1 Introduction
Chabazite (CHA topology) is a small pore, 8-membered ring zeolite. During the last few years, Cu-modified zeolites with CHA topology in the form of silicoaluminates or silicoaluminophosphates (such as e.g., Cu-CHA, Cu-SSZ-13, Cu-SAPO-34) gained great scientific interest due to the high catalytic performance (in a large temperature range) and superior hydrothermal stability in NOx reduction [1,2]. These exceptional properties of Cu-CHA led to its implementation as part of the emission control systems for diesel-powered passenger vehicles (reduction of NOx under the highly oxidizing lean-burn conditions). Since that time, various aspects of SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalysts based on copper-modified chabazite were studied. Factors such as the form of active Cu sites [e.g., Refs. [3–5]], type of ammonia species formed on the catalyst surface and their interaction with the catalyst [e.g., Refs. [6–8]], poisoning effect of propene during SCR of NOx [e.g., Refs. [9,10]] and impact of different hydrothermal treatment and aging conditions [e.g., Refs. [10–12]] were investigated. Moreover, various experimental and kinetic modelling studies were performed [e.g., Refs. [13–15]] concerning different Cu-CHA catalysts.
Recent trends in zeolite modifications are mainly focused on the generation of mesoporosity [16,17]. The presence of micropores (pore size <2 nm) is a very important feature of zeolites, which is responsible for their various catalytic properties, including shape selectivity. However, they are also responsible for the low rate of molecule access into the zeolite crystals, as well as the unwanted adsorption effect of reactants and/or products during the catalytic process. Thus, by steric limitations, the accessibility of micropores is restricted and the catalytic potential of zeolites is not being used effectively, especially in the case of bulky molecules. It is very important to mention that the modification of zeolite porosity, despite the textural properties, also affects their acidity as well as the content, form and reducibility of the introduced transition metal species. The modification of such properties is very important for catalytic reactions (with the participation of significantly smaller molecules, such as the DeNOx process or N2O decomposition), which proceed on acid or red-ox active sites.
As found in our previous studies, micro-mesoporous zeolites obtained by different techniques such as the mesotemplate-free method [18–20], desilication [21] or delamination as well as pillaring of layered zeolites [22] are characterised by enhanced catalytic activity, improved stability and increased resistance against the coke deposit formation.
In contrast to the other zeolite topologies, the modification of the CHA framework by mesopore generation is still an open field for scientists. The reports presenting studies in this area are connected with the following methods of CHA modification: (i) preparation of the hierarchical CHA structure using the supramolecular (double templating) method [23–25] e.g., for the CO2 capture under moderate temperatures and high pressure conditions, (ii) desilication of SSZ-13 with NaOH solution for the application in the methanol-to-olefin (MTO) process [26], (iii) dealumination of CHA and SSZ-13 zeolites using ammonium hexafluorosilicate [27] and (iv) the generation of mesopores by solid templating using carbon nanoparticles or nanotubes [28].
In the presented studies, commercial CHA zeolite supplied by Clariant was modified with different amounts of copper and tested as a catalyst of two environmental processes, which is related to the reduction of nitrogen oxide emission into the atmosphere: (i) NO reduction with ammonia (DeNOx process) and (ii) N2O catalytic decomposition. The emission of NOx into the atmosphere is one of the main factors contributing to acid rain, depletion of the ozone layer and the greenhouse effect. One of the major sources of NO emission is the transportation sector and its selective catalytic reduction (DeNOx) with NH3 (Eq. 1) is considered one of the most promising technologies [29]. While in the case of N2O, the production of nitric acid is the most important anthropogenic emission source. Direct catalytic decomposition of N2O (in the presence of oxygen, which is a typical component of tail gases and is regarded as a reaction inhibitor), presented in Eq. 2, is a preferable way for its emission abatement [20].
| 4 NO + 4 NH3 + O2 → 4 N2 + 6 H2O | (1) |
| 2 N2O + O2 → 2 N2 + 2 O2 | (2) |
In the second part of the studies, the parent CHA catalyst was modified by treatment with different basic and acidic solutions (under various treatment conditions) in order to modify its physicochemical properties. The sample chosen with the optimal textural parameters was modified with copper and tested in both of the above-mentioned catalytic processes.
2 Experimental methods
2.1 Catalyst preparation
Commercial CHA zeolite used in this work was delivered in H-form by Clariant Company (Germany) in the form of silicoaluminophosphate (3.5 wt. % Si, 20.2 wt. % Al, 55,8 wt. % O, 18.7 wt. % P, and 1.8 wt. % Ti).
In the first part of the studies, the parent CHA zeolite was modified with copper by the wet-impregnation method with water solution of copper acetate tetrahydrate: Cu(CH3COO)2·4H2O. The concentration of the copper acetate solution was adjusted to introduce 1, 5, 10 and 15 wt. % of copper to the samples. After impregnation, the samples were dried at 60 °C and calcined at 600 °C for 6 h. The obtained samples were denoted as x%Cu-CHA, where x is the assumed, calculated percentage content of Cu in the samples.
In the second part of the studies, the parent CHA sample was modified in order to generate mesoporosity. For this purpose, two techniques were applied: (i) base treatment (BT) (NaOH or TPAOH (tetrapropylammonium hydroxide)) and (ii) acid treatment (AT) (HCl or Na2H2EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)). The obtained samples were denoted as: CHA(BT/AT_CMA_MA_T)t, where BT/AT is the type of modification, CMA is the concentration of the modification agent, MA is the modification agent, T is the temperature of treatment, and t is the duration of treatment. Sample codes and conditions of the performed modifications are presented in Table 1.
Sample codes, modification conditions and textural parameters of the mesostructured CHA samples.
| Sample code | MA∗ | CMA/M | Time/h | Temp./°C | SBET [m2/g] | SEXT [m2/g] | VMIC [cm3/g] | VMES [cm3/g] |
| CHA | – | – | – | – | 706 | 54 | 0.246 | 0.078 |
| CHA(BT_0.1_NaOH_20)0.5 | NaOH | 0.1 | 0.5 | 20 | 18 | 14 | 0.003 | 0.016 |
| CHA(BT_0.1_NaOH_20)1 | NaOH | 0.1 | 1 | 20 | 17 | 13 | 0.002 | 0.015 |
| CHA(BT_0.1_NaOH_20)2 | NaOH | 0.1 | 2 | 20 | 19 | 15 | 0.003 | 0.017 |
| CHA(BT_0.2_NaOH_65)0.5 | NaOH | 0.2 | 0.5 | 65 | 21 | 14 | 0.004 | 0.023 |
| CHA(BT_0.2_NaOH_65)1 | NaOH | 0.2 | 1 | 65 | 14 | 11 | 0.002 | 0.016 |
| CHA(BT_0.2_NaOH_65)2 | NaOH | 0.2 | 2 | 65 | 14 | 12 | 0.001 | 0.017 |
| CHA(BT_0.1_TPAOH_65)0.5 | TPAOH | 0.1 | 0.5 | 65 | 38 | 27 | 0.006 | 0.036 |
| CHA(BT_0.1_TPAOH_65)1 | TPAOH | 0.1 | 1 | 65 | 40 | 30 | 0.007 | 0.039 |
| CHA(BT_0.1_TPAOH_65)2 | TPAOH | 0.1 | 2 | 65 | 38 | 28 | 0.006 | 0.039 |
| CHA(BT_0.025_TPAOH_65)0.5 | TPAOH | 0.025 | 0.5 | 65 | 713 | 22 | 0.259 | 0.040 |
| CHA(BT_0.05_TPAOH_65)0.5 | TPAOH | 0.05 | 0.5 | 65 | 631 | 27 | 0.231 | 0.053 |
| CHA(BT_0.2_TPAOH_65)0.5 | TPAOH | 0.2 | 0.5 | 65 | 176 | 88 | 0.057 | 0.180 |
| CHA(BT_0.3_TPAOH_65)0.5 | TPAOH | 0.3 | 0.5 | 65 | 205 | 181 | 0.016 | 0.260 |
| CHA(AT_0.2_HCl_65)0.5 | HCl | 0.2 | 0.5 | 65 | 531 | 38 | 0.188 | 0.059 |
| CHA(AT_0.2_HCl_65)1 | HCl | 0.2 | 1 | 65 | 538 | 37 | 0.191 | 0.056 |
| CHA(AT_0.2_HCl_65)2 | HCl | 0.2 | 2 | 65 | 525 | 36 | 0.185 | 0.054 |
| CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_25)4 | Na2H2EDTA | 0.2 | 4 | 25 | 746 | 29 | 0.265 | 0.037 |
| CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_50)4 | Na2H2EDTA | 0.2 | 4 | 50 | 743 | 32 | 0.264 | 0.043 |
| CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4 | Na2H2EDTA | 0.2 | 4 | 100 | 258 | 189 | 0.030 | 0.292 |
| CHA(AT_0.04_EDTA_100)4 | Na2H2EDTA | 0.04 | 4 | 100 | 819 | 35 | 0.290 | 0.044 |
| CHA(AT_0.1_EDTA_100)4 | Na2H2EDTA | 0.1 | 4 | 100 | 657 | 54 | 0.225 | 0.064 |
| CHA(AT_0.15_EDTA_100)4 | Na2H2EDTA | 0.15 | 4 | 100 | 324 | 166 | 0.062 | 0.188 |
| CHA(AT_0.3_EDTA_100)4 | Na2H2EDTA | 0.3 | 4 | 100 | 247 | 190 | 0.025 | 0.261 |
In the case of each modification, a solution of acid or base was introduced into a round-bottomed flask and heated using an oil bath. When the proper temperature was achieved, CHA zeolite was added to the solution with 1 g of zeolite per 100 mL of solution and stirred. After the proper time, the sample was filtered and washed three times with double-distilled water. In the next step, the sample was dried at 60 °C and calcined at 600 °C for 6 h (synthesis details are presented in Table 1). When Na2H2EDTA or NaOH were used, an additional synthesis step was applied–triple ion-exchange with a solution of NH4NO3 (0.5 M, Sigma–Aldrich) at 80 °C for 1 h (ion-exchange Na+ → NH4+). Finally, the samples were washed, dried and calcined to convert NH4+ to H+ under the same conditions as in the case of the samples obtained directly in H+-form.
The chosen micro-mesoporous sample obtained in the second part of the studies (CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4) was modified with 5 wt. % of copper by using the wet-impregnation method using aqueous solution of copper acetate tetrahydrate: Cu(CH3COO)2·4H2O. After impregnation, the sample was dried at 60 °C and then calcined at 600 °C for 6 h.
2.2 Catalyst characterization
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples were recorded using a Bruker D2 Phaser diffractometer (Cu Kα radiation; λ = 1.54056 Å). The measurements were performed in the 2 theta range of 5–50° with a step of 0.02°.
Textural properties of the samples were determined by N2 sorption at −196 °C using a 3Flex v1.00 (Micromeritics) automated gas adsorption system. Prior to the analysis, the samples were degassed in a vacuum at 350 °C for 24 h. The specific surface area (SBET) of the samples was determined using the BET (Braunauer–Emmett-Teller) model according to the recommendations of Rouquerol at al [30]. The micropore volume was calculated using the Harkins and Jura model (t-plot analysis, thickness range 0.55–0.85 nm). The mesopore volume was calculated from the desorption branch using the BJH model (Kruk-Jaroniec-Sayari empirical procedure) in the range of 1.7–30 nm.
Coordination and aggregation of Cu introduced into CHA zeolite were studied by using UV–vis-DR spectroscopy. The measurements were performed using an Evolution 600 (Thermo) spectrophotometer in the range of 200–900 nm with a resolution of 2 nm.
Surface acidity (concentration and strength of acid sites) was studied by temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia (NH3-TPD). The measurements were performed in a flow microreactor system equipped with QMS detector (Prevac). Prior to ammonia sorption, a sample was outgassed in a flow of pure helium at 600 °C for 30 min. Subsequently, the microreactor was cooled to 70 °C and the sample was saturated in a flow of gas mixture containing 1 vol. % of NH3 diluted in helium for about 120 min. And then, the catalyst was purged in a helium flow until a constant base line level was attained. Desorption was carried out at a linear heating rate (10 °C/min) in a flow of He (20 mL/min).
2.3 Catalytic tests
Catalytic studies of NH3-SCR were performed in a fixed-bed quartz microreactor. The experiments were performed at atmospheric pressure and in the temperature range from 100 to 400 °C. The reactants concentration was continuously measured using a quadrupole mass spectrometer (Prevac) connected directly to the reactor outlet. For each experiment, 0.1 g of catalyst (particles sizes in the range of 0.160–0.315 mm) was placed on a quartz wool plug in the reactor and outgassed in a flow of pure helium at 600 °C for 1 h. The gas mixture containing 2500 ppm of NO, 2500 ppm of NH3 and 25,000 ppm of O2 diluted in pure helium (at a total flow rate of 40 mL/min) was used.
Catalytic studies of N2O decomposition were performed in a fixed-bed quartz microreactor. The experiments were performed under atmospheric pressure and in the temperature range from 300 to 600 °C in intervals of 50 °C. The composition of outlet gases was analysed using a gas chromatograph (SRI 8610C) equipped with TCD detector. For each experiment, 0.1 g of catalyst (particles sizes in the range of 0.160–0.315 mm) was placed on a quartz wool plug in a microreactor and outgassed in a flow of pure helium at 600 °C for 1 h. And then, the gas mixture containing 1000 ppm of N2O and 40,000 ppm of O2 diluted in pure helium (at a total flow rate of 50 ml/min) was passed over the catalyst and the reaction proceeded for about 1 h to stabilise the catalyst. The analysis of the outlet gases was performed 20 min after temperature stabilisation and a steady state regime was achieved.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Conventional (microporous) CHA zeolite
The crystalline structure of the parent CHA zeolite and the samples modified with different amounts of Cu were investigated by using the XRD method (Fig. 1). The XRD pattern of the starting material corresponds to patterns of the CHA chabazite structure [31]. However, the analysis of the parent sample diffractogram with X'Pert HighScore (PDF-4+ database) revealed the presence of impurities in the form of silicoalumnophosphate SAPO-11 (AEL topology) and titanium-phosphorus oxide (TiP2O7). The modification of CHA with copper by using the incipient wetness impregnation method (with the assumed Cu wt. % of about 1, 5, 10 and 15) did not influence the crystalline structure of the samples; however, the intensity of the reflections slightly decreased. Moreover, in the case of the samples with the copper content above 1%, new reflections at about 35.7° and 38.9° 2θ appeared, which is connected to the formation of CuO aggregates on the catalyst surface. The average CuO crystal sizes calculated using Scherrer's equation (k = 1, λ = 0.154 nm) for (111) reflection are in the range of 30–40 nm.

XRD patterns of the parent CHA and the samples modified with Cu.
The textural properties of the parent CHA zeolite and its modifications with different amounts of copper were characterised by using the low-temperature N2 sorption (Table 2). CHA zeolite used in the presented studies is characterised by the relatively high BET surface area (about 700 m2/g) and micropore volume (about 0.240 cm3/g). After modification of the samples with copper, values of textural parameters (such as BET surface area, external surface area, and volume of micro- and mesopores) decreased. The observed changes can be connected to a partial blocking of the zeolite pores by CuO aggregates, which led to a decrease in BET and external surfaces of the samples. Not all changes in the textural properties had a similar trend, which can be connected to the random deposition of copper oxide aggregates; however, the BET surface area and the volume of micropores decreased together with an increase in the Cu content of the samples. Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms obtained for all the samples (Fig. 2) are of type I(a) (according to the IUPAC classification [32]), which is characteristic of microporous materials. The slight increase in the adsorbed N2 volume at higher partial pressures can be connected to the inter-particle porosity. After modification with copper, the sorption isotherms shifted to lower values of adsorbed nitrogen, which corresponds to a decrease in the BET surface area and micropore volume of the samples.
Textural properties of the samples determined from the N2-sorption measurements.
| Sample code | SBET [m2/g] | SEXT [m2/g] | VMIC [cm3/g] | VMES [cm3/g] |
| CHA | 706 | 54 | 0.246 | 0.078 |
| 1%Cu-CHA | 679 | 14 | 0.243 | 0.030 |
| 5%Cu-CHA | 631 | 33 | 0.222 | 0.053 |
| 10%Cu-CHA | 570 | 19 | 0.202 | 0.026 |
| 15%Cu-CHA | 550 | 23 | 0.193 | 0.031 |
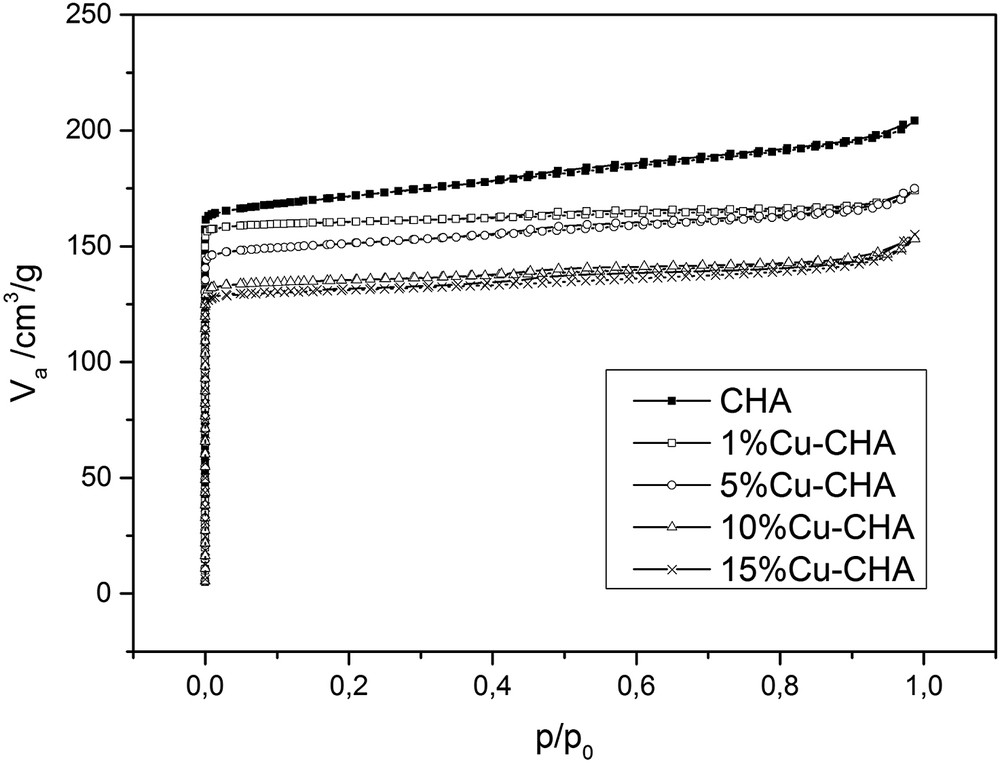
Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms of the parent CHA and the samples modified with Cu.
The coordination, aggregation and oxidation state of copper species deposited on CHA zeolite was examined by using the UV–vis-DR spectroscopy (Fig. 3). The obtained spectra indicated the presence of four absorption bands, which can be assigned to (i) charge transition between the zeolite lattice oxygen and isolated Cu+/Cu2+ cations (about 220–230 nm), (ii) two charge transfer bands in CuxOy complexes, which can be attributed to OCuO and CuOCu respectively (about 250–450 nm) and (iii) d–d transitions in dispersed CuO particles, where Cu2+ is surrounded by oxygen in distorted octahedral coordination (about 600–800 nm) [33–35]. Moreover, the absorption at about 650 nm is related to the presence of bulk CuO, the presence of which was also confirmed by XRD analysis [36,37]. Together with an increase of the copper content in the samples, the bands related to aggregated copper species appeared. The absorption in the range of 400–900 nm was observed for the sample with Cu loading above 5 wt. %, which is in agreement with the presence of CuO reflections in XRD patterns for this series of samples.
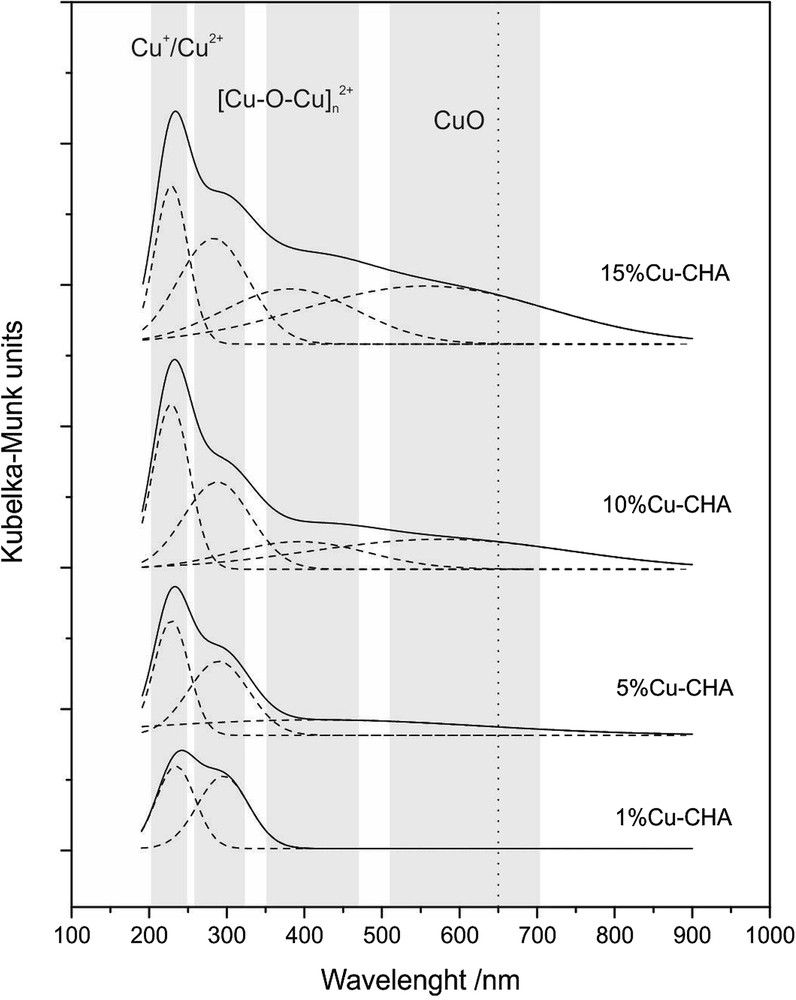
UV–vis-DR spectra of the CHA samples modified with Cu.
The obtained samples modified with copper were examined in two catalytic reactions: DeNOx process (Fig. 4A) and N2O decomposition (Fig. 5). In the case of both reactions, the unmodified CHA sample does not show any catalytic activity. After modification with copper, the catalytic activity of the samples significantly increased. In the case of the former reaction, the NO conversion increased together with an increase of the copper content up to 10%. The differences in NO conversions obtained for the samples modified with 5, 10 and 15 wt. % of Cu are very small and close to the experimental error. However, the conversion drop observed in the case of 15%Cu-CHA could be connected to the high Cu content resulting in the formation of CuO aggregates on the catalyst surface and partial blockage of micropores (decrease in the catalyst BET surface area). The reaction selectivity to N2 is significantly high in the case of all samples (above 90%) and remains stable over a wide temperature range (only slight drop at high temperatures was observed). The lower reaction selectivity to nitrogen was connected with the increased Cu content, which is especially evident in the case of the 15%Cu-CHA sample. Yu et al. [38] identified surface CuO aggregates as a phase responsible for the consumption of ammonia and the formation of N2O at high temperatures. Also, Yashnik et al. [39] recognised CuO-like species as copper sites with the relatively low activity in NO-SCR, which corresponds to the presented results.
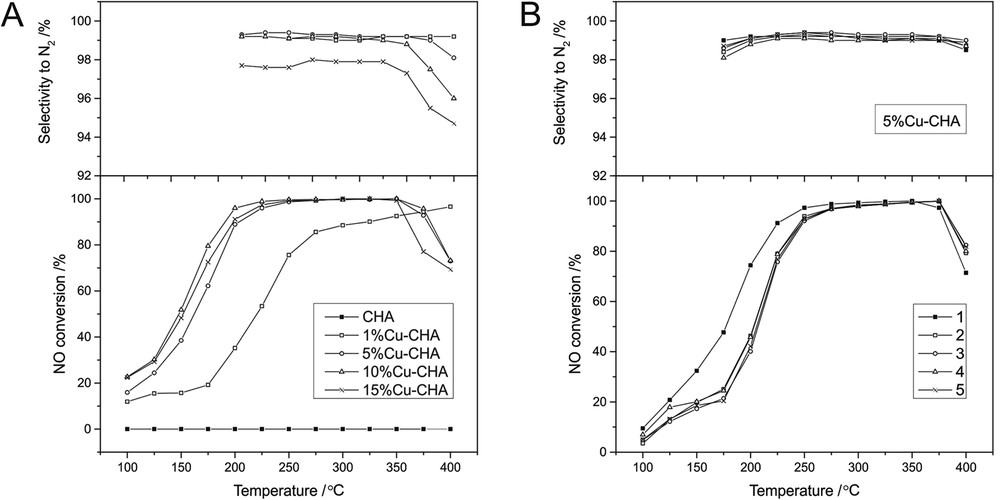
Temperature dependence of NO conversion and N2 selectivity in SCR of NO with NH3 for the CHA samples modified with Cu (A) and for 5%Cu-CHA (stability test) (B). Conditions: the balancing gas is 2500 ppm NO, 2500 ppm NH3, 25,000 ppm O2; He; the total flow rate is 40 ml/min; and the weight of the catalyst is 0.1 g.
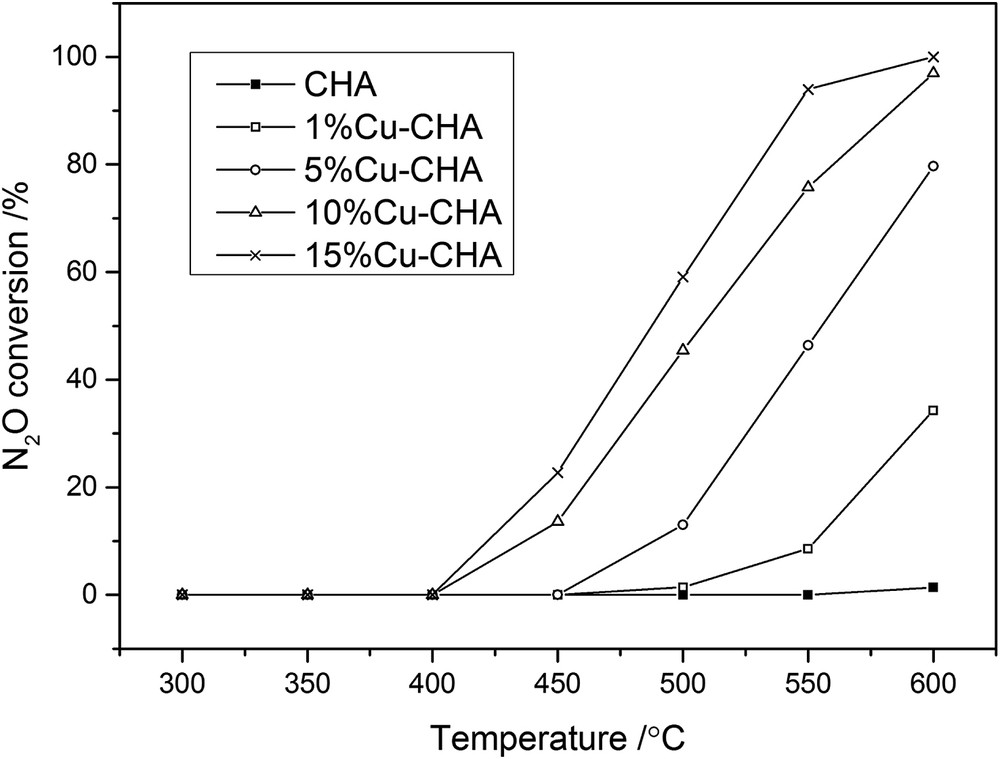
Temperature dependence of N2O conversion for the CHA samples modified with Cu. Conditions: the balancing gas is 1000 ppm N2O, 40,000 ppm O2; He; the total flow rate is 50 ml/min; and the weight of the catalyst is 0.1 g.
This phenomenon can be connected to the competition to the DeNOx process side-reaction of direct ammonia oxidation by oxygen at high temperatures. Ammonia can be oxidised to different nitrogen oxides (Eq. 3–5), which was also observed in the present studies; together with an increase in the copper content, the reaction proceeded toward N2O (Eq. 4). N2O could also be produced by the non-selective reduction of NO with ammonia (Eq. 6). However, a decrease in NO conversion highlights ammonia consumption in a side-reaction.
| 4 NH3 + 3 O2 → 2 N2 + 6 H2O | (3) |
| 2 NH3 + 2 O2 → N2O + 3 H2O | (4) |
| 4 NH3 + 5 O2 → 4 NO + 6 H2O | (5) |
| 4 NO + 4 NH3 + 3 O2 → 4N2O + 6 H2O | (6) |
In the case of the second studied reaction (N2O decomposition, Fig. 5), the catalytic activity increases continuously with an increase in the copper content (the best results were obtained for the 15%Cu-CHA sample). The only nitrogen product detected in this reaction was N2. Taking into account the mechanism of N2O decomposition, in which the rate-determining step is the recombining of desorbing oxygen atoms adsorbed on Cu sites, the overall reaction rate is higher for samples with higher Cu loading (shorter CuCu distance) [40]. Groothaert et al. [41,42] attributed the high catalytic activity of Cu-modified zeolites in N2O decomposition to the presence of Cu-dimers, bridged by two adsorbed oxygen atoms (from which O2 can be easily desorbed), which are the so-called bis(μ-oxo)dicopper species. Thus, the increased catalytic activity in the Cu-CHA series can be related to the increase in the Cu content (decreased distance between the active sites) which facilitated oxygen desorption. It is worth noting that together with an increase in the copper content, the contribution of the CuxOy oligomeric species, which are expected as the most active in this reaction, also increased (Fig. 3).
Taking into account the very high activity of the Cu-modified CHA samples in the DeNOx process, the stability of such a system in this reaction was examined. Among the catalysts with different Cu contents, the 5%Cu-CHA sample was chosen (due to its high NO conversion and selectivity to N2 with simultaneous low copper content (economical issue)) to perform the stability test. Over the chosen sample, five cycles of the catalytic test were conducted without any catalyst regeneration (Fig. 4B). After the first catalytic test, a small drop in NO conversion was observed in the low temperature range (100–275 °C). At higher temperatures (275–350 °C), when the conversion reaches about 100%, the results do not practically differ from each other. During subsequent cycles, NO conversion remained practically unchanged. Also, in the case of reaction selectivity to N2, no significant changes were observed. It seems that after the first catalytic run, the steady-state was obtained and the 5%Cu-CHA sample showed high stability during further cycles.
3.2 Mesopore-structured CHA zeolite
In the second part of the studies, CHA zeolite was modified by the use of base and acid solutions of various agents (with different concentrations), temperatures and durations of treatment (all modification parameters are presented in Table 1). The efficiency of the base and acid treatments was evaluated based on the changes in textural properties of the samples (SBET, SEXT, VMIC, and VMES; Table 1). Upon base treatment with NaOH (the most frequently used desilication agent), a significant dissolution of CHA was observed. All of the textural parameters decreased significantly, even under relatively mild conditions (0.1 M NaOH, 0.5 h, 20 °C), which can be related to the low stability of aluminophosphate domains in alkaline media [43] (the content of phosphorus in the sample is significantly high). The application of weaker base solutions, such as quaternary amines (TPAOH), is known as a way for the generation of mesoporosity in zeolites with better preservation of their microporosity [44,45]). The best results were obtained with the use of TPAOH, when 0.2 and 0.3 M solutions were used, at 65 °C and for 0.5 h (the CHA(BT_0.2_TPAOH_65)0.5 and CHA(BT_0.3_TPAOH_65)0.5 samples). In the case of these samples, base treatment resulted in a significant development of the external surface area and mesopore volume, accompanied by a decrease in the BET surface area and micropore volume. In the case of the CHA(BT_0.3_TPAOH_65)0.5 sample, such modification of treatment conditions enabled the mesopore volume of CHA to increase by about 3 times. The use of strong acidic conditions (0.2 M HCl, 65 °C, 2 h) did not significantly influence the CHA porosity (all the textural parameter values were slightly decreased), in contrast to the use of NaOH solution, showing the higher sensitivity of the parent sample for the alkaline conditions. Acid treatment with Na2H2EDTA under mild conditions (low concentration–0.04 M or low temperature–25–50 °C; the CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_25)4, CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_50)4 and CHA(AT_0.04_EDTA_100)4 samples) enhanced the crystallinity of the CHA material. Both the BET surface area and volume of micropores increased, which could be connected to the dissolution of extra-framework aluminium or other impurities and resulted in enhanced microporosity [43]. More severe conditions resulted in a significant enhancement of mesoporosity and external surface area of the samples. The best results were obtained in the case of the CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4 sample, which was characterised by a mesopore volume that was almost 4 times greater than that of the parent CHA. Thus, the best results for mesopore formation were obtained with the use of TPAOH and Na2H2EDTA; however, taking into account the greatest volume of generated mesoporosity and the smallest decrease in SBET and VMIC, the CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4 sample was chosen as the most promising for further modification with copper and expanded physicochemical characterisation.
A comparison of N2 sorption isotherms of the parent CHA and the mesopore-modified CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4 sample is presented in Fig. 6A. A decrease in the adsorbed N2 volume at low partial pressures is connected with the loss in microporosity. At higher partial pressures after porosity modification, a hysteresis loop, which is the result of capillary condensation, appeared in mesopores. The shape of the loop can be classified as H4 (according to the IUPAC classification [32]), which is characteristic of mesoporous zeolites with a wide distribution of pore sizes.
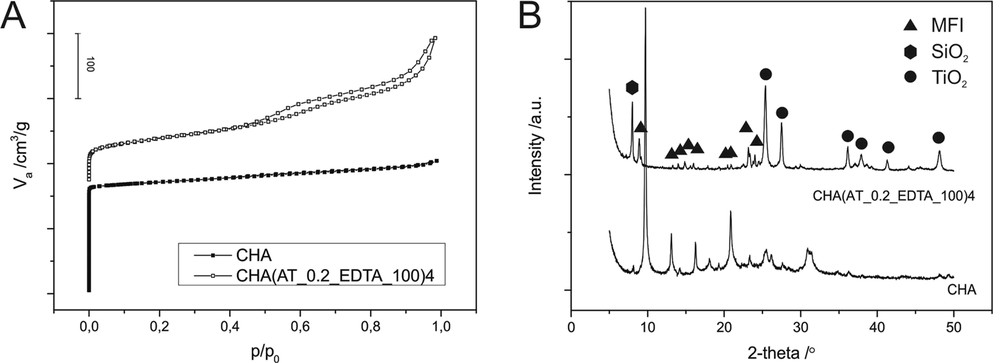
Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms (A) and XRD patterns (B) of the parent CHA and the micro-mesoporous sample CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4.
The modification of the porous structure also resulted in the changes of phase composition of the parent sample. Fig. 6B shows XRD patterns of the unmodified CHA material and the sample after treatment with Na2H2EDTA. The analysis of the obtained diffractogram with X'Pert HighScore (PDF-4+ database) revealed the presence of silicoaluminate of the MFI structure, silicon oxide and TiO2 in the form of rutile and anatase. This result suggests the dissolution of the parent material and the formation (besides Si and Ti oxides) at high temperatures (100 °C) of a new phase with MFI topology or selective dissolution of the zeolite framework (dissolution and reverse incorporation), which resulted in a different zeolite structure. It is worth noting that, despite the partial transformation of the zeolitic matrix into MFI zeolite, the properties of the resulting material are significantly different in comparison to conventional ZSM-5 zeolite. The volume of micropores in the modified material is very low for the zeolite material, which means that the content of the MFI phase is relatively low and the majority of the sample consists of mesoporous TiO2 and SiO2.
The changes in the porous structure and phase composition observed after acid treatment of CHA were accompanied by changes in the strength and concentration of acid sites. Fig. 7A shows the NH3-TPD profiles of CHA and the modified CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4 sample. In the case of both samples, two desorption maxima attributed to weak (about 200 °C) and strong acid sites (about 400 °C) were obtained [1,46]. After the modification of CHA with Na2H2EDTA, the concentration of acid sites significantly decreased (about 4.5 times), which can be connected to both a decrease in the external surface area and the extraction of framework aluminium. Moreover, the high-temperature peak was shifted to lower temperatures in comparison to the parent sample (overlapped with the low-temperature peak). This proves that the applied modification method disturbed the structure of CHA and resulted in a smaller quantity of acid sites of lower strength.
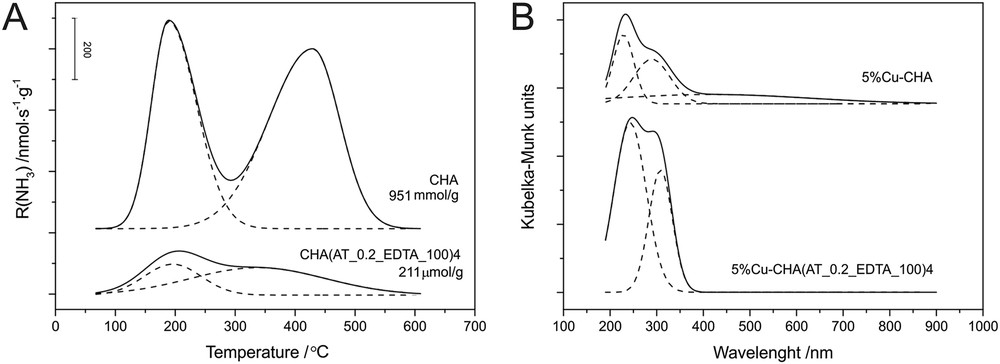
NH3-TPD profiles (A) and UV–vis-DR spectra (of the samples modified with Cu) (B) of parent CHA and the micro-mesoporous sample CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4.
The changes in the porous structure and acidity caused by dealumination of zeolite with Na2H2EDTA also influenced the form and content of the introduced copper species. Fig. 7B shows the UV–vis-DR spectra of CHA and CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4 modified with 5 wt. % of copper by using wet impregnation. The generation of mesoporosity resulted in the introduction of copper, mainly in the form of monomeric cations and small CuxOy aggregates (absorption at about 200–400 nm). Moreover, the contribution of the oligomeric CuxOy species increased in relation to monomeric copper cations. It can be concluded that the modified porous structure increased accessibility to the ion-exchange positions in the sample. Thus, the formation of Cu sites with high dispersion was favoured and the formation of bulk CuO on the catalyst surface was not observed.
The influence of the applied modifications of the parent zeolite on its catalytic activity in both considered processes (NO reduction with NH3 and N2O decomposition) is presented in Fig. 8. In the case of the DeNOx process (Fig. 8A), the NO conversion over the modified CHA sample slightly decreased in comparison to conventional zeolite. The difference in the catalysts' activities was observed, especially at higher temperatures (300–400 °C). The drop in NO conversion at this temperature range can be connected to the competitive side-reaction of direct ammonia oxidation (Eq. 3–5), which suggests that the CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4 sample could be considered a better catalyst of the ammonia oxidation reaction. Especially, the selectivity of this process to nitrogen did not change significantly (results are not shown), which means that the main product of ammonia oxidation was nitrogen (Eq. 3).
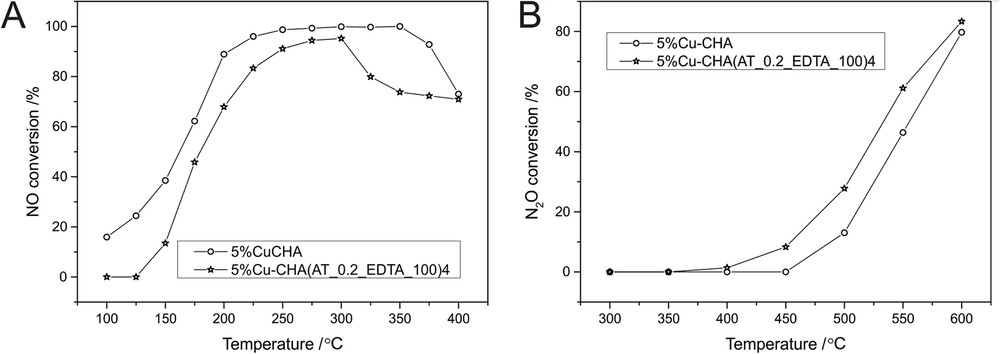
Temperature dependence of NO (A) and N2O (B) conversion over 5%Cu-CHA and 5%Cu-CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4. Conditions: the balancing gas is 2500 ppm NO, 2500 ppm NH3, 25,000 ppm O2 and the total flow rate is 40 ml/min (A) and the balancing gas is 1000 ppm N2O, 40,000 ppm O2 and total flow rate 50 ml/min (B); He is the balancing gas and the weight of the catalyst is 0.1 g.
The lower activity of the modified sample in comparison to the parent CHA material can be connected to the decreased BET surface area and acidity, which are important factors in the DeNOx process.
The comparison of catalytic activity of the 5%Cu-CHA and 5%Cu-CHA(AT_0.2_EDTA_100)4 samples in N2O decomposition is presented in Fig. 8B. The treatment of CHA with Na2H2EDTA resulted in an increase in the catalytic efficiency. N2O decomposition proceeds with the contribution of red-ox active sites, so that the higher catalytic activity of the modified sample can be related to the higher contribution of oligomeric CuxOy species; these were found as active Cu forms in this reaction. However, the high contribution of TiO2 in the modified sample can also play a significant role in N2O decomposition. TiO2 is known as an active component in this reaction, used both as the catalyst promoter [47] and the support [48]. The role of TiO2 in this process could be related to the facilitation of oxygen species migration (through the oxygen vacancies sites) and its easier recombination [49] (oxygen desorption from the catalyst surface is regarded as a rate-determining step of this reaction).
4 Conclusions
Commercial CHA zeolite supplied by Clariant Company, modified with copper by wet impregnation method, was examined as a catalyst in two catalytic reactions: NO reduction with NH3 and N2O decomposition; this showed high catalytic activity, especially in a former reaction. Among the studied catalysts with various Cu contents (1, 5, 10 and 15%), the sample modified with 5 wt. % was chosen as the optimal sample; for this sample, the high catalytic stability in five subsequent reaction cycles was observed.
Modification of CHA by base and acid treatment with NaOH/TPAOH and HCl/Na2H2EDTA under various conditions enabled the selection of optimal modification parameters, resulting in the highest generated mesopore volume. Based on the results of nitrogen sorption measurements, the sample modified with 0.2 M Na2H2EDTA at 100 °C for 4 h was chosen as the most promising for the more detailed catalytic studies. The physicochemical characterisation of the mesopore-modified sample by using X-ray diffraction, NH3-TPD and UV–vis-DR spectroscopy (the sample modified with Cu) revealed the changes in the phase composition, decrease in surface acidity and differences in the form of introduced copper species. The applied modification methods increased the catalytic efficiency of the Cu-CHA zeolite in N2O decomposition, which can be related to the higher contribution of Cu species in a less-aggregated form (mainly in the form of monomeric cations and CuxOy aggregates, which are known to be active in this reaction) and the higher contribution of TiO2.
In conclusion, modification of the CHA zeolite by the applied methods enabled the adjustment of its porous and crystalline structure, acidity and form of introduced transition metal species, which increased its catalytic activity in the process of N2O decomposition. Thus, based on the presented results, modification of the commercial CHA zeolite (Clariant) can influence its activity in catalysis.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Clariant Company for the providing of the CHA zeolite material for this research work.
This work was financed from the budget for science of the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education in the years 2016/2019, under project No. 0670/IP3/2016/74.
One part of the research was carried out with the equipment purchased thanks to the financial support of the framework of the Polish Innovation Economy Operational Program, the European Regional Development Fund (contract No. POIG.02.01.00-12-023/08).


