1. Introduction
In the coming years, the increase in world population and in average per capita income would inexorably lead to the growth of fossil fuel demand. However, this heavy dependence on fossil fuels results in a series of environmental problems, e.g., global warming and air pollution, and generates sustainability problems in the face of a continuously increasing demand. Thus, to solve the energy crisis and environmental degradation, exploring clean and renewable energy alternatives is crucial [1, 2].
In Tunisia, the vast majority of renewable energy capacity comes nowadays from wind (46%) and solar photovoltaic (42%) sources, which are expected to increase by 2030. With a high percentages of organic waste (nearly 70% of organic waste released in landfills) and only 12% of total energy production expected to come from biomass sources, Tunisia should consider focusing more research on renewable energy recovery from biomass. The biomass resources are often locally available as is waste. Hence, biomass allows not only waste management but also energetic conversion of fermentable waste [3].
Among the organic substrates, onion (Allium cepa L.) is the second most commonly cultivated vegetable worldwide, after tomatoes [4]. Its production is witnessing an annual growth given a consumer demand increase (the current annual production of onions is around 93 million tons). Simultaneously, huge amounts of onion waste are produced from different parts and onions processing, affecting the environment in various ways [5]. These onion waste materials are problematic for the industry as they are not suitable as feed for livestock due to their unpleasant smell while the phytopathogenic agents presence makes them also unsuitable as organic fertilizers [6, 7]. So far, the main solution for onion waste management was to discharge it in landfills, which has high economic and environmental impacts. However, onion waste consists of a significant amount of functional components as flavonoids, organosulfur and phenolic compounds [8]; its dry weight is composed roughly of 65% of nonstructural/soluble carbohydrates including glucose, fructose, sucrose, and fructooligosaccharides, which are specific functional compounds of onion waste that should be valorized.
Onion valorization is part of some pretreatment methods based on technologies such as organic extraction, supercritical carbon dioxide, supercritical water treatment, microwave, assisted microwave, hydro diffusion, and gravity or high-pressure processing [5]. However, few studies looked into the fermentable potential of onion waste as a renewable raw material for biohydrogen production identified as a clean renewable energy carrier and an ideal candidate to replace fossil fuels [4]. Among the biological processes for waste treatment, anaerobic digestion (AD) is suggested as a truly sustainable process which can handle the contained high organic contents [9].
Dark fermentation (DF) is considered as the simplest process of anaerobic digestion of organic matter, since it is a pollution-free, renewable, and low-cost alternative to conventional processes [10]. Theoretically, in DF processes, the yield of hydrogen production depends on the bacteria involved and acid formation. The various metabolic pathways are influenced by the operating conditions (substrate concentration, pH, temperature, hydraulic retention time, reactor type, and seed sludge). Temperature is one of the most influencing factors since thermophilic conditions are widely used in H2 production from organic waste [11]. High temperature accelerates reaction rates and offers technical advantages including reduction of viscosity, improvement of mixing efficiency, reduction of the contamination risk, absence of reactor cooling, and enhancement of hydrolysis complex substrates rate [12, 13]. The majority of (hyper) thermophilic microbial species producing hydrogen belong to Clostridium, Caldicellulosiruptor, Thermoanaerobacter, Thermotoga, Thermococcus, and Pyrococcus genus. Thermotoga maritima (TM) is one of several hyperthermophilic bacteria (optimal growth temperature around 80 °C), which have received considerable interest recently as potential sources of hydrogen [14]. TM can produce H2 at levels that approach the Thauer limit (theoretical H2∕C6max = 4; [15]), using a wide range of inexpensive polysaccharide sources, such as cheese whey, molasse, potato starch, or fruit and vegetable waste [16, 17]. Nevertheless, it is needed to add inorganic sulfur and nitrogen sources to enhance TM growth. These additions could be replaced by using cost-effective fruits or vegetables providing the whole essential components for its growth. Among the different fruit and vegetable, onion (Allium cepa L.) is a vegetable rich in carbohydrates (structural and nonstructural) being a good source of dietary fiber and fructooligosaccharides [18] as well as organic acids [19]. It also has significant amounts of vitamins, minerals, and trace elements [20]. Moreover, onion represents one of the main sources of bioactive compounds, such as flavonols and organosulfur compounds (e.g., S-alk(en)yl-L-cysteine sulfoxides) [21], and as nitrogen inorganic source in the ammonium form [22].
In the past years, several research studies focused on the production of hydrogen from a variety of waste mixtures in the form of complex substrates, such as lignocellulosic waste, combinations of fruit and vegetable, sewage sludge, and livestock waste. However, a limited number of studies considered the energy recovery of a single waste—as a rich and complete substrate. In this study, we tested the ability of TM to ferment carbohydrates naturally present in onion in a batch stirred tank reactor (STR) supplemented with seawater. The stated objectives were (i) to use a cost-effective simplified medium providing all the needed components for TM growth and biohydrogen production and (ii) to preserve fresh water considered as a scarce resource. Thus, several onion concentrations were tested to evaluate the maximum concentration that TM could tolerate. Thereafter, to optimize biohydrogen production, essential microelements, for the optimal growth of TM, were added in low concentrations in the mixture of seawater and OWJ. Finally, a sequential fed-batch culture was conducted to remove the substrate limitation and optimize the biohydrogen production.
2. Material and methods
2.1. Strain and culture medium
T. maritima (TM) strain MSB8 (DSMZ 3109) was cultivated as previously described [23]. The Basal medium contained, per liter: NH4Cl 0.5 g, K2HPO4 0.3 g, KH2PO4 0.3 g, CaCl2 0.1 g, KCl 0.1 g, NaCl 20 g, MgCl2 0.2 g, yeast extract 2.0 g and glucose 20 mM. Balch trace-mineral-element solution (10 mL) was added [23]. The inoculum was obtained from three bottles of 100 mL each, containing 50 mL of liquid culture.
2.2. Experimental system and operating conditions
TM was batch cultivated in a 2L well-mixed double-jacket glass bioreactor (STR) (FairMenTec, France) with a 1.5-L working volume [23]. The pH was controlled at 7.0 ± 0.1 by the addition of sodium hydroxide (NaOH = 0.5 mM) and the temperature was maintained constant at 80 ± 1 °C (Figure 1). The inlet gas stream of N2 was controlled at 50 standard cubic centimeters per minute (SCCM) via a mass-flow meter (Bronkhorst, range 0–500 SCCM). The online measurements of bioreactor liquid volume, NaOH consumption, CO2 and H2 concentrations, were as previously described [23]. The stirring was set to 500 rpm. For each experiment, three successive batches were carried out. Fermentation juice samples were taken every two hours and the kinetics of substrate consumption, metabolite productions, and biohydrogen production were analyzed. The sequential fed-batch operation was carried out after a first batch mode, more precisely after the decrease of the maximal H2 production rate. The sequential feeding in fed-batch mode was realized using a controlled peristaltic pump connected to a serum bottle containing 1 L of concentrated OWJ supplemented with 30 g/L of sea salt. Each addition was of 10% (v/v) of OWJ about the final volume of the bioreactor. During the experiments, the data of N2 flow rates and the gas analyses (N2, H2, and CO2) were recorded and used to calculate CO2 and H2 flows, which then led to the cumulative amounts of CO2 and H2 produced in the bioreactor [23].
Experimental set-up for batch and fed-batch cultures.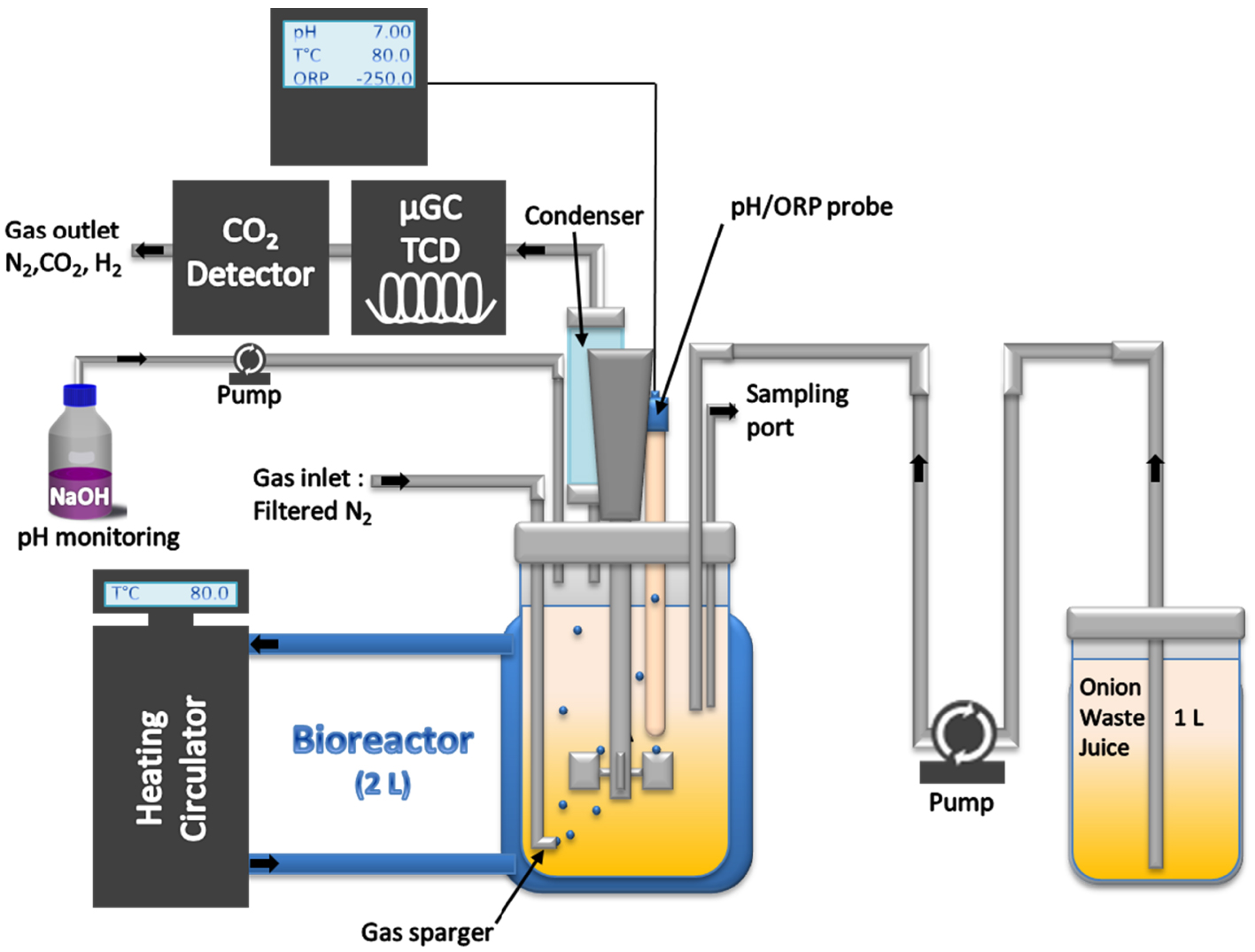
2.3. Culture medium for the bioreactor experiments
A culture medium was made with natural SW taken directly from the “Bay of Gammarth” located near Tunis (Tunisia). This SW was filtered under vacuum through a 0.45 μm cellulose nitrate filter (Sartorius, Germany). White Onions used in this work came from municipal markets in Tunis. For the OWJ, onions were crushed with an electric juice extractor (OMEGA J8226) fitted with a worm screw system and an Ultem-plastic sieve to filter (0.3 mm) for the filtration and separation of liquid–solid phases. The separated OWJ was directly stored at −20 °C. First, the TM growth was studied in a rich complete medium in presence of 17% (v/v) of OWJ (∼20 mM of Glucose and 20 mM fructose), 0.5 g/L of NH4Cl, 0.25 g/L of Cysteine-HCl, 2 g/L of yeast extract, and 1% (v/v) of Balch’s oligoelement [24], complemented at 1200 mL with natural seawater (experiment E1), to evaluate the ability of TM to ferment the sugar fraction of OWJ. Thereafter, experiments (E2, E3, E4, E5 and E6) were carried out in bioreactor using 17% of OWJ as a basal medium for biohydrogen production with and without NH4Cl (0.5 g/L as a source of nitrogen), FeCl2 (10 mg/L as a source of iron) and yeast extract (YE: 2 g/L) to evaluate (i) the efficiency of TM fermentative H2 production using OWJ as a limiting factor and (ii) the importance of nitrogen, iron and YE in presence of onion. Elsewhere, several experiments (E2, E7, E8, E9 and E10) including respectively different volumes of OWJ (200, 400, 600, 800, and 1000 mL) supplemented with natural seawater (SW) for a final volume of 1200 mL were prepared in order to increase the TM growth and fermentative performance. The fermentability of onion waste under the best conditions was finally tested in a culture medium containing the optimal volume of OWJ.
2.4. Analytical methods
The total solids (TS), volatile solids (VS), humidity, chemical oxygen demand (COD) and the pH of the substrates were estimated according to the procedure listed in Standards Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater [25]. Glucose, acetate, lactate, and fructose concentrations were determined by HPLC as previously described [23]. Pyruvate was determined with Waters equipment comprising a 1525 pump, a 2996 diode array detector, a Rheodyne injector fitted with a 20 μl loop, a temperature control system, and a degasser. The separation was performed with an Amidex HPX-87H strong cation exchange column (Biorad 300 × 7.8 mm) protected with a pre-column. The column was thermostated at 60 °C and the mobile phase was composed of 0.01 M H2SO4 with a flow of 0.5 mL/min. The eluent was monitored at 210 nm. Standard solutions of pyruvate were run from 0.5 to 20 mM. The calibration curve was linear within this range. An injection volume of 20 μl was used for standard and samples. These were harvested immediately after the OWJ was added to the SW. All analyses were performed in triplicate. For each batch experiment, liquid samples of 2 mL were collected and centrifuged for 5 min at 14,000 g. The supernatants were filtered through Minisart cellulose acetate syringe filters (0.22 μm) and the filtrate (20 μL) was then injected into the column eluted with a sulfuric acid solution (5 mM) with a fixed flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The data were presented in the Agilent ChemStation software. The analyses were performed in triplicate and the average values were expressed in millimoles per liter corresponding to standard solutions. For total carbohydrate concentration, the anthrone sulfuric acid method was used [26] with modifications. A 0.2% solution of anthrone (w/v) was made up fresh in 75% (v/v) sulfuric acid on the day of measurement. The procedure consists in mixing a 1 mL sample with 2 mL of 75% H2SO4 and 4 mL of anthrone reagent by a vortex. Samples were placed on the heating block at 105 °C for 15 min and then cooled down to room temperature. The absorbance of each sample was determined at 625 nm using a UV-visible spectrophotometer. The gas produced during fermentation runs was analyzed continuously with a micro-GC and a CO2 probe [23]. The micro-GC was dedicated to H2 and N2 measurements with temperatures of injector, column, and detector adjusted to 90, 120, and 100 °C, respectively. Argon was used as carrier gas with a pressure of 200 kPa. The gas-analysis frequency was 2 min.
2.5. Determination of kinetic parameters
It is important to note that the kinetic parameters reported to compare the efficiency of hydrogenogenic fermentation are: H2 total production (HP in mM); H2 production rate or H2 productivity (HPR in mM/h) and molar H2/C6 yield (HY in molH2∕molHexose). All these kinetic parameters have been obtained from experimental data and their processing using part of the models presented in [23, 27].
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Onion composition
The sugars and pyruvate concentrations were determined in four preparations of OWJ in 1000 mL: 139 ± 14 mM of glucose; 143.2 ± 8.4 mM of fructose; 8.3 ± 2.6 mM of sucrose and 14.8 ± 1.8 mM of pyruvate (equivalent ammonium). None other volatile fatty acids or sugars were detected (Table 1). These values were close to those found in the literature with a difference related to the solubility of sugars essentially present in the juice part [8, 28] and the decrease of sucrose after OWJ preparation attributed to sucrose hydrolysis to glucose and fructose due to the acidic pH of 4.0–4.8.
Onion waste characterization (g/100 g)
| Parameter | Values | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Humidity | 90.3 ± 3.5 | This study |
| Total solids (TS) | 6.7 ± 0.5 | |
| Volatile solids (%TS) | 90.0 ± 1.0 | |
| Ashes | 0.7 ± 0.2 | |
| COD | 6.1 ± 0.9 | |
| pH | 4.4 ± 0.5 | |
| Total sugars | 5.7 ± 1.3 | |
| Glucose | 2.5 ± 0.2 | |
| Sucrose | 0.3 ± 0.1 | |
| Fructose | 2.6 ± 0.4 | |
| Pyruvate/ammonium | 0.13 ± 0.03 | |
| Iron, Fe (mg/100 g) | 0.21 | [15] |
| Total protein | 1.1 | |
| Organic acids | 0.17 | [5] |
| Sulfur compounds | 0.09 |
H2 Production (HP, empty symbol) and H2 production rate (HPR, full symbol) by Thermotoga maritima with 200 mL (17% v/v) onion waste juice (OJ) as the sole carbon and energy source (blue square) and in rich medium in presence of 200 mL onion waste juice (gray triangle).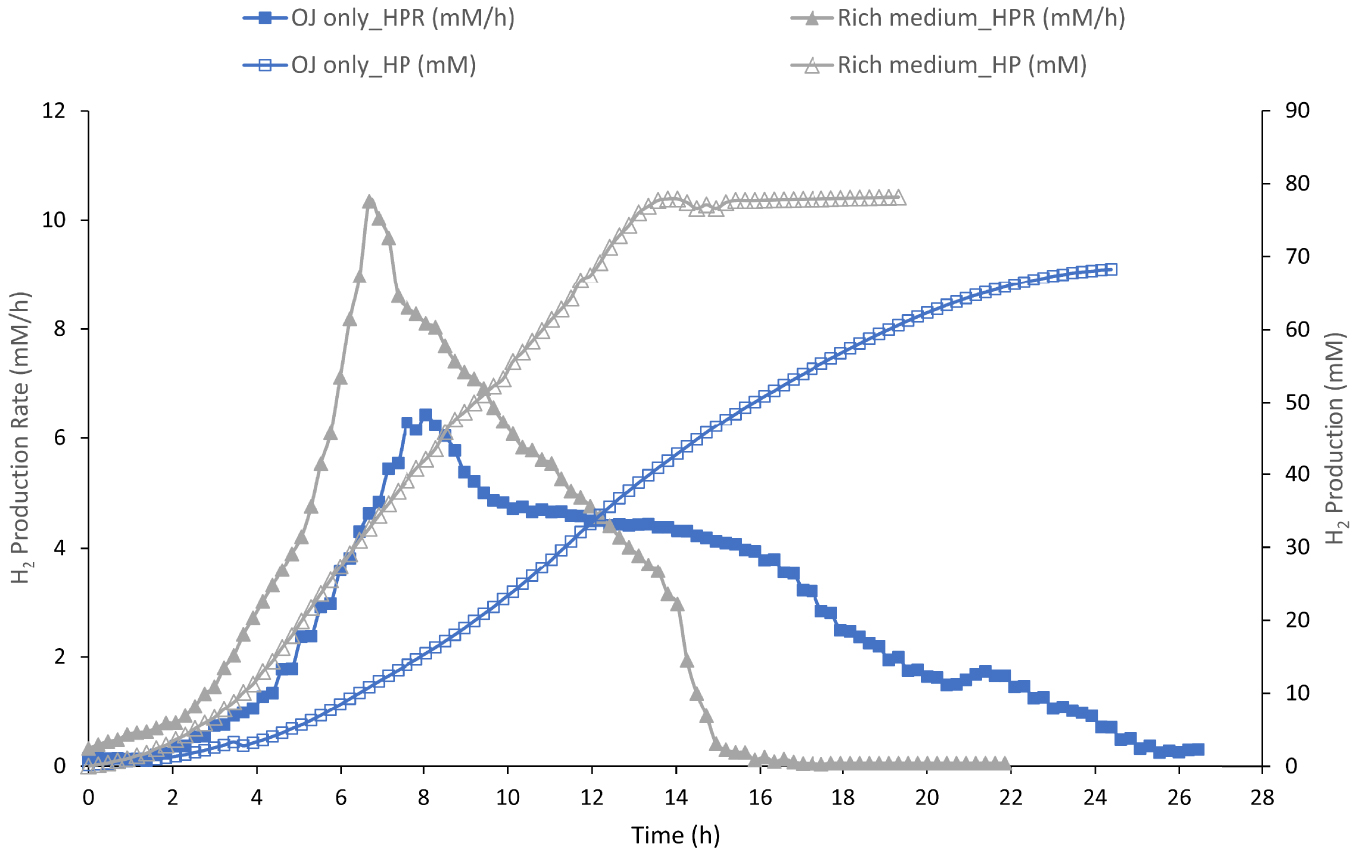
The carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N) of the onion was 15.3 [29]; this ratio was considered appropriate for prototroph anaerobic bacteria and therefore no additional nutrients were necessary [9, 30].
3.2. The onion waste juice fermentation
The fermentative potential of onion indigenous bacterial communities was initially evaluated in anaerobic batch STR reactor with a culture medium containing 200 mL of OWJ mixed with SW in a total volume of 1200 mL (∼17% OWJ) without TM (abiotic control). The operating conditions were the same than with TM culture (80 °C, pH 7.0). During these experiments, no production of H2 nor other compounds (acetate and lactate) was observed. This could be explained by the absence of indigenous extremophilic and/or halotolerant microflora able to produce H2 by fermentation.
3.2.1. OWJ fermentation in rich medium
To evaluate the ability of TM to ferment the sugar fraction of OWJ, rich in inhibiting compounds, the TM growth was studied in a rich complete medium in presence of 17% (v/v) of OWJ. This was considered as a complete medium limited only by the substrate (glucose). The kinetic parameters (HPR and HP) for this experiment (E1) are represented in Figure 2.
The maximal HPR with the rich medium was 10.3 mM/h ± 1.1 with a total HP of 78 mM ± 4.3. The molar H2 yield (HY) was 2.40 (mMH2/mMHexose) (Table 2, E1). Maximal HPR of some Thermotoga strains was reported between 2.7 and 12.4 mM/h from equivalent carbohydrate concentrations [31]. In this condition, the H2 productivity was close to the highest values obtained during other experiments using various biomass-based materials as feedstock [32]. In our conditions, TM was able to ferment sugars, without significant inhibition. Indeed, the onion has been used in biomedicine since antiquity and has long been known to have antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral effects [33]. The broad-spectrum activity of onion waste juice has been attributed to phytotherapeutic sulfur compounds mainly represented by allicin [34] and by aromatic compounds. However, TM was capable to ferment the soluble sugar present in the liquid fraction of onion waste despite the presence of inhibitory compounds. We could assume that in our conditions these inhibitory compounds did not act on the strain performances. Allicin is a thermolabile compound with a half-life of approximately 17 h at 42 °C [35] which could explain its non-inhibition at 80 °C.
Average results obtained for batch fermentations for experiments in a rich medium, and in presence of only 200 mL of onion juice or supplemented with NH4Cl, and/or FeCl2 and/or YE. Each experiment was performed in triplicate
| OWJ volume (ml or gram) in 1200 mL | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E5 | E6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200+Rich medium | 200 | 200+NH4 | 200+Fe | 200 Fe+NH4 | 200 Fe+NH4+YE | |
| Total carbohydrates (mM) | 47.4 ± 2.7 | 44.6 ± 0.8 | 48.8 ± 2.9 | 44.0 ± 1.2 | 44.6 ± 1.6 | 46.9 ± 2.1 |
| Glucose (mM) | 22.6 ± 0.8 | 23.2 ± 1.2 | 23.7 ± 1.5 | 22.5 ± 1.3 | 21.4 ± 0.6 | 23.6 ± 1.5 |
| Fructose (mM) | 24.8 ± 1.8 | 21.4 ± 1.5 | 25.2 ± 3.1 | 21.6 ± 2.1 | 23.2 ± 1.3 | 23.4 ± 1.4 |
| Consumed carbohydrates (mM) | 32.5 ± 1.1 | 32.8 ± 1.7 | 33.9 ± 0.9 | 30.8 ± 1.7 | 31.3 ± 2.3 | 34.1 ± 1.0 |
| Glucose (mM) | 22.6 ± 0.8 | 23.2 ± 1.2 | 23.7 ± 1.2 | 22.5 ± 0.8 | 21.4 ± 0.7 | 23.6 ± 0.6 |
| Fructose (mM) | 9.9 ± 1.6 | 11.3 ± 1.3 | 10.2 ± 0.6 | 8.3 ± 0.6 | 9.9 ± 0.5 | 10.5 ± 0.6 |
| Total volatil fatty acids (mM) | 49.7 ± 1.1 | 47.7 ± 5.6 | 53.9 ± 4.5 | 45.32 ± 2.6 | 48.1 ± 0.8 | 57.2 ± 0.9 |
| Acetate production (mM) | 43.8 ± 1.9 | 38.6 ± 3.0 | 43.1 ± 2.1 | 39.8 ± 1.2 | 43.2 ± 1.6 | 52.0 ± 1.8 |
| Lactate production (mM) | 5.9 ± 0.5 | 9.1 ± 3.2 | 10.8 ± 0.7 | 5.53 ± 0.8 | 4.8 ± 0.4 | 5.2 ± 0.4 |
| Total H2 production (mM) | 78 ± 4.3 | 71.8 ± 5.3 | 81.5 ± 5.4 | 76.1 ± 5.2 | 86.2 ± 4.6 | 98.0 ± 3.7 |
| H2 yield YH 2∕C6 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 2.9 |
| Maximal H2 production rate (mM/h) | 10.3 ± 0.3 | 7.4 ± 0.6 | 7.5 ± 0.9 | 8.7 ± 0.3 | 9.4 ± 0.6 | 9.7 ± 0.3 |
| Produced CO2 (mM) | 35.8 ± 3.2 | 32.9 ± 4.6 | 38.6 ± 3.7 | 33.8 ± 2.5 | 42.4 ± 2.8 | 47.6 ± 2.6 |
| NH4Cl∗ (mM) | 10.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 |
| YH 2∕acetate | 1.78 | 1.86 | 1.89 | 1.91 | 1.99 | 1.88 |
| YVFA/C 6 | 1.53 | 1.46 | 1.59 | 1.47 | 1.54 | 1.68 |
| YGlc/Lac | 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| YH 2∕CO2 | 2.18 | 2.18 | 2.11 | 2.25 | 2.03 | 2.06 |
| Yacetate/C 6 | 1.35 | 1.18 | 1.27 | 1.29 | 1.38 | 1.52 |
∗NH4Cl is the concentration equivalent to pyruvate measured.
3.2.2. OWJ as a basal medium for biohydrogen production
A minimum culture medium containing only 17% of OWJ (200 mL in 1200 mL final) and SW, as a sole micro/macroelement, energy and carbon sources, was inoculated with TM (10% v/v) for a total volume of 1200 mL. The aim was to evaluate the efficiency of TM fermentative H2 production using OWJ as a limiting factor. The results are presented in Figure 2 and Table 2, E2.
TM produced H2 with increasing productivity reaching maximum values of 7.4 mM/h ± 0.6. The H2 total production (or cumulative production) reached the maximum value of 71.8 mM ± 2.3 mM after 24 h of growth. In parallel, simple sugars (glucose and fructose) consumption as well as volatile fatty acids (acetate and lactate) production by TM during the fermentation was followed by HPLC and represented in Figure 3.
Simple sugar consumption (glucose: blue diamond and fructose: orange square) and volatile fatty acid production (acetate: green triangle and lactate: red circle) over time by Thermotogamaritima in presence of 200 mL (17% v/v) onion waste juice as the sole carbon and energy source.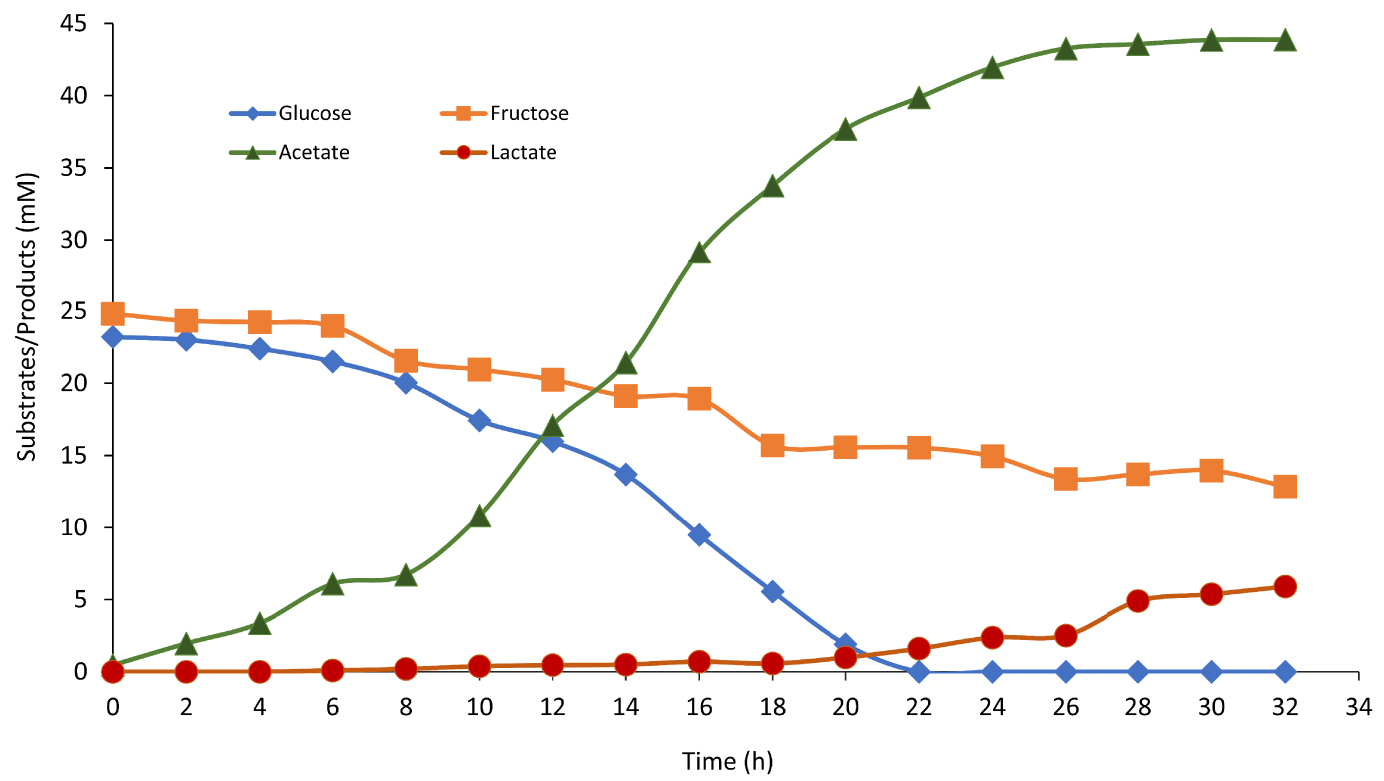
H2 production (HP; empty symbol) and H2 production rate (HPR, full symbol) by Thermotoga maritima with 200 mL (17% v/v) onion waste juice (OJ) as the sole carbon and energy source (purple square) plus: NH4Cl (blue circle); FeCl2 (orange diamond); FeCl2+NH4Cl (green triangle).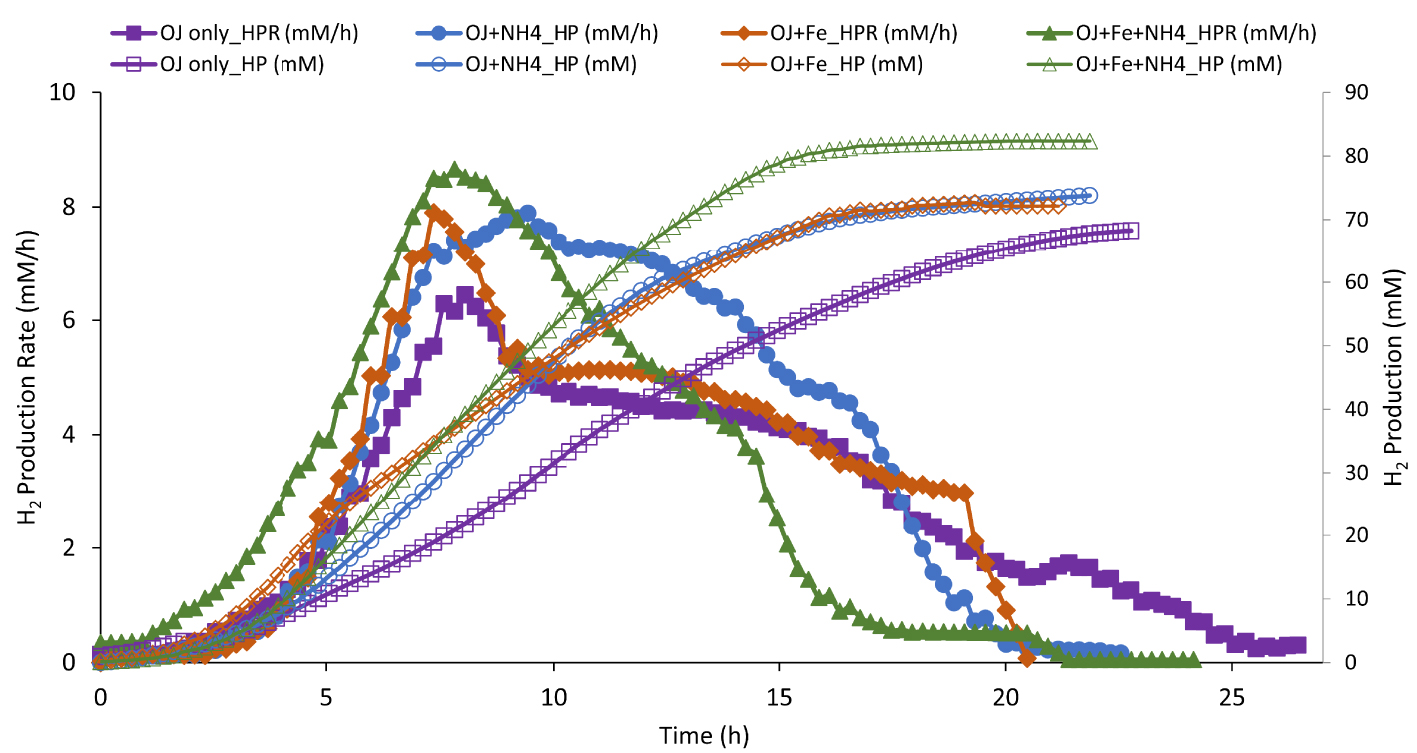
Organic waste has been used for the first time as the sole carbon, oligoelement and energy source for TM growth. Onion has the particularity to contain mainly monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) which are TM choice substrates. During the fermentation (E2), the sugars concentrations gradually decreased in correlation with increasing acetate concentration, reaching a maximum value of 43.8 mM. In fact, TM can ferment soluble sugars present in the OWJ liquid fraction and produce hydrogen following the “acetate” pathway. After 22 h, glucose (22.6 mM ± 0.8), considered as a limiting substrate, was completely consumed by TM which led to growth inhibition and biohydrogen production by directing the metabolism of TM towards the “lactate” pathway. Indeed, fructose is hardly degraded by TM because it does not have a specific fructose transferase system [36].
Although TM was able to grow on onion as a sole oligoelement, carbon and energy sources, kinetic parameters obtained for the experiment with 200 mL of OWJ and SW, were lower than those obtained in complete rich medium. This demonstrated a lack of essential elements in OWJ which limit the dihydrogen production compared to a rich medium. In previous work focusing on H2 production from organic waste, the medium culture has to contain preferentially reduced sulfur compounds, an inorganic nitrogen source and oligoelements especially iron [31]. Since onion is known to be one of the richest vegetables in organsulfur compounds, represented by cysteine derivatives such as S-alk(en)yl-L-cysteine sulfoxides [21], the addition of Cys-HCl did not give any significant difference on the fermentative kinetic parameters, whatever the culture conditions tested (data not shown). In OWJ, the sulfur compounds would bring the organosulfur compounds easily assimilable by TM. Moreover, these sulfur compounds and the antioxidant ones naturally present in onion could protect TM from free radicals produced during oxidative stress. Along the same line, these sulfur compounds allow rapid reduction of the medium redox potential, inducing the metabolic activity initiation of TM.
3.3. Supplied compounds for fermentation optimization
Results of H2 productivity and total H2 production during fermentation from culture mediums containing NH4Cl and/or FeCl2, as a sources of nitrogen and iron respectively, are represented in Figure 4 and Table 2.
3.3.1. Nitrogen supply
To determine if the only ammonium source provided by OWJ was limiting for H2 production by TM, 0.5 g/L of NH4Cl ( mM) was added to 17% of OWJ mixed with SW. Results showed (Figure 4 and Table 2, E3) that HPR (7.52 mM/h ± 0.93), HY (2.41), and THP (81.5 mM ± 7.4) were appreciably equal to those obtained without the addition of nitrogen.
Nitrogen is an essential component of proteins, nucleic acids, and enzymes and thus, of a great importance for hydrogen producers. In previous study, a significant increase in biomass yields was observed with NH4Cl feed concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 1.0 g/L in continuous culture [33]. In our conditions, OWJ preparation led to pyruvic-acid release accompanied by equimolar ammonium production. Early studies showed that the perceived pungency of fresh onions is correlated with high levels of pyruvate, a by-product of the enzymatic hydrolysis, catalyzed by allinase, of the alliin (alkyl-cysteine sulphoxide) into allicin, pyruvic acid, and ammonium [28]. After cutting the onion, this enzyme, originally present in the vacuole, is released into the cytoplasm, where is its substrate. Under these conditions, the enzymatic transformation of this major sulfur compound by the alliinase into allicin and pyruvic acid [37] leads to the stoichiometric production of ammonium:
3.3.2. Iron supply
Biohydrogen production requires essential oligoelements for microbial metabolism during fermentation. Among these, iron represents the most important nutrient element to form hydrogenase or other iron proteins required for almost all biohydrogen production [39].
In our conditions, iron concentrations supplied by OWJ (the natural seawater contains between 0.05–2 nM; [40]) did not exceed 0.07 mg/L (0.21 mg/100 g of fresh onion; [20]).
The Fe ion supplementation in fermentative H2 production processes influences them positively and increases the hydrogen activity [35]. Indeed, iron is a major constituent of bifurcating Fe–Fe hydrogenase in TM, the key enzyme involved in pyruvate oxidation to acetyl-CoA and CO2 and proton reduction to molecular H2 [41]. The Fe–Fe hydrogenase contains a bimetallic Fe–Fe active center and Fe–S centers and its limitation reduces biohydrogen production by decreasing the TM growth. A previous report revealed that temperature was a governing factor in determining the Fe2+ effect on hydrogen production. It was observed that optimum Fe2+ concentrations decreased at higher temperatures [42].
Elbeshbishy et al. [43] presented a summary of optimal iron concentrations in several hydrogen-producing microorganisms with concentrations ranging from 10 to 1600 mg/L. Laboratory experiments have shown that the optimal iron supply (FeCl2) did not exceed 10 mg/L for an optimal fermentation with TM. Beyond this concentration, the additional iron did not increase the TM fermentative metabolism (data not shown). Thus, 10 mg/L have been supplied in media culture comprising 17% (v/v) of OWJ with SW (Figure 4, Table 2, E4). HPR (8.66 mM/h ± 0.9), HY (2.47 molH2∕molHexose), THP (76.1 mM ± 5.2) were significantly higher than those obtained with only OWJ. Little lactate quantity (5.53 mM ± 0.8) was produced during the fermentation into an iron supply medium comparatively with 200 mL OWJ, with or without NH4Cl (10.8 and 9.1 mM). Lactate is a byproduct of TM metabolism from the reduction of pyruvate by lactate dehydrogenase when the hydrogenase no longer oxidizes NADH [12]. Lactate levels reported during fermentation by Thermotoga species have varied from trace amounts up to levels rivaling that of acetate [44].
Dabrock et al. [45] demonstrated that a lactate significant amount was produced during glucose fermentation by Clostridium pasteurianum when the iron concentration was limiting. In our case, during growth in NH4Cl condition, lack of TM iron led to process the pyruvate into acetyl-CoA and shifted its metabolism towards lactate production.
3.3.3. Iron plus nitrogen supply
Maximal H2 production rate (blue bar chart) and total H2 production (orange curve) by Thermotoga maritima with 200 mL (17% v/v) onion waste juice (OJ) as the sole carbon and energy source (OJ only) plus: NH4Cl (OJ+NH4); FeCl2 (OJ+Fe); FeCl2+NH4Cl (OJ+Fe+NH4); FeCl2+NH4Cl+YE (OJ+Fe+NH4+YE).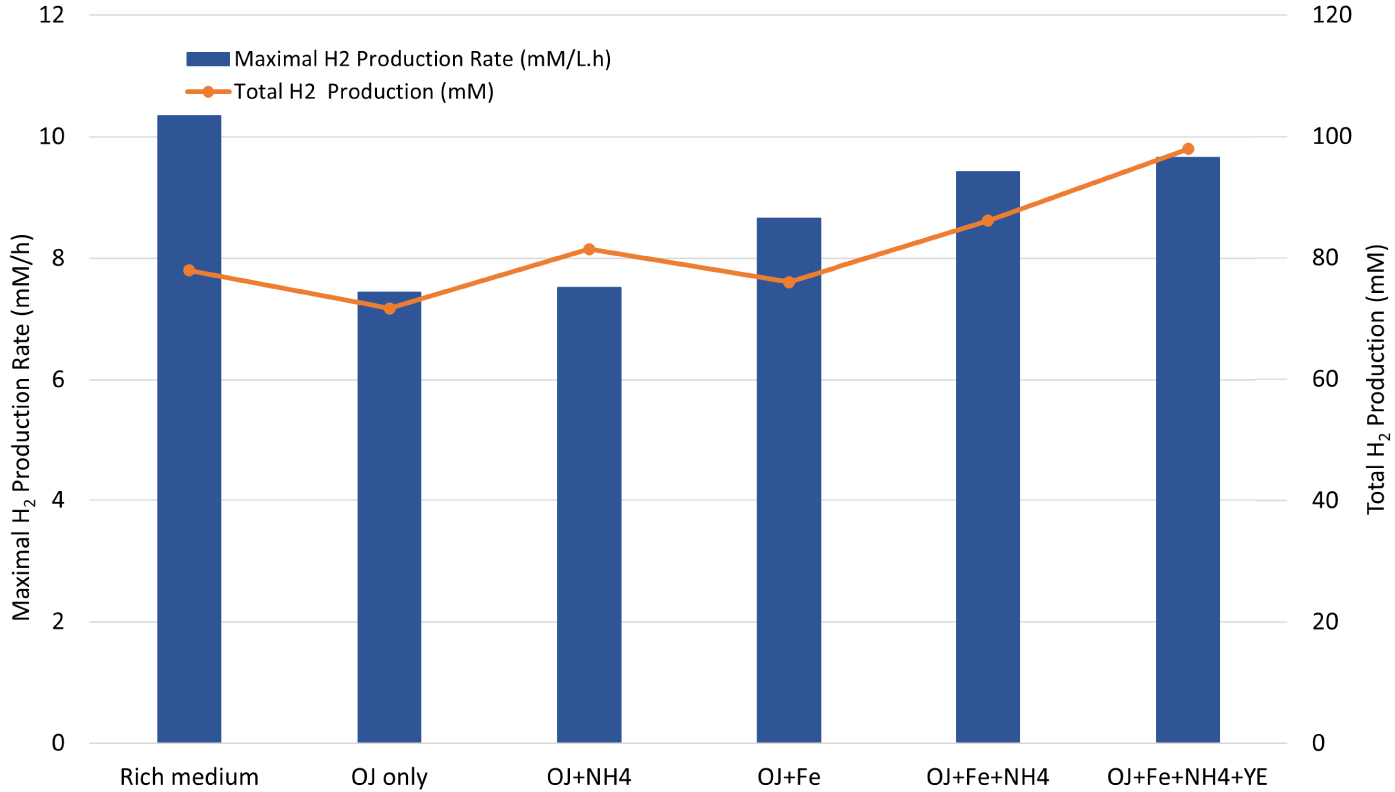
Effect of iron on ammonia-based cultures was further investigated by adding 10 mg/L of FeCl2 and 0.5 g/L of NH4Cl to OWJ medium mixed with SW (E5). The batch culture in this condition showed a distinct improvement in the fermentation of onion waste by TM (Figure 4). The HPR, HY and THP values with NH4Cl+FeCl2 were of 9.42 mM/h ± 0.6, 2.76 and 86.2 mM ± 4.6 respectively (Table 2, E5). These values were similar to results obtained in the presence of a rich medium (10.34 mM/h ± 0.3, 2.4, 78 mM ± 4.3). Effect of yeast extract on biohydrogen production was also investigated (Figure 5, Table 2, E6). A comparison was established between H2 productivities and maximum production rates for a mixture (200 mL OWJ+NH4+Fe) supplemented or not with yeast extract (E6 and E5). Results showed that HPR, THP, and HY were similar with or without YE (Figure 4 and Table 2). This indicated that OWJ contained amino acids and micro/macronutrients, necessary for TM growth.
These results proved that despite the presence of appropriate materials in OWJ for TM growth, this substrate was not sufficient on its own to ensure optimal growth and H2 productivity. It is therefore required to provide OWJ with a source of iron and inorganic nitrogen to optimize the TM fermentation performance.
3.4. Optimization of OWJ concentration
To increase the TM growth and fermentative performance and confirm whether the H2 production inhibition was related to a limitation of the OWJ organic load, the experiments using different volumes of OWJ (from 0 to 1000 mL) supplemented with natural seawater (SW) were initially carried out in flasks and then in bioreactor. No production of H2 or other compounds (acetate and lactate) was observed (data not shown) for the mixture without OWJ (only seawater). The maximum production rate, as well as the total H2 production, is represented in Figure 6 and Table 3 (E2, E7, E8, E9 and E10) for the different volumes of OWJ (200, 400, 600, 800, and 1000 mL).
Maximal H2 production rate (blue bar chart) and total H2 production (orange curve) by Thermotoga maritima with increasing volumes of onion waste juice (OJ) (for 1200 mL final volume: 200; 400; 600; 800 and 1000 mL of onion waste juice).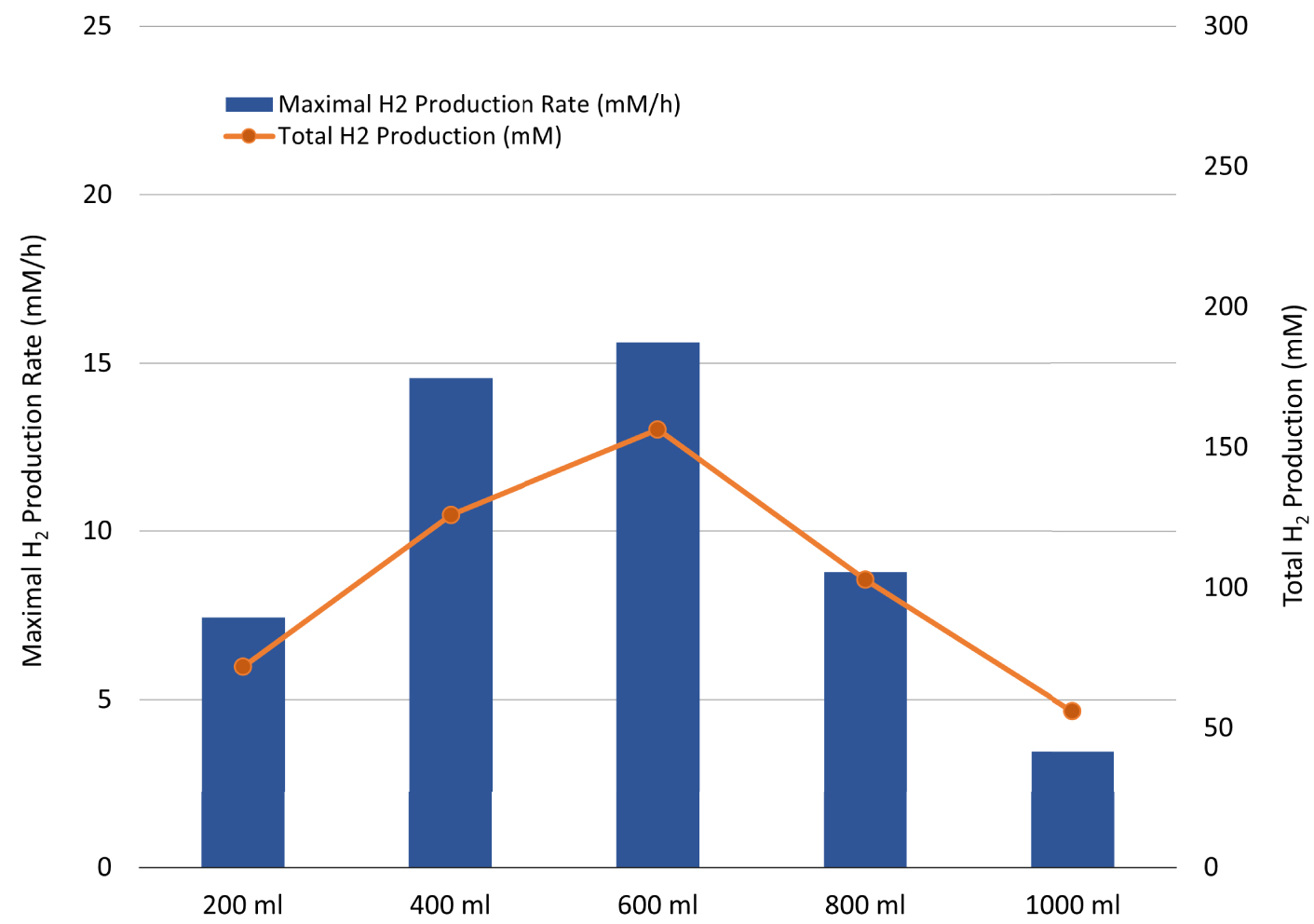
Average results obtained for batch fermentations for experiments in different volumes of onion juice. Each experiment was performed in triplicate, except for the condition with 1000 mL of onion juice performed only in duplicate
| OWJ volume (ml or gram) in 1200 mL | E2 | E7 | E8 | E9 | E10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | |
| Total carbohydrates (mM) | 44.6 ± 2.1 | 93.2 ± 3.9 | 131.6 ± 5.2 | 189 ± 6.3 | 255.6 |
| Glucose (mM) | 23.2 ± 1.2 | 45.4 ± 2.8 | 71.6 ± 1.2 | 111.6 ± 1.4 | 130.2 |
| Fructose (mM) | 21.4 ± 1.5 | 49.8 ± 3.2 | 61.6 ± 4.9 | 76.2 ± 9.2 | 125.4 |
| Consumed carbohydrates (mM) | 32.8 ± 1.7 | 56.3 ± 3.8 | 59.01 ± 2.5 | 44.6 ± 1.3 | nd |
| Glucose (mM) | 23.2 ± 1.2 | 35.6 ± 0.8 | 37.16 ± 0.5 | 39.26 ± 1.2 | nd |
| Fructose (mM) | 11.3 ± 1.3 | 20.7 ± 1.3 | 21.85 ± 1.4 | 5.34 ± 0.8 | nd |
| Total volatil fatty acids (mM) | 47.7 ± 5.6 | 83.3 ± 7.4 | 97.9 ± 4.8 | 88.3 ± 3.7 | nd |
| Acetate production (mM) | 38.6 ± 6.0 | 72.6 ± 3.6 | 82 ± 3.2 | 56.8 ± 4.6 | nd |
| Lactate production (mM) | 9.1 ± 3.2 | 10.7 ± 2.3 | 15.9 ± 3.6 | 31.5 ± 4.8 | nd |
| Total H2 production (mM) | 71.8 ± 5.3 | 125.7 ± 9.6 | 156.1 ± 7.5 | 102.6 ± 10.8 | 55.9 |
| H2 yield YH 2∕C6 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.6 | 2.3 | nd |
| Maximal H2 production rate (mM/h) | 7.4 ± 0.6 | 14.6 ± 0.9 | 15.6 ± 0.7 | 8.8 ± 1.6 | 1.5 |
| Produced CO2 (mM) | 32.9 ± 4.6 | 55.6 ± 5.7 | 70.7 ± 10.3 | 69.5 ± 5.3 | nd |
| NH4Cl∗ (mM) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 5.9 ± 0.6 | 7.0 ± 0.7 | 9.2 |
| YH 2∕acetate | 1.86 | 1.73 | 1.90 | 1.81 | nd |
| YVFA/C 6 | 1.46 | 1.48 | 1.66 | 1.98 | nd |
| YGlc/Lac | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.71 | nd |
| YH 2∕CO2 | 2.18 | 2.26 | 2.21 | 1.48 | nd |
| Yacetate/C 6 | 1.18 | 1.29 | 1.39 | 1.27 | nd |
∗NH4Cl is the concentration equivalent to pyruvate measured. Nd: not defined.
The optimum OWJ volume was 600 mL (50% of volume, v/v) (E8) with a corresponding HPR (15.6 mM/h ± 0.7) and THP (156.1 mM ± 7.5), correlated with the greater degradation of sugar (59.1 mM ± 2.5). These values were the highest compared to the other volumes used. Over 600 mL, the onion started to inhibit hydrogen production correlated with a metabolism deviation towards lactate production. The HPR (8.8 mM/h ± 1.6) and HY (2.3) decrease, correlated with high lactate production (31.5 mM ± 4.8) for a volume of 800 mL (E9), could be explained by the high substrate concentrations [11, 46]. Most of the batch studies were carried out with initial substrate concentrations of 1–50 gCOD/L and a majority of these studies have suggested that initial substrate concentrations above 20 gCOD/L may decrease H2/substrate yields via substrate inhibition for both thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria [43, 47, 48]. The total measured COD in the prepared OWJ was 61.2 g/L ± 9.3. At 800 mL of OWJ, the COD was about 41 gCOD/L whereas for 1000 mL of OWJ no fermentation was performed in these conditions with a COD supply of about 50 gCOD/L.
3.5. Optimal hydrogen production from 50% OWJ (v/v)
To evaluate the fermentability of OWJ under the best conditions, we tested the TM fermentation in a culture medium containing 50% v/v of OWJ supplemented with iron (10 mg/L of FeCl2) and ammonium (0.5 g/L of NH4Cl). This experiment provided a total production of 272.4 mM of biohydrogen. The maximum HPR and HY were also increased to 23 mM/h and 3.2 molH2∕molHexose respectively. These values were close to the highest obtained with TM during a batch culture, under pH and temperature regulation conditions. Interestingly, the addition of YE in the latter condition showed a significant decrease in the kinetic parameters (Figure 7). The addition of YE could lead to a fermentative process limitation due to a COD increase in the culture medium. As beyond about 30 gCOD/L, TM seemed to undergo an inhibition by the substrate. The exact inhibitory substrate concentration requires further experiments in synthetic culture medium in the presence of increasing concentrations of glucose and YE, while following conventional growth kinetic parameters (growth rate, H2 productivity, total H2 production …). However, these results showed that the YE contribution seems unnecessary to improve the OWJ nutritional intake, which consequently would contribute to reducing the synthetic compounds price in feedstocks.
Maximal H2 production rate (blue bar chart) and total H2 production (orange curve) by Thermotoga maritima with 600 mL (50% v/v) onion waste juice (OJ) as the sole carbon and energy source (OJ only) plus: NH4Cl (OJ+NH4); FeCl2 (OJ+Fe); FeCl2+NH4Cl (OJ+Fe+NH4); FeCl2+NH4Cl+YE (OJ+Fe+NH4+YE).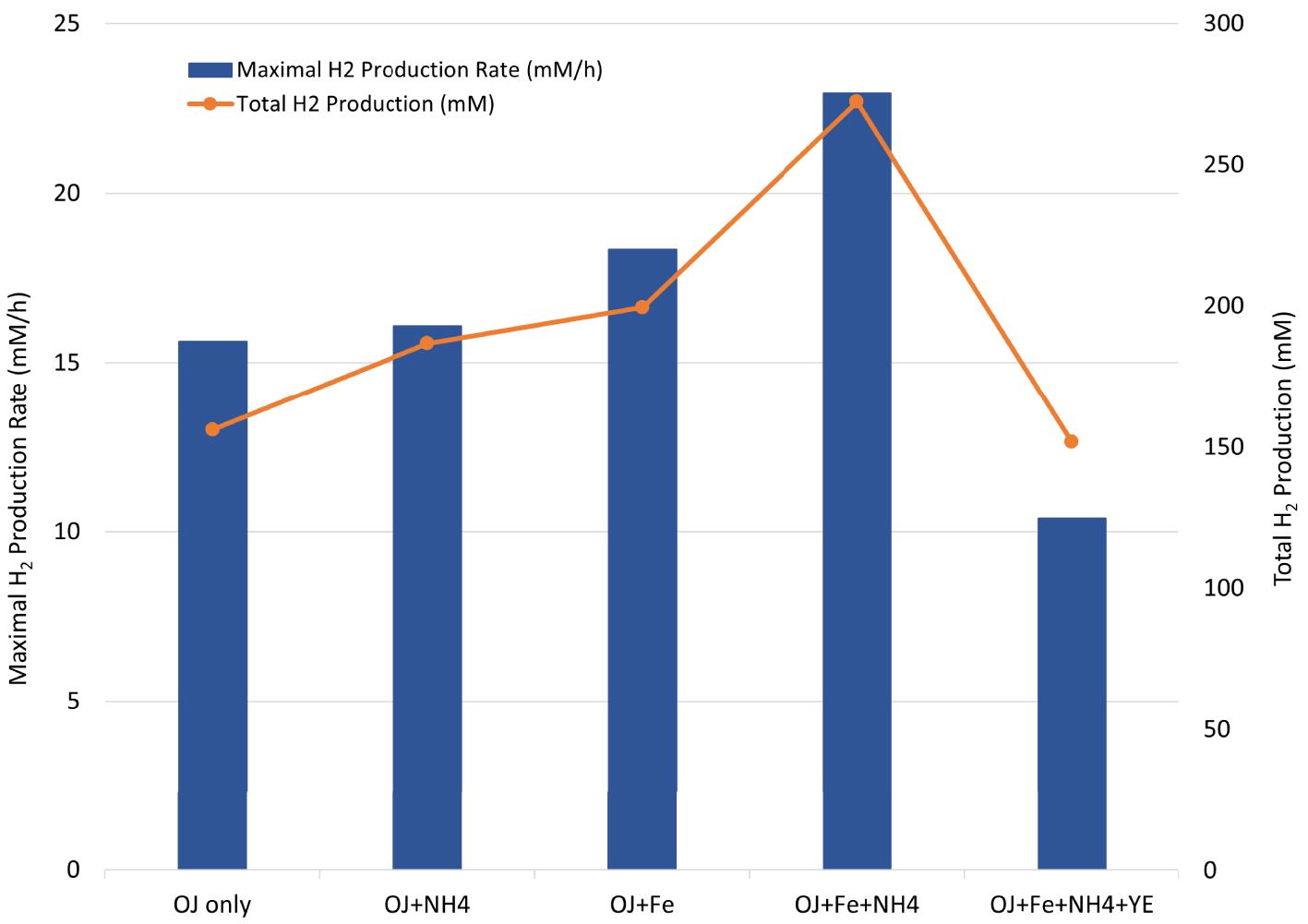
3.6. Optimization of fermentation mode
Most of the dark fermentation studies for hydrogen gas production from feedstock substrates were performed by discontinuous cultures. Batch fermentations are usually subject to substrate and product limitations yielding low hydrogen gas productivities. In our conditions, above 50% v/v of OWJ (31 gCOD/L), hydrogen production decreased due to the inhibition by the substrate charge. In this case, the fed-batch operation could have considerable advantages as compared to batch operation and could be used to overcome substrate/product and toxic compound inhibitions encountered at high substrate concentrations. The substrate solution was added with a rate sufficient to support the bacterial community and to eliminate the substrate inhibition with no effluent removal. To develop a larger-scale H2 production system in overcoming the problem linked to the substrate limitation in batch cultures, fermentation in the fed-batch mode was carried out with OWJ addition in different stages (Figure 8). Each addition of concentrated OWJ mixed with sea salt was performed when the HPR began to decrease. Figure 8 shows the comparison between batch and fed-batch cultures with 50% OWJ as the only sources of oligoelements, energy and carbon. The first addition of 120 mL of OWJ (10% v/v) in the batch culture condition was made one hour after the HPR was decreased. H2 production increased again but with a significant decrease in the previous maximum hydrogen production rate (Figure 8). Subsequent additions showed the same effect with an overall decrease in H2 production. As noted, ammonium and iron are essential for optimal growth. Cell multiplication is dependent on these micro/macro elements. In our Fed-batch experiments, we assumed that the lack of iron and ammonium led to this decrease in hydrogen production combined with a significant COD-increasing effect. However, this experiment showed that it is possible to exceed the limiting concentration of COD in our culture media with TM. After four additions and about 40 h of growth, the maximum H2 production reached 330 mM. Under optimal conditions with iron and ammonium addition, this H2 production was doubled (data not shown) showing the efficiency of the fed-batch operation with TM to produce biohydrogen from OWJ.
H2 production (HP; empty symbol) and H2 production rate (HPR, solid symbol) by Thermotoga maritima with 600 ml (50% v/v) onion waste juice (OWJ) as the sole carbon and energy source under batch (gray triangle) and fed-batch (blue square) conditions. In the fed-batch operation, an initial addition of 120 ml of onion waste juice was performed followed by the sequential addition of 10% (v/v) of the initial volume of the culture medium.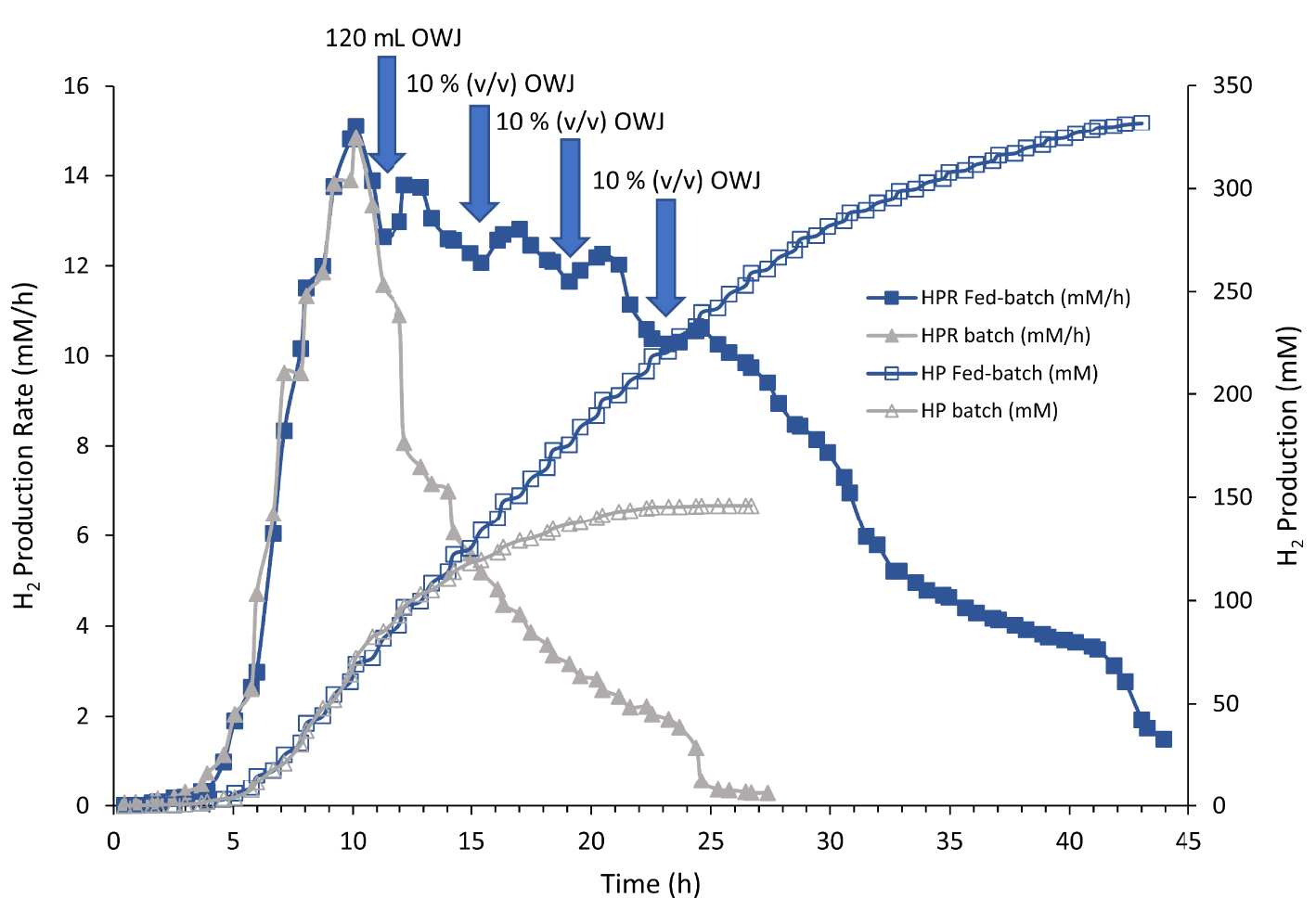
4. Conclusion
Onion is one of the world’s most versatile and traded vegetables (85 million tons) generating a lot of waste at a low cost. These waste materials represent an environmental problem since they are not suitable, in high concentration, for livestock feeding due to onion unpleasant smell and as an inorganic fertilizer given the rapid herbicide and antimicrobial agents development. To date, only few studies focused on the onion waste recycling process for the production of value-added by-products as functional compounds, or of biogas (methane and H2) by anaerobic digestion [26]. In this work, biohydrogen fermentation by Thermotoga maritima (TM) was successfully performed from a mixture of Onion Waste Juice and seawater, in a batch STR system. The presented results indicated that the highest H2 production parameters were obtained for mixture of OWJ with SW and iron/ammonium input. These results were nearly 1.3-fold greater than those in batch cultures without iron/ammonium supply. The fed-batch culture of TM in the 2-L STR bioreactor showed a high production of H2 despite a COD above 30 gCOD/L. The maximal H2 production achieved was 330 mM at 40 h. These results could potentially be used in assessing the feasibility of TM use in OWJ conversion into H2 on an industrial scale.
Conflicts of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
This work received financial support from the IRD JEAI program (JEAI BIOTECH2). The authors are grateful to Richard Auria, Guillaume Pillot, Yannick Combet-Blanc and Jean Lorquin for their support. Many thanks to the Higher Institute of Applied Biological Sciences of Tunis (ISSBAT) and Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research for providing their facilities to the research team.



 CC-BY 4.0
CC-BY 4.0