1 Introduction
Considering the means of defence and communication that the evolution gave to plants, flavonoids are among the more important chemical classes. They appeared early, 500 millions years ago, with some green algae, and result from the fusion of two biogenetic pathways, i.e. the cinnamate and the ancient polyketide route. They have then seemed to get more and more complexity with plant evolution 〚1〛. If we consider (subjectively indeed) that evolved characters are beneficial to life, we can then attribute to flavonoids a large biological importance, not only for the vegetal kingdom itself, but also for animals. In fact, flavonoids are increasingly suspected of being responsible for the longer life expectancy of populations with well-balanced and healthy diets. Such a diet usually contains a large part of fruits and vegetables as well as beverages from vegetal origin, particularly tea and red wine, which make it rich in flavonoids and in other polyphenols 〚2, 3〛. This nutritious phenomenon has often been referred to as the ‘French paradox’ 〚4〛.
Beyond their ‘vitamin P’ activity, which has been known for a long time 〚5, 6〛, many other biological properties have been discovered. Because one of the main physicochemical features of flavonoids is their powerful anti-oxidant and radical scavenger properties, they may be involved in defences against oxidative stress 〚7, 8〛 and ageing processes in cells that are responsible for degenerative diseases (cardio-vascular diseases 〚9–11〛, cancer 〚12〛 and even Alzheimer disease 〚13〛). It has been demonstrated in vitro that such compounds inhibit LDL (Low Density Lipoproteins) oxidation 〚9〛, lipoperoxidation and the inflammatory response 〚11, 13〛. Moreover, chelation of iron by flavonoids in cells may prevent the Fenton reaction, responsible for HO• free radical formation 〚14〛. Besides this experimental data, epidemiological studies have comforted the role of flavonoids in the prevention of many degenerative diseases 〚3–4, 15–17〛.
Nevertheless, flavonoids would only be able to produce such activities in vivo if they were absorbed through the intestinal wall after ingestion. There is little experimental data about their absorption and their metabolism, especially in the conditions of a normal meal 〚18, 19〛. Although some studies have shown that flavonoids are bioavailable, even though as degradation metabolites 〚20〛, the results are still quite variable, depending on the authors. In order to obtain more precise information about the natural bioavailability of flavonoids (which occurs after a normal meal), we decided to use isotopically labelled compounds. These could be detected by isotopic mass spectrometry and quantified independently of compounds naturally present in the diet. We chose carbon-13 as a good tracer within the skeleton of our molecules and possibly of their metabolites. The flavan-3-ol derivatives (+)-catechin 1, (–)-epicatechin 2 and (–)-procyanidin B3 3 (Fig. 1) were chosen as good representatives of flavonoids that are present in a typical healthy diet. This review focuses on the synthetic venture that was undertaken to produce such 13C-labelled compounds in a gram scale and in an asymmetric manner, describing all the chemical routes that were explored during this work.
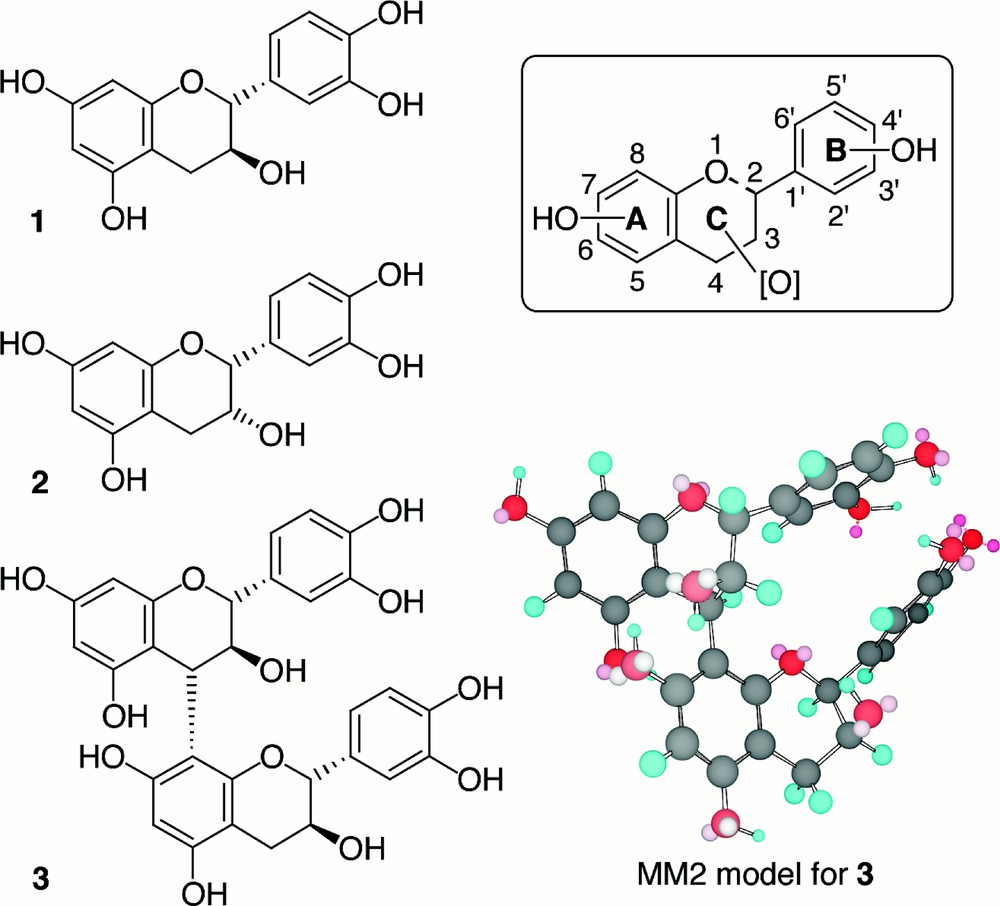
General structure of flavonoids (in frame) and compounds of interest: (+)-catechin 1, (–)-epicatechin 2, (–)-procyanidin B3 3.
2 General structure of flavonoids
Flavonoids are polyphenolic natural products. Their structures include two phenolic rings (A and B), linked by a small chain of three carbons (Fig. 1). Usually, this linkage is part of the ring C fused to the first aromatic ring A to form a benzopyran heterocycle. Each of the three cycles of this skeleton can be diversely oxidised, giving rise to different classes of flavonoids. The more distinctive characteristic of each of these classes is the oxidation level of the oxygenated heterocycle C. This heterocycle in the highly oxidised species (3-hydroxyflavones, anthocyanidins) has a planar geometry, associated with highly conjugated unsaturation, which is also responsible for their visible character (from yellow to violet). For the classes with a saturated heterocycle, such as the flavan-3-ols, of interest in this paper, some chirality arises, due to 1 to 3 possible stereocentres.
3 Synthetic strategies
The C6–C3–C6 flavonoid skeleton can be accessed following two of the more obvious retrosynthetic analyses (Fig. 2) 〚21〛.
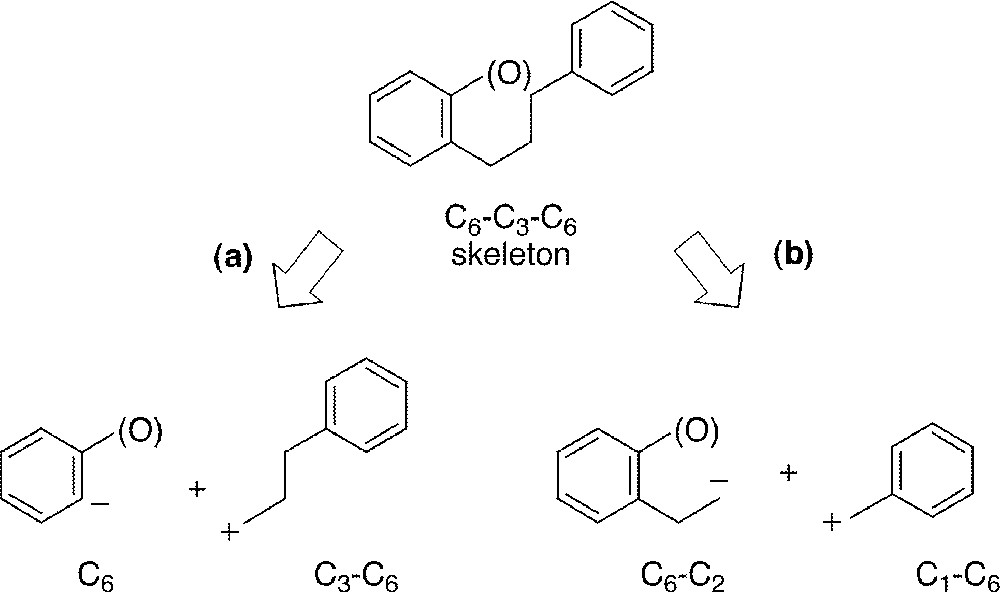
Retrosynthetic analysis: C6 + C3–C6 strategy (a) and C6–C2 + C1–C6 strategy (b).
On the one hand (Fig. 2a), it is possible to unravel the structure into a C6 phenolic and a C3–C6 cinnamic synthon that could either be a carboxylic acid, an aldehyde or an alcohol (Fig. 3). The process involved either a retro-acylation (into a cinnamic acid 4, route A) or a retro-allylation (into a cinnamaldehyde 5, route B, or a cinnamic alcohol 6, route C), respectively. Each oxidation state of these precursors could be valuable in the specific synthesis of different classes of flavonoid intermediates (e.g., chalcones 7, 2-phenyl-2H-chromenes 8 or cinnamylphenols 9, respectively). Usually, these reactions are not simple and the alternative strategy is often preferred.
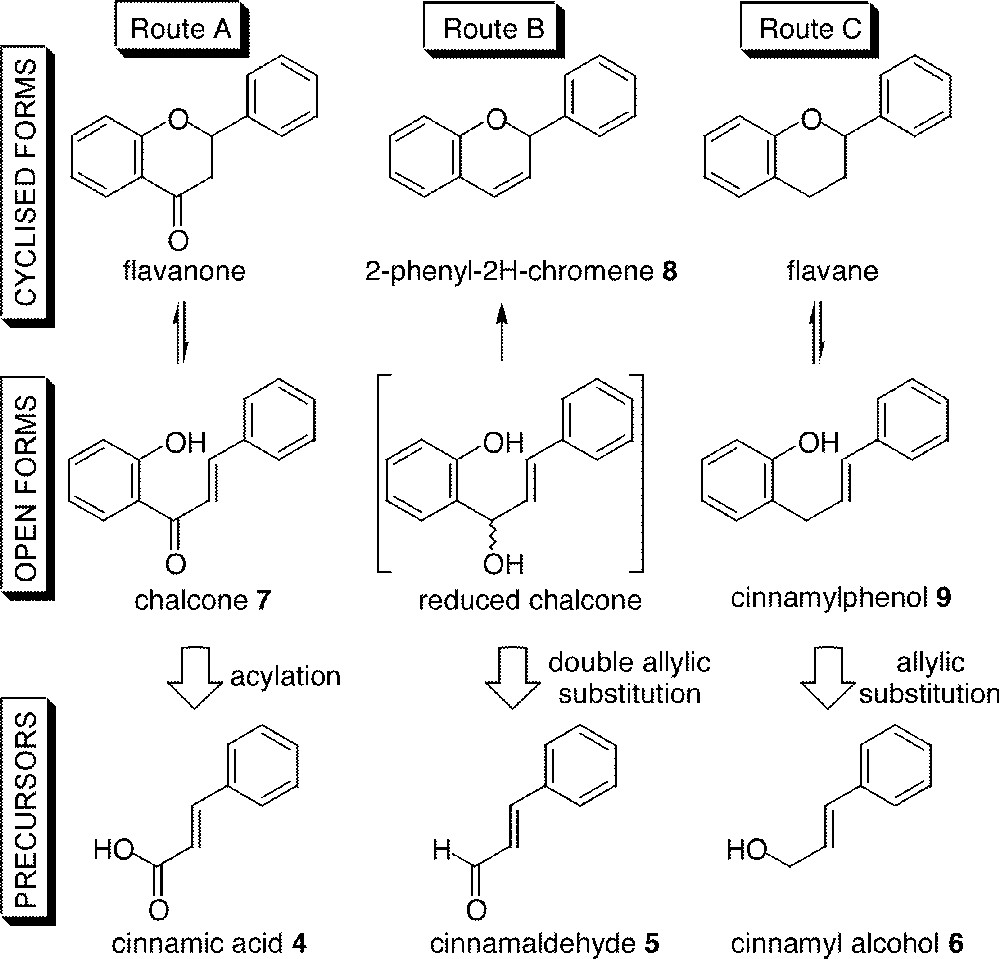
Three alternative routes in the C6–C3–C6 strategy.
In this second strategy (Fig. 2b), the flavonoid skeleton is unravelled into a C6–C2 acetophenone part and a C1–C6 benzaldehyde unit, thanks to a retro-crotonisation operation. This route is used more frequently in the literature and is the result of the easy accessibility of the starting materials (acetophenones and benzaldehydes).
4 The contribution of organometallic chemistry to the C6 + C3-C6 strategy
Among the two possible strategies of synthesis of the C6–C3–C6 flavonoid skeleton, the C6 + C3–C6 ‘biomimetic’ type has often been neglected for the benefit of the C6–C2 + C1–C6 one. Indeed, it involves the difficult arylation step of a cinnamic moiety by a phenolic nucleophile. Some examples have been reported in the literature 〚22–24〛, but they always displayed side-reactions or poor yields when using either a very nucleophilic synthon such as phloroglucinol ring or an electrophilic caffeic acid derivative, and yet both could be turned to good account in an easy access to flavan precursors bearing the hydroxylation pattern of catechin.
As shown in Fig. 3, we can envisage the synthesis of the C6–C3–C6 skeleton thanks to an allylic substitution of a suitable leaving group on a cinnamyl derivative by a phenolic nucleophile (routes B and C). Allylic substitutions are well described in the literature, particularly in organometallic catalysis. Palladium and molybdenum catalysts are often used in such reactions, so we decided to explore their chemistry to reach potential precursors in the synthesis of flavonoids.
4.1 Palladium(0)-catalysed allylic substitutions
This reaction 〚25〛, often referred to as the Tsuji–Trost reaction (Fig. 4) 〚26, 27〛, was chosen to substitute cinnamyl acetate 10 by a phenol, even though aromatic nucleophiles are rare in this kind of substitution 〚28, 29〛.
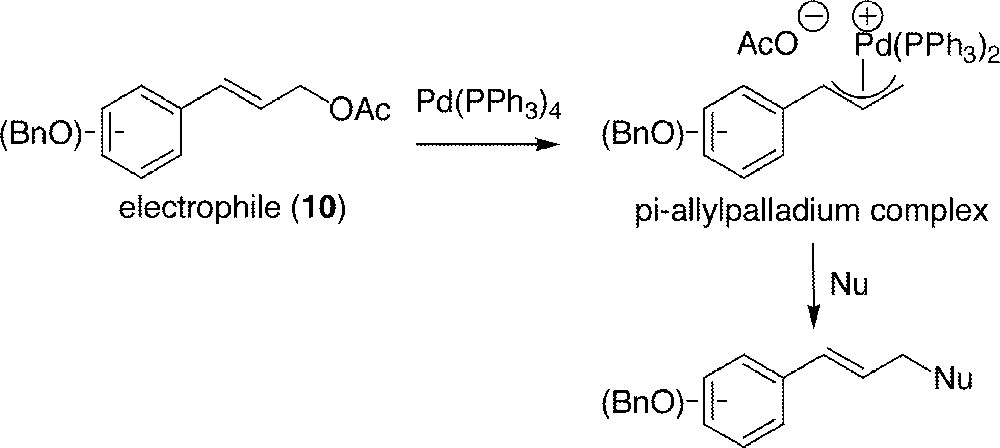
The Tsuji–Trost reaction applied to cinnamyl acetates 10.
All phenols were used under their native form, the protected derivatives being unreactive. Reagents are listed in Figs. 5 and 6. It is noticeable that cinnamaldehyde diacetyl acylal 16 〚30〛 contains two leaving groups, thus being a promising electrophile in front of the doubly nucleophile phloroglucinol 13.
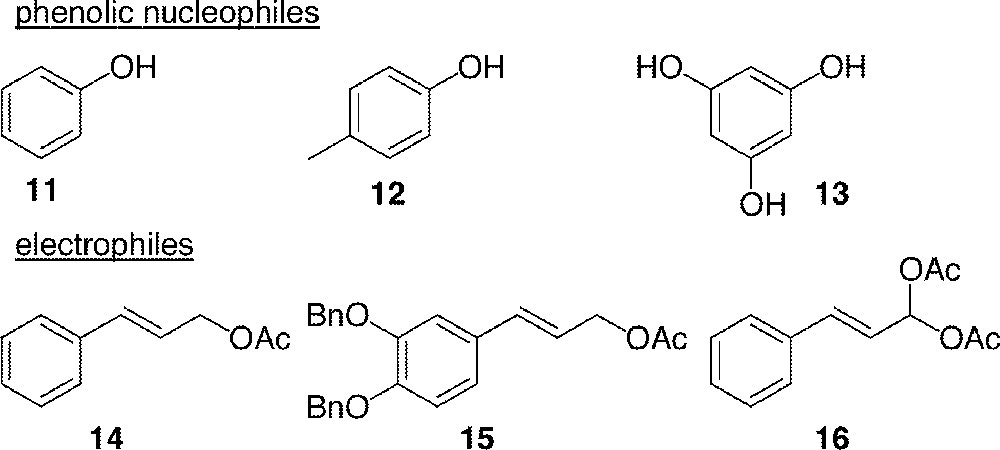
Substrates for the Tsuji–Trost reaction.
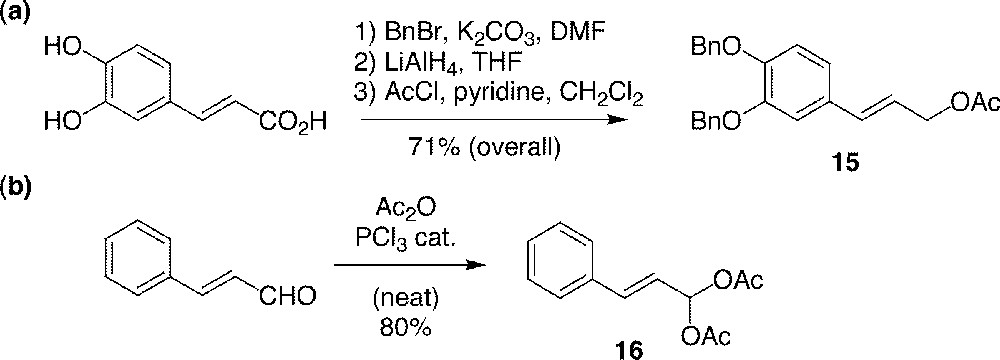
Synthesis of cinnamyl substrates 15 (a) and 16 (b).
Results for the coupling reaction are shown in Table 1 〚25〛. It is noteworthy that simple phenols (entries 1–3) react through their oxygen to form ether 17 or acetals 18–19 with cinnamyl acetate 14 or acylal 16, respectively. On the contrary, phloroglucinol 13 reacts through its nucleophilic carbons in a C–C bond formation, giving the flavonoid skeleton 20–22 (entries 4–6), in spite of disappointing yields.
Results of palladium-catalysed couplings between phenols and cinnamyl acetates (all reactions performed in THF with 10 mol% Pd(PPh3)4 in the presence of K2CO3 except for 13).
A particular interest was found when reacting 13 with acylal 16 (entry 6). This reaction gave a chromene 22, both acetate groups of 16 being substituted, firstly by the aromatic ring and secondly by the phenolic oxygen in a cyclisation step. Possible mechanism is described in Fig. 7a. The yield was low and product 23 very unstable, even in its more manipulable methylated form (22). This was explained by the ability of this 5,7,8a-trihydroxylated chromene to form the highly stabilised allylic cation 24 〚31〛 and/or quinone methide 25 〚25〛 (Fig. 7b). Owing to this instability and to the low yields, this route was not considered for a total synthesis of labelled flavonoids.
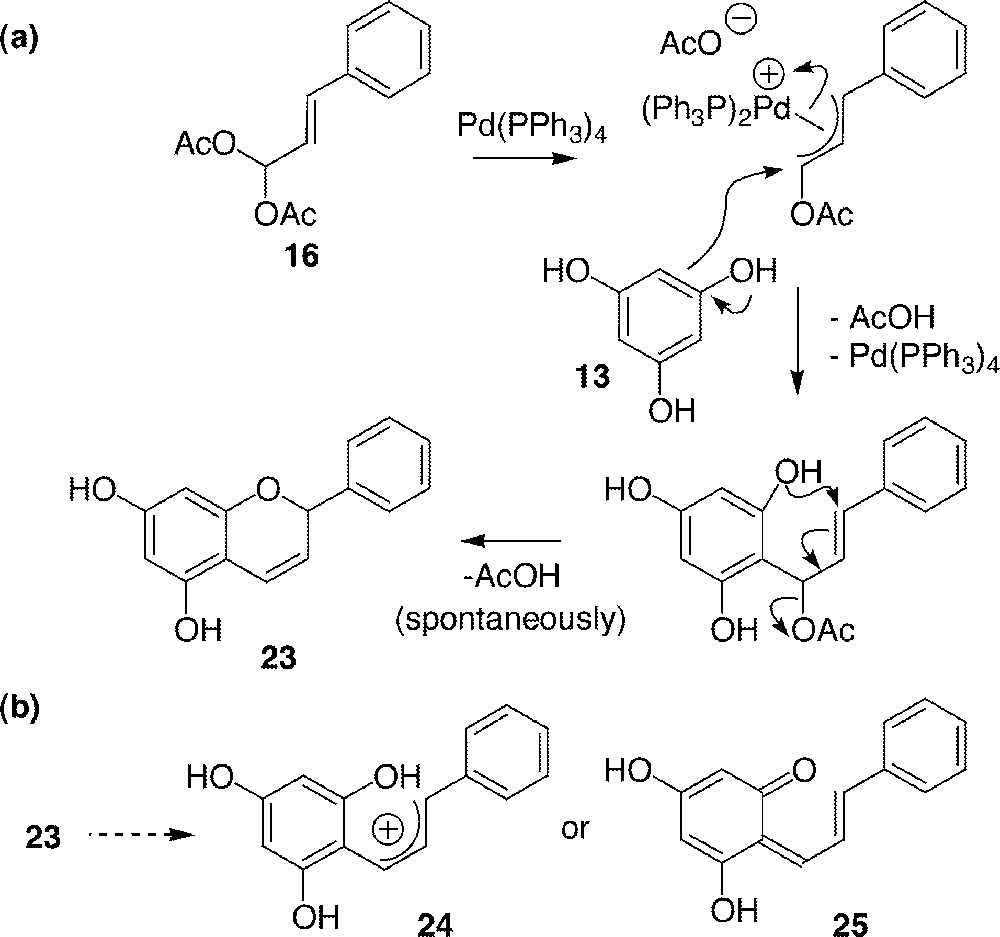
Mechanism of the formation of chromene 23 (a) and rationalisation of its instability (b).
4.2 Molybdenum(IV)-catalysed allylic substitutions
Based on the work of Malkov et al. 〚32〛, we used the catalyst MoIV(acac)2(SbF6)2 to substitute cinnamyl alcohol by phloroglucinol derivatives 〚33〛. This mild Lewis acid catalyst is able to generate smoothly an allylic cation from the corresponding alcohol. Moreover, it is noteworthy that phloroglucinol was expected to be more nucleophilic than simple phenols and that the allylic cation from 3,4-dibenzyloxycinnamyl alcohol could be stabilised by the para alkoxy group.
Results are shown in Table 2. Using simple phenol derivatives, only poor yields and regioselectivities were obtained (not shown). However, phloroglucinol derivatives were more reactive. Free or acetylated phloroglucinol reactions with cinnamyl alcohol yielded only complex mixtures (entries 1 and 2). Phloroglucinol trimethyl ether furnished 30% of the unexpected product 26 from SN2’ substitution (a neoflavonoid skeleton was then built up, entry 3), but when reacted with 3,4-dibenzyloxycinnamyl alcohol (entry 4), the SN2 product 27 was isolated as the major adduct (21% yield). This indicates the possible influence of the substitution pattern of the cinnamic part on the outcome of the reaction.
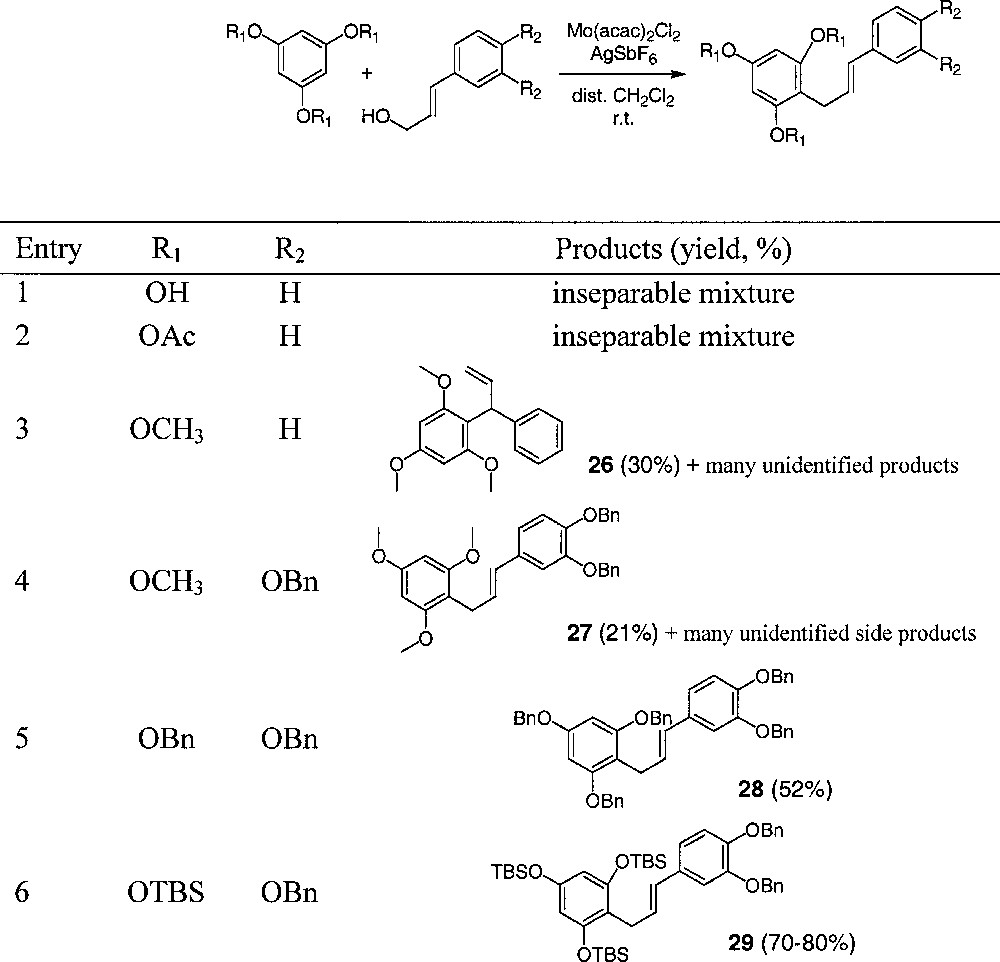
Molybdenum(IV)-catalysed couplings of phenols to cinnamyl alcohols: results.
Phloroglucinol tribenzyl ether gave good yields of the expected product 28 (52%, entry 5), which bears all the oxygens of the catechin series. Finally, phloroglucinol tris〚t-butyl(dimethyl)silyl〛 ether provided product 29 in 70–80% yield (entry 6), which is the best yield of adducts obtained in this study.
Compound 28 was later subjected to asymmetric dihydroxylation. According to Sharpless rules for the use of AD-Mix reagents (Fig. 8a) 〚34, 35〛, product 30 from AD-Mix β oxidation (86% yield) should have occurred with the central hydroxyl group consistent with the (–)-epicatechin configuration (Fig. 8b) 〚36, 37〛. An enantiomeric excess of 50% was found by NMR. This low selectivity was explained by steric hindrance resulting from the conformation of the phloroglucinol ring, which would be perpendicular to the double bond to be oxidised (Fig. 8a). Palladium-catalysed hydrogenolysis in methanol and in the presence of K2CO3 furnished 1,3-diarylpropan-1,2-diol 31 in 56% yield. Unfortunately, all attempts to cyclise this highly hydroxylated product into 1 or 2 under acidic or basic conditions failed.
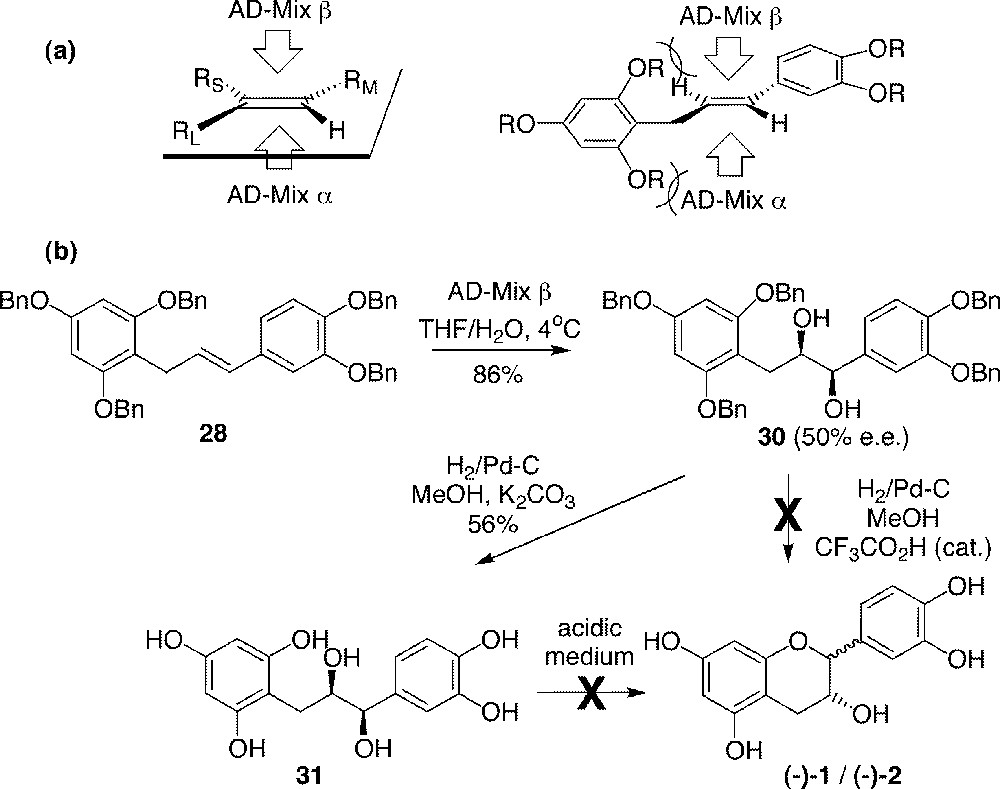
Predicting rules for asymmetric dihydroxylation of 1,3-diarylpropenes (a) and application to 28 (b).
5 Application of the C6 + C3–C6 strategy to the synthesis of an isotopically labelled chalcone intermediate: first route to racemic 4-〚13C〛catechin
Besides the studies of Pd- and Mo-catalysed allylic substitutions, the acylation of protected phloroglucinol by a cinnamic acid to get a chalcone was developed (Fig. 3, route A) 〚38〛.
Phloroglucinol tribenzyl ether 32 can be obtained by two different methods (Fig. 9). The first consists of direct benzylation of phloroglucinol 13, using benzyl bromide in the presence of K2CO3 and in DMSO. The yield was poor, although better than that of the same reaction in DMF, which gave many C-benzylated products. The second method was developed by Kawamoto et al. 〚39〛 and gave good yields of 32 via triacetate 33 without C-benzylation. Therefore, this method was later chosen in order to obtain large quantities of 32.
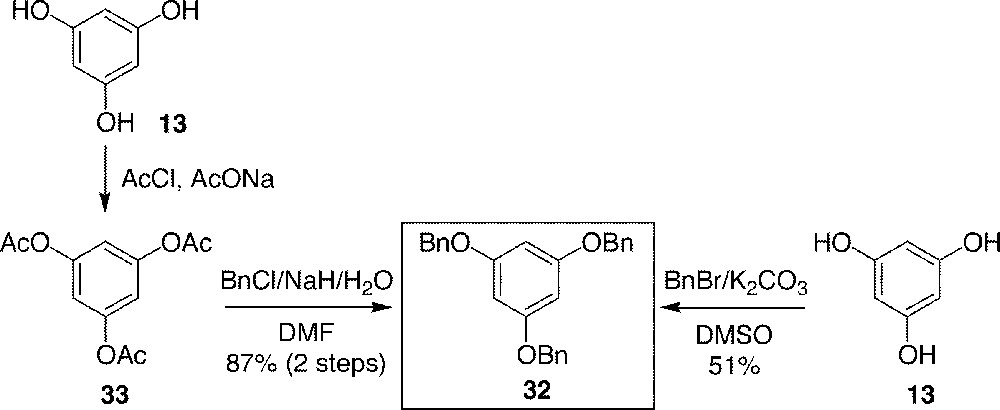
Synthesis of phloroglucinol tribenzyl ether 32.
The cinnamic acid derivative, 3,4-dibenzyloxycinnamic acid 38 from the caffeic acid family, was synthesised from K13CN via 1-〚13C〛acetonitrile 34, which was added to 3,4-dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 35 (Fig. 10). The alcohol 36 was then transformed into acid 38 by dehydration and hydrolysis.
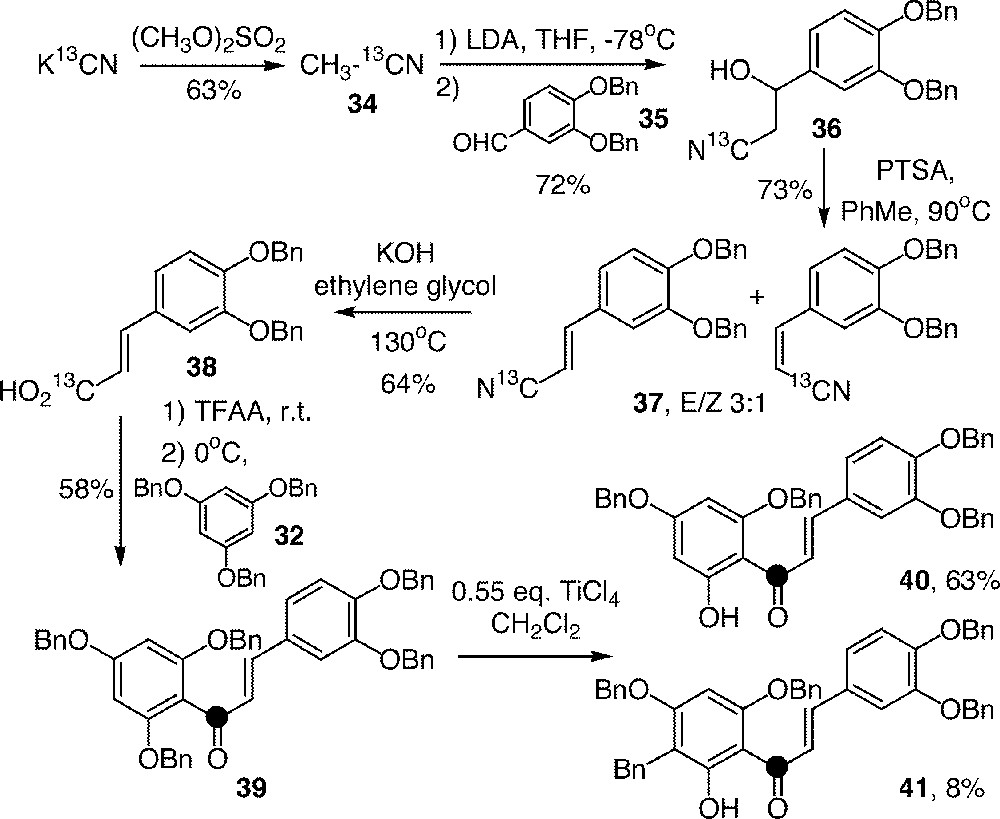
Synthesis of 13C-labelled chalcones from K13CN using the C6 + C3–C6 strategy (the black point figures the carbon 13).
The acylation of 32 by acid 38 was performed using a mixed anhydride formed in situ in the presence of trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFAA) 〚40〛. The yield was rather satisfying if we consider the difficulties that usually arise with other methods during the acylation of the very nucleophilic phloroglucinol derivatives 〚23〛. This reaction provided chalcone 39, which was selectively monodeprotected by TiCl4 to give 40. However, a small amount of the undesired C-benzylated product 41 was formed during this deprotection step by displacement of the benzyl group.
Reduction of hydroxychalcone 40 using NaBH4 followed by BF3–OEt2 catalysed ring closing provided chromene 42 (Clark–Lewis method 〚41, 42〛, Fig. 11). Due to its instability, it was readily dihydroxylated by OsO4 to give 43 in a diastereoselective manner. Flavan-3,4-diol 43, a common derivative in flavonoid chemistry, was deoxygenated on labelled carbon 4, furnishing tetrabenzyl ether 44 of racemic labelled catechin, which was deprotected by palladium-catalysed hydrogenation.
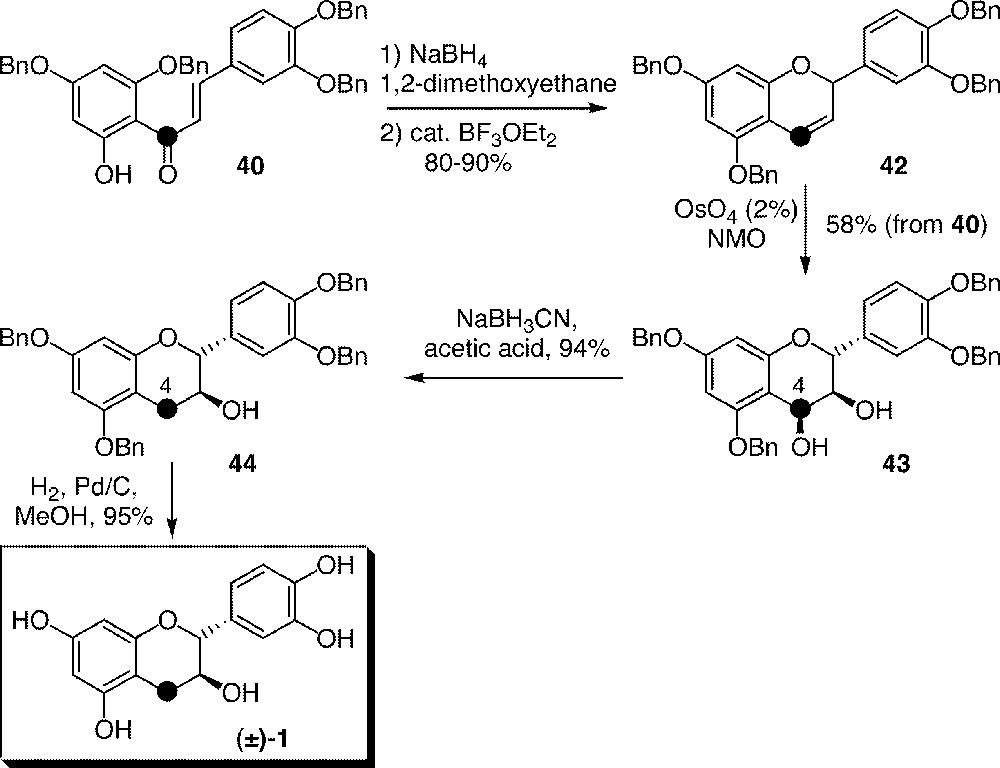
Synthesis of racemic 13C-catechin 1 from chalcone 40: the Clark–Lewis method.
The C6 + C3-C6 strategy allowed us to perform the total synthesis of 40 mg of racemic 4-〚13C〛catechin 1 〚38〛. Nevertheless, we did not consider it convenient enough for a large-scale application and we explored the other strategy as follows.
6 Application of the C6–C2 + C1–C6 strategy to the synthesis of an isotopically labelled chalcone intermediate: first access to 13C-labelled (–)-procyanidin B3
As explained above (Fig. 2), this alternative route consists in the crotonisation of an acetophenone with a benzaldehyde 〚43〛. In our case, 13C-labelled phloroacetophenone derivative 45 was obtained by mean of the acylation of 32, using 1-〚13C〛acetic acid, which was transiently activated with TFAA 〚40〛 (Fig. 12). Compound 45 was then selectively deprotected by TiCl4 as for chalcone 39 〚42〛, giving acetophenone 47, which reacted with benzaldehyde 35, affording chalcone 40 in high yield.
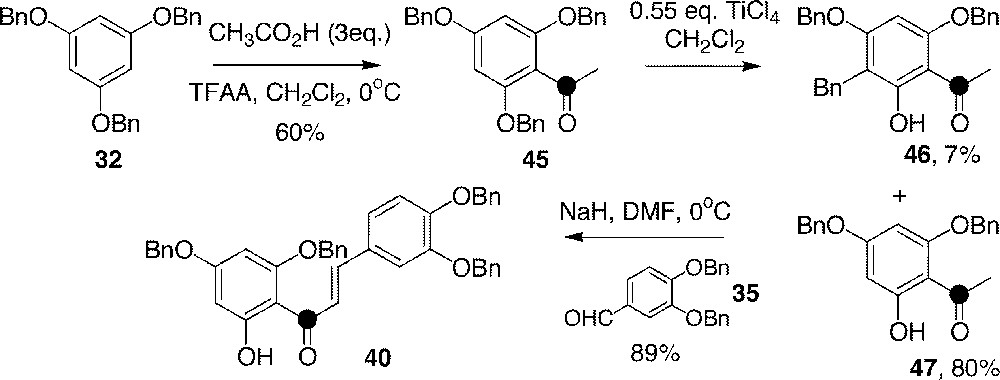
Synthesis of 13C-chalcone 40 using the C6–C2 + C1–C6 strategy.
At this step, the synthesis was joining the route previously described in Fig. 11 to yield flavan-3,4-diol 43. This diol is an interesting precursor of catechin dimers 〚44〛. Indeed, it possesses a good electrophilic carbon on position 4, which can be activated by the use of a Brønsted or a Lewis acid, TiCl4 in the present case, to form the corresponding stabilised benzylic cation. This electrophilic intermediate was trapped by (2R,3S)-tetra-O-benzylcatechin 48, derived from unlabelled natural (+)-catechin 1 and which reacts specifically through its nucleophilic C-8 in the used conditions (Fig. 13). Since diol 43 was racemic and facial selectivity was not complete, four dimeric isomers were obtained from this condensation (two pairs of diastereoisomers): 49 (6%), 50 (13%) and a mixture of two inseparable dimers 51 + 52 (65%, 1:1 ratio) including benzylated dimer B3 (52). Hydrogenolysis of 51 + 52 gave the corresponding procyanidins (53 and 3, 30% yield each from diol 43) and small amounts of catechin due to the reduction of interflavanolic linkage 4C-8D.
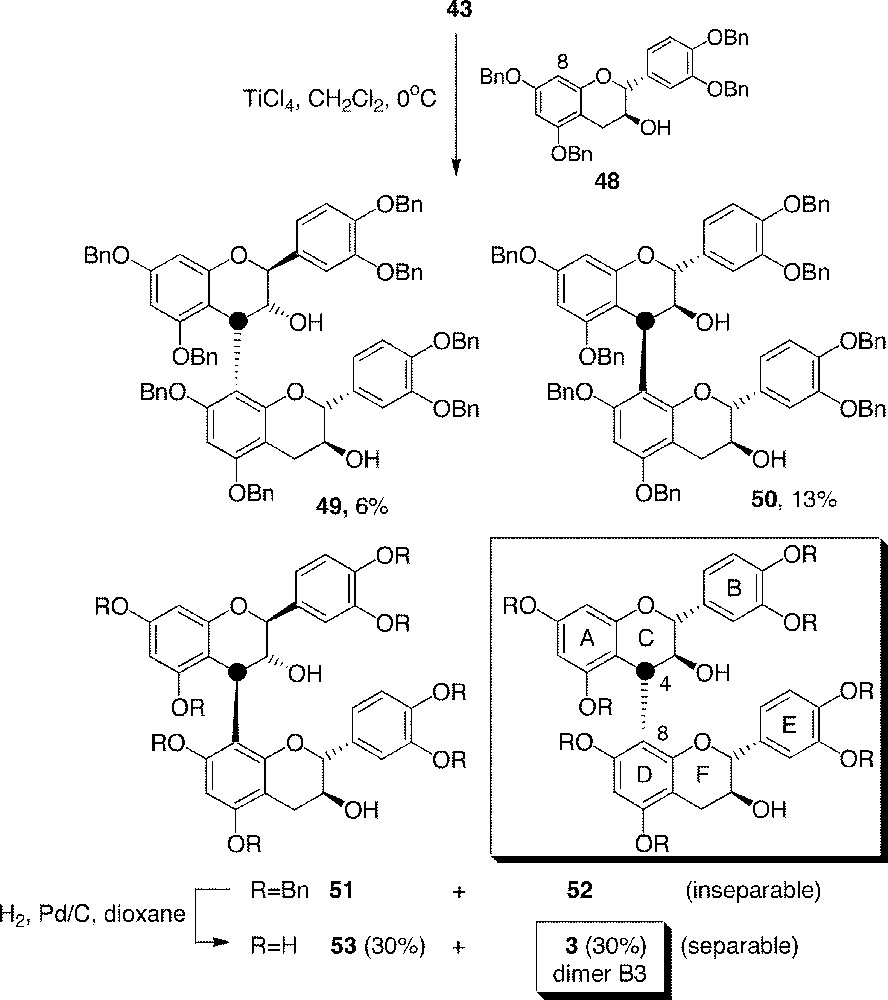
Synthesis of dimer B3 (3) from racemic diol 43.
By this way, 33 mg of (–)-4C-〚13C〛procyanidin B3 dimer 3 were obtained 〚43〛. In comparison with the C6 + C3–C6 route, the C6–C2 + C1–C6 strategy proved to be more convenient, shorter and with better yield. It was later chosen for a gram-scale synthesis. However, the use of racemic derivative diol 43 gave rise to troublesome purification (four stereoisomers), which was particularly unwelcome for preparation on a gram-scale. Furthermore, the use of labelled racemic catechin (±)-1 for studies in human beings was not tolerable, as the non-natural enantiomer ((–)-1) is poorly known on a pharmacological point of view. Therefore, we should synthesise enantiomerically pure derivatives to get rid of these problems. Such requirements were overcome as described in the next part.
7 Catechin, epicatechin, dimer B3: the gram-scale synthesis of optically pure derivatives
7.1 About the asymmetric synthesis of catechin derivatives
Numerous attempts have been made to synthesise catechin derivatives in an asymmetric manner, but all of them failed in our hands. The efficient and outstanding methods developed by Ferreira 〚36, 37〛, Kozikowski 〚31〛 or Chan 〚45〛 were not suitable for the present synthesis. Our failure in epoxidation and dihydroxylation of chalcones 39 and 40 or flavene 42, and asymmetric reduction and cyclisation of chalcone 40 were attributed to the unfavourable electronic properties of the double bond of interest. Indeed, it is strongly influenced by the vicinity of phloroglucinol ring and the multiple resonance forms it is able to induce. Especially in the case of flavene 42, no chirality could be detected after reactions in asymmetric conditions. The one eventually formed would be shattered by equilibrium of 42 with the open forms 54 〚31〛 and/or 55 〚25〛 (Fig. 14).
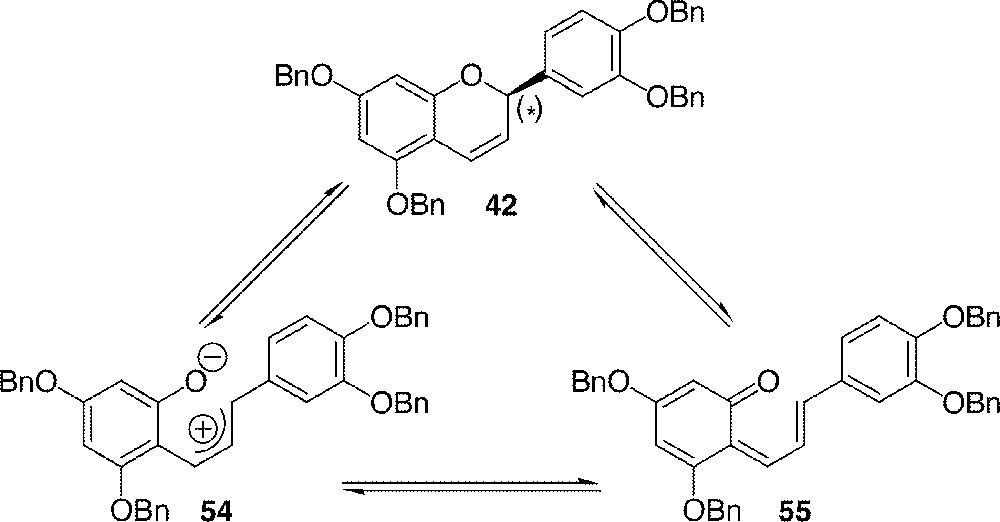
Rationalisation for the difficult use of 42 in asymmetric synthesis of flavonoids.
7.2 Resolution of racemic catechin derivatives
To circumvent the difficulties experienced in asymmetric synthesis, we rather chose to investigate some resolution processes on our racemic compounds. We found that coupling racemic benzylated catechin 44 to a chiral derivative (Fig. 15) provided an easy access to enantiomerically pure products 〚46〛.
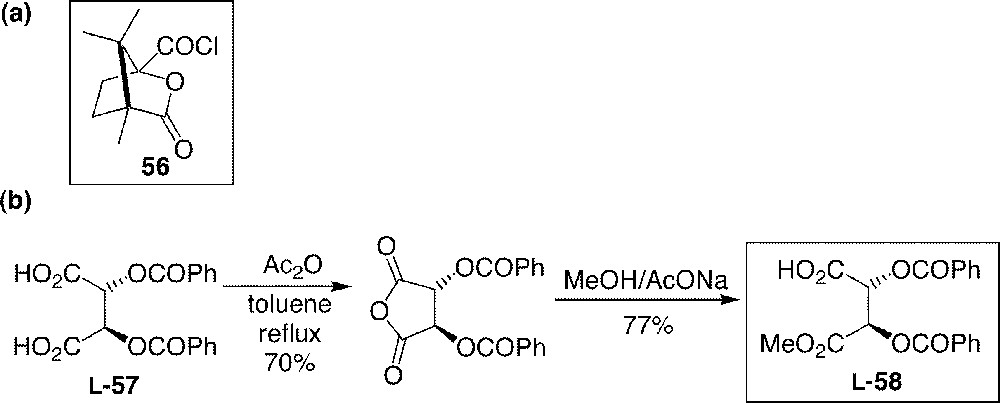
Chiral reagents chosen for the resolution of 44.
Benzylated catechin 44 was first esterified with commercially available (–)-(1S)-camphanyl chloride 56, giving two stereoisomeric compounds in a 1:1 ratio. Although these products were distinguished by analytical HPLC, they were neither separable by column chromatography nor by preparative HPLC. Alternatively, compound 44 was esterified by chiral tartaric acid derivative L-58 (Fig. 16), which was easily synthesised from commercially available dibenzoyl-L-tartaric acid L-57 (Fig. 15b). Here again, no satisfactory chromatographic separation was found for a preparative purpose, even by HPLC. However, we could enjoy the fact that an abandoned solution (hexane/dichloromethane 4:1) was found crystallised after three days. Analysis of the crystals and comparison with those reproduced from natural (+)-catechin showed that the natural enantiomer of benzylated catechin 44 esterified by the acid L-58 had crystallised. Therefore, from the solution of (–)-59 and (–)-60 (1:1 ratio) in hexane/dichloromethane 4:1, (–)-59 was able to crystallise selectively and with > 99% d.e. after recrystallisation from the same solvent. The other isomer (–)-60 did not crystallise and gave colourless oil, with 70–83% d.e., upon concentration of mother liquids.
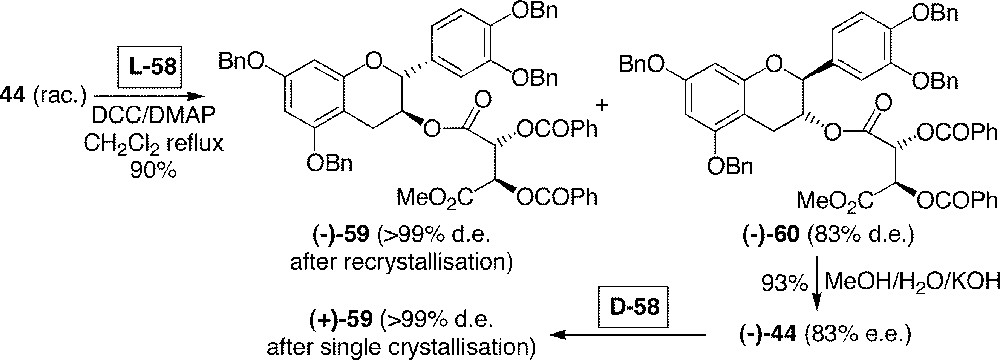
Resolution process of 44 using tartaric acids L-58 and D-58.
After hydrolysis of (–)-59 and hydrogenolysis, (+)-catechin 1 was obtained in more than 99% e.e. 〚46〛 and displayed all the spectrometric and optical data of the natural product. This method provided an efficient way of preparation of (+)-catechin and proved to be applicable on a large scale.
7.3 Gram-scale synthesis of (+)-4-〚13C〛catechin and (–)-4-〚13C〛epicatechin
Based on the results obtained when applying the C6–C2 + C1–C6 strategy 〚43〛 and the resolution of racemic catechin 〚46〛, we have been able to perform the gram-scale synthesis of asymmetric 〚13C〛flavan-3-ols with the aim of their use in biomedical studies 〚47〛.
Labelled racemic compound 44 (25 g) was synthesised according to Fig. 12 and 13, starting from 117 g of 32. Application of the resolution process outlined in Fig. 16 allowed us to obtain each enantiomer of 44 with > 99% enantiomeric excess. Particularly, the antipodes (non natural configuration) of (+)-catechin derivatives were attained after hydrolysis of oily ester (–)-60 (83% e.e.) and then esterification with the antipodal D-tartaric acid D-58, reaching crystallisable ester (+)-59 of (–)-catechin.
We took benefit of both enantiomers to synthesise labelled catechin 1 and epicatechin 2 with natural configurations. (+)-〚13C〛Catechin tetrabenzyl ether (+)-44 yielded 3.6 g of (+)-4-〚13C〛catechin (+)-1 in >99% e.e. after deprotection (Fig. 17a). (–)-4-〚13C〛Epicatechin (–)-2 (1.3 g, >99% e.e.) could be obtained from deprotection of (–)-44 to (–)-4-〚13C〛catechin (–)-1 and then epimerisation at carbon 2 in Na3PO4 buffer (pH 11.4), taking care of the strict absence of oxygen during this reaction (Fig. 17b). The gram-scale synthesis of labelled flavan-3-ols (about 7 g altogether) has been performed in 8% global yield from starting material 32.
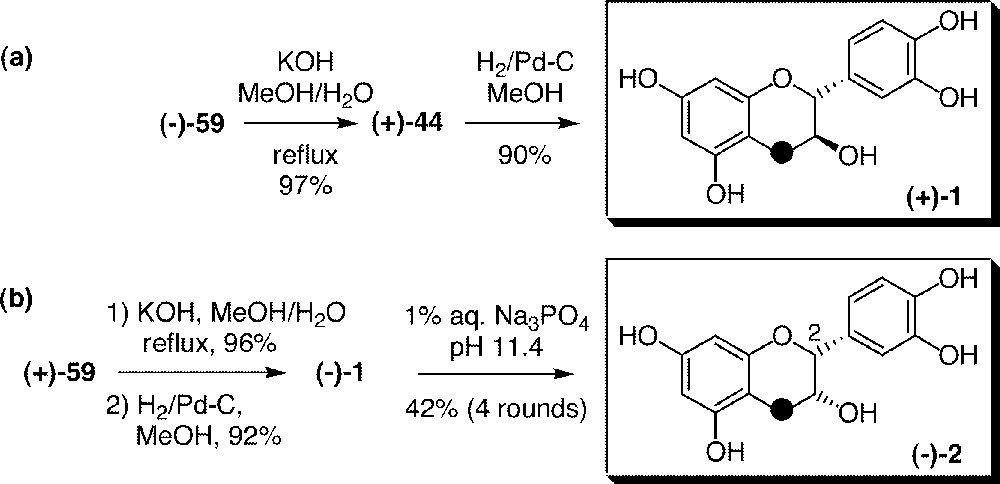
Access to optically pure labelled catechin 1 and epicatechin 2.
7.4 Gram-scale synthesis of 4C-〚13C〛procyanidin B3
As shown in section 6, the synthesis of dimers on a gram-scale was compromised by the use of racemic diol 43, which caused difficult purification due to the four stereoisomers formed. After reducing diol 43 to 44 and by mean of resolution, enantiomerically pure methylated diol (+)-61 could be obtained after reoxidation of (+)-catechin derivative (+)-44 on benzylic carbon 4 (Fig. 18). Then (+)-61 was condensed to (+)-catechin tetrabenzyl ether 48 in the presence of TiCl4, providing two stereoisomers, 50 and 52, instead of four. Consequently, purification was easily carried out before deprotection and the yield was not lowered by stereoisomeric dilution. This approach allowed us to complete the synthesis of 1.5 g of stereomerically pure (–)-4C-〚13C〛procyanidin B3 (–)-3 〚48〛.
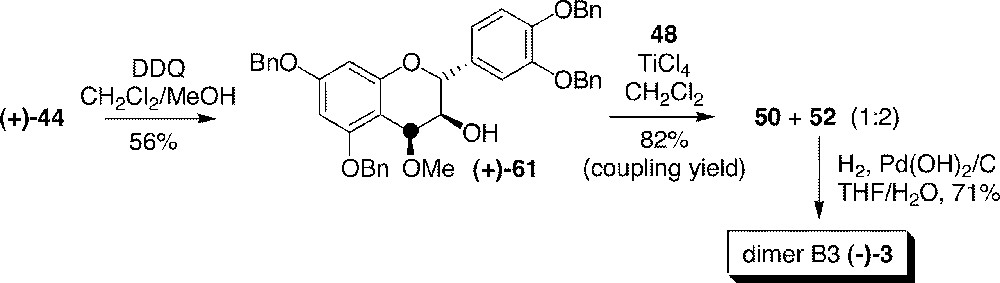
Access to gram amounts of (–)-4C-〚13C〛procyanidin B3 (3).
8 Conclusion
The gram-scale synthesis of 13C-labelled (+)-catechin 1, (–)-epicatechin 2 〚47〛 and (–)-procyanidin B3 3 〚48〛 has been successfully achieved using the C6–C2 + C1–C6 strategy 〚43〛 and an efficient method of resolution of racemic benzylated catechin 44 〚46〛. Thanks to their carbon 13 that does not have the toxicity of its radioactive isotopes, these natural products of the food are now used in vivo in pharmacokinetic studies in human beings. Natural amounts have been incorporated in red wine and swallowed at mealtime. Carbon-13 can serve to trace the compounds and their metabolites using isotopic mass spectrometry without interfering with unlabelled flavonoids of the diet, in order to quantify the data.
This study should let us know how much of the food flavonoids pass through the intestinal wall after a meal. By the end, we should be able to see if these polyphenolic compounds reach the required blood concentration to fully exert their biological activities, thus confirming (or refuting) their involvement in such epidemiological observations, as low incidence of degenerative diseases, or French paradox, in some populations.
Acknowledgements
We thank the ‘Région Aquitaine’ (France) and the French MRT for financial supports. B.N. acknowledges receipt of a scholarship from the MRT. We are particularly grateful to Miss Amanda Royle for her kind help concerning English language.



