1 Introduction
Most of the time, protection of metallic substrates (e.g., aluminium, steel, galvanised steel…) against corrosion by organic coatings involves multilayer systems. These systems include at least three painting layers of different types: the primary layer – directly applied on the substrate – confers a good adhesion on the system of painting, an intermediate layer, which generally provides the thickness of the coating and its barrier function, and finally, the topcoat to protect all the underlying layers. This layer often brings the esthetical aspect. Each painting layer is usually formulated from five constituents [1–4]: the binder matrix (usual binders are epoxy, polyurethane or alkyde), inorganic or metallic pigments, extenders, additives for specific properties (anti-foamers, fire retarding agents, anti-coalescence agents, UV-absorbers…) and solvents (to reduce the viscosity of the coating and to control the drying).
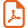
The major disadvantage of the use of these three coat-painting systems is related to the coating process (time and cost). In order to simplify the sequence, the key step is to elaborate a single layer (unilayer system) gathering all properties of a three-layer-based system. To reach this objective, various properties of polymers (low water permeability, good mechanical properties…) have been combined using diblock copolymer as a monocomponent system (Fig. 1).
Schematic representations of a block copolymer and a system of paintings.
In a diblock copolymer, the two segments are covalently bonded [5]. The presence of covalent bonds between the blocks definitely improves the mutual miscibility of the two polymers. Thus, a nanoscale self-organization can be easily achieved for such copolymers (not for statistical copolymers). Various nanostructures could be obtained from sphere, cylinder, bicontinuous to lamellae organization, which are mainly governed by the composition of the diblock copolymer [6].
In this work, we have studied the protection of Al substrates against corrosion using two types of unilayer systems based on block copolymers that have been synthesized using the NMP technique (Nitroxide-Mediated Polymerisation) [7,8]. In both cases, the first block (poly(n-butyl acrylate) (PBA)) has been chosen for its amorphous and elastomer properties and the second block, consisting of a fluorinated polymer, has been selected for its rigidity and its good water impermeability. The difference between the two block copolymers is the nature of the fluorinated block:
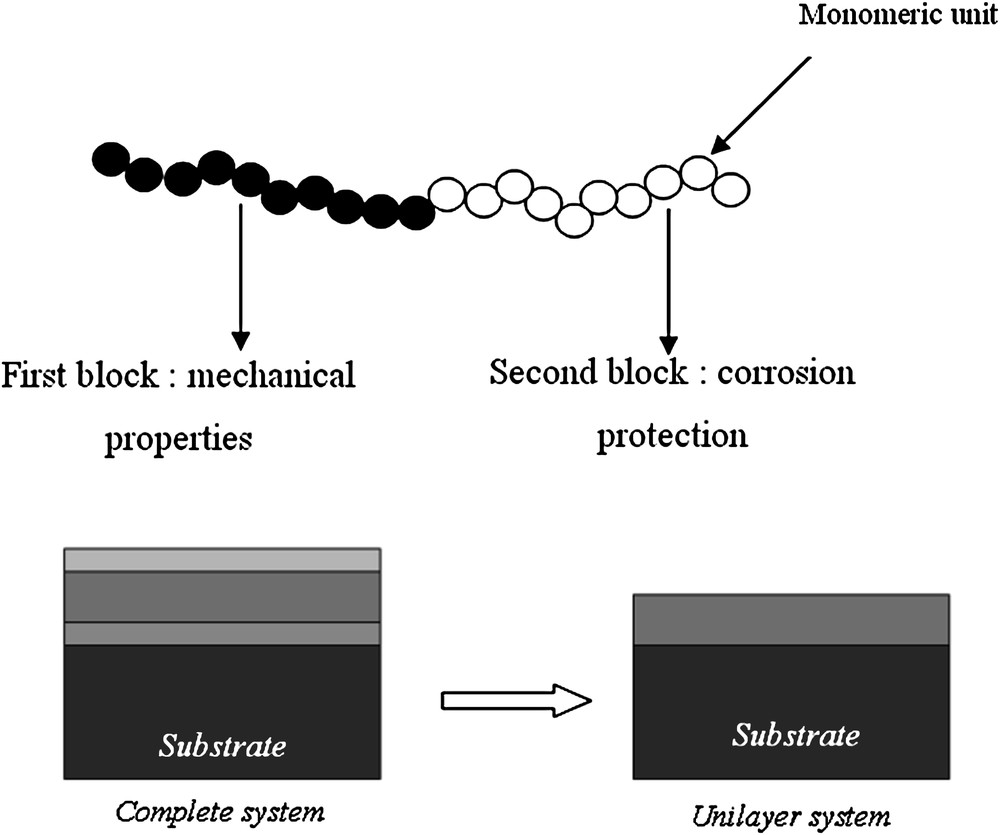
- (1) poly(n-butyl acrylate-b-trifluoroethyl methacrylate) diblock copolymer (PBA-b-PTFEMA) (Fig. 2a);
- (2) poly(n-butyl acrylate-b-heptadecafluorodecyl methacrylate) diblock copolymer (PBA-b-PHFEMA) (Fig. 2b).
(a) PBA-b-PTFEMA diblock copolymer, (b) PBA-b-PHFEMA diblock copolymer.
2 Experimental
2.1 Synthesis of copolymers
All monomers were purchased from Aldrich and used as received. BlocBuilder™ was provided by Arkema company.
2.1.1 PBA-b-PTFEMA diblock copolymer
This diblock copolymer was elaborated by NMP (Nitroxide-Mediated Polymerisation). n-Butyl acrylate monomers (BAs) (3.1 × 10−1 mol) and BlocBuilder™ alcoxyamine initiator (2.0 × 10−3 mol) (Fig. 3) were charged in a glass reactor provided with a cooler and an inflow of sluggish gas (N2). The medium of polymerisation is deoxygenated by nitrogen bubbling during 20 min and placed under magnetic stirring in a thermostated oil bath and then heated from room temperature to 110 °C. After the removal of residual monomer under reduced pressure, PBA block (Mn = 14,200 g/mol, calculated by SEC) was used as a macro-initiator to synthesise the PTFEMA block (Mn = 8570 g/mol, calculated by 1H NMR). The procedure is similar (n(PBA) = 6.1 × 10−4 mol and n(TFEMA) = 6.9 × 10−2 mol), but is performed at 90 °C. Finally, the monomer is eliminated by stripping under reduced pressure.
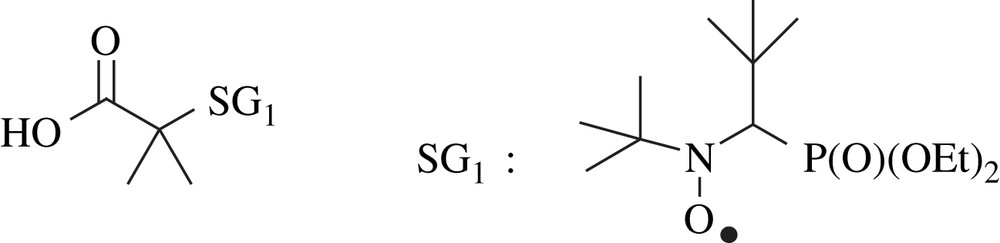
BlocBuilder™ alkoxyamine initiator.
2.1.2 PBA-b-PHFEMA diblock copolymer
This diblock copolymer was elaborated by NMP. The procedure is similar to that of the PBA-b-PTFEMA synthesis. n-Butyl acrylate monomers (3.9 × 10−1 mol) (BA) and BlocBuilder™ alkoxyamine initiator (3.0 × 10−3 mol) were charged in a glass reactor provided with a cooler and an inflow of sluggish gas (N2). After purification, the obtained PBA block (Mn = 13,900 g/mol, calculated by SEC) was used as a macro-initiator to synthesise the PHFEMA block (Mn = 23,950 g/mol, calculated by 1H NMR). The diblock copolymer was purified by precipitation in pentane.
2.2 Elaboration of coatings
Prior to film deposition, aluminium panels (3105 H24) (6.5 cm × 6.5 cm) were successively cleaned in acetone and ethanol using an ultrasonic rinse and then dried under airflow. PBA-b-PTFEMA and PBA-b-PHFEMA films were deposited using a three-step sequence: dissolution of the copolymer in a solvent (tetrahydrofuran for PBA-b-PTFEMA copolymer and 1,3 bis-trifluoromethyl benzene for PBA-b-PHFEMA copolymer), deposition of the solution obtained (450 mg/mL) on the substrate with an automatic bar coater and evaporation of the solvent. After solvent evaporation (1 h in air), the coatings were annealed at 120 °C during 24 h.
A Positector 6000 Defelsko and an FNS2 Defelsko probe have been used to estimate the thicknesses of coatings that have been found to be in the 90 ± 2 μm range.
2.3 Atomic force microscopy (AFM)
AFM images of the samples and the corresponding average surface roughness measurements were obtained using an Autoprobe CP (Park Scientific Instrument) in non-contact mode. All observations were performed in “Topographic Mode”. All AFM measurements were carried out in air at 25 °C with a standard silicon nitride cantilever.
2.4 Contact angle measurements
For the determination of the surface free energy of the coating, selected test liquids, with different γsl for a common solid, depending upon the dispersion and dipolar interaction of the liquids, were utilized. For reliable determination of the surface free energy, different test liquids are usually preferred, as indicated in Table 1. A “KRUSS” EasyDrop contact-angle measuring system was employed. Each test liquid was placed (3 μL) on the sample using an automatic syringe. The baseline is measured automatically and the angle is determinated between the baseline of the drop and the tangent at the drop. The corresponding free energy of the coating has been calculated by means of the Owens–Wendt method [9], in which the polar and dispersive parts of the surface free energy are obtained by plotting the (1 + cos θ)γl/2(γld)1/2 versus (γlp)1/2/(γld)1/2. The slope of the fitted line and the intercept gives (γsp)1/2 and (γsd)1/2, respectively.
Surface free energy of the test liquids
| Liquid | γld | γlp | γl |
| Water | 21.8 | 51.0 | 72.8 |
| Formamide | 39.5 | 18.7 | 58.2 |
| Diiodomethane | 48.5 | 2.3 | 50.8 |
| Ethylene glycol | 26.4 | 21.3 | 47.7 |
2.5 Electrochemical characterization
The electrochemical characterization was performed using a traditional three-electrode electrochemical cell with a platinum grid as counterelectrode and a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as reference electrode. The Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy tests were carried out in a 3 wt% sodium chloride solution at open-circuit potential, with a 20 mV amplitude signal, a frequency range from 105 to 10−2 Hz for further measurements. All electrochemical experiments were performed with a frequency response analyser (Solartron 1260) connected to a potentiostat (Solartron 1287). In order to perform accurate measurements, the electrochemical cell was placed in a Faraday cage.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 AFM measurements
The image of a bare aluminum sample obtained after immersion in acetone and ethanol is shown in Fig. 4. The surface appears very rough (rms rough = 352 nm) and scratches are clearly visible due to the polishing process.
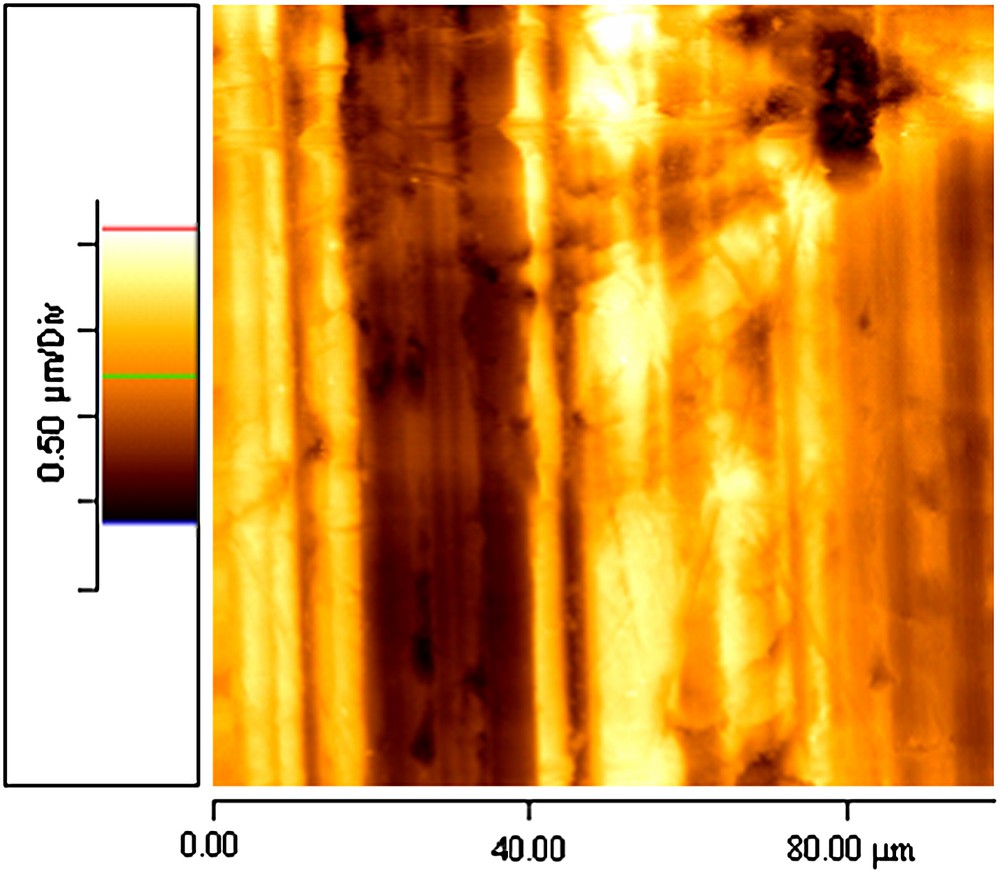
AFM observation of bare aluminium.
However, scratches disappear after deposition of the PBA-b-PTFEMA coating on aluminum suggesting that the unilayer spreads perfectly on the substrate (Fig. 5). Clearly, the sample surface is relatively homogeneous, with a lower roughness. Some small islands with a diameter of about 1 μm are present on the entire surface and are probably due to the evaporation process of the solvent. This phenomenon has been also reported by To et al. [10] with THF and diblock copolymer poly (styrene-b-2-ferrocenylethyl methacrylate) (PS-b-PFEMA).
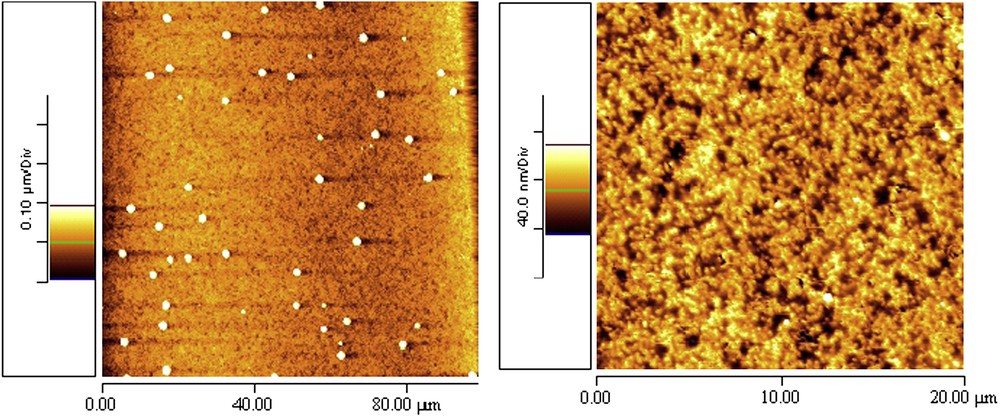
AFM images of PBA-b-PTFEMA on aluminium.
The morphology of the PBA-b-PHFEMA sample differs from that of the previous sample. Indeed, the AFM image (Fig. 6) shows a significant porosity over the entire surface. The expansion of the image shows that the pore size is between 0.5 and 1 μm. From this result, it is impossible to conclude about the significance of the pore-depth.
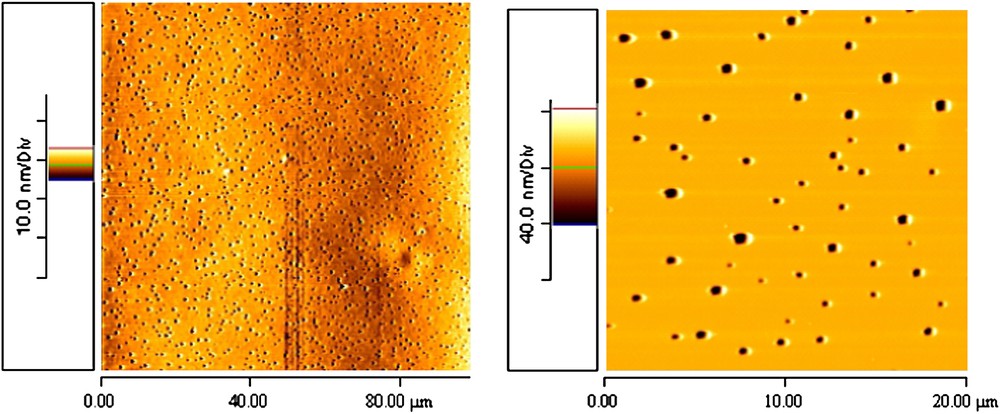
AFM images of PBA-b-PHFEMA on aluminium.
3.2 Contact angle results
The measurement of the contact angle gives information about the wettability of a surface. A drop of a liquid in contact with a solid will adopt a particular shape (spherical), which shows the interaction between the liquid and the solid. The contact angle of the drop with the surface reflects the minimum free energy of the system. The measurement of this angle with water used as a solvent allows deducing the hydrophobic nature (wide angle of contact) or hydrophilic (small contact angle) of the coating. If one uses different kinds of solvents (non-polar and polar), the surface energy of the coating can be deduced using the Owens and Wendt method [9].
The hydrophobicity at the low surface energy properties of fluorinated polymers is well known. In the case of a mixture of polymers, Jones and Kramer [11] have shown that compounds with very low surface energy are very good coating materials. Thus, the comparison of contact angle measurements of each copolymer compared with those obtained for homopolymer can give an indication of the orientation relative to the surface.
3.2.1 Contact angle measurements with water as a solvent
The contact angles measured with water are reported in Table 2. The values of contact angle measurements for the PBA, PTEFEMA and PHEFEMA homopolymers are, respectively, 75, 97 and 120°. Thus the values of the contact angles obtained for the PBA-b-PTFEMA and PBA-b-PHFEMA coatings are comparable to those of PTFEMA and PHFEMA coatings. One can assume in both cases that the fluorinated blocks are present at the surface of the coating, indicating a preferential orientation of the copolymer.
Contact angles with water
| Polymers | Contact angle (°) |
| PBA | 74 |
| PTFEMA | 97 |
| PHFEMA | 120 |
| PBA-b-PTFEMA (VR 82) | 101 |
| PBA-b-PHFEMA (VR 89) | 120 |
3.2.2 Surface energy of coatings
The values of polar and non-polar components of the surface energy and the sum of these two components, for all samples, are reported in Table 3.
Surface free energy of coatings
| Polymers | Polar component (A) | Non-polar component (B) | Energies (mJ/m2) (A + B) |
| PBA | |||
| PTFEMA | 3.16 | 16.76 | 19.92 |
| PHFEMA | 0.55 | 7.58 | 8.13 |
| PBA-b-PTFEMA (VR 82) | 1.77 | 16.91 | 18.68 |
| PBA-b-PHFEMA (VR 89) | 0.43 | 8.02 | 8.45 |
The surface energy of copolymer PBA-b-PTFEMA (18.68 mJ/m2) is of the order of magnitude of the fluoride PTEFEMA homopolymer (19.92 mJ/m2). The surface energy of the PBA-b-PTFEMA copolymer (18.68 mJ/m2) is of the order of magnitude of the fluorinated PTEFEMA homopolymer (19.92 mJ/m2). The same observation can be made for the PBA-b-PHFEMA copolymer (8.45 mJ/m2) and PHEFEMA homopolymer (8.13 mJ/m2).
These results are in agreement with previous measurements of the angles of contact with water, confirming, in both cases, the preferential orientation of the fluorinated block at the interface between air and coating. It is remarkable that the non-polar component of the surface energy is clearly higher than the polar one, showing the highly non-polar nature of both coatings and, therefore, the hydrophobic behaviour of such a unilayer.
Finally, the surface energy of the PBA-b-PHFEMA is lower than that of the PBA-b-PTFEMA, indicating a more hydrophobic behaviour. This result is entirely consistent with the fact that the PBA-b-PHFEMA copolymer contains a more significant amount of fluorine atoms compared to PBA-b-PTFEMA. The decrease in surface energy associated with the increase in the concentration in fluoride atoms is generally fast until a certain value. The hydrophobic properties are maximum when this critical value is reached and cannot be improved with the addition of fluorine atoms [12].
3.3 Impedance results
The barrier properties of an organic coating are very important for its corrosion resistance. The water entering through the coating, even in small quantities, can cause a corrosion reaction at the interface with the metal. The formation of corrosion products can also drastically decrease the adhesion of the coating.
The electrochemical behaviour of an organic coating can be described by different models depending on its porosity. When the layer is perfectly watertight, it can be modelled by an equivalent electrical circuit type ReQc (Fig. 7a), where Re is the resistance of the electrolyte and Qc the Constant Phase Element (CPE) of the organic coating. In the case of a fast penetration of electrolyte within the protective layer, the impedance diagrams must then be fitted with a Re(RpoQc) circuit type (Fig. 7b), where Rpo is the resistance of the electrolyte into the pores of the coating.
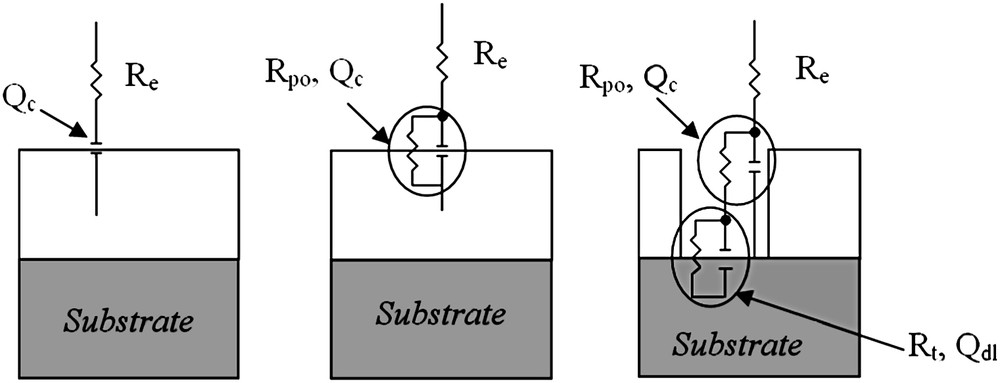
Equivalent electrical circuit models for an organic coating.
Finally, if the organic coating contains defects crossing, the contribution from the substrate at the bottom of the defects leads to the following circuit: Re (RpoQc (RtQdl)) (Fig. 7c), where Rt and Qdl are, respectively, the charge-transfer resistance and the double layer CPE of the substrate.
Here, Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy measurements were carried out in a 3 wt% NaCl solution for durations varying between 60 and 90 days. All impedance diagrams were fitted by choosing the appropriate model among the three models described above.
3.3.1 Evolution of the CPE of the organic coatings and water uptake
The evolution of the organic coating CPE (Qc) versus immersion time in 3 wt% NaCl for both samples is reported in Fig. 8. All values lie in the same range which is characteristic of an organic coating. While the CPE of the coating PBA-b-PTFEMA increases significantly during immersion time, that of PBA-b-PHEMA changes very little, even after 60 days of immersion. It is possible to correlate directly the evolution of the CPE of an organic coating to the quantity of electrolyte that penetrates in the coating. For this, the water uptake using the relationship of Brasher and Kingsbury (1) [13] has been determined for each sample (Fig. 9).
| (1) |
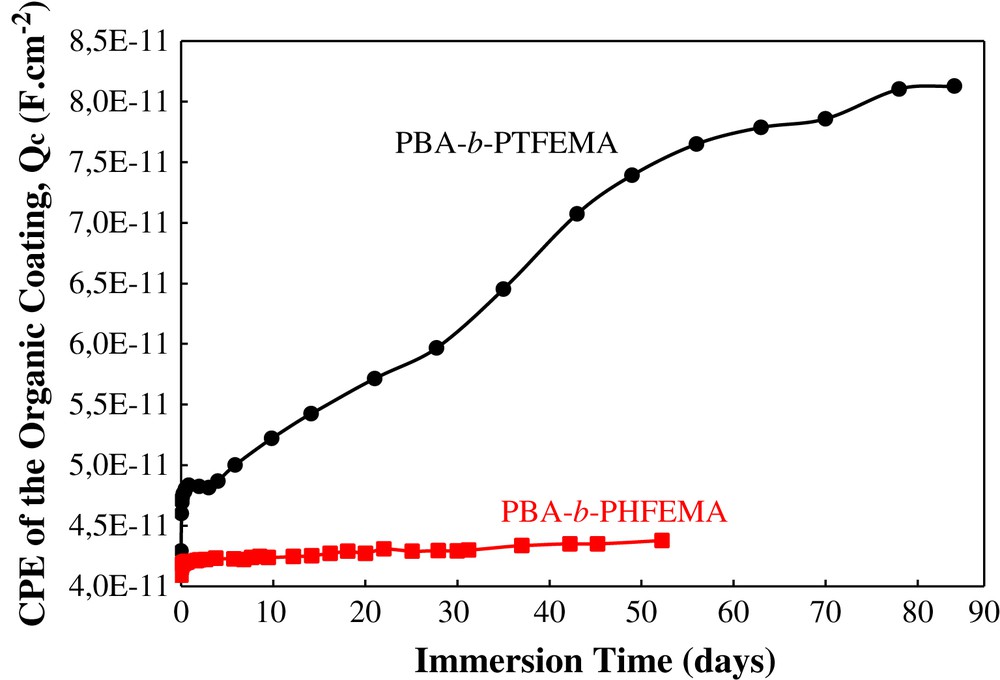
Evolution of the CPE of the organic coating (Qc) versus immersion time in 3 wt% NaCl.
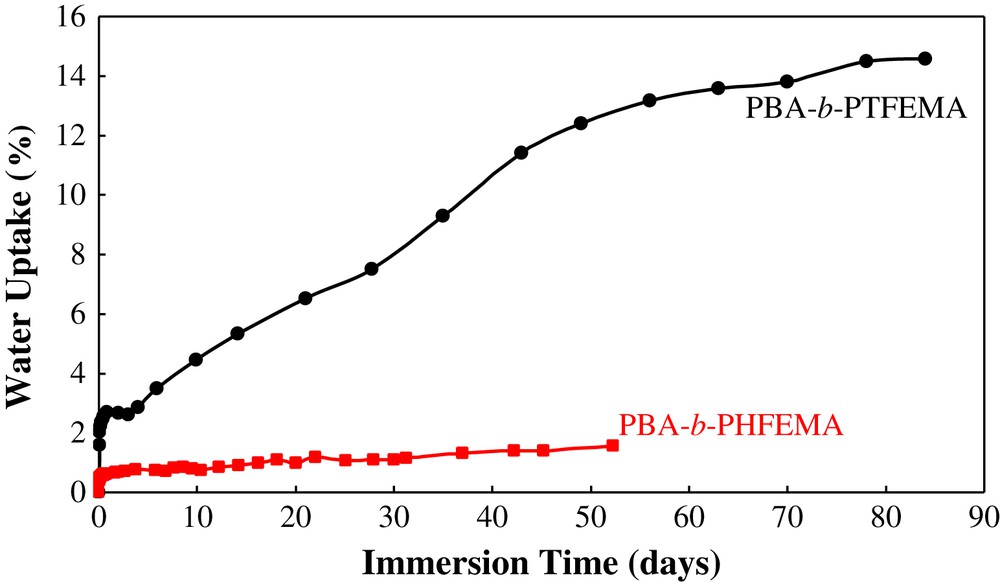
Evolution of the water uptake in the coatings versus immersion time in 3 wt% NaCl.
Thus, one can see that the water uptake of the PBA-b-PTFEMA coating is about 14% after 90 days of immersion. This value is very high and shows phenomena more complex than the simple ingress of water into the coating and suggests delamination of the coating. However, the water uptake in the PBA-b-PHFEMA coating is slightly modified, remaining below 2% after 60 days of immersion. These results confirm those obtained from contact angle and surface energy measurements, highlighting the more hydrophobic behaviour of the PBA-b-PHFEMA coating due to higher concentration in fluorine atoms. Therefore, even if AFM examinations revealed a larger number of holes for the PBA-b-PHFEMA sample compared to the PBA-b-PTFEMA, this porosity is certainly superficial and does not reach the substrate. The relative high hydrophobicity of the coating can prevent infiltration of the electrolyte through these defects.
3.3.2 Evolution of the barrier effect (Rpo)
A coating is usually considered as protective when the impedance diagram exhibits only one time constant, i.e. when the metallic substrate is not “visible”, which corresponds to an Rpo threshold value of roughly 106 ohm cm2. The evolution of the capacitance of an organic coating during the immersion time is directly dependent on the amount of water that has penetrated through the coating. The resistance of the electrolyte into the pores (Rpo) indicates the presence of defects or diffusion paths until substrate. Thus, a decrease in Rpo demonstrates the increasingly easy access of the electrolyte to the substrate with all damaging risks as well as delamination of the coating and formation of corrosion products.
The evolution of Rpo for each sample is presented in Fig. 10. It is apparent that the Rpo of the PBA-b-PTFEMA sample falls rapidly. After 15 days of immersion, Rpo values are below 107 ohm cm2. In contrast, the Rpo of the PBA-b-PHFEMA sample remains high: in the order of 109 ohm cm2 even after 60 days of immersion. Clearly, these results confirm the good corrosion barrier properties of the coating based on diblock copolymer PBA-b-PHFEMA.
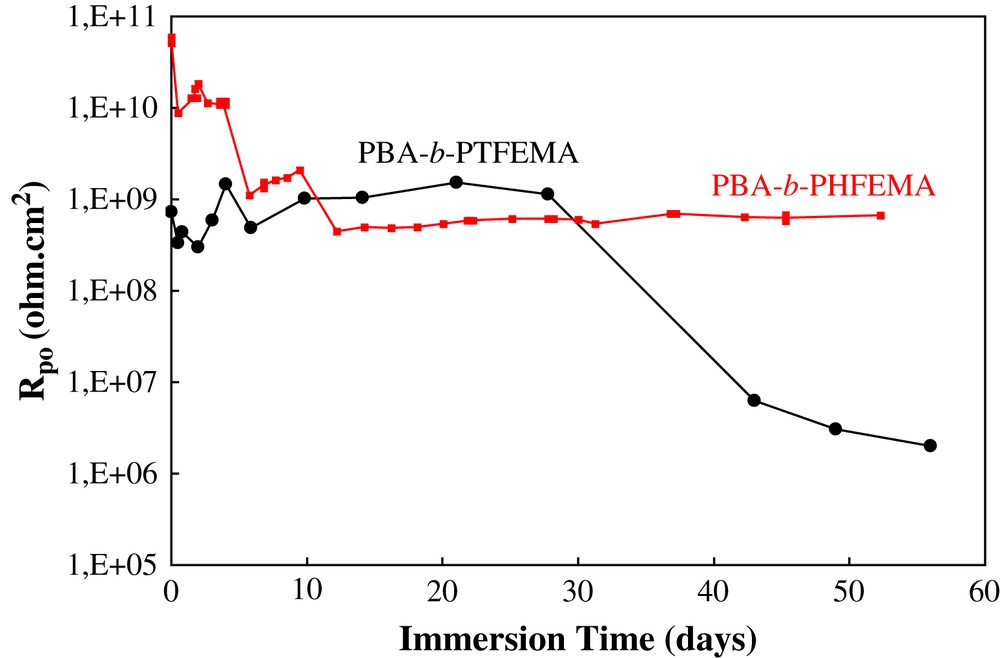
Evolution of the resistance of the electrolyte in the pores of the organic coating (Rpo) versus immersion time in 3 wt% NaCl.
4 Conclusions
Two types of diblock copolymers: poly(n-butyl acrylate-b-trifluoroethyl methacrylate) diblock copolymer (PBA-b-PTFEMA) and an (n-butyl acrylate-b-heptadecafluorodecyl methacrylate) diblock copolymer (PBA-b-PHFEMA) were synthesized by Nitroxide- Mediated Polymerisation using BlocBuilder™ alkoxyamide initiator. These two copolymers have been used for unilayer-based coatings to protect Al substrates protective against corrosion. The contact angle (with water) and the surface energy measurements have shown in both cases that the fluorinated blocks are present at the surface of the coating, indicating a preferential orientation of the copolymer. The results suggest a higher hydrophobic behaviour of the PBA-b-PHFEMA coating due to the higher concentration in fluorine atoms.
Finally, the impedance measurements pointed out the very low penetration of the electrolyte in the PBA-b-PHFEMA film (lower than 2%) in contrast to the PBA-b-PTFEMA layer (higher than 14%). Due to the very high hydrophobic behaviour and the high resistance of the electrolyte, it has been found that the use of a PBA-b-PHFEMA-based unilayer is a promising candidate for blocking corrosion processes on Al after 60 days of immersion.