1 Introduction
Oxadiazinones are quite important biologically-active compounds which have gained more interest thanks to their utility as central nervous system stimulants [1,2] and as oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitor [3]. As far as we know, no works reporting the antibacterial or antifungal activities of this class of heterocycles have been reported.
The high synthetic value of oxadiazinones has been demonstrated specially in Diels–Alder cycloaddition [4,5] and Favorski ring contraction [6]. Recently, fluorinated oxadiazinones have been proposed as a rare example of low molecular weight (LMW) hydrogelators [7].
On the other hand, the synthesis of optically-active oxadiazinones has recently attracted considerable interest in the asymmetric organic synthesis. Optically-active 1,3,4-oxadiazin-2-ones have been successfully investigated by Hitchcock et al. and Vaughn and Hitchcock [8,9] as chiral auxiliaries in the aldol reaction. Moreover, these compounds have been utilised by Husson et al. as chiral auxiliaries to perform diastereoselective alkylations [10].
Among oxadiazinones, 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones are not very broadly explored and little is known about these compounds which were prepared only once by Hussein et al. [11]. Hussein et al.’s method was not general and gave 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones with moderate yields ranging from 12 to 73% and with no indication of the product's optical purity. Therefore, there is further scope to explore more efficient synthetic methods. Herein, chemically speaking, we report a simple and practical method to achieve the synthesis of new optically pure 5-alkyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones by the condensation of chiral 1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime with chiral 2-(S)-2-bromoacid chlorides, followed by cyclization in the presence of one equivalent of sodium hydride. Some tests have been conducted in order to evaluate the antibacterial and antifungal activities of our new 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Chemistry
The synthetic route to the target compounds 4a–f is outlined in Scheme 1. We have successfully converted commercially available (l)-proline to the corresponding optically pure (2S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile 1 [12]. The treatment of this compound with hydroxylamine hydrochloride and two equivalents of triethylamine overnight at room temperature led to the corresponding chiral (2S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidine-2-carboxamidoxime 2. The condensation of amidoxime 2 with different α-bromoacid chlorides, easily prepared from the corresponding α-aminoacids following a known procedure [13], gave the chiral (O-bromoacyl) (2S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidine-2-carboxamidoximes 3a–f with chemical yields ranging from 79 to 87%. The final step of this sequence is the intramolecular cyclization of 3a–f in the presence of one equivalent of NaH affording the corresponding 5-alkyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones 4a–f with good chemical yields and excellent diastereomeric excesses.
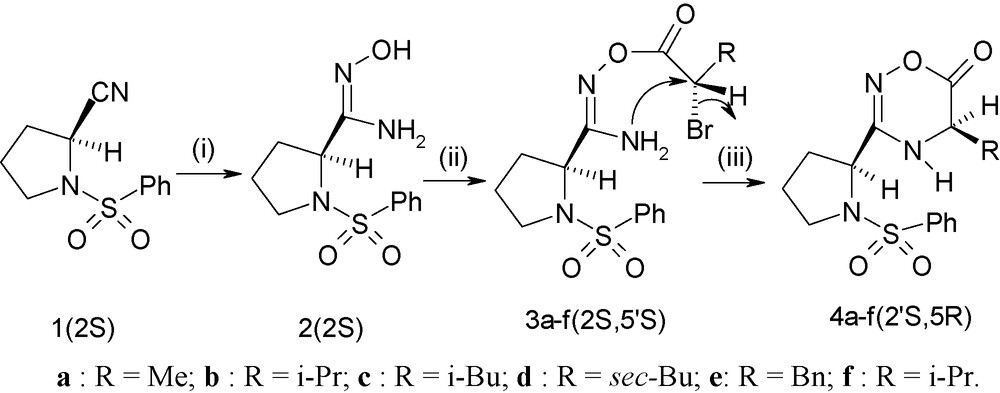
Synthesis of (2′S, 5R), 5-alkyl-3-(1’-benzenesulfonyl-pyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones 4a–f. Reaction conditions: (i) NH2OH.HCl/Et3N/CHCl3; (ii) 2-(S)-2-bromo-acid chlorides/Et3N/CH2Cl2, 0 °C ; (iii) NaH/THF, 3 h, −25 °C.
The addition reaction of amidoxime to the activated carboxylic acid derivatives has always been described as an easy method for the synthesis of 1,2,4-oxadiazoles [14,15]. As part of our work, directed towards the synthesis of new heterocyclic compounds from amino acids [16,17], we investigate chiral new (2S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidine-2-carboxamidoxime to cyclise with α-bromoacid chlorides yielding new 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones.
The synthesis of the amidoxime group, mostly involve the preparation of the cyano group, followed by the conversion into an amidoxime group. During this study, we describe the first synthesis of chiral (2S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidine-2-carboxamidoxime 2. This compound was easy prepared by treatment of (2S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile 1 with a hydroxylamine alkaline solution. However, unfortunately, the treatment of α-aminonitriles derived from other amino acids did not provide the corresponding amidoxime with good yields even after heating and prolonging the reaction time.
Work on condensation of amidoximes with acid chlorides has been described before. It is well known that acid chloride reacts with the O-part of the amidoxime [18,19]. The desired esterification products 3a–f were afforded with use of one equivalent of α-bromoacid chloride and 1.2 equivalent of triethylamine. Reaction was performed in an ice bath with short reaction times (45–60 min). In the event of longer reaction times, the reaction leads to a complex mixture.
Finally, the intermediates 3a–f undergo an intermolecular cyclization in the presence of one equivalent of NaH to yield compounds 4a–f within 3 h at −25 °C with good yields. Only one equivalent of NaH has been used in order to avoid the racemisation of the initial stereocenter of the proline by a possible elimination of the proton. We have found that compounds 4a–f were formed without a significant racemization of the asymmetric carbon 5 of the oxadiazinone ring. This result is proved by NMR and by HPLC studies.
According to 1H NMR spectra of compound 4f prepared from optically pure (2′S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidine-2′-carboxamidoxime 2 and (d,l) valine, the signal relative to the proton linked to the asymmetric carbon of oxadiazinone ring resonates in different positions for each pair of diasteromers. As shown in Fig. 1, the signal of the C*-H proton of the mixture of the two diastereomers (2′S,5R) and (2′S,5S) 4f appeared as two doublets. A first doublet at 3.95 ppm (J = 5.7 Hz) corresponding to the diastereomer (2′S,5S) and a second doublet at 3.99 ppm (J = 5.1 Hz) corresponding to the diastereomer (2′S,5R). However, the signal of the C*-H proton of the single diastereomer (2′S,5R) 4b prepared from optically-pure(2'S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidine-2’-carboxamidoxime 2 and (l)-valine, appeared as one doublet at 3.99 ppm (J = 4.2 Hz) showing the high diastereoselectivity of the intramolecular cyclization (Fig. 1). In the same way, 1H NMR spectra of compounds 4a, c–e indicated the absence of peaks expected from racemisation.

The signal of the C*-H proton of (2′S, 5R), (2′S, 5S) 4f and (2′S, 5R) 4b 5-isopropyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4oxadiazin-6-ones.
The optical purity of 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones 4a–e was confirmed by HPLC. According to the HPLC studies, compounds 4a–e are single isomers, and no peaks corresponding to other diastereomers were detected.
Finally, based on 1H NMR and HPLC, we can conclude that the nucleophelic intermolecular substitution of bromine by the amino group affording the oxadiazinone ring has occurred in a typical SN2 manner.
2.2 Biological activities
The synthesized compounds were tested at concentration ranging from 1 to 0.0018 mg mL−1 for antibacterial activity against bacterial strains. The strains of microorganisms employed were Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Klepsiella pneumonie (clinically isolated) and Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212. The same compounds were also tested to assess their activity against fungi. The yeasts were Candida glabrata ATCC 90030, C. albicans ATCC 90028, C. kreusei ATCC 6258 and C. parapsilosis ATCC 22019.
Antibacterial activities of synthesized 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones 4a–f were studied along with an antibacterial drug named levofloxacin. The obtained minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) values of the tested compounds and standard are shown in Table 1. The results revealed that all compounds showed superior activity than levofloxacin. Reported compounds 4a–f were found to be very effective at low concentrations, in some cases, the value of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of our compounds was 10 times lower than levofloxacin. Compound 4c shows a good antibacterial activity against E. faecalis at a concentration of 0.12 mg mL−1. Compounds 4e against S. aureus and 4b against E. coli exhibit a very significant antibacterial activity at a very low concentration, respectively, 0.06 and 0.03 mg mL−1.
Antibacterial and antifungal activities of 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones 4a–f (MIC, mg mL−1).
| Bacteria | MIC 4a | MIC 4b | MIC 4c | MIC 4d | MIC 4e | MIC 4f | Amphotericin B | Levofloxacin |
| K. pneumonie (clinical isolated) | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.25 | nd | 0.3 |
| S. aureus ATCC 27950 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 0.25 | nd | 0.61 |
| E. faecalis ATCC 29212 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.5 | nd | 1.22 |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | nd | 0.3 |
| Yeasts | ||||||||
| C. parapsilosis ATCC 22019 5 45 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.05 | nd |
| C. kreusei ATCC 6258 2.5 45 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.05 | nd |
| C. albicans ATCC 90028 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.05 | nd |
| C. glabrata ATCC 90030 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.5 | 0.05 | nd |
Table 1 shows also the antifungal activities of the synthesized 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones 4a–f in comparison with the antifungal amphotericin B. Based on the obtained values, the synthesized compounds showed moderate antifungal activities with MIC values ranging from 0.03 to 0.25 mg mL−1. In all cases, the minimum inhibitory concentrations of the active compound are higher than the standard used antibiotic, except for compound 4e against C. glabrata which was found to show a good antifungal activity at concentration (0.03 mg mL−1) lower than amphotericin B (0.05 mg mL−1).
It should be pointed out that this evaluation of the antibacterial and antifungal activities of 1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones was performed for the first time during this study.
3 Conclusion
In summary, we have synthesized novel biologically important 5-alkyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones 4a–f using chiral 2-(S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime and 2-(S)-2-bromoacid chlorides, both derived from inexpensive and readily available amino acids. The synthetic method has been developed for the first time during this work giving 4a–f in high chemical yields and occurring without a racemisation as shown by the 1H NMR and HPLC. The reported compounds were screened for their antibacterial and antifungal activities against a spectrum of microbial organisms. These studies proved that all compounds 4a–f showed excellent antibacterial activities, much better than levofloxacin. As for compound 4e against C. glabrata, it showed a beneficial antifungal activity at a minimum concentration (0.03 mg mL−1). The test dealing with other biological activities of these new products is under investigation in our laboratory.
4 Experimental section
4.1 Chemistry
TLC was performed on Merck 60F-254 silica gel plates (layer thickness 0.25 mm). Column chromatography was performed on silica gel (70e230 mesh) using ethylacetate and cyclohexane mixture. CH2Cl2 was distilled over CaH2 whereas THF was distilled over sodium. Melting points were determined on an electrothermal 9002 apparatus and are uncorrected. NMR spectra were recorded on AC-300 Bruker apparatus (1H at 300 MHz and 13C at 75 MHz). All chemical shifts are reported as δ values (ppm) relative to internal tetramethylsilane. IR spectra were recorded on FTS-6000 BIO-RAD apparatus. Elemental analyses were carried out by the Service of Microanalysis of the “Institut national de recherche et d’analyse physicochimique de Tunis”. HPLC analyses were conducted on a heptane/isopropanol system with a UV detector at 254 nm, using a chirobiotic V column (250 × 46 mm) and a 0.6 mL/min flow rate.
4.1.1 General procedure for the preparation of 5-alkyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones
A mixture of (2S),2-alkyl-2-bromoacid (5 mmol), SOCl2 (20 mmol) and three drops of dry DMF in anhydrous dichloromethane was stirred overnight at room temperature under N2. After the removal of the SOCl2 excess under vacuum, the residue was dissolved in dry dichloromethane and added slowly to a cold solution of (2S)-1-bzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime (5 mmol) and 1.2 equivalent of triethylamine (6 mmol) in dry dichloromethane at (0 °C). The reaction mixture was stirred for 60 min in an ice bath, and then 20 mL of saturated ammonium chloride solution was added. After separation, the aqueous layer was extracted with chloroform (3 × 50 mL). The chloroformic combined extracts were dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo and the residue obtained was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (40% ethylacetate: 60% cyclohexane) to give (O-bromoacyl) (2S)-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime 3a–f.
4.1.2 (2S)-N-phenylsulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carbonitrile 1
Yield = 89 %; mp = 99–101 °C; [α]D −1040; (CHCl3, c = 0.5); IR (cm−1): νCN = 2236 (CN); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) : δ 2.02–2.19 (m, 4H), 3.33 (m, 2H), 4.58 (dd, 1H, J = 6.9 Hz, J = 2.7 Hz), 7.53–7.88 (m, 5H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 24.73, 31.97, 47.58, 48.66, 118.03 (CN), 127.55, 129.42, 133.59, 137.29, MS/EI m/z = 236 (M+.). Anal. Calcd for C11H12N2O2S,236.29: C 55.91, H 5.12, N 11.86 . Found: C 56.13, H 4.99, N 11.75.
4.1.3 (2S)-N-phenylsulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime 2
Yield = 94 %; mp = 54–56 °C; [α]D −112; (CHCl3, c = 0.5); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) : δ 1.62–1.78 (m, 2H), 1.86–1.95 (m, 1H), 2.12–2.19 (m, 1H), 3.16–3.24 (m, 1H), 3.55–3.69 (m, 1H), 4.13 (dd, 1H, J = 6.7 Hz, J = 3.1 Hz), 5.10 (l.b, 2H; NH2); 7.54–7.88 (m, 5H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 24.56, 30.23, 49.76, 59.35, 127.87, 129.41, 133.38, 135.94,153.93, MS/EI m/z = 269 (M+.). Anal. Calcd for C11H15N3O3S,269.32: C 49.06, H 5.61, N 15.60. Found: C 49.13, H 5.69, N 15.65.
4.1.4 O-2-bromopropanoyle-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2’-carboxamidoxime 3a
Yield = 84 %; mp: 129–131 °C; [α]D = −16.3, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); IR (cm−1); νCO = 1752; νCN = 1605; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.09 (d, 3H, J = 6.9 Hz), 1.71 (m, 2H), 1.99 (m, 1H), 2.21 (m, 1H), 3.19 (m, 1H); 3.71 (m, 1H); 3.98 (q, 1H, J = 7.1 Hz); 4.33 (dd, 1H, J = 8.2 Hz, J = 3.9 Hz); 5.71 (s.l, NH), 7.65 (m, 3H); 7.91 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ; 19.91, 23.76, 31.54, 50.14, 53.45, 59.45, 128.48, 129.65, 134.16, 136.15, 160.18, 166.98.
4.1.5 O-2′-bromo-3′-méthylbutanoyle-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime 3b
Yield = 86%; mp: 140–142 °C; [α]D = −14.2, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); 1 IR (cm−1); νCO = 1761; νCN = 1610; H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.09 (d, 3H, J = 6.5 Hz), 1.16 (d, 3H, J = 7.3 Hz), 1.55 (m, 1H), 1.67 (m, 1H), 1.84 (m, 1H), 2.21 (m, 2H), 3.14 (m, 1H); 3.59 (m, 1H); 4.15 (d, 1H, J = 4.3 Hz); 4.31 (dd, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, J = 4.1 Hz); 5.84 (s.l, NH), 7.63 (m, 3H); 7.84 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ; 20.23, 20.59, 24.95, 31.92, 32.85, 50.42, 53.68, 59.10, 128.36, 129.93, 134.11, 135.50, 160.38, 166.77.
4.1.6 O-2′-bromo-4′-méthylpentanoyle-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime 3c
Yield = 81%; mp:146–148 °C; [α]D = −12.1, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); IR (cm−1); νCO = 1750; νCN = 1604; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.08 (d, 6H, J = 5.6 Hz), 1.51 (m, 3H), 1.74 (m, 2H), 2.28 (m, 1H); 2.39 (m, 1H); 3.18 (m, 1H); 3.88 (m, 1H), 4.16 (dd, 1H J = 7.5 Hz, J = 6.2 Hz), 4.32 (dd, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, J = 3.1 Hz); 5.71 (s.l, NH), 7.71 (m, 3H); 7.81 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 21.18, 23.84, 25.21, 26.02, 30.54, 33.54, 50.48, 52.21, 60.44, 128.64, 129.98, 134.04, 135.61, 161.12, 166.81.
4.1.7 O-2′-bromo-3′-méthylpentanoyle-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime 3d
Yield = 85%; mp:132–134 °C; [α]D = −17.8, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 0.88 (t, 3H, J = 4.2 Hz), 0.98 (d, 3H, J = 7.1 Hz), 1.27 (m, 1H), 1.61 (m, 1H), 1.68 (m, 2H), 1.79 (m, 1H), 2.03 (m, 1H); 2.16 (m, 1H); 3.11 (m, 1H); 3.54 (m, 1H), 4.17 (d, 1H, J = 4.1 Hz); 4.23 (dd, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, J = 3.2 Hz); 5.66 (s.l, NH); 7.58 (m, 3H); 7.80 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 11.07, 16.72, 24.94, 26.71, 31.82, 38.87, 50.41, 52.32, 59.21, 128.33, 129.89, 134.06, 135.57, 160.00, 166.87.
4.1.8 O-2′-bromo-3′-phénylpropanoyle-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime 3e
Yield = 79%; mp:154–156 °C; [α]D = −21.6, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); IR (cm−1): νCO = 1751; νCN = 1611; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.51 (m, 1H), 1.65 (m, 1H), 1.82 (m, 1H), 2.15 (m, 1H), 3.12 (m, 2H), 3.33 (m, 1H), 3.58 (m, 1H); 4.13 (m, 1H); 4.49 (m, 1H); 5.16 (s.l, NH),7.21 (m, 5H); 7.52 (m, 3H), 7.82 (m, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 24.89, 31.72, 41.67, 50.38, 57.07, 59.22, 127.80, 128.31, 129.09, 129.14, 134.01, 135.64, 136.24, 159.70, 166.82.
4.1.9 O-2′-bromo-3′-méthylbutanoyle-1-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2-carboxamidoxime 3f
Yield = 87%; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.04 (m, 6H), 1.62 (m, 1H), 1.83 (m, 2H), 2.19 (m, 2H), 3.08 (m, 1H); 3.66 (m, 1H); 4.11, 4.16 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, d, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H); 4.29 (m, 1H); 5.86 (s, 2H, NH2),7.58 (m, 3H); 7.84 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 20.25 (20.33), 20.84, 24.52, 31.45 (31.76), 32.24 (32.37), 50.83, 52.57, 60.56 (60.88), 128.89, 129.62, 134.81, 135.58, 160.76, 166.15 (166.23).
After purification, the products 3a–f were dissolved in dry THF and added slowly to a solution of 1 equivalent of NaH in dry THF cooled to −25 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred for 3 h. After warming to room temperature, 10 mL of saturated ammonium chloride solution and 50 mL of chloroform were added. After separation, the aqueous layer was extracted with chloroform (3 × 50 mL). The chloroformic combined extracts were dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo and the residue obtained was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (20% ethylacetate: 80 cyclohexane) to give the 5-alkyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-ones, which was recrystallized from (20% ethylacetate: 80% hexane).
4.1.10 (2′S, 5R)-5-methyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-one 4a
Yield = 91 %; mp:112–114 °C; [α]D = −6.0, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); d.e > 99 % [HPLC analysis using a chirobiotic V column 4.6 mm × 250 mm under the following conditions: heptane/isopropanol (95/5) as mobile phase, rt, λ ( 254 nm; flow rate = 0.6 mL/min. Retention time: 22.12 min]; IR (cm−1): νNH = 3254; νCO = 1750; νCN = 1600; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.17 (d, 3H, J = 7.1 Hz), 1.64 (m, 2H), 1.88 (m, 1H), 2.15 (m, 1H), 3.17 (m, 1H); 3.59 (m, 1H); 3.95 (q, 1H, J = 7.2 Hz); 4.27 (dd, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz, J = 3.6 Hz); 7.59 (m, 3H); 7.84 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 8.88 (s.l, NH); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 17.82, 24.56, 30.23, 49.76, 59.35, 79.87, 127.87, 129.41, 133.38, 135.94, 150.25, 166.48. Anal. Calcd for C14H17N3O4S, 323.37: C, 52.00, H, 5.30, N, 12.99. Found: C, 52.06, H, 5.37, N, 13.03.
4.1.11 (2′S, 5R)-5-isopropyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-one 4b
Yield = 93%; mp:125–127 °C; [α]D = −16.2, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); d.e > 99% [HPLC analysis using a chirobiotic V column 4.6 mm × 250 mm under the following conditions: heptane/isopropanol (95/5) as mobile phase, rt, λ ( 254 nm, flow rate = 0.6 mL/min. Retention time: 20.44 min]; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.07 (d, 3H, J = 6.7 Hz), 1.13 (d, 3H, J = 7.1 Hz), 1.68 (m, 2H), 1.93 (m, 1H), 2.38 (m, 2H), 3.22 (m, 1H); 3.57 (m, 1H); 3.99 (d, 1H, J = 4.2 Hz); 4.27 (dd, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz, J = 4.3 Hz); 7.65 (m, 3H); 7.85 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 8.89 (s.l, NH); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 17.51, 18.82, 24.51, 27.43, 29.44, 49.82, 58.58, 80.78, 127.88, 129.61, 133.80, 135.40, 150.81, 166.09. Anal. Calcd for C16H21N3O4S,351.43: C, 54.69, H, 6.02, N, 11.96. Found: C, 54.74, H, 6.09, N, 12.03.
4.1.12 (2′S, 5R)-5-isobutyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-one 4c
Yield = 90%; mp: 107–109 °C; [α]D = −22.8, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); d.e > 99 % [HPLC analysis using a chirobiotic V column 4.6 mm × 250 mm under the following conditions: heptane/isopropanol (95/5) as mobile phase, rt, λ ( 254 nm, flow rate = 0.6 mL/min. Retention time: 25.09 min]; IR (cm−1): νNH = 3256; νCO = 1754; νCN = 1607; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 0.93 (d, 6H, J = 5.8 Hz), 1.48 (m, 3H), 1.67 (m, 2H), 2.15 (m, 1H); 2.33 (m, 1H); 3.14 (m, 1H); 3.46 (m, 1H), 4.04 (dd, 1H J = 7.7 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz), 4.25 (dd, 1H, J = 7.9 Hz, J = 3.2 Hz); 7.63 (m, 3H); 7.83 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 8.78 (s.l, NH); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 18.28, 19.84, 24.31, 25.02, 29.66, 33.45, 51.08, 59.15, 80.44, 128.83, 130.25, 133.84, 135.61, 151.15, 166.77.
4.1.13 (2′S, 5R)-5-Sec-butyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-one 4d
Yield = 92%; mp:102–104 °C; [α]D = −25.7, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); d.e > 99% [HPLC analysis using a chirobiotic V column 4.6 mm × 250 mm under the following conditions: heptane/isopropanol (95/5) as mobile phase, rt, λ ( 254 nm, flow rate = 0.6 mL/min. Retention time: 26.03 min]; IR (cm−1): νNH = 3252; νCO = 1749; νCN = 1596; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 0.86 (t, 3H, J = 4.8 Hz), 0.96 (d, 3H, J = 6.9 Hz), 1.38 (m, 1H), 1.57 (m, 3H), 1.86 (m, 1H), 2.12 (m, 1H); 2.28 (m, 1H); 3.16 (m, 1H); 3.50 (m, 1H), 4.00 (d, 1H, J = 4.2 Hz); 4.21 (dd, 1H, J = 8.1 Hz, J = 3.4 Hz); 7.58 (m, 3H); 7.80 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 8.75 (s.l, NH); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 12.08, 14.43, 24.89, 26.02, 29.46, 34.33, 50.16, 58.95, 79.41, 128.23, 129.95, 134.14, 135.81, 151.06, 166.80. Anal. Calcd for C17H23N3O4S,365.45: C, 55.87, H, 6.34, N, 11.50. Found: C, 55.92, H, 6.40, N, 11.55.
4.1.14 (2′S, 5R)-5-benzyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-one 4e
Yield = 77%; mp:120–122 °C; [α]D = −31.6, (CHCl3, c = 0.16); d.e = 97% [HPLC analysis using a chirobiotic V column 4.6 mm × 250 mm under the following conditions: heptane/isopropanol (95/5) as mobile phase, rt, λ ( 254 nm, flow rate = 0.6 mL/min. Retention time: 28.59 min]; IR (cm−1): νNH = 3250; νCO = 1753; νCN = 1601; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.64 (m, 2H), 1.92 (m, 1H), 2.30 (m, 1H), 3.19 (m, 2H), 3.34 (m, 1H), 3.56 (m, 1H); 4.25 (m, 1H); 4.37 (m, 1H); 7.32 (m, 5H); 7.59 (m, 3H), 7.75 (m, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 8.84 (s.l, NH); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 24.83, 29.30, 34.64, 50.17, 58.92, 78.52, 127.21, 128.24, 128.84, 130.01, 134.16, 135.71, 136.75, 151.37, 166.40. Anal. Calcd for C20H21N3O4S,399.47: C, 60.14, H, 5.30, N, 10.52. Found: C, 60.18, H, 5.34, N, 10.58.
4.1.15 (2′S, 5R) and (2′S, 5S)-5-isopropyl-3-(1′-benzenesulfonylpyrrolidin-2′-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazin-6-one 4f
Yield = 89%; two diastereomers (2′S,5R) and (2′S,5S) [HPLC analysis using a chirobiotic V column 4.6 mm × 250 mm under the following conditions: heptane/isopropanol (95/5) as mobile phase, rt, λ ( 254 nm, flow rate = 0.6 mL/min. Retention times: 20.44 min and 23.89 min]; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.07 (m, 6H), 1.72 (m, 2H), 1.93 (m, 1H), 2.36 (m, 2H), 3.23 (m, 1H); 3.56 (m, 1H); 3.95, 3.99 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, d, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H); 4.28 (m, 1H); 7.66 (m, 3H); 7.87 (d, 2H, J = 8.1 Hz), 8.87 (s.l, NH); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3), δ 17.25 (17.50), 18.84, 24.52, 27.45 (27.76), 29.24 (29.37), 49.83, 58.57, 80.56 (80.88), 127.89, 129.62, 133.81, 135.38, 150.76, 166.05 (166.23).
4.2 Micro-well dilution assays
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values were determined by a micro-titre plate dilution method described by Sahin et al. [20]. The inoculum of the bacteria and yeasts were prepared from 12 h broth cultures and suspensions were adjusted to 0.5 McFarland standard turbidity. The synthesized compounds 4a–e were first dissolved in 10% DMSO and then diluted to be tested. In brief, the 96-well plates were prepared by dispensing into each well 100 μL of nutrient broth and 5 μL of the inoculum. A 200 μL stock solution of the compound initially prepared at the concentration of 1 mg mL−1 was added into the first well. Then, 100 μL from their serial dilutions was transferred into nine consecutive wells. The last well containing 100 μL of nutrient broth without compound and 5 μL of the inoculum on each strip was used as negative control.
The plate was covered with a sterile plate sealer and then incubated for 18 h at 37 °C. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of the compound 4a–e to inhibit the growth of microorganisms, after incubation. The results were expressed in milligram per milliliter.
Each test was carried out in triplicate. The microorganisms tested in this study were provided from European Hospital of George-Pompidou (HEGP) (France).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Hayet Edziri from University of Monastir (laboratoire des maladies transmissibles et des substances biologiquement actives, faculté de pharmacie, Monastir, Tunisia) for making biological activities and the DGRSRT (Direction générale de la recherche scientifique et de la rénovation technologique) of the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Research and Technology for the financial support of this research.


