1 Introduction
One-D to 3D polymerized structures of transition metal complexes have received much attention for the last decade. Not only mononuclear complexes but also various types of clusters, di-, tri-, tetra-, and hexanuclear ones, were used as building blocks. Preparation of a novel polymeric structure with paddlewheel complexes is one of our recent efforts. Paddlewheel complex is a useful building block, because it has rich redox chemistry with various electronic states depending on its bridging ligands, and strained bonding direction to its axial sites. We have synthesized 1 to 3D structures of halide-bridged rhodium or ruthenium paddlewheel complexes. The reaction of a dirhodium or diruthenium cation with halide anion gave only 1D chain structure [1–3]. The reaction of a mixture of cation and neutral complexes with halide linker afforded a 2D structure of [{Rh2(acam)4}3(μ3-Cl)2]n·4 n H2O [4] and a 3D structure of [{Rh2(acam)4}2(μ4-I)]n·6 n H2O [5]. For the former structure, removal of the crystalline water molecules improved its electric conductivity. On the other hand, the latter has 105 higher conductivity in the hydrated form than in the partially dehydrated one. Other than halide bridges, only a few 2D and 3D polymer structures of paddlewheel dinuclear complexes with organic or anionic mononuclear complex linkers have been reported [6–9].
Hexametal cluster is also a good building block to make multi-dimensional frameworks, because they have a variety of cluster charges and electronic states with M6Z8 core (M = Mo, W, Re; Z = halide, chalocogenide). Some network structures with Re6Z8n+ (Z = S, Se, Te) [10–12] or W6S8 [13] have been reported in the recent years. A novel framework constructed with paddlewheel complexes and hexametal clusters may lead to new physical properties and/or porosity. In this paper, we report synthesis and two types of crystal structures of [{Ru2(O2CCMe3)4}2{(Mo6Xi8)Xa6}] (Xi, Xa= Cl, Cl; Cl, Br; Br, Cl).
2 Experimental
2.1 Synthesis
2.1.1 General methods
[Ru2(O2CCMe3)4Cl(H2O)] was prepared according to a literature procedure [14] and [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)2]BF4 was synthesized from it by a modification of the method of Barral and coworkers for [Ru2(O2CC6H4-p-CMe3)4(THF)2]PF6 [15]. (nBu4N)2[(Mo6X8)X′6] (X = Cl, Br; X′ = Cl, Br; I) was obtained by the reaction of Mo6X12 with Bun4NX′ in HX′. Dichloromethane, n-hexane and acetonitrile were distilled from CaH2 before use.
2.1.2 [{Ru2(O2CCMe3)4}2{(Mo6Cl8)Cl6}] (1)
A CH2Cl2 solution of (nBu4N)2[(Mo6Cl8)Cl6] (0.026 g, 0.017 mmol) was added to a CH2Cl2 solution of [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)]PF6 (0.024 g, 0.033 mmol). Reddish-brown powder was collected, washed with CH2Cl2 and dried in vacuo. Yield 0.026 g (69%). Anal. Calc. for C40H72Cl14Mo6O16Ru4; C, 21.02; H, 3.18%. Found: C, 21.02; H, 2.96%.
2.1.3 [{Ru2(O2CCMe3)4}2{(Mo6Cl8)Br6}] (2)
A CH2Cl2 solution of (nBu4N)2[(Mo6Cl8)Br6] (0.031 g, 0.017 mmol) was added to a CH2Cl2 solution of [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)]PF6 (0.022 g, 0.030 mmol). Reddish-brown powder was collected, washed with CH2Cl2 and dried in vacuo. Yield 0.024 g (62%). Anal. Calc. for C40H72Br6Cl8Mo6O16Ru4; C, 18.83; H, 2.84%. Found: C, 18.89; H, 2.67%.
2.1.4 [{Ru2(O2CCMe3)4}2{(Mo6Br8)Cl6}] (3)
A CH2Cl2 solution of (nBu4N)2[(Mo6Br8)Cl6] (0.020 g, 0.011 mmol) was added to a CH2Cl2 solution of [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)]PF6 (0.016 g, 0.022 mmol). Reddish-brown powder was collected, washed with CH2Cl2 and dried in vacuo. Yield 0.020 g (72%). Anal. Calc. for C40H72Br8Cl6Mo6O16Ru4; C, 18.19; H, 2.75%. Found: C, 17.93; H, 2.74%.
2.2 X-ray structure determination
Crystals of 1·CH2Cl2, 2·CH2Cl2 and 3·CH2Cl2 were obtained as follows: (nBu4N)2[(Mo6Xi8)Xa6] was placed in a 6-mm-diameter glass tube and CH2Cl2 was gently added to it. Tightly rolled filter paper was put into the tube just above the solution and then a CH2Cl2 solution of [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)]PF6 was layered. After standing at 15 °C for 3 days, brown crystals were obtained. Diffraction measurements were carried out on a Rigaku AFC7R Mercury CCD diffractometer with graphite monochromated Mo Kα radiation (λ = 0.71069 Å). Because crystals of 1·2 CH2Cl2, 2·2 CH2Cl2 and 3·2 CH2Cl2 easily lost CH2Cl2 molecules in a crystal, reflection data were collected at low temperature using a Rigaku XR-TCS-2-050 temperature controller. All structures were solved and refined using the teXsan® crystallographic software package. Scattering factors for neutral atoms were from Cromer and Waber [16] and anomalous dispersion [17] was used. A numerical absorption correction [18] was applied. The structures were solved by direct methods SIR92 [19] and expanded by DIRDIF [20]. Full matrix least-squares refinement was employed. Final least square cycle included non-hydrogen atoms with anisotropic thermal parameters except disordered t-butyl groups were refined as rigid groups. Hydrogen atoms are not included in the refinement. Crystallographic data are summarized in Table 1.
Crystallographic data of 1·2 CH2Cl2, 2·2 CH2Cl2 and 3·2 CH2Cl2
| 1·2 CH2Cl2 | 2·2 CH2Cl2 | 3·2 CH2Cl2 | |
| Chemical formula | C42H76Cl18Mo6O16Ru4 | C42H76Br6Cl12Mo6O16Ru4 | C42H76Br8Cl10Mo6O16Ru4 |
| Formula weight | 2455.13 | 2721.83 | 2810.73 |
| Crystal system | triclinic | triclinic | monoclinic |
| Space group | P | P | P21/n (No. 14) |
| a (Å) | 14.551 (3) | 14.757 (3) | 15.374 (6) |
| b (Å) | 14.765 (3) | 14.946 (3) | 17.851 (7) |
| c (Å) | 20.559 (5) | 20.632 (5) | 15.364 (6) |
| α (°) | 108.656 (5) | 109.179 (5) | |
| β (°) | 104.429 (5) | 104.016 (7) | 91.247 (5) |
| γ (°) | 91.671 (10) | 91.26 (1) | |
| V (Å3) | 4024 (1) | 4144 (1) | 4215 (2) |
| Z | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| d (calcd) (g cm–3) | 2.026 | 2.181 | 2.214 |
| μ (mm–1) | 2.275 | 4.917 | 5.721 |
| T (°C) | –40 | –100 | –40 |
| Reflections collected | 33228 | 34466 | 34969 |
| Reflections independent | 18262 | 18869 | 9640 |
| Reflections with I > 2 σ(I) | 14028 | 13194 | 6003 |
| Rint | 0.032 | 0.044 | 0.086 |
| R, Rwa | 0.047, 0.106 | 0.053, 0.107 | 0.108, 0.287 |
| Residual (min, max) (e Å−3) | –1.29, 1.77 | –1.93, 2.14 | –4.48, 2.70 |
| Goodness-of-fit | 1.31 | 1.13 | 1.44 |
a R = Σ ||Fo| – |Fc||/Σ |Fo| for data with I > 2 σ(I), Rw = [Σ w (Fo2 – Fc2)2/Σ w Fo4]1/2 for all data.
3 Results and discussion
In a preliminary experiment, we have tried to make crystals of [{Ru2(O2CMe)4}2{(Mo6Cl8)Cl6}] in acetonitrile. Mixing of solutions of [Ru2(O2CMe)4]PF6 and (nBu4N)2[(Mo6Cl8)Cl6] did not precipitate crystals. Although evaporation of the solution afforded brown crystals, they include ruthenium complexes with axial acetonitrile ligands and discrete molybdenum clusters. In dichloromethane, reddish-brown powder was precipitated immediately after mixing of solutions of [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)2]BF4 and (nBu4N)2[(Mo6Cl8)Cl6]. To make good crystals, very slow mixing of the solutions is needed.
A sheet structure of 1 in 1·2 CH2Cl2 is shown in Fig. 1. Structure of 2·2 CH2Cl2 is isostructural with 1·2 CH2Cl2. There are four independent ruthenium complexes and two independent molybdenum clusters in a unit cell, all of which are at inversion centers (Mo6: (0, 0, 0) and (0.5, 0, 0.5), Ru2: (0.5, 0, 0), (0, 0.5, 0), (0, 0, 0.5) and (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)). In each of two independent 2D sheets at c = 0 and 0.5, the centers of Ru2 complexes and those of Mo6 clusters are located exactly in the plane. The sheet is made by squares of which corners are molybdenum clusters and edges are ruthenium complexes. Each hexamolybdenum cluster linked to four ruthenium complexes by axial halide ligands. A couple of axial ligands remain as terminal ones. The solvating dichloromethane molecules are sited between the sheets, which are easily lost even at room temperature. The selected distances and angles are summarized in Tables 2 and 3. The distances and angles in two independent sheets are almost identical. The average Ru–Ru distances (1·2 CH2Cl2: 2.272 (1) Å, 2·2 CH2Cl2: 2.274 (3) Å) are in the range of those observed in other Ru2(O2CCMe3)4+ complexes [21–23]. The Mo–Mo distances in 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2·2 CH2Cl2 (2.607 (5) and 2.608 (5) Å, respectively) are similar to other hexamolybdenum clusters with capping chloride [24,25]. The ruthenium–halogen distances (2.622 (10) Å for 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2.737 (15) Å for 2·2 CH2Cl2) are similar to those observed in diruthenium halide-bridged chain structures [26,27]. The bond distances between molybdenum and bridging axial halides for 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2·2 CH2Cl2 are 2.480 (19) and 2.613 (21) Å, respectively, which are longer than those between molybdenum and terminal one, 2.395 (1) and 2.548 (4) Å, respectively. These elongated molybdenum–halide distances are also observed in MoCl2 (= [(Mo6Cl8)Cl4/2Cl2]) in which each Mo6Cl8 unit connects to the four neighboring ones using four outer-chloride as bridges. The Ru–Br–Mo angles for 2 (122.73 (3)–126.24 (3)°) are slightly smaller than the Ru–Cl–Mo angles for 1·2 CH2Cl2 (127.08 (6)–131.34 (6)°), which is due to the long Ru–X distance in 2·2 CH2Cl2.
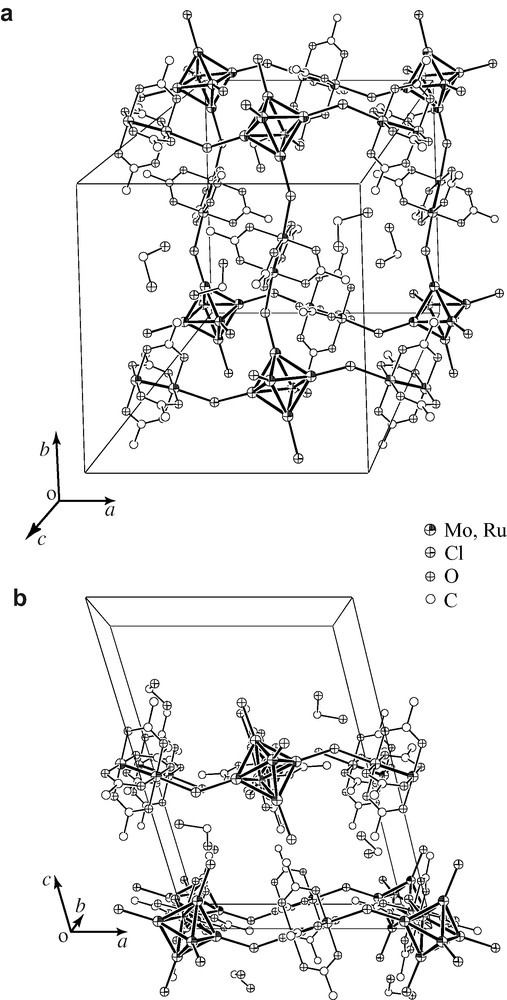
Crystal structure of 1·2 CH2Cl2. (a) Top view and (b) side view of the 2D sheet structure. Capping chloro ligands of the hexamolybdenum cluster and methyl carbon atoms are omitted for clarity.
Selected bond distances (Å) and angles (°) of 1·2 CH2Cl2a
| Ru1–Ru1I | 2.2734 (9) | Mo2–Mo3V | 2.6077 (6) |
| Ru2–Ru2II | 2.2715 (8) | Mo4–Mo5 | 2.6026 (6) |
| Ru3–Ru3III | 2.2709 (9) | Mo4–Mo5VI | 2.6116 (7) |
| Ru4–Ru4IV | 2.2740 (9) | Mo4–Mo6 | 2.6085 (6) |
| Ru1–Cl5 | 2.616 (1) | Mo4–Mo6VI | 2.6004 (7) |
| Ru2–Cl6 | 2.616 (1) | Mo5–Mo6 | 2.6143 (6) |
| Ru3–Cl12 | 2.619 (1) | Mo5–Mo6VI | 2.6087 (6) |
| Ru4–Cl13 | 2.637 (1) | Mo1–Cl5 | 2.471 (1) |
| Mo1–Mo2 | 2.6135 (7) | Mo2–Cl6 | 2.482 (1) |
| Mo1–Mo2V | 2.6007 (6) | Mo3–Cl7 | 2.396 (2) |
| Mo1–Mo3 | 2.6071 (6) | Mo4–Cl12 | 2.460 (1) |
| Mo1–Mo3V | 2.6044 (7) | Mo5–Cl13 | 2.505 (1) |
| Mo2–Mo3 | 2.6095 (6) | Mo6–Cl14 | 2.394 (2) |
| Ru1I–Ru1–Cl5 | 176.25 (4) | Ru1–Cl5–Mo1 | 127.71 (5) |
| Ru2II–Ru2–Cl6 | 176.82 (5) | Ru2–Cl6–Mo2 | 131.34 (6) |
| Ru3III–Ru3–Cl12 | 173.32 (4) | Ru3–Cl12–Mo4 | 127.08 (6) |
| Ru4IV–Ru4–Cl13 | 174.52 (5) | Ru4–Cl13–Mo5 | 130.44 (6) |
a I: 0.5 – x, –y, –z, II: –x, 0.5 – y, –z, III: –x, –y, 0.5 – z, IV: 0.5 – x, 0.5 – y, 0.5 – z, V: –x, –y, –z, VI: 0.5 – x, –y, 0.5 – z.
Selected bond distances (Å) and angles (°) of 2·2 CH2Cl2a
| Ru1–Ru1I | 2.274 (1) | Mo2–Mo3V | 2.6117 (8) |
| Ru2–Ru2II | 2.271 (1) | Mo4–Mo5 | 2.6021 (8) |
| Ru3–Ru3III | 2.273 (1) | Mo4–Mo5VI | 2.6105 (8) |
| Ru4–Ru4IV | 2.278 (1) | Mo4–Mo6 | 2.6088 (7) |
| Ru1–Br1 | 2.7207 (9) | Mo4–Mo6VI | 2.6012 (9) |
| Ru2–Br2 | 2.7309 (9) | Mo5–Mo6 | 2.6155 (8) |
| Ru3–Br4 | 2.7394 (9) | Mo5–Mo6VI | 2.6108 (8) |
| Ru4–Br5 | 2.7562 (9) | Mo1–Br1 | 2.602 (1) |
| Mo1–Mo2 | 2.6113 (8) | Mo2–Br2 | 2.6119 (9) |
| Mo1–Mo2V | 2.6002 (8) | Mo3–Br3 | 2.5505 (9) |
| Mo1–Mo3 | 2.6092 (8) | Mo4–Br4 | 2.594 (1) |
| Mo1–Mo3V | 2.6050 (9) | Mo5–Br5 | 2.6422 (9) |
| Mo2–Mo3 | 2.6097 (8) | Mo6–Br6 | 2.5455 (9) |
| Ru1I–Ru1–Br1 | 174.56 (4) | Ru1–Br1–Mo1 | 123.60 (3) |
| Ru2II–Ru2–Br2 | 177.61 (4) | Ru2–Br2–Mo2 | 126.24 (3) |
| Ru3III–Ru3–Br | 172.45 (4) | Ru3–Br–Mo4 | 122.73 (3) |
| Ru4IV–Ru4–Br5 | 176.24 (4) | Ru4–Br5–Mo5 | 125.39 (3) |
a I: 0.5 – x, –y, –z, II: –x, 0.5 – y, –z, III: –x, –y, 0.5 – z, IV: 0.5 – x, 0.5 – y, 0.5 – z, V: –x, –y, –z, VI: 0.5 – x, –y, 0.5 – z.
Crystals of 3·2 CH2Cl2 includes another type of sheet structure that is shown in Fig. 2. The structure refinement is relatively poor due to the low quality of the crystals of 3·2 CH2Cl2. However, it is sufficient to discuss the main feature of the structure. In this structure, the sheet extended on a dihedral plane between a and c axes is also built by squares which consist of four molybdenum clusters as corners and four ruthenium complexes as edges. In the structure of 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2·2 CH2Cl2, the sheet is flat, while in the structure of 3·2 CH2Cl2, Ru2 complexes are repeatedly sited above and below a plane made up of Mo6 clusters, along b-axis. It means that the sheet is waved. Selected bond distances and angles are listed in Table 4. Mo–Mo distances are slightly elongated from those in 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2·2 CH2Cl2 and are similar to other bromide-capped clusters [28]. The Ru–Ru distance is very similar to those observed in 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2·2 CH2Cl2. A largely different structural parameter from 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2·2 CH2Cl2 is only the Mo–Cl–(Ru2)–Cl–Mo torsion angle which is 180° in 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2·2 CH2Cl2 and 53.6 (3)° in 3·2 CH2Cl2.
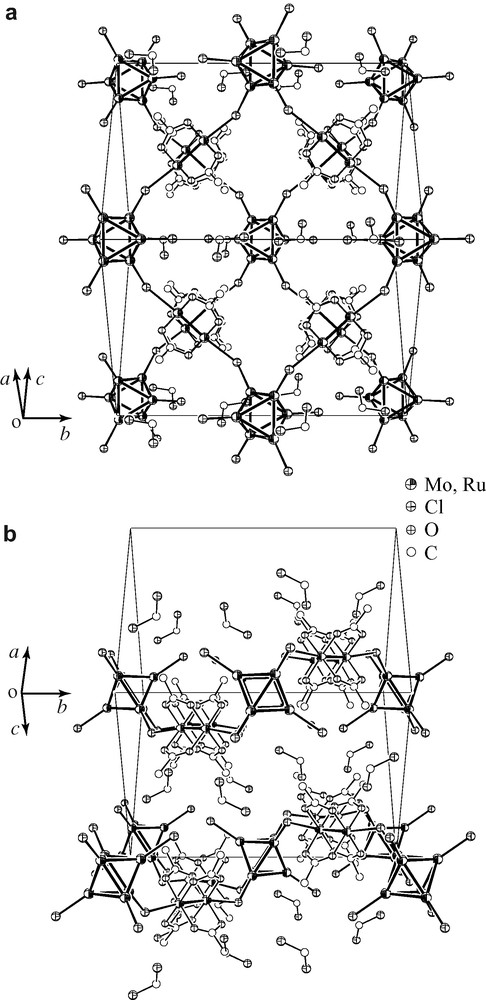
Crystal structure of 3·2 CH2Cl2. (a) Top view and (b) side view of the 2D sheet structure. Capping bromo ligand of the hexamolybdenum cluster and methyl carbon atoms are omitted for clarity.
Selected bond distances (Å) and angles (°) of 3·CH2Cl2a
| Ru1–Ru2 | 2.273 (2) | Mo1–Mo3′ | 2.631 (2) |
| Ru1–Cl1 | 2.598 (5) | Mo2–Mo3 | 2.629 (2) |
| Ru2–Cl2” | 2.580 (5) | Mo2–Mo3′ | 2.626 (2) |
| Mo1–Mo2 | 2.623 (2) | Mo1–Cl1 | 2.450 (4) |
| Mo1–Mo2′ | 2.618 (2) | Mo2–Cl2 | 2.459 (5) |
| Mo1–Mo3 | 2.623 (2) | Mo3–Cl3 | 2.425 (4) |
| Ru2–Ru1–Cl1 | 170.7 (1) | Ru1–Cl1–Mo1 | 128.7 (2) |
| Ru1–Ru2–Cl2” | 170.7 (1) | Ru2′–Cl2–Mo2 | 128.6 (2) |
a ′: 1 – x, –y, 1–z, ′′–x, 0.5 – y, –z.
Although the reaction of [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)2]BF4 with other Mo6 clusters (Xi, Xa = Cl, I; Br, Br; Br, I) gave only very small crystals, cell constants of the crystals suggest that these complexes may have a similar flat sheet structure to 1·2 CH2Cl2 and 2·2 CH2Cl21. In the structure of Cs2[{Fe(H2O)2}{Re6S8(CN)6}] [29], sheet structure of [{Fe(H2O)2}{Re6S8(CN)6}]2– in which square is made up of alternating Fe ion and Re clusters is waved as the Fe ions are up and down from a plane of the Re6 clusters. An amplitude and a period of the wave in this complex are 1.65 and 18.55 Å, respectively, while those of 3· CH2Cl2 are 2.27 and 17.85 Å, respectively. The difference of the amplitude is due to the bent Ru–Br–Mo angle compared with the Fe–N–C one.
In summary, two types of structures of [{Ru2(O2CCMe3)4}2{(Mo6Xi8)Xa6}], flat and waved sheets are obtained by mixing of the solutions of [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)2]+ and [(Mo6Xi8)Xa6}]2–. Unfortunately all crystals degrade by a loss of crystalline dichloromethane molecules. We are investigating to make stable crystals with other paddlewheel complexes and/or molybdenum clusters.
4 Supplementary material
Crystallographic data (excluding structure factors) for the structural analysis have been deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center, CCDC Nos. 247469–247471 for 1·2 CH2Cl2, 2·2 CH2Cl2 and 3·2 CH2Cl2. Copies of this information may be obtained free of charge from The Director, CCDC, 12 Union Road, Cambridge, CB2 1EZ, UK [Fax: +44 1223 33 6033; E-mail: deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk or www: http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk].
1 Cell constant of the crystals obtained by the reaction of [Ru2(O2CCMe3)4(H2O)2]BF4 with (nBu4N)2[(Mo6Xi8)Xa6] are as follows: Xi, Xa = Cl, I; a = 15.217 (10), b = 15.288 (10), c = 21.14 (1) Å, α = 108.961 (7), β = 104.147 (8), γ = 90.594 (5)°, V = 4487 (4) Å3. Xi, Xa = Br, Br; a = 14.844 (7), b = 14.969 (7), c = 20.65 (1) Å, α = 107.85 (1), β = 104.42 (2), γ = 91.25 (3)°, V = 4205 (3) Å3. Xi, Xa = Br, I; a = 15.25 (1), b = 15.34 (1), c = 21.02 (2) Å, α = 109.45 (3), β = 103.72 (3), γ = 91.14 (6)°, V = 4477 (6) Å3.


