1 Introduction
Microorganisms are widespread in all natural environments and are particularly abundant in soils that are considered as huge reservoirs of all main protists, i.e. bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoa.
Among soil microorganisms, bacteria present a large diversity of functional communities including photolithotrophs (using light as a source of energy and inorganic compounds as carbon source), photoorganotrophs (using light as source of energy and organic compounds as carbon source), chemolithotrophs (using inorganic compounds as carbon source and inorganic compounds as energy source), and chemoorganotrophs (using organic compounds as source of energy and carbon as well).
Most bacteria are chemoorganotrophs, but very interesting groups, having a major ecological and functional impact (e.g., sulphur-oxidizing, iron-oxidizing, nitrifying bacteria) are chemolithotrophs. If all chemoorganotrophic and chemolithotrophic bacteria need either organic or inorganic compounds that can be oxidized for providing energy, they need also inorganic or organic electron or proton acceptors that can be reduced (Fig. 1). The nature of electron acceptors and pathways for energy generation allow distinguishing respiration from fermentation. Respiration is an energy-yielding process where the oxidation of energy substrate (organic or inorganic electron donors) is coupled to the reduction of an exogenous electron acceptor, either molecular oxygen under aerobic conditions or any other inorganic or organic compound, e.g., nitrate, ferric iron, sulphate, fumarate..., under anaerobic conditions. The fermentation is an energy-yielding process where the energy substrate gets oxidised in the absence of exogenous electron acceptors. Usually, organic compounds serve as both electron donors and acceptors, i.e. the oxidation of the organic compounds (initial substrate used as the energy source) is coupled with the reduction of an organic compound (electron acceptor) generated from the initial substrate (no electron acceptor is supplied by the medium or the environment). Fig. 1 presents a simplified sketch of bacterial activities in soil environments.
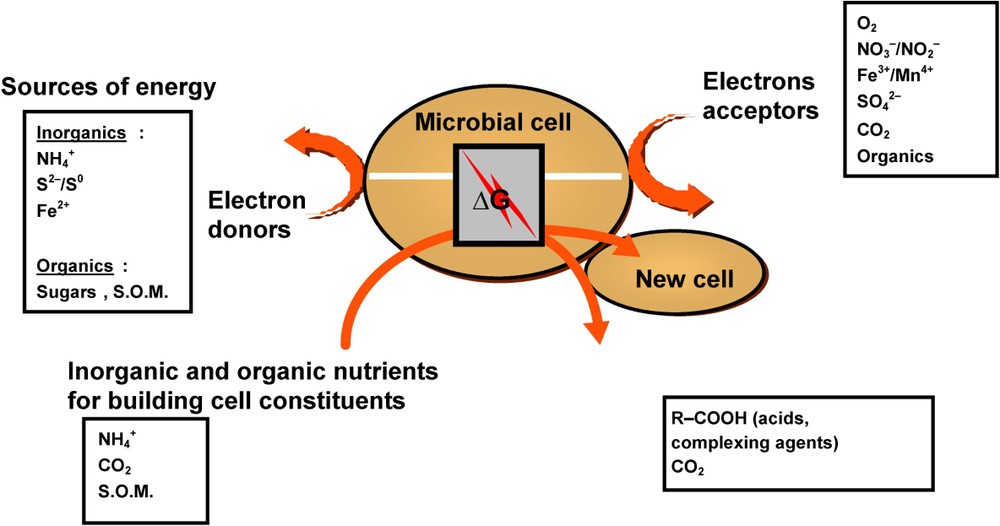
Diagram of general bacterial activities and simplified representation of cell machinery in soil environments (SOM soil organic matter) [4].
Schéma général des activités bactériennes et représentation simplifiée des modes de fonctionnement cellulaire de bactéries du sol (SOM, matière organique du sol) [4].
Eq. (1) summarises these redox energetic processes where DH2 is the electron donor and A the acceptor:
| (1) |
Various bacterial communities (i.e. iron-oxidizing bacteria, iron-reducing bacteria, bacteria forming iron-complexing agents) are involved in both the dissolution or deposit of iron compounds in rather different redox and acido-basic conditions [1,3,4,9,12,15,19,35] and thus involved in the weathering and formation of minerals. The major role of bacteria in iron cycle and some main associated processes can be briefly reminded. Chemolithotrophic iron-oxidizing bacteria promote ferric oxyhydroxide formation either in acidic conditions (e.g., Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Leptospirillum ferrooxidans for the ferrous sulphide pyrite dissolution and weathering) or in circumneutral conditions (e.g., Gallionella ferruginea in aerobic conditions). Different bacterial communities are able to produce complexing or chelating agents, which are able to play an efficient role in the solubilisation and transport of iron [4,9,13]. Such soluble organic iron complexes can also be biodegraded by microorganisms and iron can precipitate later. A third group of bacterial communities are, in anaerobic conditions, involved in the reduction of ferric iron provided or present either as soluble compounds or within solid such as (oxyhydr)oxides.
The purpose of this paper is to illustrate the occurrences of bacterial reduction processes of ferric species, and more specifically the reduction–dissolution and weathering phenomena of solid ferric compounds, e.g., (oxyhydr)oxides, and to discuss about the formation of ferrous–ferric ‘green rust’ mineral recently identified.
2 Diversity and abundance of iron-reducing bacteria (IRB) in soils
It is well recognized that soils and sediments contain not only aero-anaerobic (facultative anaerobic) and anaerobic well identified bacterial strains, but also large ill-defined bacterial communities able to reduce ferric to ferrous iron. Such bacteria can dissolve and weather efficiently (at least for some populations and communities) ferric (oxyhydr)oxides, e.g., ferrihydrite, goethite, hematite, lepidocrocite, by ferrireduction [1,2,5–7,9,16,25,28,32–34].
Although the molecular mechanisms of the bacterial iron reduction remain not completely understood, two bacterial groups should be differentiated on the basis of their metabolism: the non-fermentative (or iron respiring) bacteria and the fermentative iron reducing bacteria. In the first group, facultative anaerobic bacteria such as Shewanella sp. or strict anaerobic bacteria such as Geobacter sp. use ferric iron as terminal electron acceptor for their anaerobic respiration as indicated in simplified reactions (2) and (3):
| (2) |
| (3) |
These IRBs use mainly organic compounds as carbon and energy sources (reaction (2)), but they can also use inorganic compounds, e.g., hydrogen, as indicated in reaction (3). For fermentative bacteria, iron reduction may accompany fermentation of facultative or strict anaerobic bacteria such as Bacillus sp. or Clostridium sp., respectively, and in this case, ferric iron serves as supplementary terminal acceptor as shown in simplified reactions (4) and (5).
| (4) |
| (5) |
Works performed using Most Probable Number techniques (MPN) to evaluate the pools of IRB involved in the dissolution of ferric (oxyhydr)oxides have shown that large communities are present in different types of soils. Depending on the horizon depth, the site (rhizospheric or non-rhizospheric soil), the soil type, the nature and amount of available energetic and carbon sources, communities ranging from 102 to 108 IRB per gram of dry soil have been evaluated in upper soil horizons [14,32] (Table 1). Fermentative bacteria occur to be more abundant than non-fermentative.
Most-Probable Number (MPN) of Iron-Reducing Bacteria (IRB, bacteria g−1 dry soil) in different types of soils (from [14,32])
Nombre le plus probable (NPP) de bactéries ferriréductrices (bactéries g −1 de sol sec) dans différents types de sols (d'après [14,32])
| Fermentative bacteria | |
| • Hydromorphic soils (Reductisols and Redoxisols) | 103 to 106 |
| • Carbonated soils (Rendosols) | 104 to 108 |
| • Brown soils (Brunisols) | 104 to 107 |
| • Podzolised soils (Podzosols) | 103 to 108 |
| • Ferrallitic soils (Ferralsols) | 103 to 108 |
| Non-fermentative bacteria | |
| • Hydromorphic soils (Reductisols and Redoxisols) | 103 to 105 |
| • Ferrallitic soils (Ferralsols) | 102 to 105 |
3 Parameters controlling bacterial iron reduction and ferric (oxyhydr)oxides dissolution
Several authors have reported that IRB can use different well-defined organic compounds (glucose, acetate, methanoate...) as carbon and energy sources [9,17,22]. However, it was only recently that a significant correlation between the bacterial degradation (oxidation and mineralization) of soil organic matter and the bacterial iron reduction and dissolution of ferric (oxyhydr)oxides has been determined (Fig. 2) [32]. Different stages appeared in the correlation indicating that in the three sampled soil horizons, the limiting factor was the ferric iron availability. However, the discrepancy that is often observed between the amount of mineralized organic matter (O.M.) and the extent of iron reduction and dissolution underlines the fundamental role played by the quality and biodegradability of O.M. during the process [32].
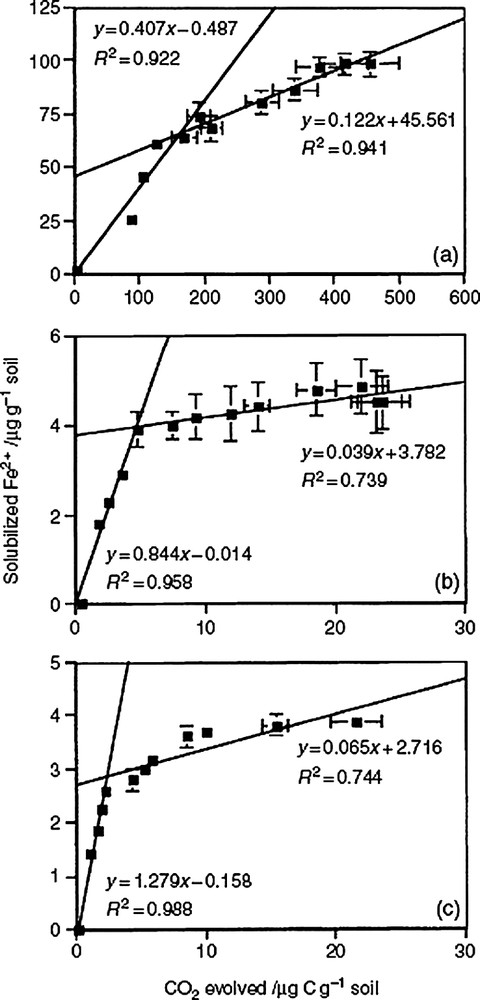
Relation between bacterial iron reduction (Fe2+) and soil organic matter biodegradation (CO2 evolved by mineralization) in three horizons of a tropical Reductisol (Gleysol) [32].
Relation entre la réduction bactérienne du fer (Fe2+ solubilisé) et la biodégradation des matières organiques du sol (CO2 dégagé par minéralisation) dans trois horizons d'un Réductisol tropical (Gleysol) [32].
The addition of plant origin material, e.g., cellulose, promoted IRB activity [28]. These IRB reduced soluble and solid forms of ferric iron (e.g., ferric citrate, ferric (oxyhydr)oxides, phyllosilicates) [6,25,28,35].
Different physical, chemical and biological parameters control these dissolution and weathering processes. Poor crystalline features and small particle size (large specific surface area) promote reduction and dissolution [20,29]. Metal substitution in the mineral structure has effects that depend on the nature and substitution rate of the metal: aluminium substitution decreases the goethite dissolution kinetics but manganese or cobalt has no effect on [6].
The presence of ligands (complexing agents) of ferric iron [9], as well as that of an electron shuttle such as anthroquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) [9,25] promote iron reduction. Quinone bearing compounds like humic substances seem to be able to increase electron transfer [18]. The contact between bacteria and oxyhydroxides [21,30] promotes bacterial reduction and dissolution. Interactions at the interface (including contact) seem to be of major importance that has to be more clearly defined.
Bacterial reduction of solid ferric species seems also able to take place not only in waterlogged but also in better drained soils when microbial activities consume oxygen during organic matter biodegradation, thus promoting the development of anoxic conditions and anaerobic microsites [33]. Acidification of soil by fermentative bacteria can also increase Fe(III) solubility and stabilise Fe2+ in aqueous solution [2,5].
4 Impact of IRB activity on weathering of minerals and redistribution of metals
Bacterial dissolution of Fe and Mn oxides promotes solubilisation of substituted metals (Co, Ni, Cr...), as observed during waterlogging of a Ferralsol of New Caledonia [28]. Moreover, such bacterial weathering modifies the metal distribution within the geochemical soil compartments. Metal content (Fe, Mn, Co, Ni and Cr) of most labile water soluble and exchangeable compartments increased. It has also been observed that metal concentrations of amorphous and poorly crystallised Fe oxides increased significantly [28]. Table 2 summarizes these results after weathering of oxides by aero-anaerobic and anaerobic bacteria that have mineralised 1.4% of soil organic carbon and solubilised 0.19% Fe and 17% Mn.
Effect of microbial weathering by IRB on the redistribution of iron in different geochemical compartments of a Ferralsol (in mg Fe kg−1 of dry soil) (from [28])
Effet de l'altération microbienne par des bactéries ferriréductrices sur la redistribution du fer dans divers compartiments d'un Ferralsol (mg Fe kg −1 sol sec) (d'après [28])
| Before microbial weathering | After 140 days IRB activity | |
| Water soluble | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 27.0 ± 4.0 |
| Exchangeable | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 18.0 ± 10.0 |
| Hydroxylamine extractable | 115 ± 37 | 67.0 ± 12.0 |
| Oxalic acid–oxalate extractable | 9100 ± 1999 | 10768 ± 347 |
| Alkaline-soluble | 31 ± 36 | 73 ± 9 |
When weathering was more intense after bacterial solubilisation of 0.77% Fe and 32% Mn, a more pronounced amorphisation of mineral constituents was noted: transmission electron microscope observations and microanalysis then revealed the formation of amorphous FeSi gel containing also Mn, Ni, and Cr [28].
5 Presence and activity of IRBs in soils where was discovered fougerite
The mixed Fe(II)–Fe(III) compound green rust was primarily found to be formed during corrosion processes of iron-based materials [10,23,31]. Recently its natural occurrence was demonstrated in hydromorphic soils [36,37] and in particular in a Reductisol of the forest of Fougères (Brittany, France), where IRB activity can occur significantly. Works have been done to screen and evaluate the presence of IRBs that are able to reduce and dissolve ferric iron from oxihydroxides in different horizons. Simultaneously, laboratory experiments were performed to determine the soil IRB activity using soil organic matter (SOM) as carbon and energy sources and soil ferric species as ferric substrate. The presence of relatively large communities of IRBs (fermentative and non-fermentative) has been observed in upper soil horizons (from 0- to 80-cm depth) using the Most Probable Number technique in different liquid media [32] in microplates in anaerobic conditions (Table 3). After incubation of suspension of the soil horizon samples (soil/water ratio: 1/10) in anaerobic conditions, the number of IRBs increased strongly, particularly for fermentative bacteria (Table 3). So IRBs are able to grow in Fougères Reductisol, using SOM as carbon and energy sources.
Most-Probable Number (MPN) of fermentative (IRB F) and non-fermentative (IRB NF) Iron-Reducing Bacteria, in horizon samples (F1 to F8) of the Reductisol of Fougères (bacteria g−1 dry soil at beginning (
Nombre le plus probable (NPP) de bactéries ferriréductrices fermentaires (IRB F) et non fermentaires (IRB NF) dans les échantillons de huit horizons (F1 à F8) du Réductisol de Fougères (bactéries par g de sol sec avant et après 100 jours d'incubation, n.d. : <10)
| Soil horizons (depth, cm) | IRB F | IRB NF | ||
|
|
|
|
100 | |
| F1 (0–20) | 2.0×104 | 6.3×107 | 1.1×103 | 9.0×103 |
| F2 (20–30) | 2.0×104 | 1.1×108 | 1.5×103 | 4.0×104 |
| F3 (30–40) | 1.0×104 | 7.0×105 | 5.0×102 | 6.0×103 |
| F4 (40–60) | 2.1×104 | 6.0×105 | 4.0×102 | 7.0×103 |
| F5 (60–70) | 2.0×104 | 6.5×105 | 5.0×102 | 1.0×104 |
| F6 (70–80) | 3.3×104 | 3.0×105 | n.d. | n.d. |
| F7 (80–90) | n.d. | 2.0×103 | n.d. | n.d. |
| F8 (90–100) | n.d. | 1.1×103 | n.d. | n.d. |
Simultaneously to IRB counting before and after soil sample incubations, measurements have concerned the biodegradation of SOM evaluated by organic carbon mineralization, i.e. CO2 evolution and iron dissolution as Fe2+ ions in the same incubation devices. Neither a significant dissolution of iron nor a production of CO2 was observed in abiotic controls. The mineralisation of SOM by anaerobic bacteria occurs in all soil horizons from 0- to 100-cm depth (Fig. 3). This organic matter biodegradation, expressed by carbon mineralisation (C–CO2 evolved) per thousand of total soil organic carbon, appears to be more important in upper horizons where organic matter biodegradability is relatively higher than in deeper horizons.

Cumulative net production of CO2 (C from CO2‰ total organic carbon) during biodegradation in anaerobic conditions of soil organic matter (SOM) of samples (F1 to F8) of the Fougères Reductisol (depth of horizons is indicated in Table 3).
Production cumulée de CO2 (C du CO2‰ du carbone organique total) au cours de la biodégradation de matières organiques du sol (SOM) dans des incubations anaérobies d'échantillons de huit horizons (F1 à F8) du Réductisol de Fougères (la profondeur des horizons est indiquée dans le Tableau 3).
Fig. 4 shows the dissolution of iron as Fe2+, occurring simultaneously to SOM biodegradation. This indicates relatively high IRB activity in upper horizons and particularly in 20–30-cm depth horizon where fougerite was observed [36,37]. This reductic horizon, where fougerite formed, presents large IRB communities able to grow significantly using soil organic matter as source of carbon and energy and having a very efficient iron-reducing activity. Such IRB activity can be involved in the formation or in the control of the chemical and physicochemical parameters controlling fougerite formation.
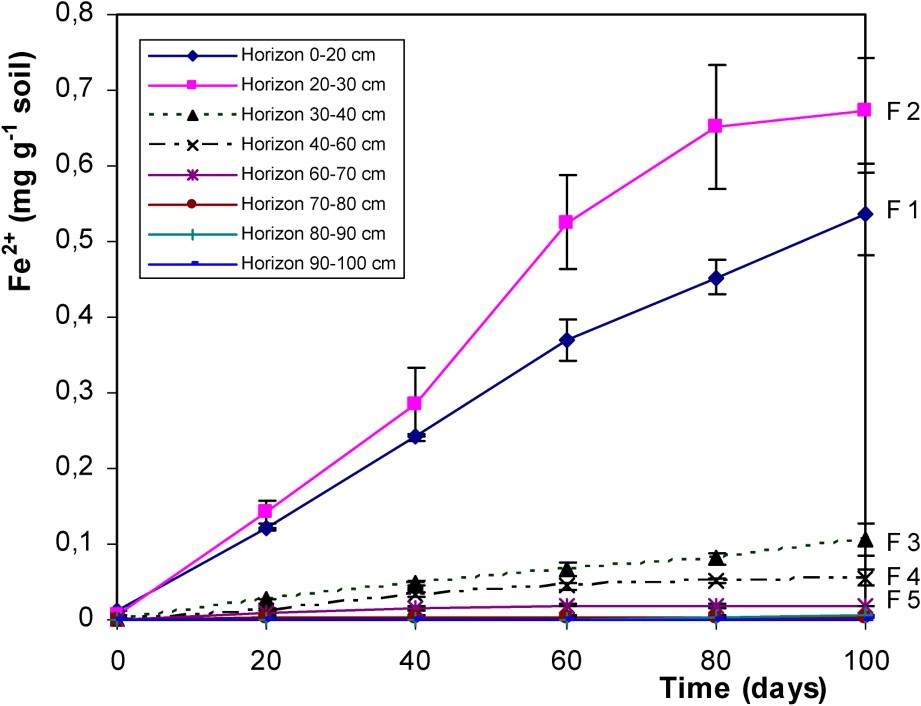
Solubilisation of Fe2+ (soluble reduced iron) in the biotic treatments of F1 to F8 horizons of the Fougères Reductisol (respective depth 0–20; 20–30; 30–40; 40–60; 60–70; 70–80; 80–90; 90–100 cm) (Fe2+ in mg per g of dry soil).
Solubilisation de Fe2+ dans les traitements biotiques des échantillons des horizons F1 à F8 du Réductisol de Fougères (profondeur respective 0–20 ; 20–30 ; 30–40 ; 40–60 ; 60–70 ; 70–80 ; 80–90 ; 90–100 cm) (Fe2+ en mg par g de sol sec).
6 Green rust formation controlled by iron-reducing bacteria
Experiments were performed in laboratory-controlled conditions in batch devices as described by Ona-Nguema et al. to determine the possible role of IRBs in green rust (GR) formation [25]. The non-fermentative bacterium Shewanella putrefaciens was cultivated in anaerobic conditions (N2 atmosphere) in 100-ml flasks receiving a basic liquid nutrient medium (pH 7.5). Each flask received 80 mM of Fe(III), the source of ferric iron and electron acceptor as oxyhydroxyde (lepidocrocite γ-FeOOH). Electron donor was provided by 23–75 mM of methanoate (
| (6) |
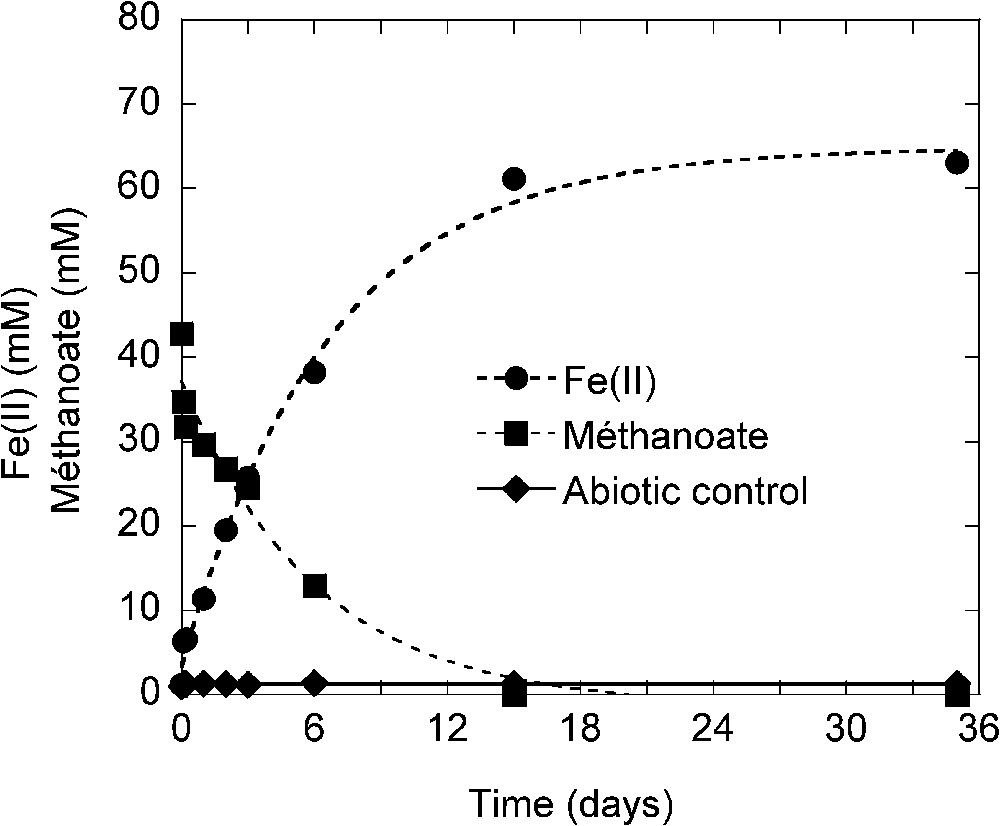
Production of Fe(II) and consumption of methanoate during culture of Shewanella putrefaciens in presence of lepidocrocite. The initial amount of Fe(III) (as lepidocrocite) and of methanoate were respectively 80 and 43 mM [24].
Production de Fe(II) et consommation de méthanoate dans une culture de Shewanella putrefaciens en présence de lépidocrocite. Les quantités initiales de Fe(III) sous forme de lépidocrocite et de méthanoate sont respectivement de 80 et 43 mM [24].
After 15 days of incubation, 62 mM of Fe(III) are reduced in Fe(II) and almost all methanoate was used (Fig. 5). The balance indicates that 12 mM of methanoate have been used or removed from the solution in excess of the 31 mM necessary to reduce 61 mM of Fe(III). So, part of methanoate can be absorbed on green rust and/or on siderite that have been formed but another part is likely incorporated into the bacterial biomass.
In abiotic control iron reduction was not observed (Fig. 5). Bacterial reduction and GR formation occurred efficiently without AQDS in the medium [25].
The colour of the solid phase changed during the bacterial reduction of lepidocrocite. From orange (lepidocrocite colour), the medium became orange-brown then dark green testifying the formation of green rust. Green rust was clearly characterised using different methods indicated here. In these experimental conditions, hydroxycarbonate green rust of type 1, was formed. XRD analysis performed after 15 days of incubation indicated a mixture of a GR1 and of few siderite (Fig. 6). The observed
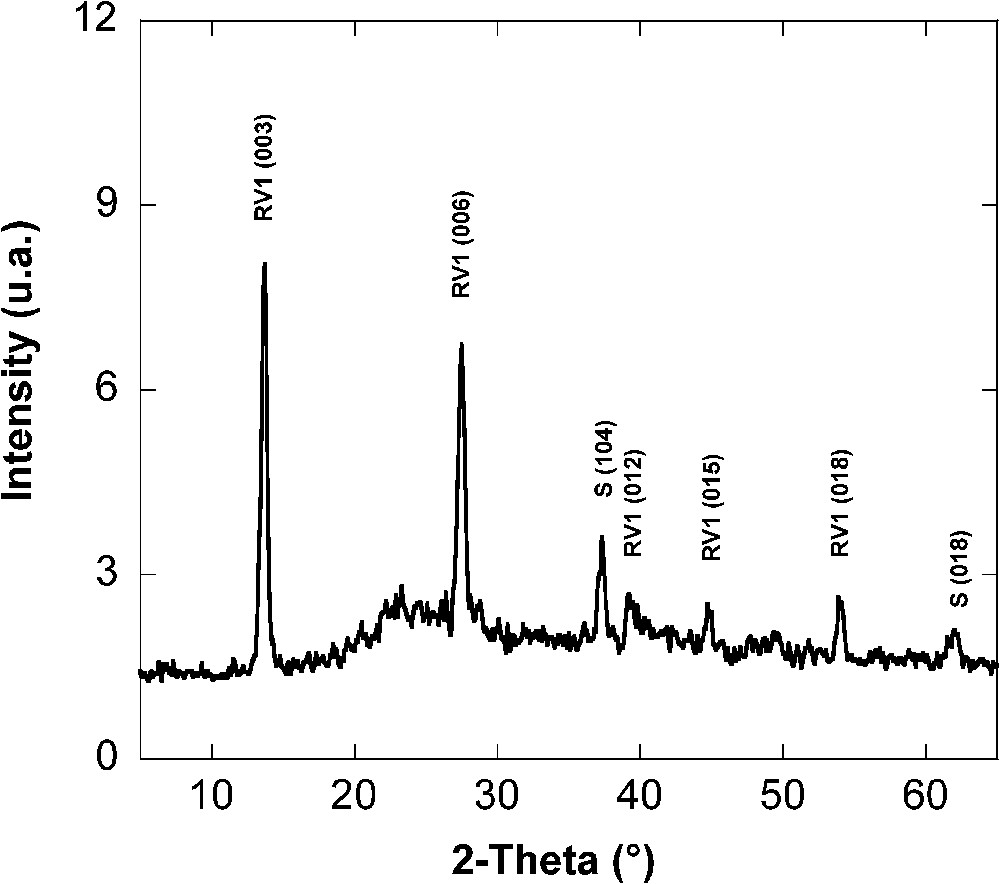
X-ray diffractogram of the solid phase of incubation experiments: mixture of green rust (GR1) and siderite (S) obtained after 15 days of incubation of S. putrefaciens [24].
Diffractogramme de rayons X (DRX) de la phase solide après 15 jours d'incubation d'une culture de S. putrefaciens : mélange de rouille verte (GR1) et de sidérite (S) [24].
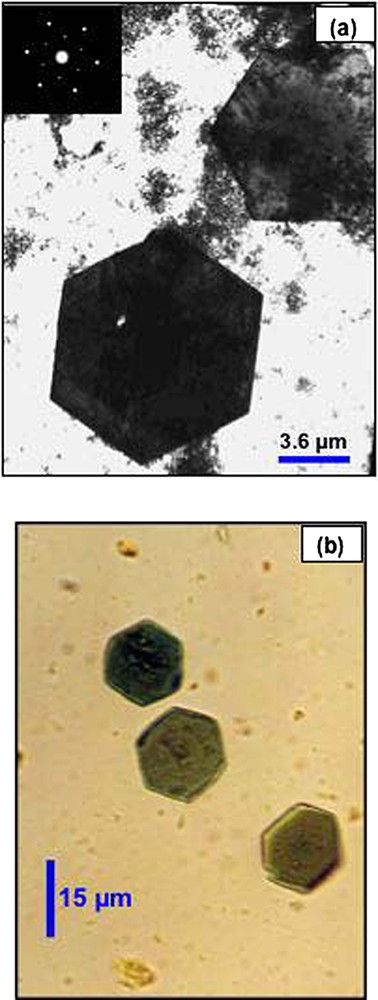
Transmission electron microscopy (a) and optical microscopy (b) of hexagonal crystals of green rust obtained in culture of S. putrefaciens in the presence of lepidocrocite [24].
Observation en microscopie électronique à transmission (a) et en microscopie optique (b) de cristaux de rouille verte, obtenus en culture de S. putrefaciens en présence de lépidocrocite [24].
7 Conclusion
Soils contain aero-anaerobic and anaerobic bacteria that use, in the absence of oxygen, either fermentation processes or anaerobic respiration to reduce organic and inorganic electron acceptors other than oxygen such as
Natural occurrence of GR has been observed in Reductisols (Gleysols) and Redoxisols (pseudogley), and was well characterized in a Redoxisol of the forest of Fougères (France). It was named fougerite. The Fougères Redoxisol contains, in the horizons where fougerite was discovered, large fermentative and non-fermentative IRB communities, which present efficient iron-reducing activities, using soil organic matter as carbon and energy sources. The fermentative IRB communities appear larger than the non-fermentative and have a high potential activity in the soil horizons where GR formed. However, their involvement in GR formation is not yet defined. The significant relation between bacterial iron-reducing activity and GR formation, has been well established in laboratory experiments with a non-fermentative bacterium Shewanella putrefaciens, used as a reference IRB cultivated in the presence of methanoate as electron donor and of lepidocrocite as source of iron and electron acceptor. By bacterial reduction of iron, the concomitant productions of Fe(II) and
Iron-reducing bacteria appear as the main factor involved in GR formation. However, environmental parameters such as the availability of carbon energy sources and of ferric iron, dynamic and activity of bacterial populations have to be defined more accurately in field conditions to progress in the knowledge of the processes and of their impact and possible application in the cycling of iron and associated elements in soil functioning.
Acknowledgements
Part of these works has been supported by PROSE-PNSE program.


