1 Introduction
Palaeoenvironmental evidence for the character of lowland cultural landscapes during the last 3000 years in Burgundy (France) is poorly understood because of the scarcity of lowland mires. The Fénay marsh is a wetland located in Burgundy (Fig. 1), between Dijon and the vineyard and village of Gevrey-Chambertin. The swamp developed along a stream called “La Sans-Fond”. The spring on this small stream is located at about 1 km from our site. The stream runs into the “Vouge”, a tributary of the Saône River. The swamp covers an area of about 3 ha at an altitude of 224 m a.s.l. The predominant land-use in this sector is pasture and arable cultivation. The exploitation of vineyards begins at about 4 km further west, on the “la Côte dijonaise” side. The stream has its origin in a spring created by the intersection of groundwater in southern Dijon. This groundwater circulates in the formation of the “Gravels of Domois” using a rather shallow section of the superficial geomorphological relief of the plain. This formation is linked to the Eburonian stage [1] associated with the old Quaternary in its current definition [2].

Location of the studied area.
2 Archaeological and historical data
Archaeological data show an important settlement from the Bronze Age and during the Iron Age. Archaeological remains near the swamps are represented by burials in circular enclosures dating from the Late Bronze Age and inhumations in square enclosures dating from La Tène 1. Other similar structures, circular or quadrangular, have been located by aerial survey. Some of them could be related to other burials or Iron Age structures [3]. During the Roman period, the Roman road from Lyon (France) to Trèves (Germany) ran at about 1 km from the swamp. The dense settlement developed in the area is represented by the ruins of several buildings, one of them situated in the swamp upstream.
Fénay (Fedenniacus) is mentioned for the first time in 679 cal. AD in texts from the Merovingian period [4]. The “Sans-Fond” stream is well-known as a model of medieval hydraulic development: its course was diverted over more than 14 km by the Cistercian monks in the 13th C in order to bring water and hydraulic energy to the abbey of Cîteaux.
Textual data refer to a fortified house situated near the site, in the hamlet of Chevigny [5] in 1387 and again in 1469, and from 1164 to a mill in the locality “le moulin des étangs” (the mill of ponds) situated just downstream from the Fénay marsh. Two mills are recorded in the 13th C as belonging to the Cîteaux Abbey [6], and a single mill, still existing in the 17th C, “as established on the road of the Pond”.
A potter and several tiliers settle in the village of Fénay in the Modern period. On the Cassini map, the land registry at the end of the 18th C indicates a “swamp” where the pond was located and therefore it existed from at least the 12th to the 17th C.
3 Methods
The core (241 cm long) was performed with a Russian corer in March 2007. Pollen sampling was performed every 4 cm. Sediment samples were processed for pollen and NPP (non-pollen palynomorphs) analysis using standard techniques [7]: they were treated with HCl (10%), NaOH (10%), HF (40%), ZnCl2 and acetolysis. A minimum of 400 pollen grains of terrestrial plants (Cyperaceae, Alnus, aquatic taxa, spores and non-pollen palynomorphs were excluded from the pollen sum) was counted for each sample to ensure statistical significance.
Pollen grains were identified with the aid of keys [7,8], photographs [9] and a reference collection. Non-pollen palynomorphs were identified according to Bell [10], van Geel [11], van Geel et al. [12,13] and van Geel and Aptroot [14]. NPP identification followed van Geel's terminology [11] for known types; these types are indicated in the text as ‘HdV-xxx’ (HdV = Hugo-de-Vries Laboratory, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands). Percentages were calculated on the basis of the same pollen sum used for the pollen diagram [15]. Some few samples were poor in NPP (from 15 to 100 fungal and other remains). In most cases, abundance of spore and algae enabled counts from 100 to 450 NPP.
The palynological diagram was constructed using TILIA and TGView software [16]. Pollen assemblage zones are defined by a constrained cluster analysis (CONISS) developed by Grimm [17].
4 Radiocarbon dating and age–depth model
A total of five AMS radiocarbon dating measurements (Fig. 2) were performed and calibrated using the CALIB 5.0.1 program [18]. Interpolated dates for undated events were obtained by a mixed-effect regression model according to the procedure standardized by Heegaard et al. [19]. The most recent sample was 34 cm but pollen data were recovered as far as 2 cm. Therefore, we extended the age-depth curve over the undated 32 cm on the basis of the sedimentation rate estimated on the previous section (34-2 cm).

AMS Radiocarbon dates and age-depth diagram based on AMS radiocarbon dates from terrestrial plant macrofossils.
5 Results and discussion
A simplified percentage diagram with selected curves of pollen and non-pollen palynomorph taxa (NPP) is presented in Figs. 3 and 4.
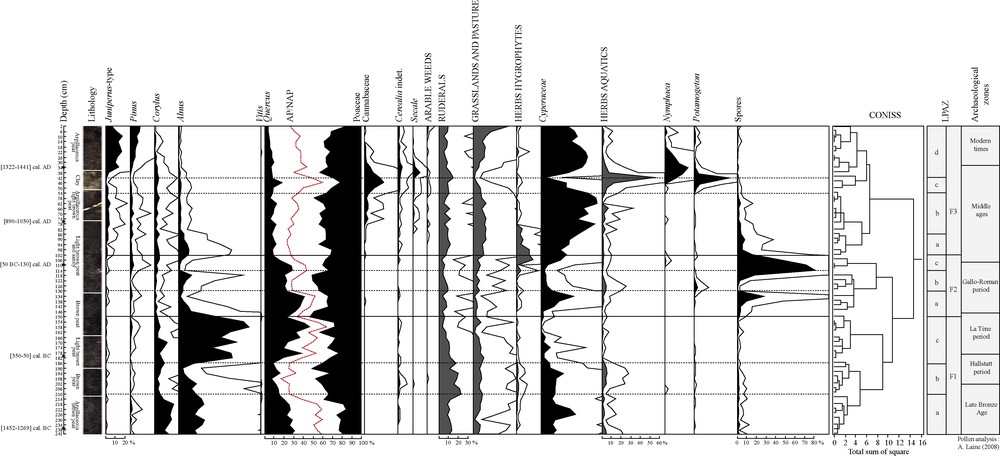
Simplified pollen diagram from Fénay (Burgundy) based on a relative percentage calculation. Exaggeration curves × 5.

Non-pollen palynomorph (NPP) diagram Fénay (Burgundy). HdV = Hugo-de-Vries Laboratory in Amsterdam Exaggeration curves × 5. Coprophilous fungi (A), Vegetative remains of Nymphaeaeceae (B), Unidentified microfossil probably of aquatic origin (C), Green algae (D), Fungi indicator of wet conditions (E), Microfossil indicator of eu- to mesotrophic wet conditions (F), Fungi indicator of dry conditions (G), Parasitic fungi (H).
5.1 From the Late Bronze Age to the Gallo-Roman period (LPAZ F1 and 2)
Zone F1a (241–210 cm – ca. 1300–900 cal. BC) represents a period of mostly open ground (AP = 55/60%), with Poaceae and Cyperaceae as the dominant pollen types. A non-pollen palynomorph, Clasterosporium caricinium, shows a trend similar to the Cyperaceae curve: fossil remnants of HdV-126 are usually identified as Hyphopodia material. The co-occurrence with local Carex species is often obvious and shows that Cyperaceae constituted an element of the local vegetation.
Quercus, Alnus and Corylus are the only tree taxa substantially represented. Anthropogenic indicators (Cerealia, ruderals and plants from grassland pasture) show a moderate human impact. Coprophilous fungi (Sordaria type, Sporormiella, Podospora, Cercophora…) are related to herbivore dung probably due to grazing cattle in the surroundings [20]. Considering the 14C data and the depth-age model, the palaeoecological record probably begins with the Late Bronze Age. This period was connected with the first archaeological records in the area. Increasing human activities could be responsible for the development of the swamp [21]. The end of LPAZ F1a is characterized by a decrease in green alga and the higher values of fungi spores and Clasterosporium caricinium, suggesting a drier environment and the formation of peat deposit. According to pollen data from others studies [22,23], the Late Bronze Age represents an important threshold in the landscape history. During the Neolithic, the agricultural system was based on shifting cultivation on slash-and-burn fields and abandoned to reforestation after four to five years [24]. Deforestation, the arrival of numerous settlers, the establishment of perennial fields with short fallow phases, man-made obstructions of flow probably led to a transformation of landscapes, with more intense soil erosion [23,24] and a change in water circulation in the catchment area, favouring peat inception with the formation and accumulation of organic sediment in the wet zone [25].
In zone F1b (210–186 cm – ca. 900–580 cal. BC), Alnus decreases and the increase in aquatic plants and HDV-128 (probably from algal origin) suggests a wetter environment. HdV-128 [26,27] occurs in shallow open water under meso- to eutrophic conditions. However, fungi related to dry conditions (HdV-200 and 201) appear in this zone and suggest frequent fluctuations of the water depth and periodic emersions of the bottom of the ponds [28]. The emersion of the wetland can activate the fungal decomposition of organic materials on the surface. According to the age–depth model, this zone is dated from the beginning of the Iron Age and could correspond to Episode 5 (800–400 cal. BC) determined by Magny studies on lake-level records [29]. Episode 5 coincides with a concurrent and an abrupt decrease in low lake-level and an increase in high-lake level scores. Despite climate change [30,31] and the lack of archaeological data, there is no abandonment of farming activities. An increase in coprophilous fungi sum suggests a growing grazing pressure and a new taxon appears: Coniochaeta lignaria (HdV-172). This ascospore is common on dung, wood and other degraded organic matter [14]; it is also known to be a pyrophilous fungi [32].
Zone F1c (186–150 cm – ca. 580–100 cal. BC) is characterized by a sudden increase in Alnus and Quercus frequencies (AP = 40 to 60%). The establishment of alder in eutrophic swamps is a part of the natural pattern of plant succession. Its abundant wind- and water-dispersed seeds allow it to colonize early successional sites with herbaceous species such as Phragmites sp. and Carex sp. [33]. In the pollen diagram, Poaceae and Cyperaceae decrease together with ruderals and, at the end of the zone, with plants from grassland, pasture and coprophilous fungi. Diminishing values of HdV-128, aquatic herbs and regular occurrences of spores from dry habitat fungi (HdV-200 and 201) suggest a drier environment suitable for the establishment of alder. An oak forest grew around the swamp. This pollen zone is dated from the very end of the Hallstatt period to La Tène period. Despite the Alnus and Quercus reforestation, human impact is still perceptible and only decreases at the end of the zone. Alder expansion seems to be a local event, concerning the swamp and its nearby surroundings: archaeological remains of this period (burial enclosures) show the continuity of settlement in the area.
LPAZ F2a (150–130 cm – ca. 100 cal. BC–179 cal. AD) shows a major change in environment: Alnus percentages fall and Quercus becomes the dominant pollen type. A widespread deforestation of Alnus could have resulted from an expansion of agricultural activities [34]. However Cerealia type occurrences are sparse and pastoral indicators (grassland and pasture plants, ruderals, coprophilous fungi except Coniochaeta cf. lignaria…) decrease. The disappearance of Alnus could then be linked to a change in the water table. The zone becomes an open marsh and HdV-715 suggests more particularly the development and helophyte marsh with varying water table and eu- to mesotrophic condition [35]. The swamp is probably surrounded by an oak forest. The increase in spores of Ustulina deusta, (often classified nowadays as Kretzschmaria deusta (Hoffm.) P.M.D. Martin) suggests a nearby oak forest. This parasite causes soft-rot of wood. Its regular occurrence on a variety of host trees including Quercus has been observed. A close relationship between the incidence of the fungus and the pollen curves of its potential host plants is evident [14].
The disappearance of Alnus leads to a more open landscape (AP = 50 to 25% by the end of the zone). Zone F2b (130–114 cm - ca. 179–380 cal. AD) and F2c (114–102 cm – 380–540 cal. AD) are marked by low frequencies of anthropogenic indicators (Cerealia type disappear) and coprophilous fungi. Curves of Cyperaceae, Equisetum, Potamogeton, Nymphaea, spores of fern and non-pollen palynomorphs of algal and aquatic origin (HdV-128) are very irregular, suggesting a rapid environmental shift, with a change from very wet phases to drier phases characterised by a peak of HdV-200 [26]. According to the age–depth model, this zone spans the second part of the Gallo-Roman period and the beginning of the Early Middle Ages (3rd–6th C).
5.2 The Middle Ages (LPAZ F3a, b, c and d)
A significant decrease in total AP percentages is observed during the Early Middle Ages at LPAZ 3a (102 cm to 86 cm – ca. AD 540–700), reaching minimum percentages of 25% TLP. This decline in tree frequencies is related to the increase in abundance and/or regularity of Cyperaceae, grassland and pasture plants, ruderals, hydrophytes and dung indicators. The increase in HdV-128 begins toward the end of zone 2c and is concomitant in zone 3a with an increase in green algae often linked to meso-eutrophic conditions. Mougeotia sp., Spirogyra sp., Zygnema sp. and Botryococcus sp. suggest stagnant waters and a low-water level [27,36,37]. There are also occurrences in ascospores of Valsaria cf. variospora (HdV-140) related to the formation of a peat deposit under wet eutrophic conditions [14]. The site then remains a wet zone, occasionally subject to floods and the formation of a temporary pond.
The increase in Sordaria type, Sporormiella and Apiosordaria cf. verruculosa points to a high density of domesticated herbivores in the surroundings in LPAZ F3b (86–54 cm – 700–1180 cal. AD). New cultures occur with the first record of Secale, arable weeds and Cannabaceae. The first peaks of Cannabaceae pollen (5%) were reported at a depth of 74 cm (ca. 900 cal. AD). However, the curve begins at a depth of 86 cm (LPAZ 3a), suggesting the onset of hemp cultivation circa 700–750 cal. AD in the region. The first evidences of hemp cultivation in Eastern France are often recorded between the 8th C [36] and the 11th C in mountainous areas [22,38]. These dates coincide with the spread of hemp between the 5th and the 9th C in other European regions [32,39–43].
The development of aquatic taxa in LPAZ 3c (54–42 cm – 1180–1340 cal. AD), the disappearance of low-water level taxa (Spirogyra sp., Mougeotia sp., Zygnema sp.) and the clay deposit in the lithography are probably related to a period of higher water level. Written sources indicate that the course of the stream was diverted over more than 14 km by the Cistercian monks in the 13th C, in order to bring water and hydraulic power to the abbey of Cîteaux [6]. The swamp became a pond during this period and Cannabaceae reach their maximum values (20%). The peak of Cannabaceae (42 cm) is concomitant with a peak of green algae, Pediastrum. There are peaks of Potamogeton, suberized cells of Nymphaeaceae and finally an increase in Nymphaea in the following level (38 cm). Cannabaceae declines from 34 cm but other cultivated plants, such as the Cerealia type and Secale, increase. The existence of a deeper pond, the increasing Cannabaceae percentages and the eutrophic indicators raise a question: was the pond used for hemp retting?
Some authors consider that hemp pollen percentages exceeding 10–15% could be attributed to retting [44,45]. By contrast, other authors consider that these percentages should be higher than 25% [46,47]. With maximum values attaining 20%, our pollen percentages of Cannabaceae allow us to interpret the existence of hemp cultivation and hemp retting in the pond. Furthermore, high percentages of hemp pollen, together with an increase in Potamogeton, have been used as indicators of retting [32].
Historical sources often record the problems of pollution due to hemp retting. It is common knowledge that the retting process in pools brings about changes in water chemistry, increasing acidity, eutrophication and toxicity [32,48]. The water was not used by the Cistercians in Burgundy for drinking purposes [6]. Most of the Cistercian ponds in this area were used for hydraulic power (mill), fish farming or hemp retting. The pond could have been used for hemp retting on some occasions, but it was not only used for this purpose. Heavy pollution caused by hemp retting would not have permitted the development of Pediastrum sp. [49]. It is surprising to note that zone F3b is contemporaneous with a cold phase (Episode 2: 1200–1300 cal. AD) recorded by Magny [29]. This climate reversal could have favoured and made it easier to enlarge the pond.
The decrease in Pediastrum sp., Cannabaceae, and the increase in HdV-128, LPAZ F3d (42-2 cm – ca. 1340–1875 cal. AD) suggest different ecological conditions: a wet zone with a smaller pond. The persistence of a small pond is suggested by the peak of Nymphaea. However, the increase in Cyperaceae shows a drier zone. The increase in Secale and Cerealia, immediately after the decrease in Cannabaceae, could reveal a common Cistercian practice: the culture of cereal in a dry pond [6]. The main arboreal taxa are Pinus and Juniperus type: the latter suggest the development of this taxon in the drier part of the zone. Juniperus, together with Thuya and Salix are the main trees growing in the swamp today. The creation of the nearby Gevrey-Chambertin vineyard (5 km) does not appear in this diagram. Vitis has a very sparse pollination and the absence of this taxon is not surprising [22,50].
6 Conclusion
The pollen and non-pollen palynomorph profiles from the Fénay marsh in Burgundy record more than three millennia of vegetation history and human impact. NPP are very reliable indicators of edaphic change as well as of farming activities and grazing pressure [46], and allow a very detailed reconstruction of past ecological conditions and evolution.
The base of the sequence records an open environment that is correlated with the Late Bronze Age. Pollen and NPP evidence from this period suggest that human settlement occurred in a landscape characterised by farming and grazing activities. The increase in algae during the Hallstatt period suggests a wet phase with a temporary pond, perhaps linked to the Iron Age climate reversal. The establishment of Alnus during La Tène period in this swamp is related to a natural pattern of plant succession. Alder values suddenly decrease with the beginning of the Gallo-Roman period. However, the circumstances surrounding this disappearance are not clear. Deforestation seems difficult to envisage in a context of decreasing human impact. A change in the water table could have created wetter ecological conditions unfavourable to alder. The entire Gallo-Roman period and the beginning of the Early Middle Ages are marked by rapid environmental shifts, with a change from very wet phases to drier phases. An oak forest remains in the surroundings of the swamp. This forest disappears by the end of the 6th C. The very open landscape around the swamp is characterised by a mixed economy based on cereal cultivation and pastoral activities until the 13th C. Cannabaceae seems to be cultivated by the end of the 10th C. This culture is particularly developed between the 13th and the 14th C, and the Cistercian monks transform the swamp into a pond during this period. The use of the pond for hemp retting is uncertain: pollen clearly shows a period of high-water level and NPP from low level and temporary ponds disappear. The main green alga is Pediastrum sp. (mainly Pediastrum boryanum); however this alga could not develop in the very polluted environment created by hemp retting. The transformation of the swamp into a pond is correlated with a climate reversal, a first hint of the Little Ice Age. The pond becomes smaller and finally dries out during the 15th C. Cereal cultivation is probably developed on the surface of the dry pond. Cultivation in the swamp is abandoned during the 16th C and the swamp progressively appears as it is today: a wet zone covered with Cyperaceae and Juniperus type, surrounded by farming zones.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest affecting author and co-authors.


