Abreviations
As(V)
arsenate
As(III)arsenite
HMmaleic hydrazide acid
SODsuperoxide dismutase
G-PODguaiacol peroxidase
APXascorbate peroxidase
CATcatalase
MImitotic index
MNmicronucleus
NBTnitro blue tetrazolium
DETAPACdiethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid
FBfresh biomass
PCprotein contents
ROSreactive oxygen species
1 Introduction
With the development of modern industry and agriculture, problems due to arsenic pollution are attracting increasing attention. Inorganic arsenic species (As(V) and As(III)) have long been used in the formulation of pesticides and herbicides [1]. The toxic effects of arsenic disrupt crop growth and development [2–4]. This effect varies with the form and concentration of arsenic in the soil, with the tolerance of the genotype species to the toxic element and with the environmental conditions governing growth [3,5–7]. Some authors have reported that metalloids and heavy metals (As, Cd, Pb) pollution induce free radicals that lead to the readjustment of transport and of metabolic processes, inhibit growth [8,9] and may damage major cell macromolecules (proteins, lipids and DNA) [10–12]. However, plants do possess several anti-oxidative defence systems to scavenge toxic free radicals to protect themselves from oxidative stress, including that caused by heavy metals and metalloids [13]. These systems include:
- (I) reduced uptake and accumulation of metals by binding the metal to extracellular exudates and cell wall constituents;
- (II) compartmentation of metals in the vacuole;
- (III) complexation of heavy metals and metalloids by different substances;
- (IV) activation or modification of plant metabolism;
- (V) production of antioxidant enzymes.
Anti-oxidative defence falls into two main categories:
- (I) low molecular mass antioxidants, consisting of lipid soluble membrane-associated antioxidants (e.g. α-tocopherol and β-carotene) and water soluble reductants (e.g. glutathione–GSH and ascorbate);
- (II) enzymatic antioxidants (e.g. SOD, CAT, G-POD, APX [14–18]).
Induction of oxiradicals by arsenic may be linked to the mechanisms involved in genotoxicity. Plant bioassays, which are considerably less expensive than animal assays, have been proposed to monitor pollution. Some plant bioassays, i.e. Tradescantia palludosa [19–21], Allium cepa [22–24] and Vicia faba [25], have been used for over 60 years to study the mutagenic effects of ionizing radiation and chemical mutagens, but also more recently to evaluate the mutagenicity/clastogenicity of environmental pollutants. In recent years, a correlation between arsenic exposure, cytotoxicity and genotoxicity, mutagenicity [3], and tumour promotion has been established [26]. The causes of the toxic effects of excessive arsenic have been the subject of many studies [7,9,27]. Trivalent forms of arsenic are more toxic than pentavalent forms [28]. Two arsenic species have been shown to induce apoptosis in several cellular systems [29] and are capable of triggering apoptosis [30]. In addition, arsenic causes induction of chromosome/chromatid breaks or exchanges (clastogenicity) [8], formation of apurinic/apyrimidinic sites [10], DNA and oxidative base damage [12], DNA-protein cross-links [31], chromosomal aberrations and interaction with spindle function during mitosis or meiosis inducing chromosome segregational errors (non-disjunction and non-congression), leading to aneuploidy and/or polyploidy (aneugenicity) [32]. The study of the potential biochemical and genotoxic effects of arsenic on plants (i.e. the first stage in the food chain for humans) must guarantee plant quality. Zea mays, a member of the Poaceae family, is one of three most important crop plants in the world. Maize is one of the plant species used for evaluating the potential genotoxicity of environmental chemicals [33,34]. Since many plants are known to be injured by arsenic contamination [1,35], some plant systems have been suggested as indicators of arsenic exposure [10,36]. In this study, to evaluate biochemical and genotoxic responses to different types of As pollution, Z. mays was grown hydroponically for eight days with different As treatments: arsenate As(V) and arsenite As(III) at 134 and 668 μM, at pH 4, 7 and 9. The effects of As on the growth and activity of the enzymatic antioxidant system (SOD, APX, G-POD, CAT) in the leaves and roots were studied. To understand the toxic effects of arsenic on plant cells in more detail, mitotic activity was investigated in Z. mays and V. faba roots by monitoring the MI. In addition, MN assays were performed on root tips of Z. mays and V. faba. The results obtained should lead to a better understanding of the adaptation mechanisms of this agronomic species to As and of the mechanism of cytological damage.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant material, growth conditions and treatment procedures
Z. mays seeds were obtained from Limagrain in Auvergne, France. The seeds were rinsed with distilled water and transplanted in 1.2-litre plastic (PVC) pots for 1 month. The plants were maintained in a Hoagland medium [37] comprising KNO3: 101.1 mg L−1; KH2PO4: 236.5 mg L−1; CaNO3, 4H2O: 54.44 mg L−1; MgSO4, 7H2O: 73.94 mg L−1; MnSO4, H2O: 1.5 mg L−1; ZnSO4, 7H2O: 0.5 mg L−1; CuSO4, 4H2O: 0.25 mg L−1; H3BO3, 4H2O: 1.5 mg L−1; Na2MoO4, 2H2O: 0.025 mg L−1 and 100 μL L−1 Fe-masqualate. Before the medium was autoclaved, its pH was adjusted to respectively 4, 7 and 9 [33]. The solutions were placed in a controlled environment room at 25 ± 1 °C with a photoperiod of 16 h/8 h light/dark. For the experiments, 10 plants, replicated three times, were taken from the stock cultures and exposed to different concentrations of arsenate and arsenite (134 and 668 μM) at three different pH for eight days, according to the procedure described in Tu et al. [34]. Briefly, arsenate (As2O5, 99% purity, Sigma, France) and arsenite (AsO3, 99.99% purity, Sigma, France) were dissolved in growth medium (1 l of Hoagland medium) and the pH was adjusted with NaOH (10 M) or KCl (1 M).
2.2 Biomass determination
After arsenate and arsenite treatments, plants were washed three times with distilled water and the fresh biomass of leaves and roots was determined.
2.3 Enzyme extraction and protein determination
To obtain the enzyme extract, 300 mg of fresh leaves or roots were homogenized in 2 mL of cold potassium phosphate – PVP (4%) buffer (50 mM, pH 7.8). The homogenate was centrifuged for 15 min at 15,000 × g at 4 °C and the supernatant was stored at −20 °C for later determination of enzyme activities. Protein content was determined according to Bradford (1976) using bovine albumin for calibration.
2.4 Enzyme assays
In the supernatant, SOD (EC 1.15.1.1) was measured using the photochemical method described by Deschamps and Fridovich [38] and by Oberley and Spitz [39] with some modifications. In the presence of SOD, the photochemical reduction of NBT is inhibited and the level of inhibition is used to quantify the enzyme activity. SOD was determined using the xanthine oxidase-cytochrome c (1.1 mM) method. NBT solution consisted of 2.4 mL phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.8), 39 mL DETAPAC (1.33 mM), 1.5 mL NBT (2.24 mM) and 5.1 mL xanthine (1.8 mM). The reaction mixture (3 mL) consisted of 600 μL phosphate buffer (50 M, pH 7.8), 2.4 mL NBT solution, 0.1 mL diluted xanthine oxidase 1 M (0.05 unit/mL, Sigma Aldrich supplier) and appropriately diluted enzyme extract (5–10 μL). One unit of SOD activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required to achieve a 50% inhibition of the rate of NBT reduction measured at 560 nm. Enzyme activity (katal kg−1) is proportional to (V/v − 1)/mg protein, where V equals the change in absorbance (560 nm) per minute in the absence of SOD and v equals the change in absorbance per minute in the presence of SOD. To measure the activity of G-POD (EC 1.11.1.7), the reaction mixture, consisted of 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.8), 100 mM H2O2, 1% guaiacol and enzyme extract (10 μg protein). Enzyme activity was measured by monitoring the increase in absorbance at 470 nm (extinction coefficient of 26.6 mM−1 cm−1) during polymerisation of guaiacol into tetraguaiacol according to Chance and Machly [40]. APX activity (EC 1.11.1.11) was measured by the decrease in absorbance of substrate at 290 nm [41]. The reaction mixture contained potassium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.8), Na-ascorbate (0.5 mM) and enzymatic extract (10 μg of protein). The reaction was started by adding 150 μL hydrogen peroxide (100 mM) and the decrease in absorbance was recorded for 1 min at 25 °C. Correction was made for the low, non-enzymatic oxidation of ascorbate by hydrogen peroxide. CAT (EC 1.11.1.6) activity was measured by spectrophotometry by measuring the consumption of H2O2 at 240 nm, according to Aebi [42], in potassium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7.8) containing 100 mM H2O2 and enzyme extract (10 μg of protein) in a final volume of 1.5 mL. The reaction was started by adding H2O2.
2.5 Genotoxic assays
Seeds of V. faba and Z. mays L. Banguy (Limagrain) were used in the present investigation. The As used for the experiment was made from arsenate (As2O5, 7H2O) or arsenite (As2O3) at concentrations of 134, 334, 534 and 668 μM. Arsenic concentrations were based on those found in polluted sites in Auvergne [43] and those reported in studies by Tu and Ma [44] and Tu et al. [34] on Pteris vittata species. To reproduce the toxic effect of arsenic binding due to environmental factors (pH, oxido-reduction potential, etc.), three pH were used: pH 4, pH 7 and pH 9, according to Scott [33]. HM (4×10−3 M) was used as positive control. At this concentration, HM is known to inhibit the root mitotic process in the model plant as well as its clastogenic effects [35]. The hydroponic solutions were prepared according to Hoagland and Arnon [37] in water and adjusted to the different pH with HCl (10 M) or NaOH (1 M). This solution was used for the control experiment. The seeds were left to soak in distilled chlorinated water overnight. The integuments were then removed to allow quicker germination. The seeds were allowed to germinate and produce roots in Petri dishes at a temperature of 25 °C. The seeds were protected from direct sunlight. Three days later, 10 primary roots from each species were long enough (2–3 cm) to be treated with different As concentrations for 42 h. Treatments were reproduced three times. Twenty root tips in each treatment group were cut and fixed in Carnoy solution (ethanol/acetic acid 3:1) for 12 h and transferred into 70% ethanol for storage. Colour disruption, root thickness and root length were evaluated in each treatment. Roots were hydrolyzed in 1 M HCl for 7–8 min (V. faba) or 15–16 min (Z. mays), at 60 °C. To measure the mitotic index and micronucleus aberrations, 10 root tips were squashed in aceto-orceine acid solution (2%) [25]. Three replicates were performed for each treatment and three roots of each replicate were used for scoring. A minimum of 1000 mitotic cells were counted on each slide [36].
2.6 Statistics
In all the experiments, three replicates were performed for each concentration of arsenate and arsenite. All experiments were repeated at least three times. Data presented here are the means ± S.D. of at least three independent experiments. The significance of differences between samples was determined by Student's t-test and P-values ≤ 0.05 were considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 Fresh biomass
After eight days treatment with 134 μM As, the FB of Z. mays leaves was identical to that in the control medium (without As) except with As(III) at pH 9, when it decreased significantly (−52.1%) (Table 1). As(III) treatment led to reduced growth of roots (−42.8%) at pH 9, while both As(V) or As(III) at pH 7 led to a significant increase (+38.9% and +41.8%) in FB. In all other conditions, growth was maintained. With higher As concentrations (668 μM As(V) and As (III)), leaves FB decreased significantly at pH 4 (−55.8% and −57.5%) and at pH 9 with As(V) (−53.4%). Roots FB decreased at pH 9 (−39.5%) but increased significantly at pH 7 (+45.1%). With higher concentrations of As(V) at all three pH, the FB of maize roots was maintained.
Fresh biomass (g) of leaves and roots of Zea mays treated with low (134 μM) and high (668 μM) concentrations of arsenate and arsenite at three different pH for 8 days.
| Species | Parts | Concentrations (μM) | Arsenate | Arsenite | ||||
| pH4 | pH7 | pH9 | pH4 | pH7 | pH9 | |||
| Zea mays | Leaves | 0 | 1.29 ± 0.6a | 0.46 ± 0.12 | 1.46 ± 0.34a | 1.29 ± 0.6a | 0.46 ± 0.12 | 1.46 ± 0.34a |
| 134 | 1.18 ± 0.39a | 0.52 ± 0.23 | 1.48 ± 0.51a | 1.16 ± 0.34a | 0.64 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.09b | ||
| 668 | 0.57 ± 0.16b | 0.47 ± 0.17 | 0.68 ± 0.37b | 0.62 ± 0.16b | 0.56 ± 0.26 | 1.47 ± 0.48a | ||
| Roots | 0 | 1.19 ± 0.66 | 0.96 ± 0.34b | 1.52 ± 0.35 | 1.19 ± 0.66 | 0.96 ± 0.34b | 1.52 ± 0.35a | |
| 134 | 1.52 ± 0.28 | 1.57 ± 0.13a | 1.12 ± 0.38 | 1.01 ± 0.26 | 1.65 ± 0.26a | 0.87 ± 0.28b | ||
| 668 | 0.84 ± 0.45 | 1.34 ± 0.25b | 1.09 ± 0.46 | 1.47 ± 0.48 | 1.75 ± 0.08a | 0.92 ± 0.2b |
3.2 Protein contents
After eight days of treatment with 134 μM As, the PC of Z. mays remained unaffected in the leaves except with As(V) at pH 4 when PC increased significantly (+43.1%) (Table 2). In the roots, PC was not affected except at pH 9 with As(III) when PC increased significantly (+56.3%). With higher concentrations of As(V), PC in the leaves increased at pH 4 (+43.1%), while at pH 7 and 9, leaf growth was the same as that in the control medium. Inversely, treatments with higher concentrations of As(III) led to reduced PC in the leaves (−30.5% at pH 4; −58.3% at pH 7; −65.5% at pH 9). PC in the roots decreased significantly at pH 4 with As(III) (−94.94%) whereas the other As conditions did not alter PC.
Total protein content (mg/g fresh weight) of leaves and roots of Zea mays treated with low (134 μM) and high (668 μM) concentrations of arsenate and arsenite at three different pH for eight days.
| Species | Parts | Concentrations (μM) | Arsenate | Arsenite | ||||
| pH4 | pH7 | pH9 | pH4 | pH7 | pH9 | |||
| Zea mays | Leaves | 0 | 40.59 ± 6.86b | 73.94 ± 29 | 61.31 ± 9 | 40.59 ± 6.86a | 73.94 ± 29a | 61.31 ± 9a |
| 134 | 71.4 ± 19.6a | 43 ± 24 | 58.32 ± 19.3 | 27.12 ± 14 | 40.08 ± 13a | 78.31 ± 23a | ||
| 668 | 71.34 ± 7.19a | 69.6 ± 34 | 101.33 ± 81 | 28.21 ± 9b | 30.81 ± 16b | 21.17 ± 7.6b | ||
| Roots | 0 | 13.63 ± 9.8 | 21.43 ± 13.9 | 16.12 ± 1.1 | 13.63 ± 9.8a | 21.43 ± 13.9 | 16.12 ± 1.1b | |
| 134 | 13.86 ± 2 | 12.13 ± 2.9 | 14.86 ± 4 | 9.4 ± 2a | 11.31 ± 2.5 | 37 ± 12.5a | ||
| 668 | 9.94 ± 4.3 | 10.33 ± 1.3 | 14.5 ± 9 | 0.69 ± 0.57b | 9.11 ± 4.4 | 15.38 ± 4.1b |
3.3 Antioxidant enzymatic system
3.3.1 Superoxide dismutase activity
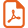
The lowest concentrations of As(V) at pH 4 and pH 9 led to a significant decrease in SOD activity in Z. mays leaves (Fig. 1). The other As conditions resulted in the same activity as in the control medium. With higher As concentrations, SOD activity in the leaves was reduced at all three pH. In the roots, As treatments (134 μM and 668 μM) at pH 7 and pH 9 decreased SOD activity, while treatment at pH 4 maintained the level of activity.
Activities of SOD in the leaves and roots of Zea mays treated with low (134 μM) and high (668 μM) concentrations of arsenate and arsenite at three pH for 8 days. All values are means of three independent experiments (three replications each), n = 9. Vertical bars indicate ±S.E. Means followed by the same letter to that of the control were not significantly different at P ≤ 0.05. Means followed by different letter to that of the control denote significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
3.3.2 Guaiacol peroxidase activity
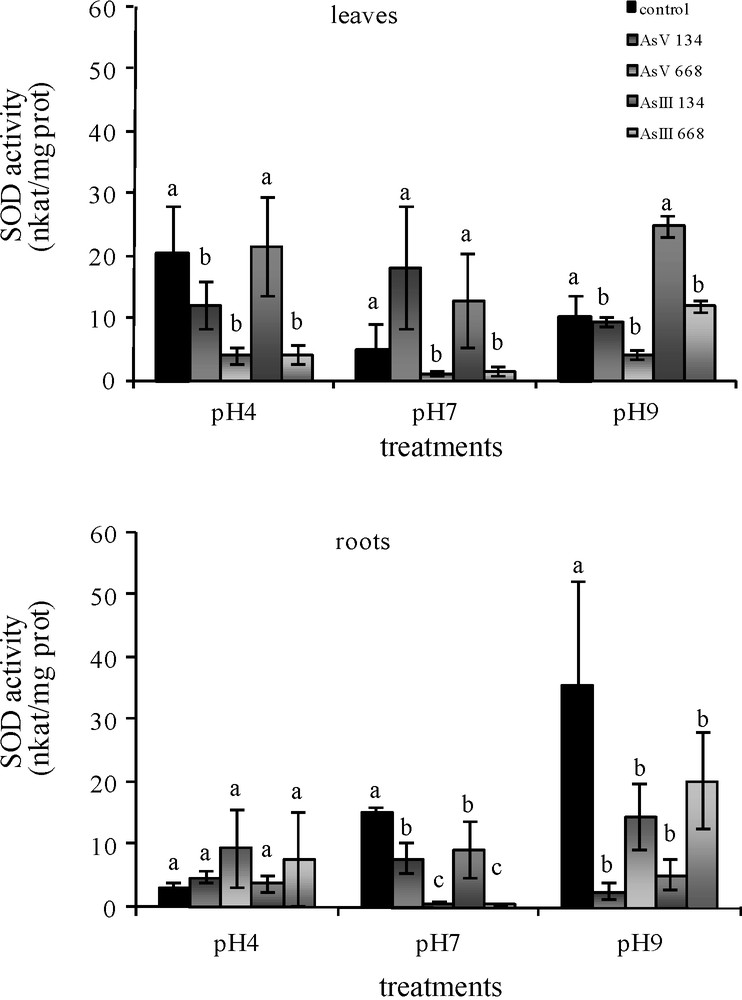
With 134 μM As(V), G-POD activity in the leaves of Z. mays was maintained at all three pH (Fig. 2). With As(III), a pH of 9 caused a decrease in activity (−96.7%). In the roots, G-POD activity was stimulated by As(V) (+49% at pH 4; +65.8% at pH 7; +49.1% at pH 9). With As(III), G-POD activity was maintained at pH 4 and pH 7, while pH 9 caused a significant decrease in activity (−51.2%). With higher concentrations of both forms of As, pH 4 stimulated G-POD activity in the leaves (+36.9% for As(V); +18.2% for As(III)) and pH 9 for As(III). In all conditions, both forms of As resulted in the same G-POD activity in the leaves as in the control medium without As. With higher concentrations of As(V), G-POD activity in the roots decreased (but not significantly) and with As(III) treatments, a significant increase was observed at pH 4 and a decrease at pH 9.
Activities of G-POD in the leaves and roots of Zea mays treated with low (134 μM) and high (668 μM) concentrations of arsenate and arsenite at three pH for eight days. All values are means of three independent experiments (three replications each), n = 9. Vertical bars indicate ±S.E. Means followed by the same letter to that of the control were not significantly different at P ≤ 0.05. Means followed by different letter to that of the control denote significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
3.3.3 Ascorbate peroxidase activity
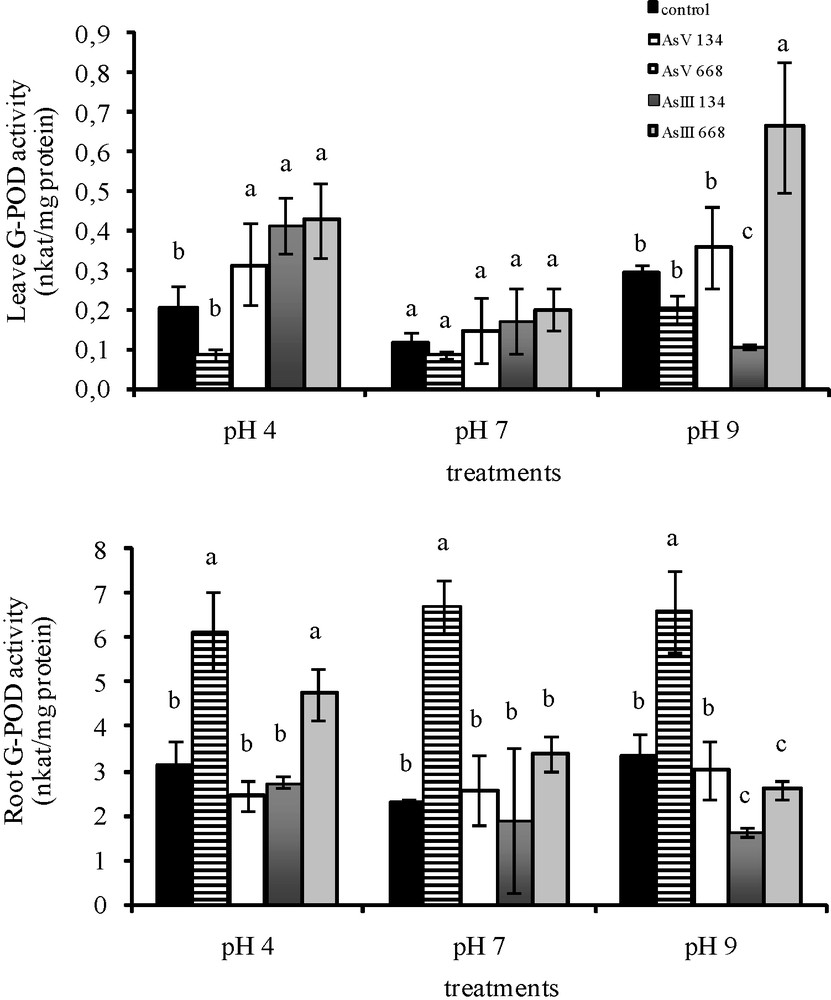
With 134 μM As(V), there was a significant decrease in APX activity in Z. mays leaves at pH 4 (−53.6%), while at the two other pH, the APX activity was not affected (Fig. 3). Treatments with 134 μM As(III) resulted in the same APX activity in the leaves at pH 4 and pH 7 as in the control medium without As, while pH 9 caused a significant decrease (−46.3%) in APX activity. The majority of higher concentrations of As stimulated leaf APX activity, except As(V) treatment at pH 4 and pH 9, which led to a decrease in activity (−43.4% at pH 4; −47.1% at pH 9).
Activities of APX in the leaves and roots of Zea mays treated with low (134 μM) and high (668 μM) concentrations of arsenate and arsenite at three pH for eight days. All values are means of three independent experiments (three replications each), n = 9. Vertical bars indicate ±S.E. Means followed by the same letter to that of the control were not significantly different at P ≤ 0.05. Means followed by different letter to that of the control denote significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
In the roots of Z. mays, APX activity was not affected by low As(V) treatments at pH 4 and by As(III) treatments at pH 7, but decreased by As(III) treatments at pH 4 and by both forms of As at pH 9. The majority of higher As concentrations stimulated APX activity in the roots, except for As(III) treatment at pH 9 (−57.7%), which caused a decrease in activity.
3.3.4 Catalase activity
CAT activity in the leaves of Z. mays varied with the pH as well as with the form and concentration of As (Fig. 4). Thus, CAT activity in the leaves was not affected by low As concentrations, except by As(V) at pH 4 when leaf CAT activity decreased (−47%) and by As(III) at pH 4 and pH 7 when CAT activity increased (+57.9%; +12.2%). Higher concentrations of As(V) at pH 7 and of As(III) significantly increased CAT activity in the leaves (+43.4% with As(V) at pH 7, +78.1% at pH 4, +71.5% at pH 7 and +71.3% at pH 9 with As(III)). In the other conditions, CAT activity in the leaves was the same as that in the control medium. In the roots, As(V) treatments led to the same CAT activity as that in the control medium whatever the concentration. A significant reduction in CAT activity was observed in the roots with 134 μM As(III) (−57% at pH 4, −83.2% at pH 7, −55.7% at pH 9), while higher concentrations of As(III) stimulated CAT activity in the roots (+70.75% at pH 4, +61% at pH 7, +58.1% at pH 9).
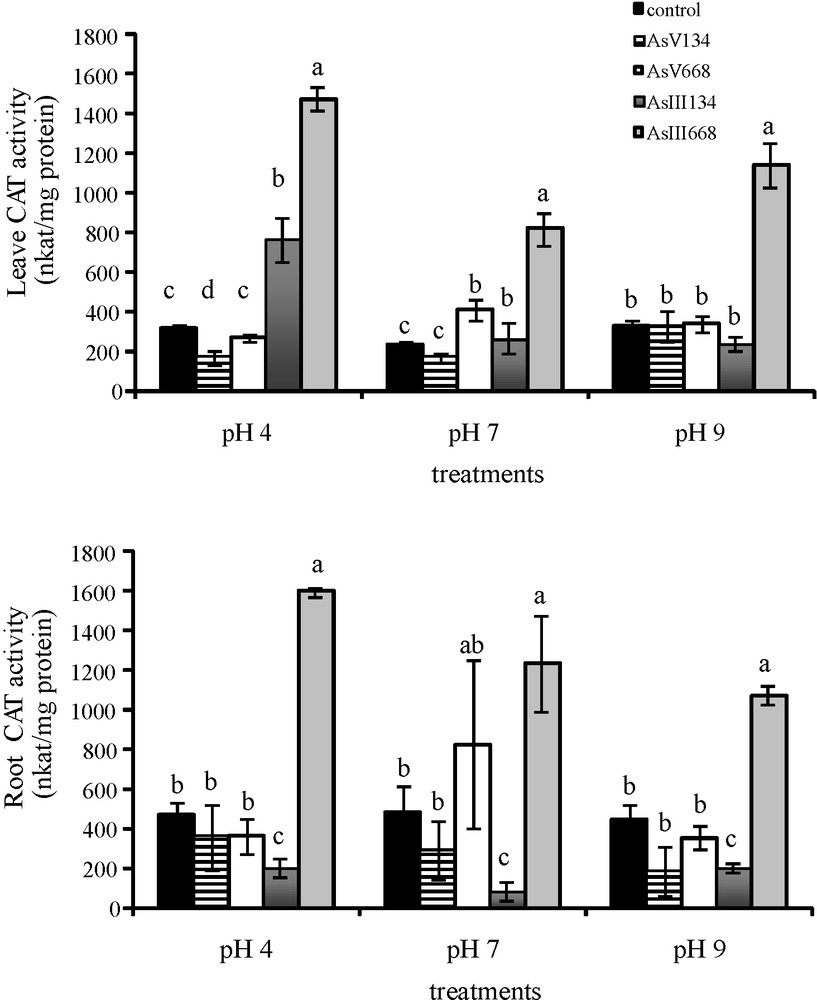
Activities of CAT in the leaves and roots of Zea mays treated with low (134 μM) and high (668 μM) concentrations of arsenate and arsenite at three pH values for eight days. All values are means of three independent experiments (three replications each), n = 9. Vertical bars indicate ±S.E. Means followed by the same letter to that of the control were not significantly different at P ≤ 0.05. Means followed by different letter to that of the control denote significant differences at P ≤ 0.05.
3.4 Root growth
The effects of arsenic on the root morphology of V. faba and Z. mays varied with the concentration of As(V) and As(III), at pH 4, pH 7 and pH 9 (Fig. 5). With As(V) at all three pH, V. faba roots were slightly yellow, became brown at 334 μM and twisted with an increase in the concentration. With the highest concentrations, especially at pH 9, the root tips of V. faba turned black. With As(III), black colour was observed at 534 μM, especially at pH 4 and pH 9. In Z. mays, no significant disruption of root growth was observed. Root thickness increased significantly with an increase in arsenic concentrations and V. faba roots were always thicker than Z. mays roots. In addition, whatever the pH, As(V) treatments resulted in significantly thicker roots than As(III) in both species. The length of V. faba roots was significantly reduced (Fig. 6), by respectively −37%, −44% and −34% with As(V) and −47%, −35% and −20.5% with As(III) at pH 4, pH 7 and pH 9, whatever the arsenic concentration. Conversely, there was no significant decrease in the length of Z. mays roots with an increase in arsenic concentration.
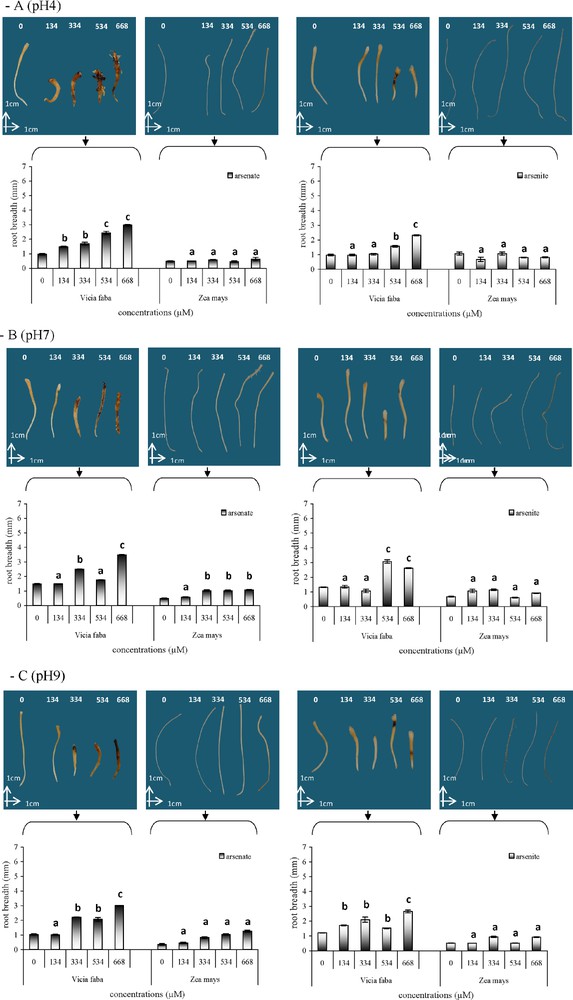
Mean root width at the level of the crown in Vicia faba and Zea mays after As(V) or As(III) treatments at pH 4 (A), pH 7 (B) and pH 9 (C). Vertical bars denote S.E. (n = 10). a: no significant effect compared to the control; b: significant increase compared to the control (P < 0.05); c: higher significant increase compared to the control (P < 0.005).
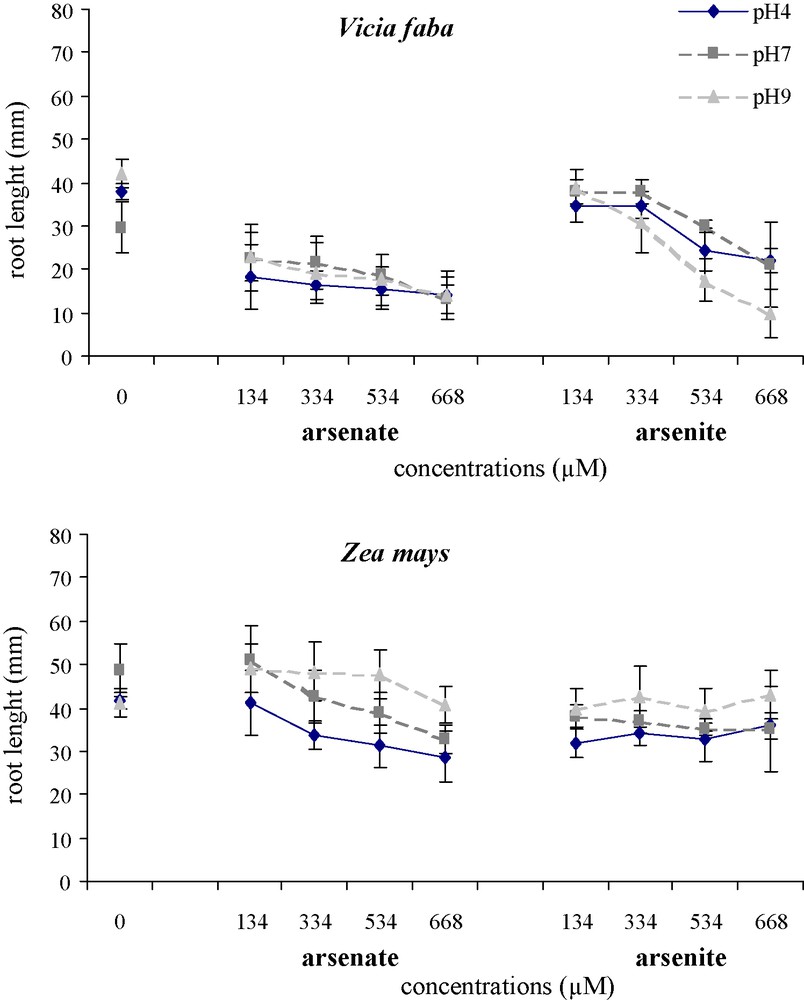
Effects of different As(V) and As(III) concentrations on mean root length of Vicia faba and Zea mays at three pH.
Vertical bars denote S.E. (n = 10).
3.5 Root cell division
3.5.1 Root mitotic index
The mitotic index reflects the frequency of cell division and is considered to be an important root growth parameter. Arsenic treatment revealed a reduction of the mitotic index in V. faba and Z. mays roots (Fig. 7) compared to the control, whatever the pH of the medium (MI control: 23, MI HM treatment: 7). In both species, an increase in As(V) and As(III) concentrations in the nutrient solutions led to a decrease in the MI compared to the control. No significant difference was observed between the different pH of the solution (except at pH 9 with 534 and 668 μM arsenate in V. faba). At all three pH, the MI of V. faba decreased by respectively −44%, −36% and −34% after exposure to As(V), and by −78%, −74% and −76% after exposure to As(III). In Z. mays there was also significant reduction of MI of −18%, −25% and −35% with As(V) and −56%, −54% and −51% with AsIII. Whatever the pH and the species, As(III) led to greater MI reduction than As(V). V. faba was more sensitive to As than Z. mays. As(V) had little effect on the MI of Z. mays.
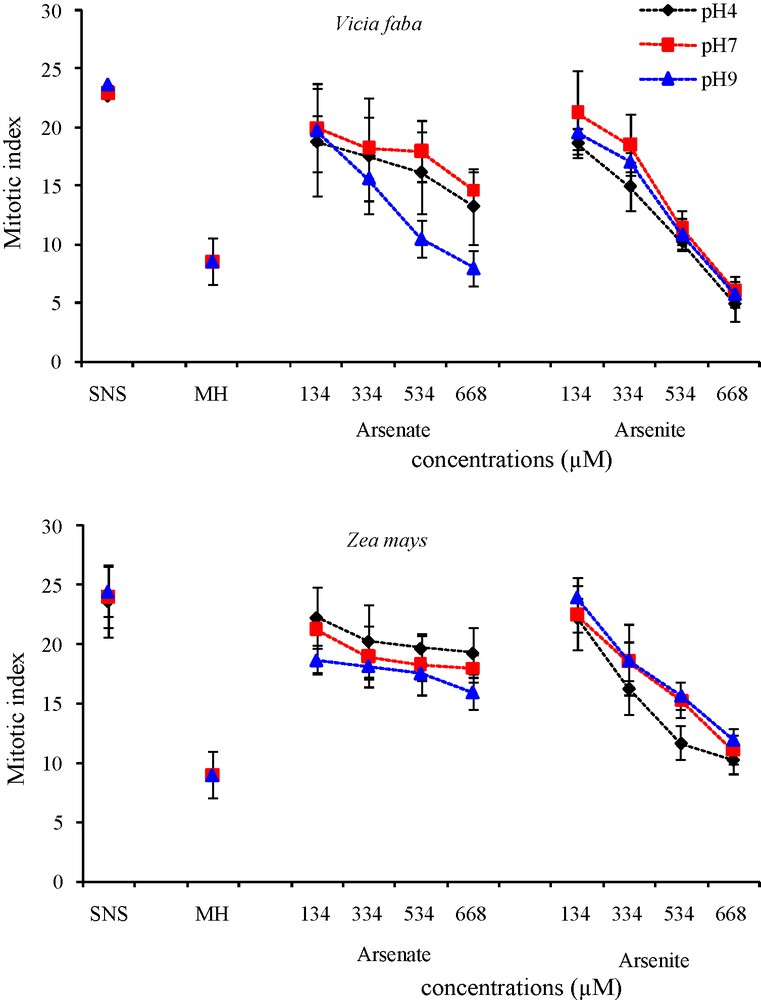
Effects of different arsenate and arsenite concentrations and positive control HM on cell division in root tips of Vicia faba and Zea mays at three pH.
Vertical bars denote S.E. (n = 10).
3.5.2 Root micronuclei
Standard aberrant chromosome behaviour was studied in the root tip cells of V. faba and Z. mays with arsenate and arsenite treatments (Table 3A and B). Arsenic generated significant MN abnormalities in both V. faba and Z. mays root meristems, but these were more pronounced in V. faba (MN 18) than in Z. mays (MN 11) whatever the pH of the medium. However, the MN of the Z. mays control was higher than that of V. faba. In V. faba, MN abnormalities were greater than in the negative control but less than with As treatment whatever the form or concentration of As and whatever the pH. Nevertheless, with the highest concentrations of As(III), a significant MN abnormality was observed, as soon as at 334 μM at pH 4 and pH 7, and at 668 μM at pH 9. In Z. mays roots treated with arsenate, no significant MN abnormality was observed at pH 4 and pH 7 compared to both negative and positive controls. However, at pH 9, the highest concentrations of As(V) induced significant MN abnormalities at 534 μM. As(III) exposure led to MN abnormalities at the highest concentrations, and a significant MN abnormality was observed as soon as at 334 μM at all three pH. Results showed that both As(V) and As(III) had genotoxic effects. In V. faba, the MN increased whatever the form and concentration of As and whatever the pH. In Z. mays, the MN increased with an increase in the concentration of As(V) at pH 9 and in the concentration of As(III) as soon as at 334 μM.
Micronuclei (MN) induced in root meristem cells of Vicia faba and Zea mays by negative control, positive control MH (4 × 10−3M), As(V) and As(III) at different concentrations at respectively pH 4, pH 7 and pH 9.
| Vicia faba | ||||
| Treatments | Code | Micronuclei number | ||
| pH4 (SCE) | pH7 (SCE) | pH9 (SCE) | ||
| Negative control | SNS | 1 (±0.9) | 2 (±0.9) | 6 (±1.5) |
| Positive control | MH | 17 (±2.3) | 18 (±2.3) | 19 (±1.4) |
| Arsenate | As(V)134 | 8 (±0.6) | 8 (±0.9) | 6 (±1.0) |
| As(V) 334 | 8 (±0.6) | 8 (±0.8) | 6 (±0.5) | |
| As(V) 534 | 9 (±0.6) | 7 (±0.5) | 8 (±0.5) | |
| As(V) 668 | 9 (±0.7) | 9 (±0.6) | 9(±1.9) | |
| Arsenite | As(III) 134 | 6 (±0.7) | 8 (±1.7) | 6 (±1.0) |
| As(III) 334 | 12 (±0.9) | 10 (±0.3) | 7 (±1.3) | |
| As(III) 534 | 12 (±1.0) | 12 (±0.3) | 7 (±1.4) | |
| As(III) 668 | 12 (±1.0) | 12 (±0.3) | 9 (±1.0) | |
| Zea mays | ||||
| Treatments | Code | Micronuclei number | ||
| pH4 (SCE) | pH7 (SCE) | pH9 (SCE) | ||
| Negative control | SNS | 7 (±1.7) | 7 (±0.8) | 5 (±0.6) |
| Positive control | MH | 11 (±1.0) | 11 (±0.7) | 10 (±0.6) |
| Arsenate | As(V) 134 | 6 (±0.5) | 7 (±1.1) | 7 (±1.4) |
| As(V) 334 | 8 (±0.6) | 7 (±0.6) | 8(±0) | |
| As(V) 534 | 7 (±1.0) | 8 (±0.9) | 9 (±1.0) | |
| As(V) 668 | 8 (±0.8) | 9 (±1.1) | 10 (±0.6) | |
| Arsenite | As(III) 134 | 8(±0) | 8 (±0.6) | 6 (±1.0) |
| As(III) 334 | 10 (±0.6) | 11 (±1.7) | 7 (±0.6) | |
| As(III) 534 | 12 (±1.0) | 13 (±1.2) | 9 (±1.3) | |
| As(III) 668 | 9 (±0.8) | 12 (±2.0) | 9 (±0.9) |
4 Discussion
The presence of heavy metals in higher plants is often accompanied by a variety of intracellular changes, some of which directly contribute to the sensitivity or tolerance of plants to metals and metalloids [45,46]. In the present study, the impact of arsenic on the growth of Z. mays leaves assessed in terms of leaf fresh weight revealed that a low level of As (134 μM) did not significantly affect leaf fresh weight. Our results suggest that maize plants were able to tolerate low doses of As. Similar observations have been made by Requejo and Tena [16] in maize grown for 24 h in nutrient solutions containing respectively 250 μM sodium arsenite or 300 μM sodium arsenate. These authors have reported that their plants show no visible symptoms and there is no decrease in fresh weight during this short period. Our results suggest that plants were able to tolerate As with an increased fresh weight in roots at pH 7. Experimental results obtained by Kamala et al. [47] have shown that biomass exposed to As is not sensitive to variations in pH within the range of 6–8. Our results at pH 9 showed that 134 μM As(III) led to a reduction in the fresh weight of leaves and roots, while 668 μM As(III) caused only a reduction in the fresh weight of the roots but had no effect on leaves. pH values appeared to play a role in As specific toxicity. Under mildly reducing conditions and at a pH below 9, As(III) exists predominantly as H3AsO3 [48]. It can thus be inferred that Z. mays biomass is capable of binding nonionic H3AsO3 within the typical pH range of natural environments (pH > 8). In our experimental conditions, pH 9 appeared to be much more toxic than the two other pH. The changes that occurred in protein content in leaves and roots with different As treatments were analysed. Analysis showed that low As concentrations led to a significant increase in protein levels at pH 4 with 134 μM As(V) in the leaves and at pH 9 with 134 μM As(III) in the roots. High As(V) concentrations led to an increase in protein levels at pH 4. Our results confirmed those of Li et al. [49]. Some authors have reported that wheat seedlings grown at different As concentrations (0.5, 1, 5, 15, 20 mg/kg) show an increase in soluble protein contents with an increase in As concentration. However, in our study, whatever the pH, higher As(III) concentrations led to a decrease in protein contents in leaves, and to a decrease in roots only after exposure to As(III) at pH 4. Sinha et al. [46] have reported that irrespective of the length of the exposure period, with Cr treatments, PC can decrease in the roots and leaves of Pistia stratiotes grown in culture solution. Requejo and Tena [15,16] have reported that about 15% of total proteins in the aboveground parts of maize and 10% of total proteins in maize roots detected after 2-DE and silver staining are affected by arsenic exposure, and that the metalloid thus has a profound effect on maize root metabolism. Our results showed that decreased growth could be associated with high PC (668 μM As(V) at pH 4 in the leaves, 134 μM As(III) at pH 9 in the roots) or with low PC (668 μM As(III) at pH 4 in the leaves) as the same growth was observed as in the control with a significant decrease in PC (668 μM AsIII at pH 7 and 9 in the leaves, and at pH 4 in the roots). Heavy metals may cause molecular damage to plant cells either directly or indirectly through the formation of ROS [50,51]. ROS production in plants is regulated by the activities of a particular group of enzymes [52]. Inadequate regulation of ROS generation may cause oxidative damage. In our study, a significant decrease in SOD activity was observed in the leaves and roots of Z. mays with the majority of As concentrations (16 cases/24). Similar observations have been made by Li et al. [49] in wheat seedlings exposed to low (0–1 mg/kg) and high concentrations of As (5–20 mg/kg). These authors have reported that in plants treated with As, low concentrations lead to a significant decrease (P < 0.05) of SOD activity. However, the same authors have observed a significant increase in SOD activity with high concentrations of As, while our results suggest that high As concentrations inhibited SOD activity in leaves and caused an insignificant increase in SOD activity in roots at pH 4. Mishra et al. [53] have shown that SOD activity in Ceratophyllum demersum decreases significantly after seven days of exposure to a high concentration of arsenate (250 μM). A similar observation has been made in an arsenate-tolerant Holcus lanatus, where a decrease in SOD activities has been observed with high As concentrations [13]. It is possible that antioxidative enzymes fail to capture ROS at high concentrations of As, reflected by the reduced growth of maize. G-POD, APX and CAT are H2O2-capturing enzymes. The present study showed that, whatever the pH, the lower response of G-POX activity to As in leaves might be compensated by roots above 134 μM As(V). Concerning APX activity, As stress led to an increase in APX activity in the leaves and roots with increasing concentrations of AS, except for As(V) at pH 4 and pH 9 in the leaves, and As(III) at pH 9 in the roots when there was a significant decrease in APX activity. With low concentrations of As, CAT activity was the same as in the control after exposure to As(V), while As(III) treatments led to an increase in CAT in leaves and a decrease in roots. CAT activity increased in both leaves and roots with increasing concentrations of As(III) whatever the pH. Khan et al. [17] have shown that in Indian mustard leaves exposed to As, APX and CAT activities are significantly higher than in the control. In our study, comparison of the three enzyme activities showed that the lower response of SOD activity to As in Z. mays might be compensated by the increased activities of G-POD, APX and CAT, showing that the three enzymes were functioning concurrently to remove H2O2 in the different parts of the plant. A similar pattern of enzymatic activity has been reported in response to As abiotic stress [54]. These authors have shown that the lower response of CAT activity to As in Pteris vittata fronds may be compensated by the increased activities of APX and G-POD, and that the inadequate response of APX and GPOD activity to As in roots is compensated by increased CAT activity. An increase in the activity of antioxidant enzymes can be attributed to the induced transcription of their genes, probably mediated by free radicals [23]. Coordinated responses of various enzymes thus appear to be related to plant tolerance to oxidative stress [16,55]. In our study, As(V) treatment led to the disruption of root colour, an increase in root thickness and inhibition of root growth of V. faba at the highest concentrations. As(III) induced similar effects, but less pronounced than As(V). In Z. mays, arsenic treatments had no drastic effect. Thus, As(V) appeared to be more toxic than arsenite for Vicia roots even though As(III) is more phytotoxic than arsenate in natural conditions [3,7,27,56]. In our study, disruption of V. faba root colour was observed after exposure to arsenate but not in Z. mays roots. Otte and Ernst [57] have suggested that P-deficiency, which results in metalloid stress, causes dark leaves and inhibits various physiological and biochemical processes. Arsenic treatments led to an increase in root thickness that was more pronounced with exposure to arsenate than to arsenite. Our results thus confirmed those of Jiang et al. [58] and of Seregin and Ivanov [59]. Environmental stress causes metabolic disruption through lignification [60] leading to visible stiffness. The process of membrane strengthening via lignification and formation of secondary phenolic compounds leads to a marked change in thickness, creating ROS. ROS are believed to be responsible for chromosome abnormalities, which could damage DNA [61,62]. The change in the MI, especially with the highest arsenic concentrations, could be due to inhibition of DNA synthesis [63] or to blocking of the G2-phase in which tubulin is required for the formation of mitotic spindle [64]. MI effects can be considered as the initial mutagen impact of heavy metals and arsenic leading to chromosome abnormalities, such as MN and other nucleus abnormalities [25]. Marcano et al. [35] have suggested that the type of micronucleus is due either to an alteration during the cellular division cycle or to the development of an isolated chromosome unit. In both cases this leads to unequal distribution of the genetic elements, thus generating nuclear abnormalities. After exposure to arsenic, the induction of MN in root meristems of V. faba resulted in disturbance of the mitotic process and damage to chromosomes [65,66]. Thus, the induction of MN suggests that the arsenic was either a spindle inhibitor and consequently aneugenic or a clastogen [26]. The fact that it is possible to score MN has already been reported for Allium cepa [67,68], C. capillaris [69] or Hordeum vulgare [70], H. annus L. [58] treated with other metalloids and heavy metals (Al, Cd, Cu, Cr, Hg, Pb, Se, Zn). MN induction by As(V) may be a consequence of the competition between As(V) and phosphate uptake, altering several factors such as the proper structure of DNA and RNA molecules. By reacting with thiol residues or with sulfhydryls present in many cellular structures (functional enzymatic groups, receptors or coenzymes), As(III) can disturb important biochemical processes, is likely to generate chromosome aberrations, can interfere with DNA-ligase [3], and thus be responsible for the inhibition of the DNA process or molecule restoration linked to DNA ligase activity [11] and so induce micronuclei. As(III) is thus considered not only to be a direct mutagen agent but also a powerful co-mutagen element [26]. Moreover, MN alterations appear to depend on the concentration and on the chemical form of As. As(V) exists predominantly as 100% ionic forms, respectively 50% H2AsO4− and 50% HAsO42−; As(III) exists predominantly as anionic H3AsO3 at pH 4 and 7 and as ionic H2AsO3− [34]. Our observation of several genotoxic effects of exposure to As at pH 9 corroborated our observations concerning FB, PC and antioxidant enzymes, which were drastically affected at this pH.