1 Introduction
The synthesis and characterization of various multinary sulphide tin-based semiconductors have recently attracted considerable attention [1–6]. Also the grafting and incorporation of metallic clusters with appropriate ligands on polymer or ceramic surfaces has been widely applied to intermetallics or bimetallic complexes [7–9]. We have focused our interest on the synthesis of sulphur-containing tin–iron heterobimetallic complexes and their functionalisation by tin–nitrogen bonds. Here, we present our results on the synthesis of several Fe2SnSn complexes that contain reactive tin–nitrogen bonds.
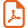
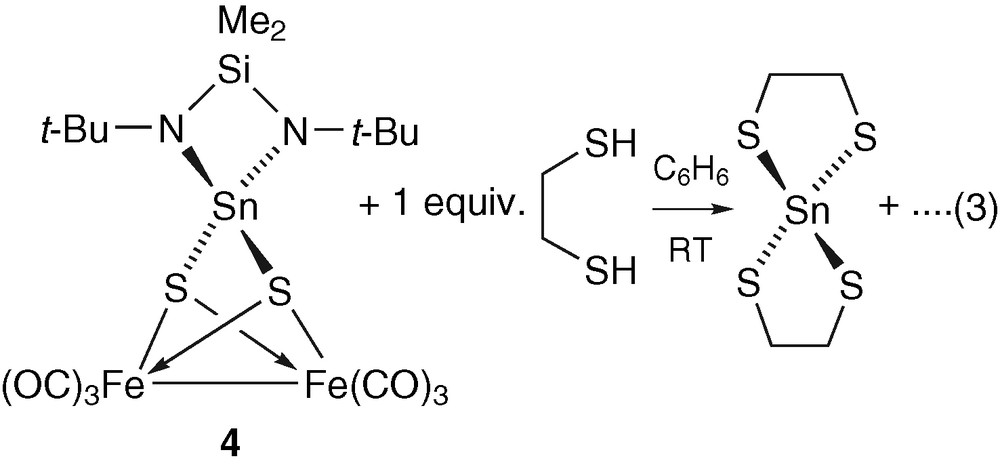
In the early eighties, Seyferth and co-workers developed the chemistry of Fe2(μ2-η2-S2)(CO)6 (1) [10]. This complex has been independently used by different groups as a precursor for the synthesis of various heteropolymetallic complexes and clusters, obtained by reaction with [CpNi(μ-CO)]2 [11], [CpCr(CO)3]2 [12], [CpMo(CO)3]2 [13], [Mn2(CO)10] [14], Co2(CO)8 [15] or, more recently, Cp2MoH2 [16]. However, sulphur-containing tin–iron compounds are rare, and clusters with reactive tin–nitrogen bonds have proved to be very versatile [17]. To gain further insight into the reactivity of functionalised iron–tin–sulphur clusters, we have attempted to synthesize a new iron–tin–sulphur cluster by reacting 1 with the bis(amino)stannylene Sn(μ-Nt-Bu)2SiMe2 (2).
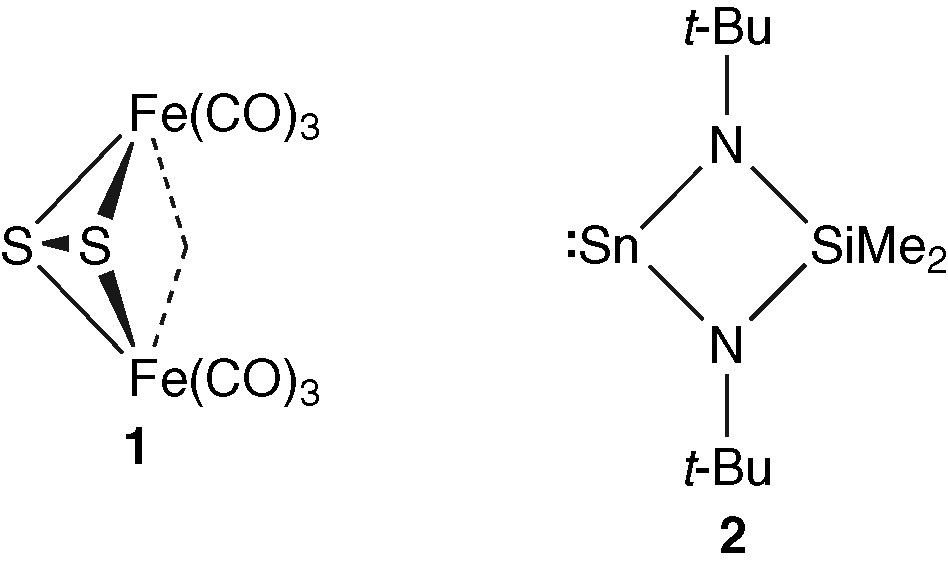
Since 1 can be viewed as an inorganic compound that mimics the organic disulphides owing to the behaviour of its sulphur–sulphur bond [10b], and since stannylenes are known to react with organic disulphides or with sulphur to give tetravalent Sn(IV) species [18], it is not surprising that the reaction of 1 with SnMe2 has afforded the heterometallic complex 3 (equation (1)) [10e].
Therefore, the idea to react 1 with 2 seemed a straightforward approach to the desired target. Furthermore, the Sn–N bonds could provide reactive sites for the addition of thiols. In this paper we describe the synthesis of the new heterometallic complex Me2Si(μ-Nt-Bu)2SnFe2(μ3-S)2(CO)6 (4) and its reactions with the thiols HSCH2CH2SH and HSCH2CH2SiMe3.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Synthesis and structure of the sulphur-containing tin–iron heterodimetallic cluster 4
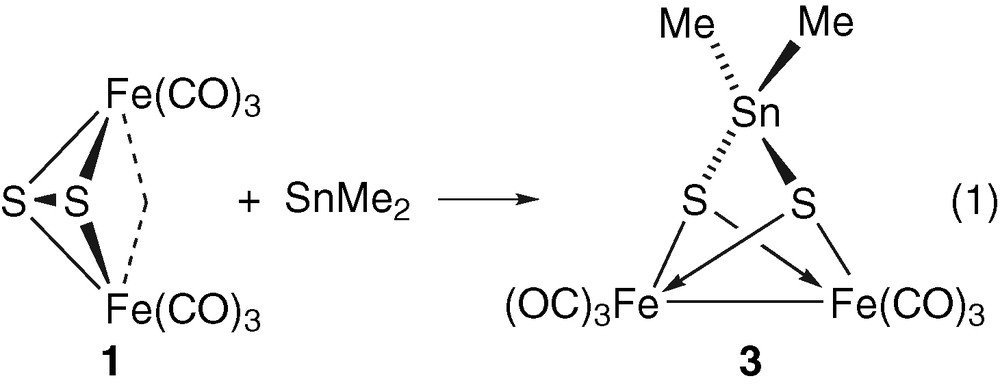
The reaction of Fe2(μ2-η2-S2)(CO)6 (1) with one equivalent of the bis(amino)stannylene Sn(μ-Nt-Bu)2SiMe2 (2) in hexane was almost quantitative and afforded a brown complex 4 in 64% isolated yield (equation (2)). This new cluster has been fully characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction, IR, and NMR spectroscopic methods, and elemental analysis.
Cluster 4 is very soluble in most common organic solvents (hexane, C6H6, THF), and can be isolated as solvent-free crystals. In a reaction similar to the one that led to 3, the tin atom has inserted itself into the sulphur–sulphur bond of 1 and its oxidation state has increased from +2 to +4. This can also be deduced from the 119Sn{1H} NMR chemical shift of δ –24.73, which corresponds to an upfield shift of 701 ppm with respect to the stannylene 2, in which the tin atom is divalent. The nature of the reaction product is again consistent with the sulphur–sulphur anti-bonding character of the LUMO of 1. Similar upfield shifts have already been observed in tin-alkoxides when changing the tin oxidation state from +2 to +4 and are attributed to an increase in the coordination number of the tin atom [19]. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra are in accord with a C2v (mm2) symmetry for molecule 4 (one signal for each one of the methyl and tert-butyl groups in the 1H NMR spectrum and four signals for the carbon atoms in 13C NMR, all carbonyl groups being equivalent). The ν(CO) region in the infrared spectrum is consistent with the NMR findings and compared to 1, the number (always 3) and intensity of the absorptions in 4 is unchanged, which is in accordance with a reaction of the stannylene 2 at the S–S edge of 1.
The molecular structure of 4 has been determined from single crystal X-ray data. The compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/m with two molecules per unit cell and has a crystallographic mirror plane containing the atoms S(1), S(2), Sn(1), Si(1), C(5) and C(6) (Fig. 1 and Table 1). A closer look at the distances and angles within 4 reveals (Table 1) that the distortion away from C2v symmetry is only small. The Fe2S2 quasi-tetrahedral arrangement in 1 becomes a butterfly-type geometry in 4, since the tin atom has inserted itself into the S–S bond and the S–S distance increases from 2.021(4) Å in 1 [20a] (typical σ-bonding distance for sulphur-sulphur bonds, see for example 3,3,6,6-tertamethyl-S-tetrathiane [21]) to 3.046(4) Å in 4. The Fe2S2Sn cage part of the molecule and the four-membered SnN2Si cycle share a common apex. The cage part of 4 is reminiscent of the structural features found in other Fe2S2M clusters (where M = Pd, Mo, Ti, Ni) [10b, 10d, 10e,16].
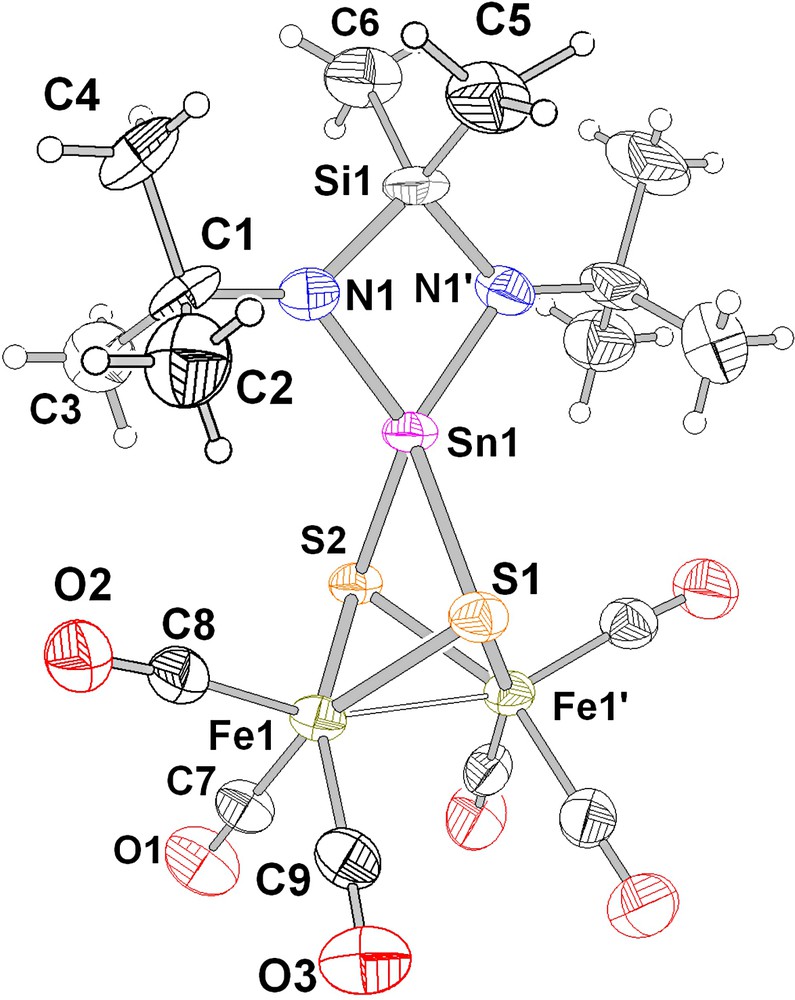
Ball and stick view (with 50% thermal ellipsoids) of the molecular structure of 4 [31]; the small circles designate the locations of the hydrogen atoms.
Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (°) for 4
| Bond distances | |||
| Sn(1)–S(1) | 2.447(3) | Fe(1)–S(1) | 2.309(3) |
| Sn(1)–S(2) | 2.455(3) | Fe(1)–S(2) | 2.324(3) |
| Sn(1)–N(1) | 2.042(7) | Si(1)–N(1) | 1.747(7) |
| Fe(1)–Fe(1′) | 2.489(2) | Si(1)–C(5,6) mean | 1.867(9) |
| Fe(1)–C(7,8,9) mean | 1.78(1) | C(7,8,9)–O(1,2,3) mean | 1.15(1) |
| Bond angles | |||
| N(1)–Sn(1)–S(1) | 126.7(2) | Fe(1′)–S(1)–Fe(1) | 65.2(1) |
| N(1)–Sn(1)–S(2) | 129.2(2) | Fe(1)–S(2)–Fe(1′) | 64.7(1) |
| N(1′)–Sn(1)–N(1) | 76.5(4) | S(1)–Fe(1)–S(2) | 82.3(1) |
| S(1)–Sn(1)–S(2) | 76.9(1) | ||
| Torsion angles | |||
| N(1′)–Sn(1)–N(1)–Si | 6.37(1) | Fe(1)–S(1)–Fe(1′)–S(2) | 53.18(1) |
The small distortions away from C2v symmetry in 1 to Cm in 4 can be exemplified by the pairs of distances Fe(1)–S(1)/Fe(1)–S(2) (difference 0.015 Å) or Sn–S(1)/Sn–S(2) (difference 0.008 Å). Since the structural data of 1 and 2 are known [20,22], a comparative analysis of the molecular structure of 4 is possible.
The sulphur atoms have become μ3-bonded and the Sn–S distances (mean: 2.450(6) Å) are in the range of normal Sn(IV)–S distances in molecules with tin bonded simultaneously to nitrogen and sulphur (the mean Sn–S bond length in [(Me3Si)2N]2Sn(μ-S)]2 is 2.417(8) Å) [23]. The insertion of the tin atom in the S–S bond in 1 is accompanied by its formal oxidation and consequently, the Sn–N distances shrink as compared to the starting molecule 2 (from 2.092(4) to 2.042(7) Å in 4), because the atomic radius of Sn(IV) is smaller than that of Sn(II) [24], and the N–Sn–N angle in the four-membered ring N(1)–Si(1)–N(1′)–Sn(1) of 4 (76.5(4)°) is enlarged compared to that in 2 (73.2°). The opening of this angle can be understood in terms of a change in hybridisation of the tin atom, which in the stannylene 2 uses only p orbitals for bonding (the non-bonding electrons in a first approximation are in the s orbital), whereas it is approximately sp3 in 4. The angle deformation at tin away from the idealized situation is 16.8° (90–73.2°) in 2 and 33° (109.5–76.5°) in 4. The mean Sn–N distances in 4 compare well with bond lengths in molecules such as [SeSn(μ-Nt-Bu)2SiMe2]2 and [TeSn(μ-Nt-Bu)2SiMe2]2 (2.023(8) and 2.030(9) Å) [25], and the S2Sn(μ-Nt-Bu)2SiMe2 part of the cluster is identical to the corresponding subunit in [SSn(μ-Nt-Bu)2SiMe2]2 synthesized several years ago [26].
The Fe2S2(CO)6 part of 4 also reveals some further information when compared to the structure of 1. Insertion of tin in the S–S bond results in an elongation of the Fe–S bonds (from Fe–Smean = 2.235(7) in 1 to 2.317(7) Å in 4) and a shrinkage of the Fe–Fe bond length (2.556(2) to 2.489(2) Å) [20]. This is in accordance with expectations: the separation of the two sulphur atoms in 4 makes the Fe2S2 bisphenoid flatter and therefore more flexible, allowing a tighter Fe–Fe bond. The withdrawal of electron density due to the Sn–S bonds from sulphur should elongate the adjacent bonds. The spirocyclic tin atom occupies the centre of a strained tetrahedron with acute N–Sn–N and S–Sn–S angles of 76.5(4) and 76.9(1)°.
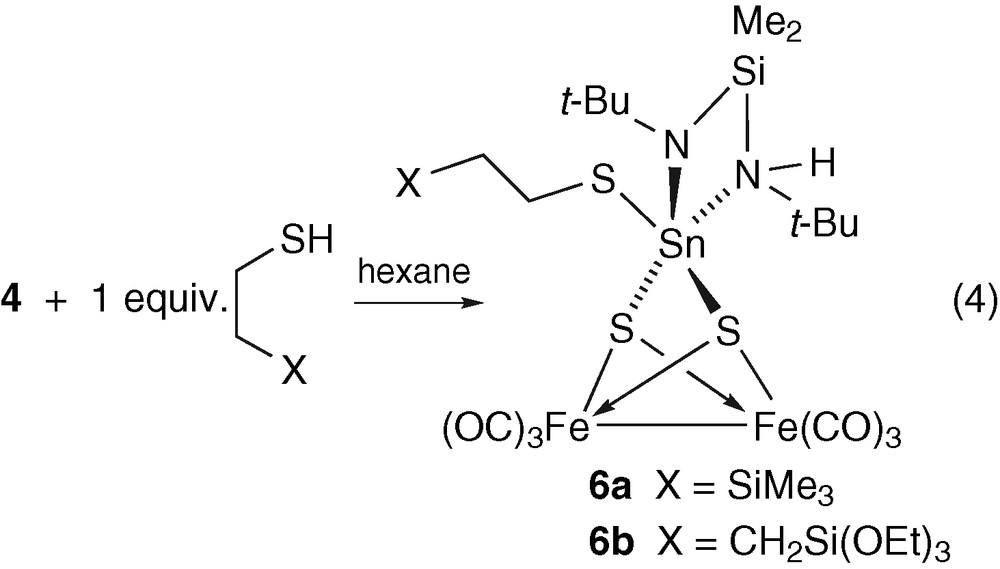
In summary, the structure of the new heterodimetallic cluster 4 is reminiscent of those found in other Fe2S2M clusters [10b, 10d, 10e,16] with the peculiarity of having two acute angles at tin and therefore a certain strain. We were therefore interested to examine whether the SnN2 or the SnS2 part of the molecule would be more reactive towards thiols and looked at the reaction of 4 with either HSCH2CH2SH or HSCH2CH2SiMe3.
2.2 Reactions of the heterodimetallic cluster 4 with thiols and dithiols
The reaction of tin–iron–sulphur complex 4 with the dithiol HSCH2CH2SH in a 1:1 molar ratio led to cluster degradation. We were not able to separate and isolate all the products, but could recrystallise the Sn(IV) thiolate 5 after dissolution of the brown precipitate in a THF/hexane (1:1) mixture (equation (3)). It was fully characterized by X-ray structure analysis and compared with the data of the published structure [27].
Since it appears that the thiol attacks both the SnS2 and SnN2 moieties of complex 4, we blocked one end of the thiol by a trimethylsilyl group to reduce its reactivity. The reaction of 4 with 1 equiv of Me3Si(CH2)2SH is shown in equation (4). It can also be run with (EtO)3Si(CH2)3SH (in place of Me3Si(CH2)2SH) in a similar way (1H NMR, IR evidence), but so far no complete characterization of the product 6b has been possible1.
The new cluster 6a was isolated as the only product in 51% yield and this adduct between the two molecular precursors has been fully characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction, IR, 1H, 13C, 119Sn NMR and elemental analysis.
Compared to 4, cluster 6a has a lower molecular symmetry. This can already be seen from the IR spectrum in the CO region (five absorptions) in contrast to the C2v symmetry molecules 1 and 4, which show only three absorption bands. The dimethylsilyl group gives rise to two singlets in 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and the two tert-butyl groups appear as two signals. The splitting of one of these signals in the 13C NMR spectrum indicates some hindered rotation of the tert-butyl-N(H) group around the C–N bond; we assume that this rotation is more hindered than that of the other tert-butyl group owing to the tetrahedral coordination geometry of the nitrogen atom (atom N(2) in Fig. 2). Although there are two stereogenic centres in the molecule (tin and nitrogen atom N(2)), which are (from a dynamical point of view) fixed in the crystal structure (see below), there is clear indication that these stereogenic centres convert to the mirror image on the NMR timescale in solution. The resonance of the tin atom in the 119Sn NMR is shifted from δ = –24.7 (molecule 4) to δ = –152.8 in 6a, which is consistent with an expansion of the coordination sphere.
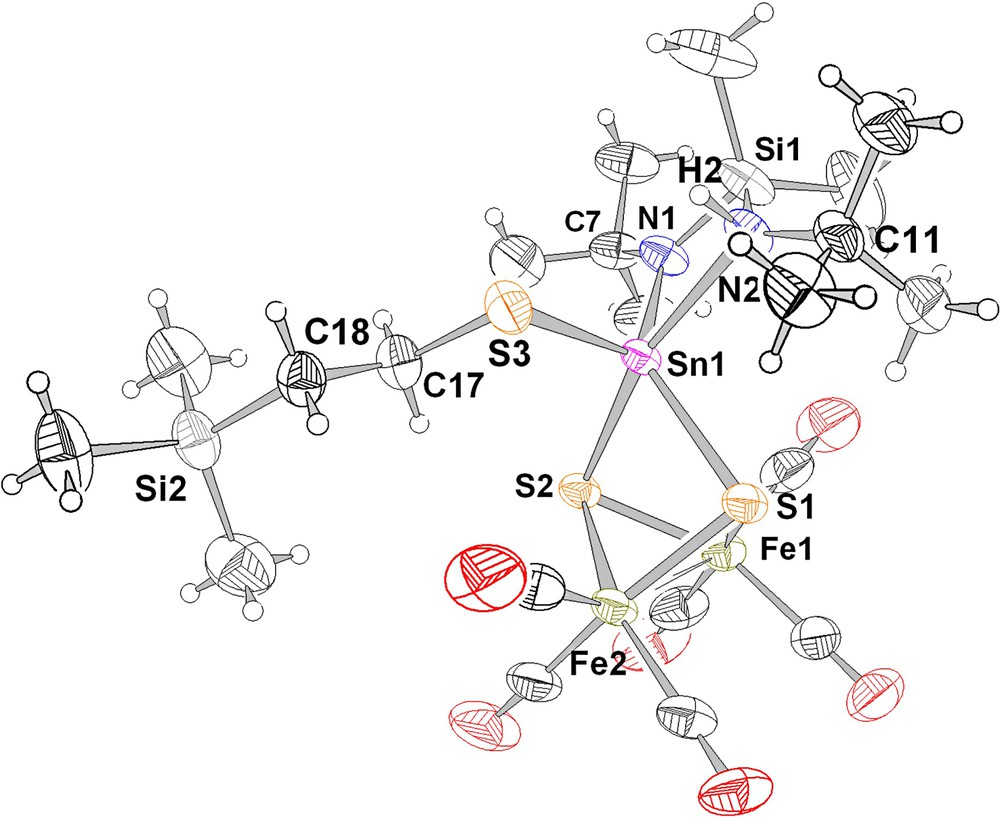
Ball and stick view (with 50% thermal ellipsoids) of the molecular structure of 6a [31]; the small circles designate the locations of the hydrogen atoms. The unlabelled atoms are either carbon or oxygen atoms (please refer to Fig.1).
A ball and stick view with thermal ellipsoids of Me2Si(μ-Nt-Bu)[μ-N(H)t-Bu]Sn{S(CH2)2SiMe3}(μ3-S)2Fe2(CO)6 (6a), obtained by X-ray diffraction methods, is shown in Fig. 2. The atoms Sn(1) and N(2) are stereogenic centres and two (of the four possible) diastereomers are present in the unit cell. The Fe2S2(CO)6 butterfly moiety of 6a is almost unchanged compared to 4, with all carbonyl groups being terminal. The most obvious difference between the structures of 4 and 6a is the environment of the tin atom, which in 6a has a distorted trigonal bipyramidal coordination sphere constituted by three sulphur and two nitrogen atoms. To the best of our knowledge, no other tin compound displaying two nitrogen and three sulphur ligands has been structurally described before.
From a chemical point of view, the sulphane (thiol) has added across one of the Sn–N bonds in 4 (the S(3)···H separation is only 2.88(1) Å). A related addition of an N–H bond across a Sn–N bond of 2 (or stannylene insertion into a N–H bond) has been reported recently [28]. As a consequence of this addition reaction, the sum of the bond angles around N(2) amounts to 349.2° (neglecting the hydrogen atom), compared to the sum of the bond angles around N(1), which retains its almost trigonal planar coordination geometry (359.7°). The addition of the hydrogen atom also leads to an elongation of the Sn–N(2) bond length compared to Sn–N(1) by 0.291 Å (Table 2). The equatorial ligands around tin are S(1), N (1), and S(3), while N(2) and S(2) are in axial positions. An alternative description of the coordination geometry around tin would be that of a distorted square pyramid with S(3) in the apical position. This would neglect the very wide S(2)–Sn(1)–N(2) angle of 163.5(1)°, but could account for the similar Sn–S(1,2) bond lengths and the shorter Sn(1)–S(3) distance, although this difference is also due to the λ2/λ3 nature of the sulphur atoms (Table 2) (see also [29]). The expansion of the tin coordination sphere in 6a compared to 4 has almost no effect on the Fe(1)–Fe(2) distance, but is reflected in smaller Fe–S distances in 6a (Fe–Smean: 2.29(1) Å) compared to 4 (Fe–Smean: 2.32(1) Å). The latter effect is due to less tight bonding of the tin atom to the Fe2S2(CO)6 butterfly moiety in 6a because of its involvement in bonding to three electronegative ligands instead of two.
Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (°) for 6a
| Bond distances | |||
| Sn(1)–S(1) | 2.510(1) | Fe(1)–S(1) | 2.273(1) |
| Sn(1)–S(2) | 2.506(1) | Fe(1)–S(2) | 2.310(1) |
| Sn(1)–S(3) | 2.420(1) | Fe(1)–Fe(2) | 2.494(1) |
| Sn(1)–N(1) | 2.077(4) | Fe(2)–S(1) | 2.284(1) |
| Sn(1)–N(2) | 2.368(4) | Fe(2)–S(2) | 2.298(1) |
| Si(1)–N(1) | 1.694(4) | Si(1)–C(15,16) mean | 1.860(7) |
| Si(1)–N(2) | 1.816(4) | Si(2)–C(18–21) mean | 1.873(6) |
| Bond angles | |||
| N(1)–Sn(1)–N(2) | 69.8(1) | S(3)–Sn(1)–N(2) | 89.6(1) |
| S(2)–Sn(1)–S(1) | 73.64(4) | S(2)–Sn(1)–N(2) | 163.5(1) |
| N(2)–Sn(1)–S(1) | 96.2(1) | S(1)–Sn(1)–N(1) | 131.1(1) |
| N(1)–Sn(1)–S(2) | 106.8(1) | S(1)–Fe(1)–S(2) | 81.98(5) |
| S(3)–Sn(1)–S(1) | 115.25(5) | S(1)–Fe(2)–S(2) | 82.00(5) |
| S(3)–Sn(1)–S(2) | 106.42(5) | Fe(1)–S(1)–Fe(2) | 66.36(4) |
| S(3)–Sn(1)–N(1) | 111.4(1) | Fe(1)–S(2)–Fe(2) | 85.53(4) |
3 Experimental section
The syntheses of the dinuclear complex Fe2(μ2-η2-S2)(CO)6 (1) [20] and of the bis(amino)stannylene Sn(μ-Nt-Bu)2SiMe2 (2) [22] were carried out following the established procedures. All experimental manipulations were performed in a modified Schlenk-type apparatus taking stringent precautions against atmospheric moisture. Solvents were purified by standard methods and stored over appropriate desiccating agents. The single crystal X-ray diffraction study was performed on a IPDS instrument of STOE (Darmstadt, Germany), using the Mo Kα radiation (Table 3). The structures were solved by direct methods and refined with anisotropic temperature factors for all non-hydrogen atoms [30]. The hydrogen atoms were refined as idealized rigid groups [30]. The infrared spectra were recorded as KBr discs on a BioRad FT-IR-165 spectrometer. NMR spectra were measured on a Bruker (Karlsruhe) 200-MHz apparatus (ACF) with 5% deutero-benzene in benzene as a solvent. The C,H-analyses were obtained with a LECOTM apparatus (St. Joseph, MI, USA).
Crystallographic data for 4 and 6a
| Compound | 4 | 6a | |
| Formula | C16H24Fe2N2O6S2SiSn | C29H37Fe2N2O6S3Si2Sn | |
| Mr | 662.97 | 797.28 | |
| Crystal group | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | |
| Space group | P21/m | C2/c | |
| F(000) | 660 | 3232 | |
| A (Å) | 6.470(1) | 17.781(4) | |
| b (Å) | 17.418(3) | 18.354(4) | |
| c (Å) | 11.903(2) | 21.555(4) | |
| β (°) | 104.91(3) | 95.83(3) | |
| V (Å3) | 1296.2(4) | 6998(3) | |
| Z | 2 | 8 | |
| Abs. coeff. (Mo Kα) (mm–1) | 2.299 | 1.807 | |
| Theta range (°) | 1.77–24.20 | 1.80–24.04 | |
| Indep. reflections | 2008 | 5399 | |
| Parameters | 159 | 338 | |
| R-value [I > 2 σ(I)] | 0.0546 | 0.0399 | |
| wR2 | 0.0993 | 0.0971 | |
| 1.008/–1.374 | 1.303/–0.919 |
3.1 Me2Si(μ-Nt-Bu)2SnFe2(μ3-S)2(CO)6 (4)
In a 250 ml flask were placed together 1 (3.56 g, 13.2 mmol) and 2 (4.20 g, 13.2 mmol) in hexane (100 ml) at 0 °C. The solution was stirred for 1 h and then warmed up to room temperature. From the solution held at –20 °C in hexane, red-brown needles of 4 crystallized (5.50 g, 8.3 mmol, yield: 64%). Selected IR data (C6H6) : ν(CO) 2067 (s), 2030 (s), 1999 (w) cm–1. 1H NMR (C6D6) δ: 0.23 (s, 6H, SiMe), 1.24 (s, 18H, t-Bu). 13C{1H} (C6D6) δ: 6.7 (s, SiCH3), 36.6 (s, CCH3), 54.0 (s, CCH3), 208.67 (s, CO). 119Sn{1H} (C6D6) δ: –24.73. Anal. calcd for C16H24Fe2N2O6S2SiSn (663.00): C, 28.99; H, 3.65; N, 4.23. Found: C, 27.77; H, 3.62; N, 4.17.
3.2 Me2Si(μ-Nt-Bu)[μ-N(H)t-Bu]Sn{S(CH2)2SiMe3}(μ3-S)2Fe2(CO)6 (6a)
In a 100-ml flask, 0.550 g of 4 (0.83 mmol) was dissolved in 20 ml of hexane. To this solution was slowly added a solution of HSCH2CH2SiMe3 (0.111 g, 0.83 mmol) in hexane (2 ml). The solution turned brown within a few minutes; it was stirred overnight and separated from solid residues. The filtrate was concentrated and cooled to –20 °C upon which brown, parallepipedic crystals of 6a were formed (0.340 g, 0.43 mmol, 51%). Selected IR data (hexane): ν(CO) 2068 (s), 2030 (s), 1999 (s) 1988 (m) 1975 (m) cm–1. 1H NMR (C6D6) δ: 0.02 (s, 9H, SiMe3), 0.16 (s, 3H, NHSiMe), 0.24 (s, 3H, NSiMe), 1.04 (s, 9H, NHt-Bu), 1.14 (m, 2H, CH2SiMe3), 1.33 (s, 9H, Nt-Bu), 1.81 (s br, 1H, NH), 3.10 (m, 2H, CH2SSn). 13C{1H} (C6D6) δ: –0.2 (s, SiCH3), 5.5 (s, SiCH3), 6.2 (s, Si(CH3)3), 21.4 (s, CH2SiMe3), 25.2 (s, CH2SSn), 31.4 (s, CCH3), 34.5 (s, CCH3), 34.9 (s, CCH3), 53.9 (s, CCH3), 54.1 (s, CCH3), 209.7 (br s, CO). 119Sn{1H} (C6D6) δ: –152.8. 119Sn (C6D6) δ: –152.8 (pseudo t, 3JSn-H = 40 Hz, Sn–SCH2). Calcd for C29H37Fe2N2O6S3Si2Sn (797.32): C, 31.64; H, 4.80; N, 3.51; Found C, 30.30; H, 4.96; N, 3.37%.
The most relevant crystallographic data for compound 4 and 6a are assembled in Table 3. Further details on the crystal structure investigations may be obtained from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), 12 Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1 EZ (UK) on quoting the depository numbers CCDC-250612 and 250613.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the ‘Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft’ (DFG) for providing financial support in the framework of the European Network for the formation of PhDs (Graduiertenkolleg) GRK 532 and the French ‘Ministère de la Recherche’ and the CNRS (Paris) for a PhD grant to N.A. and funding and the ‘Deutsch-Französische-Hochschule’ (DFH) for mobility support. The ‘Fonds der chemischen Industrie’ is also acknowledged for support.
1 Selected data for 6b: 13C {1H}NMR (C6D6) δ = –1.8 (s, SiCH3), 1.3 (s, SiCH3), 15.5 (s, SiOCH2CH3), 21.9 (s, SiCH2CH2CH2S), 25.7 (s, SiCH2CH2CH2S), 31.9 (s, CCH3), 33.8 (s, SiCH2CH2CH2S), 35.2 (s, CCH3), 54.4 (s, CCH3), 54.6 (s, CCH3), 65.8 (s, SiOCH2CH3), 210.2 (br s, CO).