1 Introduction
Mitochondrial disorders initially considered as being uncommon, now appear as relatively frequent, although often unrecognized because symptoms are extremely variable and usually insidious at the onset. Mitochondrial impairment is observed in many widespread cardiovascular, skeletal muscle, neurological disease states [1] and age-related degenerative diseases, including Parkinson's disease (PD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) [2,3]. The most severe inherited mitochondrial disorders become clinically apparent during infancy, and many of them are lethal. Additionally, mitochondrial syndromes in which symptoms do not appear until early adulthood have also been described and are characterized by striking variability in severity and symptom patterns [4,5].
Given this perplexing complexity and despite the huge advances in the understanding of molecular and biochemical bases underlying organelle dysfunction, our ability to counteract mitochondrial pathologies remains very limited [6]. Accordingly, classical interventions with vitamins or co-factors are only marginally beneficial [7], while organ transplantation is limited to the few cases in which the phenotype is dominated by an isolated organ failure [8]. For these reasons, alternative strategies, such as gene therapy, aimed at correcting disturbed energy metabolism are under development in an array of laboratories worldwide. However, a main limitation to succeed in this challenge and then proceed to its transfer to clinic is the scarcity of reliable animal models required for evaluating safety and efficacy of gene therapy [9–11]. Besides, the availability of animal models is also important considering which tissue could be triggered by gene therapy for ensuring limited body dissemination and avoiding harmful side-effects. In this respect, the eye possesses many features that make it particularly suitable as a target organ for gene therapy; its compartmentalized anatomy enables local vector delivery with low systemic dissemination and is accessible for in vivo assessment by optical imaging and electrophysiological techniques [12]. Up to date, 192 genes and 232 loci have been associated with inherited photoreceptor degenerations (http://www.sph.uth.tmc.edu/RetNet/). The function of their products are diverse, including: phototransduction, RNA splicing factors, intracellular trafficking molecules and cytoskeletal proteins, phagocytosis, intracellular pH regulation, and energy metabolism [13]. Accordingly, mitochondria being central to retinal cell function and survival, there is increasing evidence to support an association between mitochondrial dysfunction and a number of retinal pathologies, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma [14,15], [16,17]. In addition, inherited optic neuropathies are largely due to mitochondrial impairment, either by mutations in the organelle genome or in nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial proteins [18,19]. This review focuses on:
- • mitochondrial genetics and function;
- • how mitochondrial dysfunction can contribute to retinal cell death and vision loss;
- • our latest developments aimed at providing a protocol safe and efficient for Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON), which will eventually be translated to clinical research.
2 Mitochondrial genetics and functions
Mitochondria are cytosolic organelles whose primary function is the use of oxygen to generate the energy required for cellular growth, function, and maintenance. Accordingly, tissues with high energy requirements such as brain, retina, heart, skeletal muscle, liver and endocrine systems are frequently affected in mitochondrial diseases. In mammalian cells, mitochondrial biogenesis and function require ∼1500 proteins [20,21], whose encoding genes are located in either the maternally inherited mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) or the nuclear DNA (nDNA).
2.1 Genetics
The mtDNA is a double-stranded, closed-circular molecule of 16,569 base pairs (bp) in humans [22]. In addition to the 13 polypeptide genes all of which are integral components of the respiratory chain complexes, mtDNA encodes 22 tRNAs, 12S and 16S rRNAs, that are necessary for intramitochondrial protein synthesis [23,24]. To understand mitochondrial inheritance and clinical expression of disease we should realize that mammalian cells contain approximately 103–105 mtDNA copies/cell. Mutations in an individual cell can affect all mtDNA molecules (homoplasmy), or part of them (heteroplasmy). When wild-type mtDNA copies drop below a critical level, mitochondrial function is impaired, since sustaining normal cellular functions is no longer possible. Thus, as functional mitochondria become insufficient for tissue to function, a threshold is crossed, cell death possibly initiated and disease phenotype becomes visible [25]. This “threshold effect” is tissue-specific, thus, tissues which rely heavily on adenosine triphosphate (ATP) like the central nervous system (CNS), the optic nerve, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and photoreceptors (PRs) may have lower thresholds for mutant mtDNA than less metabolically active tissues [26]. A higher level of complexity related to mitochondrial genetics is that mtDNA mutations accumulated throughout human history leading to the classification of human populations into a small number of mitochondrial haplogroups. A mitochondrial haplogroup is defined as a collection of groups characterized by specific Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms [7]. Several studies have shown mitochondrial haplogroups to be associated with differences in the amount of superoxide and other ROS produced by the electron transport chain [27–29]. For example, haplogroup F mtDNAs are associated with low complex I activity [30] and predilection to diabetes [31] and individuals with haplogroup J present lower oxygen consumption than other haplogroup variants [32]. Thus, specific haplogroups may constitute either a risk or a protective factor in the origin of age-related diseases such as PD, AD [28], ischemic cardiomyopathy [33,34] and cancers [35]. Obviously, this bioenergetic perspective should not be underestimated for the presymptomatic diagnoses, reliable prognosis, and effective treatment and prevention for all mtDNA diseases [28].
2.2 Functions
The mitochondria perform a number of essential functions varying according to cell/tissue type, which if impaired could lead to disease:
- • provide the majority of the cellular energy in the form of ATP (oxidative phosphorylation);
- • generate and regulate reactive oxygen species;
- • catabolism of carbohydrates, some amino acids and fatty acids;
- • control apoptosis;
- • iron and calcium homeostasis.
2.2.1 Oxidative phosphorylation
Mitochondria house in their inner membrane oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) enzymes – i.e., a respiratory chain (RC) composed of almost 100 polypeptides. OXPHOS requires the orchestrated action of complexes I–V: the first four complexes oxidize NADH and FADH through a controlled series of oxidation-reduction reactions, the resultant electrochemical gradient or transmembrane potential (ΔΦ) across the inner membrane is used by proton-utilizing ATP synthase or complex V which drives the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Since a few years, data are gathered from different organisms, which show that RC is organized within an array of supercomplexes that function to facilitate efficient electron flow thus minimizing ROS formation. For instance, in bovine heart mitochondria, complex I is mostly extracted in combination with other respiratory chain complexes, in particular as a I + III2 + IV super complex (Fig. 1) [36]. Further, non-OXPHOS complex proteins were identified as part of supercomplexes; their function appears to assist individual complexes to form stable assemblages that prevent electron leakage [37,38]. OXPHOS comprise also additional complexes that supply electrons to coenzyme Q (ubiquinone), including complex II (succinate–ubiquinone oxidoreductase), which also participates in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and the electron-transfer flavoprotein–ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETF–QO) that transfers electrons from electron-transferring flavoprotein in the matrix, to the ubiquinone pool in the inner membrane.

(Color online.) Oxidative phosphorylation enzymes. Reduced equivalents from sugar-derived organic acids, from amino acids, or from fatty acids enter the respirasome thanks to various competing dehydrogenases, including complexes I and II (I, II) and the electron transfer flavoprotein (ETF). Electrons are next transmitted to oxygen through the ubiquinone pool (Q), complex III (III), cytochrome c (c) and complex IV (IV). The electron flow (white head arrows) is associated with proton extrusion from the matrix space to the intermembrane space. The resulting electrochemical gradient is further used by the ATPasome associating ATP synthase (complex V; V), adenylate translocator (Ant), and phosphate carrier (Pic) to produce ATP.
2.2.2 Reactive oxygen species
A small fraction of the electrons transferred to the RC escapes to the divalent transport, which results in monovalent reduction of oxygen and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Under physiological conditions, ROS production is highly regulated by the tight channeling of electrons through the complexes themselves organized as supercomplexes and the action of manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2) or the Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) which converts mitochondrial O2− to H2O2. However, when O2− production is increased, it gradually damages proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, especially mtDNA, which is less protected from radical damage than nDNA. When mitochondrial ROS production exceeds the antioxidant cell protection system, premature organ failure will eventually occur [39,40]. Accordingly, increased mtDNA somatic mutation levels have been documented in ischemic heart disease [41,42], AD brains [43,44], PD brains [45], Huntington disease brains [46], and Down syndrome with dementia brains [47,48].
2.2.3 Intermediate metabolism pathways
The mitochondrial matrix contains the enzymes of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates. TCA enzymes oxidize carbon substrates acetyl CoA, derived from pyruvate, fatty acid and amino acid breakdown to generate CO2 and reduce NAD+ to NADH and FAD2+ to FADH2; thus providing reducing equivalents to the RC. [49]. Mitochondria also harbor all enzymes necessary for fatty acid oxidation. Fatty acids are rapidly converted to acyl-CoAs after translocation across the plasma membrane, for their import into mitochondria. Once inside the mitochondria, acyl-CoAs are degraded into acetyl-CoA units via four enzyme reactions involved in the cyclic process of β-oxidation.
2.2.4 Apoptosis
Mammalian mitochondria mediate apoptosis or type-I programmed cell death; a key event in this process involves mitochondrial inner membrane permeabilization caused by the opening of the permeability transition pore (PTP). The exact composition of the PTP is still unknown; however, it contains the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), the adenine nucleotide translocators (ANTs), and cyclophilin D [50]. The activation of PTP leads to matrix swelling, depolarization of the ΔΦ and opens a channel in the mitochondrial inner membrane inducing the release into the cytosol of cytochrome c (cyt c), procaspase-9, Apoptosis Inducing Factor (AIF), and endonuclease G. Next, activated caspases dismantle the cell while AIF and endonuclease G are translocated to the nucleus for degrading chromatin. Additionally, apoptosis is regulated by the relative abundance of various pro-apoptotic (e.g., Bax and Bak) and anti-apoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family [51].
2.2.5 Iron and calcium homeostasis
Mitochondria are main consumers of iron; indeed the RC relies on iron-containing redox systems in the form of complexes I–III with Fe–S clusters and cytochromes with heme as prosthetic groups. Fe–S clusters are co-factors of numerous proteins with key functions in metabolism, electron transport, and regulation of gene expression. Mitochondrial biosynthesis of Fe–S proteins is accomplished by the iron–sulfur cluster (ISC) assembly machinery, which is derived from the bacterial ancestor of the organelles and is conserved from lower to higher eukaryotes. Fe–S protein maturation in the cytosol and nucleus requires the assistance of both the mitochondrial ISC assembly machinery and a mitochondrial ISC export system, involving mitochondrial ABC transporter ABCB7 and sulphydryl oxidase ERV1 [52].
Calcium handling by mitochondria is involved in energy production, in buffering and shaping cytosolic calcium and also in determining cell fate [53]. Mitochondria are known since the late 1960s to be able of accumulating Ca2+ in an energy-dependent way through Na+-dependent and independent Ca2+ exchangers [54]. The excess of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake triggers an energetic failure through the opening of the PTP, release of cyt c and of other proapototic factors leading to cellular death by apoptosis or necrosis [50].
3 Mitochondrial pathologies and available treatments
The first evidence that mitochondrial impairment yields to human disease was described in 1962 [55]; subsequently, mitochondrial structural and biochemical abnormalities were reported in the muscle of patients suffering from encephalomyopathies [56]. In 1988, mtDNA deletions were found in the muscle of patients with mitochondrial myopathy [57], and a mtDNA mutation was identified as being responsible of LHON [58]. Up to date molecular defects have been observed in both mtDNA-encoded and nDNA-encoded genes of mitochondrial proteins associated with a wide spectrum of clinical problems [59,60]. No accurate estimation of mitochondrial disease prevalence in adults due to mtDNA or nDNA mutations is available, since nothing is known about the epidemiological impact of nDNA mutations on human illness; nevertheless, it has been envisioned that the minimum prevalence of mitochondrial disorders due to mtDNA alterations is superior to 1 in 5000 births [61]. Over 200 pathogenic mtDNA mutations and numerous single large-scale deletions have been identified associated with myopathy and exercise intolerance, encephalomyopathy, gastrointestinal syndromes, dystonia, diabetes, blindness, deafness, cardiomyopathy, AD, PD [3], and cancers [62]. However, less than 20% of patients suffering from mitochondrial diseases harbor mutations in mtDNA, the remainder being caused by nuclear gene defects [63,64]. Approximately, 200 mutations in nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial proteins are responsible for impaired mitochondrial bioenergetics. These include disorders caused by mutations of proteins involved in the TCA cycle, β-oxidation, and the urea cycle. Recently, a new category of mutations in nuclear genes has been studied as involved in neurodegenerative diseases. The genes discovered encoded proteins responsible of the organelle dynamics, such as OPA1 and MSN2 for its fusion and DRP1 for its fission [65–67].
The knowledge collected in the last 25 years from patients suffering from mitochondrial diseases has been of increasing importance for physicians of all medical disciplines. It supports the development of rational treatment strategies for these conditions and also allows preventive therapy through genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis. Symptomatic therapy can be very effective and is used for minimizing disability, preventing complications and can often improve patients’ life conditions. This palliative therapy includes either surgical procedures or pharmacological medicines aimed at removing toxic metabolites [68]. If isolated organ failure dominates the phenotype, transplantation may be envisaged and can lead to a successful rehabilitation. For instance, patients suffering from chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) can be treated surgically for ptosis or pacemaker implantation can be life-saving for patients with Kearns–Sayre syndrome (KSS) presenting cardiac conduction blockade. There is increasing interest in the administration of ROS scavengers, such as antioxidants (vitamin E, alpha lipoic acid), electron donors and acceptors (coenzyme Q10, riboflavin) and alternative energy sources (creatine monohydrate). The safety of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is well-documented, even at doses as high as 2 g daily. CoQ10 is required for efficient electron transfer from complexes I and II to complex III; moreover, it plays a role as a potent ROS scavenger [69]. The benefits were generally obvious in patients with CoQ10 deficiencies [70,71]. Therapy with idebenone (a synthetic form of CoQ10 which penetrates efficiently the blood–brain barrier) has been shown to be safe and helpful in Friedreich's ataxia, resulting in improvement of cardiac function and neurological symptoms [72,73]. LHON patients treated with idebenone did not manifest any benefit for visual function in a trial conducted in Spain [74]; however, another clinical trial (NCT00747487) sponsored by Santhera Pharmaceuticals is completed. Data have been recently published: it appears that patients receiving the compound recovered vision sufficiently to read at least five letters on a standard eye-chart and patients with residual vision were partially protected from further disease progression [75]. The same group published this year a study which shows that the beneficial effect from a six-month treatment was preserved despite therapy halt from about 30 months [76]. The Italian group headed by V. Carelli also assessed idebenone in LHON patients, and it appears that the treatment partially ameliorates the visual outcome of the patients [77]. Results in these studies demonstrated that treatment was well-tolerated; however, data on visual function improvement remains controversial. In these studies, the visual acuity was measured according to the size of letters viewed on a Snellen chart and expressed as the linear LogMAR scale [75,77]; color contrast sensitivity was also assessed [78]. Furthermore, a para-benzoquinone analog, EPI-743, with improved pharmacologic properties and therapeutic efficacy [79,80] has been tested in five LHON patients for a minimum of one year. In this trial, patients enrolled developed the disease a few weeks before treatment initiation. Visual function was assessed by serial measures of visual acuity, visual field, color vision, and OCT metrics. Two patients exhibited improvements in visual field and minor improvements in visual acuity; in one of the patients visual function recovery was complete and occurred in less than four weeks. This finding suggests that EPI-743 could represent an experimental therapeutic agent that could reverse visual loss due to RGC degeneration [81]. Obviously, studies in a larger group of patients and the assessment of electrophysiological parameters such as pattern electroretinography and visual evoked potentials [82,83] are necessary to substantiate these results on visual function.
4 Ophthalmic manifestations in mitochondrial diseases
In humans, patients suffering from mitochondrial diseases manifest prominently ophthalmic troubles. The three most common eye disorders due to mitochondrial dysfunction are optic neuropathy, retinal dystrophy and CPEO [18].
4.1 Optic neuropathy
It has been clearly demonstrated that optic atrophy is a very common pathological feature in mitochondrial disorders [84,85]. LHON and Dominant Optic Atrophy (DOA) are the two most frequent mitochondrial hereditary optic neuropathies limited to a single cellular target, i.e. retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) that originate the optic nerve [19]. Moreover, optic neuropathy is widespread in multi-systemic neurodegenerative disorders such as Friedreich ataxia, deafness–dystonia–optic atrophy known as Mohr–Tranebjaerg syndrome, Charcot–Marie–Tooth type 2A, and infantile encephalopathy [84].
LHON is due to point mutations in mtDNA; in about 95% of LHON's patients mutations are located in ND1 (G3460A), ND4 (G11778A) or ND6 (T14484 C) genes, which encode complex I subunits. The pathology is characterized by the selective death of RGCs and optic nerve atrophy leading to irreversible central vision loss (large centro-cecal absolute scotoma), color vision and contrast sensitivity impairments. The age of onset ranges from 8 to 60; it typically occurs between the ages of 15 and 35. LHON exhibits incomplete penetrance with a male predominance; approximately half of the men and 20% of females harboring one of the three pathogenic mtDNA mutations develop visual loss. This suggests that additional genetic factors or environmental factors modulate the phenotypic expression of LHON [86]. Haplogroups of mtDNA have been envisioned as playing a role for disease outbreak in mutation carriers by their differential involvement in oxidative stress [28]. Haplogroup J1c and J2b are over-represented in LHON pedigrees with the T14484 C and G11778A mutations, suggesting a synergistic role of these haplogroups with either one of the deleterious mutations. Both sub-haplogroups differ by one amino acid in the cytochrome b gene, which may influence the function of complex III or supercomplex biogenesis [87–90]. Another unanticipated example was described last year: the ND1 T3394C (Y30H) variant results in a 15%-28% reduction in complex I activity when arising on haplogroup N, which explains its enhancement of LHON mutation penetrance [30].
The usual clinical presentation of LHON is a painless visual impairment generally acute or subacute, both eyes being involved sequentially with an average time interval between affected eyes between two and four months. As the disease progresses, rapid RGC axonal loss in the papillomacular bundle leads to temporal atrophy of the optic nerve head. Some patients continue in a “chronic” state characterized by a low-grade degenerative process that may consistently worsen the residual vision over the years [91]. Visual recovery may occur in few patients, especially in those with the T14484C mutation; a gradual improvement of central vision 6–12 months after the onset of visual loss is diagnosed by the appearance of small islands of vision (fenestrations) in the central scotoma, which becomes less dense [85,92]. Hence, LHON presents formidable challenges since monocular vision loss and later on the progressive worsening of visual function provides a unique clinical situation in which it becomes possible to design and conduct clinical trials [60,85].
The majority of DOA patients (between 50–60% of the cases) harbor mutations in the nuclear-encoded protein OPA1 which is a dynamin-related GTPase anchored to the inner membrane of mitochondria involved in the overall mitochondrial network organization [86]. OPA1 is also described as playing a role in membrane stabilization, apoptosis, and OXPHOS integrity [65,93,94]. OPA3 and TMEM126A (OPA7), both encoding mitochondrial proteins localize to the inner membrane, were also described as associated with optic atrophy. Two mutations were reported in OPA3; they affect the trans-membrane domain and act in a dominant negative manner [95]. In the case of TMEM126a, the recessive disease is due to a mutation introducing a stop codon in the protein, thus deleting 140 out of the 195 amino acids [96]. The typical presentation of DOA is characterized by a slowly progressive, roughly bilaterally symmetrical visual loss in childhood accompanied with defect in color vision. The disease progression may be quite variable, ranging from mild cases with visual acuity that stabilizes in adolescence, to slowly but constantly progressing cases, to cases with sudden impairment of visual acuity. Despite remarkable clinical evolution differences, the endpoint of the pathological process in DOA is clinically indistinguishable from LHON, since it is also due to selective RGC loss.
4.2 Retinal dystrophy
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is found in an array of mitochondrial disorders [97]. RP is a group of retinal degenerative diseases resulting from photoreceptor death by apoptosis, and a major cause of blindness in adults. RP is due to mutations in various genes expressed in PR, choriocapillaris (layer of capillaries that is immediately adjacent to Bruch's membrane), and the RPE. This latter is susceptible to oxidative damage during the phagocytosis of PR outer segments, presumably through the burst of ROS generated during ingestion and by exposure to blue light. Pigmentary retinopathy (generic name covering all retinal dystrophies featuring PR loss and retinal pigment deposits) is a prominent feature in the mitochondrial syndrome of neurogenic muscle weakness, ataxia, and retinitis pigmentosa (NARP). NARP is due very often to a point mutation at the mtDNA nucleotide 8993, in the ATP6 gene encoding the subunit 6 of complex V [98]. Interestingly, the 8993 mutation reflects the genetic complexity of mtDNA inheritance; indeed the mutation appears often as heteroplasmic. The phenotypic expression varies across a large spectrum: highest severity in cases where the mutation load is above 90%, leading to the maternally inherited Leigh syndrome (MILS); 60 to 70% of mutated mtDNA copies causes a mild to severe NARP phenotype and finally mutation loads below 60% are generally asymptomatic [99]. It has also been described that maternal-inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD), characterized by diabetes mellitus and neurosensory hearing loss, may present retinal dystrophy. MIDD is caused by the mtDNA point mutation A3243G (tRNA leu) [100]. Additionally, patients with mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) are prone to develop retinal degeneration, which often conforms to a classic salt-and-pepper retinopathy pattern [101]; however, in some cases, degeneration may only be confined to the macula (center of the retina with the largest concentration of cones) as in MIDD [102].
4.3 Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia and Kearns–Sayre syndrome
Chronic progressive ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) is a frequent manifestation of mitochondrial myopathies. Ocular phenotype is characterized by painless progressive bilateral ptosis (weakness of the external eye muscles), which precedes ophthalmoplegia or ophthalmoparesis (paralysis or weakness of one or more of the muscles controlling eye movements); all extraocular muscles are symmetrically affected. CPEO syndromes may develop sporadically or be inherited by mtDNA or nDNA mutations. In all the cases, mitochondrial dysfunction is caused by the accumulation of large-scale mtDNA rearrangements, which are often heteroplasmic [103]. Kearns–Sayre syndrome (KSS) does not represent a clinical entity by itself, but rather a more severe CPEO phenotype with a childhood-onset [104]. Consequently, the life expectancy is significantly shortened; often sudden death is due to heart block (cardiac conduction defects) as in CPEO patients [105]. KSS patients develop ophthalmoplegia but also pigmentary retinopathy [104,106]. The disease is also due to large-scale mtDNA deletions, the proportion and distribution among affected tissues of altered genome copies is in general higher in KSS than in CPEO, explaining the onset and severity of the disease.
4.4 Oxidative stress and mitochondrial DNA damage are associated with retinal cell loss
Oxygen metabolism plays an important role in retinal cell integrity; indeed PR have one of the highest rates of oxygen consumption in the body [107]. Moreover, cones contain a large number of mitochondria, reflecting their elevated energy requirements [108,109]. A very tight spatiotemporal regulation of Ca2+ concentrations and mitochondrial ATP production in rod and cone synaptic terminals has been described, confirming the key role of mitochondria in PR physiology [110]. Moreover, an exhaustive study demonstrated that severe RC activity defects and increased ROS generation were common hallmark of four genetic mouse models of PR degeneration. In these models, oxidative stress was evidenced prior PR loss, suggesting that it may have a direct and causal role in this process [111]. In the rd1/rd1 model, rod death is almost complete by postnatal day 21, after which cones die gradually over the following two or three months. Komeina and colleagues treated these mice daily between 18–35 days of age with an antioxidant mixture (α-tocopherol, ascorbic acid, α-lipoic acid and a metalloporphyrin superoxide dismutase). Treated animals showed a reduction in oxidative damage, a two-fold increase in cone density relative to untreated mice and some preservation of their function assessed by photopic electroretinograms [112]. Moreover, the improvement of antioxidant defenses by increasing the levels of the mitochondrial proteins SOD2 and catalase protected cone survival and preserves their function in the rd1/rd1 mice [113]. Rod survival was also attained by antioxidant treatment of the rd10/rd10 mice, which display a later onset of rod cell death (P18) whereas rod loss proceeds more slowly [114]. Thus, antioxidants significantly prevent cone apoptosis in several experimental models of RP, confirming the direct involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction in retinal pathogenesis, but also providing a potential therapeutic approach for an array of RP patients despite the great heterogeneity in pathogenic mutations.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), one of the major causes of blindness worldwide over the age of 65, is envisioned as associated with chronically mitochondrial impairment [115]. AMD, by affecting the macula, provokes central visual function loss. Central vision allows reading, driving, writing, and visage recognition. The loss of these abilities significantly impacts daily function and quality of life. Converging evidences from an array of reports establish a link between mitochondrial damage and AMD physiopathology [116]. Some investigators believe that AMD pathogenesis begins in the RPE, which ensures PR outer segments phagocytosis, nutrient transport, and growth factor supply. The earliest clinical sign of AMD, “drusen”, appears beneath the RPE as yellow lipoproteinaceous deposits. Architectural disruption of mitochondria and the diminution of their number were recently reported in RPE from an AMD patient, using electron microscopy. The progressive deterioration of mitochondrial membranes with aging occurred in association with peroxisome proliferation and accumulation of lipofuscin in the RPE; moreover, these alterations were significantly more severe in AMD compared to normal aging [117]. Proteomic analysis of the retina [118], RPE [119], and the choroids/Bruch's membrane [120] identified altered content of mitochondrial proteins in AMD donor eyes. Remarkably, in the proteomic analysis performed from enriched mitochondria of RPE samples, the amounts of three subunits of the RC complex V (ATPase α, β and γ) were decreased, especially in advanced stages of AMD, which could be detrimental for RPE integrity. Besides, a clear diminution was also demonstrated in the mitochondrial protein Hsp70 that plays an essential role in the organelle import of nuclear-encoded proteins [121]. The same laboratory performed experiments for evaluating mtDNA damage extent in RPE during aging and AMD progression. They confirmed that mtDNA damage was significantly increased in RPE from AMD patients compared to RPE samples isolated from age-matched subjects. Importantly, they also established that mtDNA damage accumulation precedes macular degeneration and visual function loss. These data are consistent with the proposal that mtDNA injury may represent a key factor leading to RPE dysfunction in the AMD disease process [122]. Recent reports described that some mtDNA haplogroups are risk factors for AMD. For instance, the prevalence of two variants defining the mtDNA T2 haplogroup was 2.5-fold higher in people with AMD than in their healthy peers. Both variants existed in the highly conserved ND4 and ND6 genes, known being involved when mutated in LHON [123]. In a report published in 2012, it was demonstrated that mtDNA haplogroups J and T are risk factors, and that mtDNA haplogroup H is a protective factor, for AMD in Caucasian populations [124].
Glaucoma is a neurodegenerative disease of the optic nerve characterized by the accelerated degeneration of RGCs and optic atrophy, as LHON and DOA, and leads to progressive visual field loss and ultimately blindness. The number of people suffering from open angle and angle closure glaucoma has been estimated for 2020 as 79.6 million people, thus placing glaucoma as the second leading cause of blindness in the world [125]. The anterior chamber of the eye, specifically the trabecular meshwork (TM), is crucial in glaucoma pathogenesis because its malfunction causes intraocular pressure (IOP), an increase that represents the most important risk factor for developing glaucoma. Numerous studies, particularly for primary open angle glaucoma (POAG), pointed out that mitochondrial dysfunction is a key player in the pathogenesis process, even it may have a primary role in the initial susceptibility to the development of glaucoma [126]. For instance, it has been reported that TM cells from individuals with POAG when compared with age-matched subjects presented both RC complex I defect, increase amounts of ROS, lower ΔΨm, and decreased ATP production [127,128]. Moreover, the extent of the common mtDNA deletion (Δ4977) was dramatically increased in TM from POAG patients while the ratio between mtDNA and nuclear DNA was diminished relative to control subjects [129]. Complementary studies demonstrated that TM cells from patients with either POAG or pseudo-exfoliation glaucoma (PEFG) presented high levels of mtDNA deletions, oxidative nDNA damage, and mitochondrial loss per cell [130]. Blood samples from patients suffering from primary angle-closure glaucoma (PACG), screened for mtDNA variations, were shown to harbor nucleotide changes in genes encoding complex I and complex V subunits; additionally, some patients carried pathogenic changes in mtDNA [131], [132]. In 2012, it was reported a systemic complex-I-linked ATP synthesis defect in lymphoblasts from POAG patients, which may contribute to RGC susceptibility [16]. Histopathological studies of glaucomatous human donor eyes [133], and experimental studies using different animal models of glaucoma have demonstrated that while optic nerve axons are progressively lost in glaucomatous eyes, RGCs die through apoptosis [134,135]. One of the proposed mechanisms for RGC death is that elevated IOP induces the disruption of axonal transport in RGCs due to changes in mitochondrial motility in cell bodies. These changes may be due to the accumulation of mtDNA alterations, which leads to ATP synthesis reduction and ROS generation. Consistent with the evidence of oxidative stress in glaucomatous eyes [136], growing facts support that mitochondrial dysfunction plays a main role in the neurodegenerative process leading to glaucoma [137].
5 Future directions on gene therapy for ophthalmologic conditions caused by mitochondrial dysfunction
Since 2007 three separate groups near simultaneously initiated open label, dose escalation, subretinal gene transfer studies in a small number of individuals with Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA) due to mutations in RPE65 using adeno-associated virus (AAV) type-2 vectors. RPE65 gene is specifically expressed in RPE cells and encodes a retinoid isomerase enzyme essential for the production of 11-cis-retinal, which forms the visual pigment in rods and cones. After six years, there were no detectable systemic safety concerns, excepted certain ocular adverse events attributable to the surgical procedure; and improved visual function was present in many of the patients, albeit to different degrees [138–143]. In 2009, the data from one of the clinical trials demonstrated that the benefits were sustained at the two-year follow-up and that the visual recovery noted in children confirmed that efficacy was superior when the treatment was applied before retinal degeneration has progressed [144]. In 2011, J. Bennett and colleagues published that the visual cortex in gene therapy-treated retinas was made responsive to visual input, measured by functional MRI (fMRI), even after prolonged (up to 35 years) visual deprivation [145]. Even more impressive, in February 2012, J. Bennett published the results obtained after readministration of AAV2-RPE65 vector to the second eye of three adults with LCA, 1.7 to 3.3 years after they had received their initial subretinal injection. Results (through six months) indicate that readministration is both safe and efficacious. Moreover, the fMRI data provide the demonstration of temporal-spatial changes in retinal and cortical activation related to the treatment [146]. The team initiates the phase 3 of the clinical trial (NCT00999609); it is planned to deliver the vector to 24 subjects, age three or older. The patients will receive the vector in both eyes via subretinal injections (on separate days). S. Jacobson's team did also publish last year data collected from the 15 patients treated with AAV2-CBSB-RPE65 in Florida and Pennsylvania (NCT00481546). In two groups they performed a 2-site vector injection and the protocol was safe in adults and children. For the team, the next step would be vector administration to three different sites of injection: the superior retina, the nasal-superior retina, and the temporal retina [147]. Overall, these clinical trials have demonstrated the feasibility and safety of subretinal vector delivery in adults and younger individuals, with some improvements in visual function. Even though the protocols of the three trials presented important differences (promoter, doses and injected volumes), they have already established the proof-of-principle of gene therapy for inherited retinal disease. Thus, they will pave the way for the development of gene therapy approaches for a broad range of eye disorders [148,149] which represents a strong opportunity for scientists working on the mitochondrial field. In this respect, the optic nerve is a unique ocular tissue because it originates in the eye yet functions in the central nervous system by carrying the electrical impulses it receives from the retina to the brain. The axons of RGCs converge into fiber bundles along the base of the inner retina, forming the optic nerve. AAV-mediated gene therapy for the optic nerve may involve both gene replacement and gene addition approaches, to which LHON and glaucoma are amenable.
LHON offers a unique “laboratory” for gene therapy setting, which could unlock the door for its generalization to a wide range of mitochondrial diseases, for essentially three reasons:
- • vision loss often occurs in a bilateral sequential fashion, the second eye becoming involved after the first with a median delay of 2–4 months; hence, a window of opportunity exists for possible therapeutic intervention after vision loss in the first eye but before second eye involvement [60,85,150];
- • some patients continue a slow process of RGC function deterioration that may consistently worsen the residual vision over the years [84,91,151];
- • LHON has the valuable characteristic that drugs, AAV or other agents may be easily and directly delivered to RGCs, by injection into the vitreous cavity.
Although the techniques required for introducing genes directly into mitochondria have not yet been developed, thus targeted repair or replacement of mutated mitochondrial genes is not presently possible. Nuclear expression of genes normally located in mtDNA called “allotopic expression” is one means of circumventing this barrier [60,150]. To ensure efficient mitochondrial uptake of the nuclear expressed mtDNA gene, the protein should have a cleavable mitochondrial targeting signal (MTS). Allotopic expression has been tried in cells harboring deleterious mtDNA mutations, but several attempts failed to obtain a complete and long-lasting rescue of the mitochondrial defect in vitro [152–155]. We developed an approach for optimizing allotopic expression [156,157] by targeting the mRNAs to the mitochondrial surface, which leads to a tight coupling between both translation and translocation processes [158], required for highly hydrophobic proteins, such as those encoded by mtDNA [159]. We successfully salvaged OXPHOS dysfunction in human fibroblasts bearing mutations in ND1, ND4 or ATP6 genes using optimized allotopic expression. Thus, we have created in these cells a situation often found in patient tissues, where mutated and wild-type mtDNA coexist in various proportions (heteroplasmy) [99]. The fully functional proteins synthesized from our vectors were efficiently imported into the organelle and rescues either complex I or complex V defect; thus, in these cells, the treatment leads to a functional shift below the pathogenic threshold [157,160]. The optimization of our strategy would prepare the development of an effective treatment for mitochondrial disorders due to mtDNA mutations if the proof-of-principle is made in vivo that the approach is harmless and beneficial on mitochondrial function. In 2007, J. Guy and colleagues showed that allotopic expression of the mutant ND4 gene in mouse eyes led to RGC and optic nerve degeneration, which could be considered as mimicking LHON [161]. The same group also reported the safety of AAV-mediated gene delivery of the human ND4 complex I subunit in the mouse visual system [162] and the expression of the ND4 gene carried by a self-complementary AAV in primate eyes ex vivo [163]. However, their approach could encounter the limitation of the inefficient mitochondrial import of the hydrophobic ND4 protein, since their AAV vector lacks a specific 3’UTR which can cooperate with the MTS for ensuring the localization of ND4 mRNA to the mitochondrial surface. We created a rat model for the mitochondrial ND4 mutation which shares similarities with LHON by sorting the human mRNA to the mitochondrial surface [164]. RGCs, which expressed in vivo the human ND4 gene harboring the deleterious G11778A mutation carried a heteroplasmy due to the coexistence of the endogenous wild-type gene and the mutant ND4 gene transcribed from our vector. Animals reproduced morphological and functional LHON characteristics:
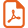
- • RGC loss (Fig. 2A) and nerve fiber degeneration;
- • macrophage infiltration (Fig. 2A), astrocytic and Müller glia hypertrophy (Fig. 2B);
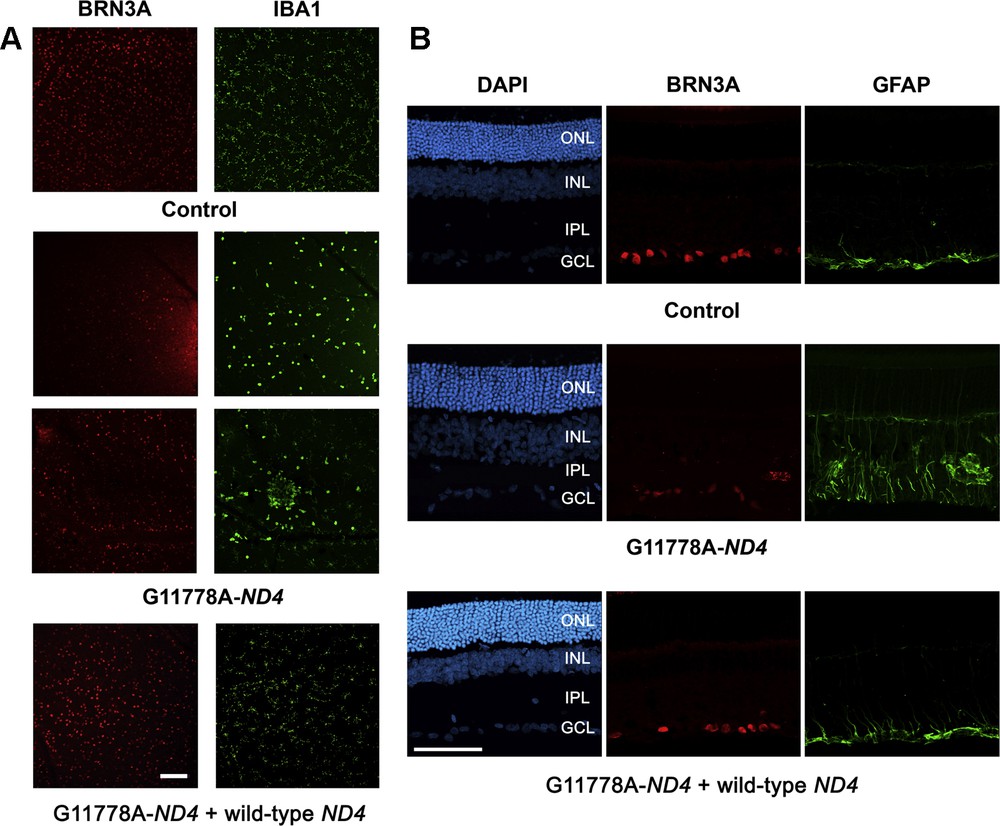
- • respiratory chain complex I defect in the residual optic fibers (Fig. 3A);
- • irreversible decline of visual performance (Fig. 3B).
Prevention of RGC degeneration and gliosis in a reliable experimental model of Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy. Mutant ND4 (G11778A-ND4) DNA was injected into the vitreous body of the left eye of eight-week-old rats, which were then subjected to ELP as previously described [164]. Rats were sacrificed 12 weeks after the unique ELP. To prevent RGC damage induced by mutant ND4, rats were subjected to two ELPs in their left eyes: first with mutant ND4 and two weeks later with wild-type ND4. Animals were sacrificed 3 months after the second intervention. A. IBA1-labeled microglia cells and BRN3A-labeled RGCs in retinal flat mounts. Enucleated eyes were treated with 4% paraformaldehyde; next immunolabeling was performed using either BRN3A (a nuclear transcription factor specifically found in RGCs) or IBA1 (ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 upregulated in activated retinal microglia). Nuclei were revealed by a DAPI staining. Neuroretinas were flattened and mounted on glass slides. Immunostaining with IBA1 (green) and BRN3A (red) in retinal flat mounts from animals subjected to a unique ELP with G11778A-ND4. The number of microglia and activated microglia (round somata) revealed with the IBA1 antibody was higher in G11778A-ND4 treated eyes than in control eyes. We notice a cluster of activated microglial cells near vessels with phagocytosis function and no BRN3A-positive cells within this area. Image for a LHON rat subjected to the treatment (mutant ND4 + wild-type ND4) is also shown. There was no significant difference observed in the immunofluorescence profile or intensity for IBA1 in eyes subjected to two ELPs compared to untreated eyes. Images were obtained using confocal laser scanning microscope (Olympus FV1000). Scale bar represents 100 μm; the two images point up different areas of retinas. B. Immunostaining for GFAP (green) and BRN3A (red) in retinal sections. A strong gliosis reaction was consistently noticed in the G11778A-ND4 group. Immunoreactive cells and processes appeared to span through all retinal layers, including the outer nuclear layer (ONL). Immunostaining of retinas from eyes subjected to two ELPs revealed intensities and distribution of GFAP expression very similar to those observed in control eyes. DAPI (blue signal) stained the nuclei in all retinal cell layers. The control image represents the immunolabeling of a retinal section from an untreated eye of an age-matched control. Scale bar represents 50 μm. GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer. For interpretation of references to color, see the online version of this article.
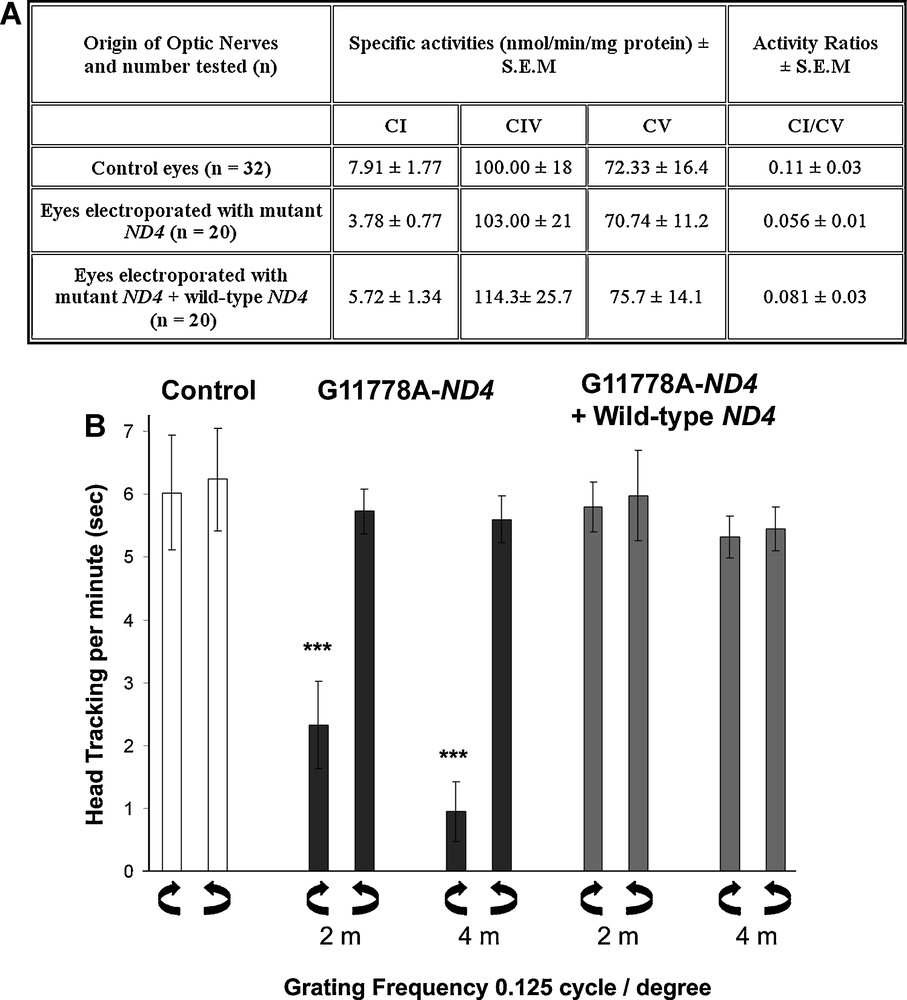
Wild-type ND4 expression protects against respiratory chain defect and visual function impairment induced by mutant ND4. A. Detection of respiratory chain complex I deficiency in optic nerves after ELP with mutant ND4. Animals subjected to one ELP were euthanized 12 weeks after the intervention; while rats subjected to two ELPs were euthanized 14 weeks after the first eye intervention. Optic nerves (ONs) were rapidly collected and kept frozen (–80°C). CI, CIV and CV activities were measured using a Cary 50 spectrophotometer, as described for retinas and ONs from mice [166,167] or from rats [168]. CI activity values were either normalized by CV or converted to specific activities after protein quantification. An approximate 50% decrease of CI activity in ONs from eyes electroporated with mutant ND4 relative to ONs isolated from control eyes was evidenced; CI/CV value in ONs from eyes expressing mutant ND4 was considerably low compared to ratios of ONs isolated from untreated eyes. The differences between the two groups were significant according to Student's t-test (p < 0.0001). When enzymatic activity of RC complexes was measured in ONs from 20 rats subjected to two ELPs, a significant protection against CI defect was observed; however, there was not a full prevention of CI defect since these values remained statistically different from the ones assessed in ONs isolated from control eyes (p = 0.0002 for CI activities and 0.024 for CI/CV). Specific activities for CIV and CV did not change in any of the ONs assessed. Abbreviations: CI–CV, various complexes of the respiratory chain; CI/CV, activity ratio of complex I for complex V; SEM, standard error of the mean. B. Assessment of visual function via optomotor tests. Optomotor tracking was evaluated with the optomotor test in control animals or animals subjected to in vivo ELP. Three groups of eight animals each were evaluated: control rats (24 weeks of age); rats subjected to intravitreal injection with G11778A-ND4 and ELP; rats subjected to a first ELP after intravitreal injection of mutant ND4 and two weeks later its wild-type counterpart was injected in the same eye and ELP was performed. The evaluations had begun two and four months after transgene administration. Tracking scores were measured three times with a four-day interval between each assessment. Values presented are the means of these assessments. The three grating frequencies of 0.125, 0.25 and 0.5 cycles per degree were tested in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions of motion. No significant difference was measured in the three grating frequencies monitored in any of the animals examined. Therefore, data for the most discriminating spatial frequency 0.125 cycles per degree, in terms of visual acuity [164,169,170] is shown in both directions of motion. Very poor clockwise scores were recorded for rats treated with mutant ND4 in the clockwise direction motion, indicating an unequivocal decline in visual performance. Head tracking per min (s) ± SEM for untreated eyes and for eyes expressing mutant ND4 are highly significantly different both at two and four months after transgene administration. Besides, animals subjected to two ELPs gave optomotor responses very similar in both clockwise and counterclockwise drum rotations, indicating that wild-type ND4 protected against visual impairment caused by mutant ND4 expression.
Last but not least, our attempt to protect against mutant ND4 deleterious effects by administrating wild-type ND4 was successful, demonstrating the effectiveness of our therapy (Figs. 2 and 3). Since the competition between wild-type ND4 and its mutant counterpart protect RGC and optic nerve function durably and safely, we can expect that the same could happen in LHON patients harboring the G11778A mutation in the ND4 gene; which represent 70% of the cases [164]. Moreover, recently, we collected data proving that an AAV2 vector carrying our “therapeutic ND4 gene” meets the criteria of robust, long-duration gene expression, and safety in both our LHON rat model (Cwerman-Thibault et al., submitted 2014) and in non-human primate retinas. Therefore, we are planning to launch a phase I/II clinical trial which intends to evaluate safety but which can also begin to address the potential for benefit in terms of visual function. At last, we look forward to be successful in the generation of a treatment aimed at improving life conditions of patients suffering from LHON due to the ND4 mutation and then initiate clinical studies on the LHON-ND1 mutation or on other devastating neurodegenerative disorders with mitochondrial etiology such as Charcot–Marie tooth syndrome [165].
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Drs. Pierre Rustin and Christophe Lechauve for useful discussions and comments on the manuscript. We thank the Cellular Imaging Facility of the Vision Institute which permitted the confocal laser scanning microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. This work was supported by funds from the INSERM and the CNRS (UMR_S 968), Association Française contre les Myopathies (AFM), Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR)/Maladies Rares and Emergence-Bio.