1 Introduction
Cancer continues to pose significant health problems worldwide. The importance of research of new robust anticancer agents is essential in improving the success rates in treating cancer because chemotherapy used for the cancer victims constantly exhibits some undesirable side effects. The biological activity manifested by many polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons makes them attractive targets for organic chemists to synthesize medicinal motifs. Cytotoxicity is one of several important biological effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Therefore, many intensive efforts have been made for the discovery and development of new cytotoxic molecules [1,2]. As far as we know, phenanthrene derivatives are one of the most stable fused aromatics [3–5]. Therefore, the synthesis and bioactivity evaluation of phenanthrenes received much attention and interests in medicinal chemistry [6–9]. They can be obtained by a near endless list of reactions and transformations [10]. The oxidative photochemical cyclization of stilbenes is an important methodology used to prepare a large number of differently substituted phenanthrenes [11]. By modifying the core phenanthrene structure, it is possible to obtain a wide variety of tricyclic compounds, which have become of particular interest to chemists because of their range of different biological properties [12]. Thus, the construction of an aryl-heteroatom bond is an important study, in particular, the formation of carbon–nitrogen [13] and carbon–oxygen bonds [14]. Such compounds have been demonstrated to possess various biological activities.
A literature survey shows that in phenanthrene 1 the electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions can be performed. However, this compound also gave rise to addition reactions on the double bond between carbons 9 and 10 (Fig. 1), which showed a strong olefinic character [15]. For instance, 9,10-phenanthrenequinone 2 can be prepared from phenanthrene 1 by several methods [16–18] (Fig. 1). Dicarbonylated compound 2 enables several types of chemical reactions of considerable importance in organic synthesis [19–21], especially electrophilic aromatic substitution and condensation, being an excellent starting material to prepare relatively simple and bioactive substances [22,23].
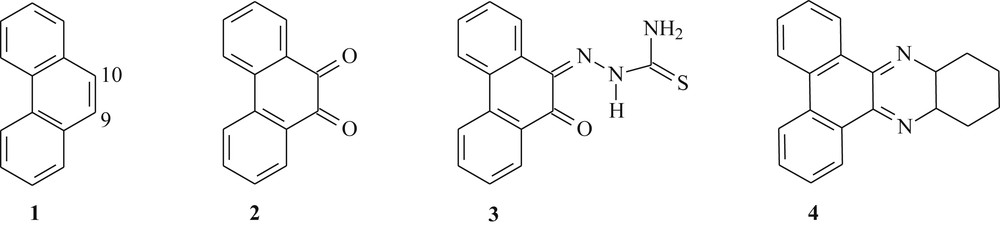
Chemical structure of the reported phenanthrene derivatives (1–4).
Quinones represent the second widest class of clinically approved antitumor agents [24]. Recently, Afrasiabi et al. [25] synthesized the phenanthrenequinone thiosemicarbazone 3 (Fig. 1) through the condensation reaction between 9,10-phenanthrenequinone 2 and thiosemicarbazide. Compound 3 has been complexed with metals, copper, nickel, and cobalt, and evaluated for anticancer activity in human breast cell line T47D rich in progesterone receptors.
Phenazine derivatives have attracted much attention because of its biological actions [26]. Thus, with the significant advances in the field of molecular biology, Einat et al. [27] prepared the phenazine 4 via condensation reaction of o-diaminocyclohexane with 9,10-phenanthrenequinone 2 (Fig. 1). This compound presented an antileukemic activity in vitro against Philadelphia-positive cells in patients with Philadelphia-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase and blastic crisis.
Unfortunately, the number of chemical and pharmacological studies on phenanthrene derivatives is limited, despite being very important with good works. To prepare new compounds with interesting biological activity it is necessary to improve research about synthesis and evaluation of derivate compounds from phenanthrene.
Thereby, with the aim of developing our ongoing research for synthesis of biologically active compounds containing a core phenanthrene structure as promising derivatives for the development of anticancer agents, herein we describe the results of an exploratory study using a simpler procedure for effecting transformations in a variety of phenanthrenes and in vitro cytotoxic activity against two tumor cell lines, including Hep-2 and Caco-2 cell lines. The present study is an attempt to investigate whether the different substituents in the phenanthrene skeleton can change or improve the activity to discern structure–activity relationships. Most compounds exerted cytotoxic effects with selectivity against both of the cell lines.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Synthesis
The starting phenanthrenes 9a–d have been prepared through a two-step sequence involving the Mizoroki–Heck coupling reaction followed by oxidative photocyclization (see Scheme 1). With respect to the Mizoroki–Heck reaction, this coupling reaction offers a simple and direct approach toward a series of stilbene as precursors for phenanthrene derivatives [28,29]. A great variety of literature conditions for the Mizoroki–Heck reactions can be performed [30,31]. The use of sodium acetate acting as a base, 1 mol % of Herrmann's palladacycle {trans-di(μ-acetato)-bis[o-(di-o-tolylphosphino)benzyl]dipalladium} as a catalyst, and N,N-dimethylacetamide as a solvent allows the straightforward and economic synthesis of substituted stilbenes mainly of (E) configuration (Scheme 1) [32,33].
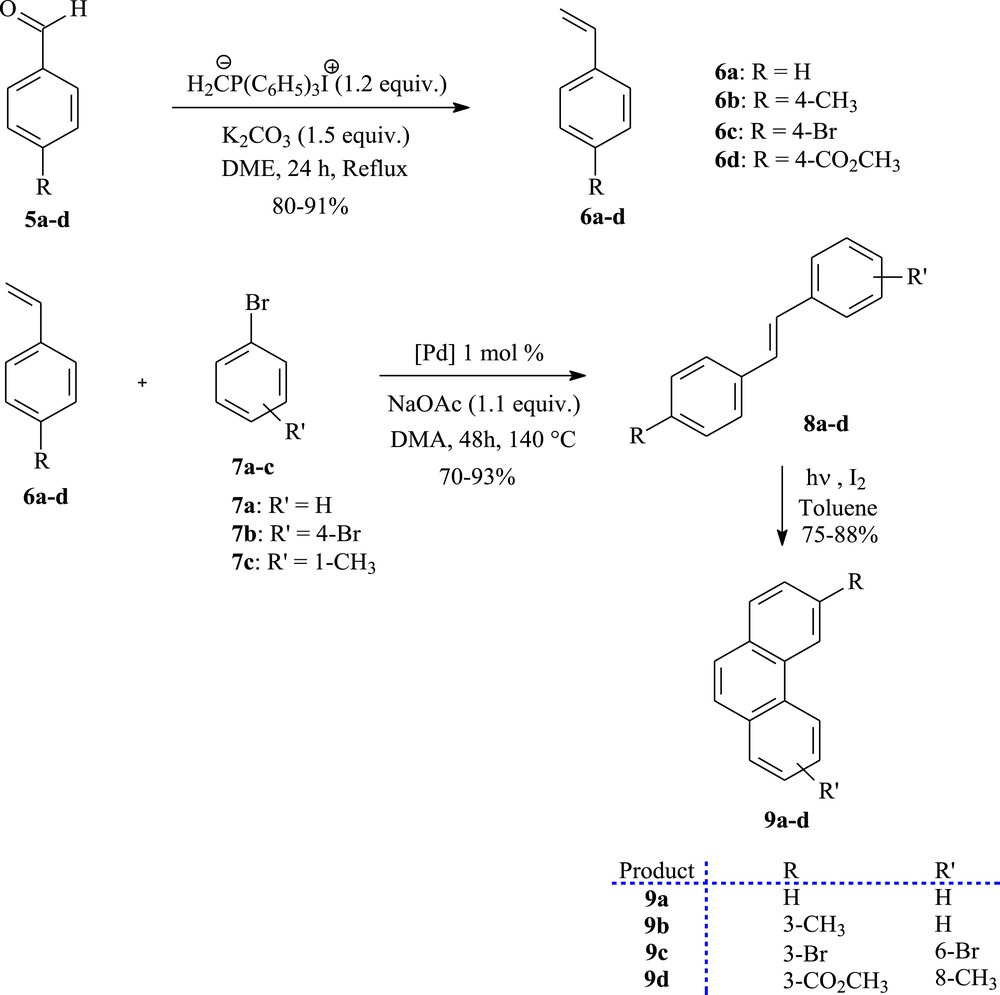
The photoconversion of stilbenes (8a–d) to phenanthrenes (9a–d).
First of all, Wittig reaction of suitable commercially aryl aldehydes 5a–d with methyltriphenylphosphonium iodide [34] in the presence of K2CO3 in DME, provided the matching styrene derivatives 6a–d as starting materials (Scheme 1). Their palladium promoted Mizoroki–Heck coupling with various bromo benzenes 7a–c gave the trans-stilbene analogues 8a–d in good yields.
Having obtained the stilbenes precursors, we were able to complete the convergent synthesis of the starting phenanthrenes skeleton 9a–d. Therefore, each olefin underwent photocyclization in the presence of a catalytic amount of iodine as the oxidizing agent [35]. Photolysis of 8a–d was performed in toluene on a 500 mg scale per run in a 1.5 L reactor for about 4 h to afford the photoproducts 9a–d in 75–88% yields, after purification by column chromatography.
Afterward, the synthetic pathway for the synthesis of the derivate compounds from phenanthrene 10a–d and 11a–d exhibiting cytotoxic activity is shown in Scheme 2. The phenanthrene derivatives were converted into the corresponding ortho-quinones 10a–d, in 75–94% yields, by oxidation using chromium trioxide in glacial acetic acid [10,36]. The dicarbonylated compounds react with o-diaminobenzene in ethanol/acetic acid to give the dibenz[a,c]phenazine derivatives 11a–d in 85–96% yields [37].
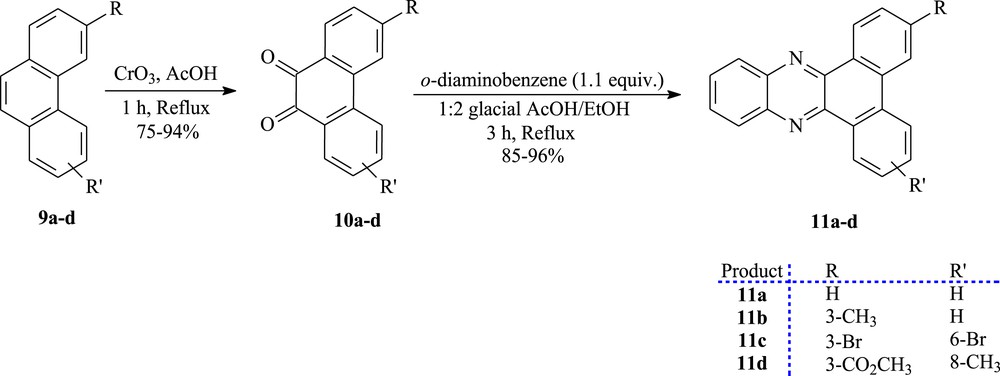
The synthesis of ortho-quinones (10a–d) and dibenz[a,c]phenazines (11a–d).
To prepare other new tricyclic systems, 9,10-phenanthrenequinone 10a was chosen as the suitable starting material. As summarized in Scheme 3, the key to the procedure is the discovery of a way to prepare the 3,6-diacetyl-9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 13 in 91% yield by the Friedel–Crafts acetylation, in the presence of 2 equiv of AlCl3, to introduce acetyl groups specifically at both 3- and 6-positions of 9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 12. The latter compound can be obtained from 9,10-phenanthrenequinone 10a. Reduction of 10a with Na2S2O4 followed by an in situ O-ethylation using bromoethane afforded the 9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 12 in 86% yield [38]. The methyl ketone 14 can also be obtained in 78% yield from the 9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 12 by acetylation. We have found that when 1 equiv of AlCl3 was used, no diacetylated product was formed [39]. On the other hand, sulfonation of phenanthrenequinone 10a with concentrated sulfuric acid, followed by neutralization with sodium hydroxide, gave the phenanthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid (sodium salt) 15 in 72% yield. The residual amount of quinone 10a was monitored by the solubility of a sample of the reaction mixture in water [40].
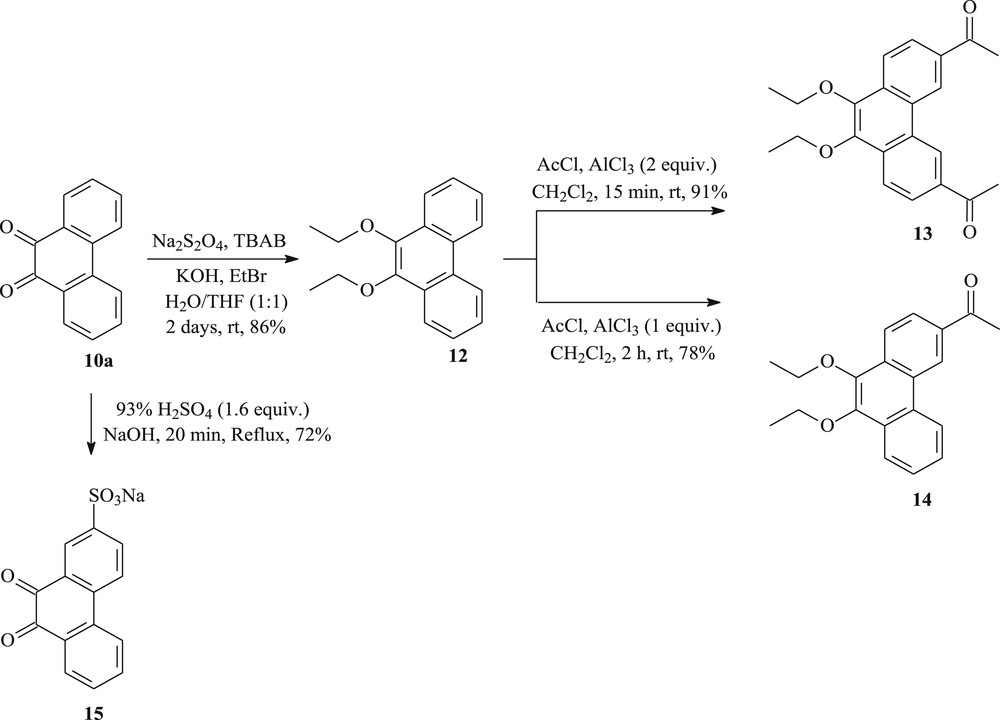
The synthesis of new phenanthrenes (12–15) from 9,10-phenanthrenequinone.
2.2 In vitro cytotoxic activity
In vitro cytotoxicity of compounds 10–15 was evaluated using the (MTT) colorimetric assay [41,42] against the human epidermoid carcinoma epithelial cells Hep-2 [43] and the human colon carcinoma cells Caco-2 [44].
The cytotoxic activity data of the derivate compounds from phenanthrene, which have been treated with test compound at various concentrations (1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 μg/mL), are shown in Fig. 2a and b. The cell growth-inhibitory potencies against both the cell lines, expressed as IC50 values are summarized in Table 1.
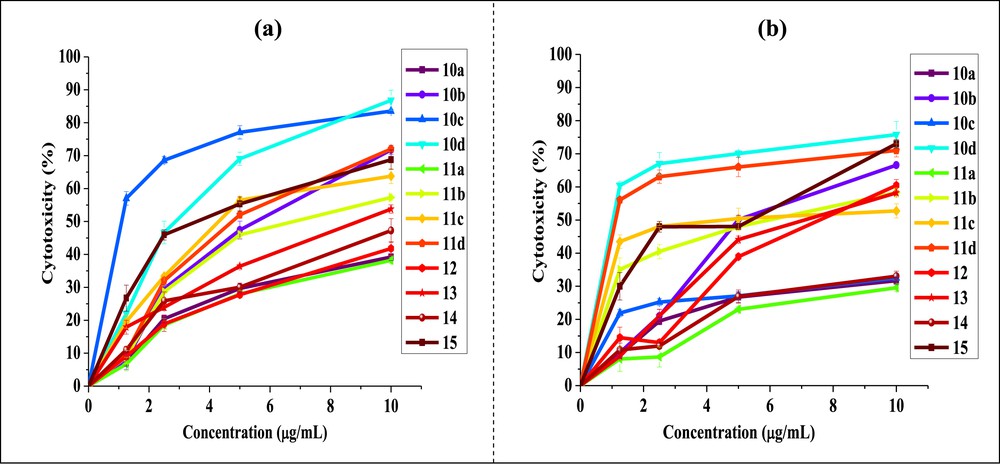
Cytotoxicity at different concentrations of phenanthrene derivatives against (a) Hep-2 and (b) Caco-2 cell lines (values were expressed as the means ± standard deviation of three experiments).
IC50 values for phenanthrene derivatives against Hep-2 and Caco-2 cancer cells.
| Entry | IC50 (μg/mL) | |
| Hep-2 | Caco-2 | |
| 10a | >10 | >10 |
| 10b | 5.50 | 4.93 |
| 10c | 1.06 | >10 |
| 10d | 2.81 | 0.97 |
| 11a | >10 | >10 |
| 11b | 6.75 | 5.64 |
| 11c | 4.24 | 3.93 |
| 11d | 4.75 | 1.09 |
| 12 | >10 | 7.51 |
| 13 | 8.88 | 6.93 |
| 14 | >10 | >10 |
| 15 | 3.55 | 5.33 |
Overall results suggested that nature and position of the substituents attached to the phenanthrene skeleton had a considerable impact of the anticancer effect of tested molecules. As shown in Table 1, most compounds exhibited significant cytotoxic activity with selectivity against both cell lines. We have made an effort to establish a correlation between the observed cytotoxicity of these compounds with the nature of substituents present on peripheral positions of the phenanthrene skeleton. In this context, unsubstituted compounds 10a and 11a show no selectivity for cancer cell lines (IC50 > 10 μg/mL). The difference in the biological activity might be linked with the following structural features: (1) derivatives bearing the electron donor substituents attached directly to the phenanthrene skeleton, and (2) the presence of substituent that displays mesomeric effects in the molecule [45]. It was clear from the aforementioned results that when these substituents were abolished the cytotoxic activity against both tested human cancer cell lines was diminished drastically.
Interestingly, new quinone 10d exhibited potent cytotoxicity against both Hep-2 (IC50 = 2.81 μg/mL) and Caco-2 (IC50 = 0.97 μg/mL) cell lines. The cytotoxicity can be enhanced by the electrophilic methyl group at position 8 of the quinone. On the other hand, new phenazine 11d was found extremely active against Caco-2 cell line with IC50 value of 1.09 μg/mL. Consequently, we can conclude that the derivates (10d and 11d) might serve as powerful new cytotoxic agents and need to be investigated further. In addition, the cytotoxicity of 10b and 11b has a noticeable decrease comparing with that of 10d and 11d against the two cancer cell lines used. It appears that the presence of ester functionality attached at the position 3 of compounds 10d and 11d may explain their promising activity compared to that of the rest of analogues.
Interestingly, derivates 10c, 11c, and 15 display a positive mesomeric effect. By taking into account the influence of both bromine atoms at the 3- and 6-positions of compounds 10c and 11c and the SO3 group at position 2 of sulfonated quinone 15 can be quite favorable for cytotoxic activity. Despite this, quinone 10c did not display activity against Caco-2 cell line (IC50 > 10 μg/mL). On the other hand the data (Table 1) suggest obviously that 10c showed the best cytotoxicity against Hep-2 cell line with IC50 value of 1.06 μg/mL, whereas phenazine 11c displayed the better cytotoxic effect whose IC50 value for Caco-2 was 3.93 μg/mL.
Furthermore, the selectivity of the cytotoxicity of derivates 12 and 13 was also observed; they showed a moderate effect against Caco-2 cell line. Namely, diacylation of derivate 12 could slightly increase the cytotoxic activity (IC50 = 7.51 μg/mL for 12 and 6.93 μg/mL for 13). The carbonyl carbon atom incorporated at positions 3 and 6 in ketone 13 was identified as an electron deficient [46]. The presence of electron donor substituents attached to the phenanthrene skeleton at positions 9 and 10 (ethoxy groups) serves to reduce the electron deficiency of the carbonyl, they can also act as stabilizing charges generated at the phenanthrene skeleton by a mesomeric effect (+M) and thus would enhance the usefulness of these compounds as anticancer agents. Despite all that, ketone 14 showed no selectivity against the two cancer cell lines used (IC50 > 10 μg/mL).
On the basis of the aforementioned results, we can conclude that although cytotoxicity is undoubtedly influenced by many considerations, a contributing factor is the extent to which a compound receives or donates electrons in the cells. This observation suggests that the incorporation of electron-donating substituents into phenanthrene skeleton may lead to derivates with acceptable cytotoxicity.
3 Conclusions
To study the significant importance of different polyaromatic hydrocarbons on cytotoxicity, we have successfully synthesized a wide range of phenanthrene derivatives. The synthetic methods are very effective, allowing the design and preparation of new potential cytotoxic agents. Most of the prepared derivatives were screened for in vitro anticancer activity against two cell lines such as Hep-2 and Caco-2 by the MTT assay. Furthermore, our study is an attempt to explore whether the different substituents attached to the phenanthrene skeleton can change or enhance the activity to discern structure–activity relationships. Interestingly, esters 10d and 11d were found remarkably active against both the cell lines and appeared to be more potent as new cytotoxic agents.
4 Experimental section
4.1 Material and physical measurements
All the chemicals used in this work were of laboratory grade available from various commercial sources and used without further purification. Solvents were carefully dried and freshly distilled according to common laboratory techniques. All reactions were performed under an argon atmosphere and were monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) Merck 60 F254 silica-gel plates (layer thickness 0.25 mm). Spots on the TLC plates were visualized using ultraviolet light (254 and 365 nm). Column chromatography was performed on silica gel (70–230 mesh) using a cyclohexane and ethyl acetate mixture as eluents. Melting points were determined on an Electrothermal 9002 apparatus and were reported uncorrected. NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AC 300 instrument in CDCl3 [300 MHz (1H) and 75 MHz (13C)]. All chemical shifts were reported as δ values (ppm). Photochemical reactions were performed using a falling-film photoreactor and a high-pressure Hg-vapor lamp (500 W, Hanovia). Time-of-flight mass spectroscopy (TOF MS ES+) was carried out using a Micromass, UK and Manchester.
4.2 Cell lines and culture medium
The human colon carcinoma cells (Caco-2; ECACC. 86010202) and the human epidermoid carcinoma epithelial cells (Hep-2; ATCC CCL-23) were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% nonessential amino acids, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen). At 85–90% confluence, cells were harvested using 0.25% trypsin/EDTA solution and subcultured onto 96-well plates according to the experimental requirements.
4.3 Cytotoxicity screening assay
The MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide) colorimetric assay is commonly used to determine mitochondrial reductive function and hence is a good indicator of cell death or inhibition of growth. After incubation of cells with a range of concentrations of each compound the MTT assay in combination with cell viability of controls containing no compound can be used to obtain an IC50 value. This is the concentration of compound where 50% of cells are viable.
Briefly, the Caco-2 and Hep-2 cell lines (1 × 105 cells/well) were grown overnight on 96-well flat bottom cell culture plates and incubated for 24 h. When a partial monolayer was formed, the supernatant was flicked off, the monolayer washed once with medium and 100 μL of different concentrations (10, 5, 2.5, and 1.25 μg/mL) of phenanthrene derivatives were added to each cell in the microtiter plates. After 24 h, the cells were washed and treated with 0.01 mL MTT reagent (Invitrogen) prepared in 5.0 mg/mL of phosphate-buffered saline per well. Plates were incubated at 37 °C under a 5% CO2 atmosphere for 4 h, and 0.1 mL of dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) was added. After an overnight incubation at 37 °C, the absorbance was measured at 550 nm using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) reader (Thermo scientific Multiskan FC) and was compared with the control cultures without compounds. Results were determined from three independent experiments, and each experiment was performed in triplicate. Percent cytotoxicity was calculated using the following equation:
Stock solutions (5 mg/mL) of pure compounds were prepared in DMSO, and the final concentration of this solvent was kept constant at 0.25%. Serial dilutions with culture media were prepared just before addition to test.
4.4 Synthesis and spectral data
4.4.1 General procedure of the preparation of styrenes 6a–d
To a solution of methyltriphenylphosphonium iodide (22.61 mmol; 1.2 equiv) in dry DME (50 mL), K2CO3 (28.26 mmol; 1.5 equiv) was added in several portions, and stirring under argon was continued for 1 h. Then the aldehyde (18.84 mmol; 1 equiv) was added and stirring was continued for overnight at 80 °C. After cooling, 30 mL of diethyl ether was added to precipitate the insoluble salts. The mixture was collected by suction filtration, washed with ether, and the solvents were evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by chromatography on silica gel using cyclohexane as an eluent.
4.4.1.1 Styrene 6a
Following the general procedure, 6a was obtained from benzaldehyde 5a as a colorless oil; yield: 90% [47a].
4.4.1.2 4-Methylstyrene 6b
Following the general procedure, 6b was obtained from 4-tolualdehyde 5b as a colorless oil; yield: 80% [47b].
4.4.1.3 4-Bromostyrene 6c
Following the general procedure, 6c was obtained from 4-bromobenzaldehyde 5c as a colorless oil; yield: 91% [47c].
4.4.1.4 Methyl 4-vinylbenzoate 6d
Following the general procedure, 6d was obtained from methyl 4-formylbenzoate 5d as a white solid; mp 35–36 °C; yield: 85% [47d].
4.4.2 Experimental procedure for the Heck coupling reaction
A solution of aryl halide 7a–c (6.37 mmol; 1 equiv) and dry NaOAc (7.64 mmol; 1.2 equiv) in N,N-dimethylacetamide (3 mL) was placed in a Schlenk tube and repeatedly degassed and purged with argon five times. The styrene derivative 6a–d (1.4 equiv) was added and the mixture was heated to 100 °C. Next, a solution of Herrmann's catalyst (59.68 mg, 1 mol %) in N,N-dimethylacetamide (2 mL) was added and the mixture was heated to 140 °C during 48 h. The product was worked up by addition of H2O and the organic phase was extracted with EtOAc (3 × 30 mL). The combined organic phases were dried over MgSO4. After removal of the solvent, the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography with cyclohexane/EtOAc (98:02) as the eluent.
4.4.2.1 (E)-Stilbene 8a
Following the general procedure, 8a was obtained from 6a and bromobenzene; yield: 90%; white solid; mp 125–124 °C [36].
4.4.2.2 (E)-p-Methylstilbene 8b
Following the general procedure, 8b was obtained from 6b and bromobenzene; yield: 81%; white solid; mp 120–121 °C [36].
4.4.2.3 (E)-4,4′-Dibromostilbene 8c
Following the general procedure, 8c was obtained from 6c and 1,4-dibromobenzene; yield: 93%; white solid; mp 212–213 °C [48].
4.4.2.4 (E)-Methyl 1-[4-(o-tolylstyryl)]benzoate 8d
Following the general procedure, 8d was obtained from 6d and 1-bromo-toluene; yield: 70%; white solid; mp 151–152 °C [49].
4.4.3 Photoconversion of stilbenes to phenanthrenes
To a solution of the diarylethene 8a–d (500 mg) in toluene (1.5 L) was added a catalytic amount of iodine. Irradiation was performed using a falling-film photoreactor and a high-pressure Hg-vapor lamp (500 W, Hanovia). The reaction was monitored by TLC. After completion, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the crude residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel with cyclohexane/EtOAc (99:01) as the eluent.
4.4.3.1 Phenanthrene 9a
Following the general procedure, 9a was obtained from 8a; yield: 85%; crystalline powder; mp 98–99 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.53–7.64 (m, 4H), 7.71 (s, 2H, H-9 and H-10), 7.83 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H), 8.63 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 120.20 (CH), 120.61 (2CH), 120.64 (4CH), 120.65 (2CH), 130.10 (C), 130.22 (C) [36].
4.4.3.2 3-Methylphenanthrene 9b
Following the general procedure, 9b was obtained from 8b; yield: 88%; crystalline powder; mp 62–63 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.63 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.43 (d, J = 8 Hz, 1H), 7.56–7.72 (m, 4 H), 7.79 (d, J = 8 Hz, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 8 Hz, 1H), 8.48 (s, 1H, H-4), 8.68 (d, J = 8 Hz, 1H, H-5); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.07 (CH3), 122.34 (CH), 122.55 (CH), 125.89 (CH), 126.25 (CH), 126.66 (CH), 128.23 (CH), 128.33 (CH), 128.45 (CH), 129.68 (CH), 129.95 (C), 130.25 (C), 132.12 (C), 136.22 (C) [36].
4.4.3.3 3,6-Dibromophenanthrene 9c
Following the general procedure, 9c was obtained from 8c; yield: 80%; colorless solid; mp 188–189 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.69 (s, 2H, H-9 and H-10), 7.71–7.76 (m, 4H), 8.69 (d, J = 1.5 Hz, 2H, H-4 and H-5); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 120.69 (2CBr), 125.02 (2CH), 126.23 (2CH), 129.57 (2CH), 129.88 (2CH), 130.09 (2C), 130.21 (2C) [11].
4.4.3.4 Methyl 8-methyl-3-phenanthrylcarboxylate 9d
Following the general procedure, 9d was obtained from 8d; yield: 75%; white solid; mp 83–84 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.77 (s, 3H, CH3), 4.02 (s, 3H, CO2CH3), 7.49 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.62 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, H-6), 7.80 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 7.91 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 8.07 (d, J = 9 Hz, 1H), 8.20 (dd, J1 = 8.4 Hz, J2 = 1.5 Hz, 1H, H-2), 8.69 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, H-5), 9.45 (s, 1H, H-4); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 19.96 (CH3), 52.37 (OCH3), 121.08 (CH), 125.49 (CH), 125.59 (CH), 126.09 (CH), 126.34 (CH), 126.86 (CH), 127.73 (C), 128.33 (CH), 128.62 (CH), 130.07 (C), 130.63 (C), 130.88 (C), 134.47 (C), 135.15 (C), 167.51 (CO) [49].
4.4.4 General procedure for synthesis of phenanthrenequinone derivatives
The oxidation was carried out using 0.4 g of chromium trioxide (4 mmol), which was added to a solution of 0.2 g of the phenanthrene 9a–d (1.12 mmol; 1 equiv) in 20 mL of glacial acetic acid. The resulting mixture was warmed gently until no material remained undissolved and then the solution was heated at reflux for 1 h, cooled to room temperature, and then poured into water. The mixture was filtered, washed with water, and then crystallized from hexane.
4.4.4.1 9,10-Phenanthrenequinone 10a
Following the general procedure, 10a was obtained from 9a; yield: 83%; orange needles; mp 207–208 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.61 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.90 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 8.06 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 123.49 (2CH), 129.07 (2CH), 129.95 (2CH), 130.50 (2C), 135.32 (2C), 135.54 (2CH), 179.77 (2CO) [36].
4.4.4.2 3-Methyl-9,10-phenanthrenequinone 10b
Following the general procedure, 10b was obtained from 9b; yield: 94%; orange needles; mp 206–207 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.49 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.25 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.45 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, H-6/H-7), 7.70 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, H-6/H-7), 7.77 (s, 1H, H-4), 7.99 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.06 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.16 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.30 (CH3), 123.81 (CH), 124.51 (CH), 128.99 (C), 129.40 (CH), 130.35 (CH), 130.44 (CH), 130.70 (CH), 131.21 (C), 135.74 (CH), 135.79 (C), 135.92 (C), 147.28 (C), 179.85 (CO), 180.60 (CO) [36].
4.4.4.3 3,6-Dibromo-9,10-phenanthrenequinone 10c
Following the general procedure, 10c was obtained from 9c; yield: 78%; orange needles; mp 260–261 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.69 (dd, J = 1.8 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, H-2 and H-7), 8.08 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, H-1 and H-8), 8.14 (d, J = 1.5 Hz, 2H, H-4 and H-5); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 127.38 (2CBr), 129.87 (2C), 132.08 (4CH), 133.42 (2CH), 135.94 (2C), 178.85 (2CO) [11].
4.4.4.4 Methyl 8-methyl-9,10-phenanthrenequinone-3-carboxylate 10d
Following the general procedure, 10d was obtained from 9d; yield: 75%; orange needles; mp 203–204 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.72 (s, 3H, CH3); 4.01 (s, 3H, CO2CH3), 7.32 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, H-7), 7.61 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, H-6), 7.99 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.06 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 8.18 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, H-5), 8.65 (s, 1H, H-4); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.86 (CH3), 52.29 (OCH3), 122.47 (CH), 125.42 (CH), 128.69 (C), 129.17 (CH), 129.32 (CH), 132.62 (C), 133.74 (CH), 134.58 (CH), 135.63 (C), 135.77 (C), 136.38 (C), 145.02 (C), 165.21 (CO), 180.81 (CO), 182.02 (CO); HRMS (MALDI-TOF) calcd for C17H12O4 [M + H]+: 281.0814. Found: 281.0812.
4.4.5 General procedure for synthesis of phenazine derivatives
Phenanthrenequinone 10a–d (0.48 mmol; 1 equiv) and 1,2-diaminobenzene (0.52 mmol; 1.1 equiv) were suspended onto 1.64 mL of a 1:2 glacial AcOH/anhydrous EtOH solution. After heating to reflux for 3 h, the color of the mixture changes from orange to yellow. Once cooled to room temperature, the solids were transferred to 20 mL of water and then suction-filtered, copiously washed with water, then EtOH, and finally hexane.
4.4.5.1 Dibenzo[a,c]phenazine 11a
Following the general procedure, 11a was obtained from 10a; yield: 85%; pale yellow needles; mp 225–226 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.69–7.86 (m, 6H), 8.28–8.34 (m, 2H), 8.53 (dd, J1 = 1.5 Hz, J2 = 9 Hz, 2H), 9.38 (dd, J1 = 1.2 Hz, J2 = 7.2 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 122.87 (2CH), 126.25 (2CH), 127.88 (2CH), 129.43 (2CH), 129.70 (2CH), 130.26 (2CH), 130.28 (2C), 132.02 (2CN), 142.15 (2C), 142.40 (2 CN) [37a].
4.4.5.2 3-Methyldibenzo[a,c]phenazine 11b
Following the general procedure, 11b was obtained from 10b; yield: 88%; pale yellow powder; mp 206–207 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.63 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.53 (d, J = 8,1 Hz, 1H), 7.70–7.83 (m, 4H), 8.20–8.40 (m, 3H), 8.51 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 9.24 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 9.37 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.09 (CH3), 122.79 (CH), 123.06 (CH), 126.27 (CH), 127.72 (2CH), 127.98 (C), 128.67 (CH), 129.25 (CH), 129.35 (CH), 129.44 (CH), 129.56 (CH), 130.13 (CH), 130.43 (C), 132.03 (2C), 140.42 (C), 142.00 (C), 142.21 (C), 142.30 (CN), 142.59 (CN); HRMS (MALDI-TOF) calcd for C21H14N2 [M + H]+: 295.1235. Found: 295.1230 [37b].
4.4.5.3 3,6-Dibromodibenzo[a,c]phenazine 11c
Following the general procedure, 11c was obtained from 10c; yield: 96%; lemon yellow powder; mp 319–320 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, 2% CF3CO2H/CDCl3): δ = 8.05 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 8.26 (dd, J1 = 3.3 Hz, J2 = 6.6 Hz, 2H, H-2 and H-7), 8.64 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 8.71 (s, 2H, H-4 and H-5), 9.16 (d, J = 9 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, 2% CF3CO2H/CDCl3): δ = 122.68 (2CBr), 125.03 (2CH), 126.79 (2CH), 127.65 (2CH), 129.89 (2C), 132.80 (2C), 133.14 (2CH), 134.67 (2CH), 136.13 (2C), 138.30 (2 CN) [37c].
4.4.5.4 Methyl 8-methyldibenzo[a,c]phenazine-3-carboxylate 11d
Following the general procedure, 11d was obtained from 10d; yield: 91%; pale yellow powder; mp 200–201 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 3.34 (s, 3H, CH3), 4.05 (s, 3H, CO2CH3), 7.53 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, H-7), 7.63 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, H-6), 7.83–7.84 (m, 2H), 8.20–8.30 (m, 3H), 8.52 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, H-2), 9.17 (s, 1H, H-4), 9.34 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, H-5); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 27.41 (CH3), 52.32 (OCH3), 121.62 (CH), 125.32 (CH), 126.34 (CH), 127.77 (CH), 128.59 (C), 129.29 (2CH), 129.46 (CH), 129.80 (CH), 129.86 (CH), 131.29 (C), 132.46 (C), 132.80 (C), 133.01 (CH), 133.72 (C), 140.43 (C), 140.98 (C), 141.46 (C), 141.89 (C), 145.43 (C), 167.01 (CO); HRMS (MALDI-TOF) calcd for C23H16N2O2 [M + H]+: 353.1290. Found: 353.1284.
4.4.6 Synthesis of 9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 12
A mixture of 9,10-phenanthrenequinone 10a (2.4 mmol; 1 equiv), Bu4NBr (1.53 mmol), and Na2S2O4 (13.80 mmol) in H2O (10 mL) and THF (10 mL) was shaken for 5 min. Then, 0.53 mL of bromoethane (7.20 mmol; 3 equiv) was added dropwise, followed by aqueous solution of KOH (35.66 mmol, in 10 mL of H2O). The resulting mixture was shaken for about 2 days, poured into H2O (75 mL), and extracted with EtOAc. The extracts were washed twice with H2O and then brine, dried over MgSO4, and filtered. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure giving 9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 12 as a yellow oil in 86% yield. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.64 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H, 2CH3), 4.44 (q, J = 6.9 Hz, 4H, 2CH2), 7.65–7.76 (m, 4H), 8.40 (dd, J = 1.8 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, H-1 and H-8), 8.71 (dd, J = 1.2 Hz, J = 9 Hz, 2H, H-4 and H-5); NMR 13C (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 15.55 (2CH3), 68.60 (2CH2), 121.96 (2CH), 122.19 (2CH), 125.28 (2CH), 126.32 (2CH), 128.24 (2C), 129.34 (2C), 142.69 (2CO).
4.4.7 Synthesis of 3,6-diacetyl-9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 13
In a 50 mL three-necked flask fitted with an HCl trap, the 9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 12 (0.37 mmol; 1 equiv) was dissolved in 5 mL of anhydrous CH2Cl2 and acetyl chloride. The mixture was stirred for 5 min and cooled in an ice bath. The cooling bath was removed, then AlCl3 (0.75 mmol; 2 equiv) was added in portions to the stirred solution. Thereafter, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15 min and carefully poured onto crushed ice. The aqueous layer was extracted twice with CH2Cl2, and the combined organic layers were washed successively with water and aqueous Na2CO3, dried over MgSO4, and filtered. The solvent was evaporated, and the residual solid was shaken with MeOH, filtered, and washed with MeOH to give the 3,6-diacetyl-9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 13 in 91% yield as a pale yellow solid; mp 164–165 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.54 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 6H, 2CH3), 2.83 (s, 6H, 2CH3), 4.38 (q, J = 6.9 Hz 4H, 2CH2), 8.20–8.25 (m, 2H, H-2 and H-7), 8.35 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, H-1 and H-8), 9.34 (s, 2H, H-4 and H-5); NMR 13C (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 15.35 (2CH3), 26.47 (2CH3), 68.80 (2CH2), 122.56 (2CH), 123.08 (2CH), 125.70 (2CH), 127.96 (2C), 132.69 (2C), 134.11 (2C), 144.27 (2CO), 197.49 (2CO).
4.4.8 Synthesis of 3-acetyl-9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 14
AlCl3 (0.37 mmol; 1 equiv) was added carefully to a solution of 9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 12 (0.37 mmol; 1 equiv) and acetyl chloride in anhydrous CH2Cl2. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h, diluted with CH2Cl2, and then poured onto crushed ice. After washing with saturated NaHCO3 and brine, then drying with MgSO4 and after evaporation of the solvent, the 3-acetyl-9,10-diethoxyphenanthrene 20 was obtained in 78% yield as a light yellow solid; mp 84–85 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.54 (t, J = 6 Hz, 6H, 2CH3), 2.83 (s, 3H, CH3), 4.37 (q, J = 6 Hz, 4H, 2CH2), 7.46 (t, J = 9 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (t, J = 9 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (d, J = 9 Hz, 1H), 8.18 (d, J = 9 Hz, 2H), 8.35 (d, J = 9 Hz, 1H, H-5), 9.31 (s, 1H, H-4); NMR 13C (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 15.39 (CH3), 26.51 (CH3), 68.82 (CH2), 122.57 (CH), 123.08 (CH), 123.45 (CH), 125.72 (CH), 127.93 (C), 129.06 (CH), 129.96 (CH), 130.48 (C), 132.67 (C), 134.05 (C), 135.33 (C), 135.51 (CH), 144.26 (CO), 197.55 (CO).
4.4.9 Synthesis of phenanthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid (sodium salt) 15
Phenanthrenequinone 10a (0.33 mmol; 1 equiv) was melted on heating to 110 °C. Under vigorous stirring, 0.028 mL of concentrated H2SO4 (0.53 mmol; 1.6 equiv) was added dropwise, and the resulting mixture was stirred for 20 min at 135 °C and poured into 5 mL of H2O. The solution was neutralized to pH = 7 by an aqueous solution of NaOH and then cooled in an ice bath. The precipitate was filtered off, thoroughly squeezed, washed with brine to remove sodium disulfonate, and dried. Phenanthraquinone-2-sulfonic acid (sodium salt) 15 was obtained in 72% yield as red brick powder; mp 209–210 °C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 7.42–7.47 (m, 1H), 7.58 (s, 1H, H-1), 7.70 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, H-6/H-7), 7.83 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.92 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, H-6/H-7), 8.03 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 8.21 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H); NMR 13C (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 110.74 (CH), 116.88 (CH), 123.31 (C), 124.21 (CH), 124.47 (CH), 129.11 (CH), 129.34 (CH), 131.17 (C), 132.65 (C), 135.48 (CH), 137.71 (C), 165.05 (CS), 177.33 (CO), 179.01 (CO); HRMS (MALDI-TOF) calcd for C14H7O5S [M + H]+: 287.0014. Found: 287.0010.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the DGRS (Direction Generale de la Recherche Scientifique) of the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research.



Vous devez vous connecter pour continuer.
S'authentifier