1 Introduction
The maintenance dredging operations for coastal harbours and waterways consist in draining off tons of sediments to improve the ship traffic. In France, 50 million m3 of sediments are dredged each year into the main maritime and commercial ports, and a high amount of these sediments is actually polluted. To manage the dredged materials, a French decree (June 14th 2000) fixed limit concentrations of pollutants allowed in the drained sediments being thrown out into the sea. When the concentrations of pollutants are above the reference levels imposed by the decree, sediments are considered as waste. This implies that they have to be treated before being stored in a specific disposal site. These sediments represent both an economic and an ecological concern.
Among common inorganic pollutants, the metalloïd arsenic (As) has been largely studied because of its potential harmfulness to human health. Arsenic sources in the environment are natural (volcanic emission, minerals) and anthropic (mining activities, combustion of fossil fuels and the use of arsenical pesticides [1,2]). In a natural medium, arsenic is present in four different oxidation states: (−III), (0), (III), and (V). Even if arsenic speciation is strongly influenced by the redox conditions [3], in surface waters, the oxidized forms As(III) and As(V) are the most widespread. In soils, arsenate (As(V)) is the predominant form, under oxidizing conditions [4], whereas in saturated soils or soils with significant amounts of organic matter [5], arsenite (As(III)) is the main form of As, under reducing conditions. The mobility and the toxicity of arsenic depend on its speciation. As(V) species are less soluble and toxic as compared to the reduced form As(III). Arsenic mobility in the environment is dependent on its interaction with metal oxides. The binding of arsenic to different solid phases via surface complexation is well documented in the literature [6,7]. Among the arsenic species, arsenate binds more strongly with the metal oxides of Fe and Mn, as compared to the As(III) species. However, the binding mechanisms are dependent on the pH and redox potential of the environment.
In the case of dredged sediments stored on the ground, As(III) initially present is rapidly oxidized in As(V), within 2 months [8].
Considering the potential risk represented by the mobility of arsenic, mainly physico-chemical and biological treatments have been applied on polluted sediments. The most common are thermal treatment, bio-remediation, washing, solidification/stabilization by hydraulic binders. The process of stabilization/solidification is based on the trapping of contaminants in their matrix. An example of this process is phosphatation that was developed and patented by the Solvay Company. In this process, the sediment is mixed with phosphoric acid H3PO4. The reaction of the calcite, present in the sediment, with this acid leads to the formation of apatite. Heavy metals are trapped and fixed within this mineral [9]. Even if the phosphatation process is efficient for cationic elements, some limitations have been expressed for anionic elements such as As, for example [8].
Studies carried out on soils, lacustrine and marine sediments have shown that As(III) and As(V) were adsorbed on the iron oxide mineralogical phase of the samples [10–12]. For this reason, we propose an immobilization process based on the sorption of As onto the surface of iron oxides as mineral additives, in the context of the stabilization of aerial deposited dredged marine sediments. Preliminarily, the study of the sorption behaviour of As onto iron oxides in the salinity conditions encountered in a marine media is presented here. Indeed, even if a large amount of studies have been carried out considering low salinity, no results are available concerning intermediate to high salinity media. Two commercial iron oxy-hydroxides have been studied here: hematite and goethite. The sorptive behaviour of As was tested under a large range of concentrations, pH values and ionic strength.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Sorption experiments of arsenic were conducted onto commercial hematite and goethite. The main physico-chemical properties (Table 1) relative to the reactivity of a mineral powder are: the grain size, the specific surface area, the acid–base surface acidity constants (pKa1 and pKa2) corresponding to the protonation and deprotonation of the surface sites (S–OH is the formalism used to name an oxide surface site), and the point of zero charge (PZC) (i.e. the average of the pKa values).
Main physico-chemical properties both iron oxides.
| Mineral studied | Hematite | Goethite |
| Supplier | Johnson Matthey | Aldrich |
| D50 (μm) | 10 | 53 |
| Specific surface area (m2 g−1) | 1.66 ± 0.02 | 11.61 ± 0.19 |
| pKa1 | 6.38 ± 0.04 | 5.69 ± 0.08 |
| pKa2 | 9.81 ± 0.07 | 8.12 ± 0.08 |
| PZC | 8.1 ± 0.1 | 6.9 ± 0.2 |
The grain size (D50) was determined by laser granulometer (Mastersizer 2000, Malvern Instruments).
The specific surface area was determined by the Brunauer–Elmet–Teller nitrogen adsorption method (BET–N2).
The pKa values have been determined by acid–base titration for the surface site of hematite and goethite described by the following reactions:
| S–OH2+ → S–OH + H+ pKa1 |
| S–OH → S–O− + H+ pKa2 |
Stock As solutions were prepared by diluting a NIST standard solution of 1000 mg As(V) per liter in MilliQ water.
2.2 Sorption experiments
The sorption experiments were conducted at room temperature, using polypropylene tubes. A constant mass of solid (0.2 g) was put in contact with 50 cm3 of arsenate solution at 500 μg of As(V)· L−1 and 70 μg of As(V)· L−1. NaNO3 was used as background electrolyte for all the experiments. Two ionic strengths were studied (0.1 M/0.01 M). The pH of suspension was adjusted to values between 2 and 10 by adding either HNO3 or NaOH (1 M, 0.1 M/0.01 M). On the one hand the sorption of As(V) on hematite and goethite was determined as a function of pH (between 2 and 12) at two ionic strengths and a constant concentration of As(V), on the other hand sorption experiments were carried out as a function of pH and as a function of the initial concentration of As(V).
The tubes were elliptically shaken for 24 h until the adsorption equilibrium was reached. Then, the samples were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min for hematite and at 3500 rpm for 30 min for goethite and the supernatants were filtered through 0.45 μm pore size acetate filters. Due to the average size of goethite particles (10 μm) the procedure of separation of these particles in the liquid phase required a higher speed and a longer duration of centrifugation than for hematite particles (53 μm).
Arsenic concentration in the supernatants was measured by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP MS – Elan DRC II – Perkin Elmer). The concentration of arsenic sorbed on the solid was calculated by subtracting the final measured concentration to the initial concentration of arsenic introduced in the solution, [As(V)]0. The results are given in percentage of As adsorbed.
3 Results and discussion
All the experiments were conducted for both hematite and goethite, in order to compare the sorption behaviour of As onto these two iron oxy-hydroxides as a function of the initial concentration of As(V), the pH value, and the ionic strength.
3.1 Effect of ionic strength on arsenate adsorption onto hematite and goethite
The removal of arsenate by hematite and goethite for different pH values is shown in Figs. 1 and 2. For both solids, the sorption of As is maximum at acidic pH values and negligible at basic pH values. Considering the PZC values calculated for each solid, one can notice that on one hand when the pH value is inferior to 8.1 for hematite and 6.9 for goethite, the whole amount of As is adsorbed at the surface of the solid considered. On the other hand, for pH values superior to the PZC value of each solid, the whole amount of As remains in the solution.
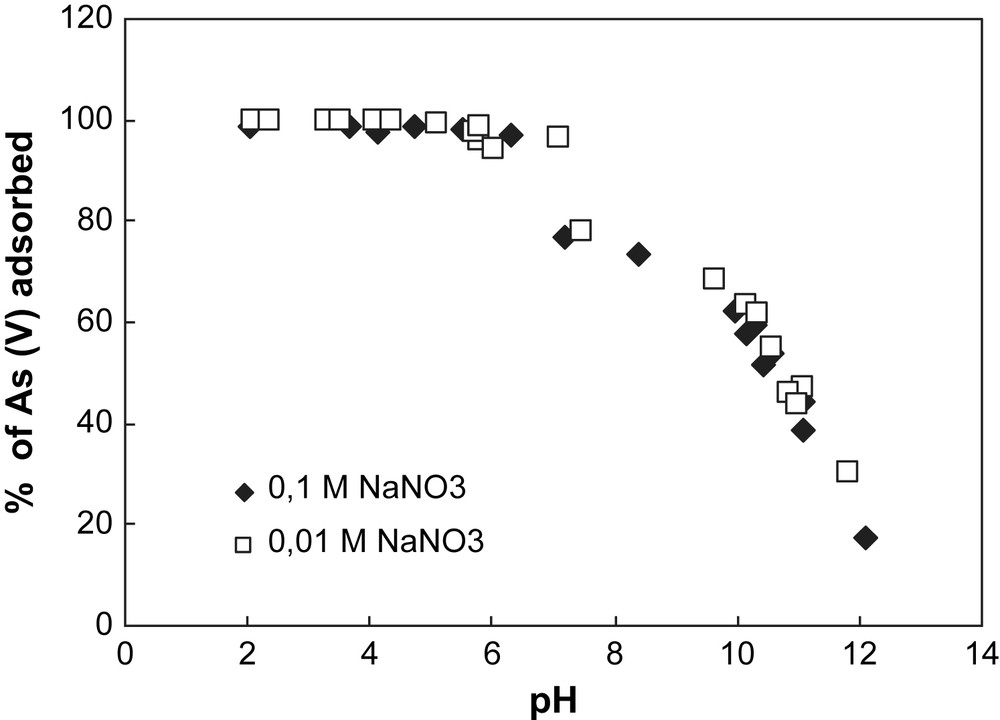
Adsorption of arsenate onto hematite at different pH values for two ionic strengths. Experimental conditions: [As(V)] = 500 μg L−1, (m/v) = 4 g L−1.
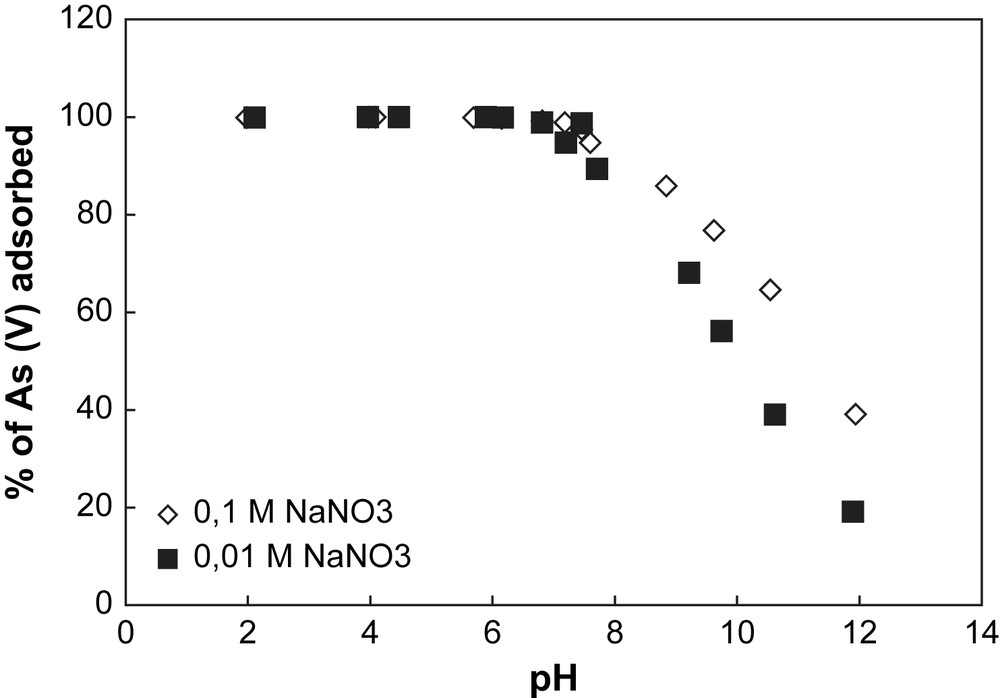
Adsorption of arsenate onto goethite at different pH values for two ionic strengths. Experimental conditions: [As(V)] = 500 μg L−1, (m/v) = 4 g L−1.
This trend is observed whatever the ionic strength studied, suggesting that the background salt (NaNO3) used has no effect on arsenate adsorption onto both solids. This behaviour of As at the surface of iron oxy-hydroxides shows that arsenate has a direct chemical bond to the surface, implying a specific sorption mechanism [13,14]. Surface complexation models developed from macroscopic data to predict arsenate adsorption behaviour consider the formation of inner sphere complexes species [15], which is in good accordance with spectroscopic investigations [16,17]. Even if recent spectroscopic studies [18,19] proposed the existence of As(V) outer sphere complexes onto hematite, the experimental conditions used for these measurements (high As concentrations) are not comparable to the trace concentrations encountered in a natural media.
The pH dependence of As adsorption for both solids is usually explained in terms of ionization of both adsorbates (As(V)) and adsorbents (hematite and goethite) [20,21]. For iron oxy-hydroxides, the surface charge occurs by direct proton transfer, since the surface hydroxyl group (S–OH) is amphoteric. Surface ionization (protonation and deprotonation) reactions take place depending on the pH of the solution in contact with the solid. The protonation of the surface
According to the arsenic speciation (Fig. 3), two species are predominant for the pH range studied in the experiments (H2AsO4− and HAsO42−). H2AsO4− is predominant for pH values from 2 to 5, while HAsO42− is predominant for pH values from 7 to 10. In the pH range corresponding to the predominance of HAsO42−, the surface of both solids is negative because the pH values are superior to the PZC value. In these conditions, the electrostatic attraction of As toward the surface is not favoured [22,23]. On the other hand, at pH values above the PZC, the surface charge of the solid is positive, thus the electrostatic attraction between the anionic species and the positively charged surface sites is promoted.
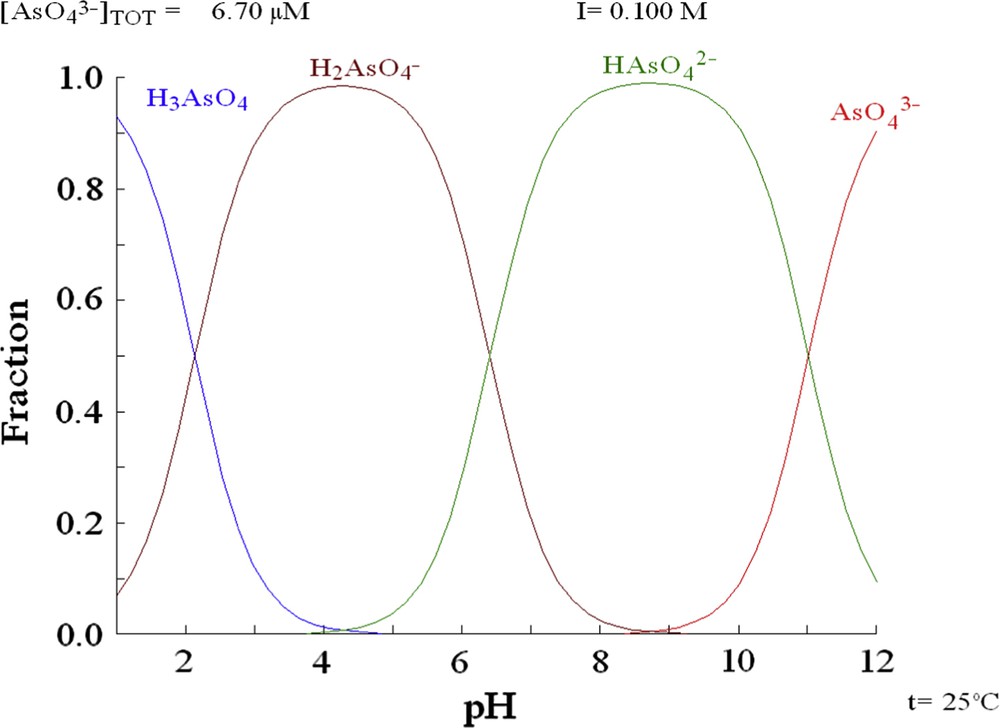
Arsenic speciation, calculated using the hydrochemical equilibrium-constant database (HYDRA).
In Fig. 2, the decrease of arsenate removal by goethite for the ionic strength 0.1 M NaNO3 can be explained by the formation of colloids in alkaline pH conditions. Indeed, metal oxides or metal hydroxides are easily soluble in acidic and strongly basic solutions because of their amphoteric characteristics. The formation of colloid particles during the goethite dissolution in alkaline condition decreases the number of surface sites, decreasing arsenate adsorption.
3.2 Effect of the initial arsenate concentration on adsorption to hematite and goethite
When two initial concentrations of As are considered for both solids (70 μg L−1 and 500 μg L−1) (Figs. 4 and 5), the sorption capacity of each solid can be established. In Table 1, the specific surface area value measured with the BET method for the goethite is higher than for the hematite. This indicates that the concentration of surface sites is higher for goethite than for hematite, implying a sorption capacity of goethite greater than hematite. This observation is confirmed by the results obtained in Figs. 4 and 5. In Fig. 5, the sorption profile of As on goethite is unchanged whatever the initial concentration of As, whereas in Fig. 4 a discrepancy for the sorption profiles of hematite is observed depending on the initial concentration of As. This discrepancy is explained by the partial saturation of the surface sites of goethite by arsenic.
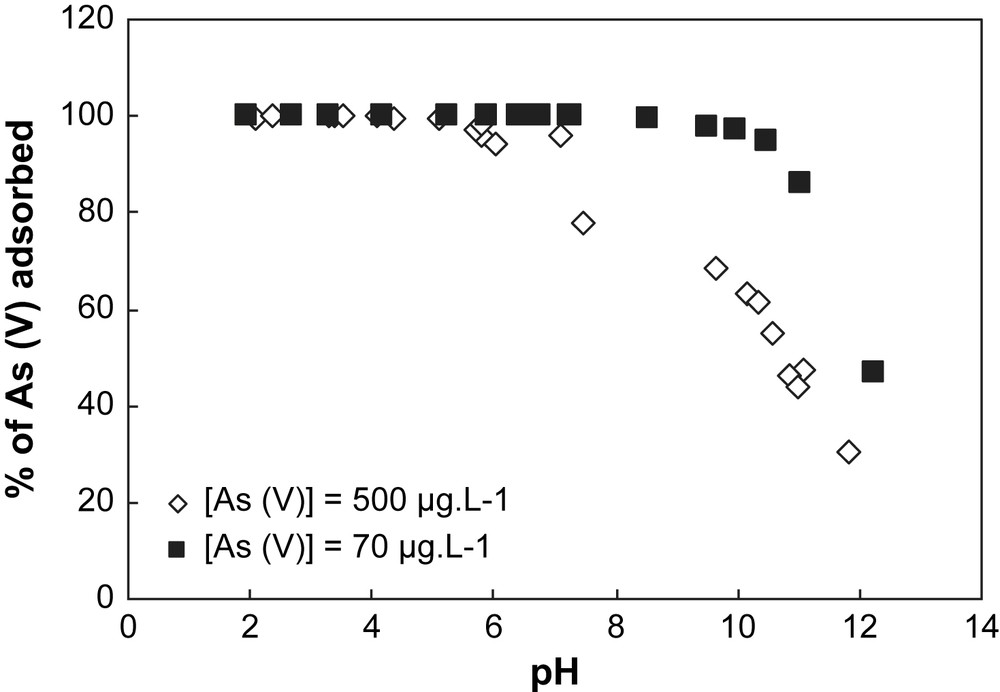
Adsorption of arsenate onto hematite at different pH values for two concentrations of As(V). Experimental conditions: I = 0.01 M NaNO3, (m/v) = 4 g L−1.
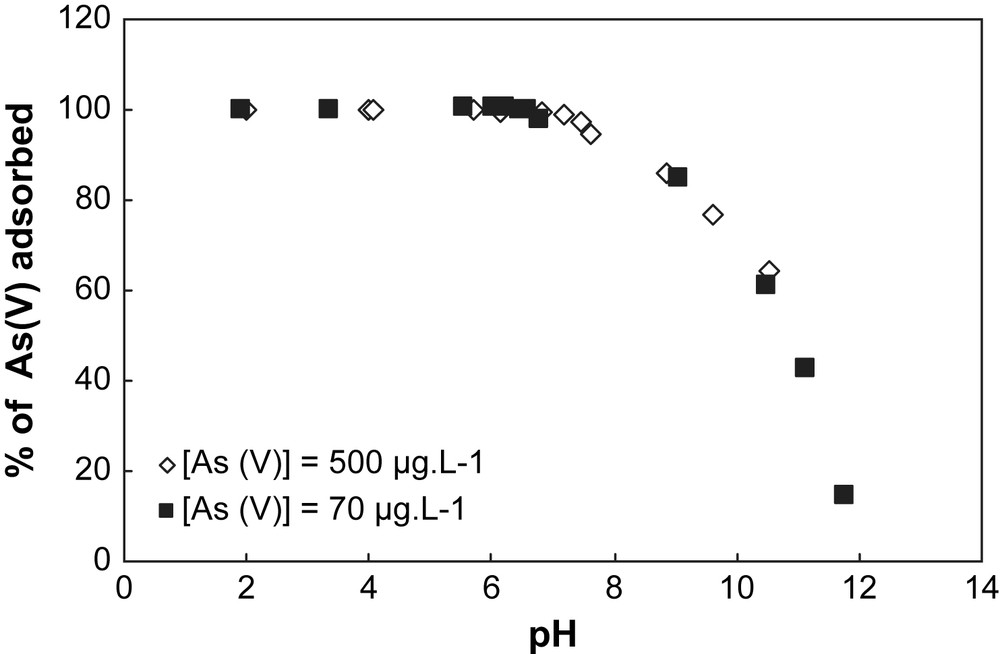
Adsorption of arsenate onto goethite at different pH values for two concentrations of As(V). Experimental conditions: I = 0.01 M NaNO3, (m/v) = 4 g L−1.
In this part, the results obtained indicate that: (i) in comparison with goethite, hematite is a good adsorbent because the pH range corresponding to the maximum of sorption of As is larger than for goethite; and (ii) the goethite allows an efficient sorption capacity for a larger range of As initial concentration than hematite.
4 Conclusion
In the context of the use of mineral additives for the stabilization of arsenic into dredged sediments, the choice of the mineral should depend on its surface site density, the concentration of arsenic in the sediment and the pH value. This study shows that the adsorption of arsenate on iron oxy-hydroxides depends on the pH value. At pH values corresponding to natural pH water, both hematite and goethite are able to adsorb more than 80% of arsenic, whatever the initial concentration may be. Nevertheless, depending on the contamination rate, the goethite should be selected for the high contamination rate, or the hematite, for the low contamination rate. Depending on the value of the natural media and the contamination rate of the media, the iron oxides used in this work should be suitable candidates as sorbents for As(V) removal technologies. Moreover, these sorbents are naturally abundant and relatively low cost materials.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the ‘Conseil Général du Var’ by means of the SEDIMARD project and the “Agence de l'eau PACA”.



Vous devez vous connecter pour continuer.
S'authentifier