1 Introduction
Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. (Madagascar periwinkle) is one of the most important medicinal plant, and also an ornamental bedding plant belonging to the family Apocynaceae. Two varieties of C. roseus can be distinguished based on the flower colour, viz. the pink-flowered rosea and the white-flowered alba [1]. C. roseus plant got commercial importance due to the presence of medicinally important alkaloids, and also owing to its ornamental value [2]. Catharanthus roseus is a perennial tropical plant belonging to the family Apocynaceae that produces more than 100 monoterpenoid indole alkaloids (MIAs), including two commercially important cytotoxic dimeric alkaloids used in cancer chemotherapy [3].
Triazole compounds are new synthetic plant growth regulators that act as antigibberellins and that are known to inhibit shoot growth in plants [4]. Triazoles have been called plant multiprotectants because of their ability to induce tolerance in plants toward environmental and chemical stresses [5]. Protection of plants from apparently unrelated stress by triazole is mediated by a reduction in free-radical damage and an increase in antioxidant potential [6,7]. Triazoles affect the isoprenoid pathway and alter the levels of certain plant hormones by inhibiting gibberellin synthesis, reducing ethylene evolution and increasing cytokinin levels [8]. Triazole-treated plants have a more efficient free-radical scavenging system, which enables them to detoxify active oxygen. We have reported previously some of the morphological and physiological changes associated with triazole treatment in various plants, including inhibition of plant growth, decreased internodal elongation, increased chlorophyll levels, enlarged chloroplasts, thicker leaf tissue, increased root-to-shoot ratio, increased antioxidant potentials, and enhancement in alkaloid production [9–13].
The plant-growth regulating properties of triazoles are mediated by their ability to alter the balance of important plant hormones, including gibberellic acid, ABA, and cytokinins. They also inhibit gibberellin and ergosterol biosynthesis in plants and fungi, respectively [6]. Triazole compounds induce a variety of morphological and biochemical responses in plants, like inhibited shoot elongation, stimulated root growth, increased cytokinin synthesis and a transient rise in ABA; they also confer protection against various environmental stresses. Triazole compounds inhibited gibberellin biosynthesis and reduced stolen length in potato by counteracting gibberellin action. Triadimefon has proved a plant-growth retardant in many of the previous works. Despite the relatively great number of reports on the medicinal aspects and stress effects on C. roseus [2,10,14–24], there are only few attempts to explain the role of the triazole compound named triadimefon in this plant. The growth-retarding properties of triadimefon are exploited in this work for reducing shoot elongation and for improving the vegetation colour and flower quality in C. roseus.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and cultivation methods
The seeds of both rosea and alba varieties were collected from the Department of Horticulture, Annamalai University, and the plants were raised in the Botanical Garden, Department of Botany, Annamalai University, Tamil Nadu. The triazole compound triadimefon (‘BAYLETON-25 WP’) was obtained from Bayer (India) Ltd., Mumbai. During the study, the average temperature was 32/26 °C and relative humidity (RH) varied between 60–75%. The seeds of the two varieties were sown separately in raised seedbeds by broadcasting method and covered with fine soil to ensure proper germination. The nursery beds were watered twice a day and weeded regularly in order to ensure healthy growth of the seedlings. The land was repeatedly ploughed and brought to fine tilth and divided into four plots prior to transplantation. Two plots for each variety were prepared; 40 plants per plot were planted for both varieties at a distance of , and irrigated immediately for better establishment. Subsequent irrigation was done two times a week to keep an optimum moisture level in the soil.
2.2 Triadimefon treatment
In the preliminary experiments, 5, 10, 15 and 20 mg l−1 concentrations of triadimefon were used for treatment to determine the optimum value. Among the treatments, a triadimefon concentration of 15 mg l−1 decreased the plant height significantly, whereas higher concentrations slightly damaged growth and pigment content. With lower concentrations, there was no change in growth and pigment content. Hence, a triadimefon concentration of 15 mg l−1 was used to study the effect of this compound in C. roseus plants. One plot of each variety was subjected to triadimefon treatment, whereas another one was kept as control. Each plant was given triadimefon @ 15 mg l−1 by soil drenching. The treatment was given during 30, 45, 60, and 75 days. The plants were uprooted randomly on the 90th day after planting, then separated into root, stem, leaves, and flowers, and used for determining growth, and photosynthetic and floral pigments.
2.3 Growth parameters
The plant height was measured from the soil level to the tip of the shoot, and root length was measured from the point of first cotyledonary node to the tip of longest root. The total number of leaves that were fully developed was counted, and the total leaf area of the plants was measured using a LICOR Photo Electric Area Meter (model LI-3100, Lincoln, USA). After washing the plants with tap water, their fresh weight was determined by using an electronic balance. After taking fresh weight, the plants were dried at 60 °C in a hot-air oven for 24 h; their dry weight was then measured.
2.4 Photosynthetic and floral pigments
Chlorophyll and carotenoid were extracted from the leaves and estimated by the method of Arnon [25]. The carotenoid content was estimated using the formula of Kirk and Allen [26]. Anthocyanin was extracted from the flowers and estimated by the method of Beggs and Wellmann [27].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Growth parameters
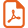
Triadimefon treatment reduced plant height in both varieties of C. roseus (Fig. 1). Paclobutrazol treatments reduced the stem elongation and plant height in C. roseus [5]. The growth-retarding effect of triazole is caused by the inhibition of GA and might be the reason for decreased plant height, as observed by Jaleel et al. in Withania somnifera [7]. Triazole treatments inhibited leaf growth in C. roseus plants, resulting in reduced number of leaves when compared to control, and also in decreased leaf area (Fig. 1). The number of leaves was reduced in paclobutrazol-treated C. roseus [5]. Paclobutrazol reduced the leaf area in Vigna unguiculata [28]. The inhibition of GA biosynthesis and the increased ABA content induced by triazole treatment could be the reason for the inhibition of leaf expansion in triazole-treated C. roseus plants.
Effect of triadimefon on the plant height (cm plant−1), number of leaves (number plant−1) and leaf area (cm2 plant−1) of C. roseus on the 90th day after sowing. Values are of seven replicates.
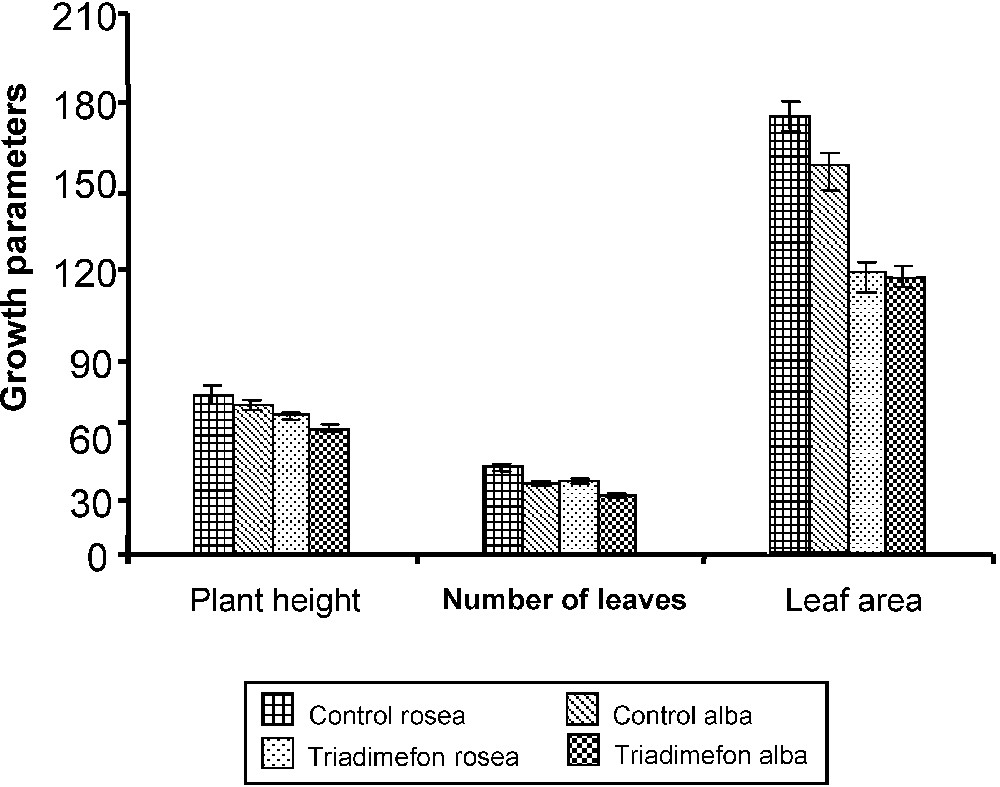
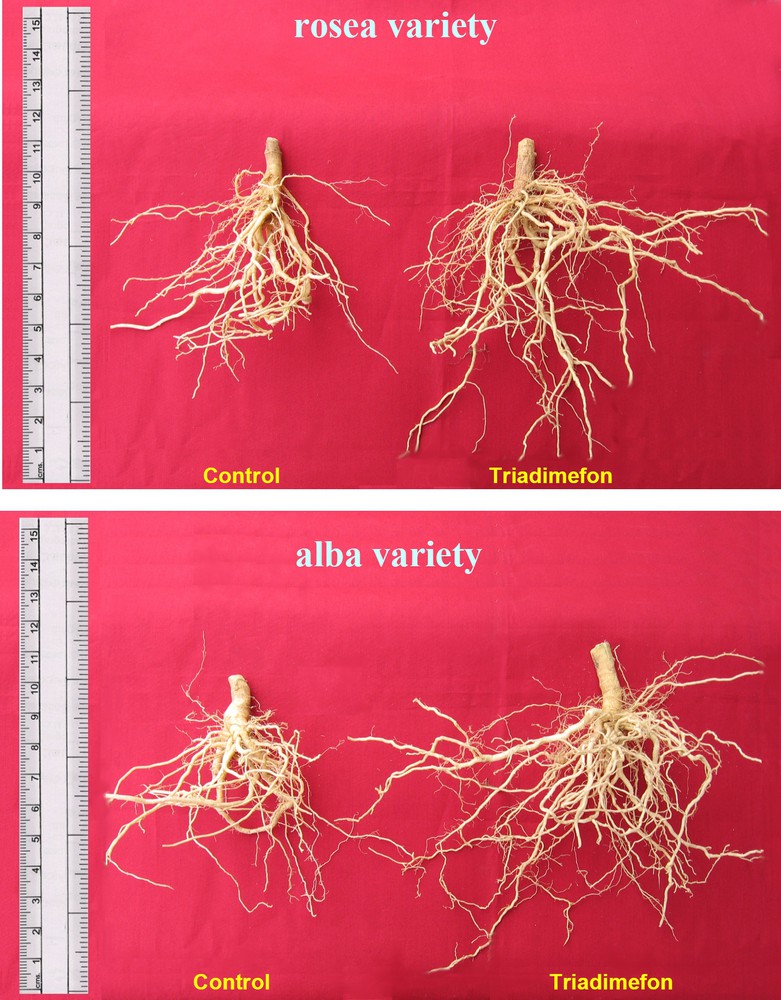
Length of roots increased with triadimefon treatments when compared to control plants of both varieties (Plate 1). However, the roots of the rosea variety were longer than those of alba. Triadimefon treatment increased largely root length in both varieties; it is paralleled to the increase in whole-plant fresh and dry weights in treated plants of C. roseus when compared to control (Fig. 2). Triazole-treated plants have exhibited thickened and fleshy roots with increased root diameter and weight in Dioscorea [4] and Vigna unguiculata [28]. This stimulation of root growth may be related to the increased partitioning of assimilates towards the roots due to decreased demand in the shoot [29]. It may also be due to the changes in growth regulators (i.e., inhibition of GA and increase of cytokinin and ABA) as observed by Fletcher and Hofstra [30].

Variations in root growth in two varieties of Catharanthus roseus undergoing triadimefon treatment on the 90th day after sowing.
Effect of triadimefon on the root length (cm plant−1), fresh weight (g plant−1) and dry weight (g plant−1) of C. roseus on the 90th day after sowing. Values are of seven replicates.
3.2 Photosynthetic and floral pigments
Chlorophyll a and b, total chlorophyll (Fig. 3) and carotenoid (Fig. 4a) contents in leaves of both varieties of Catharanthus increased with triadimefon treatments when compared to control plants. These results are in accordance with the previous reports in Withania rosea by Jaleel et al. Paclobutrazol treatment increased chlorophyll , and carotenoid pigments in C. roseus [10]. Triazole compounds increase the level of cytokinin, which might stimulate chlorophyll biosynthesis [31]. Anthocyanin content of Catharanthus flowers slightly increased under triadimefon treatment, but there was a significant difference between the varieties (Fig. 4b). Increased anthocyanin with triazole treatment has been reported in C. roseus [10].

Effect of triadimefon on the chlorophyll content (mg g−1 fresh weight) of C. roseus on the 90th day after sowing. Values are of seven replicates.
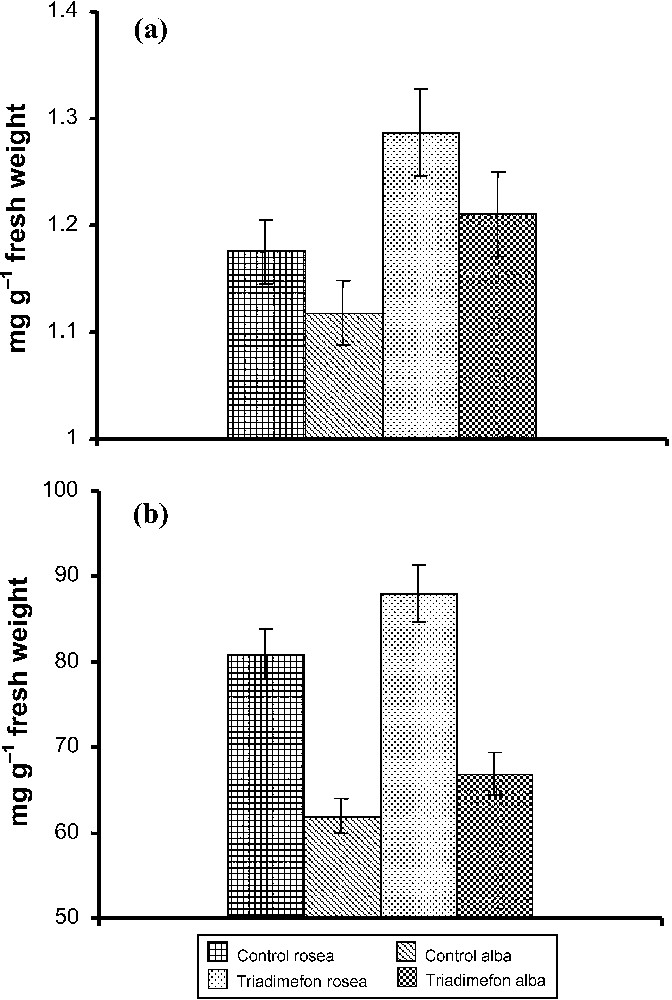
Effect of triadimefon on the (a) carotenoid and (b) anthocyanin (mg g−1 fresh weight) contents of C. roseus on the 90th day after sowing. Values are of seven replicates.
4 Conclusions
The above results showed that triadimefon treatment enhanced pigment composition and reduced growth of aerial parts, but increased root growth.
From these results, it is proved that the application of triadimefon will enhance the qualities of flowers and also reduce the stem length, and thereby minimize the necessity of hand pruning in bedding plants.