1 Introduction
Metal alkoxides represent one of the most common and attractive class of metal precursors for advanced oxide materials. Their interest lies in an easy access, the ability to tune their properties by modification of their coordination sphere in order to achieve the requirements for solution but also vapour phase chemical processes as well as their ability to provide homogeneity at a molecular level for multimetallic oxides via the formation of heterometallic species [1]. By contrast to most main group and transition metals, lanthanide alkoxides did not receive much attention until the last decade, although rare earth oxide materials are involved in a variety of high-tech applications [2]. Isopropoxides are representative of simple metal alkoxides that offer a high ceramic yield as well as most of the properties, especially solubility, required for applications in material science. While those are generally oligomers or solvates as illustrated by [Al(OiPr)3]4 or [Zr(OiPr)4(iPrOH)]2, more complex architectures are observed for lanthanides due to their demand for high-coordination numbers and their trivalent nature. The basic structural unit is a pentanuclear core corresponding to an oxoalkoxide Ln5(μ5-O)(OiPr)13 resulting from desolvation and linking of intermediate solvates. Those are more stable for tertiobutoxides affording isolable Ln3(OtBu)9(tBuOH)2 species but desolvation remains facile providing oxoalkoxides such as Ln5(μ5-O)(OtBu)13 (Ln = La, Nd, Yb) or of higher nuclearity, [Y8O6(OtBu)12]m, for yttrium [3].
We wish to report herein preliminary results illustrating the potential of yttrium alkoxides for access to nanocrystalline pure and doped yttrium oxide at low temperature as well as doped organic polymers.
2 Experimental
All molecular compounds were prepared under inert atmosphere using Schlenk tubes and vacuum line techniques and characterized as previously reported [4]. Analytical data were obtained from the ‘Centre de microanalyses du CNRS’. Homo- and copolymerization reactions were done under inert atmosphere in the presence of 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) (AIBN, 2% molar / C=C functionalities). Styrene was distilled in order to remove the stabilizer. Polymerisation was quenched by addition of alcohol.
Hydrothermal reactions (200 °C, 10 h, 17 atm) were performed with deionised water in the presence of four equivalents of NH3H2O. Precipitates were washed with water until the pH of the medium was neutral. After dialysis during three days, they were dried at 100 °C. The as prepared powders issued from hydrolyses were dried under vacuum at rt for 6 h. Compositions of the powders were reached by elemental analysis, FT–IR and X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Cu Kα radiation, Siemens D5000 diffractometer). Size and morphology were observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with a Philips CM12 spectrometer at 100 kV. EDX data were collected on a JEOL 2010 electron microscope. TGA and DTA were conducted under air using a Setaram system (heating rate 5 °C min–1). XPS data were obtained with an Escalab 200R (VG Scientific) spectrometer using the Kα Al radiation as excitation source. Fluorescence spectra were obtained using excitation with a Xe lamp and a JY H10D monochromator (λ = 430 nm). Light was collected with an UV optical fibre coupled to a JY TRIAX 320 and a CCD camera (1200 g/320 nm grating, integration time 1 s, resolution 0.65).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 The quest for low-temperatures routes to Y2O3
Yttrium oxide has a number of applications such as high index oxide for dielectric mirrors for high power UV lasers, transparent matrices for phosphors and doping with Eu, Tb [5] and Pr [6], catalyst support or even catalysts [2]. Improved performances are obtained with nanocrystalline oxides for most applications, the activity of nanocrystalline Ln2O3 for the reduction of nitrogen oxides being comparable to that of Co-ZSM-5 [7]. Most methods for access to yttria are based on thermal decomposition or precipitation reactions of their salts [8], leading to quite high (> 600 °C) temperatures of crystallization of the oxide. Herein, we have considered various wet transformations processes of metal alkoxides in order to overcome the high stability of yttrium or lanthanide hydroxides on the route to oxides and accede to nanocrystalline arrays.
3.1.1 Room-temperature hydrolytic conversions
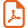
Hydrolyses of Y3(OtBu)9(tBuOH)2 (Y3), Y5(μ5-O)(OiPr)13 (Y5) and [Y8O6(OtBu)12]m (Y8) in THF (0.02–0.03M) at rt with a large excess of deionised water (hydrolysis ratio h = mole H2O/mole precursor = 300, 500 and 800 respectively) gave amorphous powders. In contrast, crystalline hydroxides Ln(OH)3 were obtained for lanthanum, praseodymium and neodymium alkoxides [9]. FT–IR spectra of the powders derived from Y5 and Y8 were similar, showing no organics, by comparison to those derived from Y3. TGA data and elemental analysis accounted for the formation of Y(OH)3H2O for Y3 and Y5 and of Y2O(OH)44.3 H2O for Y8. TGA data showed several thermal events (Fig. 1). Anhydrous Y(OH)3 and Y2O(OH)4 were obtained at 150 °C. Weight losses for powders derived from Y3 and Y5 occurred in three steps (≈ 7%) over the range 150–600 °C. The TGA pattern of Y8 showed two well-defined weight losses (9.2 and 4.5%) between 150 and 300 °C and up to 500 °C. All losses were endothermic corresponding to elimination of OH ligands and could be summarised by Eqs. (1) and (2) for the powders of Y3, Y5 and Y8, respectively:
| (1) |
| (2) |
TGA patterns under air of the powders derived from Y3, Y5 and Y8, respectively.
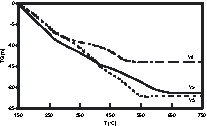
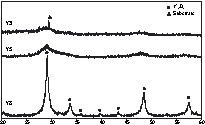
Powders derived from Y8 showed the lowest weight loss, this being associated with the lowest temperature of complete removal of –OH groups. Hence annealing powders derived from Y8 at 400 °C for 4 h gave well-crystallized cubic yttria, while crystallization was only starting for the powders derived from Y3 and Y5 (Fig. 2) – the temperature of crystallization by annealing (4 h) was lower than that observed by TGA, which is a dynamic process. TEM of powders derived from Y8 showed that Y2O3 was composed of spherical nanocrystallites of about 5–6 nm aggregated into submicron secondary particles (Fig. 3A). HRTEM images illustrate the high crystallinity of Y2O3 even at 400 °C, since no amorphous layer was observed on the surface of the nanoparticles and all diffraction peaks could be attributed (Fig. 3A and C). These data illustrate that the increase of the number O2– ligands in the precursor favours the obtaining of a crystalline oxide array at low temperature. By comparison, a sol of Y(OH)3–x(NO3)x (x ≈ 0.5) obtained from Y(NO3)3 by anion exchange in basic aqueous media required annealing above 600 °C for crystallisation of cubic Y2O3 [10].
XRD patterns of the powders derived from Y3, Y5 and Y8 calcinated at 400 °C.
(A) TEM image, (B) HR–TEM image, and (C) diffraction peaks of the powder derived from Y8 calcinated at 400 °C.
3.1.2 Hydrothermal transformations
Hydrothermal transformations have been largely used in material science for access to nanoparticles and/or special microstructures [11].
The hydrothermal transformation in the presence of ammonia of ScCl36 H2O affording ScO(OH) [12] prompted us to use a similar approach (200 °C, 10 h, 17 atm) for yttrium [13]. However, conversion of YCl36 H2O gave a crystalline chlorohydroxide (JCPDS 30-1445) Y2(OH)4.86Cl1.14(H2O)0.7 due to the poor lability of the Y–Cl bonds. The use of alkoxides, Y5O(OiPr)13 or Y3(OtBu)9(tBuOH)2 (0.05 M) as reagents in similar conditions afforded amorphous oxide in both cases. The presence of oxide in those powders was evidenced in the FT–IR by its characteristic Y–O absorption bands (560, 460 cm–1), whereas absorptions at 3615 and at 3408 cm–1 accounted for hydroxide species. XRD patterns for the powders derived from Y5 indicated cubic Y2O3 mixed with the hexagonal hydroxide Y(OH)3 phase. TEM confirmed the crystallinity of the powders and moreover showed their polymorph nature (Fig. 4). Three types of morphology were observed although needles and nanorods (700 × 10 up to 6000 × 200 nm) were predominant. Lanthanide hydroxide nanowires obtained by hydrothermal treatment of colloidal suspensions of Ln(OH)3 were reported recently but no data were given for yttrium [14]. TGA analysis allowed further identification of the various phases. The total mass loss was 12.4% for the powder issued from Y5, suggesting a composition of 65% Y(OH)3 and 35% Y2O3. Transformation into cubic yttria was complete at 300 °C, the lowest temperature reported so far for this oxide.

TEM image of powder derived from hydrothermal treatment of Y5.
TEM micrographs of the powders resulting from Y3 indicated mostly amorphous nearly spherical particles of about 35 nm diameter, crystalline platelets (200 × 200 nm to 400 × 400 nm) and crystalline needles (10-nm diameter, 450–700-nm length). The weight loss (8.2%) indicated a higher proportion of oxide than for those derived from Y5. Indeed, conversion of t-butoxides into oxides is generally favoured over that of isopropoxides due to formation of isobutylene as observed in MOCVD [1]. The TGA data suggest either a composition of 61.6% Y2O3 and 38.4% Y(OH)3 or nearly only YO(OH) (a weight loss of 7.4% is expected). The latter assumption is not very likely due to the presence of Y2O3 in the FT–IR and oxolation has been reported to be difficult for yttrium [15]. Surprisingly, in contrast with the powder issued from Y5, conversion into crystalline yttria under air required more than 900 °C. The difference between the powders derived from Y3 and Y5 might be related to their surface properties. Indeed, close examination of the FT–IR suggests the presence of carbonate ligands for the powders derived from Y3 (absorptions at 1790, 1525, 1405 cm–1) [16]. Carbonation might thus control here the temperature of crystallization, but the reactivity of those powders was not further investigated.
3.2 Toward highly homogeneous multimetallic materials
The stereolability of metal alkoxides or oxoalkoxides allows the formation of mixed-metal species by mixing of homometallic species at rt providing homogeneity at a molecular level for multimetallic materials [1,2]. The reaction between Y5(μ5-O)(OiPr)13 and Pr5(μ5-O)(OiPr)13 (4:1 stoichiometry) in THF gave Y4Pr(μ5-O)(OiPr)13 having a structure similar to that of the Ln5O14 core as established by single crystal X-ray studies [17]. Its hydrolysis (THF, 0.025 M, h = 500) afforded an amorphous pale green powder whose elemental analysis indicated a ratio Y:Pr of 4, as in the precursor. TGA analysis in air exhibits three weight losses of 9.7, 7.7 and 9.3% within the temperature ranges of 50–150, 150–300 and 300–700 °C. These overall data account for the formation of hydrated Y4PrO0.5(OH)14 with the loss of adsorbed water being followed by the elimination of the –OH groups (Eq. (3)):
| (3) |
XRD studies indicated that the onset of crystallisation of cubic Y2O3 was higher by about 100 °C (from 400 to 500 °C) compared to Y5(μ5-O)(OiPr)13 (cf. § 3.1.1). At 500 °C, the colour of the solid changes from pale green to deep orange. Cubic Y2O3 was the only crystalline phase observed up to 900 °C. The slight decay of the 2θ peak values compared to pure Y2O3 suggests that Pr atoms were incorporated in the network of the Y2O3 matrix. Average particle sizes were estimated to range from 7.7 to 15.3 nm between 500 and 900 °C according to the Scherrer equation. TEM and X-ray Energy Dispersive (EDX) data indicated a very homogeneous Pr distribution (6.75 atomic%) in the Y2O3 array. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) (0–1000 eV) displayed peaks due to O2–, Y3+ and Pr3+ atoms. No peak due to Pr4+atoms was observed. The O1s spectra displayed two broad peaks at 531.5 and 528.7 eV different from the O2– contributions of Y3+–O and Pr3+–O bonds in Y2O3 and Pr2O3 (530.5 and 529.3 respectively) [18]. This confirms that, despite the differences of the Y2O3 and Pr2O3 structures, Pr3+ atoms could substituted Y3+ ones in the Y2O3 lattice to form luminescent centres. Hence photoluminescence spectra (PL) were observed at rt for the samples calcinated at 500 °C in the IR (800–850 nm) (Fig. 5). They can be ascribed to the spin-allowed (1D2 → 3H6, 3F2) transition of Pr3+ centres via their (4f)(5d) excited state. Peaks were very sharp accounting for the high crystallinity of the sample. Very homogeneous nanosized lanthanide-doped Y2O3 materials can thus be obtained at low temperature starting from multimetallic precursors by comparison to coprecipitation reactions.
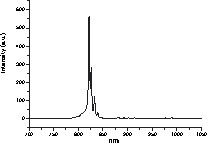
Photoluminescence spectra of the powder derived from Y4Pr(μ5-O)(OiPr)13 calcinated at 500 °C.
3.3 Alkoxides with polymerisable ligands: toward hybrid materials
The preceding examples have illustrated access to extended inorganic arrays by formation of M–O–M bonds. Yttrium and lanthanide alkoxides are active living ring-opening catalysts of lactones or lactides for instance affording biomaterials and thus organic networks [19]. Organic-inorganic materials such as doped polymers are other attractive materials [20]. Homo- or copolymerisation reactions based on M(OR)n–xZx species, where Z is a polymerisable ligand, allow access to extended organic arrays as well as inorganic ones [21]. Better homogeneity is reached when covalent association between organic and inorganic networks is achieved, the M–Z linkage thus should be stable thermodynamically and kinetically. This is achieved via Si–C bonds for silicon, but via oxygen ligation for most other elements. Chelating or bridging-chelating ligation is preferable, allylacetatoacetate (HAAA) and 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl acetoacetate (HAAEMA) are possible ligands.
The lability of the M–OR bond makes metal alkoxides choice precursor for molecular design of oxide precursors [1]. The reaction between Y5O(OiPr)13 and AAAH in toluene (1:5 stoichiometry) at rt gave compound 1 in quantitative yield. Its FT–IR and proton NMR data (two types of magnetically non-equivalent AAA ligands in a 2:3 ratio) account for a formula Y4O(OiPr)5(AAA)5. 1 is extremely unstable toward moisture; repeated attempts to get single crystals gave another, more stable compound resulting from hydrolysis–polycondensation. The crystals resulting from crystallization in ethanol/ligroine, 1a, displayed a sharp absorption at 3357 cm–1 in its FT-IR spectrum, suggesting the presence of hydroxide ligands. Its 1H NMR data indicated a decrease in the integration ratio, down to 6:10, between alkoxide namely ethoxide and AAA ligands, the latter displaying still two sets of resonances in a 2:3 ratio. The identity of 1a was established by single crystal X-Ray diffraction (monoclinic, space group C2/c, a = 21.556(4), b = 18.752(4), c = 29.485(6) Å, β = 100.11(3)] It corresponds to an octanuclear species based on the assembly of two [Y4(μ4-O)(AAA)5(μ-OEt)2] flattened tetrahedron via triply-bridging hydroxide O(101) and O(102) and ethoxide O(70) ligands giving a centrosymmetric [Y4(μ4-O)(μ,η2-AAA)2(η2-AAA)3(μ-OEt)2]2(μ3-OH)4(μ3-OEt)2] species (Fig. 6). Six of the metals are seven-coordinate, bearing terminal-chelating allylacetatoacetate ligands, whereas Y(4) and Y(4)# are octacoordinated, with two bridging-chelating AAA ligands. The Y8O32 core is quite compact [Y(3)….Y#(3) 8.776 Å] and can be seen as a small piece of yttrium oxohydroxide wrapped with polymerisable ligands. The formation of 1a results from the hydrolytic condensation of two Y4O(OR)5(AAA)5 formally derived from substitution of five OR groups of Y5O(OPri)13 and elimination of a basal Y(OR)3 moiety (Eqs. (4) and (5)).
| (4) |
| (5) |
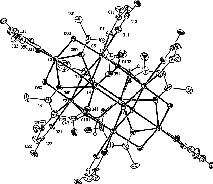
Molecular structure of [Y4(μ4-O)(μ,η2-AAA)2(η2-AAA)3(μ-OEt)2]2(μ3-OH)4(μ3-OEt)2] (thermal ellipsoids at 20% probability, the chains of the AAA ligands have been removed for the sake of clarity, only the H corresponding to the OH ligands are shown). Yttrium–oxygen bond distances: 2.196(9)–2.489(10) Å with the ranking Y–μ4-O ≤ Y–μ-OEt < Y–μ3-OH < Y–η2-AAA < Y–μ3-OEt < Y–μ,η2-AAA: Y–O(1) 2.196(9)–2.287(9), Y–μ-OEt 2.230(9)–2.276(9); Y–μ3-OH 2.314(9)–2.398(10); Y–η2-AAA 2.288(11)–2.403(10); Y–μ3-OEt(O70) 2.400(9)–2.419(9); YY distances 3.746(3) for Y(1)Y(2) to 3.506(2) Å for Y(3)Y(4). CCDC reference number: 175 661.
Similar results were obtained with Y5O(OiPr)13 and 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl acetoacetate, although no single crystals could be grown. The reaction lead to an unstable intermediate 2 giving compound 2a showing characteristic sharp Y–OH absorptions in the IR (3658 cm–1) as well as the absorption bands of the νC=O and νC=C vibrations (1722, 1633, 1537, 1514 and 1505 cm–1). The stability of the Y or Ln–OH bond, a hurdle for low temperature routes to oxides, allows aggregation as molecular oxohydroxides and thus formation of clusters of unprecedented frameworks [4]. It is also noteworthy that the Ln5O(OiPr)13 core behaves as a source of Ln4O(OiPr)10 moieties either for heterometallics with M(OiPr)4 (M = Ti, Zr) or Ln(OiPr)3 fragments as previously shown [2] or in substitution reactions.
Homo and copolymerisation reactions were investigated for 1a and 2a. Thermal activation appeared better than photochemical one due to less degradation of the complexes (< 5%). As expected, formation of the organic network was favoured for 2a with the AAEMA ligand bearing an acrylate functionality as compared to 1a, which showed a low conversion into C–C bond formation. Homopolymerisation of 2a was achieved in toluene at 75 °C in the presence of AIBN as initiator. After 6 h, the solution was transformed into a glassy gel indicating cross-linking. The Y–OR absorption bands at 571, 535, 480 cm–1 were unchanged with respect to those of 2a indicating that gelation was not due to hydrolysis. Copolymerization of 2a with styrene C6H5CH=CH2 (stoichiometry 2a: styrene = 20) gave a gel after 4 h at 75 °C. Formation of the polystyrene (PS) network was evidenced by its characteristic sharp absorption bands. Longer reaction times lead to growth of the organic network with hardening and shrinkage of the gel as a glassy, transparent insoluble polymer, whereas the Y–OR absorptions bands remained unaffected. No metallic species was found in the mother liquor nor extracted by washing the polymer with isopropanol, indicating that AAEMA allowed efficient anchoring to the PS backbone. Elemental analysis of the polymeric material obtained after washing with toluene in order to remove PS confirmed the presence of yttrium (2.8% in weight). Hydrolysis of the Y-polystyrene copolymer lead to change in the FT–IR with formation of the Y–O–Y network (broad absorption bands from 880 to 450 cm–1) and hydroxide at 3615 cm–1. This doped PS was slightly more stable thermally than the non-doped one as shown by TGA. Its EDX mapping indicated an homogeneous distribution of the metal, whereas the Y-doped PS obtained with yttrium derivatives without polymerisable ligands displayed a concentration gradient 2a [22] was less efficient for copolymerisation with styrene than Ti(OiPr)2(AAEMA)2, where all acrylate functions are born by chelating ligands and are thus more accessible [20].
4 Conclusions
Metal alkoxides as illustrated here by lanthanide ones are versatile oxide precursors, their most attractive features being an easy formation of mixed-metal species for either homogeneously doped binary or homogeneous multimetallic oxides. The stability of the Ln–OH bond, a hurdle for low-temperature routes to oxides, gives access to unique molecular oxohydroxide aggregates.