1 Introduction
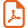
Functionalized H-phosphinates are important intermediates for the synthesis of a variety of biologically active compounds including disubstituted phosphinic acids, and phosphonic acids. Our laboratory has been interested in developing the chemistry of hypophosphorous compounds and we recently reported a novel Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction with hypophosphites as nucleophiles (Eq. (1)) [1,2]. The products of these reactions can be purified by extraction or then esterified for subsequent manipulations [3,4]. However, in some cases, it would be more convenient if the H-phosphinate ester could be obtained directly so that a separate esterification step is avoided, especially when the purification of the intermediate acid is particularly difficult. Schwabacher and coworkers first reported on the cross-coupling reaction of methyl and t-butyl phosphinates with aryl iodides that directly provides H-aryl phosphinate esters (Eq. (2)) [5,6]. However, the reaction is limited by the reactivity of the electrophile due in large part to the competing thermal decomposition of the alkylphosphinates [5]. Thus, only a handful of aryl iodides have been coupled successfully thus far.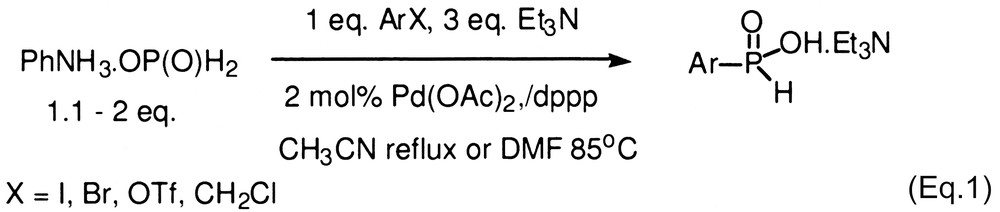
We have also reported a novel method for the synthesis of alkylphosphinates and under the reaction conditions, these compounds decomposed only slowly even over prolonged heating [7]. This opened the possibility to expand the scope of the Schwabacher reaction to a significant extent. Herein, we report on the successful cross-coupling reactions of alkyl phosphinates with aromatic and heteroaromatic electrophiles to form previously inaccessible H-phosphinates, in a single step.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Cross-coupling with anilinium hypophosphite, alkoxysilanes, and a base
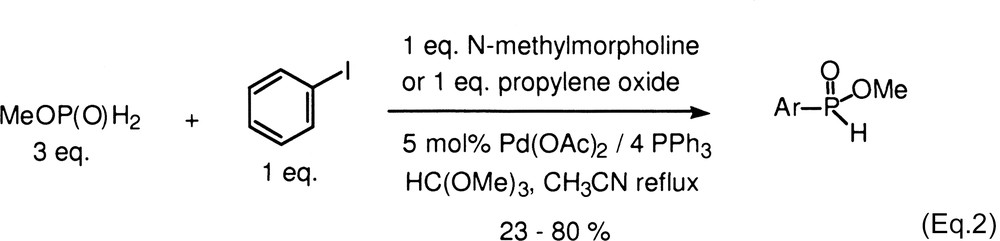
Hypophosphorous compounds are strong reducing agents, particularly under the influence of transition metals (see, for example, [8]). In previous studies, we found that cross-coupling can be conducted and the competing reduction largely suppressed, by selecting the ligand and reactions conditions [1]. For difficult cases (substrates in which oxidative addition into the C–X bond is slow) the best ligands were dppp [1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane] and dppf [1,1′-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene], whereas PPh3 worked well with iodides. In reactions with anilinium hypophosphite, the base was Et3N but even pyridine could be used. [1] With alkylphosphinates, we found that DABCO [1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane] was satisfactory for a wide range of electrophilic substrates. Thus the reaction of an aryl (or heteroaryl) electrophile (1 equiv) with an alkylphosphinate (3 equiv, generated in situ from anilinium hypophosphite and a silicate) and DABCO (3 equiv) proceeds in moderate to good isolated yield with Pd(OAc)2/dppp (2 mol%) as the catalyst (Eq. (3), Table 1). For benzylic substrates, a ligand switch from dppp to dppf is necessary.
Direct cross-coupling of aryl/heteroaryl electrophilesa
| Entry | ROP(O)H2, R = | Ar–X | Solvent | 31P NMR yield,%b (isolated yield, %) |
| 1 | Bu | C6H5–I | CH3CN | 100 (80)c |
| 2 | Et | C6H5–I | PhCH3 | 96 (61) |
| 3 | Bu | 2-MeC6H4–I | CH3CN | 100 (83) |
| 4 | Bu | 4-MeOC6H4–I | CH3CN | 99 (78) |
| 5 | Bu | 2-BrC6H4–I | CH3CN | 72 |
| 6 | Bu | 3-ClC6H4–I | CH3CN | 95 (63) |
| 7 | Bu | 4-BOCNHC6H4–I | CH3CN | 90 (82) |
| 8 | Bu | 3-I–pyridine | CH3CN | 85 (64) |
| 9 | Bu | 4-I–pyrazole | CH3CN | 72 |
| 10 | Bu | 2-I–thiophene | CH3CN | 42 (36) |
| 11 | Et | C6H5–Br | PhCH3 | 40 |
| 12 | Et | naphthyl-2–Br | PhCH3 | 96 (69) |
| 13 | Et | naphthyl-2–Br | CH3CN | 48 |
| 14 | Bu | naphthyl-2–Br | PhCH3 | 84 |
| 15 | Bu | naphthyl-2–Br | CH3CN | 78 |
| 16 | Bu | naphthyl-2–Br | DMF | 80 |
| 17 | Bu | 3-Br–quinoline | DMF | 76 (65) |
| 18 | Bu | 4-Br-isoquinoline | DMF | 100 (78) |
| 19 | Bu | N-BOC-5-Br–indole | DMF | 50 (33) |
| 20 | Bu | 4-NCC6H4Br | DMF | 75 (51) |
| 21 | Et | 4-NCC6H4Br | DMF | 78 |
| 22 | Et | C6H5–OTf | PhCH3 | 66 |
| 23 | Bu | C6H5–OTf | DMF | 74 |
| 24 | Bu | naphthyl-1–OTf | DMF | 100 (80) |
| 25 | Bu | 4-MeOOCC6H4–OTf | DMF | 95 |
| 26 | Bu | C6H5CH2Cl | CH3CN | 100 (88)d |
| 27 | Bu | 3-ClCH2pyridineHCl | CH3CN | 60 (46)d,e |
| 28 | Bu | 2-ClCH2pyridineHCl | CH3CN | 38 (24)d,e |
a See Eq. (3). For a representative procedure, see appendix. New compounds gave satisfactory spectral data.
b NMR yields are determined by integrating all the signals in the spectrum. Isolated yields are of purified products (> 95%) after chromatographic purification.
c See reference [7], Et3N was used.
d dppf was employed in the place of dppp.
e 4 equiv DABCO were used.
While our original cross-coupling with anilinium hypophosphite [1] is successful on the substrates shown in Table 1 [9], a two-step process where the cross-coupling product is subsequently esterified can be problematic, particularly with nitrogen-containing compounds. This is because the purification of these H-aminophosphinic acid salts intermediates would require cumbersome ion-exchange chromatography, while the direct esterification [3] of the crude reaction mixture is inefficient and inconvenient. For example, cross-coupling of 3-bromoquinoline following the conditions of Eq. (1), and subsequent treatment with tetrabutoxysilane (after solvent removal but without prior work-up) in refluxing toluene for 24 h only gave a 25% yield of the corresponding butyl ester (compare with entry (17)). Similarly, a multistep approach relying on the ‘Ciba-Geigy synthon’ (Eq. (4)) does not allow the selective cleavage of the acetal group without affecting the phosphinic ester [10]1
With ethyl phosphinate, toluene was the solvent of choice for the cross-coupling reaction (entry 12 versus 13), while butyl phosphinate was more generally useful and could be employed in either toluene, acetonitrile, or DMF (entries 14–16). Methyl phosphinate however generally only reacted well with aryl iodides and Et3N as the base. Aryl iodides are good substrates (entries 1–7) and the yields are as high or higher than those reported by Schwabacher [5].
However, Schwabacher's conditions were not tested on heterocyclic substrates, and they fail with aryl bromides and triflates [5,6]. Thus our conditions have a much broader scope, and several types of aromatic electrophiles can now be employed for the first time. Heterocyclic iodides and bromides (entries 8–10, and 17–19), aryl bromides (entries 11–16, and 20–21), aryl triflates (entries 22–25), and benzylic chlorides (entries 26 and 28), all reacted in acceptable yields. For bromides and triflates, DMF was the solvent of choice. The ratio of alkyl phosphinate, DABCO, and electrophile (3:3:1, respectively) is also important, and cannot be lowered without a significant loss of yield. For hydrochloride substrates, 4 equiv of DABCO are required. Unsurprisingly, aryl chlorides are unreactive under the present conditions, and it is apparent that new catalyst systems will have to be investigated to solve this problem.
Some aryl bromides (bromobenzene, 3-bromofuran, and 4-bromoanisole) are poor substrates in this reaction (for example, see entry 11), and the reason for this is unclear at this time. The rate of oxidative addition into the unactivated C–Br bond likely plays a major role [1] since aryl triflates or more electron-deficient bromides are acceptable substrates (entries 20–25). However, in our original coupling (Eq. (1)) no significant differences were observed between aryl bromides and triflates when anilinium hypophosphite was employed as the cross-coupling partner [1]. This suggests that the mechanistic details of the present reaction may be more complicated than a straightforward coupling of DABCOH3PO2 1 as the nucleophile followed by in situ esterification with the silicate (Scheme 1, path a). Preliminary experiments in fact do indicate that the reaction may proceed in a multistage pathway involving coupling of DABCOH3PO2, but it is not clear at this time why certain bromides do not react well. In addition, a DABCO salt of H-phosphinic acid 2 prepared separately is not esterified efficiently with silicates [3,9], suggesting the importance of all the components of the reaction mixture, possibly including DABCOHX which forms in the cross-coupling mixture. A two-step protocol (Scheme 1, path b), in which the alkylphosphinate 3 is first formed then coupled, gave results comparable to the one-pot reaction only when some water was present, suggesting the necessity to hydrolyze ROP(O)H2 2 to a hypophosphite salt 1 which then reacts according to path a. The direct coupling of alkylphosphinates (path b) appears to be operating only when Et3N and aryl iodides are employed [7], and the specific role played by the base must also be elucidated. A more detailed investigation is currently in progress in order to understand the mechanistic subtleties of this reaction.
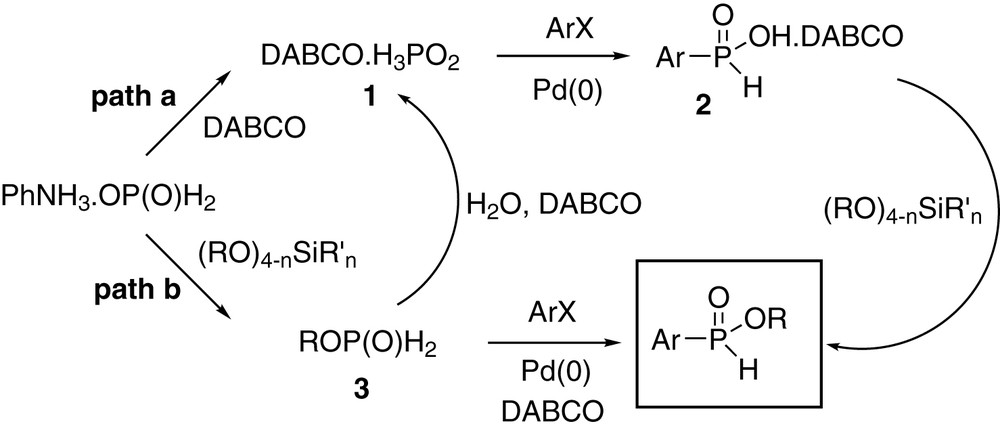
Mechanistic pathways.
2.2 Cross-coupling with anilinium hypophosphite and aminotrialkoxysilanes
We also hoped to develop a method which would facilitate the purification procedure even more, since H-phosphinates are in general polar, easily hydrolyzed compounds which can be difficult to purify in high yields by chromatography over silica gel. We reasoned that commercially available aminotrialkoxysilanes could combine in a single molecule both the silicate moiety necessary for esterification, and the base required in the catalytic cycle. A simple aqueous-organic extractive work-up would then allow the removal of the silicon-derived by-products from the desired H-phosphinate, thereby providing the crude product in much higher purity. Primary amines have rarely been used as the base in cross-coupling reactions. However, our cross-coupling did occur successfully (Eq. (5)). A preliminary investigation shows that this method is promising (Table 2), but further studies will be required to determine the scope of this reagent system. Interestingly, a nearly stoichiometric ratio of reagents is sufficient to deliver the cross-coupling product in good yield. One thing that should be pointed out is that aminotrialkoxysilanes cannot be employed with substrates containing a basic nitrogen, since extractive work-up would then be useless. Nonetheless, this system offers advantages for the preparation of products that could be pure enough for further use without the need for chromatography.
3 Conclusions
The preparation of H-phosphinic esters via metal-catalyzed cross-coupling provides many advantages over circuitous multistep approaches. In this paper, we have described a general synthesis that is applicable to a variety of electrophilic substrates, including triflates, bromides, and benzylic chlorides that had never before been employed successfully. Thus, a wide variety of aromatic and heteroaromatic H-phosphinates are now accessible. Preliminary results show that the reaction can also be conducted with commercially available aminopropyltrialkoxysilanes that then play both the role of base and esterifying agent. Under these conditions, a simple extraction protocol provides the coupled products in good purity. The initial impetus for the present study was to access synthons for the preparation of novel GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) analogs with potential biological activity. Entries 7–9, 17–19, and 27–28 (Table 1) are representative of such compounds [11], and further work along these lines, including extension to other interesting electrophiles will be presented in due course. Full mechanistic studies and further reaction developments will be reported in a forthcoming full paper. Finally, the direct formation of H-arylphosphinate esters is a requirement for the development of an asymmetric coupling (using either a chiral catalyst, or a chiral phosphinate auxiliary) since H-phosphinic acids and their salts are achiral. Efforts toward the synthesis of such P-chiral H-phosphinate esters are also underway.
4 Appendix: representative experimental procedure
4.1 Typical experimental procedure (Table 1, entry 17)
To a solution of 3-bromoquinoline (0.425 g, 2 mmol), (BuO)4Si (1.923 g, 6 mmol) in DMF (12 ml), were added anilinium hypophosphite (0.955 g, 6 mmol), DABCO (0.676 g, 6 mmol), Pd(OAc)2 (0.009 g, 0.04 mmol), and dppp (0.018 g, 0.044 mmol), and the resulting mixture was heated at 85 °C for 2 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo, the residue was treated with brine (15 ml) and extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 20 ml). The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated. Purification by flash chromatography (hexane/EtOAc 7:3, v/v, EtOAc) afforded butyl quinolin-3-yl phosphinate (0.322 g, 65% yield).
4.2 NMR yield determination
NMR yields were determined by integration of all the 31P signals in the crude reaction mixture before work-up. All the signals are assigned and a typical spectrum shows ROP(O)(H)R′, ROP(O)H2, (RO)2P(O)H (from the decomposition of the alkyl phosphinate), MH3PO2 (where M is the base), while the symmetrical phosphinate ROP(O)R′2 is usually not observed. All phosphorus species present are easily assigned based on chemical shifts and coupling constants. Previous work with H-phosphinates shows that these NMR yields are reproducible and accurate within 10% of the reported value. The difference between NMR and isolated yields does not reflect measurement error but rather the difficulty in the purification of highly polar and easily hydrolyzed H-phosphinate esters, so that isolated yields are often 10–20% lower than the NMR yields.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgments are made to the NSF (CHE-0242898), the donors of the Petroleum Research Fund administered by the ACS (36915-AC1), and the Robert A. Welch Foundation (P-1435) for the generous support of this research.
1 Froestl et al. [11] reported on the inability to form the product of Table 1, entry 28 by esterification of the corresponding H-phosphinic acid). The preparation of ethyl alkyl-H-phosphinates typically required a separate reesterification step with EtOC(O)Cl. Ethyl aryl-H-phosphinates were prepared from ArPCl2 and EtOH.