Collection spéciale à l'occasion du bicentenaire de la naissance de Pasteur
(en collaboration avec l'Académie d'Agriculture et l'Académie Vétérinaire)
Louis Pasteur est né il y a deux cents ans, le 27 décembre 1822. Les diverses académies dont il était membre (Académie des sciences, Académie d’agriculture de France, Académie vétérinaire, Académie de médecine) ont organisé, en 2022, des manifestations pour marquer l’anniversaire de celui qui a sans doute été et reste l’un des savants français les plus célèbres, et dont l’œuvre a eu des conséquences qui se font encore sentir aujourd’hui, tant dans les sciences que dans notre vie quotidienne.
Les organes de publications de ces académies, les Comptes rendus de l’Académie des sciences (séries Biologies et Chimie), les Notes Académiques de l’Académie d’agriculture de France et le Bulletin de l’Académie vétérinaire ont publié, au cours de l’année de célébration, des articles qui ont retracé, analysé les divers aspects d’un scientifique exceptionnel.
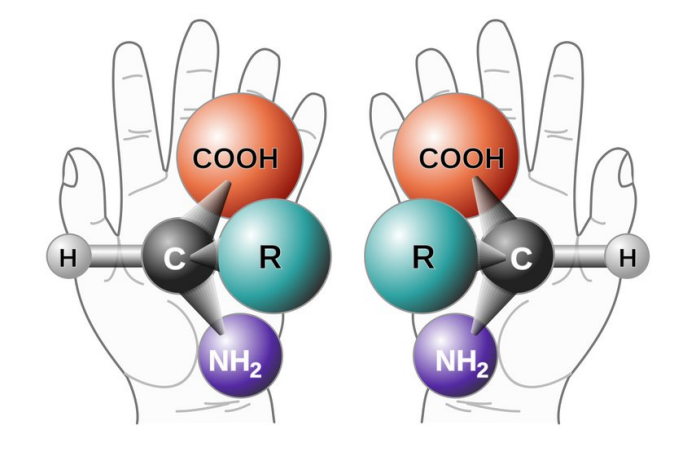
Les premiers travaux de Pasteur, sur les tartrates du vin l’ont conduit à explorer les relations entre la forme des cristaux et leur effet sur la lumière, un maillon important d’une histoire qui a débouché sur la constitution de la stéréochimie, cette partie de la chimie qui explore l’organisation des molécules dans l’espace. Pasteur avait hérité d’un autre scientifique étonnant, Jean-Baptiste Biot, l’hypothèse selon laquelle les éléments constitutifs de la matière qui constitue le vivant auraient été dissymétriques, ce qui n’aurait pas été le cas pour le monde minéral. On mesure le caractère visionnaire de ces hypothèses quand on songe que toute la biologie moléculaire moderne tente d’expliquer les phénomènes biologiques par des interactions entre molécules, interactions dictées par la forme de celles-ci. Le succès actuel d’Alphafold, un outil révolutionnaire d’intelligence artificielle, qui permet de prédire la structure tridimensionnelle des protéines et d’identifier les sites importants, soit pour leur fonction, soit pour leurs interactions avec d’autres molécules, poursuite cette quête des relations entre la forme des molécules et leurs fonctions. Surtout, ces premiers travaux montrent bien des qualités que le scientifique mit en œuvre tout au long de sa carrière : un activité extraordinairement soutenue, focalisée sur la science, et un esprit de synthèse hors norme.
Après ces travaux de chimie, Pasteur a bifurqué vers l’étude des fermentations, explorant le rôle joué par les micro-organismes dans ces phénomènes qui conduisent à la bière, au vin, au vinaigre … Il a révolutionné l’industrie alimentaire, qui a, de plus bénéficié, pour la conservation des aliments, de la « pasteurisation », un processus qu’il avait mis au point pour la conservation du vin. Tout ce travail a fondé la microbiologie.
Le rôle majeur des micro-organismes dans l’environnement, dont on mesure aujourd’hui l’importance, tant en agriculture que dans la lutte contre le changement climatique, fut mis en évidence par Pasteur lorsqu’il montra leur intervention dans la putréfaction, phénomène à la base du recyclage de la matière organique.
À l’époque de Pasteur, nombreux étaient ceux qui croyaient en la génération spontanée des microbes. Par une approche rigoureuse, Pasteur réfuta cette théorie. Il montra dans la foulée que les microbes sont présents partout, dans l’air, dans l’eau, sur tous les objets qui nous entourent, ce dont nous n’avions pas conscience auparavant.
Sa démonstration, en complément de celle de Robert Koch, que les maladies contagieuses sont dues à des microbes, a été à l’origine d’une rationalisation de l’hygiène, élément majeur de l’accroissement de l’espérance de vie au cours du siècle dernier, avec les antibiotiques et, bien sûr, les vaccins. Au-delà de cette démonstration, une révolution en médecine s’est mise en marche, les maladies commençant alors à être définies par leurs causes et non plus seulement par leurs symptômes.
La fabrication et la mise au point des vaccins contre les maladies infectieuses ont été inventées par Pasteur, même si le principe de la vaccination avait été découvert par Alfred Jenner un siècle plus tôt. Leur importance n’est plus à démontrer, surtout en cette période de pandémie. Pandémie due à un virus, tout comme celui de la rage, que Pasteur manipulait sans le voir ni le cultiver, devenant ainsi, sans le savoir, le premier virologiste !
Au-delà de ces accomplissements, Pasteur nous a légué une certaine conception de la science, que l’on qualifie parfois d’esprit pasteurien. Elle inclut en premier lieu la rigueur et l’excellence dans la manière de conduire la recherche alliant intuition, rigueur et esprit critique. En second lieu, l’entretien d’un lien permanent entre recherche fondamentale et applications. En troisième lieu l’importance de la communication, sous toutes ses formes, essentielle pour que les découvertes bénéficient rapidement au bien-être de l’humanité. Enfin, une vision planétaire se résumant par la formule de Pasteur « la science n’a pas de patrie » et qui s’est traduite par la création d’un réseau d’instituts Pasteur, répartis sur tous les continents.
Alors que la vaccination contre le covid rencontre des résistances, alors que la parole des scientifiques est mise -par des idéologues- au même rang que des discours d’opinions, alors que l’on oublie que les sciences de la nature n’ont pas d’intérêts financiers ni idéologiques, nous devons protéger nos démocraties, notamment par une réconciliation du public avec une science dont il est parfois bien éloigné.
 À ce titre, la commémoration du bicentenaire de la naissance de Louis Pasteur a été une excellente occasion de rappeler les avancées des sciences, des technologies et des techniques auxquelles Pasteur a contribué, s'inscrivant dans une lignée remarquable de savants à qui nous devons nombre de nos idées actuelles. Des collègues de diverses disciplines ont exploré l'histoire des travaux de Pasteur. Nous espérons que le panorama constitué (par ordre alphabétique des auteurs) sera un hommage efficace : inspirant pour certains qui se livrent à des travaux scientifiques, éclairant pour ceux qui n'ont qu'une vague idée des avancées réelles dues à Pasteur, utile pour ceux qui ne perçoivent pas bien l'importance des sciences dans notre vie quotidienne.
À ce titre, la commémoration du bicentenaire de la naissance de Louis Pasteur a été une excellente occasion de rappeler les avancées des sciences, des technologies et des techniques auxquelles Pasteur a contribué, s'inscrivant dans une lignée remarquable de savants à qui nous devons nombre de nos idées actuelles. Des collègues de diverses disciplines ont exploré l'histoire des travaux de Pasteur. Nous espérons que le panorama constitué (par ordre alphabétique des auteurs) sera un hommage efficace : inspirant pour certains qui se livrent à des travaux scientifiques, éclairant pour ceux qui n'ont qu'une vague idée des avancées réelles dues à Pasteur, utile pour ceux qui ne perçoivent pas bien l'importance des sciences dans notre vie quotidienne.
Pascale Cossart, Maxime Schwartz, Pierre Braunstein, Hervé This et Nadine Vivier
(Télécharger cet éditorial)
Dessin réalisé par l’artiste Fabrice Hyber
 | Essential oils and molecular chirality Aribi-Zouioueche, Louisa; Couic-Marinier, Françoise Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 24 (2021) no. 3, pp. 397-414 |
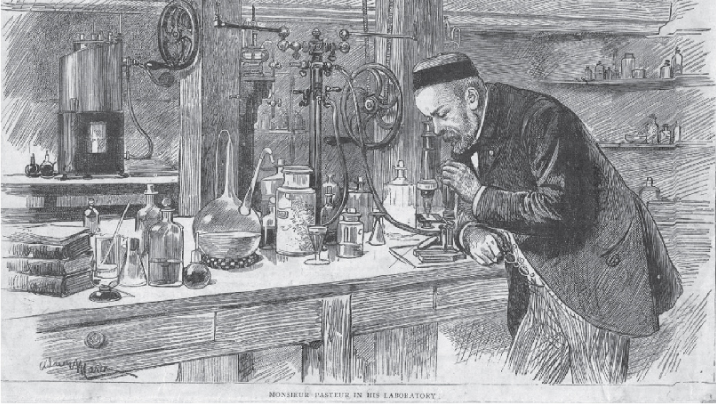 | Bas, Morgane; Hernández, Felipe; Pablo Huidobro-Toro, J. Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 23 (2020) no. 1, pp. 3-16 |
 | How has microbiology changed 200 years after Pasteur’s birth? Bikard, David Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 21-33 |
 | Louis Pasteur : L’enfant est le père de l’homme Brey, Paul T. Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 51-70 |
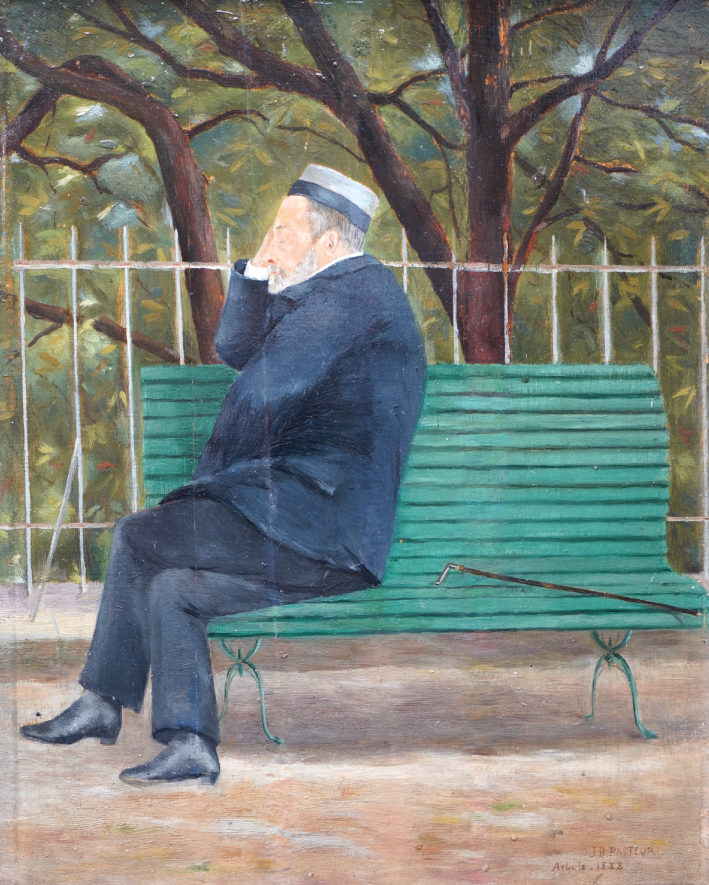 | Bruniaux, Philippe Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 121-141 |
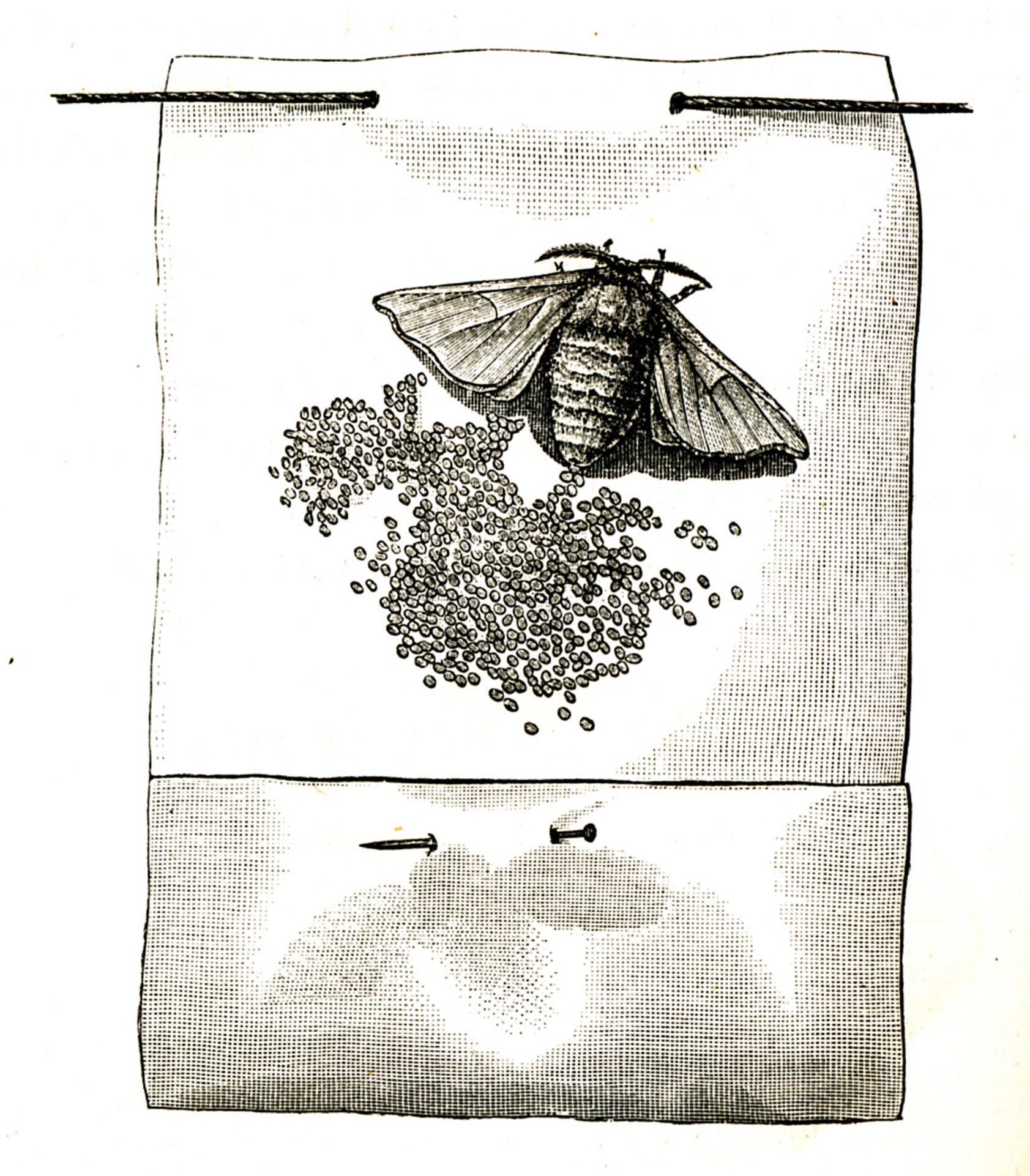 | Louis Pasteur faced with silkworm disease (1865–1870): from chemist to biologist Carton, Yves Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 25 (2022) no. G1, pp. 315-340 |
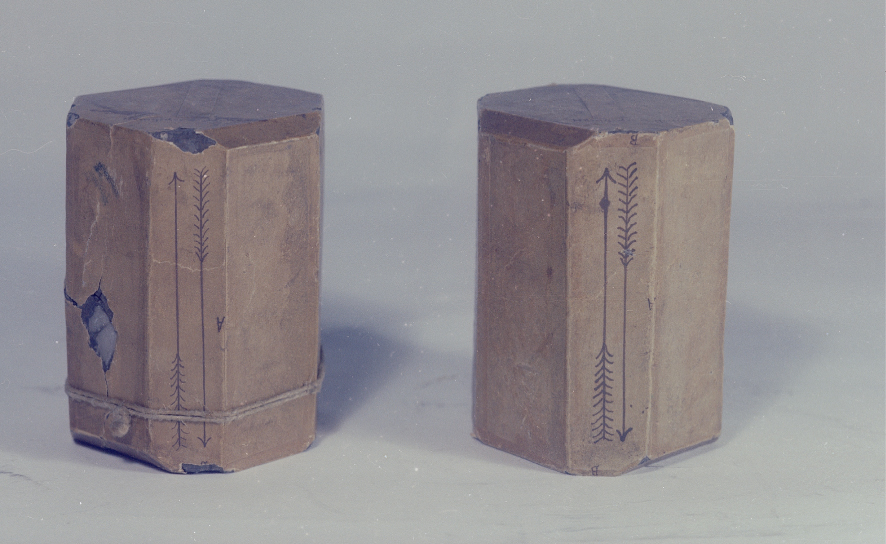 | Louis Pasteur, la dissymétrie moléculaire, la chimie thérapeutique et la neuropharmacologie Changeux, Jean-Pierre Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 7-20 |
 | Pasteur et la recherche « motivée » Danchin, Antoine Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 109-119 |
 | Pasteur à l’Académie de médecine : de l’hygiène à la théorie des germes Debré, Patrice Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 83-92 |
 | Debru, Claude Notes Académiques de l'Académie d'agriculture de France / Academic Notes of the French Academy of Agriculture, Volume 14 (2022), pp. 1-14 |
 | Louis Pasteur, lecturer in chemistry at the School of Pharmacy of Strasbourg (1849–1850) Dirheimer, Guy Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 25 (2022) no. G1, pp. 289-293 |
 | Galvez-Behar, Gabriel Notes Académiques de l'Académie d'agriculture de France / Academic Notes of the French Academy of Agriculture, Volume 14 (2022), pp. 1-15 |
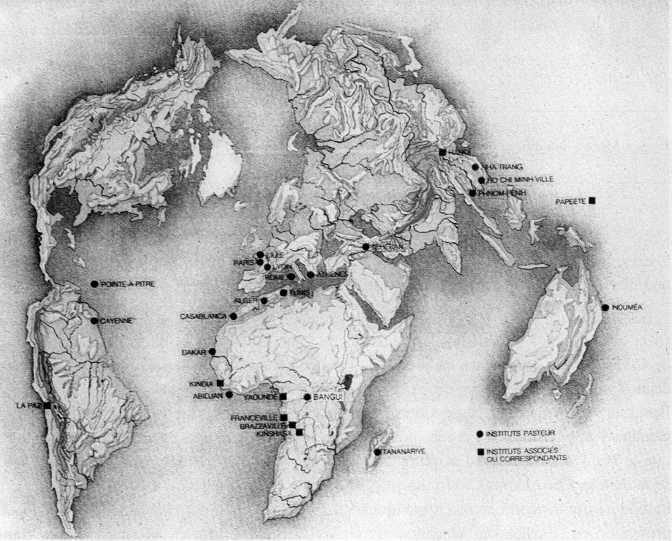 | Pasteur et pasteuriens : un certain style en science Jacob, François La Vie des Sciences, t. 4, n° 5, pp. 437-447 |
 | Lecerf, Jean-Michel Notes Académiques de l'Académie d'agriculture de France / Academic Notes of the French Academy of Agriculture, Volume 14 (2022), pp. 1-11 |
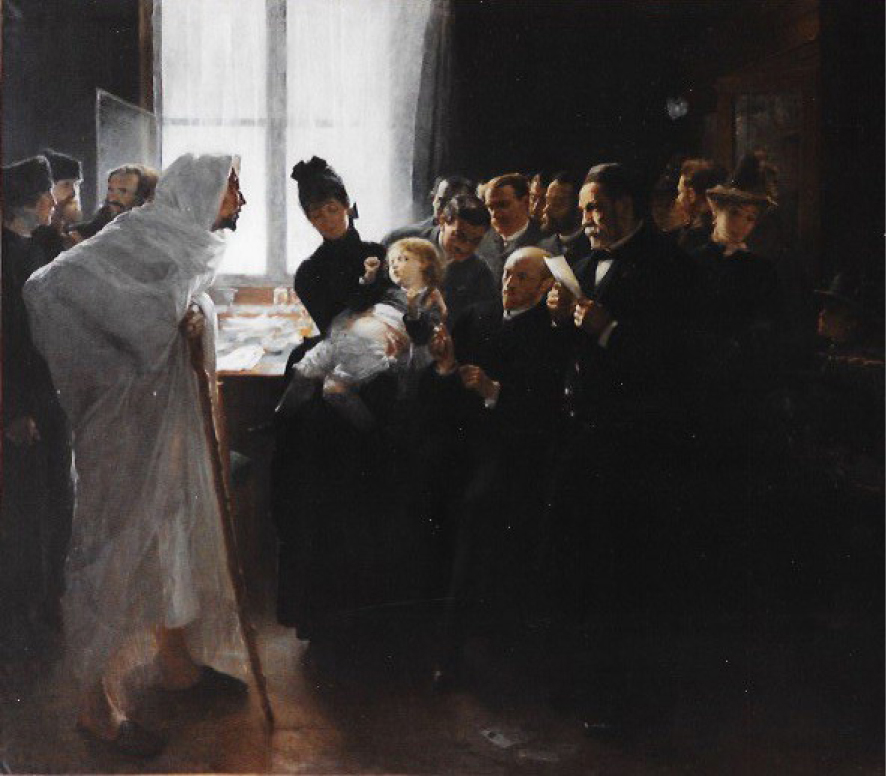 | Louis Pasteur as a bacteriologist: from virulence mitigation to vaccination Monteil, Henri Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 25 (2022) no. G1, pp. 307-313 |
 | Orth, Gérard Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 71-81 |
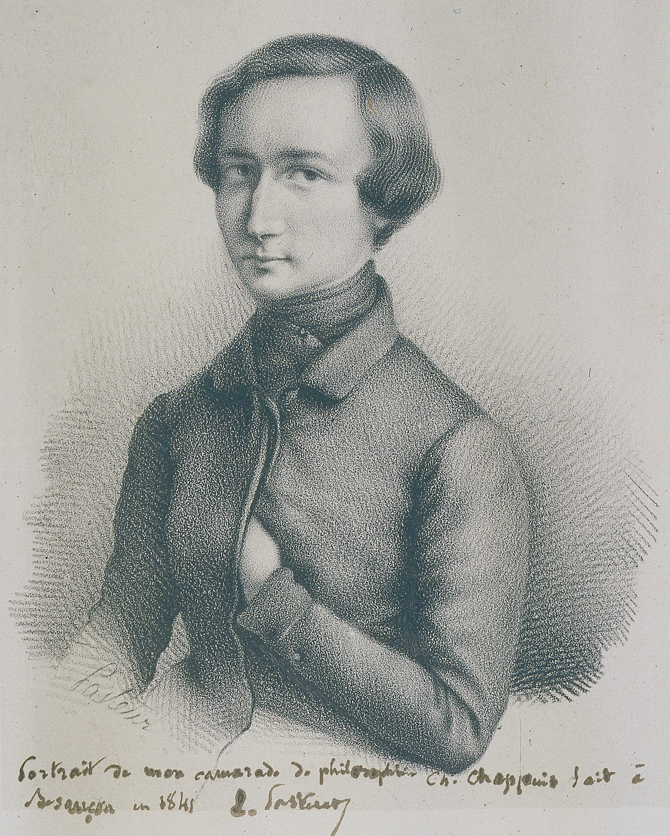 | Pasteur: the scientist beneath the artist Perrot, Annick Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 25 (2022) no. G1, pp. 171-177 |
 | Raichvarg, Daniel Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 35-50 |
 | Rosolen, Serge-Georges Bulletin de l'Académie vétérinaire de France, Volume 175 (2022) |
 | Serge-Georges Rosolen et Jean Dupouy-Camet Bulletin de l'Académie vétérinaire de France, Tome 176 (2023) p. 1-9 |
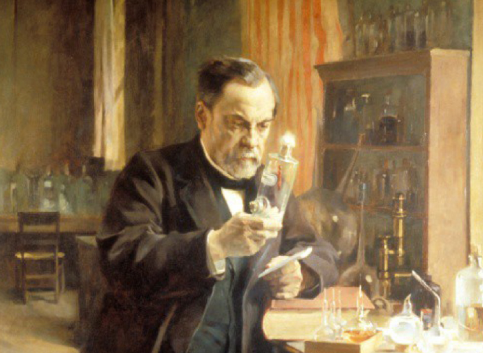 | La contribution Pasteurienne à l’histoire des vaccins Schwartz, Maxime Comptes Rendus. Biologies, Volume 345 (2022) no. 3, pp. 93-107 |
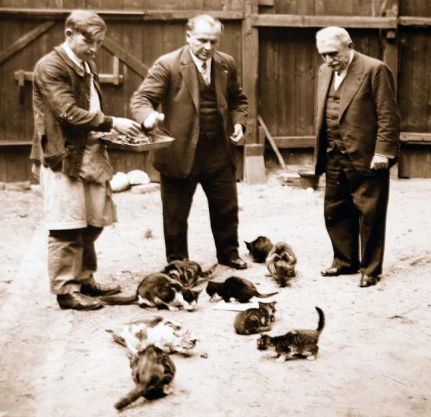 | Pasteur, son neveu, et la science vétérinaire Schwartz, Maxime Bulletin de l'Académie vétérinaire de France, Volume 175 (2022) |
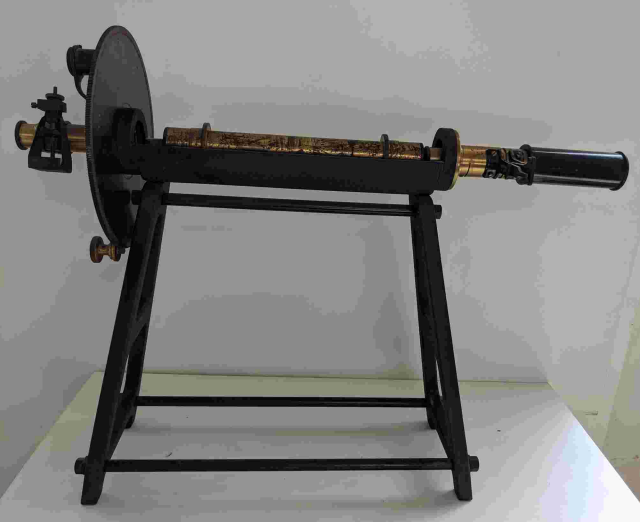 | This, Hervé Notes Académiques de l'Académie d'agriculture de France / Academic Notes of the French Academy of Agriculture, Volume 12 (2021), pp. 1-33 |
 | Louis Pasteur, from physical chemistry to biology This, Hervé Comptes Rendus. Chimie, Volume 25 (2022) no. G1, pp. 237-251 |
Consultez également les interventions de Louis Pasteur à l'Académie, retranscrites dans les anciens numéros des Comptes rendus des séances hebdomadaires de l'Académie des sciences.