1 Introduction
Bismuth(III) salts such as BiCl3, Bi(NO3)3, and Bi(OTf)3 have low toxicity and are widely used as homogeneous catalysts in a great number of organic reactions [1–5]. However, catalyst deactivation and bismuth ion leaching are the main problems when applied in chemical reactions [6]. To make waste-free processes, the immobilization of bismuth(III) salts on solid supports gives eco-friendly heterogeneous catalysts [7–10]. The main advantages of these heterogeneous catalysts are the uniformity and accessibility of active sites, chemical and thermal stability, ease of separation, reusability, and environmental acceptability.
β-Amino alcohols are compounds of interest in organic synthesis due to their wide existence in a vast number of natural compounds and pharmaceutical drugs [11]. They are prepared by the ring-opening reaction of an epoxide with amines under mild conditions in the presence of a number of Lewis acids, such as metal chlorides [12–15] and metal triflates [16–20], which are easily deactivated. Therefore, there is a need to develop greener catalysts for the synthesis of β-amino alcohols.
Recently, we have reported the remarkable catalytic activity of BiCl3/SiO2 for the Paal–Knorr pyrrole synthesis [7] and benzo[N,N]-heterocyclic condensation [8]. Considering the importance of environmentally friendly protocols in organic transformations, the aim of this study is to explore the viability of this catalyst for the ring-opening of epoxides with aromatic and aliphatic amines under microwave and classical conditions.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and methods
Melting points were measured on a Büchi B-545 melting point apparatus and are uncorrected. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker-500. All NMR samples were run in CDCl3 and chemical shifts are expressed as ppm relative to internal Me4Si. Single crystal X-Ray data were collected on a diffractometer equipped with a STOE IPDS/2T imaging plate detector, a graphite monochromator, T = 298(2) K and Mo Kα radiation (λMo Kα = 0.71073 Å). Mass spectra were obtained on a Fisons instrument. Substrates are commercially available and used without further purification. A laboratory microwave oven MW 3100 (Landgraf Laborsysteme HLL GmbH, Langenhagen, Germany) equipped with a magnetic stirrer operating at 2450 MHz was used for syntheses of β-amino alcohols. All microwave assisted reactions were performed at 420 W (70% of maximum power) while stirring.
2.2 Preparation of the BiCl3/SiO2 catalyst
To activate the silica gel surfaces, 30 g of silica gel (300–400 mesh) was refluxed under stirring with 150 mL of 6 M hydrochloric acid for 24 h. The resulting silica was then filtered off and washed with doubly distilled water to neutral and dried under vacuum at 70 °C for 24 h.
Bismuth(III) chloride (1.575 g, 5 mmol) was added to a suspension of activated silica gel (17.5 g) in toluene (30 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight and filtered off. The solid was washed with ethanol and filtered off. The obtained solid was dried at 120 °C under vacuum for 5 h to furnish BiCl3/SiO2 as a white free-flowing powder (6.1 wt% of –O–BiOCl species as determined by TGA and 5.0 mol% of Bi as determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry). Characterization details of the catalyst are given in our previous work [7].
2.3 General procedure for the preparation of β-amino alcohols
In a typical reaction, aniline (1.0 mmol), styrene oxide (1.2 mmol) and BiCl3/SiO2 (0.05 g, 0.0125 mmol) were mixed thoroughly for 5 min. The mixture was taken in an open vessel and irradiated at 420 W for 15 min and the progress was monitored by TLC. The reaction mixture was filtered and washed with 2 mL of ethanol. The organic medium was subjected to GC analysis in order to find out the conversion. The products were then analyzed by GC–MS. The crude product was purified by short column chromatography [eluted with ethyl acetate–hexane (3:7)] to give the pure product. The product was recrystallized from ethanol to obtain the single crystal.
In the case of classical reactions, the typical reaction was carried out at 50 °C for 1 h.
2.4 Selected spectroscopic data
2.4.1 2-(2,5-Dichlorophenylamino)-2-phenylethanol
Mp 90–91 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37–7.26 (m, 13H), 7.15 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 6.57–6.55 (dd, 2H, J = 2.3, 8.4 Hz), 6.39 (d, 1H, J = 2.3 Hz), 5.24 (d, 1H, J = 5.4 Hz), 4.49 (AB quartet, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz), 3.96 (m, 1H), 3.82 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.81, 160.96, 140.85, 138.76, 133.32, 129.69, 128.98 (2C), 127.96, 126.53 (2C), 117.80, 117.50, 112.49, 67.05, 59.36.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Optimization of the model reaction
Initially, the aminolysis of styrene oxide (1.2 mmol) with 4-methoxyaniline (1 mmol) was chosen as a model reaction. First, the catalytic effect of BiCl3/SiO2 and the reaction time under microwave-induced conditions were investigated (Table 1, entries 1–5). Under the optimum conditions, the aminolysis of styrene oxide in the presence of 0.05 g of BiCl3/SiO2 (1.25 mol%) under 15 min irradiation led to quantitative conversion and excellent regioselectivity (Table 1, entry 3).
Catalyzed aminolysis of styrene oxide by 4-methoxyaniline under various conditions.
| Entry | Catalyst (g) | Conditions | Time (min) | Conversion (%)b | Product selectivityc | |
| A | B | |||||
| 1 | BiCl3/SiO2 (0.05) | MWIa | 5 | 52 | 96 | 4 |
| 2 | BiCl3/SiO2 (0.05) | MWI | 10 | 89 | 96 | 4 |
| 3 | BiCl3/SiO2 (0.05) | MWI | 15 | 100 | 95 | 5 |
| 4 | BiCl3/SiO2 (0.03) | MWI | 15 | 89 | 95 | 5 |
| 5 | BiCl3/SiO2 (0.07) | MWI | 15 | 100 | 93 | 7 |
| 6 | BiCl3 (0.03) | MWI | 15 | 85 | 96 | 4 |
| 7 | SiO2 (0.05) | MWI | 15 | 32 | 91 | 9 |
| 8 | – | MWI | 15 | 25 | 82 | 18 |
| 9 | BiCl3/SiO2 (0.05) | 25 °C | 60 | 69 | 84 | 16 |
| 10 | BiCl3/SiO2 (0.05) | 50 °C | 60 | 100 | 95 | 5 |
a Microwave irradiation: 420 W.
b Conversions were determined by GC.
c Selectivities were determined by GC–MS.
Further work showed that SiO2 has poor catalytic activity, whereas the yield of the desired product sharply increased in the presence of BiCl3 to highlight its important role in catalyzing the reaction (Table 1, entries 6–8). Nevertheless, the efficiency of BiCl3/SiO2 over BiCl3 itself in the reaction is clear (Table 1, entries 3, 6).
The classical reaction was also studied in the presence of BiCl3/SiO2 at 25 and 50 °C for 1 h (Table 1, entries 9, 10). The same results were obtained under microwave irradiation and classical heating at 50 °C (Table 1, entries 3, 10) to highlight the role of the catalyst.
The higher catalytic activity of BiCl3/SiO2 is due to good dispersion of BiCl3 over high surface area of silica and may be attributed to –O–BiOCl catalytic sites.
3.2 Recycling of the catalyst
The feasibility of repeated use of BiCl3/SiO2 was also examined (Table 2). The catalyst was readily isolated from the reaction mixture. After completion of the reaction, ethanol (2 mL) was added to the reaction mixture. The catalyst is insoluble in ethanol and was simply filtered from the resulting mixture. The recycled catalyst was washed with ethanol twice more, filtered off and dried at 100 °C under reduced pressure for 2 h and then reused in the subsequent run without adding any fresh catalyst. The reused catalyst is stable under the reaction conditions, and remains active even in fifth run with no decrease in activity while high regioselectivity is maintained.
Recyclability of BiCl3/SiO2 (0.25 g) for aminolysis of styrene oxide (6 mmol) with 4-methoxyaniline (5 mmol).
| Run | Conversion (%) | Product selectivity | |
| A | B | ||
| 1st | 100 | 95 | 5 |
| 2nd | 100 | 95 | 5 |
| 3rd | 100 | 95 | 5 |
| 4th | 100 | 92 | 8 |
| 5th | 100 | 92 | 8 |
3.3 Evaluation of the reaction scope
The excellent preliminary results of the model reaction led us to expand the generality of this catalyst (BiCl3/SiO2) to a series of amines and epoxides under solvent-free microwave and thermal conditions. The results are summarized in Table 3.
Synthesis of β-amino alcohols catalyzed by BiCl3/SiO2 (1.25 mol%) under microwave and classical heating.
| Entry | R′ | R | Major regioisomer | Methoda | Conversion (%)b | TOF (h−1)c | Product selectivityd | |
| A | B | |||||||
| 1 | Phenyl | Phenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 97 | 3 | |
| 2 | 2-Chloromethyl | Phenyl | M | 94 | 301 | 10 | 90 | |
| C | 90 | 72 | 2 | 98 | ||||
| 3 | Phenyl | 2-Methylphenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 95 | 5 | |
| 4 | Phenyl | 3-Methylphenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 93 | 7 | |
| 5 | Phenyl | 4-Methylphenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 94 | 6 | |
| C | 100 | 80 | 97 | 3 | ||||
| 6 | Phenyl | 4-Methoxyphenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 95 | 5 | |
| C | 100 | 80 | 95 | 5 | ||||
| 7 | 2-Chloromethyl | 4-Methoxyphenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 0 | 100 | |
| C | 91 | 73 | 0 | 100 | ||||
| 8 | 2-Isopropoxymethyl | 4-Methoxyphenyl | M | 80 | 256 | 0 | 100 | |
| C | 72 | 58 | 0 | 100 | ||||
| 9 | Phenyl | 4-Chlorophenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 100 | 0 | |
| C | 100 | 80 | 100 | 0 | ||||
| 10 | Phenyl | 3-Chlorophenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 100 | 0 | |
| 11 | Phenyl | 4-Bromophenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 99 | 1 | |
| 12 | Phenyl | 2,5-Dimethylphenyl | M | 100 | 320 | 95 | 5 | |
| 13 | Phenyl | 2,5-Dichlorophenyl | M | 84 | 269 | 99 | 1 | |
| 14 | Phenyl | n-Hexyl | M | 40 | 128 | 30 | 70 | |
| 15 | Phenyl | Benzyl | M | 84 | 269 | 26 | 74 | |
| 16 | Phenyl | Cyclohexyl | M | 100 | 320 | 9 | 91 | |
| 17 | Phenyl | Morpholine | M | 100 | 320 | 30 | 70 | |
| C | 100 | 80 | 49 | 51 |
a Method M: microwave heating/420 W/15 min. Method C: 50 °C/1 h.
b Conversions were determined by GC.
c TOF: turnover frequency = moles of converted substrate (amine)/(moles of catalyst × reaction time in h).
d Selectivities were determined by GC–MS.
It was found that aniline derivatives bearing either electron-donating (such as methoxy, methyl, and dimethyl) or electron-withdrawing (such as bromo, chloro, and dichloro) substituents reacted smoothly to give the corresponding β-amino alcohols (Table 3, entries 1–13) in quantitative yields with high to excellent regioselectivities (from 90:10 to 100:0). Moreover, the selectivity of products is almost comparable under microwave and classical heating, when aniline derivatives are used as substrates (Table 3, entries 2, 5–9).
In contrast to styrene oxide, epoxides such as epichlorohydrin and isopropyl glycidyl ether showed lower activity (Table 3, entries 2, 7, 8).
The reaction was also carried out with aliphatic amines, e.g., n-hexylamine, benzylamine, cyclohexylamine and morpholine (Table 3, entries 14–17). Except cyclohexylamine (91%), the other aliphatic amines exhibited moderate selectivity (70%) under microwave heating. When the same reaction was conducted under thermal heating, both products A and B were obtained in a ratio of 1:1 (Table 3, entry 17).
The turnover frequencies (TOF) of all reactions were calculated to measure the catalyst activity. It was found that TOF values are in the range of 256–320 h−1 and 58–80 h−1 under microwave and classical conditions, respectively (Table 3).
In general, the reaction of epoxide with aromatic and aliphatic amines is regioselective. A tentative reaction route for the BiCl3/SiO2 catalyzed ring-opening of styrene oxide with aniline and cyclohexylamine is depicted in Scheme 1. It is well known that the nature and type of the amine molecule influence the selective ring-opening of the styrene oxide [11]. Cyclohexylamine as a stronger nucleophile, attacks on the carbon atom of the epoxide ring with a more positive charge and less steric hindrance, whereas in the case of aniline, steric factors predominate over electronic factors [21,22].
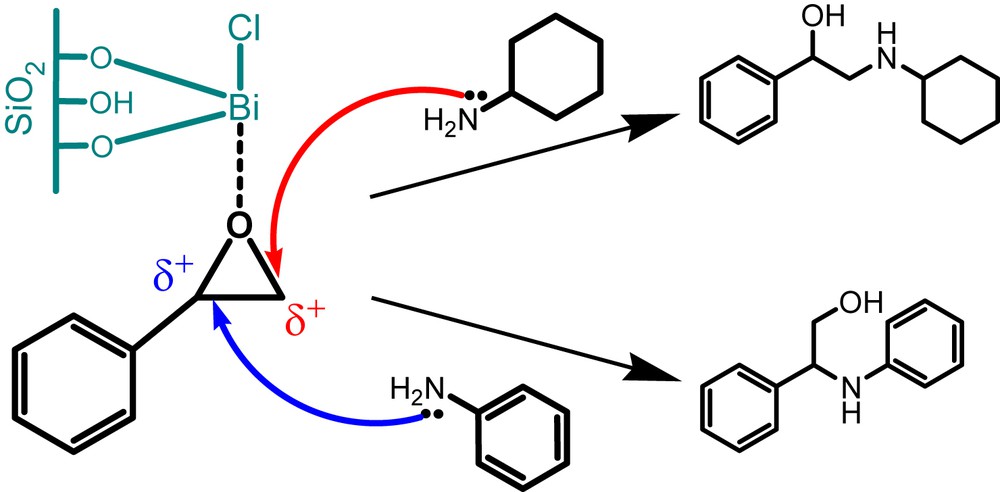
BiCl3/SiO2 catalyzed regioselective ring-opening of styrene oxide with aniline and cyclohexylamine.
On the other hand, the Lewis acidic sites on the surface of the BiCl3/SiO2 catalyst are responsible for the activation of epoxide to enhance the reaction rate.
3.4 Crystal structure of 2-(2,5-dichlorophenylamino)-2-phenylethanol
Single crystals of compound 13 (Table 3, entry 13) suitable for SCXRD measurement were grown by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution. The unit cell dimensions were determined from 2000 reflections. The structure was solved by the direct method and refined by full matrix least-squares calculations based on F2 to final R1 = 0.0793 and wR2 (all data) = 0.2262, using SHELXL-2014 and WinGX-2013.3 programs [23–29]. The compound crystallizes in the triclinic system and
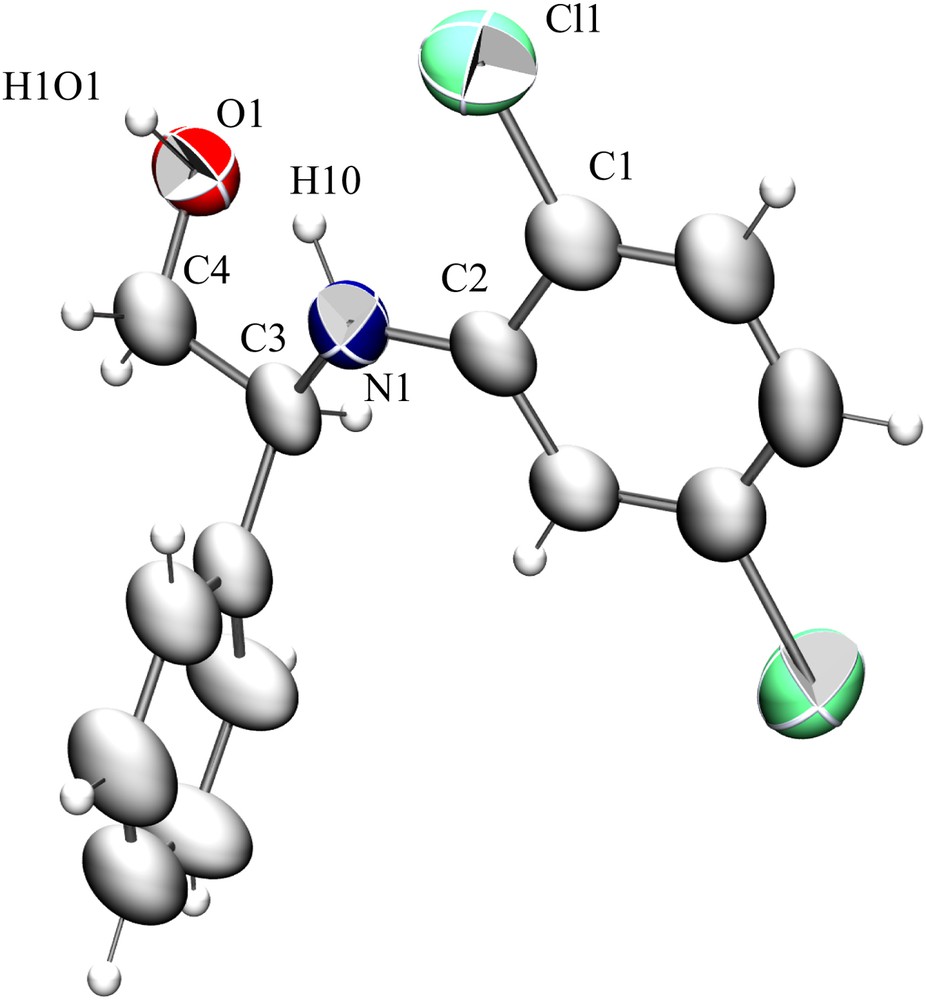
Structure of the formula unit of 13 (thermal ellipsoids set at the 40% probability level). Selected bond lengths [Å] and angles [°]: C2–N1 1.397(7), C4–O1 1.412(6), C1–Cl1 1.742(6), C3–C4 1.512(8), C3–C5 1.547(6), O1–C4–C3 112.9(5), N1–C3–C5 115.4(4), N1–C3–C4 108.4(4), C1–C2–N1 121.8(5).
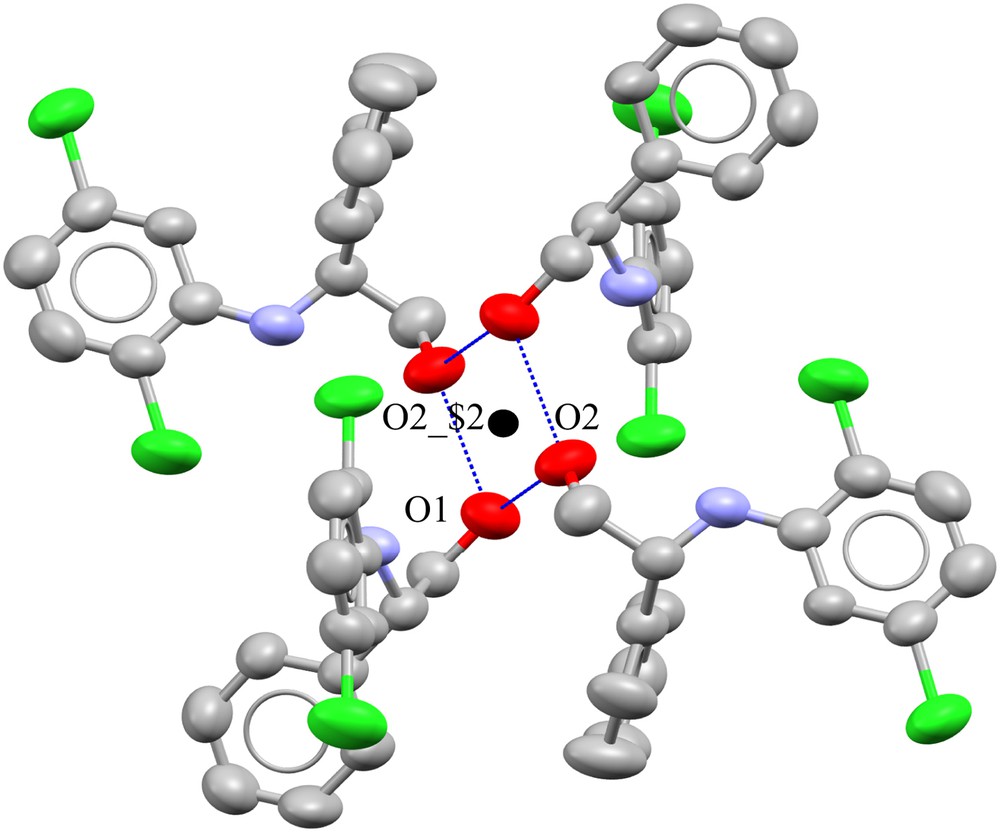
Depiction of intercellular R4,4(8) hydrogen-bonding with [O1⋯O2_$2⋯2.724(5)Å and O1⋯O2 2.754(5)Å]. Thermal ellipsoids are set at the 40% probability level. The dark spot in the middle of the rectangle indicates the location of the center of symmetry. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity. $2 is generated by x, y+1, z.
4 Conclusions
BiCl3/SiO2 as a heterogeneous Lewis acid catalyst exhibited excellent catalytic activity and high regioselectivity for the ring-opening of epoxides with aromatic and aliphatic amines to produce β-amino alcohols under microwave and thermal conditions. All the reactions have been conducted in a low loading bismuth ion (1.25 mol%). BiCl3/SiO2 is superior in terms of catalytic activity compared to homogeneous BiCl3. It could be recycled and reused for five consecutive reaction cycles with no decrease in catalytic activity maintaining high selectivity. The innocuous and non-leaching nature of the catalyst makes it a greener alternative to conventional homogeneous catalysts (e.g., Lewis acid salts) used for the aminolysis of epoxides.


