1 Introduction
Frost splitting affects especially sedimentary rocks, which are often used in construction and thus, undergo temperature variations. It causes spallings and fractures (Letavernier, 1984). Frost action can happen in matrix porosity or in cracks (Bost, 2008). This study focused on frost action in pores, which is common in buildings. It is called micro-frost action. Frost splitting is the result of interactions between the environment (water intake, frost conditions) and the mechanical strength that depends partially on rock texture (Bost, 2008). Frost weathering of sedimentary rocks is thus a complex phenomenon that depends on rock properties and environmental conditions. Many authors proposed classifications [e.g. 3], which take into account several intrinsic parameters and frost temperatures. Besides, frost weathering is the result of the combined action of processes linked to rock strength and stresses generated by freezing water (Bost, 2008), i.e. to the porous network characteristics and in particular mechanical properties (state parameters) and to the way water flows in the porous network (transfer parameters). Indeed, Bost (Bost, 2008) showed that in fractured rocks, the generated stress is due to a balance between the confining pressure induced by the ice front spreading deeply in the crack and the water leakage in the porosity network in the vicinity of the crack. It can thus be interesting to divide the rock intrinsic parameters into state and transfer parameters in order to assess their influence on frost weathering. The relevant intrinsic parameters (Bellanger et al., 1996; Guédon et al., 2008a; Guédon et al., 2008b; Panet, 1976; Perrier, 1996; Thomachot, 2002) following this classification for frost weathering study are presented in Table 1. Some studies showed the interest of measuring mechanical parameters from non-destructive tests to follow frost weathering in rocks, such as the ultrasonic velocity measurement (Remy et al., 1994) or the dynamic modulus of elasticity measurement (Prick, 1997). However, the velocity measurement has a practical disadvantage: it needs the application of grease on samples and this can affect water transfers in the samples. Thus, the dynamic modulus of elasticity has been measured for the study of mechanical behaviour evolution of rocks with frost weathering. Concerning transfer parameters, the commonly measured parameters are capillarity ones (Tharp, 1987; Thomachot, 2002). They are linked to free water circulation into the porous network. The other transfer parameter is permeability. It is linked to a forced water circulation into the porous network and thus, must be more representative of what happens during freeze. But there is a lack of experimental studies linking permeability to frost weathering. The aim of this study was thus to emphasize how the state and transfer parameters, on the one hand, were related to frost sensitivity, on the other.
Paramètres intrinsèques qui peuvent être reliés à l’altération par gel–dégel (Bellanger et al., 1996; Guédon et al., 2008a; Guédon et al., 2008b; Panet, 1976; Perrier, 1996; Thomachot, 2002).
| Rock property | Measurement method | ||
| Device or measured parameter | Standard | ||
| State parameters | Mineralogy | X ray diffraction | |
| Optical microscopy | NF EN 12407, 2007 | ||
| Porosity/Porous network | Water porosity | NF EN 1936, 2007 | |
| Skeletal and bulk densities | |||
| Mercury porosimetry | |||
| 48-hour porosity | NF B 10-504, 1973 | ||
| Electronic microscopy | |||
| Optical microscopy | |||
| Mechanical properties | Dynamic modulus of elasticity | NF EN 14580, 2005 | |
| Compression test | NF P 94-420, 2000 | ||
| Tension test | NF P 94-422, 2001 | ||
| Ultrasonic velocity | NF EN 14579, 2005 | ||
| Transfer parameters | Capillarity | Capillary head coefficient | NF EN 1925, 1999 |
| Capillary fringe migration and mass evolution | |||
| Permeability | Water permeability | ||
| From mercury porosimetry curves |
2 Experimental procedure
2.1 Rock samples
The study was on sedimentary rocks often found on buildings and thus submitted to temperature variations: limestone and sandstone. The rocks choice was made in agreement with the European standard, which determines the liability to frost damage of a rock according to its building use (Anon, 2003). The frost sensitivity estimation was obtained thanks to quarries data referring to this standard (Anon, 2003). In this paper, the expressions ‘frost-riven’ and ‘frost-resistant’ always refer to this standard. For the frost weathering follow-up, two limestones and two sandstones with similarities were selected. Two oolitic limestones, one considered as frost-resistant (called L1) and one considered as frost-riven (called L2) have been studied. They have petrophysical similarities and a quasi-pure mineralogy (99% of calcite). Their close petrophysical compositions but their differences of resistance to frost weathering were the reasons why they were chosen for this study. For the sandstones, they are called S1 and S2. Both are considered as frost-resistant compared to the standard. They have been chosen because S2 has grain size 10 times smaller than S1. Besides, for the characterization part, other oolitic limestones were added to reinforce the results interpretation. Some are considered as frost-riven (L2, L4, L6) and some as frost-resistant (L3, L5, L7, and L9) (Table 2).
Description des roches étudiées (les échantillons utilisés pour le suivi de l’altération par le gel sont en gras) : les tailles des grains sont estimées à partir d’observations microscopiques, la porosité correspond à la porosité à l’eau et la sensibilité au gel est estimée en fonction de la norme (Anon, 2003).
| Geological age | Texture | Grains size | Porosity % | Frost-cracking potential | |
| S1 | Buntsandstein (Triassic) | Vosgian sandstone | +++ | 21 | + |
| S2 | Unknown | Unknown | + | 14 | + |
| L1 | Neocomian (Cretaceous) | Oolitic | + | 14 | + |
| L3 | Bathonian (Jurassic) | Oolitic | ++ | 10 | + |
| L5 | Portlandian (Jurassic) | Oolitic | +++ | 33 | + |
| L7 | Oxfordian (Jurassic) | Oolitic | +++ | 15 | + |
| L9 | Bathonian (Jurassic) | Oolitic | ++ | 13 | + |
| L2 | Bathonian (Jurassic) | Oolitic | + | 18 | ++ |
| L4 | Bathonian (Jurassic) | Oolitic | ++ | 5 | +++ |
| L6 | Bathonian (Jurassic) | Oolitic | ++ | 13 | ++ |
On buildings, rocks are posed so that the bedding is horizontal. Thus, the samples were all cored perpendicular to the bedding to be more representative of in situ conditions. All samples were cored to obtain a cylinder 40 mm in diameter and 80 mm in length. These dimensions fitted the triaxial cell and enabled measurements of all the required parameters on the same sample.
3 Methods
3.1 Determination of a state parameter: the dynamic modulus of elasticity
The dynamic modulus of elasticity represents dynamic mechanical behaviour of a rock. It can be obtained by the resonant frequency measurement. The procedure for measuring the resonant frequency consists of exciting a specimen by means of a light external mechanical impulse and of analyzing the transient natural vibration during the subsequent free relaxation. A transducer can be used to pick up the mechanical vibration (Christaras et al., 1994; Perrier, 1996). The dynamic modulus of elasticity Ed (Pa) is linked to the resonant frequency by the following relation (Perrier, 1996):
with L the sample length (m), ρ the rock density (kg/m3) and f the resonant frequency (Hz).
3.2 Determination of a transfer parameter: the water permeability
Permeability describes the ease with which a fluid circulates through a porous network and depends especially on pores size, tortuosity and connectivity of the porous network (Guéguen and Palciauskas, 1992). Darcy (Darcy, 1856), who showed that there was a linear relationship between the water flow Q (m3/s) and the pressure gradient ΔP (Pa), defined the permeability of a connected porous medium by:
with S the section area perpendicular to the flow (m2), ΔL the length of the sample (m), η the dynamic viscosity of water (0.001 Pa.s) and k the specific permeability of the porous network (m2). The permeability k is homogeneous to a surface and represents a cross section of flow.
Darcy's law is only valid for a flow regimen where there is no chemical interaction between the fluid and the solid (absorption, dissolution). Besides, Darcy's law describes a perfect laminar flow, i.e. the fluid particles moving in one direction have a constant speed following continuous stream lines. The flow is regarded as laminar if the kinetic energy of the fluid is negligible compared to its viscous energy, i.e. for a value of Re (Reynolds number) well below 1 (Guéguen and Palciauskas, 1992):
with Nt the water porosity (%) and ρ the water density (1000 kg/m3).
The method used in this study to measure the water permeability was the steady state flow method. It consists of maintaining a constant differential fluid pressure between the two ends of the sample, and measuring the resulting flow as soon as it reaches a steady state flow. The tests were performed in a triaxial cell. After water vacuum saturation, the samples are put vertically in a tight pressure space between two porous discs (Fig. 1). The sample studied, isolated by a membrane from the confining fluid, is under a confining pressure Pc to prevent from any leakage. And to ensure isotropic stress conditions, an axial pressure equal to the confining pressure is applied. The confining and axial pressures and the water inlet Pi and outlet Po pressures are monitored and maintained constant during the test. The confining pressure must be higher than the pore pressure Pp = Pi − Po to guarantee a good tightness of the device and was thus established as Pc = Pp + 2 MPa (Ghabezloo et al., 2008). Besides, in order to be in the same confining conditions at each rock permeability measurement, the confining pressure was set at the same value once and for all. Besides, all of the rock pore pressures of this study are lower than 1 MPa. So, the confining pressure was set at 3 MPa. The pore pressure Pp was fixed to get a limited flow and thus, to have laminar conditions. In this case, when the permeability increased, the pore pressure decreased (Table 3).
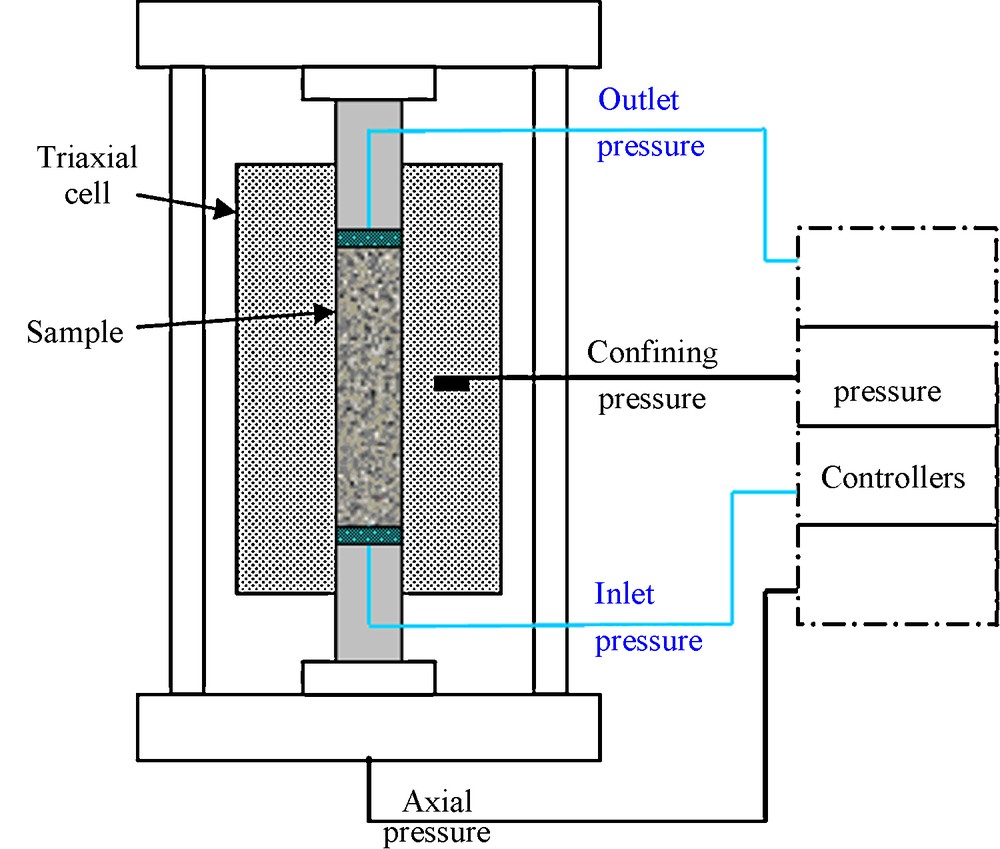
Diagram of the device for permeability measurements.
Schéma du montage de la mesure de perméabilité.
Exemples de conditions de mesure de la perméabilité.
| Sample | Pore pressure (kPa) | Confining pressure (kPa) | Flow (mm3/s) | Permeability (10−15 m2) | Reynolds number (–) |
| S1 | 10 | 3000 | 0.67 | 4.25 | 10−9 |
| S2 | 370 | 3000 | 5.85 | 1.00 | 10−9 |
| L1 | 820 | 3000 | 3.41 | 0.26 | 10−10 |
| L2 | 950 | 3000 | 0.58 | 0.038 | 10−11 |
For the sandstone samples, the chemical interaction with water is minor regarding the very low solubility of quartz (6 parts per million, in pure water at 25 °C). On the other hand, for the limestone samples, it was assumed that the proportion of calcite and other minerals that can dissolve is negligible with respect to the period during when the water stays in the porous medium. Thus, it can be considered that there was no change of the porous network during the flow (Beck, 2006).
3.3 Freeze–thaw cycles description
Freeze–thaw cycles characteristics were defined to be close to in situ conditions. They were thus performed based on the procedure used by Bost (Bost, 2008). Each freeze–thaw cycle included a phase of frost in the air at −5 °C during 6 hours and a phase of thaw in water at 20 °C during 6 hours. This cycle was programmed for a climatic chamber. The samples were placed in a tank in the chamber to undergo the automatic cycle. The temperature of each cycle was measured using thermocouples (Fig. 2). They were placed inside the climatic chamber but also within samples with a thin cylinder cored in their central part in order to put the thermocouples in it (Fig. 3) and thus, to check temperatures inside the sample for each type of rock (L1, L2, S1, S2). These samples were added to the others so the shape of the studied samples would not be modified. Since frost cracking increases with the degree of saturation (Tourenq, 1970), so in order to boost frost action, the described freeze–thaw cycles were performed on vacuum saturated S1, S2, L1 and L2 samples.
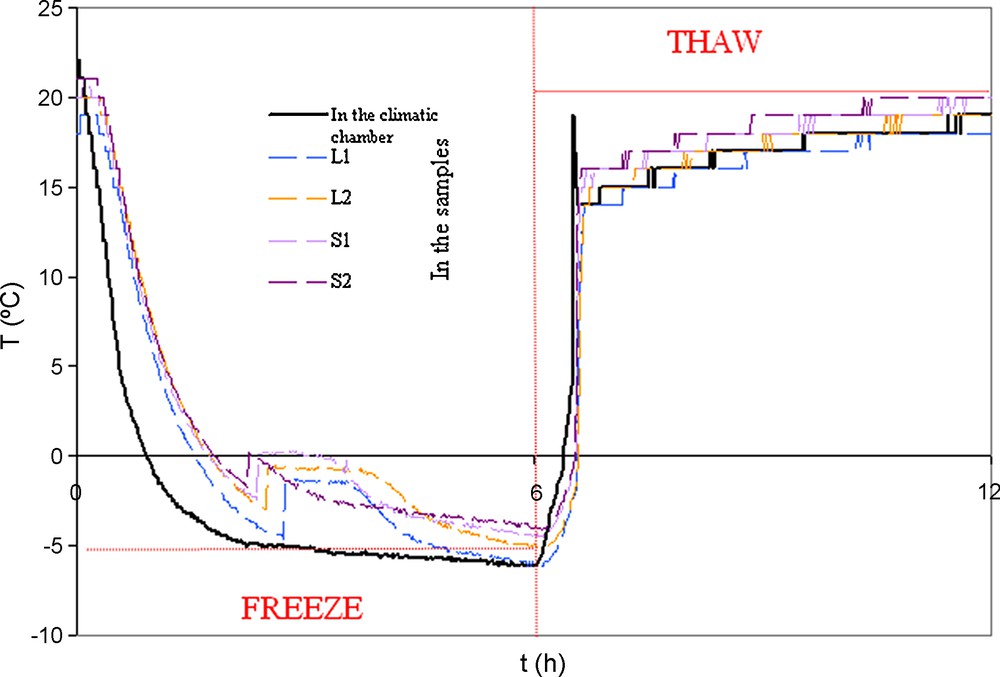
Freeze–thaw cycle in the climatic chamber and within different samples.
Cycle de gel–dégel dans la chambre climatique et à l’intérieur des différents échantillons.

Thermocouples.
Thermocouples.
4 Experimental results and discussion
4.1 Sample characterization
Fig. 4 shows the results obtained on the ten samples for permeability and modulus of elasticity measurements. Permeability values on the right (represented by circles) are in descending order: high values are at the bottom of the graph and low ones are at the top. Dynamic modulus of elasticity values on the left (represented by crosses) are in increasing order. It shows that frost-riven samples (L2, L4, L6) and frost-resistant ones (S1, S2, L1, L3, L5, L7, L9) are located on both sides of an area that can be called the ‘transition zone’ on Fig. 4. This transition works with the ten samples for permeability values and dynamic modulus values. Thus, the frost-riven samples have permeability values smaller than 7.5 × 10−17 m2 and dynamic moduli of elasticity higher than 33 GPa. Conversely, the frost-resistant samples have permeability values higher than 5.5 × 10−18 m2 and dynamic moduli of elasticity smaller than 46 GPa.
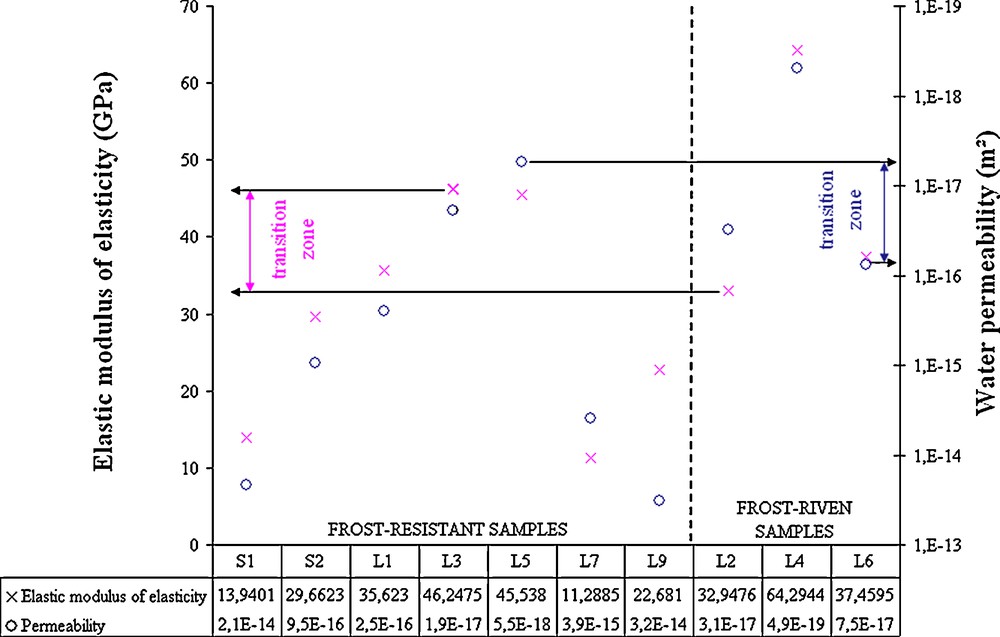
Characterization of rocks before freeze–thaw cycles (water permeability and dynamic modulus). There is a zone that separates the samples considering their frost resistance (Anon, 2003).
Caractérisation des roches avant les cycles de gel–dégel (perméabilité à l’eau et module dynamique). Il y a une zone qui sépare les échantillons en fonction de leur résistance au gel (Anon, 2003).
Thus, on the one hand, by definition, a low dynamic modulus of elasticity means that the rock matrix can reorganize easily with deformation and on the contrary, a high dynamic modulus of elasticity means that the rock will crack very quickly with deformation. On the other hand, a high permeability means that during freeze, only low pressures are induced in the porous network and a low permeability means that during freeze, induced pressures become high. So, the results show how the state and transfer parameters are related to frost damage. In other words, a rock with a low permeability and a high dynamic modulus of elasticity, such as L4 (Fig. 4), will not resist frost action and a rock with a high permeability and a low dynamic modulus of elasticity, such as S1 (Fig. 4), will resist frost action.
Freeze intensity is also responsible for the pressures induced during frost action (Bost, 2008). So, the measured values of the ‘transition zone’ are valid for the freeze–thaw cycle conditions used in this study. Indeed, if freeze is more intense (lower freeze temperature or longer freeze duration), the induced pressure is more important and thus, it affects rocks with a higher permeability and a lower dynamic modulus of elasticity. It is important to notice that there is a physical link between the dynamic modulus of elasticity and the water permeability. In fact, the permeability is related to the void connectivity and the dynamic modulus of elasticity to the number of contacts between grains. So, to simplify, the more porous is a rock, the less the grains are in contact.
The presence of a ‘transition zone’ shows that there is another parameter that should be taken into account in frost sensitivity evaluation. It could be linked to the grains size, the pore radius or the tortuosity, but it has not been identified yet.
4.2 Frost weathering follow-up
The permeability and dynamic modulus of elasticity measurements offer similar results. This point confirms what was underlined in the previous section: there is a physical link between the dynamic modulus of elasticity and the water permeability. Besides, since the results are similar, only the dynamic modulus of elasticity ones are presented in this part.
4.3 Sandstone observations
The sandstone S1, frost-resistant according to the standard (Anon, 2003), was damaged soon after vacuum saturation and has cracked macroscopically after 4 cycles (Fig. 5). Its ‘resistance’ to frost damage can be explained by the fact that, this sandstone is only partially saturated by water in natural conditions of imbibition. Indeed, the degree of saturation obtained by imbibition is given by the Hirschwald coefficient (Letavernier and Ozouf, 1987). According to the measurements, it is equal to 0.63. This means that after 48 hours of capillary suction of water, only 63% of its total porous space is filled with water. This low saturation releases enough space in the porous network for the increase in volume due to the transformation of water in ice (Chen et al., 2004; Prick, 1997). So, the low degree of saturation by imbibition of S1 might be the cause of its frost-resistance. This reasoning appears in some classifications on frost-resistance (Prick, 1997) to explain the rock sensitivity to frost action.
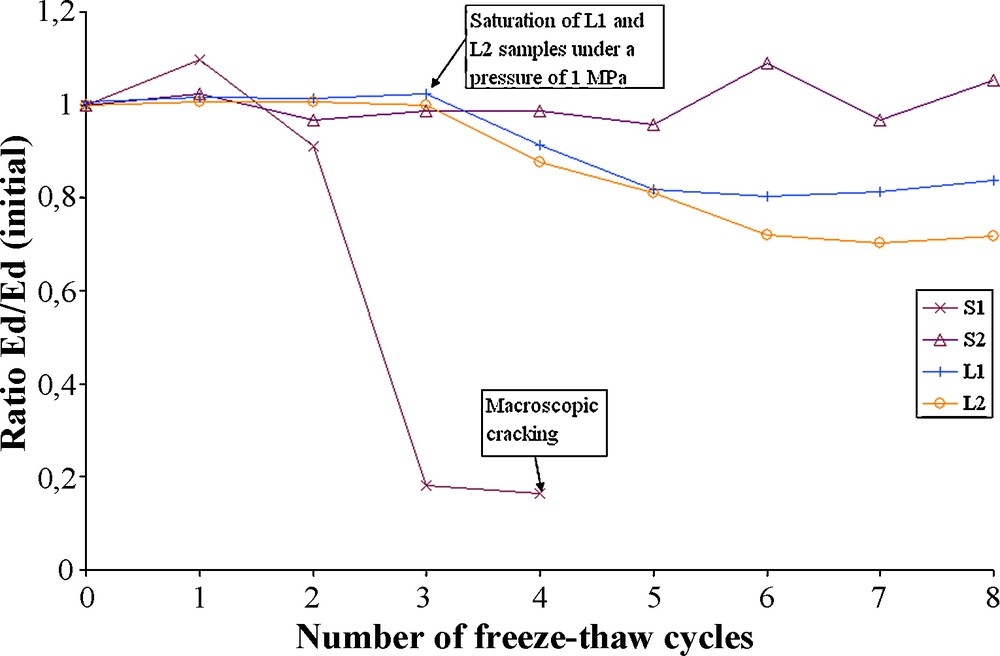
Evolution of dynamic modulus for vacuum saturated samples.
Évolution du module dynamique pour des échantillons saturés sous vide.
The sandstone S2 measurements have not been significantly modified with freeze–thaw cycles after vacuum saturation. And the reason why nothing has changed has been identified, probably another parameter is needed. S2's fluctuations on Fig. 5 must be due to the fact that measurements are made on saturated samples and S2 can easily loose water during the measurement since it has a high permeability. This reasoning can also be done on S1's fluctuation after the first freeze–thaw cycle.
4.4 Limestone observations
Concerning the two studied limestone samples (L1 and L2) no variation of the dynamic modulus was effective with a vacuum saturation (Fig. 5). So, they were saturated under a pressure of 1 MPa, by using the permeability device. This operation raised the porosity to 0.65% for L1 and 0.40% for L2. Afterwards, a decrease in the dynamic modulus of elasticity is noticeable (Fig. 5).
In addition, a stabilization phase of the dynamic modulus for samples L1 and L2 from the fifth freeze–thaw cycle appears on Fig. 5. It can be explained by permeability measurements made after each cycle. Indeed, during permeability tests, samples were put under confining and axial pressures of 3 MPa in the triaxial cell (see above). Although the stress condition was isotropic, it is possible that the samples became more and more sensitive to the confining pressure with weathering by successive freeze–thaw cycles. So, the samples were consolidated little by little when measuring permeability (Bernabé, 1987), which stabilized the dynamic modulus of elasticity values.
Finally, there is no major difference between L1 and L2 dynamic modulus evolution, although L1 is supposed to be more resistant to frost than L2. But L2's dynamic modulus of elasticity is more reduced than L1's after the same number of freeze–thaw cycles.
5 Conclusion
Frost sensitivity of a rock is resulting from the combined action of processes linked to porous network characteristics (state parameters) and to the way water flows into this porous network (transfer parameters). Our results show experimentally the complementary significance of a state parameter (dynamic modulus of elasticity) and a transfer parameter (water permeability) in determining the resistance of a rock to frost damage. More precisely, our results show that a rock with a low permeability and a high dynamic modulus of elasticity is less resistant to frost damage than a rock with opposite properties. Indeed, it means that if water cannot flow easily in the porous network of a rock when water freezes and its matrix cannot be reorganised with deformation induced by water freeze, the rock is sensitive to frost action. These two parameters are discriminating for the samples but there is still a ‘transition zone’ where some rocks are not classified precisely. The addition of a third extrinsic parameter, such as the freeze intensity or degree of saturation of the rock, should lead to a more precise identification of the sensitivity to frost action.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to J.D. Mertz, S. Ghabezloo and M. Bost for helpful discussions and advices. The authors also thank the Laboratoire de recherche des monuments historiques for its help.


