1 Introduction
It is well documented that the ascent and emplacement of many granites intrusions is significantly controlled by tectonic activity along faults and shear zones, in different tectonics settings (Castro, 1986; Hutton, 1988; Ingram and Hutton, 1994; Speer et al., 1994; Tikoff and Saint Blanquat, 1997). This relationship is well demonstrated by the synchronous timing and spatial association of many Variscan granites in the Variscan belt (Faure, 1995; Faure and Pons, 1991; Faure et al., 2002; Gébelin et al., 2006, 2007, 2009; Joly et al., 2009).
Outstanding features of the internal zone of the Iberian Variscides, the Central Iberian Zone, are a complex shear zone network and a intensive late to post-orogenic Variscan magmatism with the most active period spanning broadly the time between c. 320 and 290 Ma (Dias et al., 1998, 2009; Fernández-Suárez et al., 2011; Martins et al., 2009). In northern Portugal, this magmatic activity has left large granitoid plutons which presented highly contrasted compositions and whose emplacement was in most cases associated to major Variscan structures, namely shear zones and strike slip faults. The Lavadores granite emplacement was controlled by one of the most important structure crossing the Variscan basement, the Porto-Tomar Shear Zone (PTSZ). The PTSZ is a north-south dextral transform fault that was active throughout much of the Devonian as well as the Variscan (Dias and Ribeiro, 1995; Ribeiro et al., 2009). Other authors propose that the PTSZ is a major fault only structured since the beginning of the Variscan orogeny (Pereira et al., 2010).
The first Rb-Sr geochronological data of the Lavadores granite were obtained by Mendes (1967) in biotite and Silva (1995) in whole rock, which respectively gave an age of 346 ± 14Ma and 314 ± 11Ma, suggesting a syntectonic emplacement. However, the well-known limitations of the Rb-Sr isotopic system and because these ages are not in agreement with field and structural data, lead us to the development of a U-Pb zircon geochronology.The aim of this work is to better constrain the emplacement age of the Lavadores granite (northern Portugal) with a multidisciplinary approach: U-Pb geochronology data and structural characterization through a study of Anisotropy of Magnetic Susceptibility (AMS). Studies of AMS were preceded by detailed geological mapping and complemented by petrographic and microstructural observations. The AMS studies were performed in the Lavadores granite as well as in its country rocks.
The main results of this study show that this granite is post-tectonic and ascent and emplaced along a non-active ductile extensional shear zone.
2 Geological setting
The tectonometamorphic and magmatic features of the Western Europe Variscan belt have been explained by the collision of Laurentia-Baltica with Gondwana (Lagarde et al., 1992; Matte, 1991) and has taken place from Early Devonian to Mid-Carboniferous (390–330), followed by post-thickening extension from the Mid-Carboniferous to the Permian times (330–280). The innermost zone of the Iberian Variscan Belt constitutes the Central Iberian Zone (CIZ) in which three main ductile Variscan deformation phases (D1, D2 and D3) were recognized (Noronha et al., 1979; Ribeiro, 1974; Ribeiro et al., 1990). The D1 and D2 deformation phases correspond to the collision stage of the Variscan orogeny whereas the last ductile deformation phase D3, Namurian-Westphalian in age, is related to the post-thickening extension tectonic regime. This event develops open to tight vertical folds with subhorizontal axes and subvertical shear zones with sinistral or dextral wrench movements and was followed by a fragile deformation phase giving rise to a set of conjugate strike-slip faults (NNW-dextral and NNE-sinistral), pointing to a Late-Variscan main compression around north-south (Arthaud et al., 1975; Ribeiro, 1974). Most of the granitoids of the CIZ are correlated with D3 and define alignments closely related to the ductile shear zones. These granitoid magmatism, based on emplacement ages (Dias et al., 1998) has been classified as: synorogenic (syn-late and late to post-D3; 320–300 Ma) and late to post-orogenic (post-D3; 299–290 Ma).
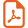
The granite rock selected for this study is located in the west boundary of the Central Iberian Zone, in northern Portugal. This boundary is marked by one of the most important Variscan structures the Porto-Tomar Shear Zone (Ribeiro et al., 2009). The PTSZ is a north-south subvertical strike-slip fault that is 2 to 8 km wide and extends ca. 170 km from Porto to Tomar (Fig. 1). This important crustal anisotropy controlled the emplacement of the Lavadores granite during the post-collisional stage of the Variscan orogeny.The geology of the studied area is dominated by the presence of metamorphic rocks, intruded by the Lavadores granite. The Lavadores granite outcrops at about 3 km south of Porto in a narrow band along the coastline, in Vila Nova de Gaia, and the massif extended to the south ca. 60 km cutting discordantly Precambrian metamorphic rocks (Chaminé et al., 2003; Oliveira et al., 2010). At southeast, the Lavadores granite has a gradual contact with the Madalena granite (Fig. 1). Most outcrops of the Lavadores granite are, however, covered by sand which difficult fieldwork and sampling.The host rocks, uncharted at this map scale, comprise different lithologies, consisting in gneiss, amphibolites and folded quartz-pelitic metasediments (micaschists and quartz-micaschists). All of these metamorphic rocks present a shearing deformation, related to the last ductile Variscan deformation phase (D3).
Geological sketch map of the Lavadores area and its location in northern Portugal (Central Iberian Zone). MVF: Manteigas-Vilariça Fault; PVF: Penacova-Verin Fault; DBSZ: Douro-Beira Shear Zone; JPCSZ: Juzbado-Penalva do Castelo Shear Zone; PTSZ: Porto-Tomar Shear Zone; TCBSZ: Tomar-Cordoba-Badajoz Shear Zone
Mappe géologique simplifiée de la région de Lavadores et sa localisation au Nord-Ouest du Portugal (Zone Centrale Ibérique). MVF : Faille de Manteigas-Vilariça ; PVF : Faille de Penacova-Verin ; DBSZ : Zone de Cisaillement de Douro-Beira ; JPCSZ : Zone de Cisaillement de Juzbado-Penalva do Castelo ; PTSZ : Zone de Cisaillement de Porto-Tomar ; TCBSZ : Zone de Cisaillement de Tomar-Cordoba-Badajoz.
The Lavadores granite has a pinkish colour and presents abundant mafic microgranular enclaves with a wide range of compositions (Silva, 2010; Silva and Neiva, 1998, 2004). This granite is porphyritic, coarse-grained biotite granodiorite-monzogranite and contains quartz + plagioclase (andesine/oligoclase) + perthitic orthoclase and microcline + biotite + zircon+ sphene + apatite + allanite ± amphibole. The main petrographic feature that distinguishes this granite is the presence of the accessory phase magnetite, which is uncommon in Late Variscan granites in northern Portugal (Dias et al., 2002; Martins et al., 2009; Mendes and Dias, 2004) and can be considered a magnetite-type granite (Ishihara, 1977). No clear shape preferential orientation of the main minerals was observed in the studied sites. Microstructural observations support the general lack of intracrystaline deformation in minerals, as shown by undeformed biotite and euhedral feldspar crystals, accompanied by large quartz grains. Slight imprints of solid-state deformation are observed, as represented by undulatory extinction in quartz (Fig. 2). Hence, the rock fabric is considered to have developed essentially in the magmatic state.

Magmatic microstructures in the Lavadores granite: undeformed biotite and feldspar and incipient undulatory extinction in quartz. All microphotographs under crossed polars. bt: biotite; Kf: K-feldspar; pl: plagioclase; all: allanite; qtz: quartz.
Microstructures magmatiques du granite de Lavadores : la biotite et le feldspath ne sont pas déformés, et le quartz présente une légère extinction onduleuse. Toutes les microphotographies ont été prises en lumière polarisée. bt : biotite ; Kf : feldspath potassique ; pl : plagioclase ; all : allanite ; qtz : quartz.
Available geochemical, mineralogical and isotopic data are reported in several papers (Martins et al., 2003, 2004; Silva, 2010; Silva and Neiva, 1998, 2004).
3 Analytical methods
3.1 Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility
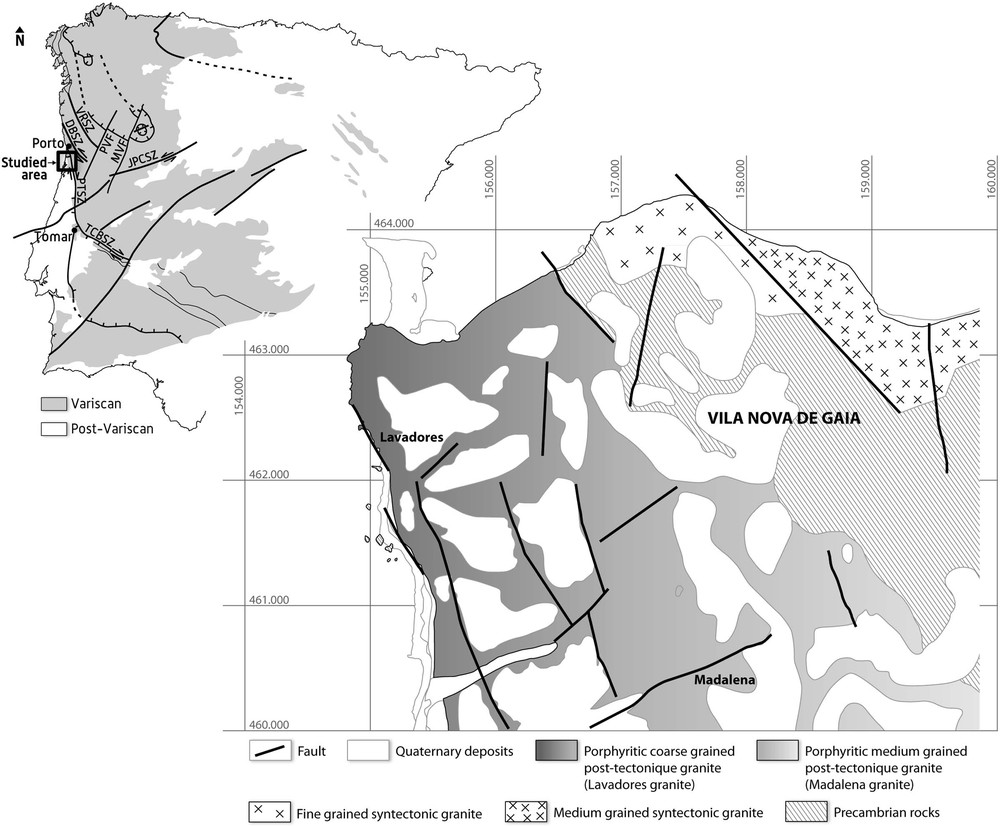
The AMS studies sampling was performed in the Lavadores granite and also in country-rocks (gneiss, micaschists and amphibolites) (Fig. 4). A total of 3/4 oriented cores were collected at each of the sampling stations corresponding to 63 rock-cylinders, 25 mm in diameter and 22 mm in length, which were prepared for magnetic measurements. Measurements were performed using KLY-4S Kappabridge susceptometer Agico model (Czech Republic) of “Centro de Geologia” of the Porto University. For each site, the AGICO software enabled us to calculate the mean susceptibility Km, which is the mean of the eight (or more) individual arithmetic means (k1 + k2 + k3)/3. There also calculated the intensities and orientations of the three axes K1 ≥ K2 ≥ K3, which are the tensorial means of the k1 ≥ k2 ≥ k3 axes for the eight specimens, and the 95% confidence angles E12, E23 and E31 corresponding to these three axes. The magnetic fabric is defined by the magnetic lineation (parallel to the long axis of the mean ellipsoid orientation average, K1) and the magnetic foliation (plane perpendicular to the orientation of K3, the short axis). P, the magnetic anisotropy ratio, corresponds to K1/K3. To describe the shape of the AMS ellipsoid the shape parameter, T, expressed by
Simplified geological map of the studied area with the sampling sites and the stereograms (Schmidt, lower hemisphere) of the magnetic fabrics.
Carte géologique simplifiée de la zone étudiée avec les sites d’échantillonnage et les stéréogrammes (Schmidt, hémisphère inférieur) de fabrique magnétique.
A Molspin pulse induction magnetizer was used to create magnetic fields at room temperature to a maximum of 1 T. The magnetization of the representative samples after each exposure was measured with a Molspin spinner magnetometer controlled by a microcomputer. The magnetization obtained in this maximum field was defined as the effective saturation Isothermal Remanent Magnetization value for each of the samples. These measurements were performed in the Earth Sciences Department of the University of Coimbra.
3.2 U–Pb dating
The U–Pb isotopic analyses were carried out at CRPG, Nancy, France, using a conventional U–Pb method on multigrain zircon fractions. The zircons were recovered by crushing the sample and sieving, followed by heavy liquid and magnetic separations and finally hand picking. Four zircon fractions were selected according to their morphology, colour, and lack of inclusions, fractures and metamictisation.
Some of these fractions were submitted to air-abrasion (Krogh, 1982) to eliminate the external zones of the crystal where Pb loss may have occurred. All zircon fractions were observed on a backscattered scanning electron microscopy (BSEM). Chemical preparation of U and Pb analysis includes:
- • HNO3 3 N warm washing of the zircon;
- • HF digestion at 240 °C and HCl 3 N dissolution of the fluorides at 180 °C in a Teflon bomb (Parrish, 1987);
- • separation of Pb and U by elution on anionic resin of two aliquots (one with the addition of a mixed 208Pb-235U spike) following Krogh (1973).
Common Pb blanks varied from 30 and 80 pg during this study.
4 Results
4.1 Anisotropy of Magnetic Susceptibility (AMS)
The results for the nine stations are summarized in Table 1.
Résultats des mesures d’anisotropie de susceptibilité magnétique pour les sites d’échantillonnage.
| Sampling Sites/Lithology | Km E−6 SI |
P | T | K1 | K3 | Foliation | E12 | E23 | E31 | n | ||
| Dec | Inc | Dec | Inc | |||||||||
| LV1- Lavadores granite |
16477.50 | 1.116 | 0.292 | 245 | 69 | 31 | 18 | N121; 72SW | 37 | 11 | 8 | 12 |
| LV2- Lavadores granite |
17426.67 | 1.206 | –0.246 | 194 | 81 | 23 | 4 | N144; 83 SW | * | * | * | 3 |
| LV3- Lavadores granite |
17031.43 | 1.164 | –0.106 | 200 | 72 | 12 | 18 | N102; 72 SW | 29 | 10 | 9 | 7 |
| LV4- Lavadores granite |
10589.00 | 1.144 | 0.214 | 241 | 79 | 20 | 9 | N119; 81 SW | 8 | 16 | 5 | 9 |
| LV5- Lavadores granite |
19302.86 | 1.192 | –0.028 | 171 | 78 | 355 | 12 | N085; 78 S | 12 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| LV6- Lavadores granite |
15000.00 | 1.251 | –0.285 | 248 | 80 | 21 | 8 | N111; 82 SW | * | * | * | 2 |
| Amphibolite | 1348.88 | 1.311 | –0.253 | 226 | 62 | 340 | 12 | N070; 78 SE | 5 | 20 | 4 | 7 |
| Micaschist | 3965.56 | 1.932 | –0.060 | 219 | 58 | 52 | 31 | N142; 59 SW | 18 | 28 | 8 | 9 |
| Gneiss | 22.71 | 1.034 | 0.079 | 316 | 77 | 123 | 23 | N33; 77 NE | 49 | 73 | 57 | 7 |
The magnetic susceptibility values fall into two major groups: K > 10 × 10−3 SI for the Lavadores granite and K < 5 × 10−3 SI for the amphibolite, metasediments and gneiss as is shown on the K histogram (Table 1 and Fig. 3a).

a: frequency histogram for bulk magnetic susceptibility; b: plots of the shape (T) and anisotropy (P) parameters showing dominant prolate ellipsoids.
a : histogramme de fréquence pour la susceptibilité magnétique ; b : représentation du paramètre de forme (T) et du paramètre d’anisotropie (P) montrant des ellipsoïdes allongés.
The magnetic anisotropy, P, has values always higher than 1.10 in the amphibolite, metasediments and Lavadores granite and less than 1.10 in the gneiss.
The shape parameter T is below zero in six sites, which is indicative of prolate AMS ellipsoids: in metasediments, amphibolite and four sites of the Lavadores granite. The gneiss and two sites of the Lavadores granite show oblate ellipsoids (Table 1).
The plot of the T and P parameters show that the prolate shape of the AMS ellipsoid is related to the highest anisotropies (Fig. 3b).
Equal-area stereographic projections of the three principal axes of magnetic susceptibility each site are presented in Fig. 4.
The Lavadores granite has very homogeneous magnetic lineations with steep dip (mean dip is 79°) trending to N203°. The magnetic foliations have also steep dip (mean dip is 77° SW) and trend to N113°.
In amphibolites and metasediments, the magnetic lineations are also subvertical. Nevertheless, in the gneiss, the magnetic lineations are poorly defined. The magnetic foliation of the metasediments have WNW-ESE trend and dip to south-west (similar to Lavadores granite). In the amphibolites, the magnetic foliation has a NE-SW trend and is subvertical.
Finally the foliation in the gneiss is subvertical with WNW-ESE trend; however, the low magnetic anisotropy of this facies, creates a wide dispersion of the AMS axes which implies a bad definition of the magnetic foliation and lineation.
The Isothermal Remanent Magnetization data obtained point out three distinct magnetic behaviors: in the granite the IRM data are due to the ferrimagnetic fraction; in the metasediments and amphibolites are due to both the paramagnetic and ferrimagnetic fractions; finally the gneiss values are controlled by the paramagnetic fraction (Fig. 5).

Isothermal Remanent Magnetization (IRM) acquisition curves for representative samples. Js: saturation magnetization; J: magnetization.
Courbes d’acquisition d’aimantation rémanente isotherme pour les échantillons représentatifs. Js : aimantation à saturation ; J : aimantation.
4.2 U–Pb geochronology
The analytical data and calculated ages with 2σ errors from Lavadores granite are presented in Table 2. The U–Pb zircon data were carried out on four zircon fractions of one sample of the Lavadores granite. A typological study (Pupin, 1980) has allowed the identification of several zircon types (Martins et al., 2003, 2004). The zircons are very limpid, colourless or light rose color. The backscattered scanning electron microscope imaging of the long prismatic zircons revealed an inner zone, sometimes partially resorbed, surrounded by a finely magmatic zoned rims. Some of them have cores that could correspond to an earlier magmatic crystallization. The prismatic acicular and flat zircons are more homogeneous crystals devoid of cores and showing generally a faint zoning.
Résultats analytiques U-Pb des zircons provenant du granite de Lavadores, Nord-Portugal. Les rapports isotopiques ont été corrigés des blancs, de la composition du plomb commun initial (Stacey et Kramer, 1975) et du fractionnement de masse (NBS 983 Standard). Les âges U–Pb, les erreurs 2σ, ont été calculés à l’aide d’une version du programme Isoplot (Ludwig, 2003). Les constantes de désintégration, utilisées pour les déterminations d’âge sont de Steiger et Jäger (1977).
| Concentrations | Isotopic ratios | Apparent ages (Ma) | ||||||||
| Fractions (shape) |
Weight (mg) |
U Total (ppm) |
Pb* (ppm) |
206Pb/204Pb | 206Pb*/238U 2σ(%) |
207Pb*/235U 2σ(%) |
207Pb*/206Pb* 2σ(%) |
206Pb*/238U 2σs |
207Pb*/235U 2σ |
207Pb*/206Pb* 2σ |
| Lav99 (Z)b (needle) |
0.95 | 1486.7 | 63.1 | 1763.79 | 0.04222 ± 0,084522 | 0.304251 ± 0,239064 | 0.052265 ± 0,158541 | 266.6 ± 0,2 | 269.7 ± 0,6 | 297 ± 4 |
| Lav99 (Z)b (short prisms) |
21 | 1665.9 | 69.1 | 1313.71 | 0.041804 ± 0,182463 | 0.301108 ± 0,369571 | 0.05224 ± 0,191685 | 264 ± 0,5 | 267.3 ± 0,9 | 296 ± 4 |
| Lav99 (Z)b (flat) |
0.16 | 1183.9 | 48.7 | 1032.34 | 0.040716 ± 0.212583 | 0.293165 ± 0.410623 | 0.05222 ± 0.2056772 | 257.3 ± 0.5 | 261 ± 0.9 | 295 ± 5 |
| Lav99 (Z)a (long prisms) |
0.43 | 1343.9 | 58 | 1628.11 | 0.04306 ± 0.120448 | 0.310184 ± 0.2559 | 0.052245 ± 0.13844 | 271.8 ± 0.3 | 274.3 ± 0.6 | 296 ± 3 |
a Fraction submitted to abrasion.
b Fraction not submitted to abrasion.
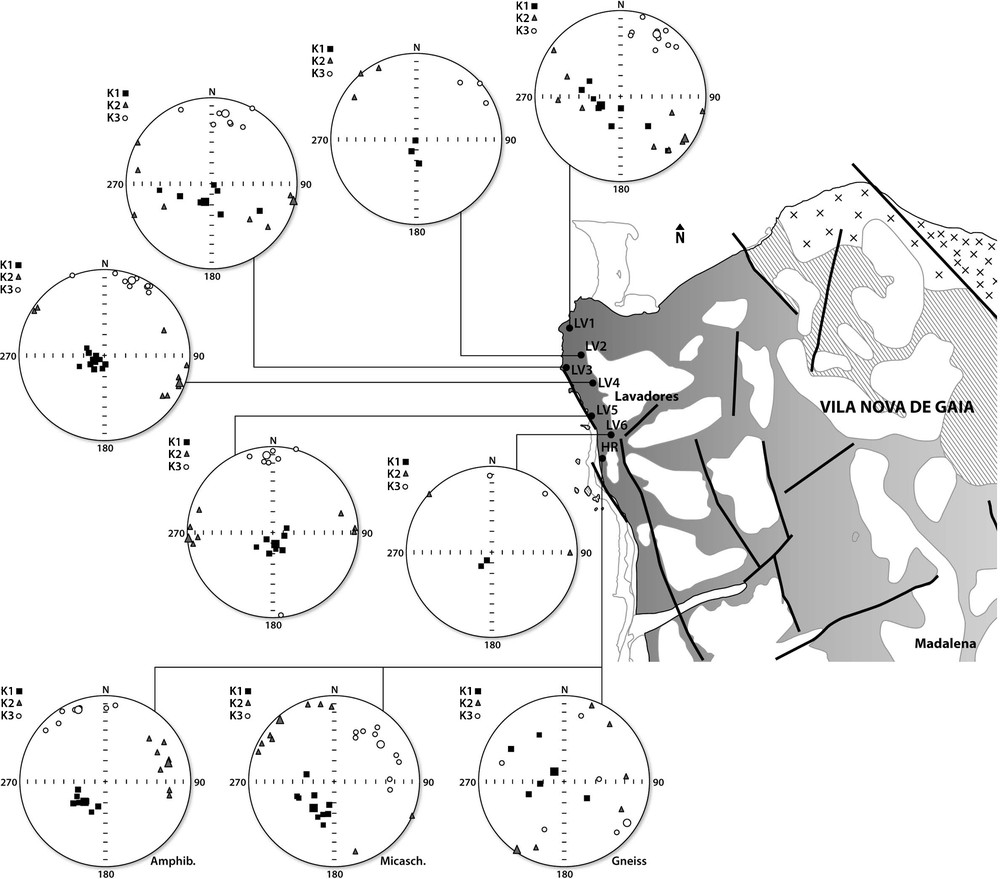
The four zircon fractions are concordant and define a line (MSWD of concordance = 0.013, probability of fit = 0.99) intersecting the Concordia at 298 ± 11 Ma (Fig. 6) that can be interpreted as the emplacement age of this granite. This new data do not confirm the age of 314 ± 11 Ma obtained by Silva (1995) using the Rb/Sr method, although the error bars are large for the two of them, since the Lavadores granite shows no evidence of being syntectonic. In fact the new age and thus the post-tectonic character is in agreement with geological and tectonic settings and corresponds to the age of Variscan late-orogenic granite magmatism, post-D3 (Dias et al., 1998, 2009; Ferreira et al., 1987; Martins et al., 2009).
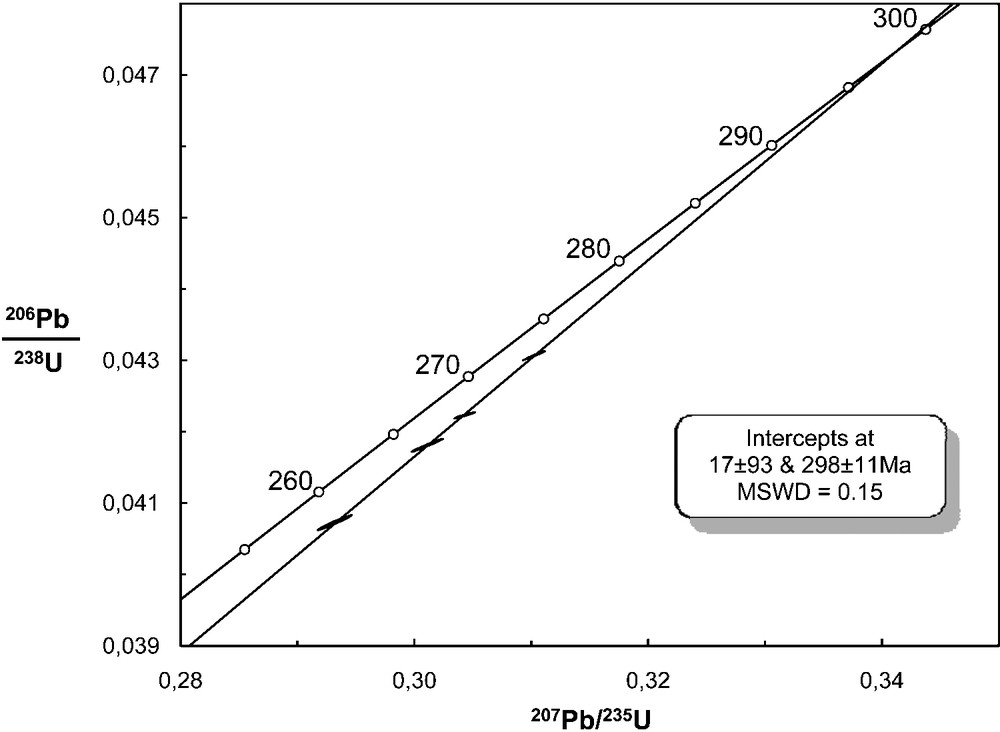
U-Pb Concordia diagram showing analytical data for zircon fractions from the Lavadores granite, northern Portugal.
Diagramme Concordia du granite de Lavadores, Nord-Portugal.
5 Discussion and conclusion
Granite bodies record the tectonic events that are related to their emplacement during magma cooling, through the orientation of the magmatic foliation and lineation, and trough solid-state deformation at high and low temperature that record the kinematics of deformation as crystallization progress (Be Mezeme et al., 2007; Gleizes et al., 2006; Verner et al., 2009). Based on petrographic overview and AMS data, we argued that the Lavadores granite structure indicates fabrics developed at a magmatic stage during magma crystallization.
Based on the AMS measurements, the inclusion of the magnetic susceptibility values in two large groups (K > 10−3 SI and K < 10−4 SI) allows the characterization of the magnetic behaviour of the studied facies. According to Tarling and Hrouda (1993), in a rock presenting K > 10−3 SI, its susceptibility and anisotropy are due to the ferrimagnetic fraction (magnetite); if K < 10−4 SI then the paramagnetic fraction controls the magnetic susceptibility and anisotropy of the rock.
Isothermal Remanent Magnetization (IRM) data pointed out two distinct magnetic behaviours: in the granites and metasediments, the IRM data are due to a ferrimagnetic fraction and in the gneiss values are controlled by the paramagnetic one (Sant’Ovaia et al., 2009).
In the case of Lavadores granite, the presence of magnetite can include this granite in the series of “magnetite type granites” defined by (Ishihara, 1977). In the case of the gneiss, the magnetic susceptibility is mainly due to iron-bearing minerals such as the biotite.
The Lavadores granite shows a high magnetic anisotropy (the average for the six sampling stations is 1.179). Even so, field and microscope observations do not show signs of low temperature solid-state deformation. Occasionally some magmatic flow is visible on the field and magmatic to high temperature solid-state deformation microstructures are present. Apparently this anisotropy is due solely to the fact that the bearer of the magnetic signal is the magnetite (which has a high susceptibility) and, though a weak alignment of magnetite grains leads to a higher anisotropy to the rock. The “subfabric” of magnetite prevails over any other “fabric” mineral, especially that of biotite or amphibole. In addition, the “subfabric” of magnetite is reflected generally in the constrict shape of AMS ellipsoids.
The magnetic foliations presents generally high dips and most of the magnetic lineations are subvertical; it is also worth noting that prolate ellipsoids characterize the studied granite. These features might suggest the presence of a feeding zone for the Lavadores granite. In this zone, the magma ascended into a conduit, the PTSZ anisotropy, towards upper-crustal levels. The Lavadores granite emplacement was controlled by transtensional structures associated with the PTSZ, which create offsets for magma emplacement, as attested by the magnetic subvertical WNW-ESE foliation associated with subvertical magnetic lineations. This magnetic fabric pattern probably records the evolution of regional tectonics during or just after the complete crystallization of the magma because only magmatic microstructures are present rather than low temperature solid-state microstructures.
In the metasediments and gneiss, the NW-SE magnetic foliations are concordant with the foliation measured in the field. In the case of metasediments the magnetic anisotropy (mean 1.932) may not be justified exclusively by the presence of magnetite. A deformation event must be taking into account as well, to explain the high magnetic anisotropy. However in the gneisses the magnetic anisotropy (mean 1.034) is an indicator of an incipient foliation and is similar with the values found in syntectonic peraluminous granites of the Central Iberian Zone (Sant’Ovaia and Noronha, 2005).
The subvertical lineations found in the metasediments are parallel to the subvertical folds axes, which are observed in the field.
The Rb-Sr age (314 ± 11 Ma) previously obtained in the Lavadores granite cannot represent an emplacement age since structural studies have evidenced a late tectonic emplacement (Late Carboniferous-Permian) of the granite body rather than a syntectonic emplacement. The lack of internal structures led to a model of magma ascent and emplacement after the last Variscan folding event occurred. In addition, the country rocks are clearly deformed by this Variscan event, which predates pluton emplacement.
The U-Pb zircon age 298 ± 11 Ma obtained in the present study is consistent with field relationships and structural data and suggest a post-tectonic emplacement. This post-tectonic feature of the Lavadores granite is also supported by the magmatic nature of the microstructures, which suggest that the magma did not suffer further significant deformation once crystallized.
In spite of a limited number of data, we may propose that the Lavadores granite can be considered a late to post-orogenic (post-D3-290-299) granite with an age constrained to 298 ± 11 Ma whose emplacement was controlled by the WNW-ESE local structures linked with a dextral movement in this sector of the north-south trending PTSZ. Nevertheless, tectonic control was only moderated since no related low temperature solid-state microstructures appear.
Acknowledgements
This research was carried out at the Geology Center (Porto University), an R and D unit from Portuguese Foundation of Science and Technology. The authors which to thank J. Leterrier for his assistance at CRPG (Nancy, France) and to the CEMUP (Porto University) for SEM analyses. We would like to thank to an anonymous reviewer and to Aude Gébelin for constructive comments that helped to greatly improve the manuscript.