Le verre
Le verre, ni liquide ni solide, partage les propriétés de l’un et de l’autre de ces deux états, dans un désordre figé parfois encore difficile à comprendre. Correspondant au quatrième état de la matière d’après une proposition de Park et Huffman en 1926, il pose encore de nombreuses questions aux scientifiques tout en nous accompagnant dans notre quotidien depuis plus de 10 000 ans. D’abord utilisé sous sa forme naturelle, les obsidiennes, en tant qu’outil depuis le néolithique, son élaboration s’est développée il y a environ 5 000 ans entre la Mésopotamie et l’Égypte pour un usage esthétique : perles de verre et autres bijoux permirent probablement de mettre du baume au cœur de nos lointains ancêtres.
Le verre a ensuite fortement contribué à l’amélioration de nos conditions de vie, aussi bien pour le conditionnement des aliments (facilitant leur préservation et leur transport) que pour la réalisation des premières ampoules électriques, permettant à des millions d’écoliers de ne plus étudier à la lueur d’une chandelle !
Ce matériau, l’un des plus importants, polyvalents et transformateurs de l’histoire, est aujourd'hui un élément fondamental dans de nombreux domaines, et présente en outre une capacité infinie à se recycler. Le matériau ”verre” représente ainsi un atout majeur pour répondre à de nombreux enjeux techniques et industriels, dont certains sont étroitement liés à la transition énergétique :
- fibre textile servant aussi bien pour les coques de voiture que pour la construction des éoliennes ;
- panneaux d’affichage, panneaux photovoltaïques, écrans, capteurs en verre ultrafin ;
- fibre optique transportant information et énergie ;
- vitrage et isolation ;
- inertage de déchets ;
- stockage de grandes quantités d’énergie au moyen de batteries en verre ;
- etc.
Le verre est également un atout majeur pour les soins de santé, sous la forme de verre bioactif, capteurs, implants dentaires ou osseux et autres applications pharmaceutiques permettant de réparer et reconstruire l’homme.
Les verres sont habituellement formés par refroidissement rapide d’un liquide, mais il est possible de fabriquer un nombre quasi-infini de verres, avec l’ensemble des éléments du tableau périodique et quelques soient les liaisons chimiques. Le verre n’est donc pas uniquement le matériau que nous utilisons dans notre quotidien, mais plutôt un état désordonné de la matière.
Cette collection d’articles parus dans plusieurs séries différentes des Comptes Rendus a pour but de faire découvrir au lecteur que le verre correspond à un état de la matière et est un matériau aux multiples facettes. La variété des disciplines concernées fait écho à cette polyvalence.
Daniel R. Neuville, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris
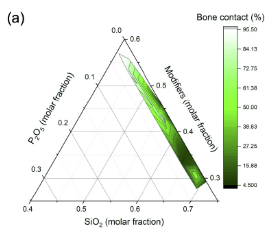 | Glass as a biomaterial: strategies for optimising bioactive glasses for clinical applications Brauer, Delia S.; Hupa, Leena Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 185-197 |
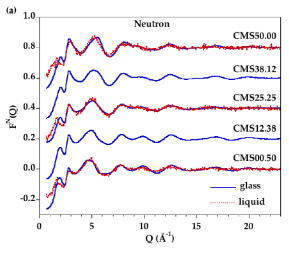 | Cormier, Laurent; Hennet, Louis; Lelong, Gerald; Cuello, Gabriel J.; Bytchkov, Alexei Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 15-34 |
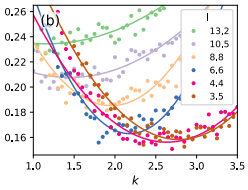 | Fernández Castellanos, David; Roux, Stéphane; Patinet, Sylvain Comptes Rendus. Physique, Volume 22 (2021) no. S3, pp. 135-162 |
 | The rose of the Sainte-Chapelle in Paris: sophisticated stained glasses for late medieval painters Hunault, Myrtille Odile Jacqueline Yvonne; Bauchau, Fanny; Boulanger, Karine; Hérold, Michel; Calas, Georges; Lemasson, Quentin; Pacheco, Claire; Loisel, Claudine Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 101-120 |
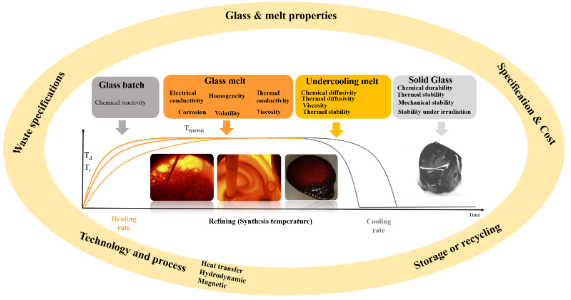 | Vitrification of wastes: from unwanted to controlled crystallization, a review McCloy, John S.; Schuller, Sophie Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 121-160 |
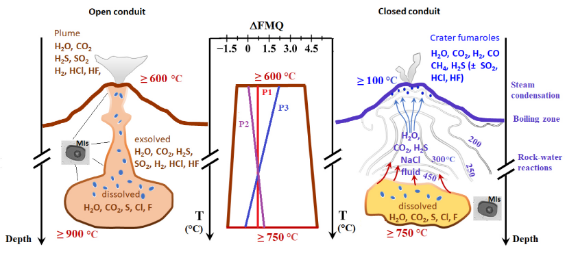 | Moretti, Roberto Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 249-279 |
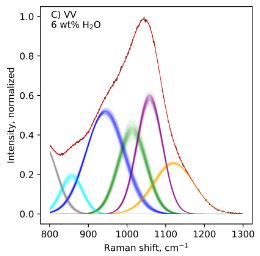 | Le Losq, Charles; Mysen, Bjorn O.; Cody, George D. Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 199-225 |
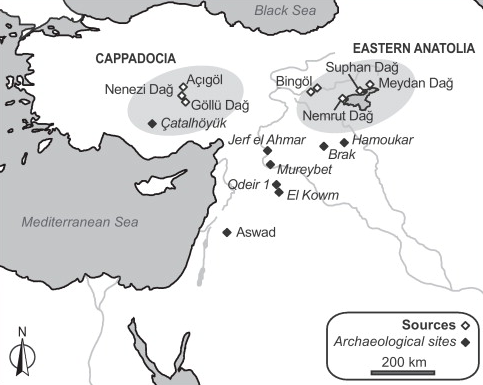 | Orange, Marie; Carter, Tristan; Le Bourdonnec, François-Xavier Comptes Rendus Palevol, Volume 12 (2013) no. 3, pp. 173-180 |
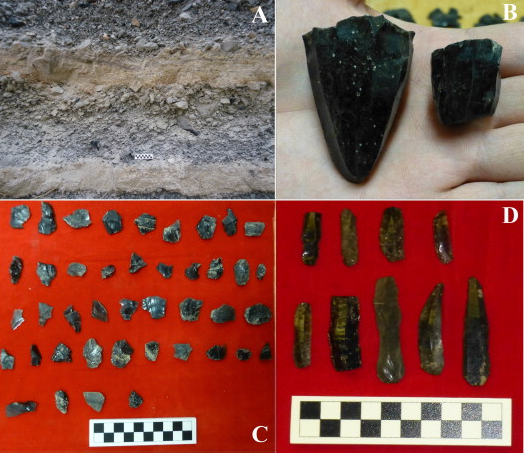 | Blade production and the consumption of obsidian in Stentinello period Neolithic Sicily Freund, Kyle P.; Tykot, Robert H.; Vianello, A. Comptes Rendus Palevol, Volume 14 (2015) no. 3, pp. 207-217 |
 | Montes, Helene; Lequeux, Francois Comptes Rendus. Physique, Volume 22 (2022) no. S5, pp. 33-50 |
 | Cherif, Sonia; Bonnet, Pierre; Frezet, Lawrence; Kane, Abdoulaye; Assadi, Aymen Amine; Trari, Mohamed; Yazid, Hynda; Djelal, Hayet Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 25 (2022) no. S3, pp. 261-279 |
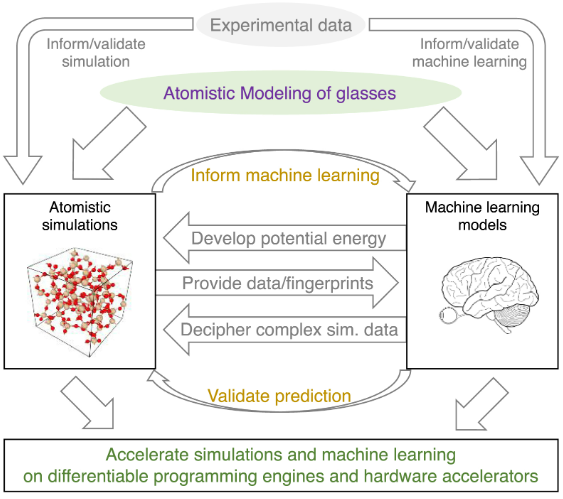 | Défis et opportunités en simulations atomiques de verres : une revue Liu, Han; Zhao, Zhangji; Zhou, Qi; Chen, Ruoxia; Yang, Kai; Wang, Zhe; Tang, Longwen; Bauchy, Mathieu Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 35-77 |
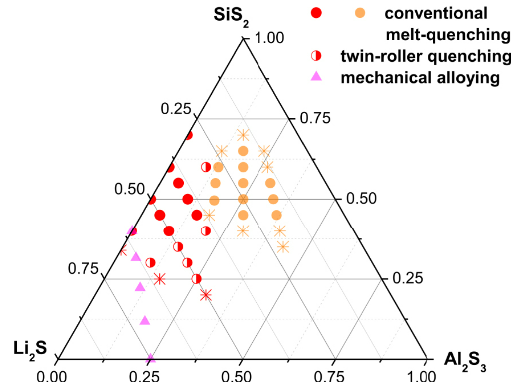 | Pradel, Annie; Piarristeguy, Andrea Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 79-99 |
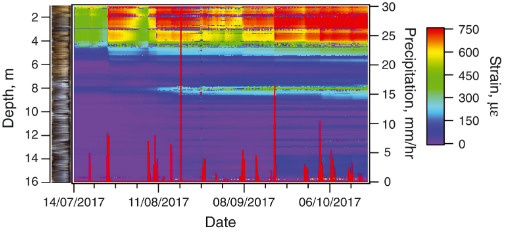 | Capteurs distribués de contrainte à fibres optiques : de la longue à la courte distance Blanc, Wilfried; Schenato, Luca; Molardi, Carlo; Palmieri, Luca; Galtarossa, Andrea; Tosi, Daniele Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 161-183 |
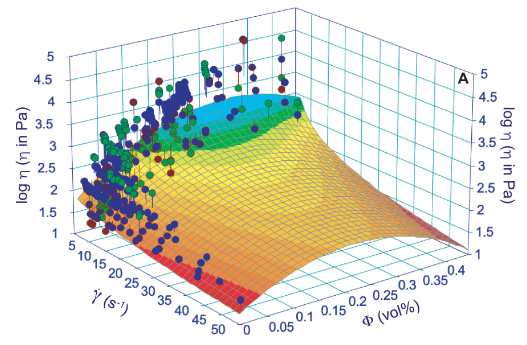 | Rheological changes in melts and magmas induced by crystallization and strain rate Vetere, Francesco; Iezzi, Gianluca; Perugini, Diego; Holtz, Francois Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 354 (2022) no. S1, pp. 227-248 |
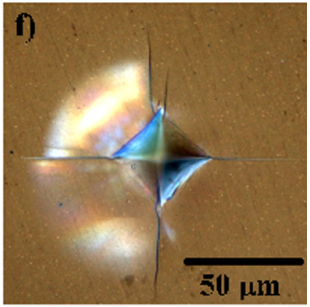 | Toward glasses with better indentation cracking resistance Rouxel, Tanguy; Sellappan, Pathikumar; Célarié, Fabrice; Houizot, Patrick; Sanglebœuf, Jean-Christophe Comptes Rendus. Mécanique, Volume 342 (2013) no. 1, pp. 46-51 |
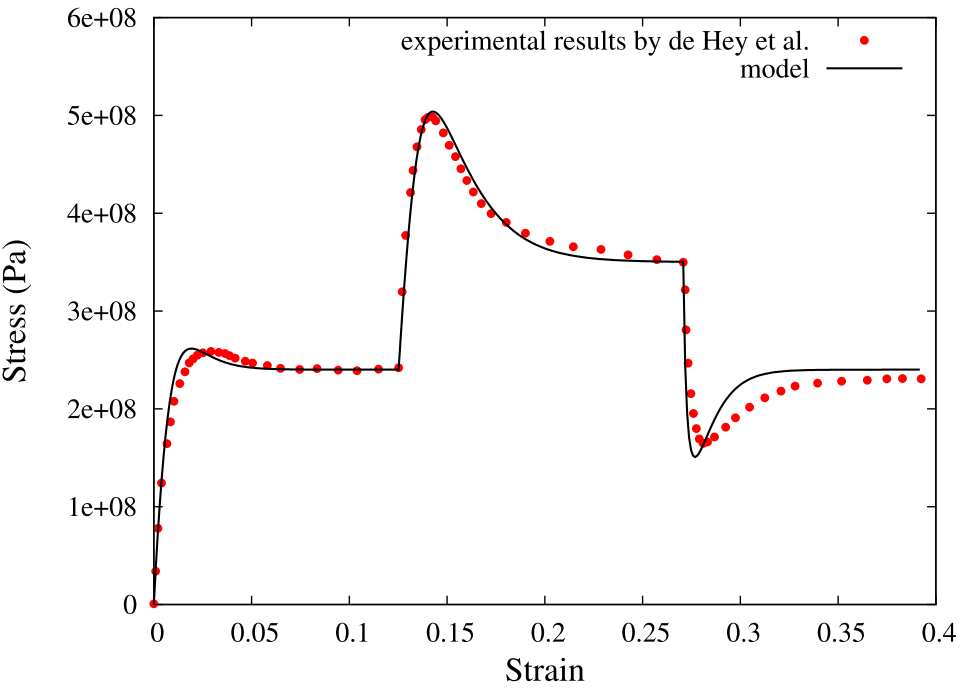 | Toward glasses with better indentation cracking resistance Rouxel, Tanguy; Sellappan, Pathikumar; Célarié, Fabrice; Houizot, Patrick; Sanglebœuf, Jean-Christophe Comptes Rendus. Mécanique, Volume 342 (2013) no. 1, pp. 46-51 |
 | Propriétés élastiques des verres : approche multiéchelle Rouxel, Tanguy Comptes Rendus. Mécanique, Volume 334 (2006) no. 12, pp. 743-753 |
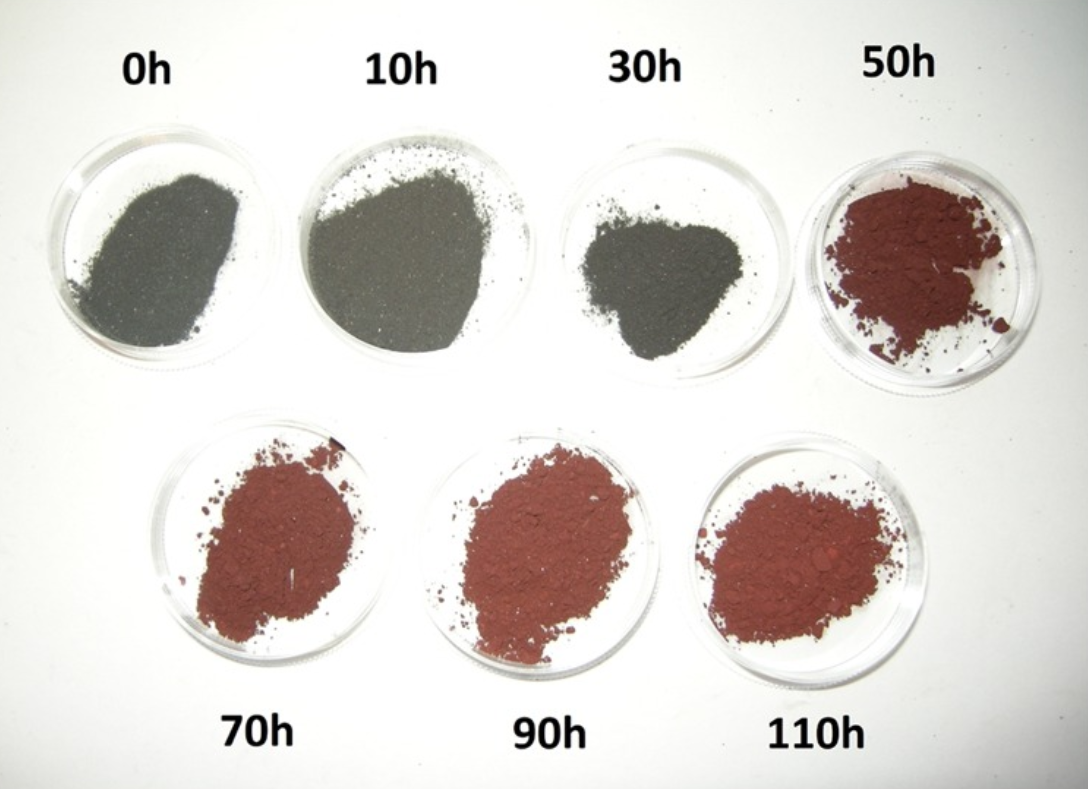 | Calvez, Laurent Comptes Rendus. Physique, Volume 18 (2017) no. 5-6, pp. 314-322 |
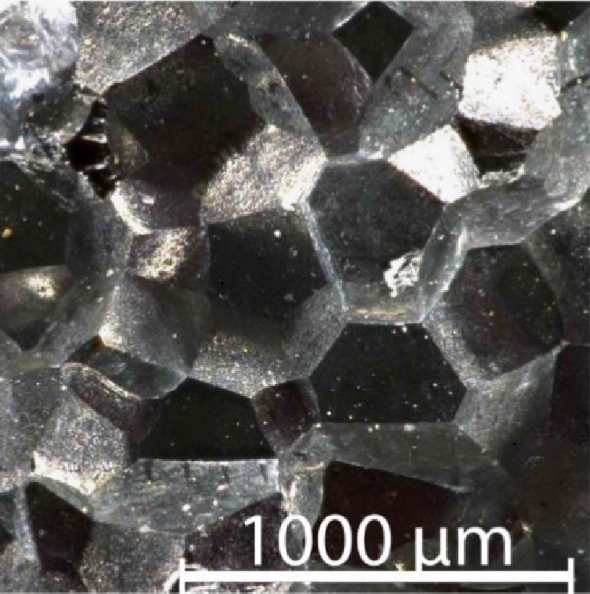 | Dynamique des fissures dans les matériaux désordonnés Bonamy, Daniel Comptes Rendus. Physique, Volume 18 (2017) no. 5-6, pp. 297-313 |
 | Importance of oxidoreduction phenomena in glass. Chopinet, Marie-Hélène; Lizarazu, Dominica; Rocanière, Cécile Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 939-949 |
 | Compositional effects and spectroscopy of rare earths (Er3+, Tm3+, and Nd3+) in tellurite glasses Shen, Shaoxiong; Jha, Animesh; Zhang, Edward; Wilson, Steve J. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 921-938 |
 | Scandium fluorophosphate glasses: a structural approach Nalin, Marcelo; Ribeiro, Sidney José Lima; Messaddeq, Younés; Schneider, José; Donoso, Pedro Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 915-920 |
 | Infrared glass fibers for in-situ sensing, chemical and biochemical reactions Le Coq, David; Michel, Karine; Keirsse, Julie; Boussard-Plédel, Catherine; Fonteneau, Gilles; Bureau, Bruno; Le Quéré, Jean-Michel; Sire, Olivier; Lucas, Jacques Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 907-913 |
 | Willot, Grégoire; Gomez, François; Vast, Pierre; Andries, Véronique; Martines, Marco; Messaddeq, Younes; Poulain, Marcel Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 899-906 |
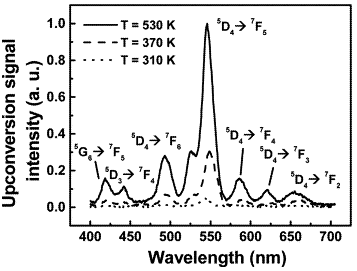 | Frequency upconversion in rare-earth doped fluoroindate glasses de Araújo, Cid B.; Maciel, Glauco S.; Menezes, Leonardo de S.; Rakov, Nikifor; Falcão-Filho, Edilson L.; Jerez, Vladimir A.; Messaddeq, Younes Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 885-898 |
 | Applications of chalcogenide glass optical fibers Sanghera, Jas S.; Shaw, L.Brandon; Aggarwal, Ishwar D. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 873-883 |
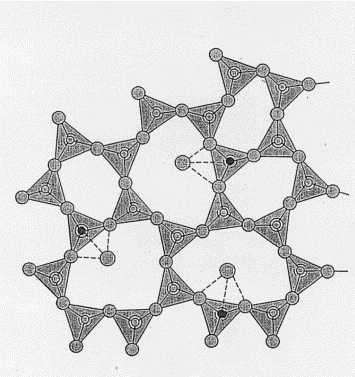 | Clustering of rare earths in GeAs sulfide glass Aitken, Bruce G.; Ponader, Carl W.; Quimby, Richard S. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 865-872 |
 | |
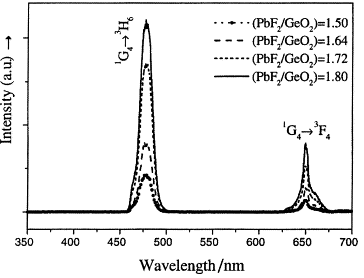 | Rare-earth-doped transparent glass ceramics Clara Gonçalves, M.; Santos, Luís F.; Almeida, Rui M. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 845-854 |
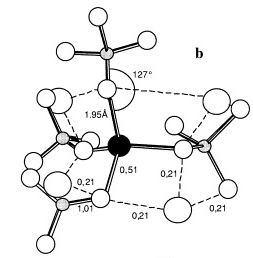 | Structure–property relationships in multicomponent oxide glasses Calas, Georges; Cormier, Laurent; Galoisy, Laurence; Jollivet, Patrick Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 831-843 |
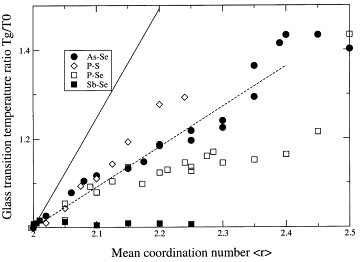 | Micoulaut, Matthieu Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 825-830 |
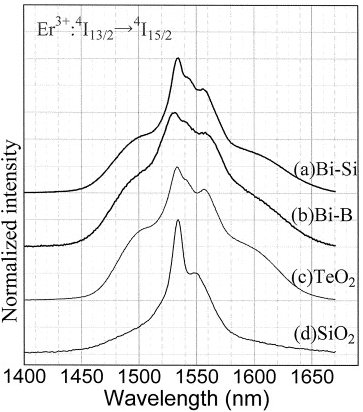 | Rare-earth-doped glasses for fiber amplifiers in broadband telecommunication Tanabe, Setsuhisa Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 815-824 |
 | Compositional effects and spectroscopy of rare earths (Er3+, Tm3+, and Nd3+) in tellurite glasses Shen, Shaoxiong; Jha, Animesh; Zhang, Edward; Wilson, Steve J. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 921-938 |
 | Scandium fluorophosphate glasses: a structural approach Nalin, Marcelo; Ribeiro, Sidney José Lima; Messaddeq, Younés; Schneider, José; Donoso, Pedro Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 915-920 |
 | Infrared glass fibers for in-situ sensing, chemical and biochemical reactions Le Coq, David; Michel, Karine; Keirsse, Julie; Boussard-Plédel, Catherine; Fonteneau, Gilles; Bureau, Bruno; Le Quéré, Jean-Michel; Sire, Olivier; Lucas, Jacques Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 907-913 |
 | Willot, Grégoire; Gomez, François; Vast, Pierre; Andries, Véronique; Martines, Marco; Messaddeq, Younes; Poulain, Marcel Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 899-906 |
 | Frequency upconversion in rare-earth doped fluoroindate glasses de Araújo, Cid B.; Maciel, Glauco S.; Menezes, Leonardo de S.; Rakov, Nikifor; Falcão-Filho, Edilson L.; Jerez, Vladimir A.; Messaddeq, Younes Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 885-898 |
 | Applications of chalcogenide glass optical fibers Sanghera, Jas S.; Shaw, L.Brandon; Aggarwal, Ishwar D. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 873-883 |
 | Clustering of rare earths in GeAs sulfide glass Aitken, Bruce G.; Ponader, Carl W.; Quimby, Richard S. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 865-872 |
 | |
 | Rare-earth-doped transparent glass ceramics Clara Gonçalves, M.; Santos, Luís F.; Almeida, Rui M. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 845-854 |
 | Structure–property relationships in multicomponent oxide glasses Calas, Georges; Cormier, Laurent; Galoisy, Laurence; Jollivet, Patrick Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 831-843 |
 | Micoulaut, Matthieu Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 825-830 |
 | Rare-earth-doped glasses for fiber amplifiers in broadband telecommunication Tanabe, Setsuhisa Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 12, pp. 815-824 |
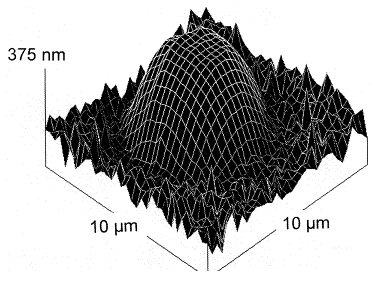 | Photoinduced fluidity in chalcogenide glasses Tanaka, Keiji Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 805-811 |
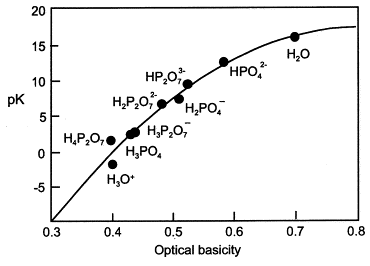 | Solvent properties of glass melts: resemblance to aqueous solutions Duffy, John A.; Ingram, Malcolm D. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 797-804 |
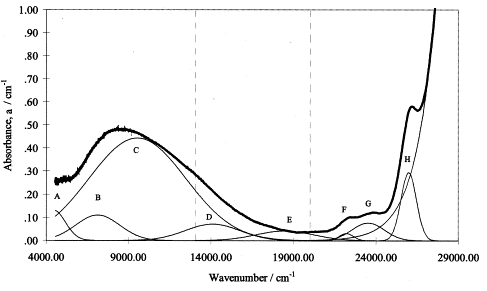 | Novel structural behaviour of iron in alkali–alkaline-earth–silica glasses Bingham, Paul A.; Parker, John M.; Searle, Tim; Williams, John M.; Smith, Ian Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 787-796 |
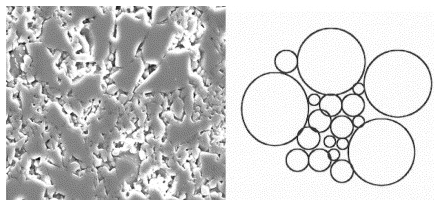 | Glass sintering with concurrent crystallization Prado, Miguel Oscar; Zanotto, Edgar Dutra Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 773-786 |
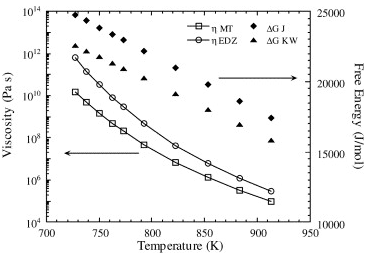 | Crystal growth and classical nucleation theory Weinberg, Michael C.; Poisl, W.Howard; Granasy, Laszlo Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 765-771 |
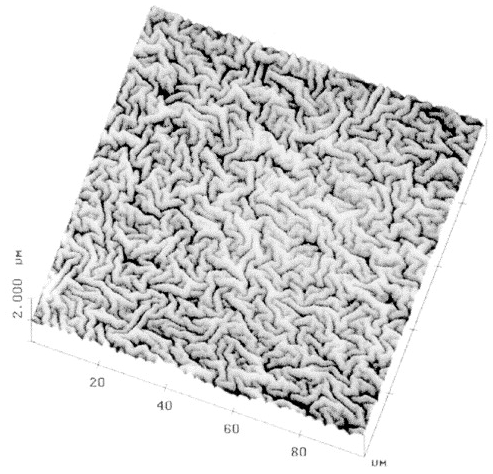 | Tin ions in float glass cause anomalies Frischat, Günther Heinz Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 759-763 |
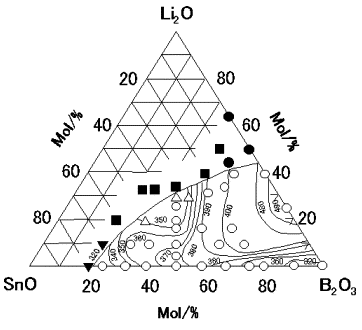 | Structure and properties of glasses in the system Li2O–SnO–B2O3 Hayashi, Akitoshi; Nakai, Miyuki; Tatsumisago, Masahiro; Minami, Tsutomu Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 751-757 |
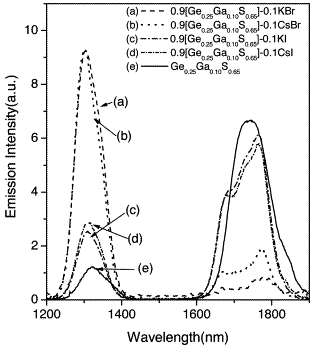 | 1.3-μm-emission properties and local structure of Dy3+ in chalcohalide glasses Heo, Jong Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 739-749 |
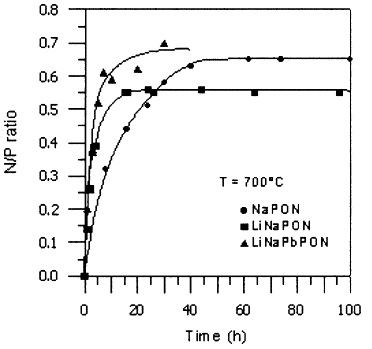 | Alkali and alkali–lead oxynitride phosphate glasses: a comparative structural study by NMR and XPS Muñoz, Francisco; Pascual, Luis; Durán, Alicia; Rocherullé, Jean; Marchand, Roger Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 731-738 |
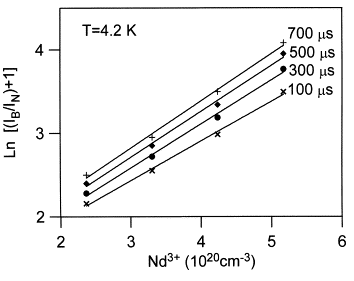 | Spectral migration of excitation energy among Nd3+ ions in fluoroarsenate glasses Balda, Rolindes; Lacha, Luis Maria; Arriandiaga, Maria Angeles; Fernández, Joaquin; Adam, Jean-Luc Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 725-729 |
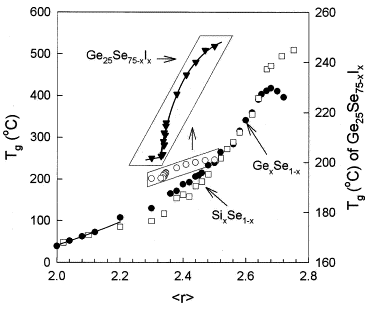 | Boolchand, Punit; Georgiev, Daniel G.; Qu, Tao; Wang, Fei; Cai, Liuchun; Chakravarty, Swapnajit Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 713-724 |
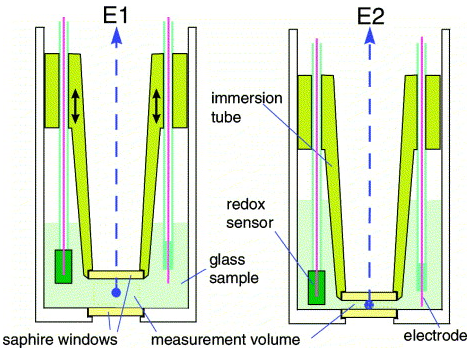 | Optical properties and redox state of silicate glass melts Faber, Anne Jans Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 705-712 |
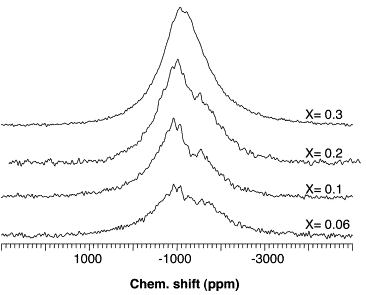 | A survey of transition-metal-containing phosphate glasses Mercier, Cyrille; Palavit, Gérard; Montagne, Lionel; Follet-Houttemane, Claudine Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 693-703 |
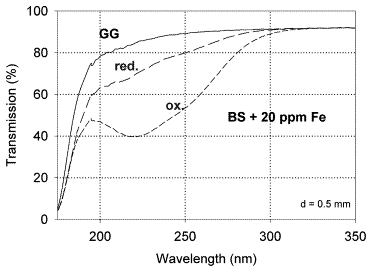 | UV-absorption and radiation effects in different glasses doped with iron and tin in the ppm range Ehrt, Doris Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 679-692 |
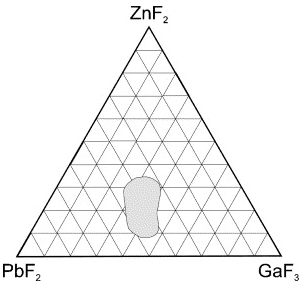 | Vapour-phase deposition of multicomponent fluoride glasses Boulard, Brigitte; Gao, Youping Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 5 (2002) no. 11, pp. 675-678 |