1. Introduction
The Upper Cretaceous Chalk of the eastern Paris Basin close to Provins (Seine-et-Marne) was cored at Poigny and Sainte-Colombe by the Craie 700 programme in 1999 [Figure 1; Mégnien and Hanot 2000]. The objective was to provide regional reference sections for the Chalk where the succession approaches its maximum preserved thickness in the Basin ( >600 m, Figure 1), and to characterise large-scale diagenetic patterns that affect seismic wave velocity, variations in which had remained unexplained despite more than 50 years of petroleum exploration.
The Poigny area (Figure 1) displays “normal” Chalk seismic velocities while the Sainte-Colombe area was chosen to represent an area of anomalous fast velocities [Mégnien and Hanot 2000]. These were shown to be caused by local bodies of dolomitized chalk: the Sainte-Colombe borehole includes a dolostone interval in the mid-Campanian and the underlying Campanian–Turonian chalks display pervasive diffuse ( <15% dolomite) dolomitization [Gély and Blanc 2004, Thiry et al. 2003]. By contrast, dolomite is absent from the Campanian at Poigny, and occurs as only a minor accessory mineral below, despite the site being located <3 km to the east of Sainte-Colombe.
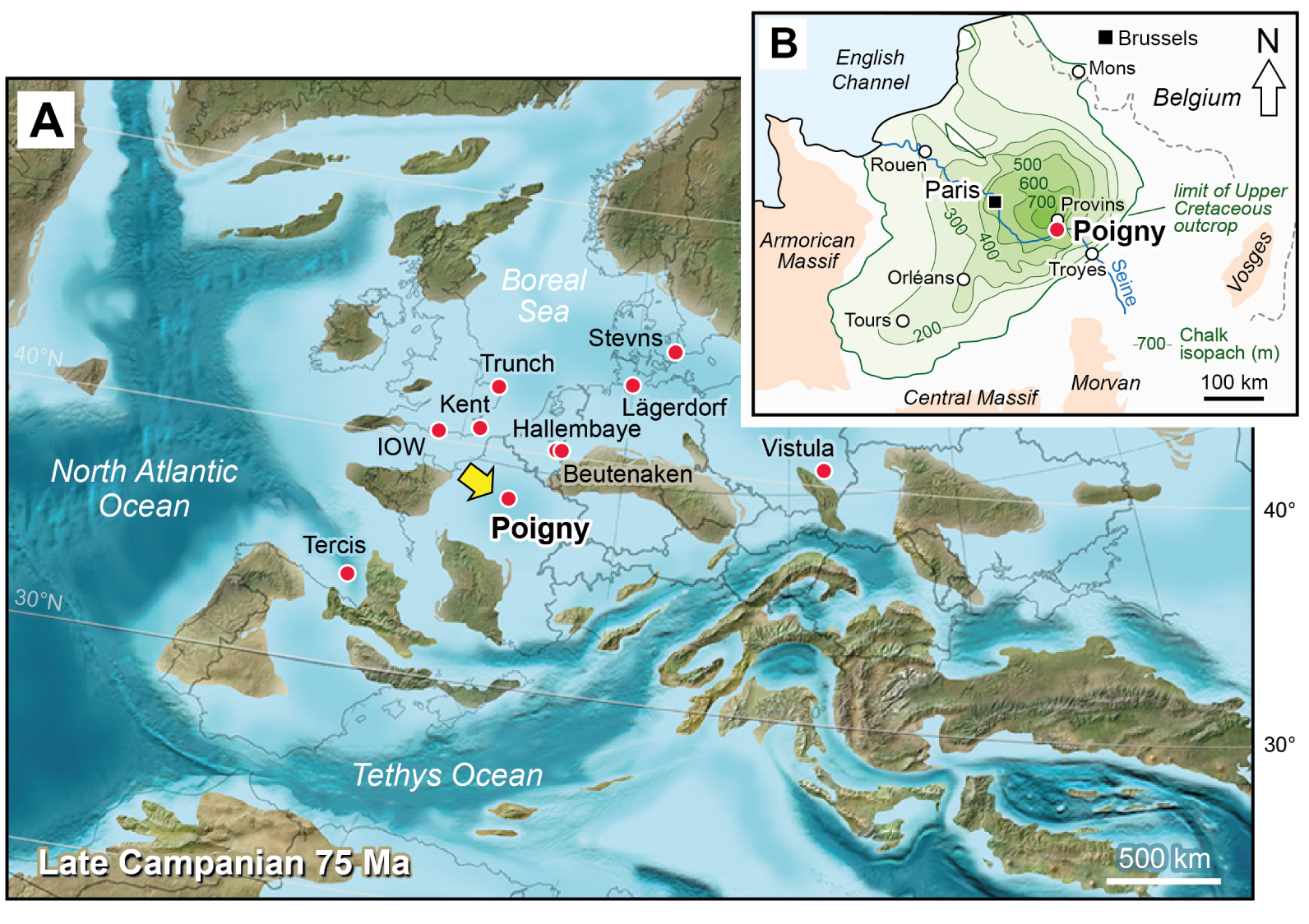
Campanian palaeogeography of Europe and geographic location of the Poigny borehole and comparative study sections. (A) Palaeogeographic map [modified from Blakey 2012] with the location of sections discussed in this paper. Poland palaeogeography after Niechwedowicz et al. [2021]. IOW, Isle of Wight, Whitecliff; Vistula, Middle Vistula River. (B) Chalk isopach map of the Paris Basin [modified from Robaszynski et al. 2005].
The Poigny and Sainte-Colombe cores have been correlated and dated using a combination of lithostratigraphy and benthic foraminifera biostratigraphy, supplemented by macrofossil, calcareous nannofossil and organic-walled dinoflagellate cysts (dinocyst) records [Robaszynski et al. 2005], although the exact placement of stage boundaries has remained uncertain. Studies of the clay mineralogy, stable-isotope geochemistry, and sequence stratigraphy of the Upper Cretaceous succession in the Provins area have been largely confined to the Poigny core [Chenot et al. 2016, 2018, Deconinck et al. 2000, Lasseur 2007, Le Callonnec et al. 2021], due to the diagenetic overprint at Sainte-Colombe.
2. Study succession
The Poigny Craie 701 borehole (48.5350° N, 3.2925° E) was continuously cored with a recovery approaching 98%; coring stopped in the lower Cenomanian at a depth of 700 m [Robaszynski et al. 2005]. The Coniacian–Campanian succession between 400–50 m depth is the focus of the present study. It comprises six lithostratigraphic units [Figure 2; Robaszynski 2000, Robaszynski et al. 2005], from base to top:
- indurated white chalk with black and grey flints; abundant platyceramid bivalve debris occurs towards the top (427.6–371 m);
- flintless indurated bioturbated white chalk; numerous inoceramid fragments [Platyceramus gr. mantelli? (de Mercey), ?Cladoceramus undulatoplicatus (Roemer)] at the base are indicative of the lower Santonian (371–345 m);
- indurated greyish white chalk with scattered flints, becoming increasingly common with thin tabular flints towards the top; between 345–320 m the chalk is very poor in flint and has been fragmented into 3–5 cm thick “biscuits” by coring; a flaser marl is present around 310 m and a 3–4 cm marl at 285 m (345–285 m);
- flinty white chalk with grey bioturbation, becoming significantly less indurated upwards, soft and friable above 250–200 m; Zoophycos flints and inoceramid debris abundant towards the summit, the lower third includes small ?paramoudra flints (285–164 m);
- soft flintless white chalk with grey bioturbation bounded by two pairs of omission surfaces at its bottom (164.2–164.0, 162.6 m) and top (142.0, 140.0–139.9 m), and a bed of “brecciated” intraclastic chalk at 158.3 m (164–140 m);
- soft white bioturbated chalk with few flints; very rare black flints in the lower half, scattered black flints in the upper half; a fossiliferous interval from 106–92 m with fragments of oysters, bryozoa, sponges, a hexacoral and fish scales, includes numerous Magas chitoniformis (Schlotheim) ( = M. pumilus of literature) brachiopods—Magas beds (140–34.75 m).
Between 600–317 m depth some beds contain dispersed ( <2%) small dolomite rhombs [Blanc and Gély 2000, Thiry et al. 2003]. Chalks above 60 m display increasing yellowish to brown discolouration and altered flints towards the Eocene unconformity at 34.75 m, particularly in the top 10 m. This is interpreted to represent the product of meteoric weathering below the unconformity.
3. Material and methods
3.1. Carbon isotopes
A total of 763 bulk sediment samples (50 g) were taken between 399.65–59.20 m depth (average spacing 45 cm) for stable isotope analysis from the Poigny core. Analytical methods are summarised in Supplemental Material A.
3.2. Palynology
For palynological analysis, 73 samples were selected from the carbon isotope sample set at approximately 5 m intervals (Figures 2, 3). Analytical methods are described in Supplemental Material A.
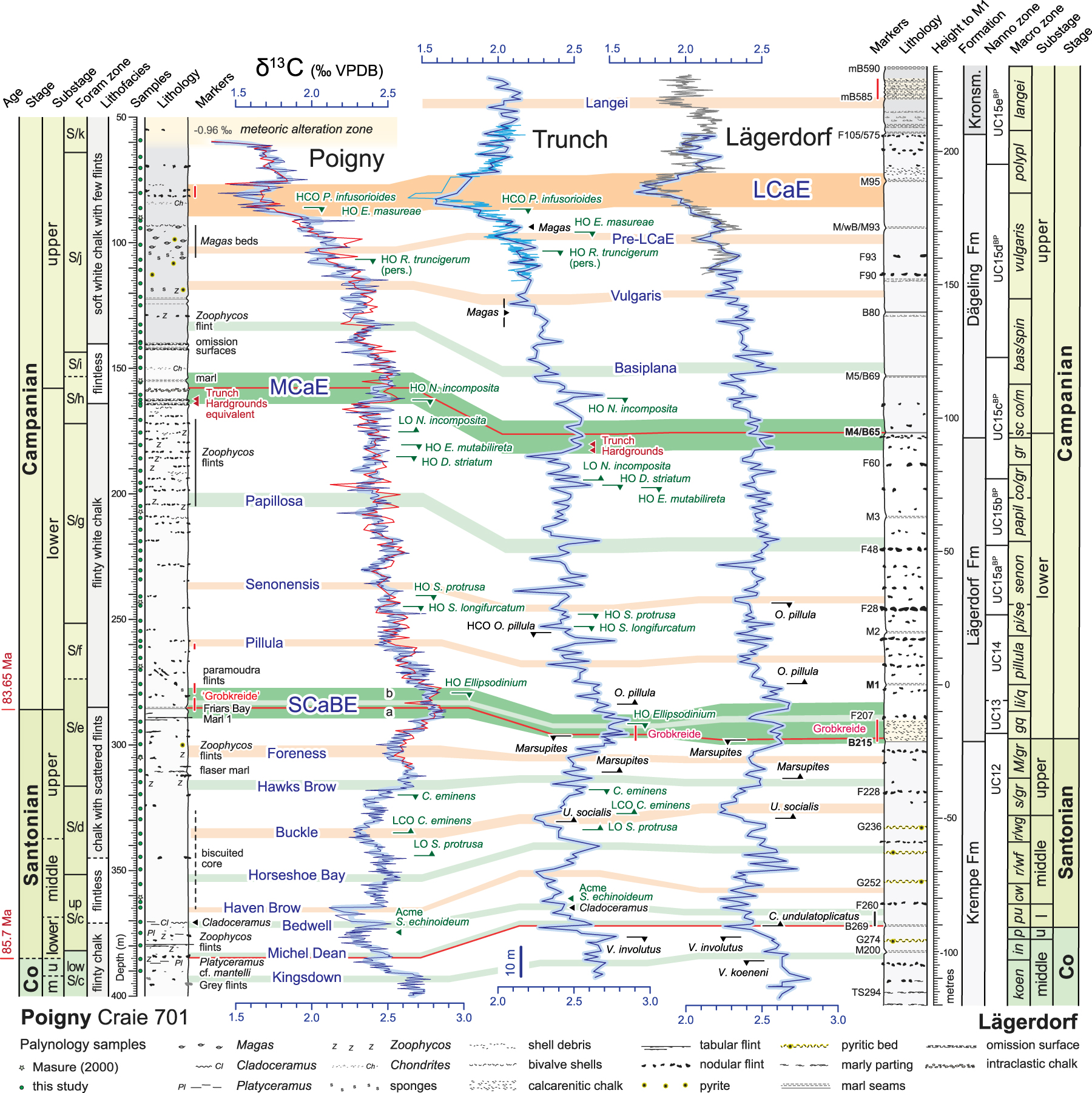
Coniacian–Campanian stratigraphy and carbon isotope event correlation of the Poigny borehole with the English Chalk Trunch borehole and Lägerdorf quarries, north Germany. Carbon isotope event terminology modified after Jarvis et al. [2002, 2006], Linnert et al. [2018], Perdiou et al. [2016], and Thibault et al. [2016]. Ages from GTS2020 [Gale et al. 2020]. Poigny benthic foraminifera zonation and stratigraphy from Robaszynski et al. [2005] with revisions based on this study; δ13C data from Chenot et al. [2016, thin red line] and this study (blue curves; thick pale blue curve is 3-point moving average). Selected dinocyst datum levels (this study, green text and symbols) are indicated. Trunch data compiled from Jarvis et al. [2002, 2006], Jenkyns et al. [1994], and Linnert et al. [2018, medium blue curve]; macrofossil datum levels (black symbols and text) from Morter et al. [1975], Pearce et al. [2020] and Wood et al. [1994]. Lägerdorf carbon isotope data from Voigt et al. [2010, grey curve is Lägerdorf–Heidestrasse]. Calcareous nannofossil zones after Burnett et al. [1998]. Lägerdorf macrofauna datum levels from Schulz et al. [1984]; zone terminology, abbreviations and relative thicknesses of units after Voigt et al. [2010]. Co, Coniacian; l, lower; m, middle; u, upper; Kronsm., Kronsmoor Formation. Masquer
Coniacian–Campanian stratigraphy and carbon isotope event correlation of the Poigny borehole with the English Chalk Trunch borehole and Lägerdorf quarries, north Germany. Carbon isotope event terminology modified after Jarvis et al. [2002, 2006], Linnert et al. [2018], Perdiou et al. ... Lire la suite
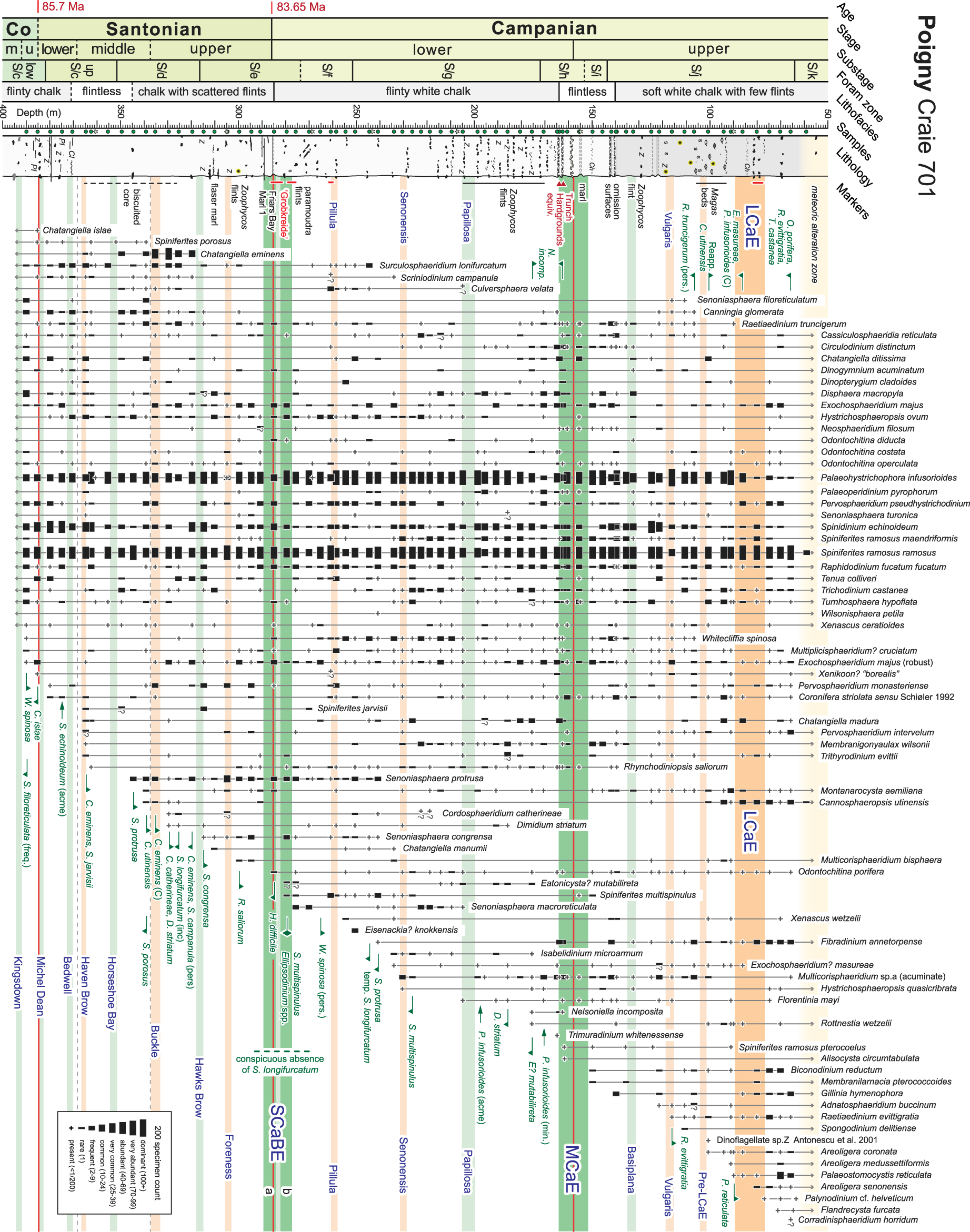
Range chart of stratigraphically significant dinocysts for the Coniacian–Campanian of the Poigny borehole. Stratigraphy after Figure 2.
4. Carbon isotope stratigraphy
Chenot et al. [2016] presented carbon and oxygen isotope curves for the upper Santonian–Campanian of Poigny based on bulk carbonate samples taken at 1 m intervals between 309 m and 50 m depth (Figure 2). The new higher resolution δ13Ccarb curve for the upper Coniacian–Campanian (400–58.5 m) obtained during the present study is plotted in Figure 2, together with the data of Chenot et al. [2016]. Excellent agreement exists for the overlapping upper Santonian–Campanian section.
Correlation of the Poigny δ13Ccarb profile with carbon isotope curves for equivalent aged successions from the southern North Sea Basin at Trunch, eastern England [Figure 1; Jarvis et al. 2002, 2006, Jenkyns et al. 1994, Linnert et al. 2018], and from Lägerdorf in the North German Basin [Voigt and Schönfeld 2010] shows remarkably similar trends and δ13Ccarb values (Figure 2). This enables the correlation of the overall long-term trends and short-term positive and negative excursions, with the recognition of all previously named carbon isotope events (CIEs) defined for the upper Coniacian–Campanian [Jarvis et al. 2002, 2006, Linnert et al. 2018, Perdiou et al. 2016, Thibault et al. 2016]. The three most significant CIEs: Santonian–Campanian Boundary Event (SCaBE); Mid-Campanian Event (MCaE); and Late Campanian Event (LCaE), are named by reference to their subage positions [cf. Chenot et al. 2016, Cramer and Jarvis 2020, Jarvis et al. 2002]. Subsidiary Coniacian–Santonian events are named principally after English Chalk marker beds, following Jarvis et al. [2006]. Secondary Campanian events are named by reference to their stratigraphic position within the macrofossil biozonation at Lägerdorf [Figure 2; cf. Thibault et al. 2016].
The top of the Poigny core above 61 m displays anomalous large negative excursions in δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb, with values falling to − 0.96‰ and − 2.6‰ respectively at 54–55 m; these values are 2.4‰ δ13Ccarb and 1.1‰ δ18Ocarb lower than the immediately underlying succession and clearly separated from other samples on a δ13Ccarb vs. δ18Ocarb cross plot [Chenot et al. 2016, figure 6]. The excursions are attributed to meteoric alteration below the Eocene unconformity, further evidenced by yellow and brown staining and Mg- and Sr-depletion of the chalks above 60 m [Le Callonnec et al. 2000]. Our single palynological sample from this interval at 59.2 m yielded a very low abundance ( <1 palynomorph per gram; ppg) and highly impoverished assemblage (Figure 3), consistent with partial oxidation of the organic fraction.
The bases of the Santonian, lower Campanian, and upper Campanian in the Poigny succession, estimated to be between 380–371 m, 290–285 m and 197–165.2 m, respectively by Robaszynski et al. [2000, 2005], are placed here using correlation of the CIE stratigraphy at: 385 m, 285 m, and 158 m (Figure 2). Overall, a succession of 17 CIEs is recognised in the middle Coniacian–upper Campanian at Poigny, offering a substantial improvement in stratigraphic resolution. Limited macrofossil records and key dinocyst marker levels occurring at both Poigny and Trunch (Figure 2) are fully consistent with the carbon isotope stratigraphy. Of note are: (1) records of Cladoceramus undulatoplicatus attributed to the level of the Bedwell CIE; (2) the presence of coarse-grained calcarenitic chalks within the SCaBE interval, noted by Lasseur [2007] at Poigny (red bars in Figure 2), and typified by the Grobkreide at Lägerdorf [Niebuhr 2006]; (3) paired omission surfaces at the base of the MCaE at Poigny correlative to the Trunch Hardgrounds; (4) records of Magas chitoniformis brachiopods at the level of the Pre-LCaE at both Poigny and Trunch.
Based on our carbon isotope correlation (Figure 2), the base of the upper Coniacian is tentatively placed at the top of the Kingsdown CIE at 392 m, the base of the middle Santonian at 368 m, mid-way between the Bedwell and Haven Brow CIEs, and the base of the upper Santonian is equated to the base of the Buckle CIE at 347 m. The marl seam at 285 m, situated within the SCaBE, is correlated to Friars Bay Marl 1 in southern England [cf. Thibault et al. 2016] rather than the Old Nore Marl, as proposed by Robaszynski et al. [2005].
5. Palynology results
A summary relative abundance range chart of selected taxa is presented in Figure 3; the entire data set is provided in Supplemental Materials B–D. Absolute abundance, specific diversity profiles and stratigraphic changes in the palynological assemblage are presented in Figure 4. Species occurrences from the preliminary palynological study of the middle Santonian to upper Campanian section by Masure [2000, seven samples at an average spacing of ∼40 m] are indicated on Figure 3 by pale green filled stars.
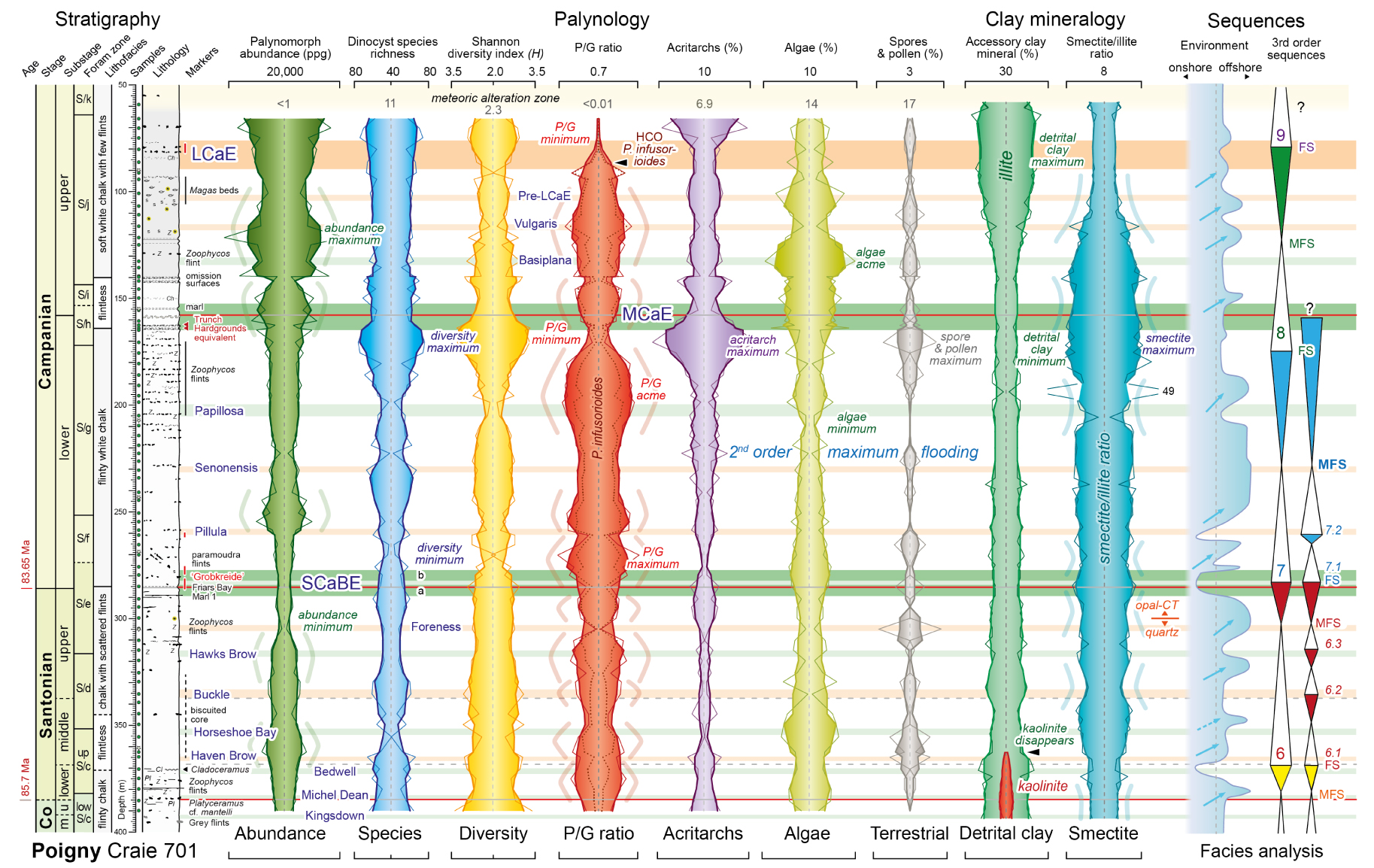
Stratigraphy, palynomorph abundance, dinocyst assemblage parameters and clay mineral assemblage plots, and third-order sequences for the Coniacian–Campanian of the Poigny borehole. P/G ratio = species number of peridinioid/gonyaulacoid cysts. Stratigraphy and carbon isotope events (coloured horizontal bars with blue annotation) follow Figure 2. Shaded areas and thick coloured lines are 3-point moving averages of individual sample data (thin lines; Supplemental Material C). Grey numerals in the meteoric alteration zone are for sample at 59.20 m. Clay mineralogy from Deconinck et al. [2000]. Sequences from Lasseur [2007] based on sediment microfacies analysis. Masquer
Stratigraphy, palynomorph abundance, dinocyst assemblage parameters and clay mineral assemblage plots, and third-order sequences for the Coniacian–Campanian of the Poigny borehole. P/G ratio = species number of peridinioid/gonyaulacoid cysts. Stratigraphy and carbon isotope events (coloured horizontal bars with blue annotation) ... Lire la suite
The palynoflora is diverse with a total of 236 species and subspecies of dinocysts recorded through the section (Supplemental Material B; taxa grouped in undifferentiated genera—i.e., Alterbidinium spp.—and the probable ecdysal pellicles of the Dinogymnioideae are included in the sum; questionable specimens are counted separately—Supplemental Material C). Assemblages are dominated by subequal amounts of Palaeohystrichophora infusorioides and Spiniferites ramosus (typical of the Spiniferites–Palaeohystrichophora (S–P) assemblage; [Jarvis et al. 2021, Pearce et al. 2003, 2009, Prince et al. 2008]), although some significant fluctuations exist in the former.
Palynomorph abundance, dinocyst species richness and diversity, and acritarch and algae abundances all generally decrease upwards through the Santonian. An abundance minimum occurs in the mid-upper Santonian and a diversity minimum coincident with a maximum in the peridinioid/gonyaulacoid (P/G) dinocyst ratio occurs in the lowest Campanian, immediately above the SCaBE.
Abundance, species richness and diversity generally increase through the lower Campanian with a diversity maximum accompanying acritarch and terrestrial palynomorph maxima and a marked P/G ratio minimum at the top of the substage, immediately below the MCaE. An algae minimum and subsequent P/G acme, dominated by high numbers of P. infusorioides (Figures 3, 4), precede the diversity maximum.
A palynomorph abundance maximum occurs in the upper Campanian around the level of the Vulgaris CIE, above an algae acme centred on the Basiplana CIE, below. A crash in numbers of P. infusorioides at the base of the LCaE leads to a marked P/G minimum spanning the LCaE, despite significant increases in palynomorph abundance.
In addition to the long-term trends summarised above, many of the parameters show a cyclic pattern at a decametre scale. This is particularly evident in the P/G ratio, which is controlled largely by variation in the abundance of P. infusorioides (Figure 4). This is discussed further below (Section 8).
6. Dinocyst biostratigraphy of the Coniacian–Campanian
Results from the Poigny borehole may be compared to similar high-resolution palynology data from key European sites (Figure 1), in Belgium (Hallembaye quarry), Denmark (Stevns-1 borehole), England (Whitecliff outcrop, Isle of Wight; Kent outcrops; Trunch borehole), France (Tercis outcrop), The Netherlands (Beutenaken quarry), and Poland (Middle Vistula River outcrops) that are constrained by CIE chemostratigraphy and/or, macro- or micro-fossil biostratigraphy. Following a brief description of the comparable sections, stratigraphically significant events are discussed.
6.1. Summary of comparable stratigraphic sections
6.1.1. Belgium and the Netherlands
Slimani [2001] carried out a sub-1 m resolution study of 21 samples through ∼20 m of the uppermost lower Campanian to upper Campanian of Beutenaken quarry (The Netherlands). A slightly lower resolution study was undertaken through the uppermost lower Campanian to upper Maastrichtian section of Hallembaye quarry (Belgium) located 15 km to the west (Figure 1). At Hallembaye, 26 samples were studied at an average spacing of ∼3 m through the ∼80 m uppermost lower Campanian to upper Maastrichtian section, with 11 samples restricted to the Campanian. Both quarries benefit from a belemnite biozonation for calibration. Only relative abundance data were presented by Slimani [2001]; however, the assemblages are very diverse and some subtle changes in relative abundance are clearly recognisable.
6.1.2. Denmark
Surlyk et al. [2013] carried out a multidisciplinary study of the Stevns-1 core containing one of the most expanded upper Campanian–Maastrichtian successions worldwide. Among other disciplines, nannofossil and dinocyst palaeontology, and δ13Ccarb data were provided; δ13Ccarb correlations to Lägerdorf–Kronsmoor [Thibault et al. 2012, figure 8] and to Gubbio [Surlyk et al. 2013, figure 3] indicate that the base of the Stevns-1 core lies some distance above the LCaE, and is therefore above the top of the Poigny core. However, the presence, absence, or relative abundance of dinocyst species in Stevns-1 have important implications for the palynostratigraphy.
6.1.3. England
Prince et al. [1999] presented a ∼1 m scale palynology study of 98 samples from the lower Santonian to lower Campanian (upper Offaster pillula Zone) outcrop section at Whitecliff (Isle of Wight). The section is calibrated by macrofossil zones and benefits from a previous δ13Ccarb study by Jenkyns et al. [1994].
Prince et al. [2008] documented the results of a study of dinocysts from the entire Coniacian–Santonian Chalk succession in Kent based on 139 1-m spaced samples from six overlapping outcrop sections. Results of a study of the Coniacian succession at Whitecliff (70 samples) supplemented the data obtained from the higher section by Prince et al. [1999]. Jenkyns et al. [1994] summarised the stratigraphy and presented stable isotope curves for a composite Kent section, constructed using data from the same localities as Prince et al. [2008].
Pearce et al. [2020] studied 267 samples from the lower Cenomanian to mid-lower Campanian (lowermost Gonioteuthis quadrata Zone) of the Trunch borehole (Norfolk) also at ∼1 m resolution. A palynological study of the remaining Campanian to lowermost Maastrichtian is ongoing, although preliminary ranges of new species were reported by Pearce [2010] and some significant events are documented here as personal observations (pers. obs.). Jenkyns et al. [1994] presented δ13Ccarb data for the Campanian of the Trunch borehole, which was extended to the lower Cenomanian by Pearce et al. [2020].
6.1.4. France
The quarry at Tercis-les-Bains near Dax in Landes, SW France, is the Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the Campanian–Maastrichtian boundary [Figure 1; Gale et al. 2020]. Antonescu et al. [2001a] provided presence/absence palynology information for 39 samples (with 31 in the upper Campanian) at an average sampling spacing of ∼4 m from the section, while Schiøler and Wilson [2001] presented full quantitative counts at an average spacing of ∼12 m (with eight in the upper Campanian). Collectively, these studies span a total of ∼160 m (with ∼115 m in the upper Campanian). Multidisciplinary biostratigraphic analyses (ammonites, benthic and planktonic foraminifera, calcareous nannofossils, ostracods, spores and pollen) were also conducted [see Odin 2001]. Walaszczyk et al. [2002] subsequently erected an inoceramid zonation and of particular interest is the recognition of the “Inoceramus” redbirdensis Zone that spans the Campanian–Maastrichtian boundary.
A δ13Ccarb record for Tercis les Bains was presented by Voigt et al. [2012]. Although Voigt et al. [2012] recognised many of the sampled horizons used by Odin [2001], the direct placement of their δ13Ccarb samples in the biostratigraphic framework had to be estimated from their position relative to marker beds. We interpret the broad positive excursion in δ13Ccarb values from 6–14 m [Voigt et al. 2012, figure 3] to be the MCaE, as proposed previously by Perdiou et al. [2016].
6.1.5. Poland
Niechwedowicz et al. [2021] and Niechwedowicz and Walaszczyk [2022] presented a detailed palynology and inoceramid biostratigraphy of the Middle Vistula River composite outcrop section. Samples (182) from seven sections across an ∼80 m upper Campanian to lower Maastrichtian composite section were analysed at <1 m resolution, producing the most detailed palynological study of the boundary interval to date. From five of the sections (Piotrawin, Raj, Raj North, Podole and Kłudzie North) 138 samples are from the upper Campanian with one sample taken from the distinctive Campanian–Maastrichtian “boundary marl” that occurs within the “I.” redbirdensis inoceramid Zone.
The stratigraphically lowest sample in the composite succession (Piotrawin) was assigned to the “Inoceramus” altus Zone, defined by the lowest stratigraphic occurrence of the nominate species. The lowest occurrence of “I.” altus at Tercis [Walaszczyk et al. 2002] was placed at the minimum of the LCaE by Voigt et al. [2012]. The LCaE occurs close to the top of the Poigny core (Figure 2) so there may be a small stratigraphic overlap between Poigny and the Middle Vistula River composite section.
6.2. Dinocyst and acritarch biostratigraphic events
Biostratigraphically significant dinocyst and acritarch events from the Aquitaine Basin (Tercis), Anglo-Paris Basin (Poigny, Whitecliff Isle of Wight, Kent), North Sea Basin (Beutenaken, Hallembaye, Stevns-1, Trunch) and Mid-Polish Basin (Middle Vistula River) are discussed below, from the stratigraphically lowest occurrence (LO) to highest occurrence (HO), and are summarised in Supplemental Material D. For the uppermost Coniacian to lower Campanian, only the Whitecliff and Kent composite outcrops, and the Trunch borehole have overlapping sections with Poigny. For the remainder of the Campanian, comparable sections from Beutenaken, Hallembaye, Stevns-1, Middle Vistula River, and personal observations from the Trunch borehole are available.
6.2.1. Upper Coniacian events
(1) LO of Whitecliffia spinosa: Pearce et al. [2020, section 7.5.1] described the temporal and spatial distribution of W. spinosa and stated that the LO has been recorded in the Coniacian. Whitecliffia spinosa is rare and sporadic in the Santonian but a specimen in the lowest studied sample from Poigny at 390 m between the Kingsdown and Michel Dean CIEs (Figure 3), confirms its presence in the upper Coniacian.
(2) Increase in Senoniasphaera filoreticulata: This species was described by Slimani [1994, as Cyclonephelium filoreticulatum] from the upper Campanian at Beutenaken quarry. Very rare specimens were recorded in the upper Campanian at Poigny at 116.2 m and 110.8 m within and above the Vulgaris CIE.
Pearce et al. [2020, figure 18, section 7.4.3.1] suggested that the temporary disappearance of persistently occurring S. filoreticulata within the lower Santonian could be a locally significant event. A highest persistent occurrence is not apparent at Poigny; however, the largest number of recorded specimens occurs in the lowest studied sample at 390 m (between the Kingsdown and Michel Dean CIEs) in the upper Coniacian (Figure 3). This is consistent with the highest abundant occurrence in the upper Coniacian at Whitecliff [Prince 1997, sample 58] and in Kent [Kingsdown; Prince 1997; Iain Prince pers. comm., sample 17].
Through the Coniacian to middle Santonian at Whitecliff and in Kent, the proximal Circulodinium–Heterosphaeridium (C–H) assemblage (i.e., that characterised by areoligeracean dinocysts such as Senoniasphaera) dominates, enabling the clear recognition of the HO of abundant S. filoreticulata specimens. At Trunch, this same interval is overwhelmingly dominated by the more distal S–P assemblage, which heavily dilutes the relative proportion of C–H assemblage species. Nevertheless, at Trunch a very slight increase in the relative abundance of S. filoreticulata is still apparent in the upper Coniacian at 375 m [Pearce et al. 2020, supplementary table 2], also between the Kingsdown and Michel Dean CIEs. Therefore, the observation of frequently occurring specimens of S. filoreticulata in our lowest sample from Poigny is a good indication for the marked higher relative abundance expected in the upper Coniacian.
(3) HO of Chatangiella islae: This species is taken in the biostratigraphy industry to have a highest common occurrence (HCO) at the top of the Coniacian and a HO in the Santonian. In the Norwegian Sea, the HO of C. islae occurs close to the HO of Heterosphaeridium difficile [see Pearce et al. 2019, figure 2, note that rare occurrences of C. islae illustrated above 2700 m are probably reworked]. At Poigny, the HO of H. difficile occurs at 285 m (lowermost Campanian), and of C. islae at 385.35 m, immediately below the Michel Dean CIE, in the uppermost Coniacian (Figure 3). As these events are separated by over 100 m, the HO of C. islae at Poigny may be related to the HCO of the species elsewhere.
6.2.2. Lower Santonian events
(4) Acme of Spinidinium echinoideum: At Poigny, a pronounced acme of S. echinoideum occurs at 374.9 m (reaching 30% of the dinocyst assemblage), immediately below the Bedwell CIE. In the Trunch borehole, common–abundant specimens span the Bedwell CIE with an acme immediately above it. The acme interval therefore approximates the Bedwell CIE (Figures 2, 3). Azema et al. [1981] similarly recorded a bloom of S. echinoideum in the “Senonian” (?Santonian) of the Duttières 3 borehole, Vendée, western France; further study is required to determine if this bloom is the lower Santonian acme.
6.2.3. Middle Santonian events
(5) LO of Chatangiella eminens: Pearce et al. [2020, figure 18] recorded the lowest stratigraphic occurrence of C. eminens at 346 m in the Trunch borehole, at the base of the Horseshoe Bay CIE. At Poigny, the same event is recorded at 364.85 m, within the Haven Brow CIE, extending the range of the species lower in the middle Santonian (Figure 3). According to Pearce et al. [2020] the LO at Whitecliff also occurs in the middle Santonian, but slightly higher again at the level of the n1 CIE (i.e., between the Horseshoe Bay and Buckle CIEs).
(6) LO of Spiniferites jarvisii: Pearce et al. [2020, figure 18, section 7.4.15] suggested that the species (described from the Trunch borehole) could be a potentially useful marker for the middle–upper Santonian boundary, but that more records were required to establish this. At Trunch the event falls immediately below the Buckle CIE, while at Poigny, the LO was found at 364.85 m at the top of the Haven Brow CIE (Figure 3), extending the range lower in the middle Santonian.
(7) First Appearance Datum level (FAD) of Senoniasphaera protrusa: Records of the distribution of S. protrusa may be unreliable prior to the emendation of the species by Prince et al. [1999]; see Pearce et al. [2020, section 7.4.8] for a brief discussion. The lowest stratigraphic occurrence of S. protrusa in the middle Santonian is consistent at Whitecliff, in Kent and at Trunch. At Trunch, the LO occurs at 339 m [Pearce et al. 2020, figures 6, 18] between the Horseshoe Bay and Buckle CIEs. At Poigny, the LO of S. protrusa occurs at 344.65 m and is apparently synchronous with Trunch (Figures 2, 3). At Whitecliff, the event occurs 3 m above the Barrois Sponge Bed [Prince et al. 1999, figure 2, sample 90] within the Horseshoe Bay CIE [Jarvis et al. 2006, figure 11], while at Whiteness [Kent, Prince et al. 2008, figure 7, sample 4] it occurs within the Barrois Sponge Bed. At Dover (Kent), where a δ13Ccarb record is available [Jarvis et al. 2006, figure 11], the Barrois Sponge Bed occurs above the m2 CIE and below the Horseshoe Bay CIE.
The LO of S. protrusa at Whiteness in the Barrois Sponge Bed was suggested by Pearce et al. [2020] to represent the FAD of the taxon, and this appears to be correct.
(8) LO of Senoniasphaera congrensa: Of the sections considered here, S. congrensa has only been recorded at Poigny and in Kent [where it was described by Prince et al. 2008 from Foreness Point, as Senoniasphaera protrusa congrensa]. In Kent, the LO of S. congrensa occurs at the summit of the middle Santonian at Whiteness, in Rowe’s Echinoid Band [ = Conulus albogalerus band; Prince et al. 2008, figure 7, sample 6], ∼2 m above S. protrusa (sample 4) and below the Horseshoe Bay CIE and presumably above the m2 CIE. At Poigny, the LO of S. congrensa occurs at 314.8 m in the upper Santonian, immediately above the Hawks Brow CIE (Figure 3), and therefore stratigraphically higher than at Whiteness.
(9) FAD of Dimidium striatum: Pearce et al. [2020, figure 18, section 7.4.14] discussed the temporal and spatial distribution of D. striatum and suggested that the stratigraphically lowest record found at Whitecliff by Prince et al. [1999, figure 2] could tentatively be taken to represent the FAD of the species. The event at Whitecliff occurs in the middle Santonian, above the Horseshoe Bay CIE. At Poigny, the LO of D. striatum occurs at 329.6 m, in the upper Santonian, above the Buckle CIE (Figure 3), close to the suggested FAD.
(10) Last Appearance Datum (LAD) of Spiniferites porosus: Pearce et al. [2020, figure 18, section 7.4.9] discussed the distribution of S. porosus and suggested that the LAD occurs in the mid-Santonian in the Northern Hemisphere and placed it at the isotope peak immediately above the m2 CIE. At Poigny, a HO of the species was recorded at 339.25 m (Figure 3), immediately below the Buckle CIE, therefore, extending the range upwards slightly.
(11) LO of Cannosphaeropsis utinensis: The LO of C. utinensis in the sections considered here, appears to occur in the Poigny core at 339.25, in the uppermost middle Santonian, immediately below the Buckle CIE (Figure 3). Moving progressively northwards, the LO occurs in the upper Santonian, Uintacrinus socialis Zone at Whitecliff [Prince et al. 1999, figure 2], and in the Marsupites Zone, below the SCaBE at Trunch [Pearce et al. 2020, figure 18]. This suggests a diachronous northward migration of the species, possibly associated with progressive Late Cretaceous cooling.
6.2.4. Upper Santonian events
(12a, b) Lowest Common Occurrence (LCO) and HO of Chatangiella eminens: At Poigny the LCO of C. eminens occurs at 335.35 m, in the lowermost upper Santonian, within the Buckle CIE. The HO occurs at 319.7 m, immediately below the Hawks Brow CIE. These events appear to be synchronous in the Trunch borehole [Pearce et al. 2020, figure 18] and at Whitecliff [see Pearce et al. 2020, section 7.4.10], making it an extremely useful species (Figures 2, 3).
(13) LO of Cordosphaeridium catherineae: In the type material from the Trunch borehole, the LO of C. catherineae was recorded at 323 m [Pearce et al. 2020, figure 18] in the upper Santonian, U. socialis Zone, base of the Hawks Brow CIE. At Poigny, the LO was recorded at 329.6 m, above the Buckle CIE (Figure 3), thereby extending the event downwards slightly.
(14) Increase in Surculosphaeridium longifurcatum: At Trunch [Pearce et al. 2020, supplemental table 2, at 335 m], Whiteness [Kent, Prince 1997, enclosures 7, 8, in sample 14] and Whitecliff [Prince et al. 1999, figure 2, in sample 114] a clear highest stratigraphic occurrence of common specimens of S. longifurcatum is observed in the O. pillula Zone. At Trunch, this event occurs within the Buckle CIE, while at Whitecliff and in Kent, we estimate it occurs slightly higher between the Buckle and Hawks Brow CIEs. At Poigny, this prominent HO of frequent specimens occurs at 325.45 m, also between the Buckle and Hawks Brow CIEs (Figure 3).
(15) HO of persistent Scriniodinium campanula: Despite two sporadic occurrences of S. campanula in the lower Campanian of the Poigny borehole (260.9 m, 234.1 m), a clear HO of persistent specimens in the upper Santonian may be significant (Figure 3). At Poigny, this event occurs at 319.7 m, immediately below the Hawks Brow CIE. At Whitecliff, a HO event was recorded by Prince et al. [1999, figure 2, sample 122] in the upper Santonian, high U. socialis Zone, ∼4 m below the Hawks Brow Flint and immediately below the Hawks Brow CIE [Jarvis et al. 2006, figure 11]. In the Kent composite section, Prince et al. [2008, figure 3] only recorded rare specimens in a single sample from the mid-Coniacian. This is predictable because the S–P assemblage, of which S. campanula is presumed to be a member, is very poorly represented in Kent. However, at Trunch (where the S–P assemblage dominates), S. campanula is recorded up to 322 m in the U. socialis Zone [Pearce et al. 2020, figure 18], within the Hawks Brow CIE.
(16) LO of Rhynchodiniopsis saliorum: In the Trunch borehole, the lowest stratigraphic occurrence of R. saliorum was recorded at 312 m in the Marsupites Zone by Pearce et al. [2020, figure 18], between the q1 and SCaBE CIEs. At Foreness Point (Kent), Prince et al. [2008, figure 8] also recorded the event in the Marsupites Zone from their lowermost sample 1 (Palm Bay Echinoid Band), ∼1 m below the Foreness Flint; this level approximates the Hawks Brow CIE at Dover [Kent; Jarvis et al. 2006, figure 11]. At Whitecliff, Prince [1997] recorded the species as Rhynchodiniopsis sp. A in sample 126 at the O. pillula–Marsupites Zone boundary, also within the Hawks Brow CIE [Jarvis et al. 2006, figure 11]. At Poigny the LO of R. saliorum occurs at 299.75 m in the upper Santonian, immediately above the Foreness CIE (Figure 3), and therefore slightly higher than at Foreness Point and Whitecliff.
6.2.5. Lower Campanian events
(17) LAD of Heterosphaeridium difficile: Pearce et al. [2020, figure 18, section 7.4.20] suggested that the LAD of H. difficile occurs in the low upper Santonian (mid-U. socialis Zone). At Poigny, generally rare and sporadic specimens occur to a highest level of 285 m, raising the LAD to the base of the lower Campanian, at the top of SCaBE peak a (Figure 3).
(18) HO of Ellipsodiniumspp.: At Poigny, Whitecliff [Prince et al. 1999], Trunch [Pearce et al. 2020] and the composite section for Kent [Prince et al. 2008], a distinctive HO of Ellipsodinium membraniferum or E. rugulosum occurs within the SCaBE. Excluding E. tenuicinctum He Chengquan from the Eocene (where we are unaware of any published occurrences outside of China), this may be broadly considered as a HO Ellipsodinium spp. event.
Prince [1997] recorded the HO of E. membraniferum in the lower Campanian, low O. pillula Zone at Whitecliff (sample c7), although the species was not mentioned in the biostratigraphic study of that section by Prince et al. [1999], and was only formally described by Prince et al. [2008]. In Kent and at Trunch, the HOs of E. membraniferum and E. rugulosum occur in the uppermost upper Santonian (top Marsupites Zone) and within SCaBE peak a, respectively. At Poigny, the HO of E. membraniferum occurs at 279.9 m in lower Campanian SCaBE peak b (Figures 2, 3).
(19a, b) LO and HO of Spiniferites multispinulus: Pearce et al. [2020, figure 21, section 7.5.4] suggested that the LO of S. multispinulus may be a potentially useful bioevent for the lower Campanian (upper O. pillula Zone). At Poigny, the LO occurs at 279.6 m in SCaBE peak b, supporting that suggestion. The HO of the species in the Trunch borehole was recorded by Pearce [2010, figure 2] in the lower G. quadrata Zone. At Poigny, this event occurs at 226.3 m, immediately above the Senonensis CIE, marginally higher than at Trunch (Figure 3).
(20) LO of persistently occurring Whitecliffia spinosa: Pearce et al. [2020, section 7.5.1] regarded a LO of persistently occurring specimens of W. spinosa in the lower Campanian to be significant. At Poigny, this event occurs at 265.65 in the lower Campanian below the Pillula CIE (Figure 3). Pearce et al. [2020] reported that at Whitecliff, the lowest persistent occurrence of W. spinosa occurs in the lower Campanian in the middle of the SaCBE. However, if this lowest persistent occurrence event is moved slightly upwards to where specimens are consecutively recorded [Prince et al. 1999, figure 2, sample c7], this occurs 1 m above the Old Nore Marl, which lies at the base of the Pillula CIE [Thibault et al. 2016].
(21) Temporary HO of Surculosphaeridium longifurcatum: The species S.longifurcatum has been recorded as high as the upper Maastrichtian of Hallembaye quarry by Slimani [2001, figure 7] and from the lower Maastrichtian of the Middle Vistula River composite section [Dziurków; Niechwedowicz et al. 2021]. It is also well distributed through the upper Campanian at Beutenaken quarry [Slimani 2001, figure 6], and has been recorded in a single sample from the upper Campanian at Tercis [Schiøler and Wilson 2001]. However, a clear HO of S. longifurcatum occurs in the low Campanian of southern Germany [Kirsch 1991], in the lower Campanian at Trunch (pers. obs.), and close to the top of the lower Campanian at Whitecliff [Prince et al. 1999]. At Poigny, the HO of S. longifurcatum occurs at 244.6 m, midway between the Pillula and Senonensis CIEs (Figure 3), and this may be a useful local event for the Anglo-Paris Basin and southern North Sea Basin.
(22) HO of Senoniasphaera protrusa: At Poigny, the HO of S. protrusa was recorded at 240.9 m between the Pillula and Senonensis CIEs (Figures 2, 3). Pearce et al. [2020] recorded the HO in their highest sample from the Trunch borehole (270 m); however, personal observations indicate that specimens continue up to 266 m in the lower G. quadrata Zone.
Slimani [2001] recorded rare and sporadic specimens of S. protrusa in the upper Campanian of Beutenaken and rare to common specimens in the upper Campanian of Hallembaye. According to the emended species description [Prince et al. 1999, p. 162]: “Senoniasphaera protrusa differs from all other Senoniasphaera species by having an elongated inner and outer body which possess two antapical horns of unequal size, giving the cyst its characteristic elongate and asymmetrical shape”.
Photographs of S. protrusa from Hallembaye [in Slimani 2000, plate 5, figures 9, 10] that conform to the original description of the species, illustrate a bilaterally symmetrical specimen of subequal width and length that we would now include in Canningia glomerata. We exclude records of S. protrusa by Slimani [2001], as he may have been unaware of the emendation. It is notable that the species has not been recorded from the upper Campanian of the Meer borehole [northern Belgium; Slimani et al. 2011] or at Tercis.
(23) HO of Dimidium striatum: Pearce [2010, figure 2] indicated that the HO of Dimidium striatum occurs in the upper G. quadrata Zone in the Trunch borehole [i.e. below the MCaE, see Jarvis et al. 2002]. This appears to be consistent with the record from Poigny, where the HO occurs at 185.9 m, between the Papillosa CIE and the MCaE (Figure 2).
(24) LO of Nelsoniella incomposita: The lowest stratigraphic occurrence of N. incomposita from the Trunch borehole occurs at 220 m [Pearce 2010, figure 2], below the MCaE [Jarvis et al. 2002, figure 3]. This appears to be synchronous in the Poigny borehole, where the event occurs at 175.6 m (Figures 2, 3).
(25) HO of Eatonicysta? mutabilireta: At Poigny, E.? mutabilireta was recorded persistently in the lower Campanian from 175.6 m (below the MCaE) to 214.3 m (between the Senonensis and Papillosa CIEs; Figure 2). Pearce [2010, figure 2] demonstrated that the range is restricted to the stratigraphically equivalent G. quadrata Zone in the Trunch borehole type material. Rare and sporadic occurrences of the species at Poigny from 275.75 m and 279.6 m, around the top of the SCaBE, indicate that the species may have an inception in the lower O. pillula Zone (Figure 3).
6.2.6. Upper Campanian events
(26) HO of Nelsoniella incomposita: Pearce [2010, figure 2] recorded the HO of N. incomposita at 192 m in the Trunch borehole, immediately above the MCaE [Jarvis et al. 2002, figure 3]. At Poigny, the same event occurs at 162.6 m, slightly lower, within the uppermost lower Campanian portion of the MCaE (Figures 2, 3).
(27) LO of Raetiaedinium evittigratia: The LO of R. evittigratia occurs at 116.2 m at Poigny within the Vulgaris CIE (Figure 3). It was persistently recorded but always rare ( <0.5%) and only encountered during scanning after the main count. The species was found in the Piotrawin opoka (siliceous chalk) at 1.5 m by Niechwedowicz and Walaszczyk [2022], close to the base of their composite Middle Vistula River section in Poland, and within the “I.” altus Zone. It was also recorded by Schiøler and Wilson [2001, figure 1] at 15.8 m in their lowest sample at Tercis, but not in the deeper samples studied by Antonescu et al. [2001a]. According to the inoceramid zonation at Tercis by Walaszczyk et al. [2002], the position recorded by Schiøler and Wilson [2001] occurs in an unzoned interval, but stratigraphically lower than at Piotrawin, and according to Voigt et al. [2012], to a level well below the LCaE. Our preliminary estimation suggests that the LO of R. evittigratia occurs within the MCaE at Tercis, therefore stratigraphically lower than at Poigny.
(28) HO of persistent Raetiaedinium truncigerum: This species is typically rare in all the sections compared here and appears to have a HO “just below” the Boundary Marl, within the “I.” redbirdensis Zone of the Middle Vistula River succession [Kłudzie North section, Niechwedowicz and Walaszczyk 2022]. It is worth noting that from other sections containing the “I.” redbirdensis Zone, the species was absent at Kłudzie South and Raj North, and extremely rare at Podole. It is rare and sporadic in the mid-Belemnitella langei Zone at Beutenaken [Slimani 2001] and was not recorded at Stevns-1 (Poul Schiøler pers. comm.).
A HO of persistently occurring R. truncigerum occurs in the mid-Belemnitella mucronata Zone at Beutenaken [Slimani 2001, text-figure 3, figure 6a] that is apparently synchronous with the HO event in the Belemnitella woodi Zone at Hallembaye [Slimani 2001, text-figure 2, figure 7a] and Trunch (pers. obs.). At Poigny, we recorded the HO of R. truncigerum at 106.8 m, immediately below the Pre-LCaE (Figures 2, 3). Masure [2000] recorded R. truncigerum slightly higher at 90 m, above the Pre-LCaE, but she did not record R. evittigratia, making it possible that specimens of the latter species may have been grouped in R. truncigerum. The precise relationship between the Upper Cretaceous belemnite zonation and the carbon isotope stratigraphy is currently uncertain, but our preliminary estimation places the Pre-LCaE within the B. woodi Zone.
At Tercis, the HO of arguably persistently occurring specimens of R. truncigerum occurs at 23.8 m [Antonescu et al. 2001a, table 1] below the LCaE [Voigt et al. 2012, figure 3] and probably well below the level at Poigny.
(29) LO of Palaeostomocystis reticulata: Marheinecke [1992] stated that the known range of this acritarch is Turonian to Danian. The species is rare and sporadic at Tercis and was recorded by Antonescu et al. [2001a, table 1] down to 80.6 m, within the “I.” altus Zone according to Walaszczyk et al. [2002]. We estimate that this horizon occurs above the LCaE [see Voigt et al. 2012, figure 3]. Niechwedowicz and Walaszczyk [2022] found the species to be particularly common in their lowest Middle Vistula River composite section (Piotrawin) and abundant in their lowest sample, also within the “I.” altus Zone.
The LO of P. reticulata at Poigny occurs at 90 m [Masure 2000; we recorded it at 86.2 m in the next sample above] immediately below the LCaE (Figure 3) and therefore, stratigraphically slightly lower than at Tercis. Slimani [2001] found the species in the B. mucronata Zone in the upper Campanian of Beutenaken quarry (that would presumably contain the Langei CIE and LCaE), together with the LO of Biconodinium reductum. At Tercis, the LO of B. reductum was recorded at 86.2 m, immediately above the LO of P. reticulata, indicating a close correlation [Antonescu et al. 2001a]. Consequently, the LO of P. reticulata appears to be broadly synchronous at Beutenaken, Poigny, Tercis and in the Middle Vistula River succession around the LCaE.
(30) HCO of Palaeohystrichophora infusorioides: At Poigny, a very prominent HCO of P. infusorioides occurs at 86.2 m in the lower LCaE and is believed to be synchronous in the Trunch borehole (Figures 2, 3, pers. obs.). No quantitative data for this species at Tercis were provided by Antonescu et al. [2001a], while Schiøler and Wilson [2001] show the species to be extremely rare throughout. In the palynological synthesis of the Tercis data, Antonescu et al. [2001b, p. 256] stated that the “last common occurrence” occurs between 34.8 m and 39.5 m, at a level we estimate to lie below between the MCaE and LCaE CIEs, and therefore slightly lower than at Poigny and Trunch.
The discrepancy in the position of the HCO of P. infusorioides at Poigny and Tercis may be the result of a palaeoenvironmental control. Two distinct dinocyst assemblages in the European chalks: Circulodinium–Heterosphaeridium (C–H) and Spiniferites–Palaeohystrichophora (S–P), are well known [Jarvis et al. 2021, Pearce et al. 2003, 2009, Prince et al. 2008]. The S–P assemblage is found to occupy more distal water masses, presumably receiving nutrients only from upwelling. For example, Pearce et al. [2009] argued that the catastrophic decline in relative numbers of P. infusorioides at the Cenomanian–Turonian boundary was the result of the shutdown of the Anglo-Paris Basin upwelling system due to thermal stratification.
Interestingly, three spot palynofacies samples at Tercis [Schiøler and Wilson 2001, table 1] indicate that black and brown wood comprises >44% of the total assemblage, outnumbering dinocysts, with <4% spores and pollen. This suggests a significant proximity to the shoreline, and the rarity of P. infusorioides further suggests relatively oligotrophic conditions due to a minimum in the runoff of continental nutrients [see Pearce et al. 2003, 2009, section 3.1].
(31) HO of Exochosphaeridium? masureae: This distinctive species was described by Slimani [1996] from the Campanian of the Turnhout borehole, Belgium. In macrofossil-calibrated material from Hallembaye, the HO was recorded in the B. woodi Zone by Slimani [2001, text-figure 2, figure 7b]. At Beutenaken, Slimani [2001, text-figure 3, figure 6a] recorded the HO in the uppermost B. mucronata (of conventional usage) and therefore, comparable with the event at Hallembaye. Personal observations from the Trunch borehole, place the HO at 136 m also in the B. woodi Zone, below the LCaE. Our observations at Poigny place the HO at 86.2 m (Figure 3), in the lower LCaE; therefore, slightly above that at Trunch, but still highly comparable. However, the HOs at Tercis at 23.8 m [Antonescu et al. 2001a, table 1] above the MCaE [cf. Voigt et al. 2012, figure 3] to the south, and Stevns-1 in the uppermost Campanian, B. langei Zone [Surlyk et al. 2013, appendix 1] to the north, indicate a pronounced diachroniety.
7. Clay mineralogy
The clay mineralogy of the Poigny core, plotted in Figure 4, has been documented by Deconinck et al. [2000, 2005] and was interpreted in a regional context by Chenot et al. [2016, 2018]. The clay mineral assemblage in the Coniacian–upper Campanian interval is dominated by smectitic minerals including R0 random illite/smectite mixed-layers and smectite (75–98%), with minor illite (2–25%) and accessory kaolinite ( <5%). Chlorite is absent. The smectite/illite ratio generally ranges from 2 to 10.
The maximum burial depth of 500 m estimated for the top Chalk at Poigny [Brunet and Le Pichon 1982] and the high proportion of smectites, which transform into illite from 60 °C [Środoń 2009], indicate that the clay mineral assemblages of the Poigny core are primary [Chenot et al. 2016]. Oxygen stable isotope values of − 2.7‰ to − 1.5‰ δ18Ocarb in a rising trend and through the Campanian at Poigny [Chenot et al. 2016] are comparable to other shallow buried chalk successions with minimal diagenetic overprint [e.g. Jenkyns et al. 1994]. However, the chalks become noticeably more indurated below 250 m and a mineralogical transition downwards from opal-CT to quartz as the dispersed silica phase occurs at 300 m depth [Figure 4; Deconinck et al. 2000]. Nonetheless, smectite continues to be the dominant mineral through most of the section down to the core base at 700 m depth.
Stratigraphic trends in the clay mineral assemblage, summarised in Figure 4, are: (1) kaolinite occurs as a minor phase at the section base in the Coniacian–lower Santonian, and is absent above 365.9 m; (2) the proportion of illite decreases upwards with an associated increasing smectite/illite ratio that reaches a broad maximum from 180 to 120 m, spanning the lower–middle Campanian boundary and the MCaE (Figure 4); (3) the illite content increases rapidly above 120 m with declining smectite/illite ratios and displays a maximum spanning the LCaE, above which illite attains a maximum of 25% before falling slightly in the meteoric alteration zone at the section top.
The smectitic fraction constitutes the background sediment of a low-terrigenous supply, attributable to the absence of significant near-by land masses and topography (Figure 1A), regional volcanic activity, and the warm humid climate and high sea level that prevailed during the Late Cretaceous in the region [Deconinck et al. 2005, Jeans 2006]. Increased proportions of illite, considered to be sourced by erosion of igneous or metamorphic continental basement rocks, represent pulses of enhanced terrigenous supply, potentially associated with climate cooling, tectonism and/or sea-level fall. Kaolinite may have a pedogenic origin or be reworked, but its close coupling with illite at Poigny and in the Campanian elsewhere favour the latter origin [Chenot et al. 2018]. It is notable that the increase in detrital clay below the Pre-LCaE is coincident with an inflection point in the Sr isotope curve towards more steeply rising 87Sr/86Sr ratios at Lägerdorf [McArthur et al. 1993], consistent with an increase in the continental weathering flux at that time.
A detrital clay maximum immediately preceding and spanning the LCaE is also seen at Tercis [Chenot et al. 2016, figure 3] where increased illite is accompanied by increasing chlorite and a large pulse of kaolinite. This evidences a regional phase of increased continental erosion accompanying the LCaE with a mineral assemblage at Poigny characteristic of semi-humid conditions contrasting to a more humid tropical climate at Tercis [Chenot et al. 2018]. A diachronous regional increase in detrital input through the Campanian has been linked to local tectonic pulses that led to the emergence of shelf areas and increased siliciclastic supply. However, additionally, there is regional evidence for a significant sea-level fall during the late Campanian—the polyplocum Regression of northern Germany [Niebuhr et al. 2000].
The associated increase in silicate weathering, driving atmospheric CO2 drawdown, may have contributed to the accelerated long-term Campanian cooling trend evidenced by rising bulk sediment δ18Ocarb values at Poigny [Chenot et al. 2016, figure 4] and, more generally, widespread rising planktonic and benthic foraminifera δ18Ocarb and falling TEX86 values through the stage [O’Brien et al. 2017].
8. Sequences and sea-level change
Lasseur [2007] undertook a facies analysis of the Poigny core based on sediment fabric, composition, and texture, incorporating thin section analysis of 95 samples from the upper Coniacian–Campanian. The coarsest grained wackestone–packstone facies were assigned to more nearshore environments and regression, with lime mudstones representing the most offshore conditions and peak transgression. An onshore–offshore relative sea-level curve was generated from these data (Figure 4).
Lasseur [2007] additionally distinguished a succession of two second-order and nine major third-order sequences through the Cenomanian–Campanian at Poigny, with the recognition of flooding “surfaces” (FS) corresponding to levels of maximum regression, and maximum flooding “surfaces” (MFS) associated with maximum transgression. It should be noted, however, that visible omission or erosion surfaces have not been documented at the designated levels in the upper Coniacian–Campanian core at Poigny, although the “Trunch Hardground equivalent” omission surfaces provide a potential level for the Sequence 8 FS. The FS and MFS might better be considered therefore as “zones” of maximum regression and maximum transgression. The Coniacian–Campanian comprises third-order sequences 5–9 (Figure 4).
It is notable that the interval of second-order maximum flooding at the Senonensis CIE lies within a long-term interval of relatively low palynomorph abundance, low dinocyst diversity, moderate P/G ratio, low algae and terrestrial palynomorph numbers, and low illite content, consistent with a deeper water more offshore setting.
The onshore–offshore sea-level curve of Lasseur [2007] correlates with variation in many of the palynological parameters. The relationship that is most strongly expressed is a positive correlation between major episodes of short-term sea-level rise (blue arrows in Figure 4) and intervals of elevated P/G ratio (highlighted by the pale red curved lines in Figure 4). A cyclic pattern at a decametre scale is evident and approximates to a 400 kyr periodicity in the Santonian (five cycles in 2.05 Myr—Figure 4). A general positive correlation also exists between cycles of high P/G ratio and episodes of increased palynomorph abundance and decreased dinocyst species richness and diversity.
The P/G ratio is generally regarded as a proxy for nutrient availability and palaeoproductivity [see discussion in Jarvis et al. 2021, p. 24], suggesting a link between sea-level rise and increased nutrient supply. The cause of this is uncertain but nutrients might be supplied, for example, by their release from coastal plain sediments and soils during flooding [cf. Jarvis et al. 2002, p. 237], and/or by the landward movement of a marine high-productivity zone supported by marine upwelling [cf. Pearce et al. 2009]. Some intervals of high P/G ratio correspond to levels with lower smectite/illite ratios (pale blue curves in Figure 4) suggesting a relationship with periods of enhanced terrestrial clay input, favouring a terrestrial nutrient source, but the relationship is not universal.
The third-order sequences of Lasseur [2007] do not correspond consistently with specific changes in the palynomorph assemblage. However, prominent changes occur particularly around the Sequences 7, 8 and 9 flooding surfaces and the SCaBE, MCaE and LCaE carbon isotope excursions (Figure 4). Flooding surfaces of third-order sequences have been identified at the upper two levels at Tercis [Chenot et al. 2016, figure 3], and the three CIEs correspond to the levels of the Marsupites Transgression, the mucronata Transgression and polyplocum Regression in Germany [Niebuhr et al. 2000].
It can be envisaged that sea-level change will significantly impact palynomorph assemblages via changes in, for example, shoreline proximity, nutrient supply, water mass distribution and sea-surface temperature. Additional quantitative palynological records are required to further address relationships between variations in assemblage composition, CIEs, sea-level and climate change in the Santonian–Campanian.
9. Conclusions
A diverse and well-preserved palynological assemblage, including 236 species and subspecies of dinocysts, is documented from the upper Coniacian to upper Campanian of the Poigny Craie 701 borehole, constituting the most detailed dataset of its kind in France. The palynoflora is dominated by dinocysts of the S–P assemblage, with low algae and terrestrial palynomorph numbers suggesting a relatively distal open-marine setting. A low terrigenous influence and semi-humid climate is indicated by a clay mineral assemblage in which smectite predominates.
New δ13Ccarb data from the upper Coniacian to upper Campanian improves the resolution of the existing uppermost Santonian–Campanian curve and extends the carbon isotope profile downwards into the middle Coniacian. A succession of 17 named CIEs is identified and correlated between France (Poigny), England (Trunch borehole) and Germany (Lägerdorf quarries). The bases of the Santonian, lower and upper Campanian are specifically picked at Poigny based on the correlation of CIEs, constrained by limited available biostratigraphy, to other European sections.
A total of 33 palynological events from 24 dinocyst and one acritarch species, considered to have biostratigraphic significance, are recognised through the Coniacian to Campanian: three in the upper Coniacian; one in the lower Santonian; seven in the middle Santonian; six in the upper Santonian; ten in the lower Campanian; and six in the upper Campanian. These offer considerable potential for improving inter-regional correlation of the European Upper Cretaceous.
An association between elevated P/G dinocyst ratios and episodes of sea-level rise is apparent and indicates episodic pulses in surface water productivity triggered by the recycling of continental nutrients during flooding, or the shoreward movement of offshore upwelling zones. Coincident changes in clay mineral assemblages, with lower smectite/illite ratios accompanying P/G ratio increases, support a terrestrial nutrient source, but the relationship is not universal.
Conflicts of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
NT and MM thank Francois Guillocheau (University of Rennes) for granting access to the Poigny core, and Damien Gendry for their help in the management of core boxes and access to laboratory facilities that greatly facilitated the sampling. Chris Mitchell (University of Exeter, Penryn Campus) supported the C and O isotope analysis. Malcolm Jones (Palynological Laboratory Services Limited, PLS) is thanked for the preparation of the palynological samples. We are particularly grateful to Mariusz Niechwedowicz and Poul Schiøler for sharing their palynology data from the Middle Vistula River and the Stevns-1 sections. Carlsbergfondet CF16-0456 funded travel expenses, sampling, and geochemical analysis by NT and JM. Support by Evolution Applied Limited to MAP and Equinor Energy AS (previously Statoil ASA) to IJ (contract 4502311303) is gratefully acknowledged. We thank the reviewers, Ligia Castro and an anonymous referee, for their useful suggestions that improved the manuscript.




 CC-BY 4.0
CC-BY 4.0
Vous devez vous connecter pour continuer.
S'authentifier