1 Introduction
Polydentate ligands combining sp2-hybridized nitrogen and σ3-λ3-phosphorus atoms continue to play an increasing role in homogeneous catalysis and have already found numerous applications in processes of synthetic importance such as allylic substitution [1–4], hydrosylilation [5,6], transfer hydrogenation of ketones [7–9], hydroboration of olefins [10–13], olefin/CO copolymerization [14–20]... Though many different types of heteroditopic PN ligands with various backbones have already been synthesized and evaluated [21–28], significant efforts have still to be achieved in the design of new structures that will allow us to rationalize and to finely tune the influence of steric and electronic effects. So far, most of the efforts focused on the derivatization of the nitrogen moiety and only a few variations have been achieved around the phosphine substituent, which, in most cases, is acyclic [20,29–33]. Recently we launched a program aimed at exploring syntheses and applications of mixed PN ligands incorporating a phosphole ligand and a nitrogen heterocycle. A first encouraging result was obtained during the study of the (2,5-diphenylphospholyl)-2-methylpyridine ligand 1 [34]. This easily available ligand, which exhibits a remarkable stability toward air oxidation, was found to be particularly efficient in the ruthenium-catalysed transfer hydrogenation of ketones (TON up to 20 × 106).
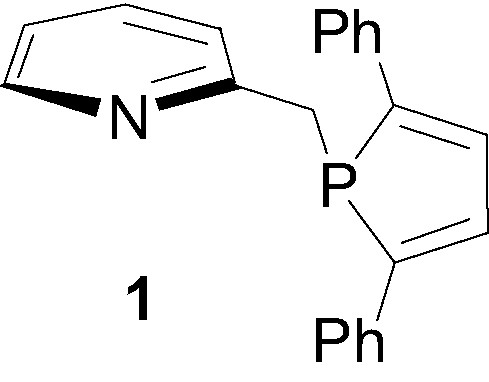
This first result prompted us to investigate more thoroughly the field of application of these mixed (2,5-diphenylphospholyl)-based PN systems. Herein, we report on the synthesis and the catalytic activity of PdCl2 complexes of this ligand and one of its oxazoline analogue.
2 Results and discussion
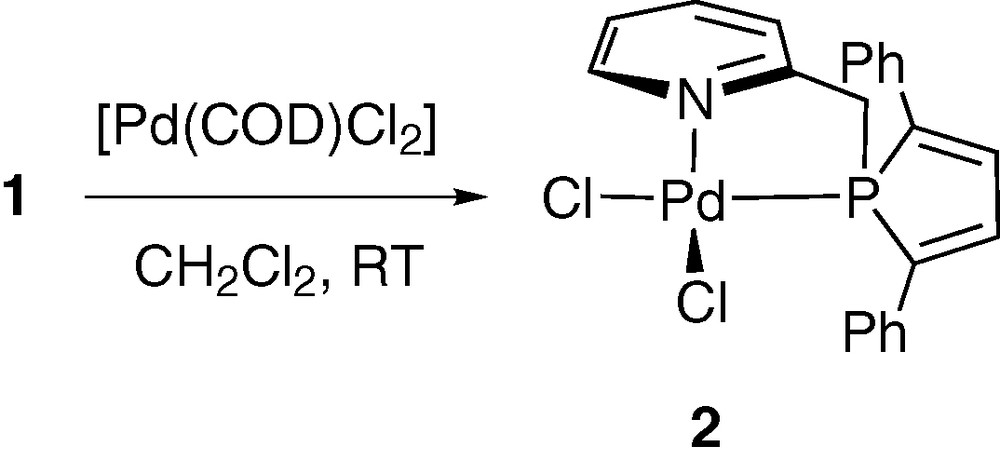
Ligand 1 readily reacts with [PdCl2(COD)] in dichloromethane at room temperature to afford complex 2, which was isolated as an orange powder (Scheme 1). All NMR data (31P, 1H, 13C) confirmed the formulation proposed. In 31P NMR, the coordination of the phosphole unit moiety is evidenced by a downfield shift of 36.5 ppm (δ(1) in CDCl3 = –0.2 ppm).
Additional evidence of the structure of 2 was given by an X-ray crystal structure analysis. Suitable crystals of 2 were obtained by diffusing hexane into a dichloromethane solution of the complex. An ORTEP view of one molecule of 2 is presented in Fig. 1. Crystal data are summarized in Table 1 and selected bond lengths and bond angles are collected in Table 2. As expected for Pd complex having the d8 electronic configuration, the overall geometry around palladium is square planar and nitrogen and phosphorus atoms adopting a cis-arrangement.
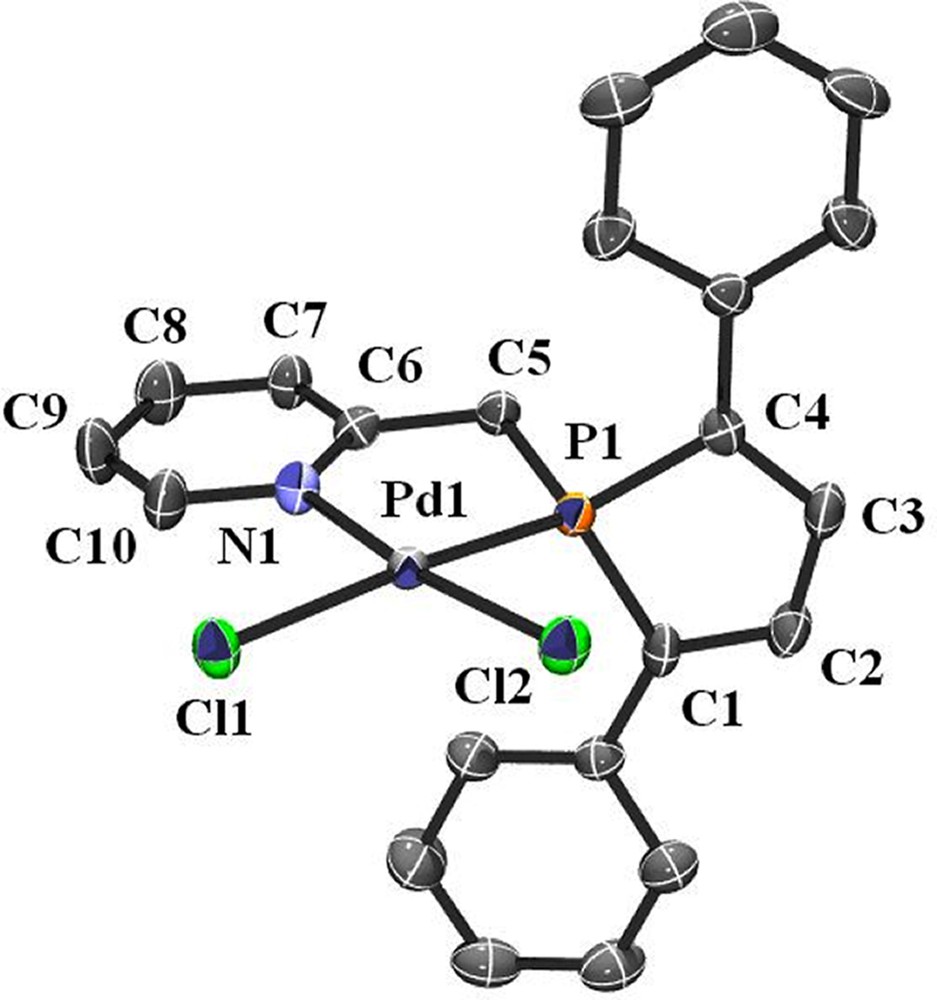
ORTEP view of one molecule of 2. Ellipsoids are scaled to enclose 50% of the electron density. The numbering is arbitrary and different from that used in the assignment of NMR spectra.
Crystal data and structural refinement details for 2
| Molecular formula | C23H20Cl4NPPd |
| Molecular weight | 589.57 |
| Crystal habit | orange plate |
| Crystal dimensions (mm) | 0.10 × 0.06 × 0.04 |
| Crystal system | orthorhombic |
| Space group | Pna21 |
| a (Å) | 15.559(5) |
| b (Å) | 11.267(5) |
| c (Å) | 13.438(5) |
| V (Å3) | 2355.7(16) |
| Z | 4 |
| d (g cm–3) | 1.662 |
| F(000) | 1176 |
| μ (cm–1) | 1.321 |
| Absorption corrections | multiple scans; 0.8793 min, 0.9491 max |
| Maximum θ | 27.46 |
| hkl ranges | –20 20; –14 14; –16 17 |
| Reflections measured | 8840 |
| Unique data | 5136 |
| Rint | 0.0316 |
| Reflections used | 4331 |
| Criterion | > 2 σ(I) |
| Refinement type | Fsqd |
| Hydrogen atoms | mixed |
| Parameters refined | 272 |
| Reflections / parameter | 15 |
| wR2 | 0.0925 |
| R1 | 0.0383 |
| Flack's parameter | –0.02(4) |
| Weights a, b | 0.0441; 0.0000 |
| GoF | 1.031 |
| difference peak/hole (e Å–3) | 0.913(0.103)/–0.933(0.103) |
Relevant distances (Å) and bond angles (°) in compound 2
| Pd1–N1 | 2.078(3) |
| Pd1–P1 | 2.190(1) |
| Pd1–Cl2 | 2.287(1) |
| Pd1–Cl1 | 2.375(1) |
| P1–C4 | 1.798(5) |
| P1–C5 | 1.827(4) |
| P1–C1 | 1.822(4) |
| C1–C2 | 1.358(6) |
| C2–C3 | 1.426(6) |
| C3–C4 | 1.364(6) |
| C5–C6 | 1.493(6) |
| C6–C7 | 1.381(6) |
| C7–C8 | 1.390(6) |
| C8–C9 | 1.379(7) |
| C9–C10 | 1.372(6) |
| N(1)–Pd(1)–P(1) | 84.2(1) |
| N(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(2) | 172.1(1) |
| P(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(2) | 88.24(5) |
| N(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 96.2(1) |
| P(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 175.40(5) |
| Cl(2)–Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 91.54(5) |
| C(4)–P(1)–C(1) | 94.1(2) |
| C(4)–P(1)–C(5) | 107.5(2) |
| C(1)–P(1)–C(5) | 113.4(2) |
| C(4)–P(1)–Pd(1) | 123.4(2) |
| C(1)–P(1)–Pd(1) | 115.4(2) |
| C(5)–P(1)–Pd(1) | 103.2(1) |
The catalytic activity of complex 2 was tested in three cross coupling reactions: the Heck [35], Suzuki [6,36–38] and Miyaura processes [39]. Modest yields and TON were obtained in the two first transformations. Thus, in the Suzuki coupling between bromoacetophenone and phenylboronic acid (in toluene under reflux), a conversion yield of 61% was obtained after 2 h heating using 1.10–3% of catalyst (TON = 61 × .103). Although this performance is reasonable, this TON does not compare with the best systems reported to date involving palladacycles [40,41]. Using the same loading of catalyst, bromobenzene reacted with styrene in the Heck coupling to yield stilbenes (ratio between Z and E not measured) with a 31% yield after 15 h of heating at 80 °C (TON = 31 × 103) in dioxanne in the presence of triethylamine as base. Other solvents such as NMP, DMF, MeCN were also tested but did not yield improvements in terms of TON. Here again the catalytic activity of complex 2 proved to be modest by comparison with other systems [40,41]. Most interestingly, catalyst 2 proved to be very efficient in the Miyaura cross-coupling reaction that furnishes arylboronic esters. Nearly complete conversion and high TON (up to 1 × 105) were obtained in the coupling of pinacolborane with iodoaromatics (see Table 3) after 48 h of heating in dioxanne at 80 °C using Et3N as a base (Scheme 2). The conversion of some bromoaromatics was also attempted. Though lower conversion yields and TON (up to 9 × 103) were obtained under the same experimental conditions, catalyst 2 still proved to be highly active compared to reported systems [42–45].
Cross-coupling reaction between iodo and bromoarenes with pinacolborane using complex 2 as catalyst in dioxanne at 80 °C
| Ar–X | t | % cat. | Yield | TON |
| C6H5I | 48 h | 0.001% | 100 | 100 × 103 |
| p-IC6H5OMe | 48 h | 0.001% | 91 | 91 × 103 |
| o-IC6H4OMe | 48 h | 0.001% | 97 | 97 × 103 |
| o-IC6H4Me | 48 h | 0.001% | 99 | 99 × 103 |
| C6H5Br | 40 h | 0.01% | 71 | 71 × 102 |
| p-BrC6H5COMe | 40 h | 0.01% | 61 | 61 × 102 |
| o-BrC6H4OMe | 40 h | 0.01% | 90 | 90 × 102 |
| o-BrC6H4Me | 40 h | 0.01% | 79 | 79 × 102 |
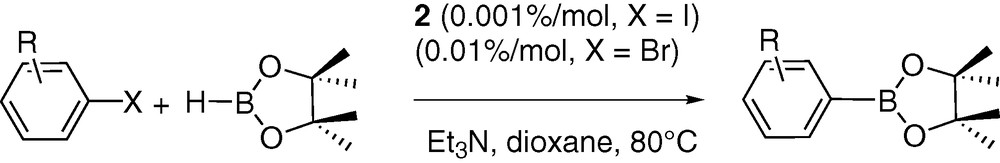
As a logical extension, we then turned our attention to the synthesis of optically active ligands featuring the 2,5-diphenylphosphole unit. The availability of numerous functional oxazolines prompted us to investigate the synthesis of a 2-methyl substituted derivative analogous to ligand 1. It must be noted that some oxazoline–phosphole-based ligands have already been reported, but with different backbones [46–48]. The synthetic strategy used is similar to that employed in the synthesis of 1. The 2-chloromethyl-5R-oxazoline was reacted with one equivalent of the 2,5-diphenylphospholide ligand in THF at room temperature (Scheme 3). Compound 3 was isolated after conventional work-up as an air-stable yellow solid. The formulation of 3 was confirmed by NMR spectroscopy, elemental analyses and X-ray crystallography. An ORTEP view of one molecule of 3 is presented in Fig. 2. Crystal data are summarized in Table 4 and selected bond lengths and bond angles are collected in Table 5.
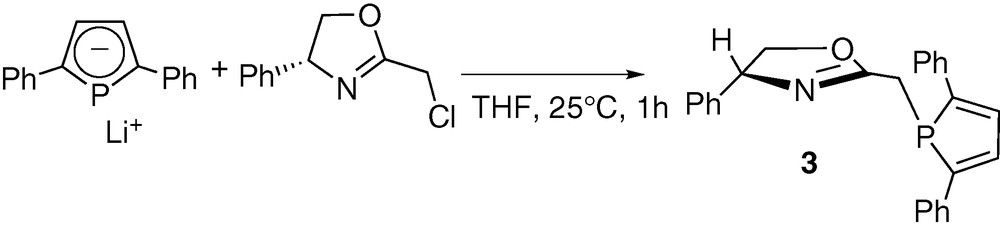
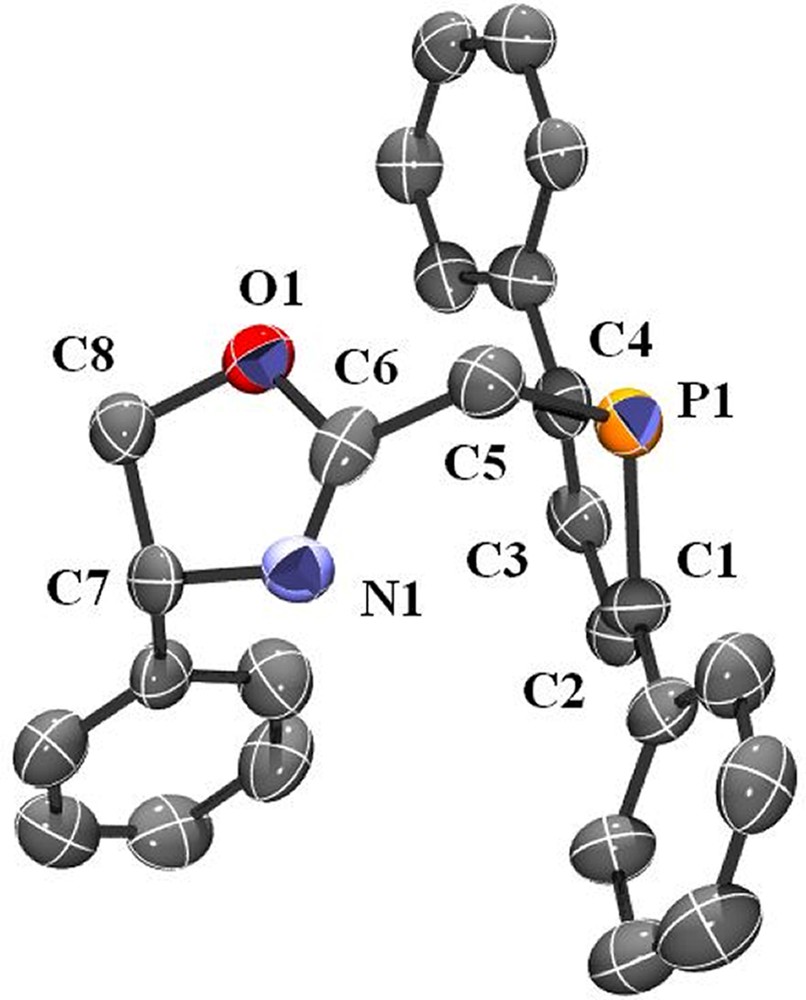
ORTEP view of one molecule of ligand 3. Ellipsoids are scaled to enclose 50% of the electron density. The numbering is arbitrary and different from that used in the assignment of NMR spectra.
Crystal data and structural refinement details for 3, 4
| 3 | 4 | |
| Molecular formula | C26H22NOP | C26H22Cl2NOPPd |
| Molecular weight | 395.42 | 572.72 |
| Crystal habit | colourless plate | orange plate |
| Crystal dimensions (mm) | 0.16 × 0.12 × 0.02 | 0.12 × 0.12 × 0.02 |
| Crystal system | monoclinic | orthorhombic |
| Space group | P21 | P212121 |
| a (Å) | 7.5430(10) | 7.0520(10) |
| b (Å) | 18.4450(10) | 10.6860(10) |
| c (Å) | 15.0630(10) | 30.7330(10) |
| β (°) | 102.4800(10) | |
| V (Å3) | 2046.2(3) | 2314.0(4) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| d (g cm–3) | 1.284 | 1.643 |
| F(000) | 832 | 1152 |
| μ (cm–1) | 0.151 | 1.121 |
| Absorption corrections | multiple scans; 0.9762 min; 0.9970 max | multiple scans; 0.8772 min; 0.9779 max |
| Maximum θ | 21.03 | 24.09 |
| hkl ranges | –7 7; –18 17; –15 15 | –8 5; –11 12; –35 30 |
| Reflections measured | 7390 | 9448 |
| Unique data | 4150 | 3605 |
| Rint | 0.0664 | 0.0597 |
| Reflections used | 2563 | 2698 |
| Criterion | > 2 σ(I) | > 2 σ(I) |
| Refinement type | Fsqd | Fsqd |
| Hydrogen atoms | mixed | mixed |
| Parameters refined | 523 | 289 |
| Reflections/parameter | 4 | 9 |
| wR2 | 0.0893 | 0.0697 |
| R1 | 0.0448 | 0.0388 |
| Flack's parameter | –0.07(18) | –0.03(4) |
| Weights a, b | 0.0000; 0.0000 | 0.0170; 0.0000 |
| GoF | 0.877 | 0.965 |
| difference peak/hole (e Å–3) | 0.172(0.048)/–0.191(0.048) | 0.594(0.086)/–0.554(0.086) |
Relevant distances (Å) and bond angles (°) in compound 3
| P1–C1 | 1.782(8) |
| C1–C2 | 1.38(1) |
| C2–C3 | 1.45(1) |
| C4–C4 | 1.35(1) |
| P1–C5 | 1.845(8) |
| C5–C6 | 1.49(1) |
| C6–O1 | 1.374(8) |
| C6–N1 | 1.27(1) |
| O1–C8 | 1.466(8) |
| C8–C7 | 1.53(1) |
| N1–C7 | 1.50(1) |
| C1–P1–C4 | 92.3(4) |
| C1–P1–C5 | 107.0(4) |
| C4–P1–C5 | 108.7(4) |
| C6–O1–C8 | 105.2(6) |
| C1–N1–C7 | 106.0(6) |
| C1–C1–P1 | 108.4(7) |
| C1–C2–C3 | 113.8(7) |
| C4–C3–C2 | 115.5(7) |
| C3–C4–P1 | 107.6(6) |
Ligand 3 was conventionally converted into the [PdCl2(3)] complex 4 in 94% yield, by reaction with an equimolar amount of [PdCl2(COD)] in dichloromethane at room temperature (Scheme 4). All NMR data support the formulation proposed. Like for complex 2, coordination of the phosphole ligand results in a 31P NMR downfield shift of Δδ = +29.6 ppm.
Single crystals of 4 were obtained by diffusing hexanes into a dichloromethane solution of the complex at room temperature. An ORTEP view of one molecule of 4 is shown in Fig. 3. Crystal data are summarized in Table 4 and selected bond lengths and bond angles are collected in Table 6. As expected, complex 4 adopts a square planar geometry and, apart from the N1–Pd1 bond length, which is slightly shortened (2.016(5) Å in 4 vs 2.078(3) Å in 2), metric parameters within the metallacycle are quite similar to those of complex 2 (bite angle in 2: 84.2(1)° and 4: 83.6(2)°).
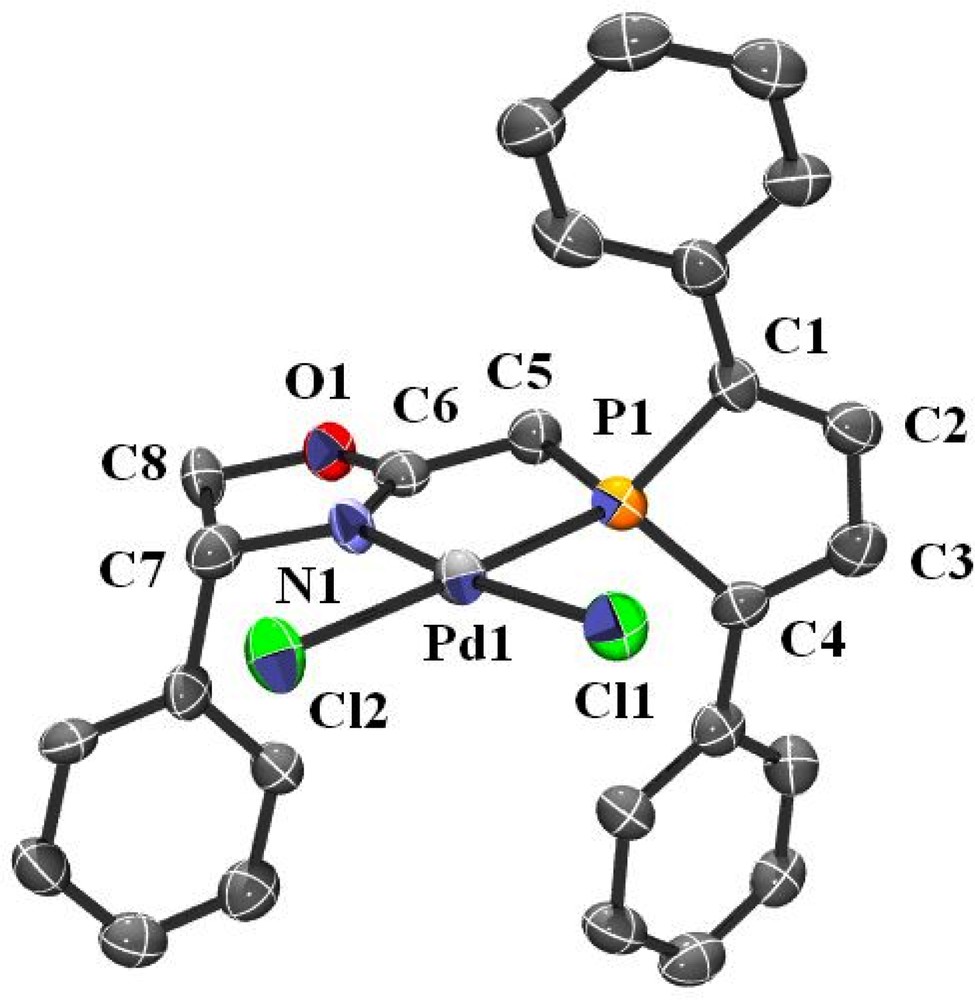
ORTEP view of one molecule of complex 4. Ellipsoids are scaled to enclose 50% of the electron density. The numbering is arbitrary and different from that used in the assignment of NMR spectra.
Relevant distances (Å) and bond angles (°) in compound 4
| Pd(1)–N(1) | 2.016(5) |
| Pd(1)–P(1) | 2.197(2) |
| Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 2.287(2) |
| Pd(1)–Cl(2) | 2.330(2) |
| P(1)–C(4) | 1.799(6) |
| P(1)–C(1) | 1.801(6) |
| P(1)–C(5) | 1.857(6) |
| O(1)–C(6) | 1.338(7) |
| O(1)–C(8) | 1.464(6) |
| N(1)–C(6) | 1.286(7) |
| N(1)–C(7) | 1.502(7) |
| C(1)–C(2) | 1.346(8) |
| C(1)–C(15) | 1.450(8) |
| C(2)–C(3) | 1.446(8) |
| C(3)–C(4) | 1.368(7) |
| C(5)–C(6) | 1.473(8) |
| C(7)–C(9) | 1.523(8) |
| C(7)–C(8) | 1.538(8) |
| C(9)–C(10) | 1.385(8) |
| N(1)–Pd(1)–P(1) | 83.6(2) |
| N(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 172.2(2) |
| P(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(1) | 88.62(6) |
| N(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(2) | 94.4(2) |
| P(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(2) | 177.87(7) |
| Cl(1)–Pd(1)–Cl(2) | 93.44(6) |
| C(4)–P(1)–C(1) | 94.5(3) |
| C(4)–P(1)–C(5) | 106.3(3) |
| C(1)–P(1)–C(5) | 108.3(3) |
| C(4)–P(1)–Pd(1) | 122.4(2) |
| C(1)–P(1)–Pd(1) | 120.7(2) |
| C(5)–P(1)–Pd(1) | 103.7(2) |
| C(6)–O(1)–C(8) | 104.7(5) |
| C(6)–N(1)–C(7) | 107.7(5) |
| C(6)–N(1)–Pd(1) | 122.0(4) |
| C(7)–N(1)–Pd(1) | 130.1(4) |
| C(2)–C(1)–C(15) | 129.3(6) |
| C(2)–C(1)–P(1) | 106.2(5) |
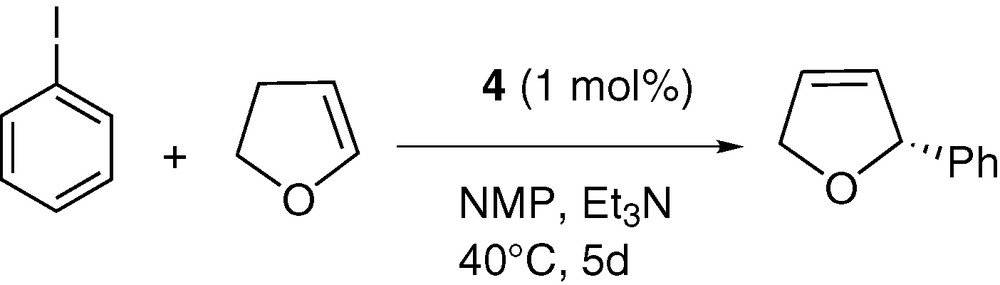
The catalytic activity of complex 4 was tested in the asymetric Heck coupling process between iodobenzene and 2,3-dihydrofuran. All the experiments were carried out in benzene or N-methylpyrrolidinone (NMP) between 40 and 60 °C using 0.1 or 1% of catalyst in the presence of triethylamine as base to yield the 2-phenyl-2,5-dihydrofuran (2-phenyl-2,3-dihydrofuran was also detected as traces < 2% in each experiment). All these results are summarized in Table 7. As can be seen, shorter reaction times and good conversion yields were obtained when NMP was used as solvent but no ee was recorded suggesting that NMP can displace the oxazoline ligand from the palladium centre. More convincing results were obtained when benzene was used as solvent, but the transformation proved to be sluggish. Thus an ee of 89% was obtained (with a 67% yield) after 5 days of heating at 40 °C with 1% of catalyst. As expected, increasing the temperature results in a significant acceleration but to the detriment of the ee. A comparison of these results with literature data clearly show that performances of catalyst 4 are modest compared to other systems (Scheme 5) [32,49–52].
Asymmetric coupling between iodobenzene and 2,3-dihydrofuran using complex 4 as catalyst
| % cat. | Solvent | Base | T (°C) | t | Yield (%) | ee (%) |
| 0.1 | NMP | Et3N | 60 | 1 d | 92 | 0 |
| 1 | NMP | Et3N | 60 | 15 h | 96 | 0 |
| 0.1 | NMP | Et3N | 40 | 3 d | 91 | 0 |
| 1 | C6H6 | Et3N | 60 | 2 d | 95 | 49 |
| 1 | C6H6 | Et3N | 40 | 5 d | 67 | 89 |
| 1 | C6H6 | i-PrNEt2 | 60 | 1 d | 89 | 54 |
In conclusion, we have shown that the [PdCl2(L)] (L = 2,5-(diphenylphospholyl)-2-methylpyridine) complex 3 efficiently catalyses the cross-coupling reaction between pinacolborane and iodo- and bromoarenes. On the other hand, the [PdCl2(L)] (L = 2-methyl-5R-phenyloxazoline-2,5-diphenylphosphole) complex 4 yielded disappointing results in terms of enantioselectivity in the asymmetric Heck coupling reaction between iodobenzene and the 2,3-dihydrofuran. Further work will now focus on the synthesis of differently substituted oxazoline-based derivatives of this 2,5-diphenylphosphole and their systematic evaluation in catalytic transformations.
3 Experimental section
All reactions were routinely performed under an inert atmosphere of argon or nitrogen by using Schlenk and glove-box techniques and dry deoxygenated solvents. Dry THF, ether, dioxanne, hexanes and toluene were obtained by distillation from Na/benzophenone and dry CH2Cl2 and CDCl3 from P2O5. Dry CD2Cl2 was distilled and stored, like CDCl3, on 4-Å Linde molecular sieves. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectra were recorded on a Bruker Advance 300 spectrometer operating at 300 MHz for 1H, 75.5 MHz for 13C and 121.5 MHz for 31P. Solvent peaks are used as internal reference relative to Me4Si for 1H and 13C chemical shifts (ppm); 31P chemical shifts are relative to a 85% H3PO4 external reference and coupling constants are expressed in Hertz. The following abbreviations are used: b, broad; s, singlet; d, doublet; t, triplet; m, multiplet; p, pentuplet; sext, sextuplet; sept, septuplet; v, virtual. Mass spectra were obtained at 70 eV with a HP 5989B spectrometer coupled to a HP 5980 chromatograph by the direct inlet method. In the Heck coupling reactions, the ee was determined with a Perichrom PR2100 gas chromatograph equipped with a Lipodex A column. Elemental analyses were performed by the ‘Service d’analyse du CNRS', at Gif-sur-Yvette, whereas [PdCl2(COD)] [53] and triphenylphosphole [54] were prepared according to literature procedures. All other reagents and chemicals were obtained commercially and used as received.
3.1 Synthesis of complex [PdCl2(3)] 2
Phosphole 1 (98 mg, 0.3 mmol) was added to a solution of [PdCl2(COD)] (85 mg, 0.3 mmol) in dichloromethane (3 ml). After strirring for 10 min at room temperature, 31P NMR spectroscopy showed the complete conversion of 1 into complex 2. The solvent was evaporated and the red powder obtained was washed three times with hexanes (3 × 10 ml) to remove 1,5-cyclooctadiene. After drying under vacuum complex 2 crystallized in a mixture of dichloromethane hexanes to afford small red crystals. Yield: 145 mg (96%). 31P NMR (CDCl3, 25 °C): δ 36.3; 13C NMR (CDCl3, 25 °C): δ 33.4 (d, 1JPC = 21.7, CH2), 121.5–138.6 (C of phenyl groups and C3,4,5 of pyridine), 135.5 (d, 2JPH = 2.9 Hz, Cβ), 137.5 (d, 1JPC = 17.2 Hz, Cα of phosphole), 149.6 (s, C2 of pyridine), 153.3 (d, 2JPC =5.2 Hz, C6 of pyridine); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 25 °C): δ 3.37 (d, 2JPH = 25.9 Hz, 2H, CH2), 7.12–7.35 (m, 11 H, Hβ of phosphole, H2, H4 of phenyl and H3, H4 and H5 of pyridine), 7.44 (dd, 3JHH = 8.2 Hz, 3JHH = 7.1 Hz, 4H, H3 of phenyl), 8.03 (d, 3JHH = 4.8 Hz, 1H, H6 of pyridine). Anal. calcd for C22H18NP: C, 52.36; H, 3.59. Found: C, 52.78; H, 3.51.
3.2 General procedure for the coupling between pinacolborane and iodo and bromoaromatics
Pinacolborane (2.4 mmol), the halogenoaromatic (iodo or bromo derivative) (1.6 mmol) and triethylamine (4.8 mmol) were successively added to a solution of catalyst 2 (0.001% for iodo- and 0.01% for bromo derivatives) in distilled dioxanne (10 ml). The reaction mixture was heated at 80 °C and the progress of the reaction was monitored by GC. At the end of the reaction, the solvent was evaporated and diethylether (10 ml) was added. After filtration and washing of the ammonium salts with ether (2 × 10 ml), the solvent was evaporated. Then, the oily residue obtained was purified by column chromatography using silicagel (previously treated with a mixture of hexanes Et3N (95:5)). The boronic ester was eluted with hexane as solvent. Formulations of boronic esters were confirmed by comparison of 1H and 13C NMR data with reported data.
3.3 Synthesis of ligand 3
One equivalent of 2-chloromethyl-5R-oxazoline (1.176 g, 6 mmol) was added to a solution of anion 1 (6 mmol) in THF (50 ml) at 25 °C. After stirring for 1 h at room temperature, a 31P NMR spectrum of the crude mixture showed the complete conversion of anion 1 into 3. After evaporation of the solvent, ligand 3 was extracted with dry ether (4 × 20 ml) and obtained as a very air-stable yellow powder. (Traces of oxide can be detected if the complex stands for several hours in chlorinated solvents such as chloroform and dichloromethane in the presence of air.) Yield: 2.374 g (85%); 31P NMR (CD2Cl2, 25 °C): δ –9.0 ; 13C NMR (CD2Cl2, 25 °C): δ 25.5 (d, 1JPC = 23.4 Hz, PCH2); 70.4 (CH); 75.1 (OCH2); 127.5–133.2 (m, C of phenyl groups), 137.1 (d, 2JPC = 15.8 Hz, Cα of phosphole), 137.2 (d, 2JPC = 15.8 Hz, Cα of phosphole), 142.7 (CH of phenyl groups), 151.7 (d, 3JPC = 3.9 Hz, Cβ of phosphole), 152.0 (d, 3JPC = 3.9 Hz, Cβ of phosphole), 165.14 (s, Cipso of oxazoline); 1H NMR (CD2Cl2, 25 °C): δ 2.89 (s, 2H, PCH2), 3.69 (dd, 3JHH = 8.9 Hz, 2JHH = 8.3 Hz, 1H, CH2 of oxazoline), 4.23 (dd, 3JHH = 9.9 Hz, 2JHH = 8.9 Hz, 1H, CH2 of oxazoline), 4.84 (dd, 3JHH = 8.9 Hz et 3JHH = 9.9 Hz, 1 H, NCH of oxazoline), 7.01 (m, 2H, Hβ of phosphole), 7.16–7.65 (m, 15 H, H of phenyl groups). [α]D (c = 0.6, CHCl3, 23.5 °C) = +52.9. MS: m/z (relative intensity): 395 (M+). Anal. calcd for C26H22NOP: C, 78.97; H, 5.61. Found: C, 79.35; H, 5.72.
3.4 Synthesis of complex [PdCl2(3)] 4
Ligand 3 was added to a solution of [PdCl2(COD)] (85 mg, 0.3 mmol) in dichloromethane (4 ml) at room temperature. After 10 min, the total conversion of 3 into complex 4 was checked by 31P NMR spectroscopy. The solvent was evaporated yielding a yellow powder that was washed three times with hexanes (3 × 5 ml). After drying under vaccum, complex 4 was isolated as a red powder. Complex 4 was crystallized into a mixture of dichloromethane and hexane (1:1) at room temperature. Yield: 161 mg (94%); 31P NMR (CD2Cl2, 25 °C): δ 20.6; 13C NMR (CD2Cl2, 25 °C): δ 24.0 (d, 1JPC = 28.7 Hz, PCH2), 66.9 (CH of oxazoline); 80.5 (OCH2 of oxazoline), 127.5–129.6 (CH of phenyl groups), 131.4 (d, 2JPC = 14.4 Hz, Cα of phosphole), 131.6 (d, 2JPC = 14. 9 Hz, Cα of phosphole), 137.2 (d, 2JPC = 16.5 Hz, CH of phenyls), 137.5 (d, 2JPC = 17.1 Hz, CH of phenyls), 138.7 (d, 3JPC = 7.3 Hz, Cβ of phosphole), 139.3 (s, CH of phenyls), 139.5 (d, 3JPC = 4.6 Hz, Cβ of phosphole), 176.2 (d, 2JPC = 22.4 Hz, Cipso of oxazoline). 1H NMR (CD2Cl2, 25 °C) : δ 3.16 (d, 2JPH = 10.5 Hz, 2H, PCH2), 4.70 (dd, 3JHH = 4.2 Hz et 2JHH = 9.4 Hz, 1 H, CH2 of oxazoline), 4.99 (dd, 3JHH = 4.3 Hz,2JHH = 9.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 of oxazoline), 5.73 (dd, 3JHH = 4.3 Hz, 3JHH = 9.4 Hz, 1 H, NCH of oxazoline), 7.16–7.65 (m, 15H, H of phenyls), 7.94 (d, 3JHH = 8.1 Hz, 1H, Hβ of phosphole), 8.01 (d, 3JHH = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Hβ of phosphole), [α]D (c = 0.6, CHCl3, 23.9 °C) = –214.4. MS: m/z (relative intensity): 395 (M+). Anal. calcd for C26H22Cl2NOPPd: C, 54.52; H, 3.87. Found: C, 54.75; H, 4.01.
3.5 General procedure for the Heck coupling reaction between 2,3-dyhydrofuran and iodobenzene
2,3-dihydrofuran (1.6 mmol) and the base (Et3N, 2.4 mmol) were added to a solution of catalyst 4 (1 or 0.1% par mol) in benzene or NMP (3 ml). The resulting mixture was heated at 40 or 60 °C and the progress of the reaction was periodically monitored by gas chromatography. When no evolution was noted, ether (15 ml) was added and the resulting mixture was washed with saturated solution of NaCl. After extraction, the organic phase was dried on MgSO4. Then, solvents were evaporated and the crude mixture was purified by chromatography on silica gel using hexane as eluent. The purity of the 2R-phenyl-2,5-dihydrofuran was checked by 1H NMR and the enantiomeric excess was determined by chiral gas chromatography.
3.6 X-ray structural determination
Data were collected at 150.0(1) K on a Nonius Kappa CCD diffractometer using a Mo Kα (λ = 0.71070 Å) X-ray source and a graphite monochromator. All data were measured using phi and omega scans. Experimental details are described in Tables 1–3. The crystal structures were solved using SIR 97 [55] and Shelxl-97 [56]. ORTEP drawings were made using ORTEP III for Windows [57]. CCDC-233758 (2), CCDC-233759 (3) and CCDC-233760 (4) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge at www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/conts/retrieving.html [or from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, 12, Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1EZ, UK; fax: (internat.) +44-1223/336-033; e-mail: deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the CNRS and the ‘École polytechnique’ for financial support of this work.


