1 Introduction
Carbonaceous chondrites, along with IDPs (Interplanetary Dust Particules) and comets, are the most primitive objects in the solar system [52]. They have recorded the chemical composition of the gas that formed our Sun and the planets. They are characterized by a high content in volatiles, especially organic matter and noble gases, and by the occurrence of primitive condensates [53]. They contain between 1 and 4 wt% of organic matter divided into a soluble fraction and an insoluble one. The soluble fraction consists of a variety of compounds: carboxylic acids, aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, amino acids and other compounds of biological interest [[39], and references therein]. Insoluble Organic Matter (IOM) constitutes more than 75 wt% of the whole organic matter. It is isolated through solvent extractions to remove soluble organic compounds and a classical HF/HCl treatment to remove silicates. The residue obtained is enriched in organic matter, but contains at least 10 wt% of inorganic material.
IOM chemical structure has been studied extensively since the 1980s by both spectroscopic and degradative methods, and by electron microscopy. Solid-state NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) or FTIR (Fourier Transform Infra Red spectroscopy) are non-destructive bulk analytical methods, whereas pyrolysis or chemical oxidations give information at molecular level, but they analyze only the more labile part of the sample. Nevertheless, the combination of data from these techniques improves the knowledge of the molecular structure of the IOM. The main results and interpretations, based on studies of IOM isolated from the most primitive carbonaceous chondrites (CI and CM), are described in this article. The isotopic composition is useful to determine the origin and evolution of IOM. Among the stable isotopes contained in the IOM, D is perhaps the most useful.
2 The molecular structure
2.1 The aromatic units
Electron microscopy, especially High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM), allows the observation of aromatic layers in the IOM. Indeed when aromatic planes are quasi parallel to the incident electron beam (i.e. under the Bragg angle) and separated by a least 0.14 nm (the resolution of this microscope), fringes appear due to interferences between the transmission electron beam and the diffracted beams and are representative of the profile of the aromatic planes [48,49]. Then aromatic layers appear as fringes in HRTEM images. Image analysis allowed the determination of the properties of aromatic units. In Orgueil and Murchison, aromatic units primarily consist of 2 to 3 aromatic rings in diameter, i.e. 2 to 7 rings in each unit [17].
This observation is consistent with 13C solid-state NMR [14,20]. NMR is useful to determine the chemical environment of atoms (Fig. 1). Spectra deconvolution allows the determination and quantification of different types of carbon. These data reveal that IOM is highly aromatic (70% of carbon atoms are aromatic), with rather small aromatic units. These aromatic units are linked by short and branched aliphatic chains (see next section for more details). Furthermore, aromatic compounds are the main aromatic products released by pyrolysis [41,55,57], reinforcing previous assumptions on the aromatic behaviour of IOM.
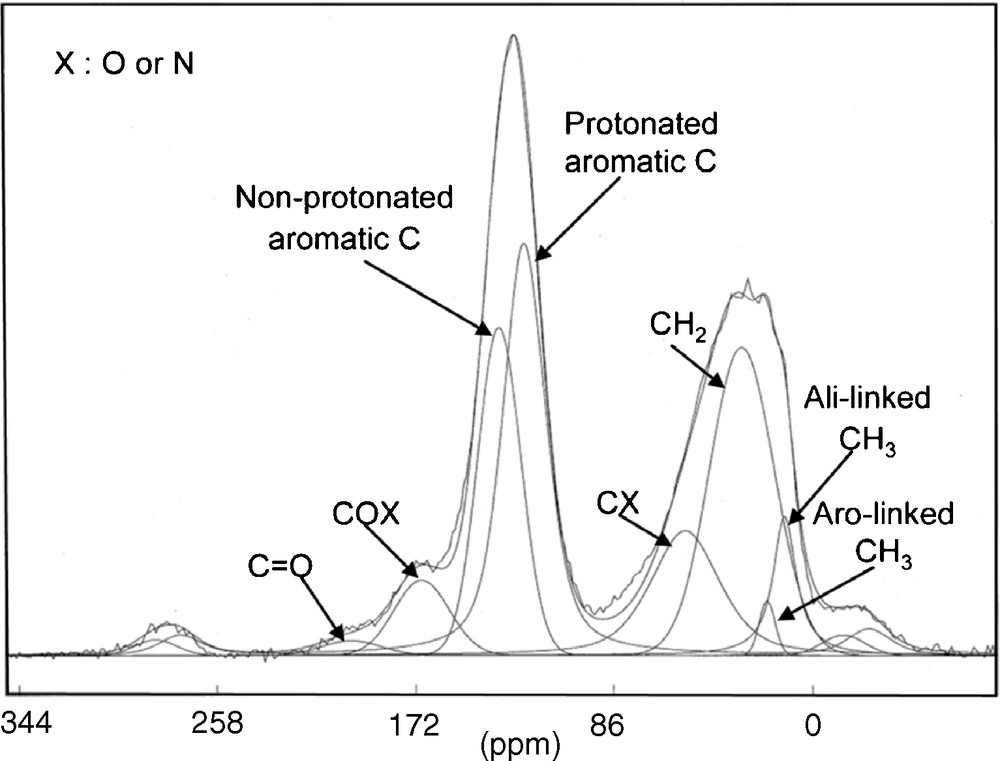
Solid-state 13C NMR spectrum of Orgueil IOM, from [20]. The chemical shift (in ppm) is characteristic of the functional group. This picture demonstrates the strong aromatic behaviour of the IOM. Moreover, the deconvolution of the signal allows us to determine the contribution of each type of C atom, leading to their distribution in the molecular structure.
Fig. 1. Spectre RMN à l’état solide du 13C de l’IOM d’Orgueil, publié dans [20]. Le déplacement chimique, exprimé en ppm, est caractéristique des groupements fonctionnels. Ce spectre démontre que l’IOM est très aromatique. De plus, la déconvolution de ce signal nous permet de déterminer la contribution de chaque type d’atomes de C, donnant leur répartition dans la structure moléculaire.
Pyrolysis releases mainly aromatic compounds, ranging from one to seven rings [31,41,56], with methyl and ethyl substitutions. These products are characterized by a great diversity: all possible isomers are detected and no isomeric preference is observed. This property is shared with soluble compounds. This is likely related to an organosynthesis by carbon addition and aromatization of aliphatic chains to form aromatic units. It must be noted that no aliphatic compound is detected by pyrolysis, revealing that aliphatic chains are shorter than 8 carbon atoms.
The occurrence of moieties with thermally accessible triplet states was reported in the IOM of Orgueil and Murchison [5]. These moieties manifest themselves in Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) by an increase in spin concentration when the temperature is increased above 150 K (Fig. 2). This feature, not observed for terrestrial organic matter, was attributed to the occurrence of diradicaloids, i.e. aromatic moieties with two unpaired electrons radicals that can be stabilized by delocalisation of electrons over the aromatic rings. By theoretical calculation, Binet et al. [5] proposed that these species could be related to aromatic units of 10 to 15 rings, making units of 3 to 4 rings in diameter, consistent with the previous estimation.
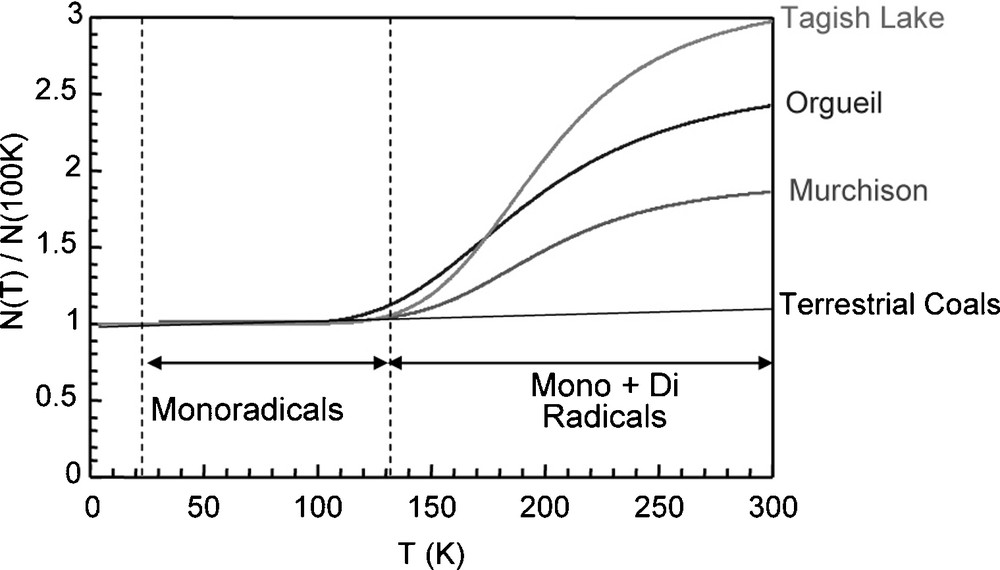
Spin concentration normalized to this value at 100 K in several IOM versus the temperature, from [6]. For extraterrestrial IOM, the spin concentration increases with the temperature, indicating the occurrence of diradicaloids. This behaviour is not observed in terrestrial organic matter.
Fig. 2. Concentration en spins électroniques, normalisée à sa valeur à 100 K dans différentes IOM en fonction de la température, tiré de [6]. Pour les IOM extraterrestres, la concentration en spins augmente avec la température, indiquant la présence de diradicaloïdes. Ce comportement n’est pas observé dans les matières organiques terrestres.
2.2 The aliphatic chains
A chemical degradation technique, ruthenium tetroxide oxidation, was chosen to investigate the aliphatic chains in the IOM of Orgueil and Murchison. Chemical degradations were performed on IOM from meteorites as far back as 1966 with the ozonolysis of Orgueil [7]. Moreover, following up this pioneering work, a number of other reagents were used in chemical degradations of IOM. They were trifluoroacetic acid, nitric acid, dichromate, copper oxide [25,26]. However, as far as we are aware of, no chemical degradation has been performed on IOM since that time. Moreover, except depolymerisation with trifluoroacetic acid, which was reported to yield C2 to C6 alkenes from Murchison IOM, no information on the aliphatic linkages could be derived from these chemical degradations.
Ruthenium tetroxide oxidation is a chemical degradation that has been largely used for characterizing the aliphatic and alicyclic portion of coals [30,58], kerogens [9,32] and humic substances [24] during the last 20 years. Ruthenium tetroxide is a mild and selective oxidising agent that preferentially destroys aromatic rings, converting them into CO2. It was also shown that it converts, oxidatively, alcohols into ketones or aldehydes, aldehydes into acids, ethers into esters or lactones [28,34]. The aliphatic and acyclic structures liberated appear as carboxylic acids the carboxylic functional group marking points of attachment in the kerogen and positions of labile functional groups, such as carbon-carbon double bonds and ether links [58].
Ruthenium tetroxide oxidation of Orgueil and Murchison IOM [40] produces a series of α,ω-dicarboxylic acids ranging from C2 to C9, along with methyl and dimethyl derivatives for the shortest compounds, without any isomeric selectivity. These compounds are related to the aliphatic linkages between the polyaromatic units in IOM. It also produces tricarboxylic acids, which are related to branched linkages between three aromatic units. No monocarboxylic acid is detected, pointing to a small size of the side chains into the IOM. Recently, Huang et al. have used a modified protocol of ruthenium tetroxide oxidation on Murchison IOM and they have recovered monocarboxylic acids from 2 to 9 carbons atoms [27], but the isotopic ratios of the longer ones should indicate terrestrial contamination. It seems likely that only the shorter ones (shorter than C5), recovered along with their methyl and dimethyl derivatives, can be considered as indigeneous products from Murchison IOM, consistently with previous data [40].
From these products, it is possible to characterize the aliphatic chains in chondritic IOM. They are quite short: less than four carbons for side chains, from two to seven carbons for aliphatic bridges between aromatic units. Oxygen is included in these aliphatic chains within ester or ether functional groups. Aliphatic linking chains are substituted by methyl and ethyl groups. These substitutions are randomized as there is an isomeric diversity. Moreover, the occurrence of aliphatic chains linking several aromatic units is consistent with a high degree of cross-linking evidence by 13C solid-state NMR.
2.3 Organic radicals
EPR reveals that radicals in Orgueil, Murchison and Tagish Lake IOM are heterogeneously distributed [4,6]. This feature is not observed in terrestrial organic samples and is specific to chondritic IOM. As shown on Fig. 3, radical concentration and the relaxation time of these radicals do not follow the trend of terrestrial organic matter. This means that radicals relax as if the concentration were higher. The only way to explain this observation is to propose that radicals are organized as clusters with high local concentrations compared to the bulk IOM.
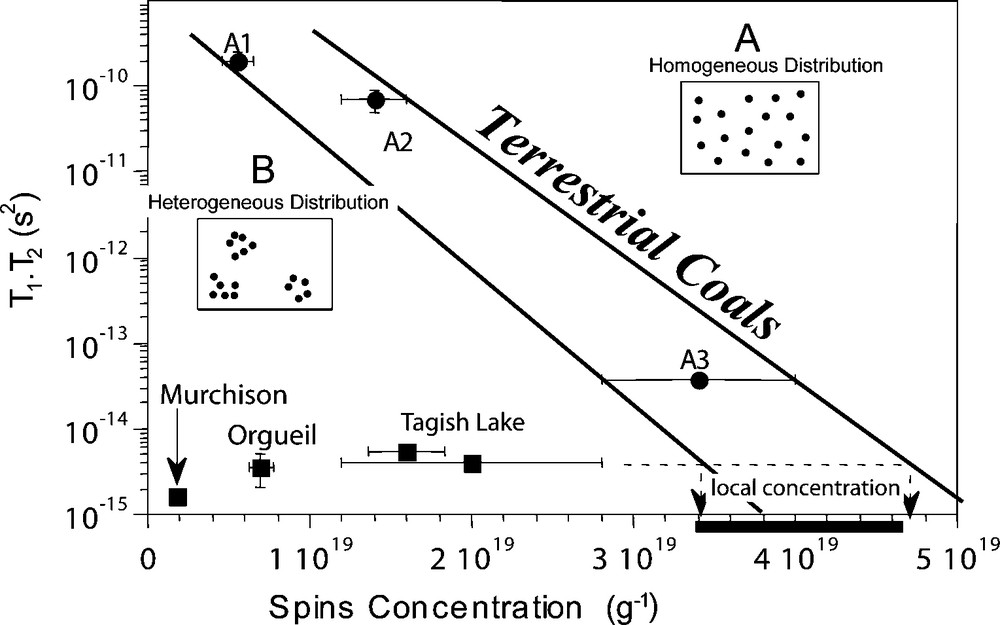
Relaxation time versus spin concentration in chondritic and terrestrial IOM, from [4]. When radicals are connected (i.e. close to each other), the relaxation time is short. When they are not, the signal is more stable and the relaxation is longer. This behaviour is expressed by terrestrial coals. Chondritic IOMs exhibit short relaxation times for low spin concentrations, and do not follow the correlation observed for coals, with homogeneous radical distribution A. The only way to face up this discrepancy is to suppose that chondritic IOM is characterized by a heterogeneous distribution of radicals B. This is illustrated in the two little cartoons where radicals are represented by dark dots. Masquer
Relaxation time versus spin concentration in chondritic and terrestrial IOM, from [4]. When radicals are connected (i.e. close to each other), the relaxation time is short. When they are not, the signal is more stable and the relaxation is ... Lire la suite
Fig. 3. Temps de relaxation en fonction de la concentration en spins dans la matière organique insoluble chondritique et terrestre à partir de [4]. Quand les radicaux sont connectés (c’est-à-dire proches les uns des autres), le temps de relaxation est court. Quand ils ne le sont pas, le signal est plus stable et le temps de relaxation est plus long. Ce comportement est caractéristique des charbons terrestres dont les radicaux sont répartis de manière homogène A. Les IOMs chondritiques ont des temps de relaxation court et des concentrations en spin faibles. La seule manière d’expliquer ceci est de supposer que l’IOM chondritique est caractérisée par une répartition hétérogène de ses radicaux B. Ceci est montré par les deux schemas, où les radicaux sont représentés par des ronds noirs. Masquer
Fig. 3. Temps de relaxation en fonction de la concentration en spins dans la matière organique insoluble chondritique et terrestre à partir de [4]. Quand les radicaux sont connectés (c’est-à-dire proches les uns des autres), le temps de relaxation ... Lire la suite
2.4 Conclusion: molecular model for IOM
All the previous results are summarized in Fig. 4. It represents the main information we have on the chemical structure of IOM of primitive chondrites. Nevertheless, for building a reliable molecular model, numerical molecular parameters are needed. Statistical parameters, obtained from several studies, are reported in table 1. Considering these parameters and the chemical functions evidenced in the IOM, it should be possible to draw a molecular model. This should be the goal of a future work.
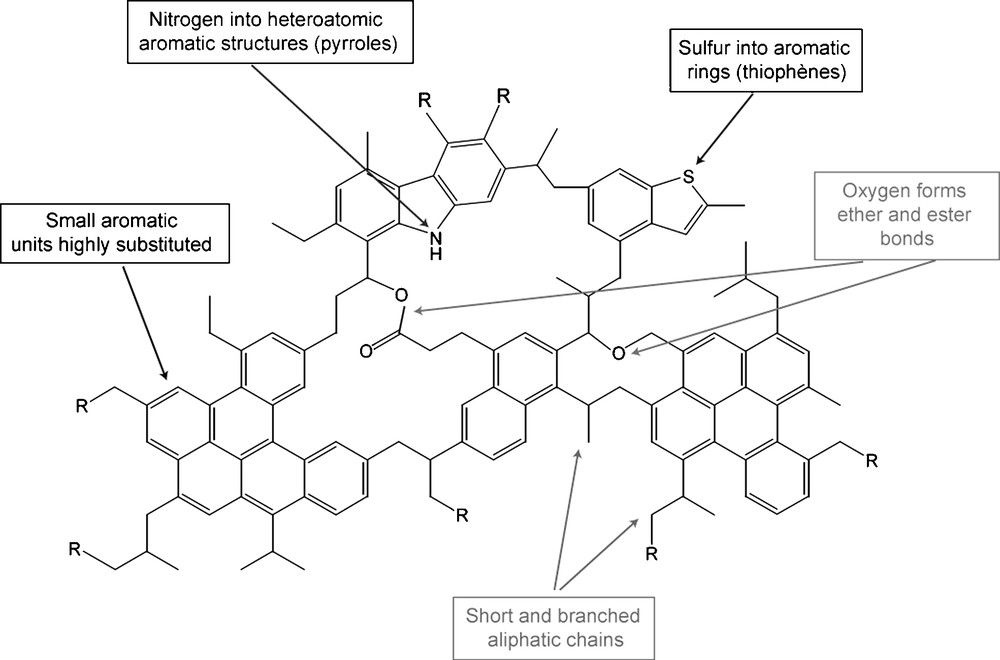
Summary of molecular information on the chemical structure of IOM of Orgueil and Murchison. R means an organic moiety. This picture was established thanks to data collected for 20 years and summarized in Table 1.
Fig. 4. Résumé des informations moléculaires sur la structure chimique des IOM d’Orgueil et de Murchison. R représente un groupement organique. Cette figure est établie à partir de données collectées depuis 20 ans et résumées dans le Tableau 1.
Summary and compilation of molecular properties of Orgueil and Murchison IOM from data collected over the last 20 years
Tableau 1 Résumé et compilation des caractéristiques moléculaires des IOM d’Orgueil et de Murchison à partir de données collectées ces 20 dernières années
| Relative molecular abundances | Analytical techniques | References | |
| Aromatic-linked C as CH3/Total C | 0.01 | 13C NMR | [14,15,20] |
| C as CH2 aliphatic/C as CH3 aliphatic | 2 | 13C NMR, IRTF | [14,15,20] |
| Non protonated Aromatic C/aromatic protonated C | 2.8 | 13C NMR | [14,15,20] |
| Aromatic C/Total C | 0.75 | 13C NMR | [14,15,20] |
| Acids C/Total C | 0.07 | 13C NMR | [14,15,20] |
| S as thiophenes/S as aliphatic S | 3.12 | Xanes S, pyrolysis GC-MS | [18,31,41] |
| N as pyrroles/Total N | 0.85 | 15N NMR, pyrolysis GC-MS | [41] |
| Relative bulk chemical composition | Compilation from: | [20,40,41] | |
| H/C | 0.70 | ||
| N/C | 0.03 | ||
| O/C | 0.22 | ||
| S/C | 0.045 | ||
| Structural informations | |||
| Small aromatic units | EPR, 13C NMR, TEM | [5,14,15,17,20] | |
| Short chains | Oxidative GC-MS, 13C NMR | [20,40] | |
| Highly branched aliphatics | Pyrolysis and oxidative GC-MS, Infrared | [20,40,41,57] | |
| Highly substituted aromatics | Pyrolysis GC-MS | [41,54,57] |
These molecular data are nevertheless useful to understand the processes involved in the synthesis and evolution of the IOM. The aromatic units that constitute the chemical structure are related to large PAHs observed in the interstellar medium. Nevertheless, the aromatic units in IOM are smaller than interstellar PAHs (Fig. 5). This could be the result of a selective preservation of smaller PAHs in IOM prior to their destruction by UV-irradiation, inducing a shift in the distribution of the size of aromatic units towards the high values. This process is shown schematically in Fig. 5.
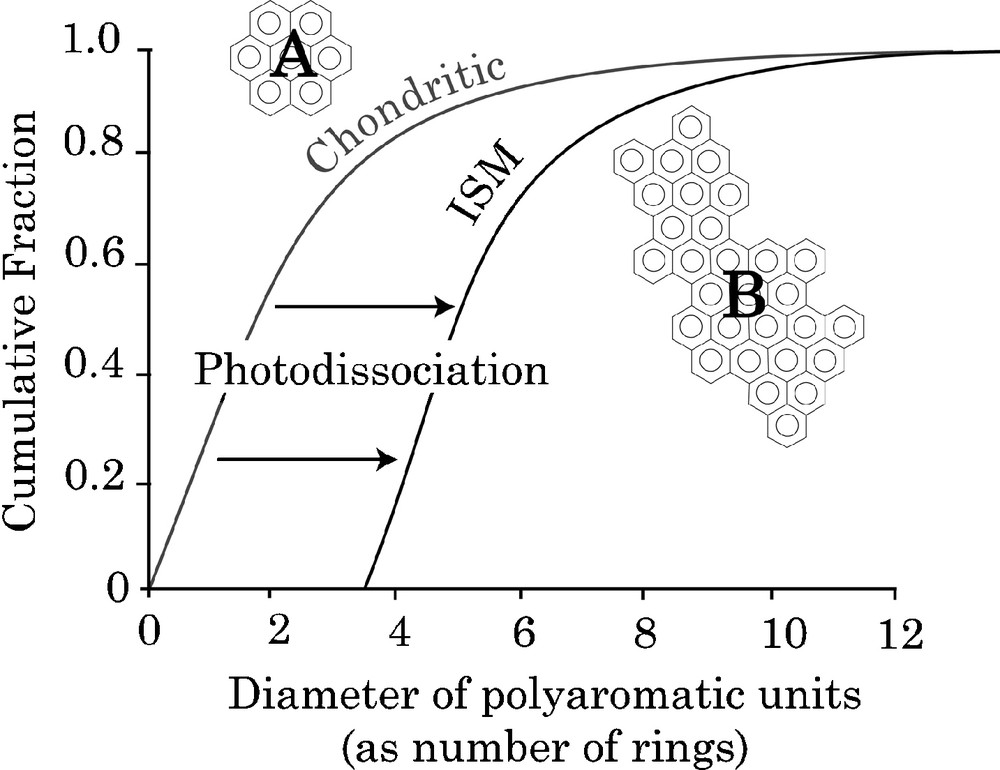
PAHs distribution in chondritic IOM and in the interstellar medium from [17]. The “chondritic” curve is obtained from image analysis of HRTEM pictures in which rather small aromatic units are observed A. The “ISM” curve is proposed to account for the observation of large PAHs in the ISM [3,37], represented by B. The shift between these two distributions is attributed to selective preservation of smallest PAHs on parent bodies.
Fig. 5. Courbes cumulatives des tailles des HAPs dans l’IOM des chondrites et dans le milieu interstellaire, d’après [17]. La courbe pour les chondrites (chondritic) est obtenue à partir de l’analyse d’images HRTEM qui montrent des unités aromatiques relativement petites, comme A. La courbe ISM est proposée pour expliquer l’observation de grands HAPs dans le milieu insterstellaire [3,37], représentés par B. Le décalage entre les deux distributions est attribué à une préservation sélective des petits HAPs sur les corps parents. Masquer
Fig. 5. Courbes cumulatives des tailles des HAPs dans l’IOM des chondrites et dans le milieu interstellaire, d’après [17]. La courbe pour les chondrites (chondritic) est obtenue à partir de l’analyse d’images HRTEM qui montrent des unités aromatiques relativement ... Lire la suite
The oxygen-containing functions are likely related to the aqueous alteration experienced by primitive carbonaceous chondrites. Indeed, warm water circulation could have resulted in an oxidation of IOM leading to the formation of ether or ester functional groups. Thanks to solid-state 15N NMR, it was shown that nitrogen is contained in aromatic moieties as pyrroles functions [41]. The sequestration of nitrogen into aromatic units should prevent IOM from being the source of amino acids. The only way to produce amino acids from IOM is to bring another reservoir of nitrogen, for instance HCN, and to involve catalytic processes [33].
3 The deuterium distribution
The origin of organic molecules in the early solar system has been under intense scrutiny since it was realized that these compounds were systematically enriched in deuterium relative to molecular hydrogen in the ProtoSolar Nebula (referred to as PSN; (D/H)PSN = 25 × 10−6 i.e. δD = −840‰ [21]). All δD numbers given in this paper are relative to SMOW (D/H = 155.76 × 10−6). For example, in the Orgueil meteorite [45], water has a D/H ratio of 160 × 10−6 or δD = +40‰, while some components of insoluble organic matter (IOM) are characterized by a D/H ratio of 350 × 10−6 or δD = +1250‰. With regard to water, it has been proposed that the D/H ratio decreased with time and temperature in the PSN [46], implying that water was initially enriched in deuterium by interstellar reactions before its incorporation into the PSN (theoretical calculations show that the D/H ratio of interstellar H2O can reach 1000 × 10−6 at 10 K; [10]). Because of the lack of experimentally measured isotopic exchange rates, similar modeling was not performed for IOM.
An interstellar origin was considered for IOM based on its systematic enrichment in deuterium [2,59,60]. However, the D/H ratio in IOM remains much lower than those measured in the organic molecules commonly observed in the dense interstellar medium (ISM; D/H ≈ 10000 × 10−6) [44]. Two qualitative interpretations have been proposed to account for the isotopic difference between the chondritic IOM and the organic molecules in the ISM. First, because stepwise pyrolysis of the IOM reveals a large isotopic heterogeneity [29,45], the bulk D/H ratio represents a mixture of various components enriched in deuterium to different degrees [2,29,59,60]. It is possible that the most deuterium-rich fraction of these components have D/H ratios as high as those observed in the ISM or in some IDPs [35], but that these components were sufficiently diluted in IOM to prevent their direct detection. Second, it has been proposed that the IOM is indeed an interstellar product (as also proposed for some soluble organic compounds [19,38]), but that the IOM formed at temperatures much higher (120 K) than canonical ISM temperatures (10–20 K) [44]. Indeed, at the first order (and as observed in Hot Cores [22,51]) the enrichment in deuterium is expected to decrease with increasing the formation temperature of IOM. As shown hereafter, neither of these interpretations can account for the measured deuterium distribution in the organic moieties of the IOM.
3.1 Deuterium enrichment in organic radicals
Pulsed Electron Paramagnetic Resonance has been used to analyze the isotopic composition of radicals in IOM of the Orgueil meteorite [16]. It is shown that radicals, which are heterogeneously distributed in the IOM, contain a very high deuterium concentration (D/H = 15000 ± 5000 × 10−6), much larger than the average bulk value D/H = 350 × 10−6 for this meteorite. This D-enrichment is comparable to the maximum enrichments observed in organics in the ISM (45,000 to 60,000 × 10−6 [36]).
3.2 Heterogeneities at the micrometer scale
The recent use of NanoSIMS ion probe provides new information on the distribution of the isotopic ratios in chondritic IOMs [12,47] with a spatial resolution of ca 100 nm. We have recently studied Orgueil IOM by NanoSIMS imaging of H, D, 12C, 14N and 16O. Maps of D/H, C/H, N/C and O/C were established to determine possible correlations between D/H isotopic ratio and any chemical or molecular feature. As previously observed for Murchison IOM [12,47], the D/H ratio is heterogeneous in Orgueil IOM, with small areas very enriched in D, with D/H ranging from 412 ± 30 to 723 ± 26 × 10−6 (see Fig. 6). In contrast, the bulk value is about 220 ± 22 × 10−6. These D-rich hot spots represent ≈ 2.8% of the IOM area. These hot spots are distributed all over the sample, without any specific pattern. No clear trend is observed between the D/H in these hot spots and the classical molecular parameters (for instance C/H, see Fig. 7) moreover, no association with inorganic acid-resistant minerals (mapped thanks to the O image) is observed.
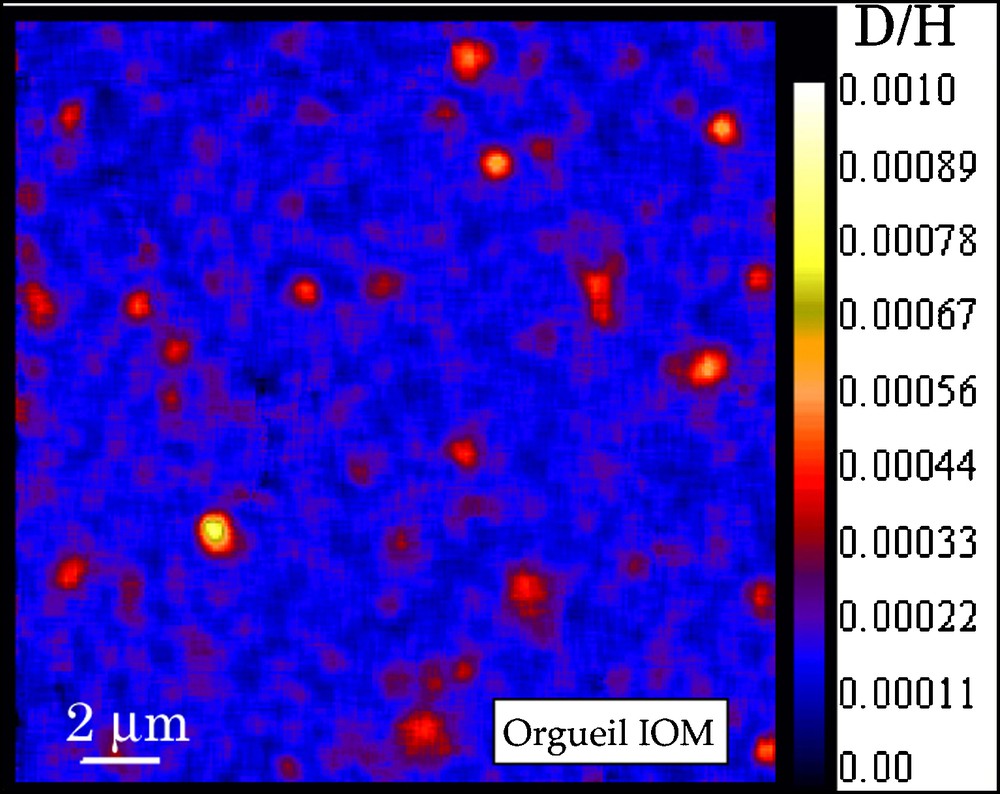
NanoSIMS D/H images of Orgueil revealing the occurrence of small areas very enriched in D, called “hot spots”. The same observation was reported in Murchison IOM [12,47].
Fig. 6. Image du rapport D/H de l’IOM d’Orgueil montrant la présence de petites régions très riches en D, appelés « hot spots ». La même observation a été publiée pour l’IOM de Murchison [12,47].
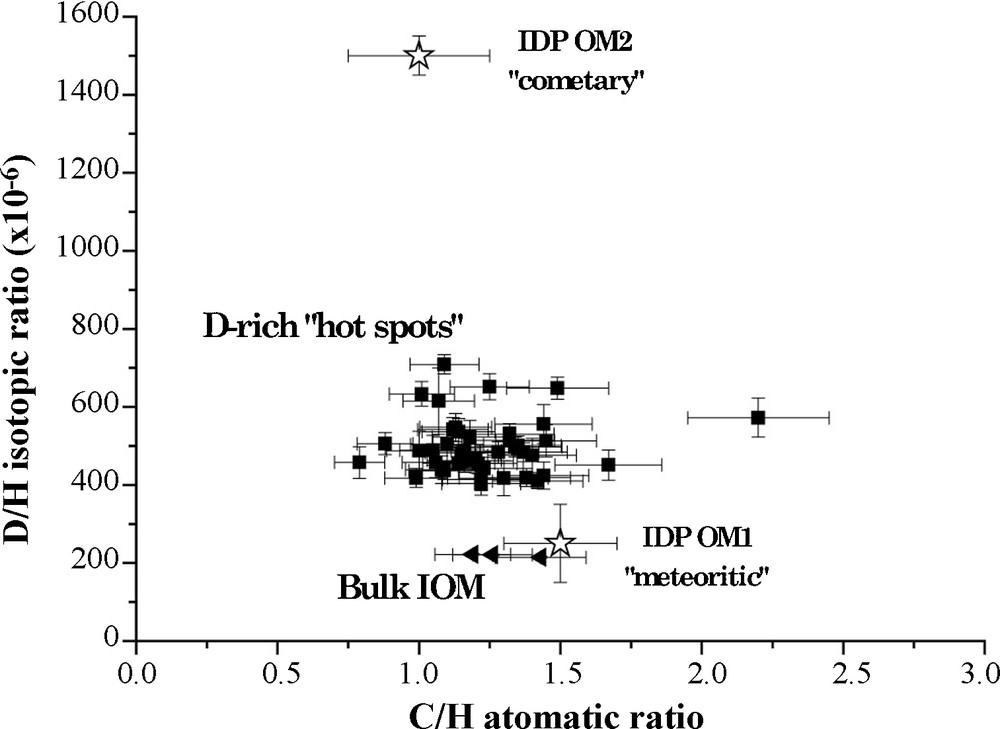
D/H isotopic ratio and C/H atomic ratio of “hot spots” determined in Orgueil IOM. On this graphic is also reported the composition of two organic end-members defined in IDPs. Hot spots exhibit almost the same molecular parameters than the bulk IOM, indicating a similar molecular structure.
Fig. 7. Rapports isotopiques D/H et atomiques C/H des « hot spots » mesurés dans l’IOM d’Orgueil. Sur ce graphique sont aussi reportés les compositions de deux pôles purs organiques déterminés dans les IDPs. Les « hot spots » ont des paramètres moléculaires similaires à ceux de l’IOM globale, montrant une structure chimique proche.
We have also acquired images of Kainsaz (CO3) IOM and a 600 °C pyrolysis residue of Murchison IOM. Kainsaz IOM is known to be depleted in radicals (between 2 and 3 orders of magnitude less compared to Orgueil and Murchison IOM), likely because it has experienced thermal stress on the parent body [43]. The pyrolysis residue of Murchison IOM should represent a thermally processed sample of Murchison IOM. As no hot spots can be detected in those two samples, it clearly shows that D-rich hot spots are thermally sensitive, as one-hour heating of Murchison IOM at 600 °C made them vanish. In the case of Kainsaz IOM, two hypotheses could be proposed: (1) the organic precursor of the Kainsaz parent body was the same as that of Orgueil and Murchison ones, so the thermal metamorphism that has experienced the Kainsaz parent body [8] should have destroyed the carrier of D-rich anomalies, or (2) there is no common precursor and Kainsaz IOM never contained this carrier. The first hypothesis seems more likely and implies that thermal effects are responsible for the loss of the carrier of D-excess in chondritic IOM. It must be noted that organic radicals are known to be destroyed by heating stress.
Two different hypotheses could be proposed to account for the D-rich hot spots: (1) these hot spots are remnants grains of interstellar organic material or (2) they are related to organic radicals occurring in IOM, as they are known to be highly enriched in D. By combining data from NanoSIMS and pulsed EPR, it is possible to prove that all the D-excess is borne by organic radicals. This will be described in more details in an upcoming paper. As these radicals are concentrated in small areas, they define small regions in the IOM which could constitute D-rich hot spots. Moreover, these radicals have no specific molecular properties compared to the rest of the IOM [5]. So it is consistent to observe that C/H atomic ratios of D-rich hot spots are quite close to bulk values [12] as shown in Fig. 7.
3.3 Distribution at the molecular level
GC-irMS (Gas Chromatography-isotope ratio Mass Spectrometry) permits the determination of the D/H ratio of aliphatic and aromatic moieties in Orgueil IOM [42]. Although aromatic moieties in chondritic IOM are known to be easily released by pyrolysis [41], the aliphatic linkages are recovered by ruthenium tetroxide oxidation [40]. Compound-specific D/H isotope measurements can then be performed on both the pyrolysis products and on the acids after derivatisation into their trimethylsilyl (TMS) esters.
Three types of organic groups (Fig. 8) hold most of the H in IOM. Type 1 is benzylic H, i.e. H bound to the first C atom linked to an aromatic ring (C atom in α position). Type 2 is non-benzylic aliphatic H. Type 3 is aromatic H. In order to understand the D/H distribution among the different products recovered during pyrolysis and chemical degradation (Table 2), three types of H were thus assumed to exhibit three different isotope compositions. For each compound the proportion of hydrogens of type 1, 2 and 3 was calculated. For this, it must be assumed that the recovered products bear the isotope labeling of the starting macromolecule before any laboratory degradation (Fig. 8); in other words, we must consider the location of H into the starting macromolecule and not in the recovered products. The C–H bond dissociation energy differs for the three types: the higher this energy, the stronger the bond. Any exchange between the hydrogen in these molecules and an external reservoir is affected by the binding energy. A stronger bond will undergo a lesser exchange and C–H bond-breaking is a prerequisite to D incorporation. The higher reactivity of the benzylic bond is well known and is reflected by a lower C–H bond dissociation energy than for the other aliphatic C–H bonds (87 kcal mol−1 and 98 kcal mol−1 for benzylic and aliphatic C–H bonds respectively). The C–H aromatic bond dissociation energy is even higher (111 kcal mol−1) than for the aliphatic C–H bonds, independently of the size of the aromatic structure. So Type 1 H is supposed to be more exchangeable than Type 2, and Type 2 more exchangeable than Type 3.
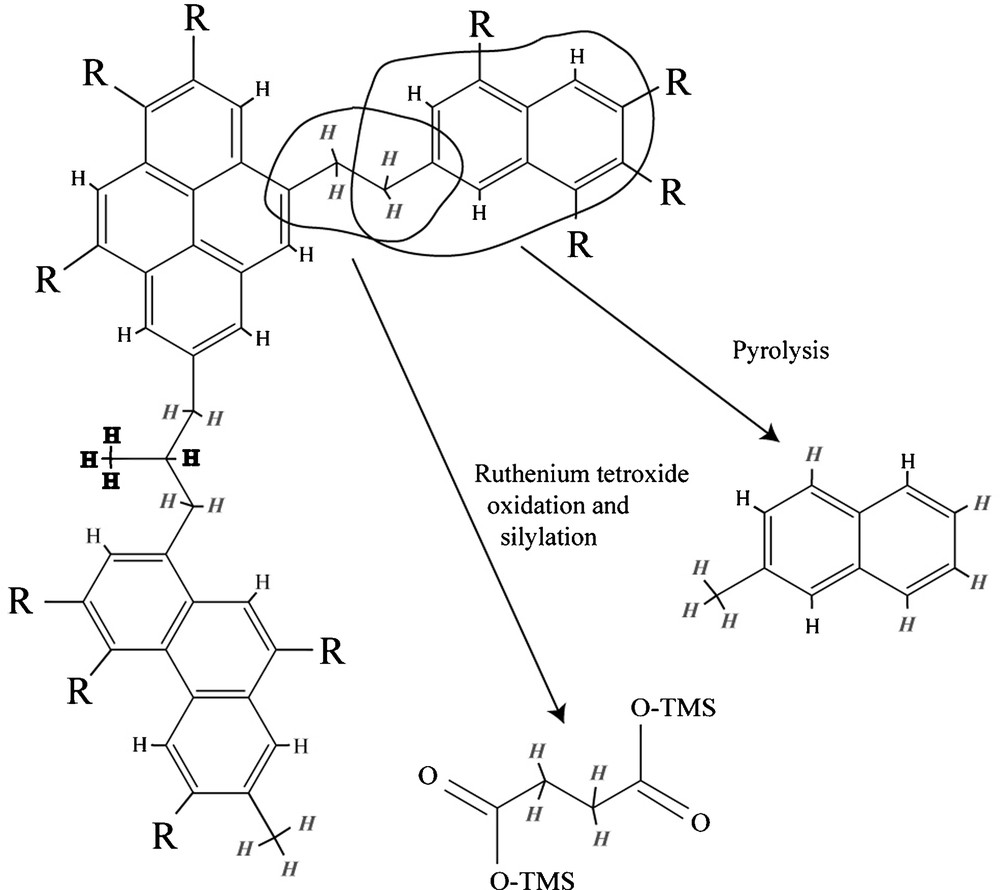
The IOM contains basically three types of H: aromatic (plain text), aliphatic (italic) and benzylic (bold). The chemical and thermal degradation generates products that are related to the initial structure [42]. It is possible to determine the number of each type of hydrogen contained in each product.
Fig. 8. En simplifiant, l’IOM est constituée de 3 types de H : les aromatiques (caractère normal), les aliphatiques (en italique) et les benzyliques (en gras). Les dégradations chimique et thermique libèrent des produits qui sont reliés à la structure initiale [42]. Il est possible de déterminer le nombre de chaque type d’hydrogène contenu dans chaque produit.
δD of aliphatic and aromatic moieties from Orgueil IOM
Tableau 2 δD des fragments aliphatiques et aromatiques de l’IOM d’Orgueil
| Compound | δD (‰)a | D/H (×10−6) |
| Aliphatic moieties | ||
| Butanedioic acid | +1270 (±112) | 353.5 (±17.5) |
| Methylbutanedioic acid | +919 (±80) | 298.9 (±12.5) |
| Ethylbutanedioic acid | +1050 (±67) | 319.4 (±10.5) |
| Pentanedioic acid | +928 (±78) | 300.3 (±12) |
| 2-methylpentanedioic acid | +801 (±77) | 280.5 (±12) |
| 3-methylpentanedioic acid | +869 (±177) | 291,2 (±27.5) |
| Aromatic moieties | ||
| C2-benzene | +945 (±110) | 303 (±17) |
| C3-benzene | +795 (±64) | 279.6 (±10) |
| C4-benzene | +866 (±77) | 290.7 (±12) |
| Naphthalene | +727 (±76) | 269 (±12) |
| C1-naphthalene | +1111 (±46) | 328.8 (±7) |
| C2-naphthalene | +931 (±30) | 300.7 (±4.5) |
| Anthracene - phenanthrene | +773 (±30) | 276.1 (±4.5) |
| Fluoranthene | +602 (±24) | 249.6 (±4) |
| Pyrene | +710 (±16) | 266.4 (±3.5) |
a The δD values are average of each GC-irMS runs. Values are reported relative to the Standard Mean Ocean Water (SMOW).
D/H isotopic ratio of each analyzed compound can be calculated by considering the number of each type of hydrogen in each compound. This gives a mass balance equation for each analyzed compound with only three free parameters: the D/H ratio of Types 1, 2 and 3 hydrogen. By comparing iteratively between calculated and measured D/H values, D/H = 350 × 10−6, 240 × 10−6, 180 × 10−6 for hydrogen of Type 1, 2 and 3, respectively [42]. The good fit between measured and calculated D/H values is still observed if these Type 1, 2 and 3 D/H values are allowed to vary within ±10 × 10−6. This numerical result does not preclude the presence of other minor types of organic H, having D/H ratio different from those of Types 1, 2 or 3, but it demonstrates that, if present, these other types of H cannot be detected within the limit of the error bars on the D/H ratio. Such minor types of organic hydrogen could be the products of hydrothermal metamorphism on the parent body [11] and might be present as functional groups not detected in our experiments (as for example –OH groups).
3.4 Conclusion: D-enrichment process involved
The molecular determination of the D carrier in Orgueil IOM can be summarized in Fig. 9. Pulsed EPR revealed that, in the D-rich radicals, D is preferentially linked to the carbon atom in α-position relative to an aromatic unit, i.e. it is a benzylic hydrogen. This helps to determine the C–H bond energy for these radicals. We postulate that the IOM was a PSN product. In this pristine IOM, the organic sites had D/H ratios with values lying somewhere between the PSN and the D/H ratio of water (given by the –OH bearing minerals present in Orgueil [45]). After its synthesis, the IOM was transported into regions of the PSN where the physical conditions were comparable to the ISM, i.e. a cold ionized medium where ion–molecule reactions [50] could take place and where IOM acquired its deuterium enrichment. In this respect, ionized molecules (and more specifically the most abundant ion in such an environment, i.e. H3+) rapidly become enriched in D even at low T [36]. Under these conditions, Type 1 hydrogens experienced a higher deuterium exchange rate than Type 2, and Type 2 higher exchange rate than Type 3, resulting in the observed relationship (Fig. 9). The radicals, exchanging even faster than the rest of the IOM should get more D-enriched than the bulk IOM, and as they are heterogeneously distributed in the IOM, could form D-rich small areas constituting the D-rich hot spots. Because the water D/H ratio also lies on the correlation defined by the three types of organic hydrogen (see Fig. 9), water might have acquired its deuterium enrichment under similar conditions.
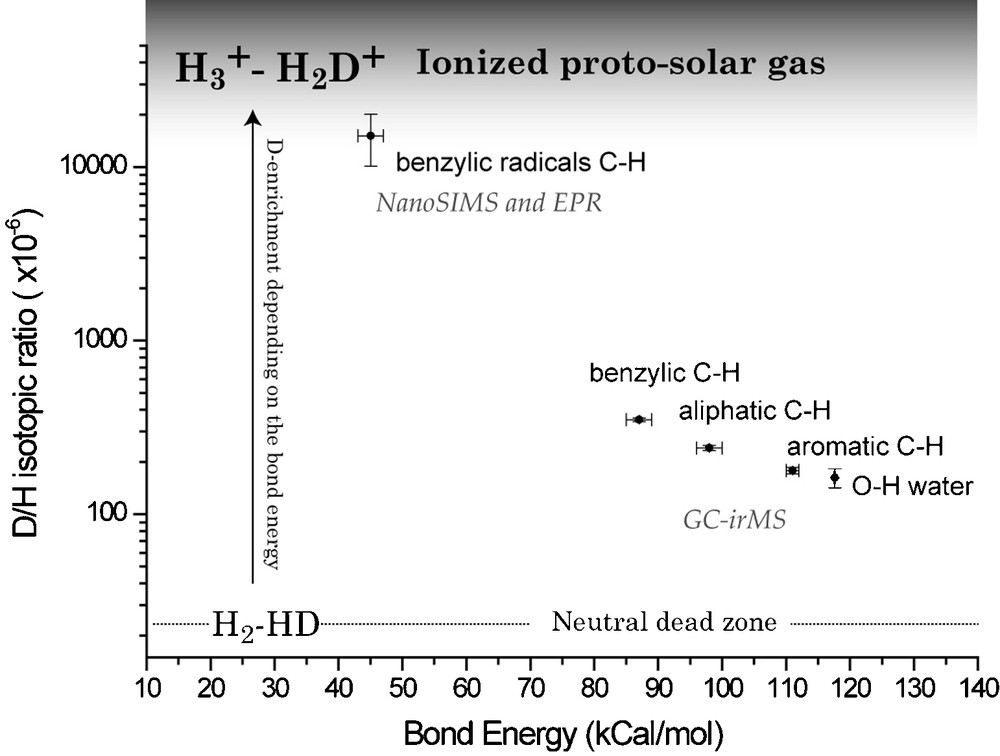
D/H isotopic ratios of D-carrier versus their C–H bond energy (from [42], modified). A clear trend appears, leading to the conclusion that the most exchangeable H have the highest enrichment in D.
Fig. 9. Rapport isotopique D/H des différents ensembles moléculaires portant le D en fonction de leur énergie de liaison C–H (inspiré de [42]). Une tendance nette se manifeste, menant à la conclusion que les H les plus échangeables ont les plus grands enrichissements en D.
Our model can be illustrated by the following reactions:
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
Taking the classical value for the exothermicity (ΔE/k = 260 K) of the reaction (1), the enrichment factor α in D can be approximated as: α = exp(260/T). No isotopic fractionation is assumed for the reactions (2) and (3); these reactions simply transfer deuterium. In an isotopic exchange between IOM and D-enriched H3+, the maximum measured D/H ratio in IOM (i.e. 15,000 × 10−6) will represent the minimum possible D/H ratio of H3+. This value gives α = (15,000 × 10−6/25 × 10−6) = 600, corresponding to T ≈ 40 K. These temperatures very likely occurred at the outer edges of the PSN as in the ISM. Recently, Ceccarelli and Dominik [13] have reported theoretical models that predict the occurrence of highly deuterated H3+ in protoplanetary disks, which could exchange its D with IOM in the protosolar nebula.
Thus, these data support the theoretical idea according to which the deuterium enrichment of solar system molecular species could have taken place in the outer part of the turbulent protosolar disk ionized by UV light from the young Sun [1,23,44]. If, as we suggest, these organic molecules are contemporaneous with our solar system, one can easily imagine that they are products of protostellar disks in general. Indeed, because the D/H ratio of meteoritic water is consistent with our model, these processes could be at the origin of the deuterium enrichment in the inner solar system.
It must be noted that in the present interpretation, the isotopic species need not to reach equilibrium: the correlation is linked only to a property of isotopic exchange rates. Due to very low temperature, organic matter should rapidly condense into grains. This process should likely stop the D exchange as organics trapped into the ices cannot be reached by the ionized gas. This implies that the duration of the exchange reaction is limited, leading to a competition between each type of hydrogen. The dynamical implications of these ideas need to be explored further in future theoretical work.
This process is attractive because it explains both the occurrence of D-rich hot spots and D/H heterogeneity observed at molecular level, revealed by GC-irMS. Then the major issue that remains should be the origin of organic radicals. Indeed the occurrence of stable radicals in IOM is not yet explained. For instance it is not known if they were formed in or before the protosolar nebula in other words if they constitute presolar organic matter or if they were formed by a protosolar process.
4 Conclusion
Molecular studies revealed that IOM in carbonaceous chondrites is different from terrestrial organic matter. It consists of small aromatic units, highly substituted linked by short branched aliphatic chains. This structure exhibits a high degree of cross-linking. Nitrogen and sulphur are embedded into aromatic units, forming respectively pyrroles and thiophene groups. Oxygen is located into ether and ester functional groups, likely related to the aqueous alteration experienced on the parent body of the most primitive carbonaceous chondrites.
Recent isotopic studies suggest that IOM acquired its D-isotopic composition in the protosolar nebula by exchange with deuterium-rich ions formed in the PSN. The occurrence of D-rich “hot spots” is the result of the occurrence of organic radicals heterogeneously distributed in the IOM. The origin of these radicals remains a major issue that is not yet resolved.
Acknowledgments
Anders Meibom is thanked for helpful comments on this manuscript. We are grateful to Marc Chaussidon for his constructive review on this manuscript. This is IPGP contribution number 2275.


