1 Introduction
Alkenylphosphines are a class of compounds that undergo numerous useful synthetic transformations due to the carbon-carbon double bond, which is directly linked to the phosphorus atom [1–3]. For example, a large variety of nucleophiles can add to the double bond to provide bifunctional or polyfunctional adducts (polyphosphines, dendrimers, polymers). Alkenylphosphines can also be used as dienophiles in cycloaddition reactions [4,5]. Due to the presence of both phosphorus and carbon-carbon double bond, they are also of great interest in coordination chemistry. Recently, they were successfully used as ligands in homogeneous catalysis. Various synthetic methods for accessing alkenylphosphine derivatives have been developed. The main methodologies are related to the preparation of racemic or achiral alkenylphosphines. They involve reaction between halophosphines and vinylic organometallic species, hydrophosphination of alkynes or C-P cross-coupling reactions [2]. Contrarily, enantiopure or enantioenriched derivatives are rare. If a few C-stereogenic derivatives have been prepared by C-P cross-coupling of enantiopure alkenyl-triflates [6–8] or halides [9], P-stereogenic derivatives are neglected and their synthesis requires resolution processes [5,10]. A more appealing route to P-chirogenic phosphines relies on the use of asymmetric catalysis. To the best of our knowledge, the only example dealing with the synthesis of an enantioenriched alkenylphosphine derivative by asymmetric catalysis was reported recently by some of us [11] in the course of our studies on the hydrophosphination reaction [12–16]. We report here the preliminary results dealing with the enantioselective coupling between an achiral alkenyltriflate and a racemic secondary phosphine-borane. Indeed, although examples of enantioselective Pd-catalyzed C-P cross-coupling reaction between an arylhalide and a secondary phosphine have recently appeared in the literature [17,18], no enantioselective variant of the coupling reaction involving alkenyl derivatives has ever been reported.
2 Experimental
2.1 General comments
All reactions were carried out under nitrogen atmosphere. All glassware was flamed before use. Cyclohex-1-en-1-yltrifluoromethanesulfonate, commercially available, was distilled under reduced pressure (Kugelröhr) before use. Methylphenylphosphine-borane was prepared according to literature procedure [19]. All commercially available ligands were used as purchased.
Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) was distilled from calcium hydride and degassed before use. DMF was stored on molecular sieves, freshly distilled and degassed before use. Toluene and THF were purified by an innovative technology Pure Solv. device (activated alumina column containing a copper catalyst and molecular sieves). Pentane was distilled from calcium hydride before use.
Column chromatography was performed on Merck silica gel Si 60 (40–63 μm). Solvents were used as purchased. Thin layer chromatography (TLC) was performed on silica gel 60 F-254 plates (0.1 mm) with iodine or UV detection.
1H, 13C, 19F and 31P NMR spectra were obtained on BRUKER DPX 250 or AC 400 spectrometers, 11B NMR spectra were recorded on a BRUKER AC 400 spectrometer. 1H and 13C NMR chemical shifts are reported relative to Me4Si used as an internal standard. 31P, 19F and 11B NMR chemical shifts are reported relative to respectively H3PO4 (85%), CFCl3 and BF3.Et2O used as external references. Coupling constants are reported in Hertz (Hz).
Abbreviations are used as follows: s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, q = quartet, quint = quintuplet, sept = septuplet, oct = octuplet, m = multiplet and br = broad.
Mass spectroscopy was performed on a QTOF Micro WATERS.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) separations were achieved using the following components:
- – For flow up to 0.5 mL/min, the components are: a Waters 600 pump, a Waters 996 photodiode array detector (190–250 nm) and Millenium Software;
- – For flow below 0.5 mL/min, the components are: a Waters Alliance 2695 pump, a Waters 2996 photodiode array detector (190–250 nm) and Empower Software.
Enantiomeric excess of compound 2 was measured by HPLC using two possible different conditions:
- – Conditions A: Daicel Chiralpack OJ-H (250 × 4.6 mm, L × ID) column (n-heptane/isopropanol 90:10, 1 mL/min, tR1 = 9.34 min, tR2 = 10.95 min) at 20 °C;
- – Conditions B: Daicel Chiralpack AD-H (250 × 4.6 mm, L × ID) column (n-heptane/(MeOH/EtOH 50:50) 98:2, 0.2 mL/min, tR1 = 36.41 min, tR2 = 40.13 min) at 12 °C.
Given enantiomeric excesses of compound 2 are average of at least two experiments.
2.2 General procedures
Enantiopure catalytic systems, (R)-Tol-BINAPPdCl2 [20], (R,R)-BDPPPdCl2 [21], (R)-i-Pr-PHOXPdCl2 [22] and (S,S)-Me-DUPHOSPdCl2 [23] were synthesized according to modified literature procedures [24].
2.2.1 General procedure for the preparation of L2PdCl2
In a two-necked round bottomed flask, containing a solution of (CH3CN)2PdCl2 (0.077 M, 1 equiv.) in toluene, a solution of ligand L2 (0.077 M, 1 equiv.) in toluene is added. The mixture is stirred overnight at room temperature. The obtained precipitate is filtered, washed with freshly distilled pentane and dried under vacuum to give quantitatively the desired complex.
2.2.2 Typical procedure for palladium-catalyzed asymmetric phosphination
In a schlenk tube, flushed under N2, L2PdCl2 (0.01 mmol, 4.8 mol%) is dissolved into the solvent (0.3 mL). Cyclohex-1-en-1-yltrifluoromethanesulfonate (38 μL, 0.22 mmol, 1 equiv.), the base (0.26 mmol, 1.2 equiv.) and methylphenylphosphine-borane 1 (30 μL, 0.22 mmol, 1 equiv.) are then introduced. The mixture is stirred during a time t at the desired temperature T. The reaction is monitored by 31P NMR spectroscopy. When the expected conversion is reached, the medium is hydrolyzed with degassed water (0.5 mL). The aqueous layer is extracted with diethyl ether (3 × 2 mL). The combined organic layers are dried over MgSO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product is then purified by silica-gel column chromatography with pentane/AcOEt (95/5, Rf = 0.30) as eluent affording pure coupling product 2 as a yellow oil. All attempts to crystallize the oily product failed. Er values are measured by HPLC using conditions A or B.
2.3 Experimental data
Coupling-product 2 [934338-23-5] [8]
Anal. calcd for C13H20BP (218.1): C 71.60, H 9.24. Found: C 71.08, H 9.79. 31P NMR (161.9 MHz, CDCl3): δ 11.4 (q, 1JPB = 64.6 Hz). 1H NMR (400.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.70-7.62 (m, 2H), 7.52-7.43 (m, 3H), 6.57 (dm, 1H, 3JHP = 18.8 Hz), 2.28-2.18 (m, 2H), 2.11-1.93 (m, 2H), 1.67-1.63 (m, 4H), 1.63 (d, 3H, 2JHP = 10.0 Hz), 0.79 (q, 3H, 1JHB = 92.0 Hz). 13C NMR (100.6 MHz, CDCl3): δ 141.0 (d, 2JCP = 10.2 Hz), 131.5 (d, 2JCP = 9.1 Hz), 130.8 (d, 4JCP = 2.4 Hz), 129.9 (d, 1JCP = 54.3 Hz), 128.7 (d, 3JCP = 9.9 Hz), 128.5 (d, 1JCP = 52.5 Hz), 26.6 (d, 3JCP = 12.8 Hz), 24.7 (d, 2JCP = 6.9 Hz), 22.3 (d, 3JCP = 6.4 Hz), 21.4 (d, 4JCP = 1.3 Hz), 9.3 (d, 1JCP = 40.5 Hz). 11B NMR (128.4 MHz, CDCl3): δ -35.6 (dq, 1JBP = 64.6 Hz, 1JBH = 92.0 Hz).
Side-product 3 was isolated as a pale yellow oil (eluent: pentane/AcOEt: 95/5, Rf = 0.41). 31P NMR (161.9 MHz, CDCl3): δ 109.4 (q, 1JPB = 63.6 Hz). 1H NMR (400.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.90-7.83 (m, 2H), 7.61-7.48 (m, 3H), 5.16-5.11 (m, 1H), 2.14-2.04 (m, 2H), 2.02-1.94 (m, 2H), 1.77 (d, 3H, 2JHP = 8.8 Hz), 1.70-1.61 (m, 2H), 1.53-1.44 (m, 2H), 0.90 (q, 3H, 1JHB = 95.5 Hz). 13C NMR (100.6 MHz, CDCl3): δ 149.4 (d, 3JCP = 7.0 Hz), 132.8 (d, 1JCP = 56.0 Hz), 132.1 (d, 4JCP = 2.4 Hz), 130.7 (d, 2JCP = 11.5 Hz), 128.6 (d, 3JCP = 10.4 Hz), 111.2 (d, 2JCP = 6.3 Hz), 28.7 (d, 4JCP = 2.3 Hz), 23.6 (s), 22.7 (s), 21.6 (s), 17.1 (d, 1JCP = 46.6 Hz). 11B NMR (128.4 MHz, CDCl3): δ -36.6 (dq, 1JBP = 63.6 Hz, 1JBH = 95.5 Hz). HMRS calcd for C13H17OP ([M-BH3]+): 220.1017, found 220.1016.
Side-product 4 was isolated as a pale yellow oil (eluent: methanol, Rf = 1). 31P NMR (161.9 MHz, CDCl3): δ 25.1 (q, 1JPB = 66.0 Hz). 1H NMR (400.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.73-7.65 (m, 2H), 7.51-7.36 (m, 3H), 2.55 (s, 1H), 1.78-1.69 (m, 2H), 1.66-1.52 (m, 3H), 1.55 (d, 3H, 2JHP = 10.0 Hz), 1.52-1.48 (m, 1H), 1.48-1.38 (m, 2H), 1.12-0.18 (m, 5H). 13C NMR (100.6 MHz, CDCl3): δ133.1 (d, 2JCP = 8.2 Hz), 131.5 (s), 128.6 (d, 3JCP = 9.7 Hz), 126.5 (d, 1JCP = 50.1 Hz), 71.2 (d, 2JCP = 39.9 Hz), 41.0 (s), 31.5 (d, 2JCP = 21.4 Hz), 31.4 (d, 1JCP = 23.1 Hz), 25.0 (s), 20.4 (s), 4.4 (d, 1JCP = 38.6 Hz). 11B NMR (128.4 MHz, CDCl3): δ-35.5 to -40.0 (m). HRMS calcd for C13H19O11BP [M-3H]+: 233.1267. Found: 233.1267. HRMS calcd for C13H19OP [M-BH3]+: 222.1173. Found: 222.1186.
3 Results and discussion
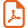
To investigate the enantioselective version, racemic methylphenylphosphine-borane 1 and achiral cyclohexenyl triflate were selected as model reaction partners. Phosphine-boranes were selected as phosphine precursors in order to ensure an easy handling of the phosphine derivatives and also to activate the P-H bond of the phosphine [25–27]. Very bulky groups on phosphorus such as isityl ((2,4,6-(i-Pr)3C6H2)) or mesityl groups were prohibited since they are not representative substituents. A preliminary study in the racemic version having shown that catalysis could take place under certain conditions by using Pd(OAc)2 and phosphine-borane 1, we decided to use only pre-formed complexes L2PdCl2 in the enantioselective version in order to avoid a possible catalysis by the susbtrate. Indeed, chiral bidentate ligands tightly bind to the metal and no displacement of the chiral ligand from the metal either by the precursor 1 or the product 2 was observed, whatever the conditions [28]. It is worthy of note that no reaction occurred in the absence of the palladium catalyst. Coupling conditions were based on those developed for the racemic coupling: 1:1 ratio of precursors (phosphine 1 and triflate), 1.2 equiv. of K3PO4 as a base, L2 chelating ligand-PdCl2 complex (4.8 mol%) as catalyst in DMSO at 80 °C (Scheme 1) [8].
Asymmetric C-P coupling of cyclohexenyl triflate and phosphine-borane 1.
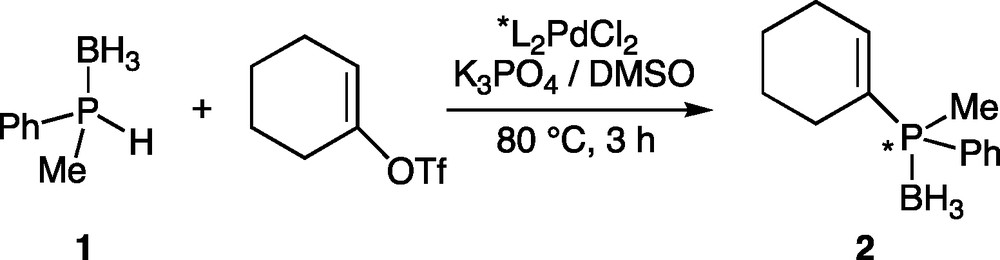
The procedure is quite simple: the pre-formed catalyst L2PdCl2 is dissolved in DMSO. Then cyclohexenyl triflate, K3PO4 and phosphine-borane 1 are added. The mixture is then heated to 80 °C and monitored by 31P NMR spectroscopy. After completion, the reaction is hydrolysed, the product is extracted and purified on silica gel chromatography under the air (allowed by the presence of the borane group) [25]. Conditions for the separation of the two enantiomers were defined by HPLC on the racemic compound, which was previously obtained by C-P cross-coupling between racemic 1 and cyclohexenyltriflate, catalyzed by dpppPdCl2 [8]. The ability of ligands L1-L4 to promote asymmetry was then evaluated (Fig. 1, Table 1).
Enantiopure ligands used in the C-P coupling reactions.
Screening of ligands.
| Entry | Ligand | Conversion of rac-1 (%)a | er of 2 (%)b,c |
| 1 | L1 | 89 | 50:50 |
| 2 | L2 | 94 | 50:50 |
| 3 | L3 | 93 | 50:50 |
| 4 | L4 | 97 | 64:36 |
a Determined by 31P NMR integration.
b Enantiomeric ratio measured by chiral HPLC (average of at least two experiments).
c Conditions used: L2PdCl2 (4.8 mol%) as precatalyst, K3PO4 (1.2 equiv.) with a 1:1 ratio of phosphine 1 and triflate, in DMSO (3 h, 80 °C).
After 3 h at 80 °C, excellent conversions were obtained whatever the ligand. Whereas most of the ligands afforded racemic 2, (S,S)-Me-DUPHOS L4, an electron-rich and rigid ligand, induced a promising level of enantioselectivity. (Table 1, entry 4). Hence, a 64:36 enantiomeric ratio was determined by HPLC. Consequently, [(S,S)-Me-DUPHOS]PdCl2 was kept for the rest of the study. A survey of reaction conditions (temperature, time) was next performed using L4PdCl2 as catalyst. Following the reaction by 31P NMR, we observed that with L4, an almost complete conversion (86%) with a similar er of 64:36 was obtained after only 30 minutes of reaction, (Table 2, entry 2) demonstrating the great efficiency of L4 compared to the achiral dppp [8], for which at least 6 h were required for a complete conversion at the same temperature (80 °C). Decrease of the temperature, from 80 to 60 then 20 °C (Table 2, entries 2–4) has only little effect on the enantiomeric ratio (er = 67:33 at 20 °C compared to 64:36 at 80 °C). However, the kinetic of the reaction was markedly lowered (86 h for a 94% conversion at 20 °C compared to 3 h for a 97% conversion at 80 °C). Furthermore, at 20 °C, together with the expected product 2, a small amount (13%) of a side-product was detected by NMR. Isolation of this product by chromatography and full characterization allowed to identify it as product 3 (Fig. 2) having an oxygen inserted in the newly created C-P bond (δ (31P) = 109 ppm) [29]. This product results from a non-catalytic process as confirmed by its formation in the absence of the palladium catalyst.
Asymmetric C-P coupling of cyclohexenyl triflate and phosphine-borane 1a.
| Entry | Temperature (°C) | Solvent | Time (h) | Conversion of rac-1 (%)b | er of 2 (%)c |
| 1 | 80 | DMSO | 3 | 97 | 64:36 |
| 2 | 80 | DMSO | 0.5 | 86 | 64:36 |
| 3 | 60 | DMSO | 3 | 93 | 64:36 |
| 4 | 20 | DMSO | 86 | 94 | 67:33 |
| 5 | 80 | DMSO | 0.08 | 23 | 66:34 |
| 6 | 60 | DMSO | 0.5 | 32 | 69:31 |
| 7 | 40 | DMSO | 2 | 24 | 74:26 |
| 8 | 20 | DMSO | 14.5 | 23 | 78:22 |
| 9d | 20 | DMSO | 14.5 | 17 | 75:25 |
| 10e | 20 | DMSO | 14.5 | 35 | 74:26 |
| 11 | 20 | THF | 14.5 | 23 | 68:32 |
| 12 | 20 | DMF | 14.5 | 20 | 75:25 |
a Catalyst: [(S,S)-Me-DUPHOS]PdCl2 (4.8 mol%), base: K3PO4 (1.2 equiv.).
b Determined by 31P NMR integration.
c Enantiomeric ratio measured by chiral HPLC (average of at least two experiments); the major enantiomer is e1.
d One equivalent of KI was added.
e One equivalent of n-Bu4NI was added.

By-product 3.
We next decided to perform the reaction under kinetic resolution conditions. Interestingly, an increase in the enantioselectivity was observed for a conversion below 50% (Table 2, entries 5–8). Hence at 60 °C, for a conversion of 32%, the enantiomeric ratio was 69:31. By lowering the temperature to 40 °C and 20 °C, enantiomeric ratios of 74:26 and 78:22 were obtained, respectively (Table 2, entries 7 and 8). Although, this enantioselectivity is not as high as might be desirable, it should be pointed out that an enantiomeric ratio of 78:22 is the best result obtained for the synthesis of P-chirogenic alkenylphosphines by asymmetric catalysis yet.1
With the aim to increase the enantiomeric ratio, various parameters were modified. First, several inorganic and organic bases were tested. The change of the base dramatically affected the rate of the coupling reaction and led to the formation of several side-products. Hence, upon replacing K3PO4 by K2CO3, side-product 3 was mainly obtained. With Cs2CO3 and Me3SiOK, 3 was formed together with another side-product 4. Characterization by NMR and HRMS allowed the determination of the structure of 4 (Fig. 3), which results from the hydrophosphination of the carbon-carbon double bond of the starting vinyltriflate, followed by the hydrolysis of the triflate into the corresponding alcohol (δ (31P) = 24 ppm). As for 3, by-product 4 results from a non-catalytic process and is formed in the absence of the catalyst. With sodium tert-pentoxide, only 4 was obtained. Moreover, whatever the base used, no improvement of the enantiomeric ratio was observed, so the preferred base was K3PO4.

By-product 4.
As already reported in the literature, adjunction of a salt like KI could influence the transmetallation step and thus affect the efficiency and the selectivity of the reaction [30]. In our case, addition of 1 equiv. of KI or n-Bu4NI showed no benefit (Table 2, entries 9 and 10). Finally, influence of the solvent was evaluated. Replacement of DMSO (ɛ = 47) (Table 2, entry 8) by a weakly polar solvent (THF, ɛ = 7.5) (Table 2, entry 11) induced a strong decrease in the enantioselectivity (er = 68:32). Interestingly, DMF (ɛ = 38) promoted a clean reaction. Hence, by-product 3, formed at 20 °C in DMSO, was totally suppressed in DMF and a satisfactory enantiomeric ratio of 75:25 was obtained (Table 2, entry 12). Conversion versus enantioselectivity was then measured in DMF at 20 °C. As anticipated, the enantiomeric ratio decreased when conversion increased (Table 3) going down from 75:25 for a 20% conversion to 70:30 for a 45% conversion and 64:36 for a full conversion.
er versus conversion at 20 °C in DMFa.
| Entry | Time (h) | Conversion of rac-1 (%)b | er of 2 (%)c |
| 1 | 14.5 | 20 | 75:25 |
| 2 | 24 | 26 | 73:27 |
| 3 | 48 | 45 | 70:30 |
| 4 | 96 | 98 | 64:36 |
a Catalyst: L4PdCl2 (4.8 mol%), base: K3PO4 (1.2 equiv.).
b Determined by 31P NMR integration.
c Measured by chiral HPLC (average of at least 2 experiments); the major enantiomer is e1.
4 Conclusion
In summary, we have demonstrated that an enantioenriched P-chirogenic alkenylphosphine could be formed by asymmetric C-P coupling reaction between an achiral alkenyltriflate and a racemic phosphine-borane. An enantiomeric ratio up to 78:22 was measured by HPLC. The evolution of the enantiomeric ratio versus the conversion seems to be in agreement with a kinetic resolution process. A mechanistic investigation to gain more information on the enantiodiscrimining step is currently underway and will be published in due course.
Acknowledgements
This work has been performed within the “CRUNCH” interregional network. We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Ministère de la Recherche et des Nouvelles Technologies, Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS), the région Basse-Normandie and the European Union (FEDER funding) for financial support.
1 Er up to 71:29 was obtained in ref. [11].