1 Introduction
The Variscan orogenic belt was formed between 480 and 250 Ma as a result [55] of the diachronous collision between Laurentia ± Baltica (Laurussia) to the northwest and Gondwana to the southeast. Small, intermediate continental plates, such as Avalonia and Armorica, have been defined between these two continents; they are separated by oceanic sutures and are generally assumed to have been detached from Gondwana during the Ordovician and docked onto Laurentia and Baltica before the Carboniferous collision between Gondwana and Laurussia. This article will consider the Sardinian and Corsican geological history (Fig. 1) within the “southern Variscan realm” (SVR) from Bohemia southward through the Alps [39], the Maures Massif [6], Corsica and Sardinia (and southward to Calabria and Kabylie) and an attempt will be made to propose a geodynamic Paleozoic scenario in the frame of European Variscides. The present organization of the “SVR” can be considered to have resulted from the Stephanian drift, over hundreds of kilometres away from eastern Bohemia [39,73], of dilacerated blocks along a transpressive dextral mega-shear zone as the result of the large clockwise rotation–translation of Gondwana towards North America [3]. Palaeomagnetic measurements [30] show that the Late Carboniferous Corsica–Sardinia batholith intruded a mosaic of exotic blocks; and that a Tethyan oceanization resulted in a partial dispersion/disappearance of Variscan chain. The final pattern was subsequently modified by Alpine collision and the opening of Mediterranean back-arc basins. Blocks within the SVR display many common characteristics, such as the association of low-grade Panafrican and Eovariscan metamorphic basements, and the presence of Mg–K granites [73]. These blocks include the Corsica–Sardinia microcontinent (CSM) which was formed after a 30° Miocene anticlockwise rotation away from Europe. The CSM recorded two main magmatic events that sealed the respective position of host formations; the first at 340 Ma (prior to the major Stephanian dismemberment of the “SVR”), and the second between 330 and 280 Ma. We have used these as “milestones” in discussing the present and the palaeo-organization of the CSM.
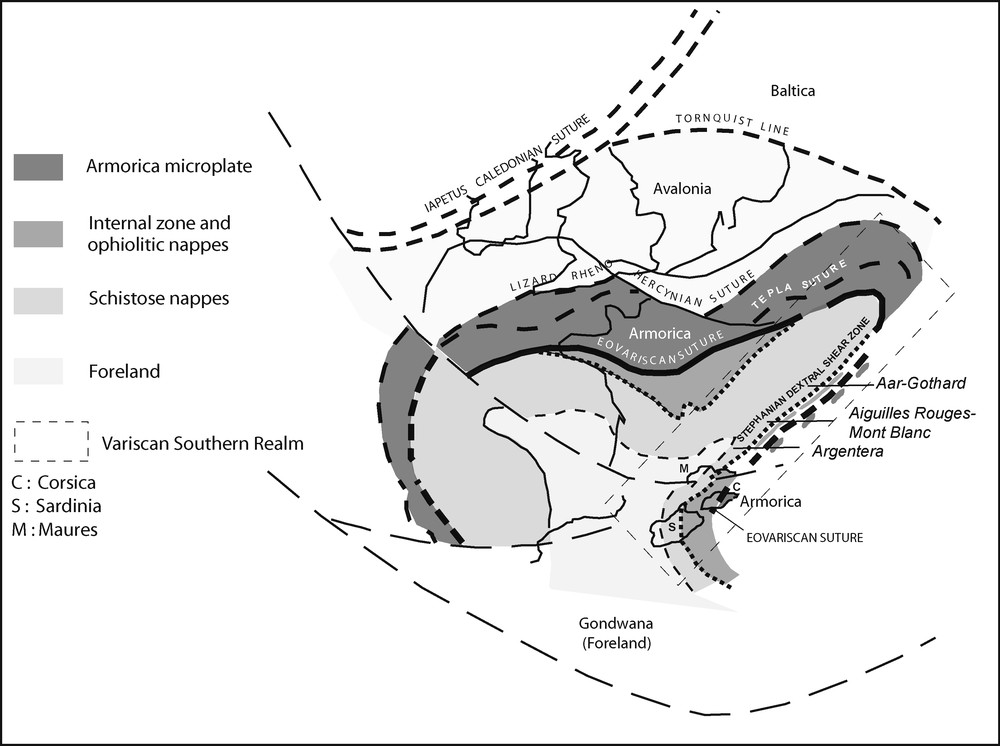
The southern Variscan realm in western Europe. Permian Variscan zonation after Matte [55].
Fig. 1. La branche varisque méridionale en Europe de l’Ouest. Zonation varisque au Permien d’après Matte [55].
A north–south transect of the CSM from the northern (Galeria) External Zone of Corsica to the southern (Iglesiente–Sulcis) External Zone of Sardinia shows in detail the general organization and lithological composition of the Internal Zone and the Nappe Zone [13]. The relation between the CSM and the Maures Massif is well explained by the original position of both Massifs before the Miocene rotation of the CSM. The palinspastic restoration reveals a close fit between Maures and northwestern Sardinia that are documented by similar collision-related prograde tectonic–metamorphic features, postcollision evolution in the Variscan basement, as well as by strong similarities in the Mesozoic covers, including a Mid-Cretaceous bauxite-bearing stratigraphic interval [53].
The structural frame of the CSM along studied transect is best exposed in Sardinia where the structural pile originated through a complex polyphase deformation [12] that is characterized by a compressional event (D1) followed by a late extensional event (D2). The D1 event can be divided into three main synmetamorphic phases: the first one generated south-verging overturned folds and top-to-south thrusts; the second is characterized by east–west shortening with top-to-west tectonic transport and exhibits a strong noncoaxial component and the third corresponds to a postnappe piling folding resulting in broad upright antiforms and synforms consistent with a north–south shortening. The D2 event was characterized by a vertical shortening responsible for recumbent folding of previously steep fabrics, reworking of an older S1 foliation, and ductile to brittle low-angle normal shearing. The D2 phase ended with the emplacement of late-orogenic granite and the formation of Late Carboniferous to Early Permian basins that are common features in the South European Variscides.
2 The External Zones
In Corsica, the best preserved External Zone formations crop out near Galeria and in the Agriate (Figs. 2 and 3). They also occur as roof pendants of the batholith's host rocks along its eastern margin up to Corte, although here they bear a strong thermal imprint and have been transformed to hornfels. The base of the succession consists of polydeformed metaquartzite to metagreywacke. The rocks were in no place metamorphosed higher than in lower greenschist facies.
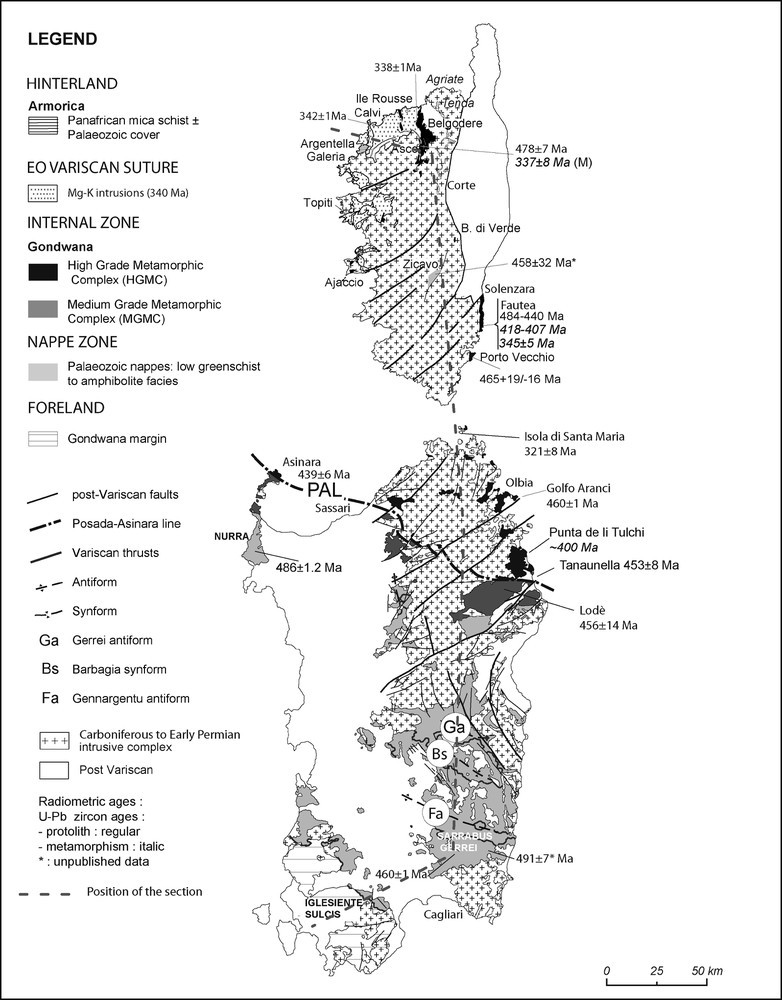
Location of the main Variscan zones in Sardinia and Corsica and position of the section represented on Fig. 3.
Fig. 2. Localisation des principales zones varisques en Sardaigne et en Corse et position de la coupe représentée sur la Fig. 3.
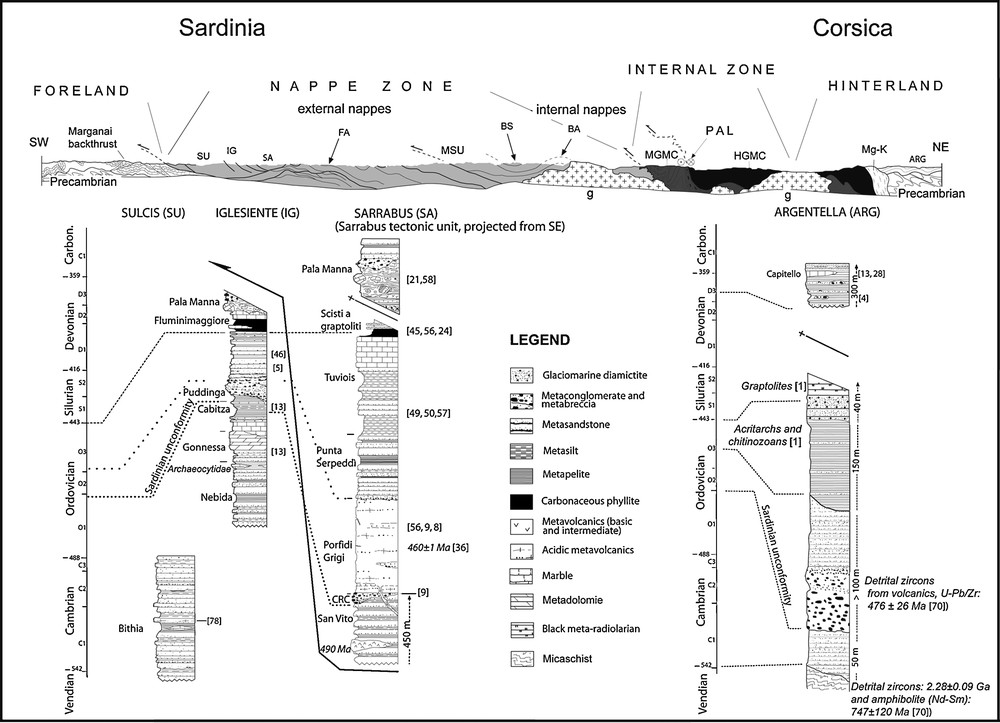
Schematic section through the Variscan southern realm along the Corsica–Sardinia transects and position of the sketch representative successions (abbreviations, see text) [45,56].
Fig. 3. Coupe schématique de la branche varisque méridionale à travers le bloc Corso-Sarde et position des logs représentatifs (abréviations, voir texte) [45,56].
Systematic dating of zircons in mica schist from the Agriate shows that these rocks were recycled from an older (2.28 ± 0.09 Ga) basement [71] with “Gondwanian” characteristics. The interbedded metabasalts were derived from enriched MOR-type basalt, suggesting an intracontinental rift-type setting. A whole-rock Nd–Sm ilmenite and amphibole isochron has provided an age of 747 ± 120 Ma [70]; although poorly defined, this age dates the metabasalt as Panafrican (Cadomian). This formation was also identified in the western part of the Maures massif (southeastern France [6]). A detrital zircon dating of mica schist from the Giens Peninsula (Maures Massif) reveals that more than 50% of the population displays a Neoproterozoic age of about 584 ± 7 Ma, with other older ages ranging between Neoproterozoic and Archaean (Fig. 6A) indicating Gondwana provenance.
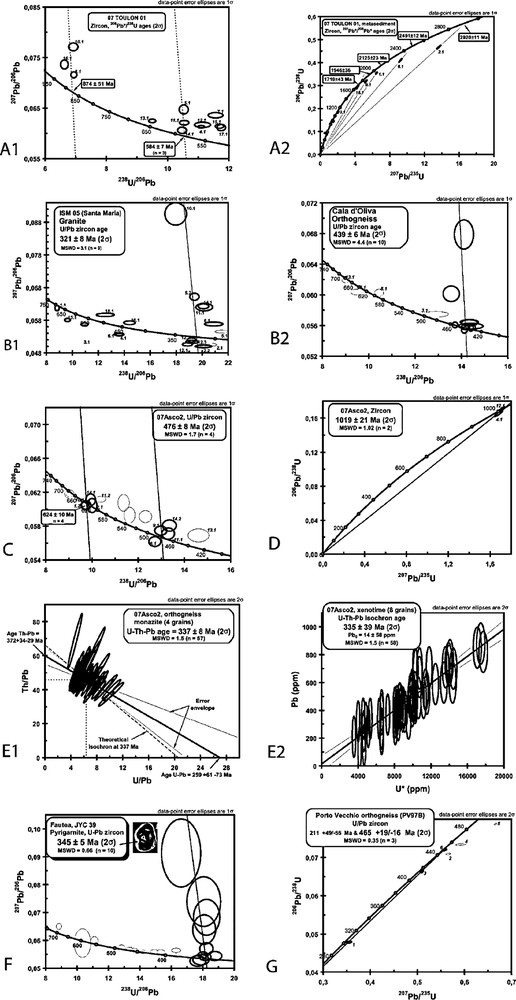
A. Zircon geochronology for paragneiss from the Giens peninsula (sample Toulon: A1). Common Pb uncorrected Tera and Wasserburg diagram [76] leading to an estimated age of 874 ± 51 Ma. Some of the remaining analyses showing evidence of Pb* loss, the second group of “young” grains is better constrained by using a conventional diagram (not represented). An age of 584 ± 20 Ma is defined using nine analyses. A2. A large set of inherited grains were dated up to 2920 ± 11 Ma. B. Zircon geochronology for Santa Maria orthogneiss. B1. Common Pb uncorrected Tera and Wasserburg diagram [76] leading to an age of 321 ± 8 Ma using nine analyses. The other analyses, close to the Concordia curve may represent inheritance ranging from 692 ± 20 Ma to 432 ± 20 Ma. Grain 13 leads to an Archean age of 2547 ± 49 Ma (diagram not represented). B2. Common Pb uncorrected Tera and Wasserburg diagram [76] for Cala d’Olivia orthogneiss. An age of 439 ± 6 Ma can be calculated using 10 analyses. The other analyses, close to the Concordia curve can represent inheritance ranging from 677 ± 20 Ma to 481 ± 32 Ma. C. Zircon geochronology for Asco orthogneiss. Common Pb uncorrected Tera and Wasserburg diagram [76] leading to estimated ages around 624 ± 10 Ma and 476 ± 8 Ma using only four analyses for each group. D. Zircon geochronology for Asco orthogneiss. Two concordant analyses give an inherited age of 1019 ± 21 Ma. E. Some rare monazite and xenotime grains could be dated using chemical EPMA dating. E1. Four monazite grains led to an average age of 337 ± 8 Ma. However, the error envelope associated to the calculated regression line does not overlap the theoretical isochron at 337 Ma. It is likely that two age populations (e.g. 350 and 320 Ma) are involved in the “average age”. The analytical precision on each individual analysis does not allow these populations to be distinguished. E2. The slope of the regression line calculated with xenotime analysis (eight grains) gave similar age at 335 ± 39 Ma. F. Common Pb uncorrected Tera and Wasserburg diagram [76] for Fautea pyrigarnite (JYC 39). An age of 345 ± 5 Ma can be calculated using 10 analyses on large zircon rims generally characterized by extremely low U content (< 10 ppm). The other analyses, mainly realized on zircon cores, plot along the Concordia curve. From geological constraints, the group of ages ranging from 688 ± 20 Ma to 555 ± 10 Ma could be interpreted as inheritance, those between 484 ± 7 Ma and 440 ± 6 Ma as the age of the protolith, and those from 418 ± 6 Ma to 407 ± 6 Ma as resulting from HP–HT metamorphism. G. Zircon geochronology for Porto Vecchio orthogneiss (PV97B) using the conventional dissolution method. An Ordovician age is calculated using the data from three fractions: 465 +19/−16 Ma. Three other fractions including various proportions of inheritance gave mixing ages without geological significance. Masquer
A. Zircon geochronology for paragneiss from the Giens peninsula (sample Toulon: A1). Common Pb uncorrected Tera and Wasserburg diagram [76] leading to an estimated age of 874 ± 51 Ma. Some of the remaining analyses showing evidence of Pb* loss, the second ... Lire la suite
Fig. 6. A. Géochronologie sur zircon des paragneiss de la presqu’île de Giens (échantillon Toulon : A1). Le diagramme de Tera et Wasserburg non corrigé pour le Pb commun [76] fournit un âge estimé à 874 ± 51 Ma. Quelques analyses montrent une évidence de perte de Pb* ; le second groupe de grains « jeunes » est mieux défini en utilisant un diagramme conventionnel (non représenté). Un âge de 584 ± 20 Ma est défini en utilisant neuf analyses. A2. Un grand nombre de grains hérités ont été datés jusqu’à 2920 ± 11 Ma. B. Géochronologie sur zircon de l’orthogneiss de Santa-Maria. B1. Le diagramme de Tera et Wasserburg non corrigé pour le Pb commun [76] fournit un âge de 321 ± 8 Ma à partir de neuf analyses. Les autres analyses, proches de la Concordia peuvent représenter un héritage allant de 692 ± 20 Ma à 432 ± 20 Ma. Le grain 13 a un âge Archéen de 2547 ± 49 Ma (diagramme non représenté). B2. Diagramme de Tera et Wasserburg non corrigé pour le Pb commun [76], pour l’orthogneiss de Cala d’Olivia. Un âge de 439 ± 6 Ma peut être calculé à partir de dix analyses. Les autres analyses, proches de la Concordia peuvent représenter un héritage allant de 677 ± 20 Ma à 481 ± 32 Ma. C. Géochronologie sur zircon de l’orthogneiss d’Asco. Le diagramme de Tera et Wasserburg non corrigé pour le Pb commun [76] fournit des âges estimés autour de 624 ± 10 Ma et 476 ± 8 Ma, en utilisant seulement quatre analyses pour chaque groupe. D. Géochronologie sur zircon de l’orthogneiss d’Asco. Deux analyses concordantes donnent un âge hérité de 1019 ± 21 Ma. E. Quelques rares grains de monazite et de xénotime ont pu être datés en utilisant la datation chimique à la microsonde électronique. E1. Quatre grains de monazite donnent un âge de 337 ± 8 Ma. Cependant, l’enveloppe d’incertitude, associée au calcul de la droite de régression, n’inclut pas l’isochrone théorique à 337 Ma. Il est vraisemblable que l’âge de deux populations (autour de 350 et 320 Ma) est fondu dans un « âge moyen ». La précision analytique sur chaque analyse individuelle ne permet pas de distinguer ces deux populations. E2. La pente de la droite de régression calculée à partir des analyses de xénotime (huit grains) fournit un âge comparable à 335 ± 39 Ma. F. Diagramme de Tera et Wasserburg non corrigé pour le Pb commun [76] pour la pyrigarnite de Fautea (JYC 39). Un âge de 345 ± 5 Ma peut être calculé à partir de dix analyses sur de larges zones périphériques de zircon, généralement caractérisées par une faible teneur en U (< 10 ppm). Les autres analyses, réalisées sur les cœurs, se disposent sur la Concordia. D’après les données géologiques, les groupes d’âges allant de 688 ± 20 Ma à 555 ± 10 Ma peuvent être interprétés comme un héritage, ceux entre 484 ± 7 Ma et 440 ± 6 Ma comme l’âge du protolithe, et ceux de 418 ± 6 Ma à 407 ± 6 Ma comme résultant du métamorphisme HP–HT. G. Géochronologie sur zircon de l’orthogneiss de Porto Vecchio (PV97B) en utilisant la méthode conventionnelle par dissolution. Un âge Ordovicien est calculé en utilisant les données obtenues à partir de trois fractions : 465 + 19/−16 Ma. Trois autres fractions incluant diverses proportions de grains hérités ont fourni des âges mixtes sans signification géologique. Masquer
Fig. 6. A. Géochronologie sur zircon des paragneiss de la presqu’île de Giens (échantillon Toulon : A1). Le diagramme de Tera et Wasserburg non corrigé pour le Pb commun [76] fournit un âge estimé à 874 ± 51 Ma. Quelques analyses montrent une évidence ... Lire la suite
In Argentella crops out the most complete nonmetamorphosed Palaeozoic succession [1,28] (Fig. 3). In fault contact with this succession is a Late Devonian “Culm” formation (Givetian to Famennian after Baudelot et al. [4]) composed of micaceous shale and sandstone with conglomerate lenses. Within the “Culm” succession occurs the Capitello limestone ranging in age from Late Famennian (at its base) to Strunian (at its top) [4].
In Sardinia, the External Zone succession (Fig. 3) begins with a Vendian succession (Bithia Formation); the formation exhibits two foliations and greenschist facies metamorphism, and includes metabasite that could be related to a rifting stage [78]. The overlying Nebida Formation is itself overlain by a carbonate platform (Gonnessa Formation) capped by Early Ordovician shale (Cabitza Formation) [13]. This succession encompasses the entire Cambrian system and the base of the Ordovician, and is unconformably overlain (Sardic unconformity) by Late Ordovician continental conglomerate of the Puddinga Formation. The Caradocian–Ashgillian transgression was followed by a new depositional sequence characterized by Uppermost Ordovician glaciomarine deposits with interbedded basic alkaline rocks [5,46]. The succession ends with Silurian–Devonian black shale (Fluminimaggiore Formation) and limestone capped by Culm-like deposits (Pala Manna Formation). The Palaeozoic succession of the External Zone of southwestern Sardinia recorded no significant metamorphic imprint after the Variscan orogenic events: both the pre-Sardic and post-Sardic sequences at Iglesiente are nonmetamorphic or anchimetamorphic. Whether metamorphism and significant deformation were associated with the Sardic phase is still matter of debate; some authors reject the concept of a Sardic “folding” phase and attribute the structuring of the External Zone exclusively to Variscan tectonism [52]. It is likely that these formations belong to the Gondwana margin based on the similarity between the External Zone Palaeozoic of Sardinia (Iglesiente) and the Montagne Noire (France) successions interpreted as Gondwana foreland.
The successions of southern Sardinia [13] can be compared with the Galeria succession of northern Corsica, although with some significant differences. The Sardinia successions lack a thick Caradocian conglomerate, similar to that at Monte Martinu of Corsica, and a Devonian silicic clastic flysch [28]. Conversely, the Galeria succession lacks the Ordovician volcanism and thick Middle Cambrian to Middle Ordovician successions found in southern Sardinia, as well as the Ashgillian “schistes troués” typical of the peri-Mediterranean and the black shale [13]. This indicates that the Palaeozoic of Galeria was not deposited in the same area as the Palaeozoic of southern Sardinia, the Maures Massif or Montagne Noire. As the Galeria formations and the Internal Zone have been dated at 340 Ma, i.e. prior to the major Stephanian continental dextral-shear episode, one can assume that this foreland zone, symmetrical vis-à-vis the Internal Zone, acted as a hinterland as it has been previously suggested [11]. It was probably part of a microcontinent that separated from Gondwana during the Ordovician, hereafter considered as Armorica [55], and keeping in mind that the latter represents a mosaic of microcontinents [75].
3 The Nappe Zone
In Corsica, several remnants of the prebatholitic host rocks dispersed as roof pendants can be related to the Nappe Zone in Zicavo and Topiti (Fig. 2). These rocks display a greenschist to amphibolite facies metamorphism. Three fault-separated compartments are identified at Zicavo [79]: orthogneiss derived from a peraluminous metagranite, dated at 458 ± 32 Ma (U–Pb; unpublished), a metaharzburgite-bearing amphibolitic complex, and metamorphosed black shale. The outcrop at Topiti consists of serpentinite with the original composition of dunite, orthopyroxenite, harzburgite and Cambrian–Ordovician metabasalt (E-MORB).
In Sardinia, the Nappe Zone comprises a stack of Palaeozoic tectonic units that extend from Sarrabus in the southeast (External nappes) to Nurra in the northwest (Internal nappes) with the metamorphic grade increasing northward from lower greenschist to amphibolite facies.
The successions of the more external nappes, in the central and southeastern parts of the island (Fig. 3), are characterized by Cambrian to Tremadocian–Early Arenigian metasandstone (San Vito Formation); they were deposited on a terrigenous shelf and host a small number of acid metavolcanic bodies dated at 490 Ma (unpublished data). These formations are unconformably (Sarrabese unconformity [9]) capped by a thin continental metaconglomerate (Rio Ceraxa conglomerate “CRC”) and thick sequence of metamorphosed calc–alkaline [57] volcanic rock (Porfidi Grigi) ranging from basaltic andesite to rhyolite [8,9].
The varied Ordovician volcanogenic formations are the most complete and best preserved within the SVR. Their origin is related to an Ordovician arc that developed on the North-Gondwana margin as a consequence of oceanic subduction [10,24,75]. The age of the volcanic activity, well constrained by both stratigraphy and palaeontology, postdates the Sarrabese (i.e. Sardic) unconformity and predates the Caradocian–Ashgillian transgression. This chronostratigraphic constraint fits the in situ U–Pb dating of the metarhyolite at Sarrabus (460 ± 1 Ma [37]). Similarly, the orthogneiss at Lodè, which is considered to be the intrusive counterpart of this volcanism, has yielded an in situ U–Pb zircon age of 456 ± 14 Ma [41]. A Caradocian–Ashgillian transgression throughout the palaeogeographic domain of the Nappe Zone led to the deposition of shoreface to shelf sandstone [49,50,57] (Tuviois and Pta Serpeddì Formations [2]). The different units of the Nappe Zone in Sardinia (Fig. 2) all reveal a Silurian succession, typically represented by black shale and black phyllite (Scisti a graptoliti). The outcrops of Silurian shales are overlain by a continuous Tentaculites-bearing metamarlstone and Clymenia-bearing shelf limestone (Pala Manna Formation) that encompass the entire Devonian and base of the Carboniferous [21,58].
4 The Internal Zone
In Corsica, the high-grade metamorphic complex (HGMC) comprises leptynite–amphibolite complexes with eclogite boudins, orthogneiss and metasediments derived from an Early Palaeozoic protolith that includes gneiss (amphibolite with granulite) which is commonly anatectic (Belgodere [64], Porto Vecchio) and locally contains eclogite boudins (Fautea [47]). The protolith of the Fautea pyrigarnite that underwent a HP (≈ 1.2–1.5 GPa)/HT (≈ 800–900 °C) metamorphism [48] has been estimated in between 484 ± 7 and 440 ± 6 Ma (Fig. 6F); the ages ranging between 418 ± 6 and 407 ± 6 Ma (Fig. 6F) are interpreted as those of the peak metamorphism. The protolith of aluminous orthogneiss has been dated (U–Pb/zircon) at 465 + 19/−16 Ma (Porto Vecchio) (Fig. 6G) and 476 ± 8 Ma (Asco) (Fig. 6C and inherited zircon at 1.02 Ga on Fig. 6D). Peak metamorphism was followed by crystallization of zircon rim at 345 ± 5 Ma (Fig. 6C, and in the monazites at 337 ± 8 Ma at Asco; Fig. 6E1). The metamorphic peak conditions (≈ 360 Ma) estimated for the Solenzara granulite were calculated at 900–1000 °C and ≈ 1.4–1.8 GPa [38]. The gneiss of Porto Vecchio is estimated to have reached peak temperature conditions (700–750 °C at less than 1.0 GPa) at c.a 350 Ma, whilst monazite dating indicates that this deformation occurred at c.a 320 Ma [38]. As previously underlined [38], the Porto Vecchio–Fautea-Solenzara complex is made up of rocks having undergone different P–T conditions at different times, reflecting the progressive foreland in sequence migration of the orogenic front.
The HGMC of northern Sardinia and Asinara Island (Fig. 2) underwent three main metamorphic events. The higher grade first (eclogitic) and second (granulitic) events are preserved only in the mafic protoliths; the third event is better recorded in the pelitic rocks. The HGMC which consists mainly of migmatite is characterized by similar orthogneiss, leptynite–amphibolite complexes and eclogite boudins with an N- to T-MORB signature [34]. Layered mafic–ultramafic bodies (including metagabbro) with HT granulitic mineral assemblages crop out at Golfo Aranci [35,36]. An eclogite boudin with a granulitic overprint is exposed at Punta de li Tulchi [22,32,54] within an orthogneiss and metapelite complex affected by widespread anatectic mobilization under amphibolite facies conditions in the stability field of sillimanite and, locally, cordierite. U–Pb zircon ages of this eclogite give 450 Ma for the protolith, whilst ages at 403 ± 4 Ma are interpreted as dating the crystallization of a second zircon population during eclogite metamorphism (Fig. 4) at 1.3 GPa, 690–760 °C [22]. Leptynite–amphibolite complexes are also found on Asinara Island [15] and near Olbia, the former exhibiting an alkaline and the latter [33] a continental tholeiitic affinity. Ortho-derived migmatitic gneiss is widespread and locally prevails over metasedimentary rocks in the Internal Zone of Sardinia; its overall composition ranges from granodiorite to monzogranite with a high-K calc–alkaline character. The latter generally exhibits an augen texture with K-feldspar porphyroclasts. Available radiometric data are 458 ± 31 Ma (whole rock Rb–Sr [26]) and 453 ± 8 Ma (in situ U–Pb zircon [40]) for the Tanaunella orthogneiss, and 460 ± 1 Ma (U–Pb zircon [39]) for the magmatic protolith of a migmatitic gneiss at Golfo Aranci. A younger age of 439 ± 6 Ma (U–Pb zircon; Fig. 6B2) was found for the Cala d’Oliva orthogneiss in Asinara Island. The P–T estimate for the leptynite–amphibolite complex from Asinara Island is ≈ 0.8 GPa and ≈ 740 °C [25]. The amphibolite retrogression in the HGMC is documented in both the metabasite and the metapelitic–metaarenaceous lithology where it triggered widespread anatexis. In northeastern Sardinia, anatexis started in the kyanite stability field [23]. Conversely, in northwestern Sardinia and Asinara Island, lower pressure following an almost isothermal uplift has been estimated in the cordierite-andalusite stability field [36,59].
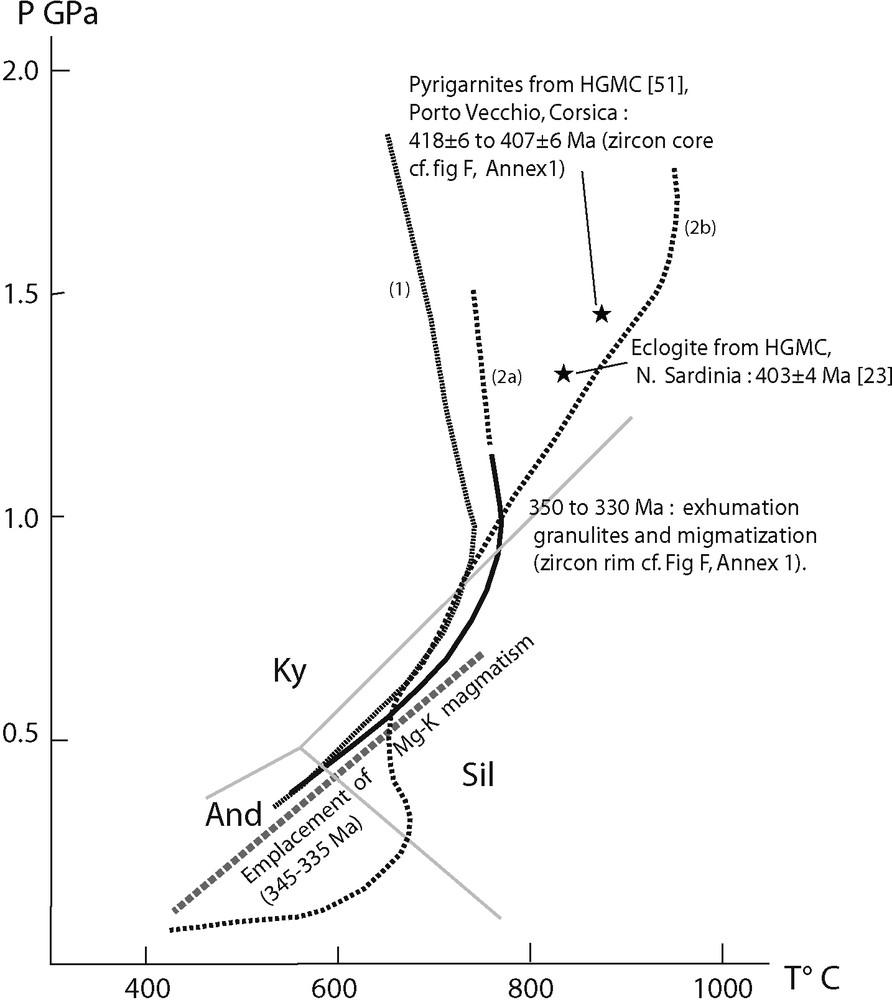
PTt paths for high-grade metamorphic complex (HGMC) rocks from southern Corsica (1): Porto Vecchio, after Giacomini et al. [36]; and northern Sardinia (2a) metabasites (2b) gneiss, after Giacomini et al. [38].
Fig. 4. Trajets P, T, t pour les roches du complexe métamorphique de haut grade de Corse du Sud (1) : Porto Vecchio, d’après Giacomini et al. [36]; et Sardaigne septentrionale (2a) métabasites (2b) gneiss, d’après Giacomini et al. [38].
The episode of Late Carboniferous–Early Permian LP–HT metamorphism is essentially preserved in central Corsica where sillimanite cordierite-andalusite garnet-bearing gneiss is reworked as panels and enclaves in the batholith. As the gneiss displays ductile deformation concordant with that affecting granite, this episode has been dated at about 290 Ma (287 ± 2 Ma [20]) from zircons in leucocratic monzogranite from the North of the Verde pass.
5 The sutures
5.1 The Eovariscan suture in the SVR
In Corsica, the collage between the Galeria External and Internal zones (Armorica–Gondwana collision) can be dated to occur between the deposition of the Early Tournaisian formations (about 360 Ma) and the emplacement of the Mg–K intrusions (Fig. 3), i.e. between 345 and 335 Ma. The Mg–K intrusions, composed of monzonitic and associated ultrapotassic mafic rocks and exposed in western Corsica between Île Rousse to the north and Ajaccio to the south, sealed the “collage” between the two basements (mica schist plus Palaeozoic cover and HGMC [70]). They generally form steeply dipping, north–south-trending sheets ranging from several hundreds of metres to a few tens of kilometres in thickness. The contacts between the sheets are locally marked by panels of anatectic gneiss showing ductile deformation with the granite; the Belgodere gneiss underwent anatexis along its western margin during the emplacement of the Mg–K intrusions under amphibolite conditions [68]. The magmatic foliation of the granitoid is at map scale, parallel to that of the mylonitic foliation in the host gneiss dated at 338 ± 1 Ma [65], and (at Asco) 337 ± 8 Ma (Fig. 6E1). Associated subhorizontal lineation in the same direction indicates that the Mg–K granite was emplaced in a context of sinistral transpression [44]. The amplitude of comparable crustal fault zones from other regions has been estimated to reach several hundred kilometres. These zones are associated with northward displacement of the western part of the European Variscan massifs, as it has been proposed for Belledonne Massif in the Alps (Autran et al., in: Keppie [42]). To the west, the Panafrican basement is cut at shallow depth by the Mg–K Argentella granite (338 ± 2 Ma; U–Pb/zircon [65]) that displays a chilled margin at the contact. The Eovariscan suture that delineates the collision between Gondwana and Armorica extends through Galicia, southern Brittany, southern Bohemia, the Alps, the Maures Massif and the CSM, and is marked by the presence of eclogite. The collision was accompanied by strong amphibolite facies retrograde metamorphism of the eclogite, along with migmatization during the Middle Devonian. Note that the collision between the Internal and External zones in the Alps is also sealed by the emplacement of Mg–K granite [39]. The belt of Mg–K granite emplaced at ≈ 340 Ma within the SVR intrudes the Eovariscan suture.
5.2 Contact between the Internal and Nappe zones
The contact between the Internal Zone and the Nappe Zone is well exposed in northern Sardinia, both in the Posada and Coghinas valleys and in Asinara Island (Figs. 2 and 3). Structural data suggest that the MGMC of the Internal Zone overrides the Nappe Zone with a top-to-south motion [10] that later reversed to top-to-west [14]. In the Posada valley, and locally in the Coghinas valley (Giuncana), this contact is complicated by a Late Variscan retrograde dextral shear zone [31] which generated a phyllonite belt under greenschist facies conditions. The strike–slip movement was still active at 301 ± 6 Ma, dated by the U–Pb zircon age of a synkinematic granodiorite emplaced within the shear zone [61]. A deeply deformed belt of mica schist, paragneiss and quartzite, associated with variably retrogressed eclogite, is interposed between the HGMC and the internal nappes. This MGMC belt exhibits an inverted Barrovian metamorphic zonation with the almandine–staurolite–kyanite isograds narrowing within a couple of kilometres towards the overriding HGMC. Eclogite boudins within this belt display a MORB chemical affinity; they exhibit relictual omphacite, but differ from the eclogite of the Internal Zone in that the HT granulitic stage is missing. The PT conditions of the eclogitic stage have been estimated from the omphacite-garnet pair as ≈ 1.5 GPa and 600–700 °C [22], with equilibration under intermediate-pressure amphibolite facies occurring at a maximum pressure of ≈ 0.8 GPa and temperature of 550–600 °C.
6 The Batholith
The peraluminous intrusions of northern Sardinia predate the metaluminous intrusions of the Corsica–Sardinia batholith. The Santa Maria (321 ± 8 Ma; Fig. 6B1) and Barrabisa (313 ± 3 Ma [U–Pb xenotime] to 308 ± 1 Ma [U–Pb/monazite]; unpublished data) massifs are closely associated with the anatexis of the metamorphic basement. Most of the presently exposed Corsica–Sardinia batholith intrusions were emplaced from 310 to 290 Ma (Late Carboniferous–Early Permian), which is a period corresponding to the translation of Gondwana towards North America [3], along a wide transpressive dextral mega-shear zone. The acid and intermediate rocks are metaluminous and the basic rocks tholeiitic. The proportions of the different exposed rock types in the batholith [63] are as follows: tonalite and granodiorite: 7%, granodiorite and monzogranite: 60%, leucocratic monzogranite and hypersolvus granite: 30% and basic rocks: 3%. The existence of structural, chronological and geochemical relationships between the volcanic and plutonic rocks has been recognized in the northwestern part of the Tenda Massif of Corsica [69] and also in Sardinia. Thus the rhyodacitic volcanism and monzo-granodioritic plutonism, on the one hand, and the andesitic volcanism and gabbro–dioritic complexes, on the other hand, would correspond to the expression of magmas having the same respective composition, but emplaced at different levels. The ages of the intermediate to acid intrusions range between 305 and 300 Ma, whereas the emplacement of the metaluminous to alkaline hypersolvus granite occurred around 290 Ma, synchronous with the leucocratic monzogranite and basic rocks [20]. Therefore, the existence of a so-called Permian–Triassic alkaline province in Corsica [7] has to be ruled out. The basic rocks of the batholith form layered basic–ultrabasic complexes, dioritic septa, net-veined complexes and dykes intersecting or coeval with the granitic intrusions between 310 to 280 Ma [20,65]. A typical tholeiitic succession of peridotite (wehrlite), anorthosite–troctolite, olivine gabbro, gabbro–norite, Fe–gabbro and diorite [62] has been identified in the Tenda layered complex dated at 288 ± 2 Ma [20] and also in southern Corsica [19,68]. Many intrusions contain hornblende-bearing gabbro (e.g.: Levie, Punta Falcone).
7 Geodynamic evolution (Fig. 5)
After a microcontinent (cf. Armorica) was detached from the North-GONDWANA margin, convergence between the Laurussia and Gondwana continents began at about 420 Ma (Silurian) with the northwestward subduction of the South-Armorican Ocean below the Armorica microcontinent [55] (Fig. 5).
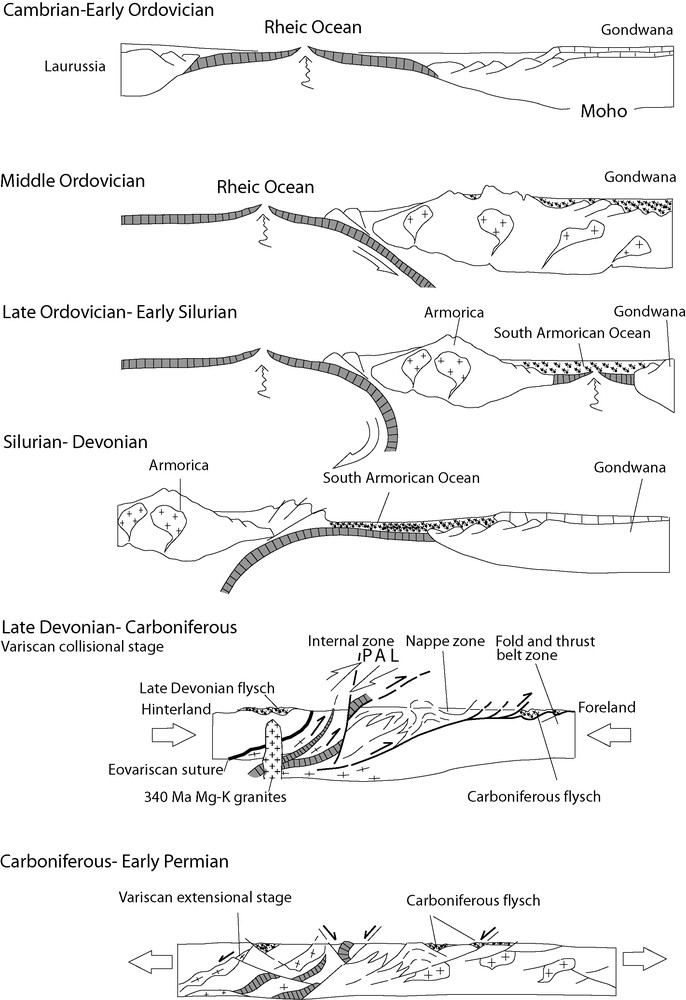
Geodynamic sketch of the evolution of the Corsica–Sardinia block. Cambrian–Early Ordovician. Opening of the Rheic Ocean between Laurussia and Gondwana. Middle Ordovician. Subduction of Rheic oceanic crust beneath the North-Gondwana continental margin and related Andean-type volcanism in Sardinia. Late Ordovician–Early Silurian. back-arc spreading and rifting on the North-Gondwana margin, opening of the South-Armorican Ocean. Silurian–Devonian: subduction of the South-Armorican Ocean beneath Armorica led to a possibly oblique collisional orogenic wedge during the Late Devonian-Early Carboniferous. Late Devonian–Carboniferous: collision between Armorica and Gondwana occurring between the deposition of Early Tournaisian formations (about 360 Ma) and the emplacement of Mg–K plutonic rocks at c.a. 340 Ma. Carboniferous–Early Permian: emplacement of the batholith during the Variscan extension. The zonation of the belt is detailed on Fig. 3. Masquer
Geodynamic sketch of the evolution of the Corsica–Sardinia block. Cambrian–Early Ordovician. Opening of the Rheic Ocean between Laurussia and Gondwana. Middle Ordovician. Subduction of Rheic oceanic crust beneath the North-Gondwana continental margin and related Andean-type volcanism in Sardinia. Late Ordovician–Early ... Lire la suite
Fig. 5. Schéma de l’évolution géodynamique du bloc corso-sarde. Cambrien-Ordovicien inférieur : ouverture de l’océan Rhéique entre Laurussia et Gondwana. Ordovicien moyen : subduction de la croûte océanique de l’océan Rhéique sous la marge continentale septentrionale de Gondwana et volcanisme associé de type andin en Sardaigne. Ordovicien supérieur–Silurien inférieur : ouverture arrière-arc et rifting de la marge septentrionale de Gondwana, ouverture de l’océan sud-armoricain. Silurien–Dévonien : la subduction de l’océan sud-armoricain sous Armorica conduit à la formation d’une collision possiblement oblique et d’un prisme orogénique au Dévonien supérieur–Carbonifère inférieur. Dévonien supérieur–Carbonifère : la collision entre Armorica et Gondwana se déroule entre le dépôt des formations du Tournaisien inférieur (vers 360 Ma) et l’emplacement du plutonisme Mg–K autour de 340 Ma. Carbonifère–Permien inférieur : emplacement du batholite pendant l’extension varisque. La zonation de la ceinture est détaillée sur la Fig. 3. Masquer
Fig. 5. Schéma de l’évolution géodynamique du bloc corso-sarde. Cambrien-Ordovicien inférieur : ouverture de l’océan Rhéique entre Laurussia et Gondwana. Ordovicien moyen : subduction de la croûte océanique de l’océan Rhéique sous la marge continentale septentrionale de Gondwana et volcanisme associé de ... Lire la suite
The good exposure of sedimentary and volcanic Palaeozoic formations in Sardinia provides the constraints for reconstructing the Variscan geodynamic evolution. The Galeria (Hinterland, Corsica) and Bithia (Foreland, Sardinia) basements share common features and can be considered as Neoproterozoic formations originating respectively from northern Gondwana and the future Armorica prior to its detachment.
No volcanic activity was recorded in the Sardinia foreland during the Early to Middle Cambrian, but a volcanic to subvolcanic activity with a transitional signature was recorded in the Late Cambrian (unpublished data). This volcanism predated the Sardic phase and could have resulted from a volcanic passive margin activity. During the Middle Ordovician, vast amounts of volcanic rocks were emplaced in the Nappe Zone above the Sardic unconformity (i.e. they must be post-Arenigian). As the rocks range from andesite to rhyolite and have a calc–alkaline geochemical imprint, an Andean-type volcanism related to Early Ordovician oceanic subduction has been proposed to explain this event [10]. The Late Ordovician saw an end of this volcanism, the collapse of the continental arc and a Caradocian–Ashgillian transgression of the North-Gondwana margin. A new volcanic cycle represented by basalt and microgabbro with an alkaline to transitional signature encompassed the Ordovician–Silurian transition all over Sardinia. As these volcanic products are lacking in the Armorica microplate, they were probably related to a rifting stage that affected the North-Gondwana margin [60]. Such a rifting might represent the onset of a back-arc spreading triggered by the retreat of the oceanic slab subducting the North-Gondwana margin. This resulted in the possible detachment of the Armorica terrane (or assemblage of terranes [75]) made up of the northern Gondwanan crust. A narrow oceanic seaway (South Armorican Ocean) could have formed between the detached terrane(s), with further subduction beneath Armorica leading to a possibly oblique collisional orogenic wedge during the Late Devonian–Early Carboniferous.
Starting with the Silurian, a widespread transgression flooded much of Gondwana and Armorica (which was already detached). Northern Gondwana acted as a passive margin during the Devonian, with carbonate shelf deposits being particularly developed in the External nappes of Sardinia. In northern Corsica (i.e. Armorica), Devonian limestone is restricted to olistoliths within the synorogenic Culm formation. In Sardinia, the Culm-like formation postdates the Tournaisian and is restricted to the Foreland and the External nappes.
The synorogenic Culm-like deposits testify to the onset of collision between Armorica and Gondwana; there is a strong evidence for diachronism between the Foreland (which is post-Tournaisian in the External nappes of Sardinia) and the Hinterland (which is Famennian in the Argentella succession of Corsica). Deformation proceeded progressively from the Internal Zone, which overrides the Nappe Zone, which in turn overrides the Foreland (Fig. 3). The timing of the collision is also constrained by the intrusion of the Mg–K plutons, and by the age of Barrovian metamorphic assemblage [23,27]. The structure resulting from the collision was a mountain chain with a well-displayed tectonometamorphic zonation in which a decompressed lower crust, namely the Internal Zone, overrode the Nappe Zone along a high-strain belt containing metapelite and quartzite (metachert?) associated with eclogite boudins differing from those embedded in the HGMC in that they have a typical subduction-related thermal gradient. This belt, namely the Posada–Asinara line, can be considered as a tectonic mélange thrust onto the Gondwana margin and rooted in the suture zone. The P–T–t environment that led to the Variscan metamorphic peak was the result of isothermal decompression of the continental crust followed by P-constant heating. This last type of evolution is characterized by an extensional regime associated with the collapse of the chain caused by the rupture of a subducted slab and/or by a mantle/lithosphere decoupling after continent–continent collision [74] (see cartoon in Rossi and Cocherie [68]).
The superheating process could have resulted from a drastic asthenospheric rise during the Carboniferous that almost immediately provoked the production of large volumes of basic/acid magma. This model fits with the “flat” thermal profile registered by the lower crust between 360 and 310 Ma, and which correlates with the decompression caused by crustal uplift, followed by drastic heating from 310 to 280 Ma due to crustal stretching and mafic magmatic underplating [68,72]. Geochemical modelling indicates that the basic magmatism was derived from 10% nonmodal partial melting of a heterogeneous mantle of spinel or amphibole peridotite without garnet [19], i.e. a lithosphere less than 60 km thick underlain by an ascending asthenosphere.
A continental source for the felsic rocks has been constrained by isotopic data. Geochemical modelling fits with 30% partial melting of a protolith of greywacke-like composition, whose mean age ranges from 800 Ma for Corsica to 1200 Ma for Sardinia [19]. The formation of the crustal sources has been related to the Ordovician magmatic event [77]. The observed variations in the model ages of the protoliths could depend upon the ratio between Proterozoic and Palaeozoic components melted after being underthrust into the lower crust following the Variscan collision. Sr–Nd data show that the composition of the rocks from the mafic tholeiitic complexes cannot be representative of that of the parental magma of Corsican A-type granite [67]. As the Corsican A-type granite composition fits with the A2 type classification [29], their origin from a source derived from the high-temperature melting of depleted continental crust could be favoured [20].
8 Conclusions
The SVR is a late Variscan structure formed by numerous blocks dispersed along a large Late Carboniferous dextral shear zone. Within these blocks, a complete, well-preserved exposure of a section of the Variscan belt is displayed in the CSM where many remnants showing characteristics of the Internal Zone are dispersed within huge granitic intrusions. In northern Corsica, the Eovariscan suture bridging the contact between remnants of the Armorica microplate (to be considered as a mosaic of microcontinents) and the HP–HT migmatitic Internal Zone was intruded by Visean Mg–K granite. The Internal Zone rooted in the Eovariscan suture overthrust the Nappe Zone in northern Sardinia.
The well-exposed products of the Ordovician volcanism in the Nappe Zone provide evidence that this collisional structure resulted from an earlier subduction of Rheic oceanic crust beneath the North-Gondwana continental margin. Beginning in the Late Ordovician, back-arc spreading led to rifting on the North-Gondwana margin, which was followed by subduction beneath the Armorica Terrane Assemblage during the Silurian–Devonian. The collision generated a Gondwana-verging orogenic wedge, as testified by both the structural and metamorphic zoning across the Corsica–Sardinia Variscan transect.
Acknowledgements
We thank the editor, K. Schulmann, and the reviewers, J. von Raumer and V. Janousek, for their critical comments that have been of invaluable help in improving the manuscript. Thanks are also due to C. Guerrot who provided U–Pb conventional age of the Porto Vecchio orthogneiss. Sir Patrick Skipwith is thanked for the translation into English. This is the BRGM contribution no 05923.
Annex 1 Geochronology
The raw data for these results are presented in Tables 1 to 5 as supplementary material (see the web version of this article), and are summarised on Fig. 6.
Due to the high probability of heterogeneous U-enriched phases suitable for geochronology, in situ techniques were generally selected. Zircon grains were dated using :
Chemical dating was applied for monazite and xenotime (electron probe microanalysis [EPMA]) accordingly to the method of data reduction [16,17]. Data error ellipses for U–Pb zircon analyses were drawn at the 1σ level in order to facilitate reading of the geochronological diagrams, but all calculations were done at the 2σ level using Isoplot [51]. As an exception, an orthogneiss sample from Porto Vecchio was dated using a conventional dissolution method developed by Krogh [43] and improved by Parrish [66].


