1 Introduction
Particulates, hydrogen sulfide, mercaptans and hydrogen fluoride constitute the major gaseous pollutants generated by the Wet manufacturing process of Phosphoric Acid (WPA). Those pollutants are frequently a source of olfactory nuisances likely to generate significant annoyance in the neighboring areas. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is the most common malodorous gas emitted due to both its high emission rate and its very low detection threshold [1, 2]. Its ‘rotten egg’ odor can be detected at a concentration of 0.4 ppb [3]. It can also cause corrosion in pipelines and thus reduce the lifetime of the plant [3,4]. Furthermore, hydrogen sulfide is a highly toxic gas which poses a serious health risk [5]. The maximum allowable exposure concentration for extended periods is 10 ppm [5]. It is reported that a long exposure to a concentration of 300 ppm of H2S in air can cause death. Concentrations exceeding 2000 ppm can be fatal if human beings are exposed to them for a few minutes [3]. To overcome this problem, the Tunisian legislation has issued regulations that deal with the emission of H2S into the atmosphere. A number of classical processes have been characterized and implemented to treat these odorous gases prior to their release in the environment. The main processes used to this end are amine absorption [6], alkaline absorption [7], dry oxidation adsorption [8], absorption using the Claus process or catalysts to recover the elemental sulfur [9, 10] and caustic absorption with chemical oxidation [5,11,12]. Even though biofilters can be an interesting alternative [12,1], absorption with chemical reaction is often the most economical method for controlling malodorous process emissions where large flow rates are involved [13].
Compared to physical absorption, chemical absorption offers several advantages, mainly the irreversible degradation of the sulfur compounds which maintains a strong driving force for mass transfer [14]. The choice of the solvent and the design of the scrubber system are equally important for the achievement of high scrubbing efficiencies [4]. Sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH) is a very effective but non-regenerable absorbent for H2S and CO2. Therefore its use is usually limited to the removal of trace amounts of these impurities [4]. Waste gases containing significantly high concentrations of malodorous substances (up to 100 ppm) can be suitably washed by scrubbing with solutions of powerful oxidizing agents. Various oxidants such as chlorine gas (Cl2) [15], sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) [7,11,16], hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) [17] and ozone (O3) [18,19,20] are able to remove H2S after its transfer to the liquid phase. Earlier work [13] showed that the preferred oxidant for a number of applications appears to be sodium hypochlorite. The most frequently used is a combination of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) because of low cost and good efficiency [5, 13,15].
In this work, the absorption of H2S using a chlorinated alkaline solution was studied. The design aspects of the chemical absorption equipment are well understood. Accordingly, we focused on the suitable chemical composition of the washing solution. Given that seawater is already available and is used by the processes belonging to the fertilizer complex of the Tunisian Chemical Group, it is used as a solvent for the chemical absorption of H2S. The concentration of sodium hypochlorite and the pH of the absorption media are the most important parameters that control the efficiency of the operation. A laboratory contactor was used to study the effect of these parameters on H2S absorption efficiency. In order to find the best operating conditions for the reactive absorption of H2S, different values were considered for the main operating parameters such as the gas flow rate, residence time, operating time and volumetric ratio.
2 Theoretical aspects
The absorption/oxidation of H2S with alkaline chlorinated seawater solution can be described by the following set of reactions. At the gas–liquid interface, the system is presented by reaction (R.1).
| (R.1) |
According to this reaction, absorption is limited by pollutant solubility in the liquid phase [17]. The solubility of hydrogen sulfide, resulting from the ionization in seawater, depends on temperature and pH in particular [21]. H2S is poorly soluble in water. Indeed, Henry’s constant for H2S is equal to 899 Pa m3/mol (at 293.15 K) [22]. Thus, to increase its solubility and achieve good absorption efficiency, it is necessary to use a scrubbing solution of high pH [15, 4]. For this reason and at the effluent temperature (35–45 °C), the absorption of H2S is conducted under high alkaline conditions (pH≥9).
After absorption (R.1), H2S is dissociated in the seawater solution according to reactions (R.2) and (R.3) and then oxidized by ClO− (R.4) into sulfur and/or sulfate compounds ((R.5) and (R.6)). Acido-basic ((R.2) and (R.3)) and oxidizing reactions ((R.5) and (R.6)) occurring in the liquid phase favor mass transfer by shifting the equilibrium of reaction (R.1) towards the formation of non-volatile species [17]. Therefore, reaction (R.2) increases directly the mass transfer by promoting the dissociation of H2S into HS− which leads to an increase in the pollutant apparent solubility and an acceleration in the inter-phase mass transfer.
| (R.2) |
| (R.3) |
| (R.4) |
| (R.5) |
| (R.6) |
Reaction (R.6) represents the complete oxidation of the dissolved H2S into sodium sulfate or
A critical issue to be considered in the chemical absorption of H2S is the presence of CO2. This compound exists in the phosphoric acid gaseous effluents at high concentrations and shows an acidic behavior similar to that of H2S. Hence, the chemical absorption of these two compounds takes place simultaneously in alkaline media [24]. CO2 absorption and dissociation are represented by reactions (7) to (10) [25].
| (R.7) |
| (R.8) |
| (R.9) |
| (R.10) |
Based on the pka values associated with reactions (R.2) and (R.9) [12], it is clear that the absorption of H2S and CO2 proceeds at similar pH values. Also, it is well-known that H2S absorption is faster than that of CO2 [26] because the latter undergoes a slow hydrolyzing step, as shown by reaction (8). This phenomenon can be exploited to increase H2S selectivity by reducing the residence time between gas and liquid in the pH range of interest.
3 Experimental procedure
The experiments were conducted in a lab-absorber connected directly to the chimney of an industrial phosphoric acid production unit belonging to the fertilizer complex of the Tunisian Chemical Group.
3.1 Hydrogen sulfide sampling and analytical method
In the daily operation of the phosphoric acid production unit, iodometry is used by the operators for H2S analysis. This method consists of using an excess of iodine (I2) and back-titrating with a sodium thiosulfate solution. However, iodometry is not well adapted to H2S analysis for this particular application because other compounds that are often found in the gaseous emissions of the phosphoric acid process are also iodimetrically active. Sulfur dioxide is, for instance, one of them.
In the interest of an accurate and fast online analysis, a new test procedure was developed using cadmium acetate. The detailed experimental procedure, including sampling of the industrial gas technique, is shown schematically in Fig. 1. The industrial gas to be analyzed was extracted using a vacuum pump at known temperature and pressure. It passed through four fritted bubblers connected in series. The first bubbler was for collecting the water droplets contained in the gas. 150 ml of a cadmium acetate solution (Cd2+), used as the sampling medium, were placed in the second and third fritted bubblers. The fourth one was left empty to ensure the protection of the vacuum pump and the gas meter. When the gas bubbled through the Cd2+ solution, the hydrogen sulfide it contained turned into cadmium sulfide (CdS) as shown by reaction 11.
| (R.11) |
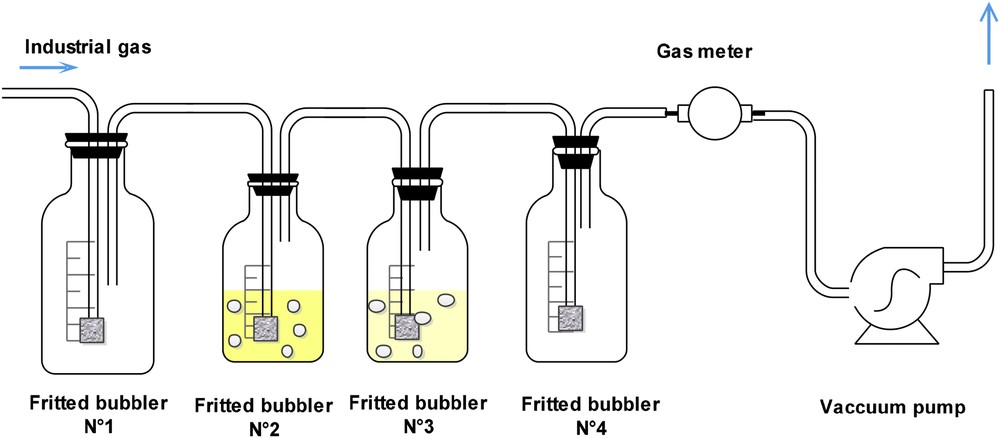
Experimental setup for sampling H2S by absorption.
A distinct yellow precipitate formed as a result of this reaction. The turbidity of the cadmium acetate solution was proportional to the H2S quantity removed from the gas. Hence, the H2S concentrations (mg/m3) were determined by the turbidimetry technique using Equation 1.
| (1) |
| (2) |
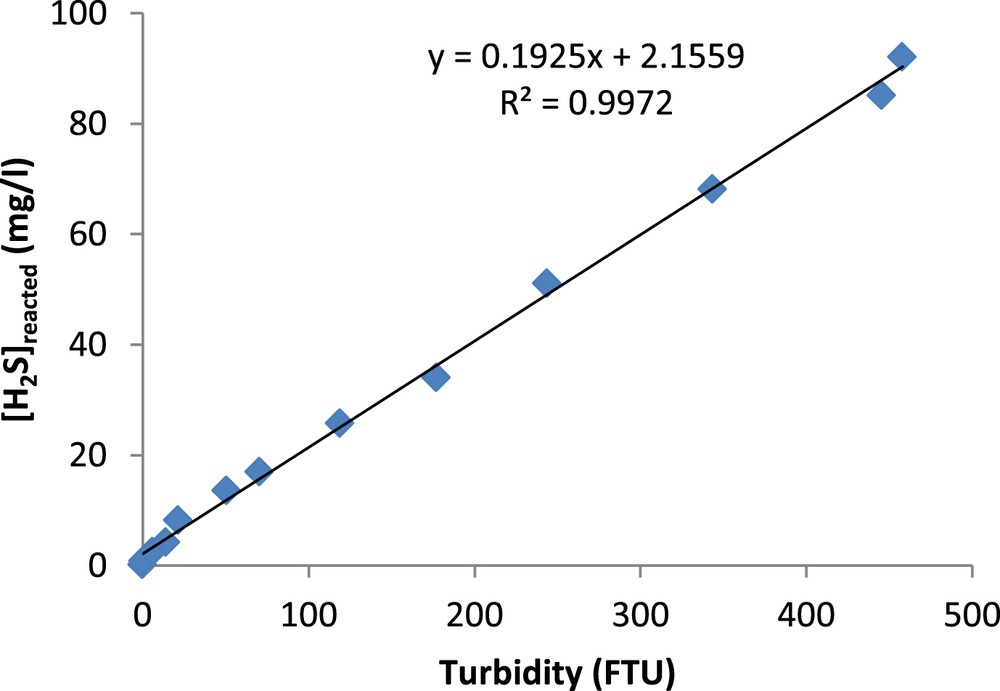
Calibration curve for the determination of H2S concentrations by turbidimetry.
The turbidity of the resulting mixture containing CdS precipitate was measured by using a spectrophotometer (HACHDR 2000) at 450 nm according to the turbidimetry method database of this apparatus.
The detection limits of this method were approximately of 0.2 mg/l and 92.16 mg/l of H2S. The repeatability and reproducibility of this technique were validated and will be included in another paper.
3.2 Experimental setup for the reactive absorption of H2S
Fig. 3 shows the experimental setup used to study the effect of different operating parameters on the efficiency of H2S absorption by alkaline oxidative seawater solutions. A laboratory fritted absorber of 2 L, containing 1 L of the oxidative seawater solution, was inserted between the first and the second fritted bubblers (Fig. 1). The gaseous effluent was bubbled continuously, at controlled flow rates ranging from 5 to 15 l/min, into the chlorinated seawater solution under alkaline conditions (9 ≤ pH ≤ 12). H2S was then oxidized into sulfur and/or sulfate according to the pH of the absorbing medium. The unreacted hydrogen sulfide was sent to the cadmium acetate solution (fritted bubblers Nos. 2 and 3). After allowing sufficient time for absorption, samples were removed for analysis. In order to evaluate the absorption efficiency, H2S concentrations were determined by turbidimetry as previously described.
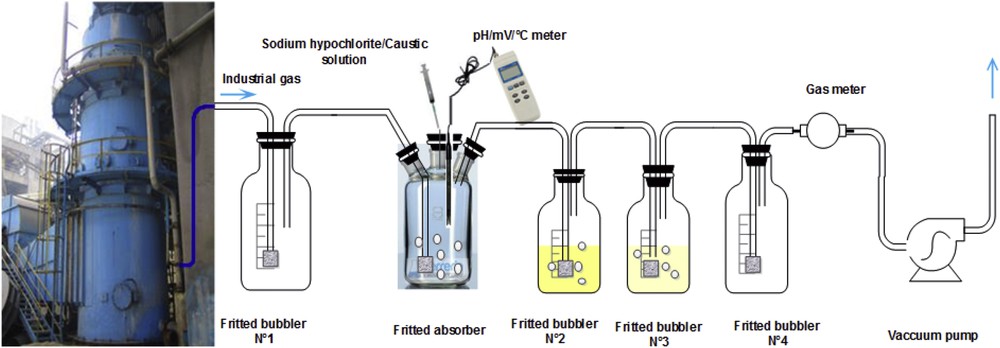
Experimental setup for the absorption of H2S using chlorinated seawater solution under alkaline condition.
Since the oxidation reaction depends mainly on pH, temperature and oxidant concentration, these parameters were monitored online during the experiments using a combined pH/mV/°C meter probe. Caustic and commercial chlorine were added, if necessary, to keep the pH and the chlorination rate of the scrubbing solution at the desired values.
During this study the applied doses of the oxidative reagent, expressed in chlorine concentration, were varied from 1 to 3 g/l. The performance of the lab-contactor was quantified through the absorption efficiency (
| (3) |
| (4) |
3.3 Material characterization
Sodium hydroxide of analytical quality supplied by Pro-Labo was used to prepare the NaOH aqueous solution (0.5 N) to adjust the pH of the oxidative seawater solution. The physicochemical properties of the seawater as well as those of the commercial sodium hypochlorite are given in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. The sodium monosulfide nonahydrate (Na2S.9 H2O) (98–100%) used to obtain the calibration curve was supplied by Anachemia (Canada).
Physicochemical properties of seawater.
| Parameters | Unit | Value |
| Ca2+ | mg/l | 496 |
| Mg2+ | mg/l | 1509 |
| Na+ | mg/l | 12,265 |
| mg/l | 170.80 | |
| mg/l | 3749 | |
| Cl− | mg/l | 22,117 |
| F− | mg/l | 2.75 |
| Fe2+ | mg/l | 0.343 |
| SiO2 | mg/l | 6.14 |
| PO4 | mg/l | 4.24 |
| pH | mg/l | 8.04 |
| K | mg/l | 456 |
| T | °C | 18 |
| Total salts | mg/l | 41,011 |
| Conductivity | ms/cm | 8.76 |
Physicochemical properties of commercial sodium hypochlorite.
| Parameters | Unit | Value |
| Chlorine concentration | g/l | 38.04 |
| Density | kg/l | 1.052 |
| Molecular weight | g/mol | 74.5 |
| pH | – | 11.5 |
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Effect of gas flow rate on H2S absorption efficiency
The gas residence time is a key parameter for the removal of H2S by chemical absorption. In order to study its effect on absorption efficiency, a set of experiments was carried out using seawater at pH 10.5 and different chlorine concentrations. The gas flow rate was varied from 5 to 15 l/min. The obtained results are shown in Fig. 4 as absorption efficiency versus gas flow rate for different chlorine concentrations.
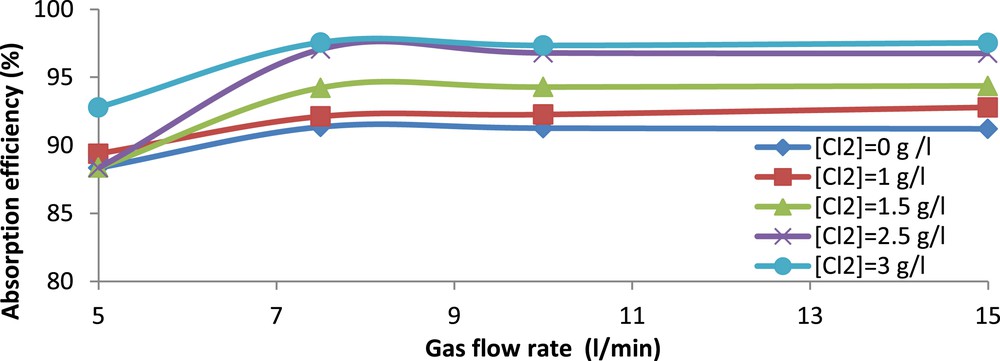
Evolution of H2S absorption efficiency (%) versus gas flow rate. (25 <
From this figure, it is clear that for any chlorine concentration, the absorption efficiency increases with gas flow rate up to about 7.5 l/min then remains constant. Bostroem (1965), on a similar apparatus, claimed that the absorption efficiency in fritted bubblers is effective for gas flow rates up to 6 l/min [27]. On the other hand, Flamm and James (1976) [28] reported in most of their studies that a total gas flow rate of 8.7 l/min is typical in practical stack sampling. In our particular case, the industrial gas stream released from the WPA production units contains not only H2S but also other acid gases mainly CO2 with a volume fraction of 5%. As indicated earlier, the longer the residence time was, the larger the absorption of CO2 was. This led to a decrease in the H2S absorption efficiency as observed for the 5 and 7.5 l/min flow rates. Such a decrease can be explained by an important reduction in the pH of the spent scrubbing solution due to the absorption of CO2.
For a gas flow rate of 5 l/min, the pH of the scrubbing solution decreased, roughly from 10.5 to 8.5, regardless of the chlorine concentration. When pH is reduced, the equilibrium of reaction (R.3) shifts towards the left and H2S is released. So, as claimed by Üresin et al (2014) [4], the H2S absorption efficiency diminishes when a competing acid gas is introduced in the oxidative absorption medium. Therefore, the gas flow rate as well as residence time should be adjusted so as to favor the absorption of H2S over that of CO2. Hence, the remaining experiments are conducted at a gas flow rate of 15 l/min to limit the effect of CO2.
It is also clear from Fig. 4 that an increase in chlorine concentration improves the overall absorption efficiency of H2S.
4.2 Effect of pH
pH is the main parameter which influences the dissociation of both H2S and CO2. To investigate the effect of this parameter, a set of experiments was carried out with pH held between 9.5 and 11.5 through the continuous addition of NaOH. A chlorine concentration of 0.5 g/l was maintained for all experiments. The obtained results are presented in Fig. 5.
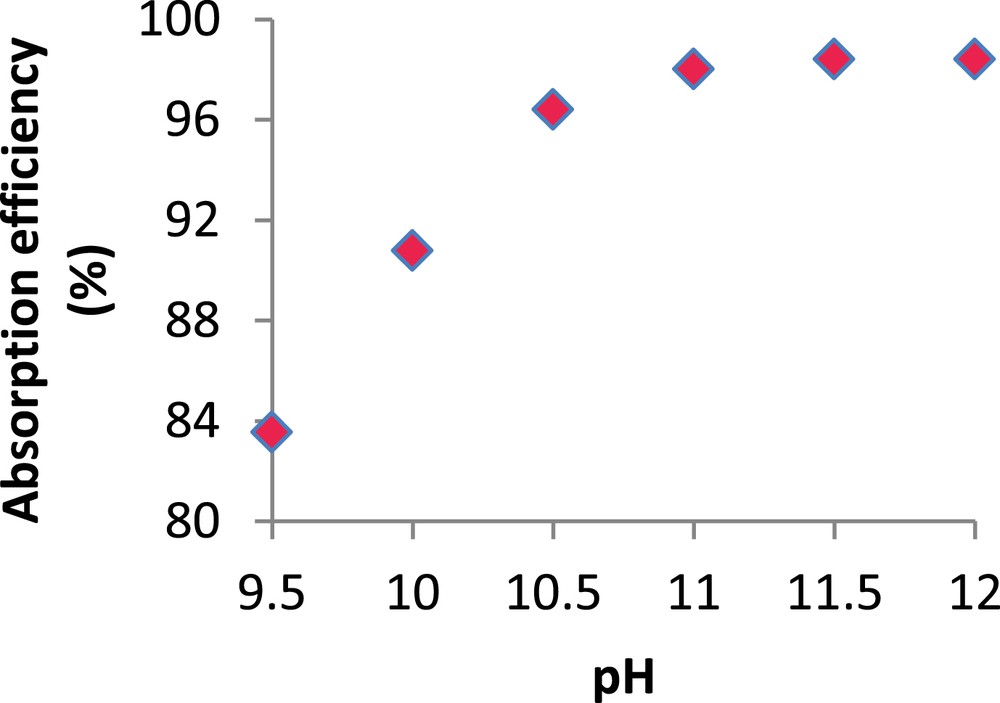
H2S Absorption efficiency (%) versus pH. (
As shown in this figure, the H2S absorption efficiency depends strongly on pH. It increases from 83.5 to 98%, when pH increases from 9.5 to 11. Beyond this value, the absorption efficiency remains almost constant at approximately 98.4%. The positive effect of pH on H2S absorption efficiency can be explained by mass transfer kinetics. In fact, the dissociation of H2S in the liquid phase leads to the formation of HS− due to the fast kinetics of reaction (R.3). Since HS− is known to be more soluble than H2S, this results in large absorption efficiencies [28]. As chlorine reacts quickly with all H2S species (H2Sdissolved, HS− and S2−), the observed phenomenon can only be attributed to the effect of pH on H2S dissociation in water according to reactions (R.3) and (R.4). Similar results were reported by Chen et al (2001) [5] and Couvert et al (2006) [17] during the chemical absorption of acidic compounds.
Nevertheless, semi-industrial experiments carried out by Biard (2009) [29] showed that for chlorine concentrations between 0.95 and 2.86 g/l, no significant variation of the H2S removal efficiency was observed for a pH range extending from 9.5 to 11. These conclusions were also reached by Bonnin (1991) [30]. He showed that in the presence of an excess of chlorine (>0.5 g/l) and for a working pH higher than 9, H2S removal efficiency does not depend on pH and that the oxidation reactions are the dominating factor. On the other hand, Vilmain et al (2014) [11] considered that during the chemical scrubbing of H2S in aqueous sodium hypochlorite solutions, both H2S dissociation into HS− and oxidation reactions maintain a strong and constant mass transfer driving force. Considering the foregoing discussion, the applied chlorine concentration of 0.5 g Cl2/l, in the particular case at hand, seems to be insufficient to ensure the predominance of the oxidation reactions. Our results show that a pH of 11 seems to be high enough to provide the required absorption efficiency even at weak chlorine concentrations. Consequently, the remaining experiments were carried out at pH 11 with higher chlorine concentrations.
4.3 Effect of chlorine concentration
To investigate the effect of chlorine concentration on H2S absorption efficiency various doses of this oxidant (from 0.5 to 3 g/l) were considered at fixed pH solution of 11. The objective was to determine the accurate chlorine concentration requirements.
It can be seen from Fig. 6 that the sodium hypochlorite concentration has a positive effect on H2S removal since the absorption efficiency keeps increasing significantly until a dose of 2 g Cl2/l. For greater doses, the improvement is less remarkable. In fact, the H2S absorption efficiency increased from 97 to almost 99% when chlorine concentration went from 0.5 to 2 g/l. However, it only increased to 99.2% when the chlorine concentration reached 3 g/l. The observed enhancement of H2S absorption can be attributed to the oxidation of sulfide ions by ClO− in the alkaline seawater solution. According to Bonnin (1991) [30], this oxidation reaction is very fast under alkaline conditions with a kinetic constant of 1.8 × 108 l/mol s. These results are in good agreement with those reported by Biard et al. (2009) [29] who demonstrated, during their study on a semi-industrial pilot unit, that the H2S removal efficiency increased from 92.2 to 95% when the chlorine concentration went from 0.95 to 2.86 g/l. It is important to note that, for all the applied chlorine concentrations, the H2S outlet concentrations were always lower than the limit fixed by the international legislation (5 ppm or 7.04 mg/m3).
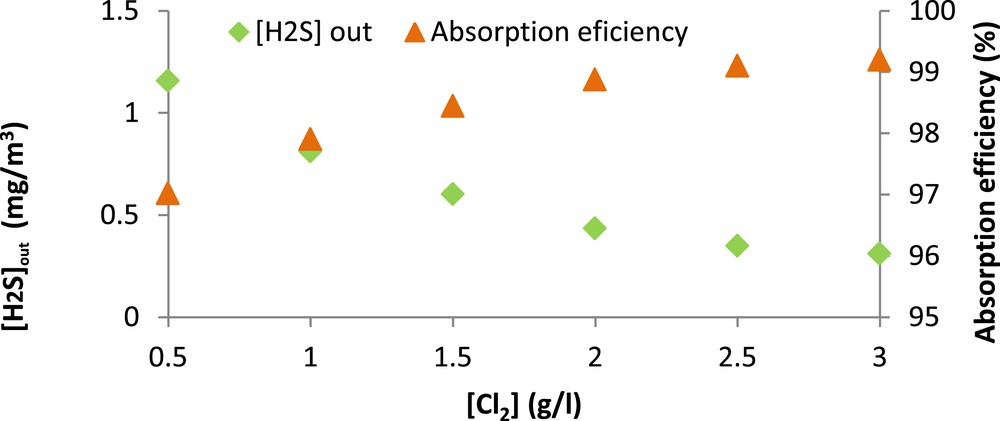
H2S absorption efficiency (%) versus chlorine concentration. (
In order to find the adequate sodium hypochlorite concentration to be used, further experiments were carried out to estimate the time up to which the oxidative seawater solution remains effective. For this reason, the evolution of H2S outlet concentration was investigated as a function of time.
In this set of experiments, after being bubbled in the oxidative absorption solution, the gas was directed into the Cadmium acetate solution. The appearance of a yellow color in that solution indicates that we reached the H2S breakthrough time.
The obtained results are illustrated in Fig. 7. As seen in this Figure, the breakthrough time depends strongly on the oxidant concentration except for 1 and 2 g Cl2/l where it is almost the same. Overall, the breakthrough time is more important when the applied chlorine concentration is higher which is expected.
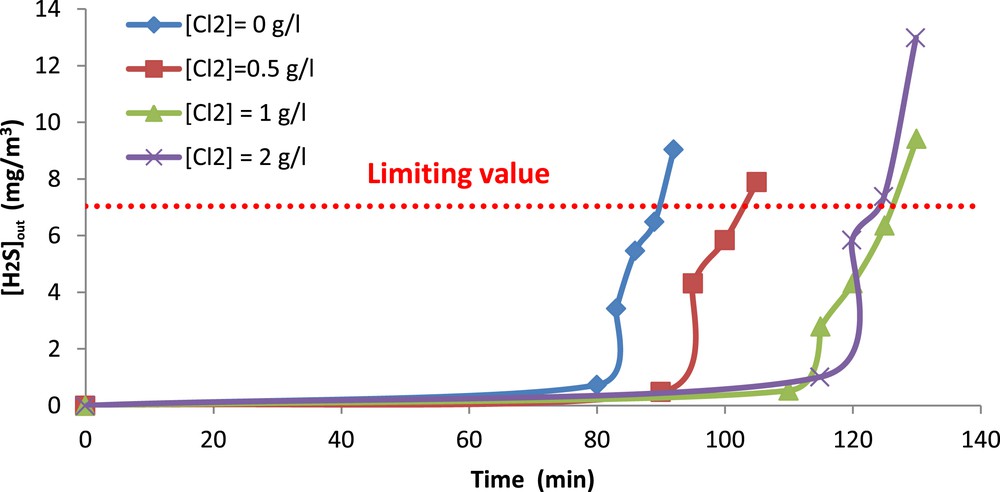
H2S outlet concentration versus absorption time. (
When the breakthrough time is exceeded, the H2S outlet concentration keeps increasing and overpasses the value fixed by the international legislation (5 ppm or 7.04 mg/m3) [31]. The time at which this value is reached is defined as the operating time of the absorber.
The values of this operating time were deduced from Fig. 7 and are presented in Table 3. According to this table, the operating time of the absorber is approximately equal to 2.1 h for both doses of 1 and 2 g Cl2/l when the H2S inlet concentration is 36.6 mg/m3. Hence, it seems that a dose of 1 g Cl2/l is sufficient for treating 1905 L of gas during 2.1 h. Accordingly, applying higher chlorination rates is not necessary for the operation of the absorber. This result is particularly interesting since the oxidative seawater solution with a chlorination rate of 1 g Cl2/l is not costly. With regard to the aforementioned results and based on economic considerations, a pH of 11 and a chlorine concentration of 1 g Cl2/l are highly recommended.
Absorber operating time.
| Chlorine concentration (g/l) | Sodium hypochlorite concentration (g/l) | Operating time of the absorber (min) | Volume of purified gas (l) |
| 0 | 0 | 89.2 | 1338 |
| 0.50 | 0.53 | 103 | 1545 |
| 1 | 1.05 | 127 | 1905 |
| 2 | 2.10 | 124.86 | 1873 |
4.4 Effect of gas volume on the breakthrough time
Several experiments were carried out using 1 L of alkaline seawater solution at pH 11 and a chlorination rate of 1 g Cl2/l, but with different volumes of gas ranging from 100 to 400 L. This corresponds to H2S inlet quantities varying from 3.68 to 14.74 mg. The evolution of the H2S escaped quantity (
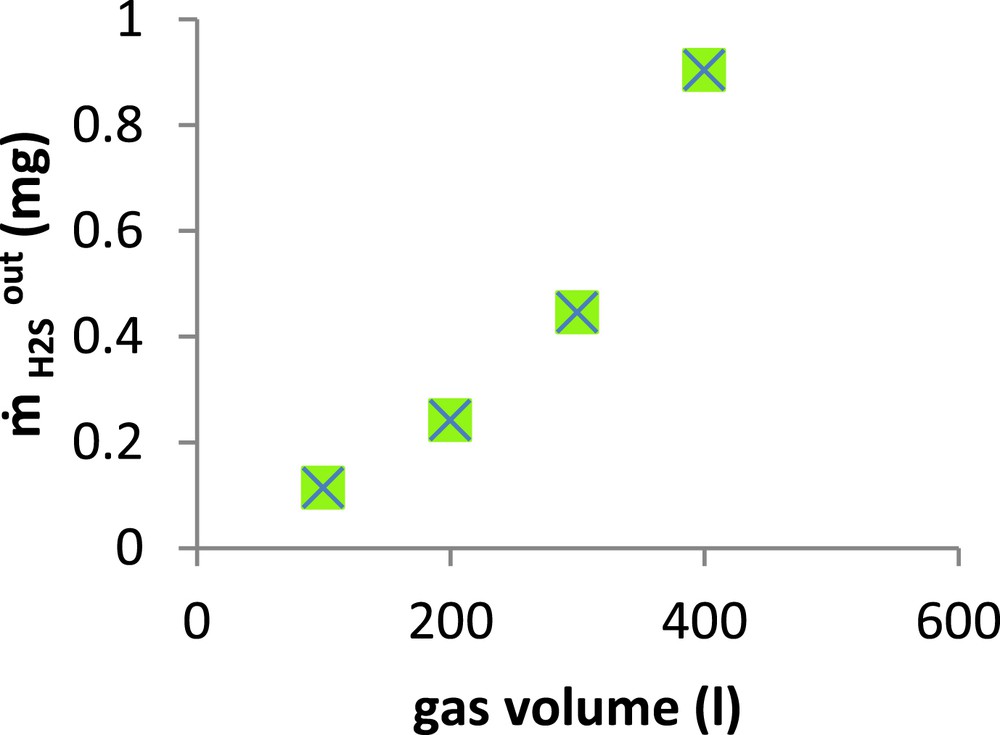
Amount of escaped H2S versus treated gas volume.(
As shown in this figure, the H2S outlet quantities escaping from the absorber increased gradually when the gas volume was varied from 100 to 300 L, whereas the increase was more pronounced when this volume went from 300 to 400 L. This result is particularly interesting given the fact that the treated gas volume was approximately 300 times that of the liquid. So to achieve the H2S chemical scrubbing in a packed column, the volumetric ratio has to be close to 3.33 × 10−3. Practically, the same ratio (3 × 10−3) was reported by Bonnin and Laplanche (1997) in a study on a pilot unit [32].
5 Conclusion
The aim of this study was to find the adequate operating conditions for the removal of H2S by chemical absorption from the gaseous effluents of a phosphoric acid production unit. The alkaline chlorinated seawater used in our experiments proved to be effective for this particular application.
The results, obtained on a lab-absorber, indicate that the highest removal efficiency corresponds to a gas flow rate of around 15 l/min. The effect of both pH and sodium hypochlorite concentration has been assessed. The chlorination rate was chosen, based on a compromise between economical and operational considerations. At pH 11 and a chlorination rate of 1 g Cl2/l, an average removal efficiency of more than 98% was reached, even at relatively high fluctuating H2S contents. For a H2S inlet concentration of 36.6 mg/m3, the operating time of the absorber at the chosen parameters was approximately 2.1 h during which 1905 L of effluent gases were treated. Besides, according to this study the gas volume treated was approximately equal to 300 times the volume of the scrubbing solution. In a future study, we will design a packed column for the removal of H2S on an industrial scale based on the findings of this work.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the workers and staff in the Tunisian Chemical Group (TCG) as well as those in the National Engineering school of Gabes (ENIG).


