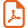
1 Introduction
Dihydropyrimidones (DHPMs) are currently being considered as an important class of molecules, since many of them show diverse biological activities such as antiviral, antibacterial and antitumor ones [1]. Moreover, they are well-known calcium channel blockers [2,3]. Recent research revealed their inhibitory activity on Ca2+-ATPase and their potentiality as immuno-restoring agents in tumor bearers [4]. Thus the structural modification of the DHPM moiety is still of the highest importance.
Alkylation and acylation of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thiones (thio-DHPMs) was demonstrated by Khanina and co-workers both in the presence and in the absence of NaH, which is a very strong base [5]. Atwal and co-workers have synthesized different S-alkyl dihydropyrimidines through cyclocondensation reactions using different substituted thioureas [3b,3c]. Singh et al. have obtained S-alkyl derivatives from thio-DHPMs using alkyl halides and K2CO3 as bases and tetrabutyl ammonium bromide as a catalyst [6]. Selective S-alkylation of thio-DHPMs with α-bromoketones using K2CO3 has also been done by Singh et al. [7]. Matloobi et al. have applied microwave irradiation to the synthesis of S-alkylated thio-DHPM derivatives [8]. Sawant et al. developed the S-methylation method using methyl iodide in the presence of pyridine [9].
Acetylation of thio-DHPMs has been accomplished by a few research groups using acetic anhydride as the acylating agent in the presence or the absence of pyridine under refluxing conditions [5,10]. Singh and co-workers were also able to synthesize N3-acylated thio-DHPMs in the presence of n-BuLi and acid chlorides at–78 °C [11]. The microwave irradiation technique was utilized by Dallinger et al. to obtain N3-acylated thio-DHPM derivatives using acid anhydrides at elevated temperatures [12,13]. But these methods have their limitations in terms of yield, reagents, and reaction conditions. Therefore a simple and efficient method for the regioselective S-alkylation and N3-acylation of thio-DHPMs is still very much in demand.
The use of cesium salts in organic synthesis has gained considerable attention in recent times due to some unique features of cesium ion. Cesium ion, due to its large cationic radius compared to that of Li+, Na+ or K+ ions, is less solvated in polar aprotic solvents, and thus Cs+ ion is more “naked” and highly reactive. Furthermore, cesium salts are well-balanced bases that are neither too strong nor too weak, and this unique feature is very much essential for selective proton abstraction. These features of Cs+ ion are sometimes referred to as the “cesium effect” [14,15].
2 Results and discussion
In the present work, a regioselective S-alkylation and N3-acylation method with the help of Cs2CO3 is demonstrated. A suitable amount of alkyl or acyl halides and 1.1 equiv of Cs2CO3 in anhydrous DMF at room temperature afforded S-alkyl and N3-acyl derivatives, respectively (Scheme 1).
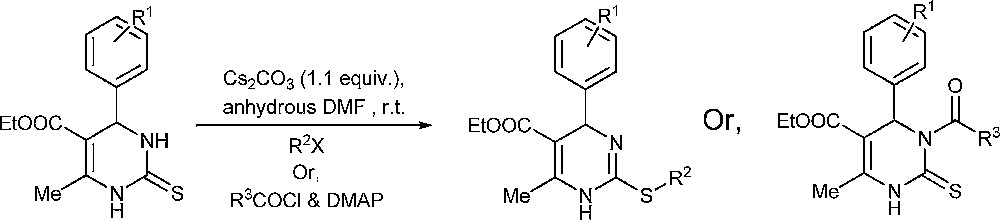
Selective S-alkylation/N3-acylation.
Most of the alkyl halides provided S-alkylated thio-DHPMs with good to excellent yields under these reaction conditions unless otherwise stated (Table 1).
Selective S-alkylation of thio-DHPM.
| Entry | DHPM | R1 | R2X | Reaction time (h) | S-alkyl DHPM | Yield (%) |
| 1 | 1 | m-NO2 | n-C16H33Br | 17 | 1.1a | 78a |
| 2 | 1 | m-NO2 | CH3I | 17 | 1.1b | 95b |
| 3 | 1 | m-NO2 | PhCH2Br | 1 | 1.1c | 86 |
| 4 | 1 | m-NO2 | p-NO2–C6H4CH2Br | 20 min | 1.1d | 74 |
| 5 | 1 | m-NO2 | CH2 = CHCH2Br | 20 min | 1.1e | 85 |
| 6 | 1 | m-NO2 | PhCH = CHCH2Cl | 17 | 1.1f | 74a |
| 7 | 2 | H | n-C16H33Br | 17 | 2.1a | 82a |
| 8 | 2 | H | p-NO2–C6H4CH2Br | 20 min | 2.1b | 79 |
| 9 | 3 | p-OMe | n-C16H33Br | 17 | 3.1a | 80a |
| 10 | 3 | p-OMe | p-NO2–C6H4CH2Br | 20 min | 3.1b | 78 |
a Using 1.3 equiv of alkyl halide.
b Using 1.5 equiv of alkyl halide.
Thio-DHPMs 1, 2 and 3 with 1.3 equiv of n-hexadecyl bromide, an aliphatic long-chain halide and 1.1 equiv of Cs2CO3 in anhydrous DMF at room temperature produced the corresponding S-hexadecyl derivatives with good to excellent yields (78%, 82% and 80% respectively, Table 1; entry 1, 7 and 9). Thio-DHPM 1 gave the S-methyl derivative with an excellent yield (95%, Table 1; entry 2). Benzyl bromide and p-nitrobenzyl bromide also furnished the corresponding S-alkyl derivatives of thio-DHPM 1 with good yields (86% and 74%, Table 1; entries 3 and 4). It must be mentioned that the reaction with p-nitrobenzyl bromide was very fast and the reaction was complete within 20 min. Similar reactivity was observed for thio-DHPM 2 and 3 with p-nitrobenzyl bromide, and 79% and 78% yields, respectively, were obtained (Table 1; entries 8 and 10). Allyl bromide and cinnamyl chloride produced the corresponding alkyl derivatives of thio-DHPM 1 with very good yields (85% and 74%, Table 1; entry 5 and 6).
The selectivity of S-alkylation was excellent for all the above-mentioned alkylations. No N-alkylated product could be isolated, but it must be mentioned that dialkylated products were identified in some cases when an excess (more than 1.5 equiv) of alkyl halides was used.
For synthesizing acyl derivatives of thio-DHPMs, acyl chlorides were used because acid chlorides are better choices as acylating agents, being easily available or synthesized compared to their anhydride analogues.
To optimize the acylation method, a number of different reaction conditions were examined. Reaction of compound 1 with 1.1 equiv of Cs2CO3 and 2 equiv of acetyl chloride at r.t. produced only trace amounts of the selective N3-acylated product. Most of the starting material remained unreacted. To increase the yield of the product, another reaction condition was employed using 1.1 equiv of Cs2CO3 and 4 equiv of acetyl chloride at r.t., but still only 35% of the acylated product was obtained. In order to facilitate the reaction, 4-(dimethylamino) pyridine (DMAP) was used as an additive. The use of 1.1 equiv of Cs2CO3, 2 equiv of acetyl chloride and 0.4 equiv of DMAP at r.t. yielded 50% of the product, but a considerable amount of the starting material remained still unreacted. Optimum reaction conditions were attained by carrying out the reaction with 1.1 equiv of Cs2CO3, 4 equiv of acetyl chloride and 1 equiv of DMAP at r.t. with an yield of 84% of the N3-acetylated product (Table 2; entry 4 and Table 3; entry 1).
Optimization of reaction condition for selective N3-acylation.
| Entry | Additive | Acetyl chloride | Reaction time (h) | Yield (%) |
| 1 | – | 2 equiv | 17 | Trace |
| 2 | – | 4 equiv | 17 | 35 |
| 3 | DMAP (0.4 equiv) | 2 equiv | 17 | 50 |
| 4 | DMAP (1 equiv) | 4 equiv | 17 | 84 |
Selective N3-acylation of thio-DHPM.
| Entry | DHPM | R1 | R3COCl | Reaction time (h) | N3-acyl thio-DHPM | Yield (%) |
| 1 | 1 | m-NO2 | CH3COCl | 17 | 1.2a | 84 |
| 2 | 1 | m-NO2 | PhCOCl | 17 | 1.2b | 72 |
| 3 | 1 | m-NO2 | PhCH = CHCOCl | 17 | 1.2c | 70 |
| 4 | 2 | H | CH3COCl | 17 | 2.2a | 87 |
| 5 | 2 | H | PhCOCl | 17 | 2.2b | 75 |
| 6 | 2 | H | PhCH = CHCOCl | 17 | 2.2c | 74 |
| 7 | 3 | p-OMe | CH3COCl | 17 | 3.2a | 85 |
| 8 | 3 | p-OMe | PhCOCl | 17 | 3.2b | 70 |
| 9 | 3 | p-OMe | PhCH = CHCOCl | 17 | 3.2c | 72 |
Under the same reaction conditions (Table 2; entry 4), thio-DHPM 2 and 3 with acetyl chloride produced the N3-acetylated product at 87% and 85% yields, respectively (Table 3; entries 4 and 7). With benzoyl chloride, compound 1, 2 and 3 produced the corresponding N3-benzoyl derivatives with 72%, 75% and 70% yields, respectively (Table 3; entry 2, 5 and 8). Cinnamoyl chloride was also found to be a highly efficient acylating agent under the similar reaction conditions and furnished the N3-cinnamoyl derivatives in good yields (70%, 74% and 72%, Table 3; entry 3, 6 and 9).
All products were characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, FT–IR, HRMS analysis and the structures of N3-acylated compounds were confirmed from the ORTEP structure (Fig. 1) generated from the analysis of single crystal X-ray diffraction data of the acyl derivative 3.2a (R-isomer). During the process of single-crystal formation from the racemic mixture of compound 3.2a, only the R-isomer was crystallized out (CCDC 930242). This phenomenon is reported as ‘chiral amnesia’ in the literature [16,17].
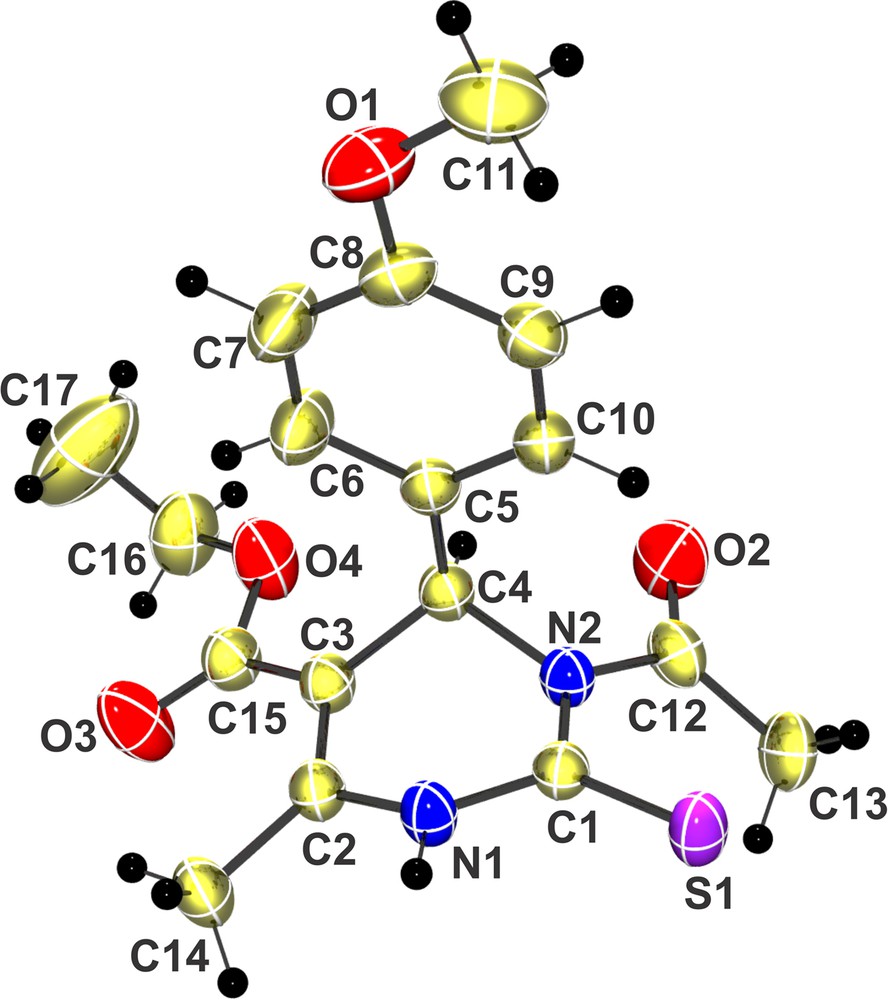
(Color online). Single-crystal X-ray diffraction structure (CCDC 930242) of compound 3.2a (R-isomer).
In the presence of a base, 2-thioxo dihydropyrimidone can exist in tautomeric equilibrium of two anionic forms (A and B in Fig. 2), where both of them act as ambidentate nucleophiles. Thus both alkylation and acylation could generate four possible products; among them, selectively, only one product is experimentally obtained. But the selectivities are different for the two paths.

Base-mediated tautomeric equilibrium of the anions.
To find out a mechanistic justification of the differential regioselection in case of alkylation and acylation, energy optimization calculations were done based on Density Functional Theory [18,19] with a hybrid functional B3LYP [20–23] for all the theoretically possible structures. Although the theoretical result shows that the S-alkyl derivative is less stable than the corresponding N-alkyl ones, the S-alkyl derivative was found to be the sole synthetically obtained product. On the other hand, in the case of acylation, the only isolable N3-acyl derivative was actually the most stable product. From the above observations, we can conclude that the anionic intermediate being an ambident nucleophile, it alkylates through more nucleophilic sulfur, which is also a softer end, whereas it acylates through nitrogen, a less nucleophilic harder end (Supplementary data).
3 Conclusion
In conclusion, we have developed an efficient synthetic method for the selective S-alkylation of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thiones using an easily available mild base Cs2CO3. Subsequently, an easy and general N3-acylation method has also been demonstrated using acyl chlorides at room temperature. A possible justification behind different regioselectivities observed is demonstrated with the help of the geometry-optimization method.
4 Experimental
All reagents were obtained from commercial suppliers and were used without any further purification unless otherwise stated. DMF was dried by distilling over CaH2 under reduced pressure. Commercially purchased ethyl acetate and petroleum ether (boiling range 60°C–80 °C) were distilled before use. Acid chlorides were distilled before use. Column chromatography was performed using a SRL 100–200 or 230–400 mesh silica gel. Thin layer chromatography was performed using Merck silica gel 60 F254 plates. The melting points were determined on a LabX India, Digital Melting Point apparatus and are uncorrected. 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded at ambient temperature using Bruker 300 MHz (Bruker AVANCE 300 or Bruker DPX-300) and Bruker 500 MHz (Bruker Ultrashield Plus 500) FT NMR spectrometers (300 MHz and 500 MHz respectively for 1H, and 75 MHz and 125 MHz respectively for 13C). Chemical shifts are reported as δ values (ppm) from internal reference tetramethylsilane. All coupling constants are reported in hertz (Hz), and proton multiplicities are labeled as br (broad), s (singlet), d (doublet), dd (doublet of doublets), t (triplet), q (quartet), and m (multiplet). HRMS were performed on Waters Micromass Q-tof Micro mass spectrometer by electron spray ionization method. Infrared spectra were recorded on a PerkinElmer Spectrum 100 FT–IR spectrometer using KBr pellets.
4.1 Typical alkylation procedure for the synthesis of ethyl 2-(benzylthio)-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.1c)
In a solution of compound 1 (321 mg, 1.0 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (3 mL), Cs2CO3 (358 mg, 1.1 mmol) was added and the mixture was stirred at r.t. for 1 h. Then, benzyl bromide (0.13 mL, 1.1 mmol) was added slowly to the reaction mixture and the reaction mixture was stirred at r.t. After completion of the reaction (1 h) as indicated by TLC, a brine solution was added. The reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 25 mL). The combined organic layer was washed with water (2 × 50 mL), then with the brine solution (1 × 50 mL). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude mass was subjected to column chromatography using 100–200 mesh silica gel when the desired product was obtained by eluting the column with 20% EtOAc/60-80 °C Petroleum ether as the eluent.
Yield: 354 mg (86%); lemon green solid; m.p. 122–123 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane); lit. [3b] 129–130 °C (isopropyl ether); lit. [6] 122–123 °C.
4.1.1 Ethyl 2-(hexadecylthio)-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.1a)
Yield: 426 mg (78%); white solid; m.p. 61–62 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.17–8.07 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 7.67 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 7.45 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 6.22 (brs, 1H; NH), 5.81 (s, 1H; CH), 4.13 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H; ester CH2), 3.17–3.00 (m, 1H; one H of S–CH2–), 2.98–2.81 (m, 1H; one H of S–CH2–), 2.34 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.58–1.53 (m, 2H; one–CH2–of n-hexadecyl), 1.30–1.20 (m, 29H; thirteen–CH2–of n-hexadecyl and one ester CH3), 0.88 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 3H; -CH3 of n-hexadecyl).
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.3, 148.3, 146.7, 133.4, 129.2, 122.2, 122.0, 60.1, 31.9, 31.1, 29.7, 29.6, 29.4, 29.4, 29.1, 28.7, 22.7, 14.2, 14.1.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3332, 2921, 2849, 1682, 1525, 1488, 1341, 1171, 1103.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H47N3O4S + H+: 546.3366 [M + H+]; found: 546.3360.
4.1.2 Ethyl 6-methyl-2-(methylthio)-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.1b)
Yield: 319 mg (95%); white solid; m.p. 84–85 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane); lit. [3b] 91.5–93 °C (ether-hexane); lit. [24] 220–221 °C (methanol).
4.1.3 Ethyl 6-methyl-2-{(4-nitrobenzyl)thio}-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.1d)
Yield: 338 mg (74%); pale yellow solid; m.p. 128–129 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.09–8.07 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 7.97 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 7.57 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 7.44-7.37 (m, 3H; Ar–H), 6.24 (brs, 1H; NH), 5.79 (s, 1H; CH), 4.36 (d, J = 14.1 Hz, 1H; one H of benzylic CH2), 4.18–4.07 (m, 3H; one H of benzylic CH2 and two H of ester CH2), 2.34 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.20 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.1, 148.3, 147.0, 146.5, 145.2, 133.3, 129.8, 129.3, 123.4, 122.3, 122.0, 60.3, 34.0, 14.2.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3327, 3096, 2973, 2930, 1694, 1645, 1517, 1345, 1259, 1161, 1088.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C21H20N4O6S + H+: 457.1182 [M + H+]; found: 457.1175.
4.1.4 Ethyl 2-(allylthio)-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.1e)
Yield: 307 mg (85%); white solid; m.p. 87–88 °C (ethyl acetate/n-Hexane); lit. [3b] 91–93 °C (isopropyl ether-hexanes).
4.1.5 Ethyl 2-(cinnamylthio)-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.1f)
Yield: 324 mg (74%); white solid; m.p. 120–121 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.16 (s, 1H; Ar–H), 7.99 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 7.67 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 7.34 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 7.25-7.14 (m, 5H; Ar–H), 6.42 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H; one H of S–CH2–CH = CH–), 6.29 (brs, 1H; NH), 6.18-6.08 (m, 1H; one H of S–CH2–CH), 5.83 (s, 1H; CH), 4.12 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H; ester CH2), 3.98–3.91 (m, 1H; one H of S–CH2–), 3.69–3.63 (m, 1H; one H of S–CH2–), 2.34 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.22 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.2, 148.3, 146.6, 136.3, 133.6, 133.4, 129.2, 128.5, 127.8, 126.3, 124.0, 122.1, 122.0, 60.1, 33.6, 14.2.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3292, 3085, 2988, 1654, 1530, 1485, 1346, 1276, 1165, 1119.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C23H23N3O4S + H+: 438.1488 [M + H+]; found: 438.1481.
4.1.6 Ethyl 2-(hexadecylthio)-6-methyl-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (2.1a)
Yield: 411 mg (82%); colorless semi-solid.
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.27–7.15 (m, 6H; one H of NH and five H of Ar–H), 5.59 (s, 1H; CH), 4.02 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H; ester CH2), 3.16–3.12 (m, 1H; one H of S–CH2–), 2.89–2.79 (m, 1H; one H of S–CH2–), 2.31 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.47–1.44 (m, 2H; one–CH2–of n-hexadecyl), 1.18–0.95 (m, 29H; thirteen–CH2–of n-hexadecyl and one ester CH3), 0.82 (t, J = 6.9 Hz, 3H; -CH3 of n-hexadecyl).
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.8, 144.5, 128.3, 127.3, 126.9, 59.8, 31.9, 31.2, 29.7, 29.5, 29.4, 29.1, 28.7, 25.8, 22.7, 14.2, 14.1.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3295, 2924, 2856, 1655, 1480, 1374, 1271, 1229, 1162, 1095.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C30H48N2O2S + H+: 501.3515 [M + H+]; found: 501.3507.
4.1.7 Ethyl 6-methyl-2-{(4-nitrobenzyl)thio}-4-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (2.1b)
Yield: 325 mg (79%); pale yellow solid; m.p. 147–148 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.91 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 7.26–7.25 (m, 8H; Ar–H), 6.09 (brs, 1H; NH), 5.69 (s, 1H; CH), 4.44 (d, J = 13.8 Hz, 1H; one H of benzylic CH2), 4.11–4.01 (m, 3H; one H of benzylic CH2 and two H of ester CH2), 2.32 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.17 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.6, 147.0, 145.6, 144.3, 129.8, 128.4, 127.4, 127.0, 123.5, 60.0, 34.1, 14.2.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3280, 3236, 3101, 2970, 1652, 1494, 1338, 1273, 1157, 1100.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C21H21N3O4S + H+: 412.1331 [M + H+]; found: 412.1328.
4.1.8 Ethyl 2-(hexadecylthio)-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (3.1a)
Yield: 425 mg (80%); colorless semi-solid.
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.26–7.23 (m, 3H; one H of NH and two H of Ar–H), 6.82 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 5.58 (s, 1H; CH), 4.11–4.07 (m, 2H; ester CH2), 3.79 (s, 3H; OCH3), 3.30–3.11 (m, 2H; one–CH2–of n-hexadecyl), 2.99–2.80 (m, 2H; one–CH2–of n-hexadecyl), 2.38 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.54–1.52 (m, 2H; one–CH2–of n-hexadecyl), 1.25–1.16 (m, 29H; thirteen–CH2–of n-hexadecyl and one ester CH3), 0.87 (t, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H;–CH3 of n-hexadecyl).
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.8, 137.0, 128.0, 113.7, 59.8, 55.2, 31.9, 31.2, 29.7, 29.7, 29.5, 29.4, 29.1, 28.7, 22.7, 14.3, 14.1.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3298, 2924, 2855, 1655, 1607, 1504, 1245, 1167, 1095.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C31H50N2O3S + H+: 531.3620 [M + H+]; found: 531.3613.
4.1.9 Ethyl 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2-{(4-nitrobenzyl)thio}-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (3.1b)
Yield: 344 mg (78%); pale yellow solid; m.p. 111–112 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 7.94 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 7.17 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 6.78 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 6.07 (brs, 1H; NH), 5.64 (s, 1H; CH), 4.43 (d, J = 14.1 Hz, 1H; one H of benzylic CH2), 4.11–4.02 (m, 3H; one H of benzylic CH2 and two H of ester CH2), 3.80 (s, 3H; OCH3), 2.31 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.18 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.6, 159.0, 147.0, 145.7, 136.8, 129.8, 128.1, 123.5, 113.7, 59.9, 55.2, 34.1, 14.2.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3304, 3082, 2985, 2934, 1652, 1512, 1475, 1344, 1268, 1247, 1158, 1105.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C22H23N3O5S + H+: 442.1437 [M + H+]; found: 442.1424.
4.2 Typical acylation procedure for the synthesis of ethyl 3-acetyl-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.2a)
In a solution of compound 1 (321 mg, 1.0 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (3 mL), Cs2CO3 (358 mg, 1.1 mmol) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred at r.t. for 1 h under anhydrous conditions. Then to the reaction mixture, DMAP (122 mg, 1.0 mmol) and acetyl chloride (0.29 mL, 4.0 mmol) were added successively and the reaction mixture was stirred at r.t. for 17 h under anhydrous conditions. After completion of the reaction as indicated by TLC, a saturated NaHCO3 solution was added. The reaction mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 × 35 mL). The combined organic layer was washed with water (2 × 50 mL), and then with the brine solution (1 × 50 mL). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and removed under reduced pressure. The crude mass was subjected to column chromatography using a 230–400 mesh silica gel when the desired product was obtained by eluting the column with 30% EtOAc/60-80 °C petroleum ether as the eluent.
Yield: 305 mg (84%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 215–216 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 11.73 (brs, 1H; NH), 8.09 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 7.94 (s, 1H; Ar–H), 7.63–7.53 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 6.36 (s, 1H; CH), 4.13–4.04 (m, 2H; ester CH2), 2.58 (s, 3H; COCH3), 2.28 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.13 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 178.0, 173.9, 165.1, 148.4, 146.2, 141.8, 133.2, 131.0, 123.5, 121.3, 106.9, 61.0, 53.0, 27.6, 17.0, 14.5.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3252, 2993, 1706, 1673, 1525, 1362, 1287, 1224, 1095, 1042.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C16H17N3O5S + Na+: 386.0787 [M + Na+]; found: 386.0787.
4.2.1 Ethyl 3-benzoyl-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.2b)
Yield: 306 mg (72%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 165–166 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.27 (s, 1H; Ar–H), 8.18-8.16 (m, 2H; one H of NH and one H of Ar–H), 7.84 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H; Ar–H), 7.68–7.65 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 7.57–7.50 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 7.40 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 6.29 (s, 1H; CH), 4.36-4.22 (m, 2H; ester CH2), 2.52 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.34 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ 178.0, 172.7, 164.8, 148.4, 144.5, 141.6, 134.7, 133.1, 132.6, 129.8, 129.1, 128.5, 123.2, 121.8, 107.2, 61.3, 56.4, 17.8, 14.2.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3220, 3133, 2987, 1709, 1652, 1525, 1341, 1291, 1227, 1092.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C21H19N3O5S + Na+: 448.0943 [M + Na+]; found: 448.0943.
4.2.2 Ethyl 3-cinnamoyl-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1.2c)
Yield: 316 mg (70%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 211–212 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 11.80 (brs, 1H; NH), 8.12–8.07 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 7.63–7.51 (m, 4H; Ar–H), 7.46–7.33 (m, 5H; three Ar–H and two alkene H of the cinnamoyl group), 6.25 (s, 1H; CH), 4.14–4.04 (m, 2H; ester CH2), 2.31 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.14 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 177.1, 169.6, 164.9, 148.3, 146.2, 142.0, 140.4, 135.0, 133.1, 130.8, 130.5, 129.3, 128.6, 123.4, 122.7, 121.3, 106.7, 60.9, 54.0, 16.9, 14.4.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3209, 2983, 1709, 1654, 1618, 1532, 1351, 1228, 1158, 1093.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C23H21N3O5S + H+: 452.1280 [M + H+]; found: 452.1274.
4.2.3 Ethyl 3-acetyl-6-methyl-4-phenyl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (2.2a)
Yield: 277 mg (87%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 141–142 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane); lit. [10] 144–145 °C (benzene-petroleum ether).
4.2.4 Ethyl 3-benzoyl-6-methyl-4-phenyl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (2.2b)
Yield: 285 mg (75%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 138–139 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane); lit. [12] 152–154 °C (2-propanol-hexane); lit. [25] 160 °C (methanol).
4.2.5 Ethyl 3-cinnamoyl-6-methyl-4-phenyl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (2.2c)
Yield: 301 mg (74%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 164–165 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 11.66 (brs, 1H; NH), 7.56–7.54 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 7.50–7.19 (m, 10H; eight Ar–H and two alkene H of cinnamoyl group), 6.23 (s, 1H; CH), 4.17-3.93 (m, 2H; ester CH2), 2.30 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.11 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 177.6, 169.4, 165.3, 145.6, 140.0, 139.8, 135.3, 130.5, 129.5, 129.4, 129.3, 129.2, 129.0, 128.6, 128.4, 128.3, 127.1, 126.6, 123.1, 107.8, 60.8, 54.4, 17.0, 14.6.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3251, 2999, 1704, 1660, 1615, 1506, 1224, 1153, 1092.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C23H22N2O3S + H+: 407.1429 [M + H+]; found: 407.1422.
4.2.6 Ethyl 3-acetyl-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (3.2a)
Yield: 296 mg (85%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 144–145 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 11.56 (brs, 1H; NH), 7.01 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 6.80 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 6.28 (s, 1H; CH), 4.05 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H; ester CH2), 3.63 (s, 3H; OCH3), 2.54 (s, 3H; COCH3), 2.26 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.10 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 178.4, 173.5, 165.3, 159.3, 145.2, 131.2, 128.0, 114.4, 107.9, 60.7, 55.5, 52.7, 27.6, 16.9, 14.6.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3184, 3134, 2993, 1705, 1514, 1375, 1230, 1180, 1091, 1028.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C17H20N2O4S + H+: 349.1222 [M + H+]; found: 349.1214.
4.2.7 Ethyl 3-benzoyl-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (3.2b)
Yield: 287 mg (70%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 136–137 °C (ethyl acetate/n-Hexane); lit. [25] 121 °C (methanol).
4.2.8 Ethyl 3-cinnamoyl-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-2-thioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (3.2c)
Yield: 314 mg (72%); lemon-green solid; m.p. 137–138 °C (ethyl acetate/n-hexane).
1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 11.70 (brs, 1H; NH), 7.62–7.59 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 7.49–7.48 (m, 2H; Ar–H), 7.42–7.38 (m, 3H; one Ar–H and two alkene H of cinnamoyl group), 7.19 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 6.89 (d, J = 9 Hz, 2H; Ar–H), 6.23 (s, 1H; CH), 4.13 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H; ester CH2), 3.72 (s, 3H; OCH3), 2.37 (s, 3H; CH3), 1.18 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H; ester CH3).
13C NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ 172.3, 164.2, 160.0, 154.2, 140.2, 134.7, 130.1, 126.3, 125.3, 124.2, 123.4, 122.9, 118.0, 109.2, 102.7, 55.6, 50.4, 48.7, 11.8, 9.4.
IR (KBr, cm−1): 3227, 2997, 1702, 1655, 1618, 1509, 1225, 1160, 1090.
HRMS (ESI): m/z calcd for C24H24N2O4S + H+: 437.1535 [M + H+]; found: 437.1533.
Acknowledgement
We gratefully acknowledge financial supports from University Grants Commission (UGC MRP No. PSW-053/10-11) to AC and UGC-SRF fellowship to SP. We also thank Dr. Dilip Kumar Maiti (University of Calcutta) for his support and Dr. Debkumar Mitra (ex-Associate Professor, Maulana Azad College) for proofreading the manuscript.