1 Introduction
Several classes of antimicrobial compounds are presently available; microorganism's resistance to these drugs constantly emerges. In order to prevent this serious medical problem, the elaboration of new types of antibacterial agents or the expansion of bioactivity of the naturally known biosensitive compounds is a very interesting research area. The synthesis and characterization of metal complexes with organic bioactive ligands is one of the promising fields for this search. The hydantoin scaffold is a useful structural motif for displaying chemical functionality in biologically active molecules [1]. Strong evidence is available, indicating the crucial effect of the nature of C-5 substituents on the pharmacological action [2]. The biological activities of the metal complexes differ from those of either the ligand or the metal ion. The results obtained thus far have led to the conclusion that structural factors that govern antimicrobial activities are strongly dependent on the central metal ion. Numerous complexes based on platinum(II) and platinum(IV) ion have been synthesized, and their antimicrobial activities have been documented [3–9]. Pt(II) complexes show several restrictions compared with those of Pt(IV) while the latter ones are also cytotoxic in nature and have some advantages in comparison to Pt(II) complexes [10–13]. In general, the use of Pd(II) and of its complexes in medicine is limited. The coordination chemistry of palladium(II) is very similar to that of platinum(II), but the higher liability in ligand exchange at the Pd center (105-fold vs. Pt) may cause rapid hydrolysis processes, leading to the dissociation of the complex and to the formation of very reactive species unable to reach their biological targets [14]. These problems could be overcome by using the bulky heterocyclic and chelating ligands. A number of palladium complexes with aromatic N-, N,N-, N,O-, and N,S-containing ligands have shown antibacterial characteristics [5–9,13–17].
Continuing our research program on the preparation of metal complexes with 5-methyl-5-pyridylhydantoin with potential biological activity [4,18–20], with a view to diversifying the coordination behavior of L and the biological importance of platinum and palladium complexes, it has been considered worthwhile to synthesize and characterize some new platinum(IV), platinum(II), and palladium(II) derivatives of 5-methyl-5-(3-pyridyl)-hydantoin, 1-4, Scheme 1, which could be proved to be antibacterial agents. All compounds have been studied by DFT calculations in order to correlate the theoretical results with the experimental ones.

Synthesis routes of complexes 1–4.
2 Material and methods
2.1 Materials and physical measurements
All necessary chemicals obtained from commercial suppliers were reagent grade and used without further purification. Carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen contents of the compounds were determined by elemental analysis carried out on a ‘Vario EL III’ elemental analyzer. IR spectra were recorded on PerkinElmer and Bruker vertex 70 FT-IR spectrophotometers in the ranges from 4000 to 400 and from 400 to 150 cm−1 on KBr and ATR cells, respectively. NMR spectra were obtained on 90 MHz Jeol and 300 MHz Bruker spectrometers in DMSO-d6 as the solvent. The melting points were determined using a SMP3 apparatus.
2.2 Computational details
Geometries of L and the corresponding complexes in the gas phase were fully optimized using the BP86 functional [21,22]. The def2-TZVP [23] basis set was employed for all atoms, and structures were optimized without symmetry restrictions. All calculations were performed using the Gaussian 03 set of programs [24]. The conductor-like polarizable continuum model (CPCM) [25] as implemented in Gaussian 03 was used for the prediction of the solvent's influence on the relative stability of complexes. The 1H and 13C NMR shielding results were obtained at the same level of theory. The 1H and 13C isotropic shielding constants were calculated using the gauge-independent atomic orbital (GIAO) method [26,27].
2.3 Antibacterial study
2.3.1 Test organisms
Standard strains of the following microorganisms were used as test organisms: Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6633), Staphylococcus saprophyticus (ATCC 15305), Escherichia coli (Lio), Proteus vulgaris (Lio), Serratia marcescens (PTCC 1330), and Bacillus cereus (ATCC 7064). Some microorganisms were obtained from Persian Type Culture Collection, Tehran, Iran and others were locally isolated (Lio). The organisms were sub-cultured in nutrient broth and nutrient agar (Oxiod Ltd.) for using in experiments while diagnostic sensitivity test agar (DST) (Oxoid Ltd.) was used in antibiotic sensitivity testing. The composition of nutrient agar culture medium is: 0.5% peptone, 0.3% beef extract or yeast extract, 1.5% agar, 0.5% NaCl, and distilled water; pH was adjusted to neutral (6.8) at 25 °C.
2.3.2 Sensitivity testing
For bioassays, a suspension of approximately 1.5 × 108 cells per cm3 in sterile normal saline was prepared as described by Forbes et al. [28]. Sensitivity testing was determined using the agar-well diffusion method [29]. In each disk, 30 μdm3 of L and complexes 1–4 were loaded. The bacterial isolates were first grown in nutrient broth for 18 h before use. The inoculum suspensions were standardized and then tested against the effect of the chemicals at amounts of 30 μdm3 for each disk in DST medium. The plates were later incubated at 37 ± 0.5 °C for 24 h, after which they were observed for zones of inhibition, an area of media where bacteria are unable to grow due to the presence of a drug that impedes their growth. The effects were compared with that of the standard antibiotic chloramphenicol at a concentration of 1 mg/cm3 [30]. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of chemicals was determined by tube dilution techniques in Mueller–Hinton broth (Merck) according to NCCLS [31]. The experiments were repeated at least three to five times for each organism and data are presented as the mean ± SE of 3–5 samples.
3 Experimental
3.1 Synthesis and characterization
3.1.1 Synthesis of (C9H9N3O2) (L)
This ligand was prepared by a previously published method [32]. Since in the original work this compound was poorly characterized, and also for comparative purposes, spectroscopic characterization of L was performed [20].
3.1.2 Synthesis of PtCl4(C9H9N3O2)2 (1)
K2[PtCl6] (0.2429 g, 0.5 mmol) in 15 cm3 water, dissolved on a steam bath within 50 min, was added to a solution of L (0.1911 g, 1 mmol) in 6 cm3 of a 50% water/ethanol mixture, and the resulting yellow solution was stirred at 600 rpm and 50 °C for 72 h under an N2 atmosphere. The solid product was precipitated from the reaction mixture by solvent evaporation. The stable complex was filtered off, washed with cold water, and dried under vacuum. The purity was checked up by thin layer chromatography with the eluent CH3COOC2H5/C2H5OH = 2:1. The substance is soluble in DMSO. Yield: 0.3460 g (96.2%). M.P. = 235–237 °C. Anal. calcd. for PtCl4C18H18N6O4: C, 30.06; H, 2.52; N, 11.68. Found: C, 29.70; H, 2.61; N, 11.33.
3.1.3 Synthesis of PtCl2(C9H9N3O2)2 (2)
K2[PtCl4] (0.2075 g, 0.5 mmol) in 3 cm3 of water was added to a solution of L (0.1911 g, 1 mmol) in 6 cm3 of a 50% water/ethanol mixture and the resulting solution was stirred at 600 rpm and 50 °C for 24 h under an N2 atmosphere. The solid product precipitated from the reaction mixture. The stable complex was filtered off, washed with cold water, and dried under vacuum. The purity was checked up by thin layer chromatography with the eluent CH3COOC2H5/C2H5OH = 2:1. The substance is soluble in DMSO. Yield: 0.2800 g (86.4%). M.P. = 330–331 °C. Anal. calcd. for PtCl2C18H18N6O4: C, 33.34; H, 2.80; N, 12.96. Found: C, 33.50; H, 2.48; N, 12.81.
3.1.4 Synthesis of PdCl2(C9H9N3O2)2 (3)
K2[PdCl4] (0.1632 g, 0.5 mmol) in 2 cm3 of water was added to a stirred solution of L (0.1911 g, 1 mmol) at 600 rpm in 6 cm3 of a 50% water/ethanol mixture for 3 h at room temperature. The solid product precipitated from the reaction mixture. The stable complex was filtered off, washed with cold water, and dried under vacuum. The purity was checked up by thin layer chromatography with the eluent CH3COOC2H5/C2H5OH = 2:1. The substance is soluble in DMSO. Yield: 0.2115 g (75.6%). M.P. = 233–234 °C. Anal. calcd. for PdCl2C18H18N6O4: C, 38.63; H, 3.24; N, 15.02. Found: C, 38.30; H, 3.39; N, 14.73.
3.1.5 Synthesis of Pd2Cl4(C9H9N3O2)2 (4)
PdCl2 (0.1772 g, 1 mmol) in 20 cm3, acetonitrile was refluxed for 24 h and then added to a stirred solution of L (0.1911 g, 1 mmol) at 600 rpm in 5 cm3 of a 50% water/acetonitrile mixture for 3 h at room temperature. The solid product precipitated from the reaction mixture. The stable complex was filtered off, washed with cold diethyl ether, and dried under vacuum. The purity was checked up by thin layer chromatography with the eluent CH3COOC2H5/C2H5OH = 2:1. The substance is soluble in DMSO. Yield: 0.3009 g (81.7%). M.P. = 285–287 °C. Anal. calcd. for Pd2Cl4C18H18N6O4: C, 29.33; H, 2.46; N, 11.40. Found: C, 29.56; H, 2.79; N, 11.63.
4 Results and discussion
Reactions of K2[PtCl6], K2[PtCl4], K2[PdCl4], and PdCl2 with L gave the complexes 1–4 (Scheme 1). The results of elemental analysis showed 1:2 and 1:1 metal/ligand stoichiometry for the complexes 1–3 and 4, respectively. The analytical results were in good agreement with those required by the general formula PtCl4L2 (1), PtCl2L2 (2), PdCl2L2 (3), and Pd2Cl4L2 (4). Crystals of these complexes could not be grown; therefore X-ray crystal determination was not possible. The compounds were characterized on the basis of the following studies.
4.1 Structural characterization
Assignment of IR and NMR peaks (Tables 1 and 2) was performed according to the optimized structure of the ligand [20]; for the numbering of atoms see Fig. 1 (to see the spectra refer to Supplementary material, Figs. A.1–A.19).
IR selected bands (ν/cm−1) of the ligand [20] and complexes; for the numbering of atoms, see Fig. 1.
| Compound | ν(NH) | ν(CO) | ν(CN) | ν(MCl) |
| L | 3244 (N2H3) 3170 (N3H4) | 1771 (C8O2) 1723 (C6O1) | 1594 | – |
| 1 | 3212 3129 | 1777 1732 | 1610 | 344 (PtCl) |
| 2 | broad 3129 | 1780 1728 | 1611 | 329 (PtCl) |
| 3 | 3257 3116 | 1778 1728 | 1606 | 360 (PdCl) |
| 4 | 3267 3119 | 1774 1725 | 1609 | 375 (PdCl, terminal) 305 (PdCl, bridging, trans to Cl) 249 (PdCl, bridging, trans to L) |
Experimental and theoretical 1H and 13CNMR chemical shifts/ppm for the ligand [20] and corresponding complexes; for the numbering of atoms, see Fig. 1.
| Compound | 1HNMR | |||||||||
| 5,6,7-H | 9-H | 2-H | 8-H | 1-H | 3-H | 4-H | ||||
| L | Exp. | 1.69 | 7.39 | 7.88 | 8.51 | 8.71 | 8.71 | – | ||
| Theo. | 1.64 | 7.31 | 8.24 | 8.87 | 9.01 | 4.38 | 5.89 | |||
| 1 | Exp. | 1.60 | 7.84 | 8.40 | 8.79 | 8.81 | 8.72 | 10.97 | ||
| Theo. | 1.68 | 7.49 | 8.62 | 9.75 | 9.96 | 4.73 | 6.00 | |||
| 2 | Exp. | 1.61 | 7.51 | 8.06 | 8.81 | 8.84 | 8.65 | 10.96 | ||
| Theo. | 1.64 | 7.29 | 8.35 | 9.33 | 9.53 | 4.70 | 5.94 | |||
| 3 | Exp. | 1.70 | 7.62 | 8.13 | 8.68 | 8.84 | 8.77 | 11.06 | ||
| Theo. | 1.63 | 7.29 | 8.36 | 9.45 | 9.67 | 4.71 | 5.94 | |||
| 4 | Exp. | 1.70 | 7.59 | 8.13 | 8.79 | 8.79 | 8.73 | 11.04 | ||
| Theo. | 1.65 | 7.24 | 8.40 | 8.37 | 9.72 | 4.71 | 5.99 | |||
| Compound | 13CNMR | |||||||||
| C-9 | C-7 | C-3 | C-4 | C-5 | C-2 | C-1 | C-6 | C-8 | ||
| L | Exp. | 25.45 | 63.24 | 123.89 | 133.78 | 136.06 | 147.14 | 149.35 | 157.29 | 177.52 |
| Theo. | 30.53 | 72.82 | 125.26 | 136.36 | 140.00 | 154.14 | 149.20 | 153.66 | 176.36 | |
| 1 | Exp. | 25.15 | 63.01 | 126.79 | 138.81 | 140.64 | 150.62 | 153.00 | 156.55 | 175.92 |
| Theo. | 31.28 | 73.04 | 126.45 | 139.54 | 142.49 | 157.24 | 154.35 | 153.14 | 175.59 | |
| 2 | Exp. | 25.65 | 62.68 | 126.68 | 136.81 | 138.91 | 150.26 | 152.71 | 156.37 | 175.93 |
| Theo. | 31.07 | 73.09 | 125.72 | 136.66 | 140.83 | 155.38 | 152.06 | 153.30 | 175.80 | |
| 3 | Exp. | 25.46 | 62.79 | 125.67 | 137.39 | 137.84 | 150.13 | 153.09 | 156.45 | 176.16 |
| Theo. | 31.14 | 73.03 | 125.98 | 137.35 | 140.99 | 156.89 | 153.54 | 153.31 | 155.77 | |
| 4 | Exp. | 25.50 | 62.82 | 125.68 | 137.40 | 137.85 | 150.13 | 153.05 | 156.43 | 176.18 |
| Theo. | 30.85 | 72.79 | 126.84 | 137.93 | 143.59 | 155.29 | 154.13 | 153.14 | 157.70 |
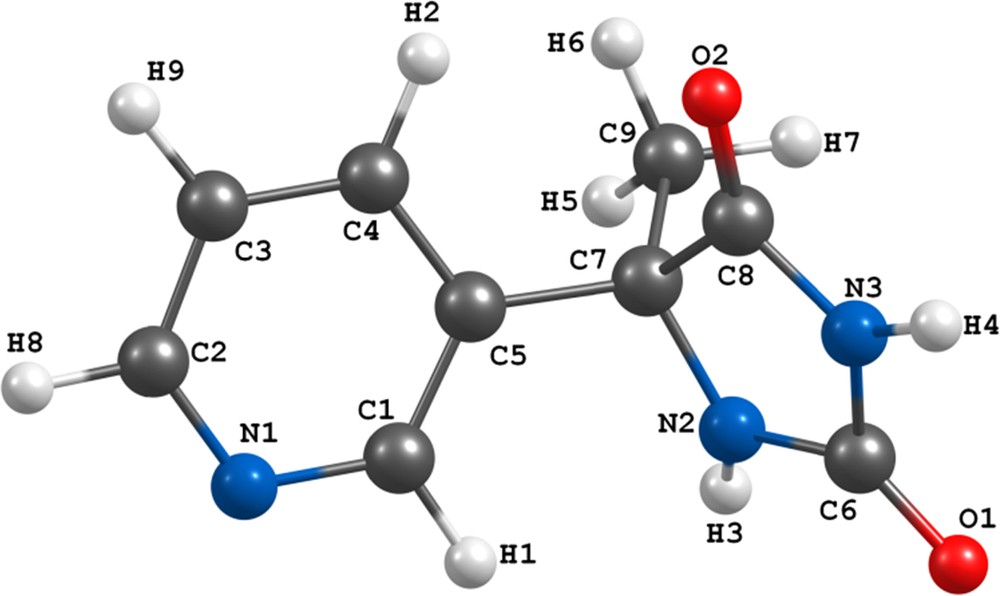
(Color online.) Optimized structure of L at the BP86/TZVP level of theory [20].
Table 1 shows the most important vibrations in the ligand and the corresponding complexes. The comparative analysis of IR spectra of the complexes and of the free ligand revealed that the absorption bands characteristic of the stretching vibrations of – CN – from the pyridine ring shifted towards the higher frequencies in the complexes. This indicates that the nitrogen atom from the pyridine ring participates in the coordination to the metal ion. The other characteristic bands of the pyridine ring of the free ligand are also shifted to the higher frequencies upon complexation. While the bands related to the stretching vibrations of the carbonyl groups remained almost unchanged in the all complexes, the stretching vibrations of NH groups have shifted to the lower frequencies. These changes may indicate a greater sensitivity of NH bonds to the coordination. The spectra of complexes 1–3 display a band in the low-energy region at 390–300 cm−1 due to the MCl stretches, indicating that these complexes have a trans configuration [33]. The IR spectrum of 4, Pd2Cl2(μ-Cl)2L2, displays three νPdCl bands attributable to the terminal and bridging PdCl stretches as usually observed for these complexes [34–36].
The chemical shifts of NMR spectra for the ligand and the corresponding complexes are shown in Table 2.
In the 1H NMR spectra of the complexes, protons signals of the pyridine ring are shifted toward the lower frequencies compared to the spectrum of the ligand. There are noticeable differences between the protons chemical shifts of the ligand and those of the corresponding complexes. These show that in these complexes the most probable bonding of the ligand with the metal ion is realized through the nitrogen atom of the pyridine ring. Proton signal of N2H3 group from the hydantoin ring slightly shifted upon complexation, while the peak related to the more acidic NH group (N3H4) had just appeared in the complex spectrum. These facts indicate that these atoms are not involved in the coordination. The impressive changes of the chemical shifts related to the carbon atoms of the pyridine ring also confirmed the participation of this ring in the binding with the metal ion. Signals of two CO groups from the hydantoin ring in all complexes slightly changed. C8O2 show greater shift toward higher frequencies than C6O1, which can be because these groups are nearer to the coordination site. These findings are an indication that the hydantoin ring does not participate in the coordination.
Interestingly, we observed an isomerization of complex 3 to its cis derivative (Figs. A.12 and A.13). Thus when we recorded the 1H and 13C NMR spectra of a solution of trans-3 in DMSO at room temperature, we observed duplicated signals. These chemical shifts indicate that the coordination remained PdCl2N2, and a plausible explanation is a reversible trans-to-cis isomerization. These newly emerged NMR peaks were assigned to a cis-configuration. It is noteworthy that this phenomenon has not been observed for other complexes and is consistent with the results of our theoretical studies indicating a small energy difference between the cis and trans isomers in solution for this compound (please see theoretical studies).
4.2 Theoretical studies
4.2.1 Geometry optimization
The optimized geometry of L is shown in Fig. 1 and representative selected calculated bond parameters are listed in Table A.1. The distorted octahedral and square planar coordination configurations were observed for complexes 1 and 2–4, respectively. For each complex, there are two possible isomers, i.e. cis and trans. We can also consider four and six conformers for trans and cis isomers, respectively. Among all optimized isomers and related conformers (Figs. A.21–A.24), only the most stable cis and trans structures are shown in Fig. 2. Calculated total energies for 1, 2, 3, and 4 indicate that the trans isomers are by 18.8, 22.9, 23.4, and 50.9 kJ/mol more stable than the cis ones, respectively. The representative selected calculated bond parameters for most stable structures of 1–4 (trans isomers in Fig. 2) are listed in Tables A.2–A.5. In the case of 4, there are varieties of bending angles between the coordination planes of two Pd atoms in all ten optimized structures. A theoretical and structural analysis of the binuclear complexes with unsubstituted bridges showed that a driving force for the bending of the molecules is the attractive metal···metal interaction that results from donor–acceptor interactions between the
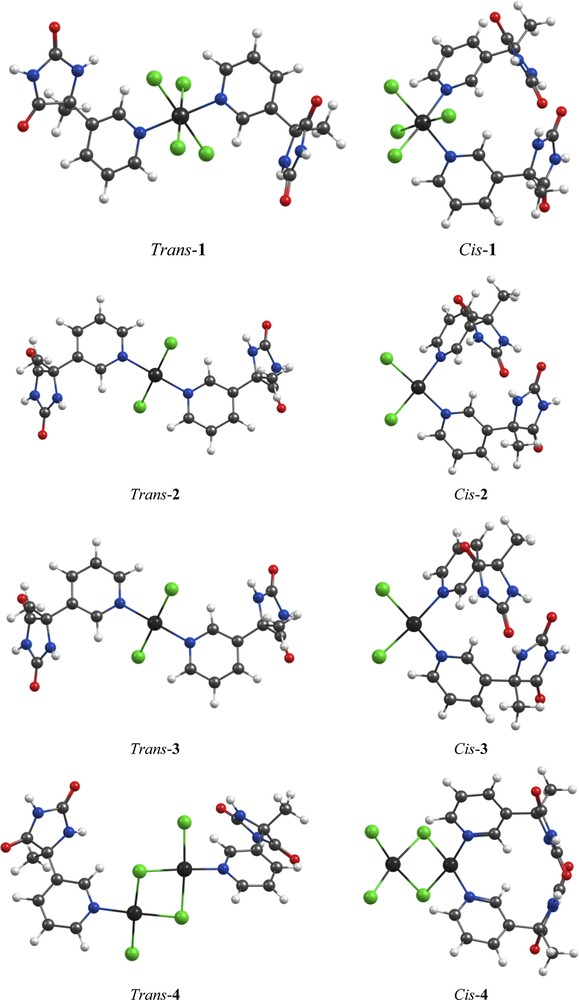
(Color online.) The most stable cis and trans isomers of the optimized structures of complexes 1–4 at the BP86/TZVP level of theory.
Since 50/50 (v/v) ethanol/water and acetonitrile/water solutions were used for obtaining complexes 1–3 and 4, respectively, the CPCM with the dielectric constant of ethanol or water for 1–3 and acetonitrile or water for 4 was used for further calculations. In order to compare the stability of the structures, an averaged value of the electronic energy of the complexes in ethanol/water and acetonitrile/water solutions was calculated. The resulting data suggest that the trans isomer in solution, similar to the gas phase, is the more stable isomer in these complexes. The difference between the stabilities of the most stable trans and cis isomers in solution are 19.2, 15, 12.2 and 45.1 kJ/mol for 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively.
4.2.2 1H and 13C NMR calculations
For considering the correlation of 1H and 13C NMR spectra of L and the corresponding complexes with calculated data obtained from their optimized structures, the quantum chemical calculations of shielding constants were performed. The absolute isotropic magnetic shielding constants (σi) were used to obtain the chemical shifts (see Eq. (1)) by referring to the standard compound tetramethylsilane (TMS) for both the H and C atoms. The reference molecule TMS was also optimized and its isotropic NMR shielding constants were calculated using the same level of theory as for the studied structures.
| (1) |
As shown in Table 2 and in Fig. 3, the experimental 1H and 13C chemical shifts of all remarkable protons, except the acidic protons (of two –NH groups), and carbons for all compounds are in good agreement with the calculated values. Calculated values of acidic protons (H3 and H4 in L, Fig. 1) are unacceptable apart from the experimental values, showing obviously that the continuum model has not correctly described the chemical shifts associated with these protons and fails in reproducing the experimental findings for them [38–40]. However, as can be seen in Fig. 3, the high linear correlation coefficients (R2) established the robustness of the assignments. Thus it seems that the optimized and selected gas phase structures are close to those of these compounds in solution.
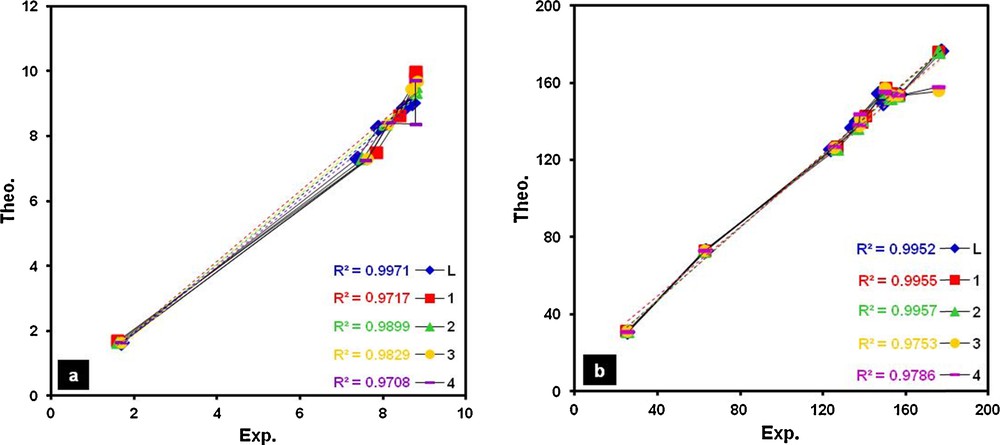
(Color online.) Correlations between theoretical and corresponding experimental values of 1H (a) and 13C (b) chemical shifts (δ, ppm) for L and complexes 1–4.
4.3 Antibacterial activities
The antibacterial screening of the ligand and the metal complexes are shown in Fig. 4 (Table A.7). The inhibition was recorded by measuring the diameter of the inhibition zone for bacteria after 24 h. The activity of all these compounds was further confirmed by determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values by the tube dilution method in which the effectiveness was observed at lower concentrations. For comparison, inhibition zones and MIC values of chloramphenicol standard were also indicated.
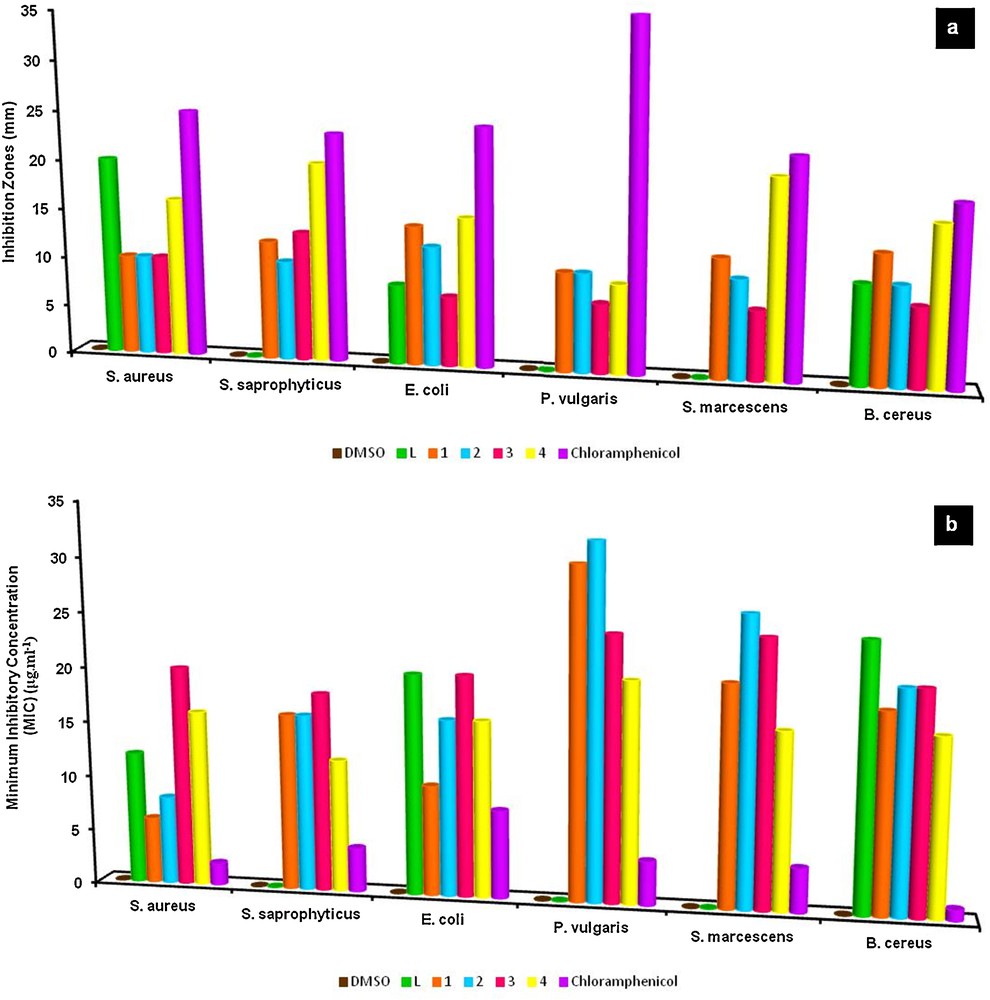
(Color online.) Antibacterial screening (a: inhibition zones (mm) and b: MIC values (μg·cm−3)) of the ligand and metal complexes; each datum represents the means ± SE of 4–5 samples.
According to data, both the ligand and complexes individually exhibited varying degrees of inhibitory effects on the growth of the tested bacterial species. The antibacterial results evidently showed that the activity of the ligand became more pronounced when coordinated to the metal. The increased activity of the metal chelates can be explained on the basis of Tweedy's chelation theory [41], according to which the polarities of the ligand and the central metal atom are reduced through charge equilibration over the whole chelate ring. This increases the lipophilic character of the metal chelate and favors its permeation through the lipoid layer of the bacterial membranes [42]. As can be seen in Fig. 4, a moderate to strong inhibition was detected towards bacteria strains with MIC values of 32–6 μg·cm−3. In this regard, the highest antibacterial effect of L was against S. aureus (12 μg·cm−3), 1 and 2 against E. coli (10 and 16 μg·cm−3), and 3 and 4 against S. saprophyticus (18 and 12 μg·cm−3). As a result, both in terms of inhibitory potency and MIC values, standard antibiotic chloramphenicol has stronger activity than the chemicals against these bacterial strains. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy that the inhibitory zone of L (against S. aureus) and 4 (against S. saprophyticus, S. marcescens, and B. cereus) is noticeable and comparable to that of chloramphenicol.
5 Conclusions
In this report, the synthesis of N:M complexes of platinum (1 and 2) and palladium (3 and 4) with monodentate 5-methyl-5-(3-pyridyl)hydantoin, L, have been presented. The experimental data and comprehensive theoretical calculations invoking geometry optimization of different isomers showed that in these complexes the nitrogen atom of the pyridine ring is involved in metal bonding forming mononuclear octahedral (1) and square planar (2 and 3), and binuclear square planar (4) complexes with trans configuration. An interesting aspect of complex 3 is the inversion of configuration, confirmed by the observation of duplicated 1H and 13C NMR peaks. The excellent agreement was observed between the theoretical and experimental chemical shifts of the compounds. The synthesized compounds were screened for their antibacterial activity against six bacterial strains. Based on the obtained results, complexes showed higher activities as compared to the parent ligand and, in general, the most active was binuclear palladium(II) complex.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Bu-Ali-Sina University for financial support.



Vous devez vous connecter pour continuer.
S'authentifier