1 Introduction
Abiotic stresses cause considerable loss to agricultural production worldwide [1–4]. In the regions with low plant cover, it is important to consider the use of salt and drought-tolerant species for soil revegetation and preservation purposes [5]. Stress conditions such as drought, salinity, or heat have been the subject of intense researches [6–9]. Plant growth in coastal salt marshes and other salt-affected areas is frequently limited by both high salt content and limited water availability. In this context, osmotic stress generated by either drought and/or salinity represents the most common environmental hazard for the plant's growth and productivity. In addition, it has been reported that when combined, high salinity and soil drying may interfere with nutrient accumulation, thereby further contributing to growth inhibition. Indeed, Brown et al. [10] reported a decrease in potassium phosphorus, and calcium contents in shoot tissues, associated with an increase in sodium level, in response to increased salinity and drought in Spartina alterniflora. Consequently, it seems a prerequisite for plant species selected for their use in these areas to have adaptations that confer drought and salt resistance through notably the optimization of the utilization of water and nutrients.
However, in field conditions, crops and other plants are routinely subjected to a combination of different abiotic stresses [11–13]. Recent studies have pointed out that the molecular and metabolic responses of plants to the combination of drought and salinity are unique and cannot be directly extrapolated from the corresponding response of plants to each of these different stresses, when applied individually [14,15]. Drought may exacerbate the adverse effects of salinity on the plant nutrient status, but only few attempts have been made to quantify the combined effect of drought and salinity [16].
Sesuvium portulacastrum is a perennial halophyte, with great potential for soil covering and landscaping. It produces attractive branches with pink-purplish and occasionally white flowers [17]. Interestingly, S. portulacastrum may accumulate large amounts of Cd2+ in its shoots, suggesting its potential use for the phytoremediation of saline soils polluted by cadmium [18]. Furthermore, this plant has medicinal value [19] and produces secondary metabolites useful as substitutes for synthetic raw materials in food, perfumery, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries [20]. Successful introduction of S. portulacastrum in arid salty ecosystems largely depends on its capacity to tolerate specific environmental issues such as salinity, drought, and nutritional disturbances. Despite the effects of individual environmental factors on this species are well documented [18,21,22], however, the effects of interacting environmental factors remain poorly investigated. Therefore, the objective of this work was to quantify the effects of associated salinity and soil drying on S. portulacastrum growth, water relationships, and nutrient status.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant material and multiplication
S. portulacastrum (Aizoaceae) is a dicotyledonous perennial halophyte thriving in sandy soils. The plants used in this study were obtained by multiplication of selected plants by cuttings. The mother plants were cultivated at our experimental station, close to the sea shore (35 km north-east of Tunis;
2.2 Water deficit and saline treatments
Individuals presenting homogeneous development and size were selected for this study. An initial harvest was achieved after a pre-treatment period with optimal watering (100% FC). Plants were then divided in two lots: the first one was irrigated with nutrient solution lacking salt, while the second lot was irrigated with the same nutrient solution supplemented with 100 mM NaCl. One week later, plants of each treatment were divided into two further batches subjected or not for three months to water-deficit stress (25% and 100% FC). After 45 days of treatment, one lot of dehydrated plants was rewatered at 100% FC. Thus, there were finally six different treatments: (i) no water-deficit with or without salt; (ii) water-deficit, with or without salt; (iii) plants previously submitted to water-deficit, then rewatered with or without salt. Eighteen pots were weighed each two days and rewatered to 100% FC or to 25% FC by replacing the corresponding amount of transpired water. All the plants received the same quantity of nutrients, independently of the level of watering. For each treatment, six pots without plants were used to monitor the evaporative water loss from the soil surface throughout each watering regime.
2.3 Growth and water relationships
At the final harvest, plants (six per treatment) were divided into leaves, stems and roots, and their respective fresh weight (FW) was determined. Leaves were counted and their surface area was measured using a portable area meter (LI-3000A). Dry weight (DW) was obtained after oven drying at 60 °C until a constant weight was reached. The tissue water content (TWC) was determined as TWC (ml g−1 DW) = (FW − DW)/DW.
Leaf succulence index was calculated as
2.4 Proline determination and cation assay
Free proline was spectrophotometrically quantified according to Bates et al. [26]. Na+ and K+ were assayed by flame emission spectrophotometry after extraction in 0.5% HNO3 of the finely grounded dry matter. For each plant, potassium use efficiency (KUE) was calculated as the ratio of the biomass produced to the amount of K+ used during the experiment. Potassium absorption efficiency (KAE) was the ratio of the amount of K+ used during the experiment to the mean root biomass.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) using AV1W MSUSTAT program with orthogonal contrasts and mean comparison procedures was performed to detect differences between treatments. Mean separation procedures were carried out using the multiple range tests with Fisher's least significant difference (LSD) (
3 Results
3.1 Growth
Both soil drying and salinity significantly reduced plant growth, with a more pronounced effect for drought in our conditions (Fig. 1). The effects of the two factors were not additive. Indeed, the same whole plant biomass production was obtained under drought, with or without salt (ca. 40% of control). Rewatering plants after 45 days partially restored plant growth, reaching approximately 75% of that of the control plants. Furthermore, there was no significant difference between the plants previously submitted to water-deficit stress alone, or to the combined effects of water-deficit stress and salinity.
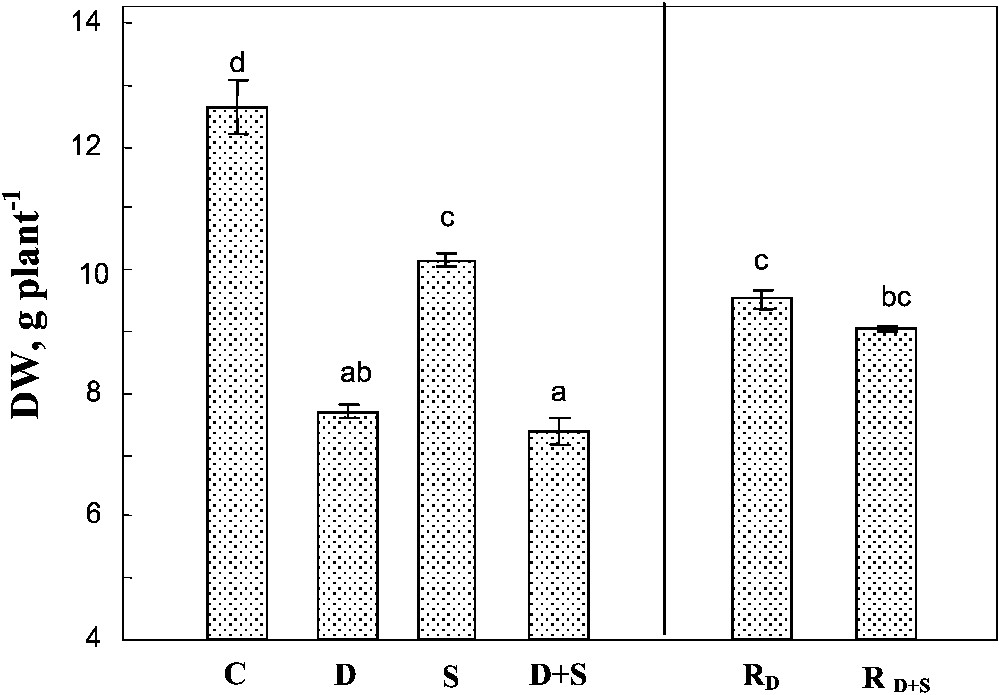
Whole plant biomass. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Whole plant biomass. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit ... Lire la suite
Changes in shoot DW were similar to those observed in the whole plant (Fig. 2A). Both salinity and soil drying significantly affected root DW (Fig. 2B). Yet, unlike shoots, root growth was more sensitive to salt than to soil drying. Moreover, drought significantly exacerbated the adverse effect of salinity on root growth. The effects of water-deficit stress and salinity were additive on these organs, so that the root/shoot ratio (Fig. 2B) increased by 28% in plants submitted to water-deficit versus only 6% in plants simultaneously exposed to drought and salt stresses. There was no significant difference between rewatered plants previously submitted to water-deficit stress alone or to the combined effects of water-deficit stress and salinity.
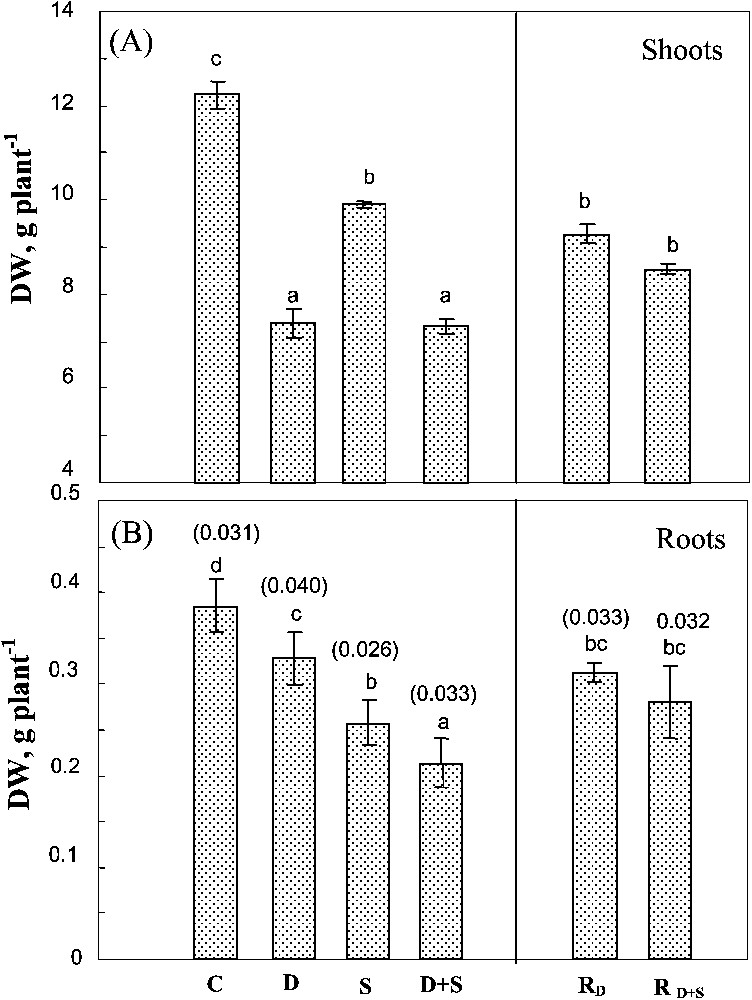
Biomass of shoots and roots. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Biomass of shoots and roots. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined ... Lire la suite
Both salinity and drought reduced leaf number (Fig. 3A) and total leaf surface area (Fig. 3B), their effects being partially additive only on the latter parameter. The individual leaf surface area was systematically higher in plants subjected to a single stress, or to the combined effects of the two constraints (Table 1). Thus, the reduction of the total leaf area of these plants was more due to a reduction in the leaf number.
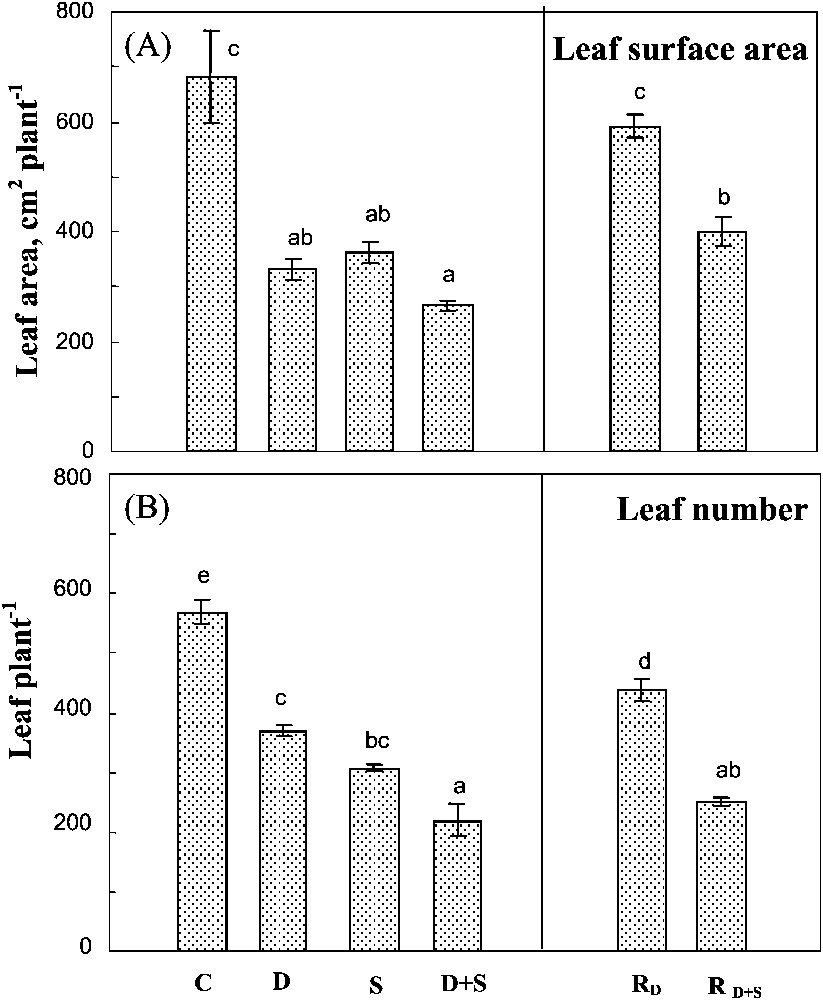
Total leaf surface area and leaf number. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Total leaf surface area and leaf number. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: ... Lire la suite
Mean biomass and surface area of individual leaves. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment
| Parameters | Treatments | |||||
| C | D | S | S+D | R D | R D+S | |
| Individual_foliar biomass (mg leaf−1) | 1.19 | 0.89 | 1.18 | 1.21 | 1.34 | 1.43 |
| Individual leaf area (cm2 leaf−1) | 8.72 | 8.89 | 14.63 | 10.06 | 15.83 | 16.12 |
Plant rehydration after a long-term water-deficit stress significantly improved both of the leaf number and the individual leaf surface area. In plants previously submitted to both stresses, rehydration only increased leaf area, without any effect on leaf number (Fig. 3B). Thus, the plant ability to recover its leaf development was better preserved after water-deficit stress than after the exposure to the combination of both drought and salinity.
3.2 Water relationships
Both drought and salinity significantly reduced the leaf water content, with a much more marked impact for the first constraint (Fig. 4A). Yet, the effects of the two constraints when combined were not additive. On the contrary, salt presence in the culture medium of plants subjected to drought was partially shown to prevent leaf tissue dehydration. Transferring the plants previously subjected to water-deficit (with or without salt) improved tissue hydration, this trend being much less pronounced following the exposure to water-deficit alone than when both stresses were combined.
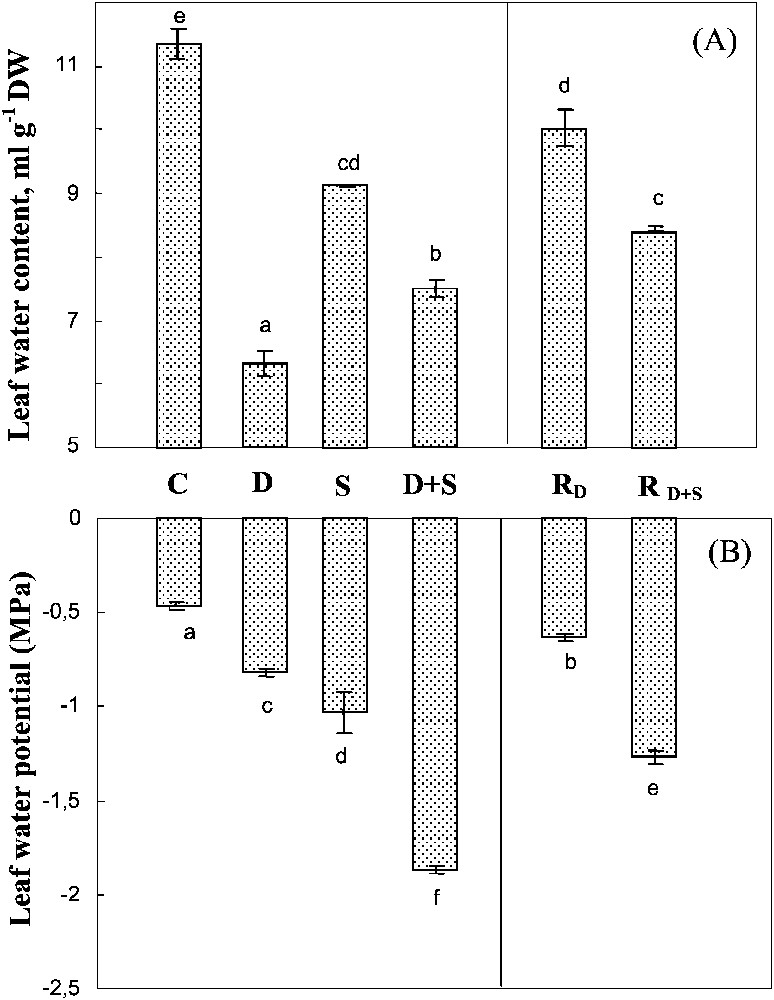
Water content and water potential of leaves. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Water content and water potential of leaves. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: ... Lire la suite
In all treatments, leaf dehydration caused by salinity, water-deficit, and their interaction was accompanied by a significant decrease in leaf water potential (Fig. 4B). However, the more negative values of the water potential were not associated with larger dehydration, but were rather due to the presence of salt, suggesting that salt accumulation contributed more efficiently than passive dehydration in lowering the leaf's water potential.
3.3 Water use efficiency and leaf succulence
Salinity and water-deficit when separately applied led to similar increases in WUE and showed additive effects when being combined (Fig. 5A). Rewatering plants after drought or drought combined with salinity did not significantly modify WUE. Drought and salinity had opposite and additive effects on leaf succulence index (Fig. 5B). In plants simultaneously submitted to both constraints, the increase of WUE due to salinity plants largely balanced the decrease due to water-deficit. Rewatering plants after drought partially restored succulence to the value observed in controlled plants, but had no effect on plants previously submitted to combined drought and salinity.
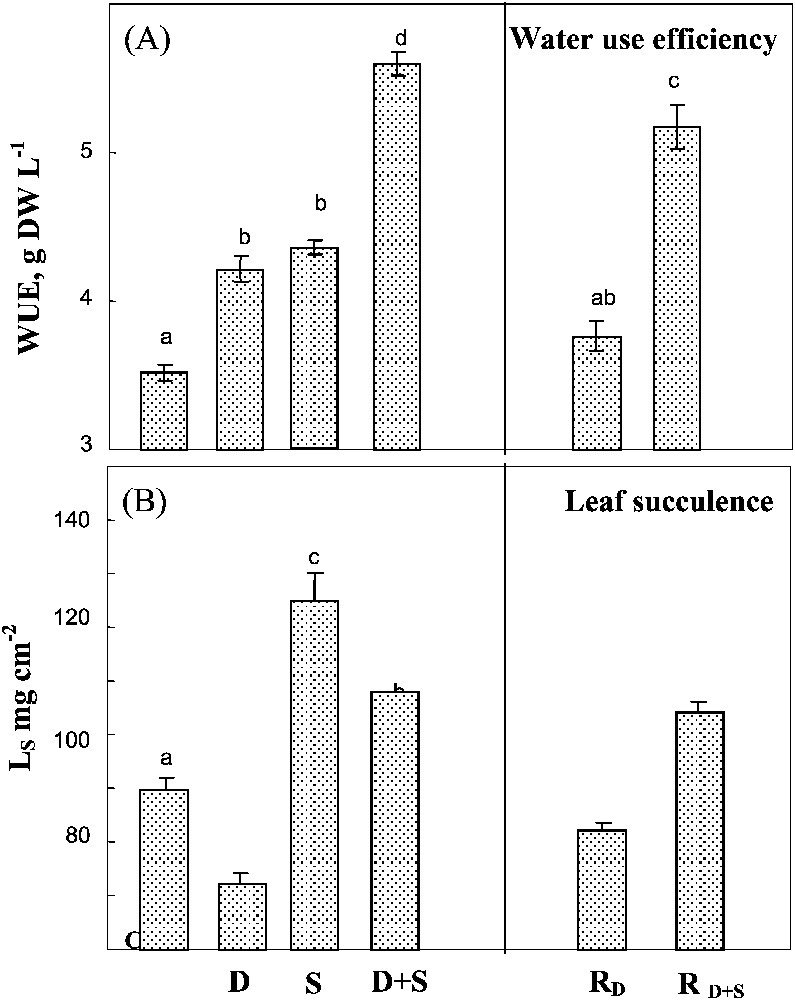
Water use efficiency and leaf succulence. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Water use efficiency and leaf succulence. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity ... Lire la suite
3.4 Nutrient status
3.4.1 Potassium
Both salinity and water-deficit restricted K+ uptake, as estimated by the whole plant K+ amount (Fig. 6B). Salinity had a significantly more drastic effect on K+ content than water-deficit stress, and there was no significant interaction between the two constraints. Potassium concentration in leaf tissues (mmol g−1 DW) was poorly affected by water-deficit stress, but was largely restricted when salt was present in the medium (Fig. 6A). Potassium status, i.e. whole plant content and leaf K+ concentration, was partially restored in plants rewatered after a water-deficit stress alone, but not after combined drought and salinity treatments.
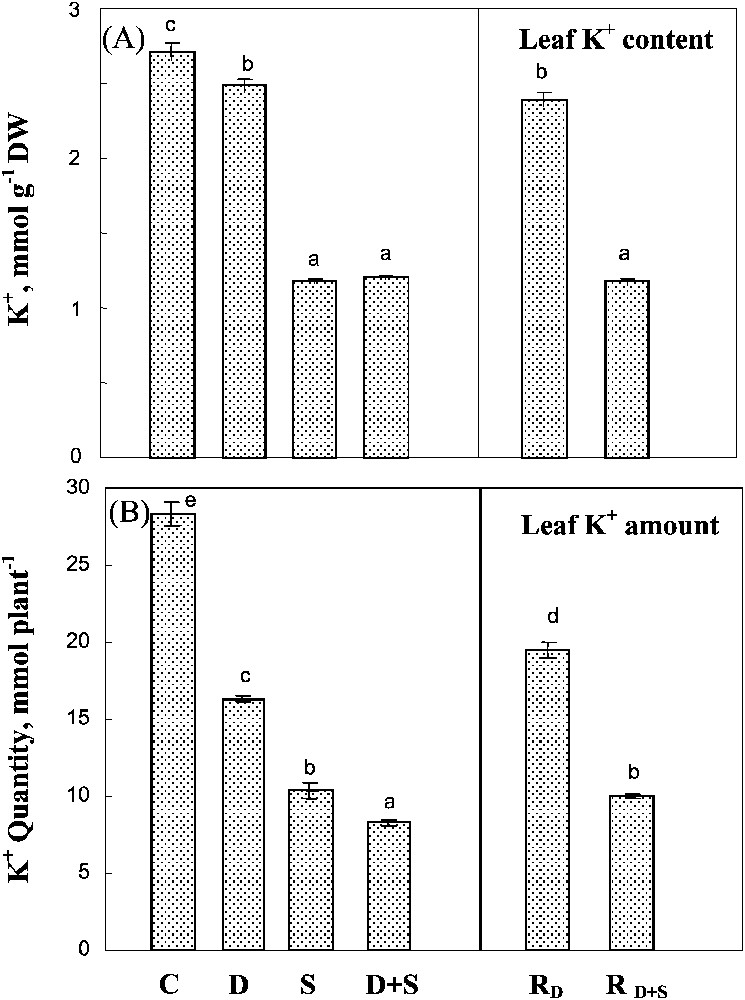
Potassium content and potassium amount in leaves. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Potassium content and potassium amount in leaves. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: ... Lire la suite
The reduction in the whole plant K+ amount was associated with a decrease in potassium absorption efficiency (KAE) in all stressed plants (Table 2). Thus, K+ uptake was limited not only by the inhibition of root growth (Fig. 2B), but also by the lower performance of the root uptake systems, especially in the salt-treated plants. However, as shown in Table 2, salinity, whether alone or combined with drought, increased the potassium use efficiency (KUE) by 50%.
Potassium nutrition. KAE is the K+ absorption efficiency, estimated by rationing the amount of K+ used during the experiment to the mean root biomass
| Parameters | Treatments | |||||
| C | D | S | S+D | R D | R D+S | |
| KAE (mmol g−1) | 219c | 136b | 103a | 113a | 201b,c | 78a |
| KUE (g mmol−1) | 0.44a | 0.47a | 0.97c | 0.91b | 0.48a | 0.90b |
3.4.2 Sodium
A preferential accumulation of Na+ in shoots rather than in roots was observed regardless of the treatments applied (not shown). High sodium concentration was observed in the leaves of salt-treated plants, and was significantly increased by the simultaneous exposure to drought and salinity of this parameter (Fig. 7). Rewatering the plants in the presence of salt slightly reduced Na+ concentration in the leaves.
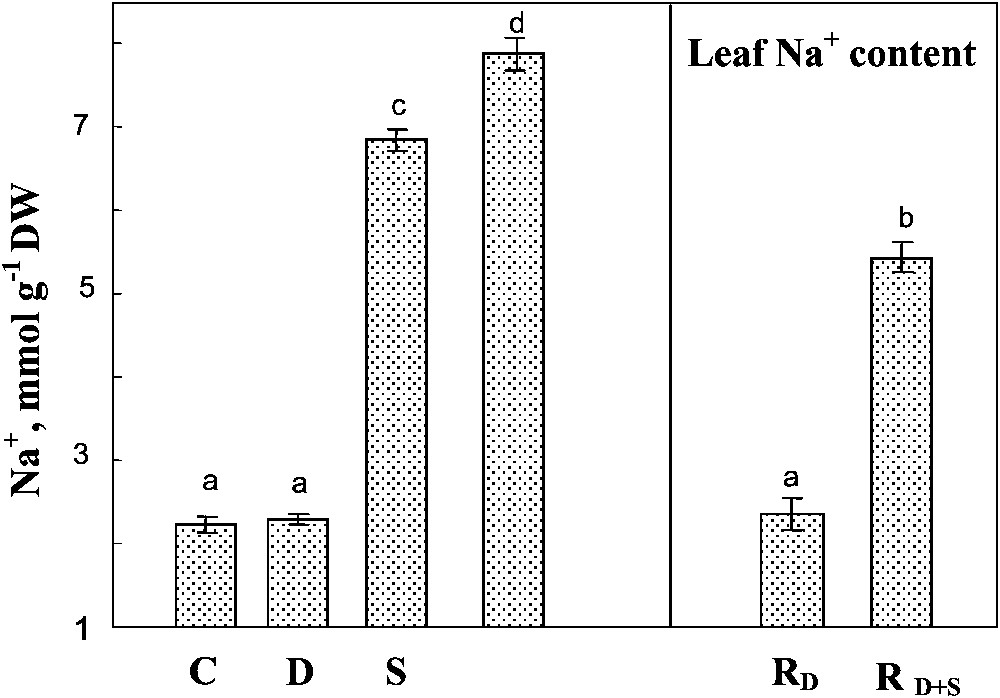
Sodium content in leaf tissues. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Sodium content in leaf tissues. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined ... Lire la suite
3.4.3 Proline accumulation
In both leaves and roots, drought and salinity applied separately increased proline concentration, and their combination resulted in higher proline accumulation (Fig. 8). Proline was more abundant in leaves than in roots, especially in plants cultivated in the presence of NaCl, and the stress-induced changes presented larger amplitude in the former organs. The high capacity to accumulate proline in leaves of salt-treated plants was maintained in the rewatered plants after a combined stress treatment.

Proline concentration in shoots and roots. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Proline concentration in shoots and roots. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity ... Lire la suite
4 Discussion
Drought and salinity are two environmental constraints that often occur simultaneously in arid regions. The ability to overcome multiple and simultaneous stresses is of great importance for the plant growth and survival in stressful environments [27]. The present study aimed at investigating the effects of long-term (three months) salinity and/or drought on growth, water status, and solute accumulation in S. portulacastrum. Relatively mild soil drying and salinity significantly were detrimental for the plant growth. The effects of salinity and soil drying were not additive on the whole plant biomass, and the presence of salt in the culture medium of plants subjected to water-deficit stress authorized lower leaf water potential associated with the maintenance of higher leaf hydration, higher accumulation of Na+ and proline in leaves, and higher use efficiency for water and K+. Although scarce, data documenting the combined effects of abiotic stresses suggest that their interaction depends on both the nature of the constraint and the plant species. For example, Stoyanova and Yordanov [28] reported that combined salinity and high temperature had both additive and interactive effects on bean plants. In the halophyte Spartina alterniflora, the effects of salinity and drought were not additive on biomass production [10]. Moreover, salt exposure might partly alleviate the negative effects of water-deficit on the plant growth. Our results show that the addition of salt to plants subjected to water-deficit stress was beneficial to the tolerance of S. portulacastrum to the latter constraint.
4.1 Dry matter partitioning
Consistently with our findings, it has been reported that water-deficit stress was more inhibiting for shoot than for root biomass, resulting in an increase of the root/shoot DW ratio. This behaviour is considered a criterion of adaptation to drought [22,29–31], although correlation between root development and water extraction ability is not always clear [32,33]. In our study, the preferential biomass allocation to roots of plants subjected to water-deficit was not maintained when plants were simultaneously submitted to salinity and water shortage. The higher inhibition of root growth by salinity, whether alone or combined with drought, led to a decreased root/shoot ratio. Thus, our results support the assumption [34] that enhancing root growth cannot confer resistance to water-deficit under salinity conditions. Indeed, high root/shoot ratio may not be a favourable trait under salt stress, since it might enhance the accumulation of toxic ions into the shoot and, consequently, might anticipate the oncoming of the salt tolerance threshold [35]. Consistently with this statement, the decreased root/shoot ratio of salt-treated S. portulacastrum, which contrasted with the increased ratio that occurred in water-deficit conditions, would enable the plant to control salt accumulation. One may hypothesize that the large reduction in root growth observed in plants subjected to salt alone or in combination with water-deficit limited their capacity to explore soil and to absorb water. However, we showed that under these conditions, leaf water content was significantly enhanced by comparison with the plants subjected to water-deficit stress alone. This suggests that the plants may have relied on other mechanisms to ensure an appropriate water supply, particularly by lowering its leaf water potential.
4.2 Aboveground dry matter accumulation
Salinity and water-deficit stress separately applied or in combination caused significant reduction of the leaf area, and a remarkable decrease of the plant dry matter accumulation. Together with the stomatal closure, the leaf area reduction under drought and saline stresses can be considered an avoidance mechanism, which minimizes water losses [16,36].
When subjected to water-deficit stress, plants reduce their transpiration as a consequence of both stomatal control and decrease in total leaf area, which enhances water use efficiency (WUE) for dry matter production [37]. WUE, traditionally defined as the ratio of the dry matter accumulation to the water consumption over a season, significantly increases under water-deficit stress, and is regarded as an important adaptive trait [38–40]. In our study, despite WUE was calculated over a relatively short period, it may match the same concept as in the traditional definition. WUE significantly increased in plants subjected to water-deficit stress or to salinity, the highest value being observed in plants subjected to the combined effects of both salinity and drought. Hence, these plants were as productive as the plants submitted to water-deficit stress alone, but with a lesser water consumption. Tissue water content represents a negligible fraction of water consumption. Therefore, water loss by transpiration was definitely lower in plants subjected to the combined effects than in those subjected to water-deficit alone. This result can be explained by a high retention of water in leaves, likely resulting form their high Na+ and organic solute content. Other mechanisms may have contributed to the improvement of WUE in plants subjected to combined salinity and drought. For instance, Na+ seems to play important role in photosynthesis [41,42].
Drought and salinity, either alone or combined, similarly reduced the total leaf surface area to ca. 40% of that observed in control plants. Plants submitted to combined constraints showed the largest reduction in leaf number, but this trend was compensated by salt-induced increase in the mean surface area of individual leaves. In addition, salt stressed plants were much more sensitive in terms of leaf area development, as compared to the aboveground dry matter accumulation. At the end of the experiment, a 40% reduction of the total leaf surface area in plants submitted to water-deficit coincided with a 60% decline in the aboveground dry matter. In contrast, in salinized plants, a 50% leaf area reduction corresponded only to a 20% reduction of the aboveground dry matter accumulation. Thus, salinity may have promoted the reallocation of photosynthates in stems and leaves, which did not occur in drought-stressed plants. One of the consequences of this reallocation was the increase in leaf thickness (Fig. 5B).
4.3 Water relations
Despite water-deficit substantially decreased the leaf water content, this effect was mitigated when salt was present in the irrigation solution of water-stressed plants. This trend was associated with a decrease of the leaf water potential and a high accumulation of Na+ and proline in leaf tissues (Fig. 9), suggesting the involvement of these solutes in osmotic adjustment [43]. S. portulacastrum may behave as a typical Na+ includer, which compartmentalizes sodium within the leaf cell vacuoles where it could be used as an osmoticum to lower the osmotic potential necessary for the maintenance of the plant hydric status. The absence of leaf toxicity symptom, in spite of the high tissue Na+ concentration, supports the hypothesis that Na+ was excluded from the cytoplasm. Finally, Na+ sequestration in the vacuole where it could replace potassium might explain the increase of K+ use efficiency (KUE) that was observed in plants grown in the presence of salt.
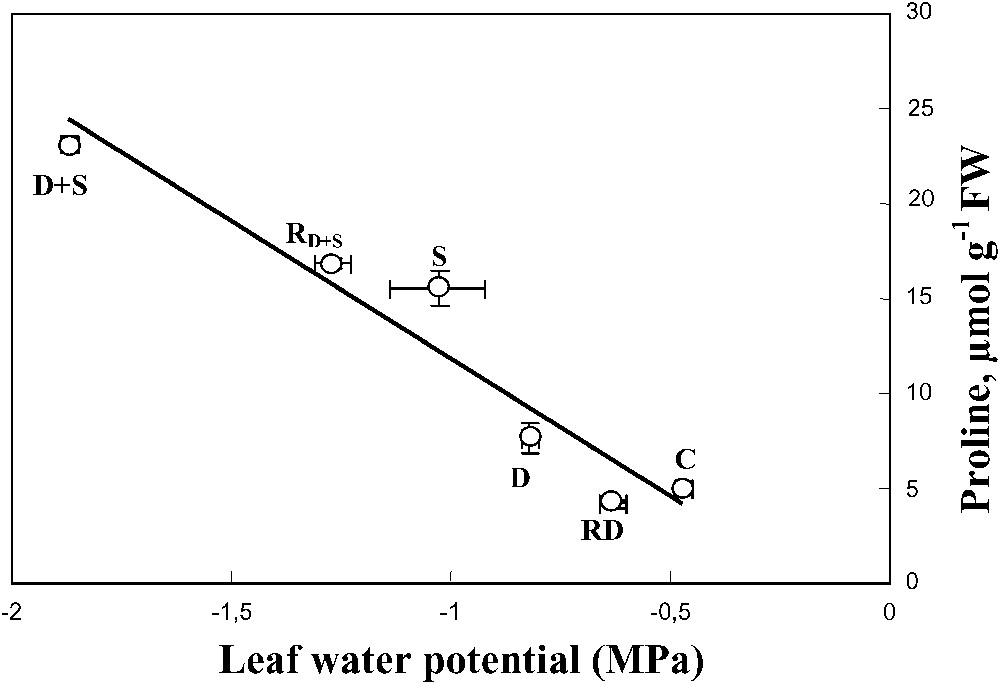
Relationship between leaf proline concentration and leaf water potential. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. The letters refer to the different treatments. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% FC); S: salinity (100 mM NaCl, 100% FC); D+S: salinity combined with water-deficit stress (100 mM NaCl, 25% FC). RD: plants rewatered to 100% FC after 45 days of treatment D.
Relationship between leaf proline concentration and leaf water potential. The plants were harvested after 90 days of treatment. The letters refer to the different treatments. C: control (no NaCl or water-deficit: irrigation at 100% FC); D: no NaCl, water-deficit (25% ... Lire la suite
When combined, drought and salinity significantly increased proline concentration in both leaves and roots. The high negative correlation between proline and leaf water potential suggests a potent role of proline in the osmotic adjustment. Although the role of proline in osmotic adjustment and drought tolerance is still debated [31,44,45], we have shown in a previous work [46,47] that in S. portulacastrum subjected to a short-term water-deficit, the osmotic balance between vacuole and cytoplasm may be primarily achieved through accumulation of proline.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, our results indicate that morphological (shoot/root ratio, leaf number and expansion) and physiological (nutrient accumulation, osmotic adjustment, water-use efficiency) adaptation mechanisms may significantly diverge between salt stress and water-deficit stress. Salt may improve the response of S. portulacastrum to water-deficit stress as a consequence of (i) decrease in water leaf potential, (ii) increase in water-use efficiency, (iii) improvement of potassium use efficiency as a consequence of Na+ utilization in the osmotic adjustment, and (iv) increase in proline accumulation. In addition, recovery for the most of the parameters related to growth, development, hydric status, and nutrition was substantial on the release of stress, in spite of the duration and magnitude of the stress applied. Hence, it could be inferred that soil drying alone or combined with salinity did not cause permanent alterations in S. portulacastrum plants, which can be expected to be a useful species in revegetation programs in arid saline areas.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Technology and by the Tunisian–French ‘Comité mixte de coopération universitaire’ (CMCU) network # 02FO924. The authors are very grateful to Prof. Claude Grignon (‘Institut de biologie intégrative des plantes’, Montpellier, France) for the critical review of the English version of the manuscript and for his constructive contribution.


