1 Introduction
In the last decades, the application of microwave as a tool for organic synthesis has gained much popularity. In theory, the organic reactions have been rewritten with the use of microwave as non-conventional energy source [1–5].
In spite of the high cost of dedicated microwave apparatus [6], the popularity of this technology has been increased enormously, mainly due to most of the authors’ claims that almost all organic reaction takes place faster under microwave with respect to the same under conventional heating, sometimes with an enormous difference on reaction time from many hours to few minutes. Other very mentioned advantages are that the reactions under dielectric heating generally show higher yields and purities, and in many cases the microwave synthesis is considered as environmental friendly since the reactions are carried out in solvent-free conditions and with evident energy saving.
Some authors attribute the marvel of microwave in organic synthesis to the phenomenon known as “specific microwave effect”. It is a non-purity thermal effect [7–9]; however, there is still considerable controversy on the exact reasons why microwave irradiation is able to enhance chemical reactions.
Alkyl polyglycosides are well-known compounds with interesting commercial applications in a number of fields, especially as surfactants and emulsifiers [10].
Continuing our interest in the development of biosurfactants [11], the Fisher glycosidation of monosaccharides with long alkyl alcohols was studied under microwave irradiation in comparison with the same reactions under conventional heating. Products were obtained in only 3 minutes under microwave irradiation at a maximum power of 5 W. Higher conversion was obtained under conventional heating in oil bath at the same temperature and time for a model reaction between d-glucose and 1-dodecanol.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Microwave-assisted synthesis of Fisher glycosidation of monosaccharides
Fisher glycosidation refers to the formation of a glycoside by the reaction of an aldose or ketose with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. Through the polyfuntionality of the carbohydrate partner, the condition of the acid-catalyzed Fisher reaction yields an oligomer mixture in which on average more than one sugar unit is attached to an alcohol molecule and secondary products, such as polydextrose, ethers and colored impurities are formed and cannot be avoided. In an optimized process, the concentration of secondary products formed by etherification remains relatively low.
Typically, Fisher glycosidation is carried out under conventional heating with vacuum at 100–120 °C and during 3–6 hours [12,13] or by transglycosidation (indirect method in two steps) at similar conditions [14,15].
The Fisher glycosidation of monosaccharides under microwave irradiation was described using short-chain alcohols (methanol, ethanol and allylalcohol) and Amberlite resin IRN 120H+ as a catalyst [16]. Reactions were performed using a CEM-Discover LabMate instrument with external IR temperature control.
Since we are interested in the synthesis of amphiphilic compounds, the reaction between glucose and 1-dodecanol was used as model reaction to establish the optimum conditions for the surfactants syntheses.
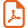
Reactions were carried out in a CEM-Discover LabMate single-mode instrument (300 W maximum magnetron output power) using an internal fiber optic (FO) sensor as a more accurate way of monitoring temperature with respect to the external IR measurement. The initial maximum power level was established at 30 W due to the high microwave absorptivity of the reaction mixtures and the reaction temperature was 100 °C to avoid glucose decomposition. Even in these reaction conditions, a temperature overshoot higher than 30 °C was observed and the reaction temperature was reached in less than 15 seconds and considerable quantity of by-products were detected after 5 minutes of irradiation (Fig. 1).

Heating (T) and power profile under microwave irradiation for the glycosidation reaction with internal temperature control with fiber optic (FO) sensor. Reaction conditions: 10 mL pyrex sealed-vessel, magnetic stirring (high), 100 °C, 5 min, maximum, power: 30 W, simultaneous cooling.
In order to prevent a strong exothermic and overheating in the synthesis of our surfactants, we evaluated two strategies: firstly, increase the temperature in two steps (30 seconds at 70 °C and 5 minutes at 100 °C, max. power: 30 W); secondly, the use of simultaneous external cooling by compressed air of the reaction mixture while heating by microwaves can, in some cases, lead to an enhancement of the overall process [17]; however, in both cases, a thermal overshoot of ∼20 °C above the desired set temperature of 100 °C and consequently the immediate reduction of power to almost 0 W in order to reestablish the reaction temperature programmed (100 °C) cannot be avoided.
As a consequence, a localized overheating took place with the corresponding partial glucose polymerisation and decomposition was observed (black solid around the immersed glass well).
The overshoot could only be avoided using a maximum power as low as 10 W, although after 50 seconds of irradiation the power remained between 1–5 W. In these conditions, temperature increases gradually and the reaction temperature (100 °C) was reached within ∼80 seconds, but product conversion was low and high yield of polydextrose was obtained (Fig. 2).
Temperature and power profile for the reaction between glucose and 1-dodecanol with internal temperature control with fiber optic (FO) sensor. Reaction conditions: 10 mL pyrex sealed-vessel, magnetic stirring (high), 100 °C, 5 min, maximum power: 10 W.
After the evaluation of a set of the reaction conditions, the best results (as determined by TLC and 1H RMN) were obtained after 3 minutes of reaction time, temperature of 70 °C, ratio sugar:alcohol of 1:3 and maximum microwave power of 5 W in solvent-free conditions. Actually, the real power showed fluctuations between 1–3 W, that is, the reaction proceeded almost without the effect of the electromagnetic field (almost under conventional heating). In these conditions, the reaction temperature increased from room temperature to 70 °C in ∼80 seconds with fluctuation between ±2 °C (Fig. 3). All additional attempts to promote higher conversion in favor of the alkylglycosides were unsuccessful.

Temperature and power profile for the reaction between glucose and 1-dodecanol with internal temperature control with fiber optic (FO) sensor. Reaction conditions: 10 mL pyrex closed-vessel, magnetic stirring (high), 70 °C, 3 min, maximum, power: 5 W.
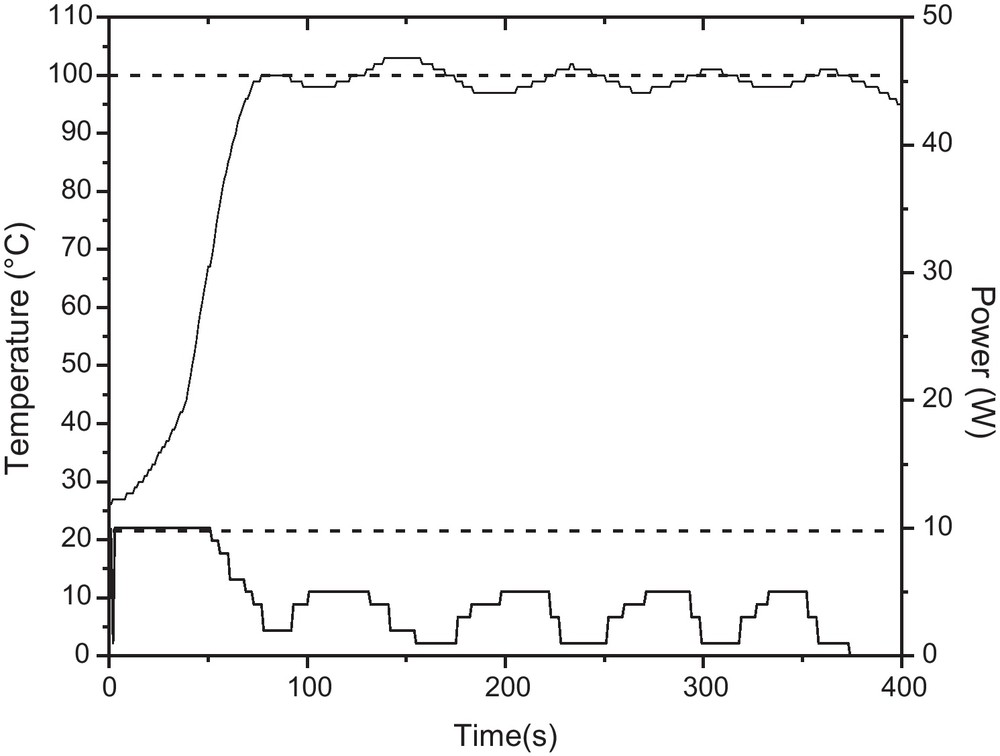
In this optimal reaction condition, all alkylpolyglicosides were synthesized from d-glucose (4a–4f) and d-manosse (5a–5f) and different long alkyl chain alcohols (Scheme 1).
2.2 Synthesis of Fisher glycosidation of monosaccharides under conventional heating
The model reaction between d-glucose and 1-dodecanol was also studied under oil bath in exactly the same reaction conditions (vessel geometry, temperature, stirring, catalyst, ratio sugar:alcohol and time) as that employed under microwave. In order to accurately compare with the results obtained by direct microwave heating, we also used the sealed-vessel system designed for microwave-assisted synthesis that allows to monitore the temperature with an FO probe device inserted into the reaction mixture. The reaction tube was immersed in the preheated oil bath (Fig. 4).
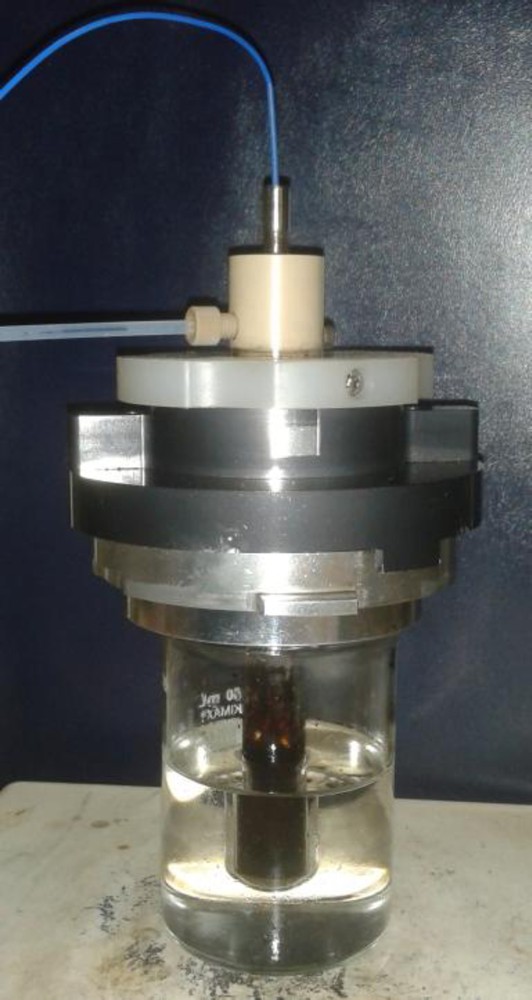

Fisher glycosidation of monosaccharides in oil bath controlling the temperature with fiber optic (FO) sensor inserted into the reaction.
According to our study, we obtained a quick conversion (residual glucose lower than 3%) under conventional heating at the same time and reaction conditions established for microwave-assisted synthesis, in contrast to the classical glycosidation procedures where the reactions are carried out under vacuum at 100–120 °C during 3–6 hours [16,17].
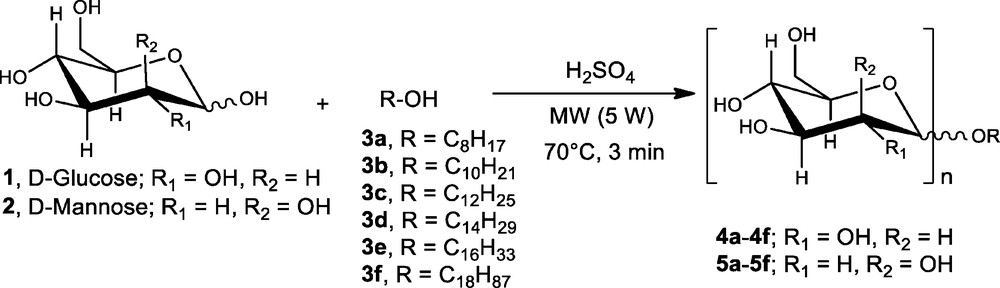
As typical for conventional heating, the reaction temperature increased smoothly, reaching the desired value 650 seconds after the reaction vessel was immersed in the preheated oil bath (Fig. 5), in contrast to the microwave heating profile where the reaction temperature was reached in 80 seconds (Fig. 3 versus Fig. 5).
Heating (T) profile of the mixture of glucose and 1-dodecanol from 24–70 °C in oil bath with internal temperature control with fiber optic (FO) sensor.
A comparison between the results obtained under conventional oil bath heating and microwave-assisted synthesis for the conversion at 70 °C during 3 minutes in sealed-vessel is shown in Table 1.
Quantification of the glycosidation reaction between d-glucose and 1-dodecanol under oil bath and microwave-assisted synthesis.
| Products from oil bath synthesis | Products from MW synthesis | ||||||||
| Monogly (%) | Digly (%) | Oligogly (%) | DPa (%) | RGb (%) | Monogly (%) | Digly (%) | Oligogly (%) | DPa (%) | RGb (%) |
| 55.2 | 17.6 | 27.2 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 63.3 | 21.6 | 15.1 | 1.6 | 8.5 |
a Degree of polymerization.
b Residual glucose.
As can be seen in Table 1, the conventional heating gave higher conversion (lower residual glucose) maybe since results of the overall reaction time are higher and the reaction temperature is reached smoothly. Differently from the reactions under microwave, the reactions under oil bath do not present localized overheating and overpressure reducing glucose decomposition.
Contrastingly, the degree of polymerization (DP) was slightly lower using microwave, and consequently lower contents of monoglucoside and higher contents of dimers and oligomers were detected under conventional heating. Maybe this fact can be explained by direct bulk heating; thus, the response time is shorter under microwave dielectric heating reducing pyrolytic wall effects [18].
When more than one potential product could be formed, as in glycosidation reaction, the outcome could be influenced by the thermal history of the reaction; thus the observed differences for this reaction under conventional heating and oil bath are a consequence of the fast increased temperatures attained by microwave.
3 Conclusions
According to our research, glycosidation reactions can be carried out in only 3 minutes under microwave-assisted synthesis at a maximum power as low as 5 W to minimize the formation of secondary products such as polydextrose and colored impurities. At the same time and temperature, higher conversion (lower residual glucose) was obtained employing thermal heating for a model reaction between d-glucose and 1-dodecanol.
4 Experimental
4.1 General
All Aldrich reagents were used without previous purification. p-TsOH was dehydrated by heating (100 °C) and vacuum during 4 hours. Melting points were measured in a Fisher Scientific apparatus with a 300 °C thermometer. 1H-NMR (500 MHz) spectra were obtained with a Varian-Gemini-300 equipment using TMS as the internal standard and the solvent specified in each case at room temperature, chemical shift (δ) are in ppm. IR spectra were recorded on a Nicolet spectrometer Nexus 470 FT-IR (KBr powder, diffuse reflectance mode). Microwave reactions were performed using a commercially available mono-mode microwave CEM-Discover, employing a 10 mL Pyrex vial in a closed-vessel mode. The reaction temperatures were monitored by an internal FO temperature probe (ruby thermometer) protected by a borosilicate immersion well inserted directly in the reaction mixtures. Total consumption of the starting material or residual glucose content was verified by thin layer chromatography (MeOH:CHCl3, 1:2) and 1H-NMR spectroscopy [12]. The content of mono-, di- and oligoglycosides was quantified by plate preparative chromatography. The reactions DP was determined by the Nuzillard model developed recently [19].
4.2 Procedure for the Fisher glycosidation of monosaccharides under microwave
In a sealed-vessel for microwave synthesis (10 mL) provided with an FO temperature sensor inserted into the reaction mixture, the carbohydrate (glucose or mannose, 5 mmol), fatty alcohol (C8–C18, 15 mmol) and the catalyst (H2SO4, 6 mmol) were heated at 70 °C with magnetic stirring under microwave irradiation at 5 W during 3 minutes. Upon reaction completion, the final product was diluted with water (10 mL) and extracted twice with ethyl acetate (20 mL). The aqueous phase was allowed to stand for water evaporation at room temperature and dried under vacuum.
4.3 Procedure for the Fisher glycosidation of monosaccharides under conventional heating
In the same reaction vessel (10 mL) designed for microwave equipment, d-glucose (5 mmol), 1-dodecanol (15 mmol) and the catalyst (H2SO4, 6 mmol) were heated in oil bath at 70 °C with magnetic stirring. The reaction temperature was controlled by inserting an FO sensor into the reaction (Fig. 1). Upon reaction completion, the final product was diluted with water (10 mL) and extracted twice with ethyl acetate (20 mL) and ethyl ether. The aqueous phase was allowed to stand for water evaporation at room temperature under airflow until dryness.
Following the general microwave procedure described above, the alkylpolyglycosides from glucose (4a–4f) and from maltose (5a–5f) were obtained and their characterization is described below.
4a: 1H-NMR (δ, D2O). 5.48–5.38 (m), 5.00 (m), 4.92 (m), 4.86 (m), 4.78 (m), 4.55 (m), 4.05 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, OCH2), 3.94–3.27 (m, glycoside protons), 1.70 (q, J = 6.8 Hz, CH2), 1.34 (m, C5H10), 0.91 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3477 (νOH), 2956 (νasymCH3), 2924 (νasymCH2), 2873 (νsymCH3), 2856 (νsymCH2), 1655, 1468 (νasym bendingCH2), 1377 (νCH3), 1221, 1157 (νasym ether linkage), 1057 (νCO), 843, 721 (νrockCH2), 586.
4b: 1H-NMR (δ, D2O). 5.44–5.32 (m), 5.22 (m), 5.18 (m), 5.10 (m), 4.96 (m), 4.65 (m), 4.51 (m), 4.20–3.23 (m, glycoside protons), 1.67 (m, CH2), 1.30 (m, C7H14), 0.88 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3456 (ν OH), 2954 (νasymCH3), 2922 (νasymCH2), 2872 (νsymCH3), 2852 (νsymCH2), 1743, 1655, 1468 (νasym bendingCH2), 1377 (νCH3), 1225, 1164 (νasym ether linkage), 1053 (νCO), 839, 721 (ν rockCH2), 590.
4c: 1H-NMR (δ, D2O). 5.44 (m), 5.37–5.35 (m) 5.23–5.10 (m), 4.96 (m), 4.65–4.63 (m), 4.53–4.50 (m), 4.27–3.24 (m, glycoside protons), 1.67 (m, CH2), 1.30 (m, C9H18), 0.88 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3359 (νOH), 2954 (νasymCH3), 2920 (νasymCH2), 2872 (νsymCH3), 2850 (νsym CH2), 1743, 1655, 1471 (νasym bending CH2), 1416, 1373 (νCH3), 1250, 1215, 1171 (ν asym ether linkage), 1053 (ν CO), 837, 721 (νrock CH2), 633, 584.
4d: 1H-NMR (δ, D2O). 5.49–5.40 (m), 5.24 (m), 5.17–5.16 (m), 5.02 (m), 4.91–4.87 (m), 4.57–4.55 (m), 4.39–3.27 (m, glycoside protons), 2.2–2.14 (m, CH2), 1.74–1.35 (m, C11H22), 0.94 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3479 (νOH), 2954 (νasymCH3), 2918 (νasymCH2), 2872 (νsym CH3), 2850 (νsymCH2), 1730, 1660, 1618, 1470 (νasym bending CH2), 1396, 1379 (νCH3), 1254, 1219, 1103 (νasym ether linkage), 1068 (νCO), 1022, 999, 831, 721 (νrock CH2), 633, 590.
4e: 1H-NMR (δ, (CD3)2SO). 5.44–5.28 (m) 5.16–5.07 (m), 4.94 (m), 4.86 (m), 4.78 (m), 4.48 (m), 4.23–3.12 (m, glycoside prótons), 1.51 (m, CH2), 1.24 (m, C13H26), 0.86 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3481 (νOH), 2953 (νasym CH3), 2918 (νasym CH2), 2870 (νsym CH3), 2850 (νsym CH2), 1716, 1662, 1616, 1470 (νasym bending CH2), 1398, 1381 (νCH3), 1257, 1225, 1186, 1107 (νasym ether linkage), 1078 (νCO), 985, 833, 721 (νrock CH2), 629, 596.
4f: 1H-NMR (δ, (CD3)2SO). 5.54–5.45 (m), 5.24 (m), 5.02 (m), 4.87 (m), 4.79 (m) 4.58–4.53 (m), 4.31–3.27 (m, glycoside protons), 1.49 (CH2), 1.24 (C15H30), 0.85 (CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3331 (νOH), 2954 (ν symCH3), 2916 (νasym CH2), 2872 (νsym CH3), 2850 (νsym CH2), 1616, 1481, 1471, 1392, (νasym bending CH2), 1371 (νCH3), 1269, 1205, 1111 (νasym ether linkage), 1068 (νCO), 1014, 991, 976, 891,831, 715 (νrock CH2), 633, 598, 584.
5a: 1H-NMR (δ, D2O). 5.48–5.28 (m), 5.25–5.12 (m), 4.98 (m), 4.86 (m), 4.93 (m), 4.89 (m), 4.81 (m), 4.77–4.59 (m), 4.15 (m), 4.09 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, OCH2), 4.06–3.46 (m, glycoside protons), 1.74 (q, J = 7.3 Hz, CH2), 1.38 (m, C5H10), 0.95 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3460 (νOH), 2954 (νasymCH3), 2922 (νasymCH2), 2872 (νsymCH3), 2852 (ν ymCH2), 1655, 1468 (νasym bending CH2), 1379 (νCH3), 1246, 1219, 1126 (νasym ether linkage), 1084 (νCO), 1024, 980, 912, 837, 723 (νrock CH2), 633, 590.
5b: 1H-NMR (δ, D2O). 5.46–5.12 (m), 4.98–4.88 (m), 4.80–4.76 (m), 4.16–4.14 (m), 4.10 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, OCH2), 4.03–3.46 (m, glycoside protons), 1.76 (q, J = 6.9 Hz, CH2), 1.38 (m, C7H14), 0.96 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3398 (νOH), 2954 (νasym CH3), 2920 (ν asymCH2), 2873 (νsymCH3), 2850 (νsymCH2), 1659, 1468 (νasym bendingCH2), 1379 (νCH3), 1250, 1219, 1149 (νasym ether linkage), 1115, 1061 (νCO), 841, 721 (νrock CH2), 634, 590.
5c: 1H-NMR (δ, D2O). 5.46–5.10 (m), 4.95 (m), 4.87 (m), 4.78 (m), 4.79 (m), 4.63 (m), 4.13 (m), 4.08 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, OCH2), 4.00–3.42 (m, glycoside protons), 1.73 (m, CH2), 1.36 (m, C9H18), 0.94 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3444 (νOH), 2954 (νasymCH3), 2920 (νasymCH2), 2873 (νsymCH3), 2850 (νsymCH2), 1653, 1468 (νasym bendingCH2), 1377 (νCH3), 1225, 1149 (νasym ether linkage), 1115, 1061 (νCO), 835, 721 (νrock CH2), 590.
5d: 1H-NMR (δ, D2O). 5.44–5.08 (m), 4.95–4.94 (m), 4.86 (m), 4.78 (m), 4.65–62 (m), 4.36–3.42 (m, glycoside protons), 1.74–1.71 (m, CH2), 1.35 (m, C11H22), 0.93 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3521 (νOH), 2954 (νasymCH3), 2918 (νasymCH2), 2872 (νsymCH3), 2850 (νsym CH2), 1662, 1616, 1470 (νasym bending CH2), 1398, 1379 (νCH3), 1257, 1209, 1130 (νasym ether linkage), 1103, 1022 (νCO), 995, 968, 831, 721 (νrockCH2), 631, 596.
5e: 1H-NMR (δ, (CD3)2SO). 4.90 (m), 4.68–4.50 (m), 3.72–3.35 (m, glycoside protons), 1.51–1.40 (m, CH2), 1.24 (m, C13H26), 0.85 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3481 (νOH), 2953 (νasymCH3), 2918 (νasymCH2), 2870 (νsymCH3), 2850 (ν symCH2), 1662, 1616, 1468 (νasym bendingCH2), 1398, 1381 (νCH3), 1257, 1225, 1186 (νasym ether linkage), 1128, 1107, 1080, 1061 (νCO), 985, 835, 721 (νrock CH2), 629, 596.
5f: 1H-NMR (δ, (CD3)2SO). 4.90 (m), 4.59 (m), 3.71–3.28 (m, glycoside protons), 1.48–2.38 (m, CH2), 1.24 (m, C15H30), 0.86 (m, CH3). IR, RD–KBr (cm−1): 3488 (ν OH), 2954 (νasymCH3), 2916 (νasymCH2), 2868 (νsymCH3), 2850 (νsymCH2), 1668, 1635, 1568, 1473 (νasym bending CH2), 1473, 1462, 1396, 1379 (νCH3), 1203, 1136 (νasym ether linkage), 1072 (νCO), 962, 937, 910, 876, 847, 793, 769, 727 (νrockCH2), 633, 590.