1 Introduction
Ultrasonic investigation of liquid mixtures consisting of polar and non-polar components is of considerable importance in understanding intermolecular interaction between the component molecules. In many industrial applications, liquid mixtures, rather than single component liquid system, are used in processing and product formulations. Thermodynamic and transport properties of liquid mixtures have been extensively used [1,2] to study the departure of a real liquid mixture from ideality. Further, these properties have been widely used to study the intermolecular interactions between the various species present in the mixture [3,4]. As alcohols are highly polar, they can be made to form azeotropes of binary complexes. Further, they play an important role in many chemical reactions due to their ability to undergo self-association with manifold internal structures. Hence, the authors have performed a thorough study on the molecular interaction existing in the mixtures of methanol, ethanol and 1-propanol with aniline, using the sound velocity data. The present work deals with the measurement of ultrasonic velocity, density and viscosity, and computation of related parameters at 303 K in three non-ideal binary mixtures of aniline + methanol, aniline + ethanol and aniline + 1-propanol.
2 Experimental details
The mixtures of various concentrations in mole fraction were prepared by taking purified AR grade samples at 303 K. The ultrasonic velocity (U) in liquid mixtures has been measured using an ultrasonic interferometer (Mittal type) working at 2 MHz frequency with an accuracy of ±0.1 ms−1. The density, or the mass per unit volume (ρ) and viscosity (η) are measured using a pycknometer and an Ostwald's viscometer, respectively, with an accuracy of 3 parts in 105 for density and 0.001 Nsm−2 for viscosity.
Using the measured data, the acoustical parameters such as adiabatic compressibility (β), free length (Lf), free volume (Vf) and internal pressure (πi) and their excess parameters have been calculated using the following standard expressions:
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
3 Results and discussion
The observed values for the system of aniline + alcohol are presented in Table 1. The values of density (ρ), viscosity (η) and ultrasonic velocity (U) show an increasing trend with increase in mole fraction of aniline in all the systems.
Values of density (ρ), viscosity (η) and ultrasonic velocity (U) of aniline (A) + methanol (B), ethanol (C), 1-propanol (D) at 303 K
| Mole fraction of A | ρ kg m−3 | η × 103 Ns m−2 | U ms−1 | ||||||
| B | C | D | B | C | D | B | C | D | |
| 0.0000 | 776.0 | 780.5 | 795.6 | 0.501 | 0.983 | 1.634 | 1103.0 | 1130.0 | 1193.0 |
| 0.1007 | 836.4 | 821.8 | 823.2 | 0.790 | 1.086 | 1.675 | 1208.7 | 1210.7 | 1238.7 |
| 0.1995 | 883.2 | 852.7 | 854.0 | 0.990 | 1.223 | 1.712 | 1301.0 | 1285.0 | 1289.6 |
| 0.2992 | 902.6 | 870.6 | 875.6 | 1.115 | 1.351 | 1.843 | 1356.5 | 1327.8 | 1325.6 |
| 0.4045 | 931.4 | 899.2 | 900.2 | 1.447 | 1.519 | 1.919 | 1432.3 | 1395.3 | 1379.3 |
| 0.5001 | 946.4 | 924.2 | 916.5 | 1.732 | 1.678 | 1.965 | 1496.2 | 1432.6 | 1407.3 |
| 0.6027 | 963.5 | 947.4 | 931.4 | 2.033 | 1.944 | 2.097 | 1515.3 | 1488.3 | 1467.0 |
| 0.7046 | 979.5 | 963.2 | 952.3 | 2.271 | 2.234 | 2.328 | 1549.2 | 1530.4 | 1514.5 |
| 0.8078 | 995.6 | 979.5 | 980.4 | 2.599 | 2.485 | 2.518 | 1569.6 | 1556.6 | 1544.3 |
| 0.9003 | 1004.3 | 992.1 | 993.6 | 2.856 | 2.732 | 2.814 | 1589.6 | 1576.2 | 1573.2 |
| 1.0000 | 1010.9 | 1010.9 | 1010.9 | 3.036 | 3.036 | 3.036 | 1614.0 | 1614.0 | 1614.0 |
As ρ increases, the number of particles in a given region is increased and this leads to quick transfer of sound energy and thus velocity also increases [7,8]. As aniline is having a high boiling point, the energy between the molecules of aniline is so high that the molecular bonds of aniline cannot be ruptured, whereas for ethanol, it is not so. The increasing mole fraction of aniline supports non-rupturing of components and hence, increase in viscosity [9] is expected. All the observed parameters vary non-linearly and this indicates the existence of interactions in the medium. This is in line with the observations made by Jacek Glinski [10] in some binary systems.
The calculated values of adiabatic compressibility (β), intermolecular free length (Lf), free volume (Vf) and internal pressure (πi) are given in Table 2. All these parameters invariably show a decreasing trend with increase in mole fraction of aniline except Vf in 1-propanol system. In 1-propanol system, unlike the other systems, Vf shows an increasing trend and all the other parameters, i.e., β, Lf, and πi show a decreasing trend with increase in mole fraction of aniline irrespective of the alcohol type.
Values of adiabatic compressibility (β), free length (Lf), free volume (Vf) and internal pressure (πi) of aniline (A) + methanol (B), ethanol (C), 1-propanol (D) at 303 K
| Mole fraction of A | β × 1010 Pa−1 | Lf × 1011 m | Vf × 107 m3 mol−1 | πi × 10−8 Pa | ||||||||
| B | C | D | B | C | D | B | C | D | B | C | D | |
| 0.0000 | 10.592 | 10.033 | 8.831 | 6.545 | 6.370 | 5.976 | 0.699 | 0.435 | 0.328 | 10.38 | 9.44 | 8.80 |
| 0.1007 | 8.183 | 8.009 | 7.917 | 5.703 | 5.641 | 5.608 | 0.505 | 0.431 | 0.336 | 10.25 | 8.85 | 8.40 |
| 0.1995 | 6.689 | 7.102 | 7.040 | 5.151 | 5.309 | 5.286 | 0.500 | 0.426 | 0.342 | 10.06 | 8.32 | 8.05 |
| 0.2992 | 6.020 | 6.515 | 6.499 | 4.885 | 5.083 | 5.077 | 0.490 | 0.423 | 0.349 | 9.12 | 8.21 | 7.90 |
| 0.4045 | 5.233 | 5.710 | 5.839 | 4.551 | 4.756 | 4.809 | 0.475 | 0.419 | 0.357 | 8.97 | 7.80 | 7.75 |
| 0.5001 | 4.720 | 5.272 | 5.509 | 4.319 | 4.567 | 4.670 | 0.449 | 0.416 | 0.362 | 8.66 | 7.57 | 7.65 |
| 0.6027 | 4.520 | 4.765 | 4.988 | 4.225 | 4.340 | 4.442 | 0.435 | 0.412 | 0.367 | 8.44 | 7.50 | 7.54 |
| 0.7046 | 4.253 | 4.432 | 4.578 | 4.098 | 4.184 | 4.253 | 0.423 | 0.410 | 0.373 | 8.06 | 7.45 | 7.43 |
| 0.8078 | 4.076 | 4.213 | 4.276 | 4.010 | 4.078 | 4.109 | 0.415 | 0.405 | 0.380 | 7.89 | 7.41 | 7.39 |
| 0.9003 | 3.940 | 4.057 | 4.066 | 3.942 | 4.001 | 4.005 | 0.403 | 0.399 | 0.385 | 7.64 | 7.31 | 7.31 |
| 1.0000 | 3.797 | 3.797 | 3.797 | 3.919 | 3.919 | 3.919 | 0.393 | 0.393 | 0.393 | 7.25 | 7.25 | 7.25 |
The compactness of the system with increase in mole fraction of aniline is indicated by reduced β values and the same is favoured by the decreasing trend of Lf. Such trends were noticed by Rajendran and Marikani [11] in some similar liquid systems. A continuous decrease in β or Lf is a clear evidence for the existence of strong interactions. Such strong interactions may be due to charge transfer, dipole–dipole, dipole–induced dipole, etc. It also reveals that both Vf and πi exhibit similar trend [12], which is normally not so.
A monotonous non-linear decrease in Vf (or πi) indicates that the chances for complex formation or charge transfer are overruled. The fluctuations in these parameters, even though non-linear, follow the same trend, which reveals that there would be no induced dipoles. As both the components are polar molecules, the existing strong interactions are supposed to be of dipole–dipole type. Further, in such cases, as they are strong and mostly of attractive nature, chances for reduction in πi are possible. The observed trend in πi confirms this view.
The increasing trend of Vf observed only in 1-propanol system with the aniline mole fraction may be due to the larger chain length of 1-propanol molecule [13]. Of course this is reflected in the viscosity variations also. The addition of aniline makes the medium to have more and more ring structured molecule that restricts the movement of linear chain molecules and thus free volume is found to increase with aniline mole fraction. This is not conflicting with the decreasing trend observed for other two alcohols as methanol is small in size, whereas for ethanol, the hydrocarbon chain has hydrophobic nature [14]. In the 1-propanol system, it is observed that Vf shows a monotonous increase, whereas a reverse trend is observed in πi values with increase in mole fraction of aniline. A continuous increase in Vf indicates that the components are packed in a cage-like structure; however, no complex formation is suspected. This compactness of the medium reduced the effective adhesive forces and thus πi shows a decreasing trend [15,16].
To ascertain these conclusions, excess values of these parameters have been evaluated using the standard relations:
| (5) |
| (6) |
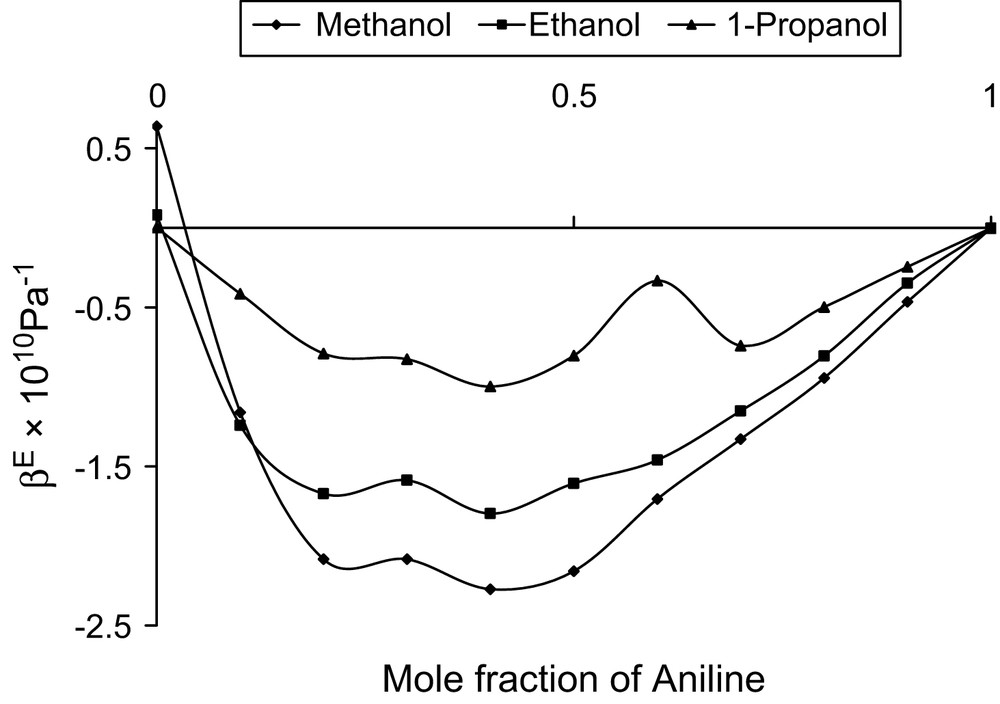
Mole fraction vs. excess adiabatic compressibility at 303 K.
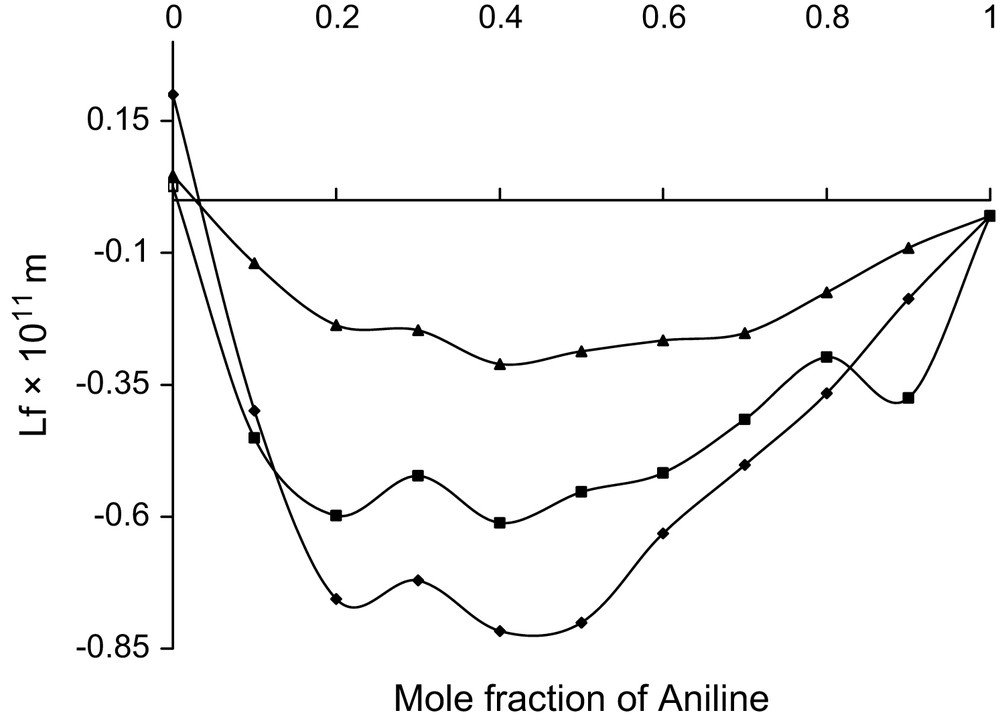
Mole fraction vs. excess intermolecular free length at 303 K.
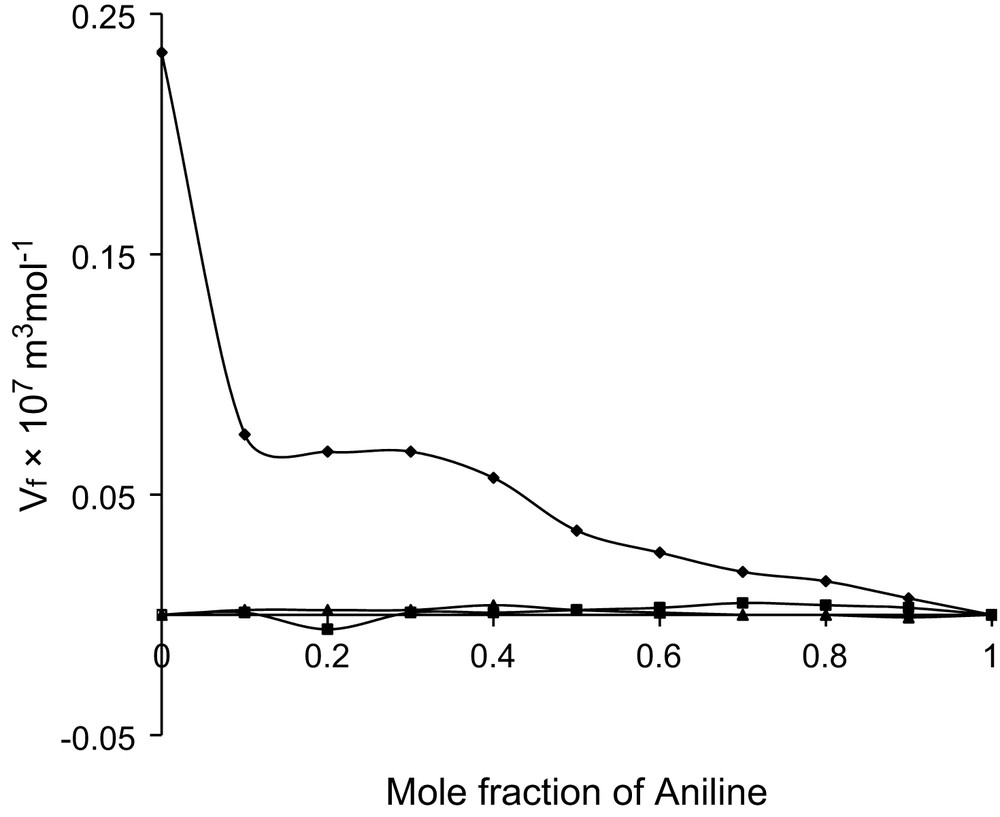
Mole fraction vs. excess free volume at 303 K.
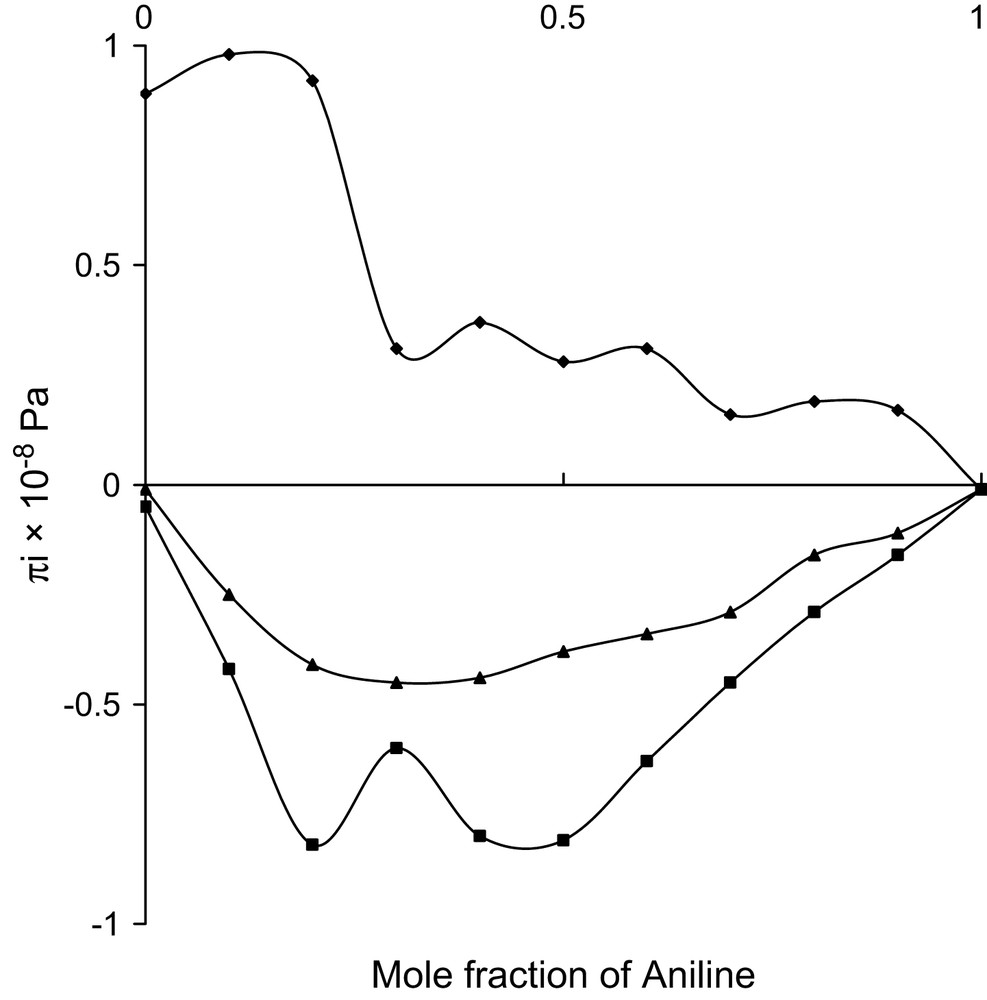
Mole fraction vs. excess internal pressure at 303 K.
All the three alcohols are having one hydroxyl group with increasing number of methyl group. The hydrophilic hydroxyl group in all the three alcohols can interact with the amino group of aniline and thus dipole–dipole interactions are evident in all the three systems. In case of ethanol, the hydrocarbon chain acts as hydrophobic, whereas in other two alcohols such properties are not evident. This hydrophobic tendency needs a non-polar group to interact. Though the amino group is comparatively a strong electron donor, the H atoms in the NH2 group can also play the role of electron-acceptor centres [19] and hence the hydrophobic nature of ethanol can create temporary dipoles in the amino group of aniline molecule and thus dipole–induced dipole interactions are additionally existing in the ethanol system. The formations of these temporary dipoles are reflected in the observed fluctuations in the trend of
In these ethanol system,
4 Conclusion
- 1. Presence of interactions is confirmed in all the systems.
- 2. Existing interactions are strong in magnitude irrespective of the alcohol chain length.
- 3. In addition to the unanimous existence of dipole–dipole interactions, dipole–induced dipole types are additionally present in the ethanol system.


