1 Introduction
In the absence of radiofrequency radiation, the contribution of chemical exchange to relaxation is dependent on the rate of the exchange process, the chemical shift differences between involved sites and the population of each site. Near coalescence, the rate of exchange is of the order of the chemical shift difference, and the contribution of chemical exchange to relaxation is therefore maximal. Regions of conformational exchange often correspond to some of the functionally most important sites in proteins, for example, sites for interactions with RNA. Although the study of exchange processes could bring valuable information about the recognition process between protein and RNA, chemical exchange is often detrimental to the NMR spectra quality resulting in broad, very weak or even unobservable signals. Several methods have been developed to characterize chemical exchange processes (for reviews, see Refs. [1–3]) and to improve NMR signal intensities in the presence of such exchange, i.e. to preserve spin coherence [4–6].
In the present report, we used previously described CPMG-like experiment [5,6] to improve HSQC spectrum of an RNA–protein complex. In this kind of experiment, the intensity of the signals involved in chemical exchange process is increased by refocusing spins during coherence transfer period. The HSQC experiment modified with a CPMG pulse train during INEPT period allowed us to improve the overall signal-to-noise ratio and to tear some signals off the noise. These NMR experiments were carried out on a complex between the HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein (NC) and an RNA hairpin that mimicks the D-arm of tRNA3Lys. The HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein (NC) is a short, basic, nucleic acid binding protein with two zinc finger domains. NC is a versatile protein which is involved in multiple functions during the virus replication cycle, many of these functions relying on the nucleic acid chaperone activity of NC (for recent reviews see Refs. [7–9]). In previous studies [10], we have highlighted a strong and specific interaction between the NC protein and the D-arm of tRNA3Lys. This interaction could be the key factor driving the unfolding process of tRNA3Lys, thereby allowing complete annealing of tRNA3Lys to the primer binding site (PBS), the first event in the HIV-1 reverse transcription. However, the NMR study of the complex between the NC protein and the D-arm of tRNA3Lys is rendered tricky by chemical exchange process in the microsecond to millisecond time scale, leading to unobservable or broadened signals.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 NMR sample
The recombinant NC55 protein was overexpressed from a recombinant plasmid (kind gift of M.F. Summers) and purified as previously described [11,12].
The RNA oligonucleotide mimicking the tRNA3Lys D-arm (24 nucleotides length) was purchased from Dharmacon Research with 2′-o-bis (acetoxyethoxy)-methyl (ACE) protection. The sample was deprotected by following the manufacturer's recommendations and dialyzed several times against deionised water. The pH was adjusted between 6 and 6.5 before freeze-drying.
The 15N-labelled NC55 and the unlabelled RNA D-arm were prepared at about 2 mM and 10 mM, respectively, in an NMR buffer (25 mM Na-d3-acetate pH 6.5, 25 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM BME, 0.1 mM ZnCl2, 10% 2H2O). The titration experiment is achieved by adding increased amount of RNA D-arm in a 0.5 mM sample of 15N-labelled NC55. After RNA addition, the sample is immediately vortexed and kept at 30 °C during 30 min before NMR data acquisition.
2.2 NMR experiments
NMR experiments were carried out on a Bruker Avance DRX spectrometer operating at 600 MHz and equipped with a 5-mm triple-resonance gradient probe with z-axis gradients. All sequences used sine-bell shaped pulsed field gradients (PFG) along the z-axis. Acquisitions of data were performed at 303 K. All experiments were recorded with 512 points in the 1H dimension with a spectral width of 4.6 ppm and 256 points in the 15N dimension with a spectral width of 30.0 ppm. NMR data were processed with NMRPipe/NMRDraw software [13]. A pure squared sine bell and a pure squared cosine bell were applied along t2 and t1, respectively. The data were zero-filled to 1024 points along t1 and to 4096 along t2 prior to Fourier transform. Spectra were analyzed with the software SPARKY (T.D. Goddard and D.G. Kneller, SPARKY 3, University of California, San Francisco).
The SE-HSQC experiment is a standard sensitivity-enhanced 2D 1H/15N correlation via double INEPT transfer [14]. Frequency discrimination with retention of absorption mode lineshape is achieved by the echo anti-echo method [15]. Sensitivity enhancement is optimized for amide cross peaks by setting both reverse transfer periods to (1/2J). Heteronuclear decoupling during acquisition was achieved by GARP sequence.
The SE-CPMG-HSQC experiment (Fig. 1) is adapted from the SE-HSQC experiment in which the INEPT and reverse-INEPT periods are modified by the inclusion of a phase-modulated pulse train. This experiment is based on previously described HSQC experiments for the observation of exchange broadened signals [6]. The sequence was modified to optimize sensitivity enhancement for amide cross peaks by setting both reverse transfer periods to (1/2J). See caption of Fig. 1 for more details on NMR pulse sequence.
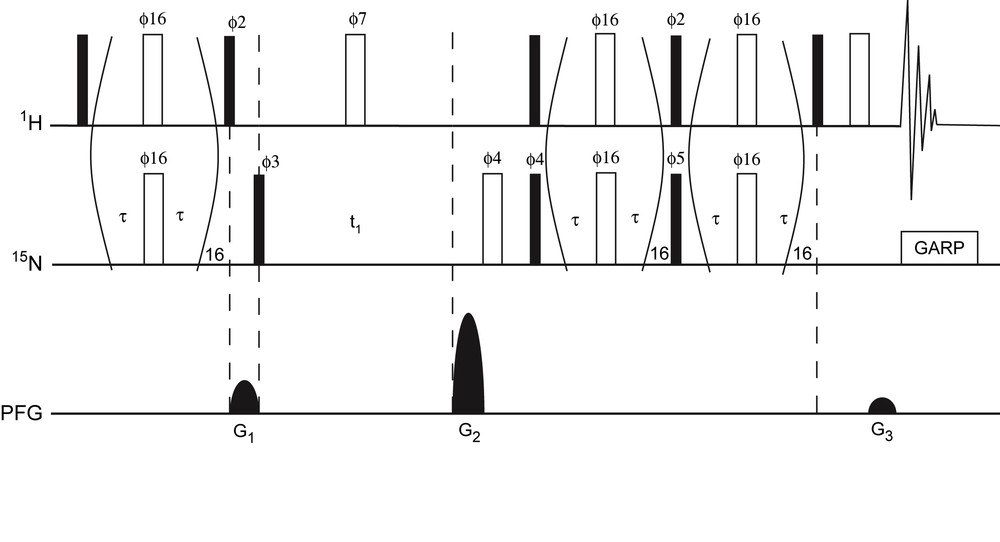
Pulse scheme of the 15N–1H SE-CPMG-HSQC experiment. Narrow (filled) and wide (open) rectangles represent 90° and 180° pulses, respectively. Unless indicated, the pulses are applied along the x-axis. The delay τ was set to 140 μs such that the total length of the spin-echo pulse train equalled 5.55 ms, i.e. 1/2J with J = 90 Hz for N–H 1J coupling. 15N pulses were achieved using a field strength γB1 = 47 kHz. The phase modulation scheme for ϕ16 is x, y, x, y, y, x, y, x, −x, −y, −x, −y, −y, −x, −y, −x. The following phase cycling was used: ϕ2 = y; ϕ3 = x, −x; ϕ7 = 2(x), 2(−x); ϕ4 = 2(x), 2(−x); ϕ5 = 2(y), 2(−y); ϕrec = x, −x, −x, x. Heteronuclear decoupling during acquisition was achieved by GARP. For each t1 increment, axial peaks were shifted to the sides of the spectrum by inversion of ϕ3 in concert with the receiver phase, similar as in States-TPPI [23]. The sequence uses sine-bell shaped pulsed field gradients (PFG) along the z-axis. To yield absorption mode spectra P- and N-type coherence selection is achieved by inversion of G2 in concert with inversion of ϕ5. The duration of all the gradients was 1 ms, followed by a 400 μs recovery delay. Gradient relative strengths were G1 = 50%; G2 = 80%; G3 = 8.1%.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Biological context
The HIV-1 virus uses a cellular tRNA, the human tRNA3Lys as a primer to initiate the reverse transcription of the viral genome. In the virus, the 3′ end of the primer tRNA is strongly bound by 18 Watson–Crick base pairs to a complementary sequence of the viral RNA called the primer binding site (PBS). The first event in viral replication is thus the annealing of tRNA3Lys to the PBS, this step being promoted by the viral NC. Most of the known functions of the HIV-1 NC involve interactions with nucleic acids (for recent reviews, see Refs. [7–9]). The structure of the free NC consists in two zinc knuckle domains, connected by a flexible linker attached to flexible N- and C-terminal tails [12,16,17]. By NMR, it was shown that NC has an inherent conformational flexibility that could be crucial to allow its binding to different nucleic acid sequences and structures along the HIV-1 replication cycle [12,18]. In the currently available structures [11,19,20] of NC with nucleic acids, most of the specific contacts between the protein and the nucleic acids occur via the zinc knuckles, notably residues F16 and W37, interacting with the guanine-rich loop of RNA hairpin. We have shown by NMR of 15N-labelled tRNA3Lys that NC interacts preferentially with the acceptor and D stems and with the nucleotides involved in tertiary interactions between the D and T loops [21]. We also performed the reciprocal experiment, i.e. the NMR footprint of tRNA3Lys binding on 15N-labelled NC (data not shown). The signals are so broadened that roughly only the C-teminal amide group and the amino groups of side chains remain observable. Indeed, the multiplicity of NC binding sites on tRNA3Lys rendered analyses using the full-length tRNA intractable, even when stringency was raised by increasing salt concentration (data not shown). Reducing the target RNA length could decrease the number of non-specific sites and still have a biological interest. Indeed, studying separate hairpins cannot obviously mimic the entire tRNA, in particular at the level of the TΨC/D loops interaction. However, in the annealing process, there is a step where the TΨC/D loops interaction are broken and where the NC protein plays a crucial role [22]. Therefore, we have previously demonstrated that NC makes a specific interaction with the D hairpin mimicking the D-arm of tRNA3Lys (dissociation constant Kd = 28 nM at 100 mM NaCl). This interaction could be a key factor driving the unfolding process, thereby allowing complete annealing of tRNA3Lys to the PBS [10]. Fig. 2a shows the HSQC experiment of 15N-labelled NC with the tRNA3Lys D hairpin. The NMR signals are quite broad for the size of the complex (14.2 kDa) and may indicate that the NC in the context of the complex is involved in a chemical exchange process in the microsecond to millisecond time scale. This chemical exchange is attributable to the equilibrium between the free and bound forms of the protein.

Contour plot of the 2D HSQC-type spectra of the complex between uniformly 15N-labelled NC and (a) unlabelled tRNA3Lys D-arm (SE-HSQC experiment), (b) unlabelled tRNA3Lys D-arm (SE-CPMG-HSQC experiment), (c) 1D SE-HSQC trace of signal 1 and (d) 1D SE-CPMG-HSQC trace of signal 1.
3.2 Analysis of the exchange process and NMR optimization of HSQC spectra
In the presence of such chemical exchange, multidimensional NMR experiments suffer from dephasing of spin coherence during periods of evolution and coherence transfer by scalar coupling [2,3]. The result of chemical exchange during periods of evolution is a broadening of the resonances, while it leads to loss of magnetization during periods of coherence transfer and therewith of signal intensity. Therefore, resonances are broad, very weak or even unobservable (Fig. 2a). The loss of magnetization during the period of coherence transfer can be minimized by using a modified INEPT block, i.e. the CPMG-INEPT block first described by Mueller and co-workers [5]. The intensity of the signals involved in the chemical exchange process is increased by refocusing them during the coherence transfer period. We then compared CPMG-HSQC [6] and SE-CPMG-HSQC described in Fig. 1, since the gain of intensity from the sensitivity-enhanced HSQC could be counterbalanced by the increase of the pulse sequence length. As a result, the SE-CPMG-HSQC spectrum shows more intense signals than those from the CPMG-HSQC (data not shown).
The comparison of the performance of the SE-HSQC and SE-CPMG-HSQC experiment is given in Fig. 2. The CPMG-derived sequence shows improved sensitivity for almost all resonances, resulting in an average enhancement of about 40%. This result confirms that the exchange process lies in the microsecond to millisecond time scale. Moreover, some unobservable signals in the classic SE-HSQC experiment grow up in the SE-CPMG-HSQC and become observable (see signals 1, 2, 3 in Fig. 2). This could be of significant importance, as these signals, which show considerably higher intensity, belong to residues directly involved in RNA binding.
Fig. 3 shows the titration of 15N-labelled NC by increased amounts of D hairpin until reaching the equivalence. Two kinds of behaviour are observed: (1) a progressive variation of chemical shifts as the amount of RNA increases (see for instance the NMR signals of C28 and C49 – Fig. 3); (2) a disappearance at the substoichiometric level of NC signals and their reappearance close to the 1:1 ratio of NC:RNA (Fig. 3). These results are consistent with an exchange relaxation constant (Rex) behaviour in the fast exchange regime. Indeed, for a simple model of two-site exchange process in the fast exchange limit, the exchange relaxation constant is given by , where kex is the exchange rate constant, Δω is the chemical shift difference between the two sites, and pa and pb the relative population of each site. For a complex with a dissociation constant more than 3 orders of magnitude smaller than the species concentrations, we can assume that the concentration of the complex in bound form is rather equal to the partner added in substoichiometric molarity. Thus, during the titration, for a fraction p of added RNA in the protein (p ∈ [0,1]), the fraction of the bound protein is p and the fraction of the free one is (1 − p) and so Rex becomes . Even if these equations apply only to the fast exchange limit (kex > Δω), they provide useful qualitative information for the interpretation of the relaxation behaviour of a complex in a fast exchange regime. For instance, the Rex maximum during the titration occurs for p = 0.5, and depends quadratically on the chemical shift difference between the free and the bound forms. Therefore, the NMR signals that experience the largest variation of chemical shifts between the free and bound forms of NC are also those that will experience the largest broadening during the titration due to the exchange regime.

Titration experiment (SE-CPMG-HSQC) of 15N-labelled NC protein by unlabelled tRNA3Lys D hairpin. In red: 1/0 protein/RNA ratio; in orange: 1/0.3; in yellow: 1/0.6, in green: 1/0.9, in blue: 1/1. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) The circled signals disappear during the titration. The corresponding residues are highlighted on the NC sequence. The major aromatic residue of each zinc knuckle is written in open letter.
We can reasonably think that these signals which present the largest differences in their chemical shifts between the free and bound forms of NC are those involved in the interaction with the RNA partner. Actually, they belong to amino acids surrounding the major aromatic residue of each zinc knuckle, i.e. F16 and W37, and to residues with hydrophobic side chain, i.e. I24, A25 and M46 (Fig. 3). These residues have been identified to largely participate in the recognition by the NC of RNA encapsidation signals SL2 and SL3 [11,20]. Indeed, in these structures, each zinc knuckle forms a hydrophobic cleft by means of the hydrophobic side chains listed above and binds to an exposed guanine nucleobase of the RNA loop. Thus the NMR footprint of the RNA D-arm on the NC (Fig. 3) suggests that the recognition mode between the NC and the tRNA3Lys D-arm is similar to that of the encapsidation signals.
4 Conclusion
In this paper, the use of modified HSQC experiment allowed us to significantly improve the signal to noise ratio in the spectra of the complex between the NC and the tRNA3Lys D-arm. This experiment also allowed us to tear some signals off the noise and could be of pronounced importance in the way of the determination of the NC/D-arm complex structure by NMR. The determination of this structure is under investigation and should confirm the recognition mode similarity between the encapsidation signals and the tRNA3Lys D-arm.
Acknowledgments
P. Barraud is supported by a studentship from Ministère de la Recherche. The French AIDS National Agency (ANRS) and 'Ensemble contre le sida (Sidaction) supported this work.