d'analcite remplissant des cavités lenticulaires à la base de l'unité B1 (Fig. 1), qui rappellent les lits d'analcite monominéralogiques décrits par [14].
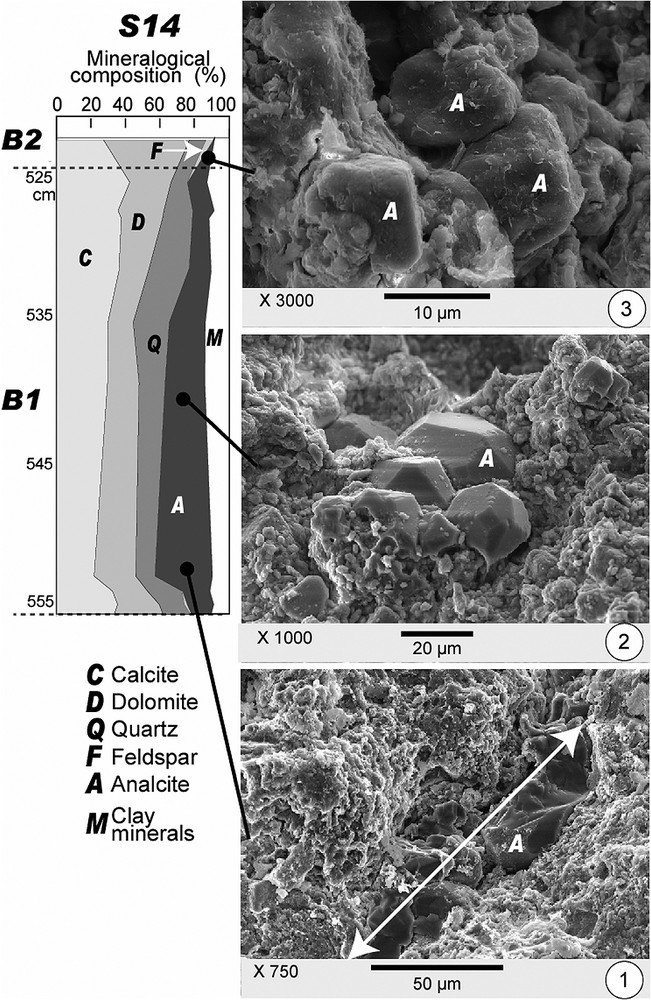

Mineralogical composition of B1 unit in S14 and SEM observed analcite habits evolution; (1) at the lower part, lens-shaped filling; (2) pristine crystals grown on host-sediment particles; (3) rounded crystals at the transition with next unit (B2).
Composition minéralogique de l'unité B1 dans S14 et évolution des habitus de l'analcime observée au MEB ; (1) à la base, remplissage de cavités lenticulaires ; (2) cristaux automorphes développés sur des matériaux de l'encaissant ; (3) cristaux émoussés au passage à l'unité sus-jacente.
Les dépôts du marais de Sarliève comportent deux téphras : le téphra CF1, déposé vers () (environ 12 000 BP), qui permet de dater les premières phases lacustres, et le « téphra de Sarliève », qui diffère de tous les autres téphras trachytiques des volcans connus de la chaîne des Puys. L'étude des assemblages polliniques des sédiments qui entourent le lit de téphra permet de suggérer que le « téphra de Sarliève » serait issu d'une éruption datant du début du Subboréal, soit postérieure de plus de 1000 ans à la dernière éruption connue à ce jour dans la chaîne des Puys. D'autre part, ces téphras, absents des dépôts de bassins distaux du marais, semblent avoir été dissous dans les eaux relativement salées et alcalines des bassins endoréiques au Tardiglaciaire ou au début de l'Holocène, ce qui explique l'authigenèse des zéolites rencontrées en abondance à la partie basale des dépôts distaux.
1 Introduction
Tephras fall out on terrestrial surface (soils, lakes and ponds, oceans) sometimes over wide areas, very far from the source volcano. Studies of their chemical composition and stratigraphic position enable to precise volcanic event chronology. When interbedded in sedimentary piles, tephras are useful chronological markers [10]. The ‘Chaîne des Puys’, the youngest volcanic complex of French Massif Central, generated numerous tephras [7], some of them reached the Limagne plain from the Oldest Dryas until the Atlantic [30,33]. The most recent identified air fall emitted in the ‘Chaîne des Puys’ corresponds to an eruption of the Pavin at about 6.6/6.7 ka (5800/5900 BP) [16] (it can yet be noted that, except for 14C BP dating, ages are given using the usual word meaning). However, a more recent tephra (5.6/5.8 ka or ) has been evidenced in the Maar of Beaunit, so-called ‘tephra de Beaunit’, but its origin has not been found [15]. Some of these tephras constitute large cover, which can be encountered, quite systematically unreworked, in numerous sedimentary fillings upon the granitic ‘Plateau des Dômes’ and in the Limagne [33]. The study of Lateglacial and Holocene lacustrine deposits of Sarliève marsh (Fig. 1), located some kilometres southeast of Clermont-Ferrand, showed two or more tephras, the distribution of which allowed to specify lacustrine infill chronology and to reveal a recent air fall, younger than Pavin eruption. Moreover, conditions of preservation and post-depositional evolution of tephras in a restricted carbonated environment may be assumed as leading to a better understanding of their occurrence and also as allowing one to detect their initial presence in sediment piles.
2 Sarliève catchment and lacustrine deposits
The Sarliève marsh (Fig. 1) is an ancient small lake (present dried area: 5 km2), at an elevation of about 345 m, mainly filled up with carbonated sediments, deposited from the Lateglacial until the 17th century. The catchment area (29 km2) is essentially made of Oligocene marly limestones, locally covered with volcanic formations. Marsh sediments were studied thanks to deep section pits during preventive archaeological prospecting (INRAP), prior to the construction of an exhibit centre (‘Grande Halle d'Auvergne’), and thanks to core drillings (GéEAC). Sediments stored in the Sarliève depression comprise delta deposits and basin deposits (Figs. 1 and 2).
Delta deposits, 4 to 5 metres thick (D type, Fig. 2), located in the median part of depression, have been observed on several deep sections [31]. From base to top, they are made up of several units: D1, beige to greenish carbonated clayey-silts (CS); T1, black pyroclastic sands; D2, plurimetric deltaic sands made of alternation of dark tephric sandy layers and light-coloured more carbonated sandy-silty layers; D3, sandy colluvium toped by a palaeosoil; D4, ochre sands; D5, homogeneous greenish calcitic CS, including in the lower part a 2-cm-thick pale pink layer of tephritic origin, T2; D6, charcoal-rich black calcitic CS; D7, greenish-grey to brown calcitic CS.
Basin deposits, 5 to 6 metres thick, observed in north and south lobes of the depression (B type, Fig. 2) are made up of clayey-silty sediments, generally carbonate-rich, showing from base to top: B1 unit, quartz-rich compact yellowish to greenish clayey-silts (CS), characterized by presence of zeolites; B2, grey to blue clayey-silts mainly made of authigenic dolomite [8,9]; B3, alternation of dark calcitic CS (centimetric layers) with bundles of dolomitic and aragonitic laminae; B4, homogeneous greenish calcitic CS; B5, charcoal-rich black calcitic CS; B6, greenish-grey to brown calcitic CS. The lower part of proximal basin deposits (Fig. 1) contains a dark sandy layer including reworked pyroclastic particles (equivalent to T1 and D2).
As shown by Fig. 2, sedimentary facies equivalences clearly appear between basin and delta deposits: the D5 unit is equivalent to B4, D6 to B5 and D7 to B6. On the other hand, macroscopic observation of sediments did not allow us to establish equivalences for units D1 to D4 and B1 to B3. Moreover, tephra-rich units (T1, D2 and T2) have only been observed in deltaic or proximal basin sediments, while they are always absent in distal basin deposits. From these observations, some questions raised about the identification and the age of volcanic fallouts, concerning their origin and their differential preservation in lacustrine sediments.
In order to answer these questions, sediments have been studied according to these procedures. Bulk sediment minerals were determined by powder X-ray diffraction (Rigaku diffractometer, copper anticathode), mineral abundances were estimated from the relative peak intensities. Sediments were studied with scanning electron microscopy (SEM LEO, Gemini, Zeiss DSM 982) coupled with energy-dispersive spectrometry (EDS, Noran, Idfix software). The pollen content was analysed in basin (S2B drilling [1]) and in deltaic deposits (SP4 section) (Fig. 1). 14C dating has been performed by ‘Centre de datation par le radiocarbone, université Claude-Bernard, Lyon-1’. Calibration has been made using INTCAL 98 calibration curve [26]; uncertainty is for 14C BP dating and is for calibrated dating.
3 Composition, origin and age of the two tephras
The sandy T1 unit is composed of coarse black-bluish coloured volcanic materials. Tephra micro-facies, heavy minerals and geochemical composition [31] pointed out a basaltic trachyandesitic volcanic product very similar to CF1 tephric complex, previously attributed to volcano La Nugère [33,34]. Large-sized thin section of T1 unit studied by Vernet revealed that it precisely corresponds to the basal part of CF1 tephric complex (CF1a or fallout of ‘rue de la Barre’ [32], whose composition is specified in [33]), and showed moreover that this material has not been reworked. This CF1 tephra, found on numerous places over the Limagne plain, dated to about () (ca. 12 000 BP, average of three dating values cited in [33]), is an essential chronostratigraphical marker for the Lateglacial series [30]. Other peat-bog tephra beds, aged around 12 000 BP and attributed to La Nugère in [17], have previously been found in Limagne: consistency of ages raises the possibility of the equivalence between these tephra occurrences. In Sarliève deposits, this tephra enables to date the beginning of lake infill at around the Oldest Dryas or the Bölling.
The thin (2-cm-thick) pale pink tephra layer (T2 unit) interbedded in the lower part of D5 unit (equivalent to B4), so-called ‘tephra de Sarliève’, has a trachytic composition [20]. According to [20], its facies, and chemical and mineralogical compositions remind those of the CF5 Boreal tephra, attributed to the Kilian or the Vasset volcanoes [33,35]. However, more accurate analysis (radioactivity, geochemistry, mineralogy with heavy minerals analysis and refractive index analysis) showed that the ‘tephra de Sarliève’ differs from CF5 [20]. The ‘tephra de Sarliève’ has been dated to () using the TL method [20]. Taking into account the TL dating uncertainty, it appears that ‘tephra de Sarliève’ could be coherent in age with underlying CF1 tephra [ () or ca. 12 000 BP] but weekly coherent with underlying sediments dated up to () (; LY-11362) (Fig. 3). Furthermore ‘tephra de Sarliève’ can be distinguished from other known trachytes due to the ‘Chaîne des Puys’ volcanoes: up to now, its origin is unknown. The ‘tephra de Sarliève’ age can be specified from pollen analysis of Sarliève basin sediments. Pollen content of unit B3 (Fig. 3) points out to a forest-rich environment (hazel tree/oak grove with elm, linden and ash trees) typical of Atlantic period according to Massif Central pollen data [3–6,12,21]. Upwards, pollen associations in B4 and D5 units (Fig. 2) are similar: Fagus is markedly spreading, and Abies increases slightly. In the whole Massif Central, Fagus dispersed at about 6.5/6.7 ka or 5800 BP and the beginning of Fagus regional spreading is around 5.3/5.5 ka or 4700 BP [22]. Argant and Cubizolle [2] proposed an average age of 5.39 ka (around 4700 BP) for the Fagus spreading, on sites located only ca. 20 km far from Sarliève in the oriental side of the Massif Central. D1 to D4 units of delta deposits contain only reworked pollen grains. After, a strong decrease of forest taxa appears in distal basin deposits (B5, B6) like in deltaic deposits (D6, D7); then, the nearly disappearance of forest corresponds to the development of an open environment with cultivations characteristic of Subatlantic. 14C dating values (Fig. 3) obtained from organic elements (seeds and wood charcoal) extracted from bulk sediment, agree with pollinic chronozones. Thus, considering these palyno-chronological data, it appears that ‘tephra de Sarliève’ of unit T2, located at the lower part of D5 unit including Fagus pollens (1) is necessarily younger than () given by TL method, and (2) should have deposited during the beginning of Subboreal at around 5.3/5.5 ka or 4700 BP within a few centuries [18]. Open conditions during ‘tephra de Sarliève’ air fall and/or strong post-deposition alteration in the lacustrine depression (as shown in next paragraph) highlighted by [8,9], leading to change tephra radioactivity (radioelement migration), or tephra dynamics (like phreatomagmatism), leading to an insufficient initial heating, should explain too old age obtained for ‘tephra de Sarliève’ using the TL method.
According to our hypothesis based on pollinic chronozones, that has to be confirmed, the age of ‘tephra de Sarliève’ (ca. 5.3/5.5 ka or 4700 BP within a few centuries [18]) would approach the age of ‘tephra de Beaunit’ at around 5.6/5.8 ka ( BP) and would confirm that volcanic eruption(s?) occurred in the ‘Chaîne des Puys’, more than 1000 yr younger than assumed until today. This vicinity in age raises the question of equivalences between these tephra occurrences. Published mineralogical data show that the ‘tephra de Beaunit’ dense minerals include amphiboles, almost brown ones [15], absent in the ‘tephra de Sarliève’ [20]. According to [15], the ‘tephra de Beaunit’ constitutes a laminae during the Tilia optimum – just before the strong Fagus extension – conferred to the Atlantic second half part, while the ‘tephra de Sarliève’ constitutes a thin layer subsequent to the Tilia optimum – during the Fagus sharp extension – attributed to the beginning of Subboreal. Although Fagus spreading age varied of about 500 years according to considered site [18], these two tephras seem to have a different origin (temporally and/or geographically), and even if there is an uncertainty about the age of ‘tephra de Sarliève’, we can hypothesize that it is probably more recent than the ‘tephra de Beaunit’. Such an age increases the problem of the ‘tephra de Sarliève’, origin already discussed by [20]. It seems weekly probable that it originated from the ‘Chaîne des Puys’ sensu stricto. Indeed, each one of the three recent trachytic volcanoes (Vasset, Kilian, Chopine) had several distinct eruptive phases, which have succeeded during a quite brief time duration, around 9.3–9.4 ka for the two most recent (Vasset and Kilian) [11]. A very late eruption of one of them would be amazing from a volcanologic point of view and would probably already have been detected in their vicinity. Nevertheless, the ‘tephra de Sarliève’ and the ‘tephra de Beaunit’ occurrences encourage to search new unknown volcanoes, especially in the Cézallier volcanic area, which is not so well known as the ‘Chaîne des Puys’.
4 Preservation and detection of tephras in sedimentary archives
The unreworked basal part (CF1a) of the tephric complex CF1, clearly identified at the lower part of deltaic D2 unit, is lacking in the basin B1 unit at the bottom of lacustrine pile, before () (ca. 12 000 BP, CF1 age) until the end of Preboreal [until before () or ; Lyon-2435(GrA)] (Figs. 2 and 3): this period includes that of CF1 deposition. These observations raise the question of the tephra initial occurrence or of a possible alteration of it in distal basins. In the same way, the ‘tephra de Sarliève’ observed in deltaic deposits is lacking in distal basin deposits.
CF1 traces in sediments have been searched in analysing mineralogical and geochemical compositions of B1 unit, where there is no visible evidence of this tephra. We did not observe any indice of mineral similar to CF1 forming minerals; however, B1 unit in all core drillings performed in distal basin deposits, systematically contains zeolites: analcite (often abundant) in the most distal deposits and clinoptilolite in the marginal distal deposits (Fig. 1). Furthermore, sediments of the B1 unit are highly enriched in silicates, particularly microcrystalline quartz, in comparison with the whole carbonated-rich sedimentary infill.
As Oligocene substratum and soils of the catchment contain zeolites, these minerals could be inherited in B1 sediments; zeolites are known to be resistant to detrital reworking and then to be stored in alluvium [19]. Nevertheless SEM observations of B1 unit samples showed pristine analcite crystals (Fig. 4). Habits evolve from base to top of the B1 unit. At the lower part of B1, where analcite is particularly abundant (Fig. 4.1), it fills lens-shaped cavities (100 μm across 30 to 40 μm). In the median part of B1 (Fig. 4.2) analcite mainly forms grapes of pristine silt-sized crystals, apparently grown on host-sediment particles. Such habits seem to prove the dominant authigenic origin of analcite. In the upper part of B1, the less abundant analcite crystals mainly form grapes of silt-sized worn clasts. Such a feature allows us to assume a dominant detrital origin from slopes, or an in situ reworking of endogenic analcite crystals.
Authigenic zeolite is described in ancient and modern lacustrine sediments in North America, East Africa and in Europe. In most cases, zeolite formation is interpreted as the result of reactions between trachytic glasses or pyroclasts, and brackish to saline and/or alkaline waters [13,23–25,27–29]. In Sarliève, high analcite concentration in B1 unit could have a similar origin. The fall of CF1 tephra at about () (ca. 12 000 BP), would have covered the whole lacustrine depression. Distal basins were endoreic, with highly restricted conditions and brackish and alkaline waters, the table of which being low. Such conditions seem to have prevailed during the Lateglacial and the Holocene until Lower Atlantic, as shown by microbial dolomite authigenesis in the B2 unit [8,9]. Trachyandesitic tephra would have dissolved in the lacustrine bottom waters, which were probably enriched in dissolved matter yielded by the weathering of tephra deposited on slopes, leading to zeolite authigenesis in the lake.
A zoning of volcanic material distribution has been observed in lacustrine sediments of Sarliève (Fig. 1): delta deposits (including T1 and D2) and proximal basin deposits comprise CF1 tephra layer and/or black ashes/sands reworked from this tephra. The B1 unit at the lower part of the distal basin deposits is in a similar stratigraphical position. In peripheral area, B1 contains clinoptilolite, while in more central area it contains analcite. The same distribution has been described in Lake Tecopa [23], where it has been proved that authigenic zeolites derived from volcanic glasses transformation in saline waters. Furthermore, as shown by [14], crystallization of NaAl silica gels due to volcanic glasses alteration can lead to analcite monomineralogical layers: a similar way can be drawn up for the analcite filling lens-shaped cavities at the lower part of the B1 unit (Fig. 4.1). CF1 dissolution and subsequent zeolite authigenesis in distal basin deposits agree with the lack of any trace of CF1 tephra in distal basins like in surficial formations on slopes.
The ‘tephra de Sarliève’ layer not observed in basins, could have been dissolved in the same way. Nevertheless, we did not observe abundant zeolites in the B4 unit: the small thickness of the tephric fallout (1–2 cm), coupled with mainly open water conditions in the depression since the end of Atlantic, have probably not allowed massive zeolite authigenesis.
Analcite authigenesis underlines the relatively brackish to saline and alkaline nature of waters in north and south basins since the Lateglacial, during and after the CF1 fallout. In sediments deposited in such environmental conditions, high pristine zeolite concentration can be useful to detect the initial presence of tephras in carbonated sediment piles.
5 Conclusions
Investigations carried out on the Sarliève catchment have highlighted two facts concerning tephras in sedimentary deposits. (1) Deltaic area sediments comprise two unreworked tephra fallout: CF1 tephra, regionally well known, deposited around () (ca. 12 000 BP), which enables to date the beginning of lacustrine phase, and ‘tephra de Sarliève’, which differs from all the known trachytic tephras of the ‘Chaîne des Puys’. Dating of this tephra from pollen data allows us to hypothesize that it is as young as the beginning of Subboreal: it emphasizes that volcanic eruption(s?) coming from a still unknown volcano of the ‘Chaîne des Puys’ or from the volcanic Cézallier occurred more than 1000 years after the last presently well-known eruption in the ‘Chaîne des Puys’. (2) These two tephras are preserved in delta pile because quickly buried under sediment layers. They are lacking in distal basin deposits of the Sarliève marsh because dissolved after their fallout. On slopes, they were quickly weathered. In lacustrine basins, tephra dissolution in relatively brackish to saline and alkaline waters induced authigenetic zeolites during Lateglacial and Lower Holocene. Different geochemical conditions of tephra alteration induced a zonation in zeolitic mineral distribution (analcite and/or clinoptilolite) in sediments. Abundant zeolites could be useful indicators of initial tephra occurrence in carbonated sediment piles.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the French CNRS ECLIPSE programme “Interactions activités humaines – production et stockage de sédiments à l'Holocène en plaine et en moyenne montagne”, the CNRS ‘ZA Loire’ programme and the ‘Région Auvergne’ (France). We thank J.-P. Bakyono, I. Pène and many other collaborators for their contribution to the acquisition of field data and sediment analysis. Thanks to the anonymous referees for their constructive comments.