1 Introduction
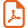
Aza-Michael addition is one of the most exploited reactions in organic chemistry [1]. In fact, it is regarded as one of the most, if not the most, popular and efficient methods for the creation of the carbon–nitrogen bond, which is a key feature of many bioactive molecules. Moreover, it is the shortest pathway to β-aminocarbonyl compounds including β-aminoacid derivatives, which are valuable intermediates for the synthesis of nitrogen containing biologically active substances and drugs [2]. Finally, the aza-Michael reaction often initiates domino transformations resulting in the formation of complex polyfunctional carbo- and heterocycles and analogues of natural compounds [3]. Highly nucleophilic amines add readily to electron-poor alkenes under mild conditions but most of the methods developed for aliphatic amines do not transpose to aromatic amines. Indeed, there are only few examples of the uncatalyzed aza-Michael addition of arylamines [4–6]. Consequently, many procedures using Lewis or Brønsted acids and transition metal salts to promote the conjugate addition of aromatic amines to Michael acceptors bearing a highly activated double bond have been reported [7–13]. However, many of them suffer from several drawbacks from economic, environmental, or synthetic viewpoints and deal often with only terminal alkenes. On the other hand, it is well known that the nucleophilicity of aromatic amines strongly depends on the solvent nature [14]. In fact, the 1,4-addition of primary anilines occurs preferentially in water, trifluoroethanol, or hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP), in the absence of any external promoter or catalyst [15]. In this context, we recently reported that the unprecedented combination of hyperbaric conditions and HFIP as a solvent promoted the conjugate addition of poor nucleophiles (primary or secondary anilines) to a wide variety of Michael acceptors [16]. We have assumed that the solvent activates mostly the electrophilic partner by hydrogen bond donation or protonation besides a potential beneficial effect on the nucleophilicity of anilines [14] (Scheme 1).
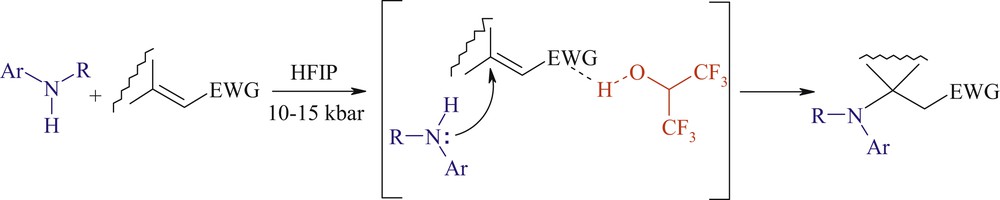
Activation of Michale acceptor by HFIP.
So, HFIP can be regarded as a “smart solvent” that activates the double bond of the Michael acceptor toward attack of weak nucleophiles without affecting the arylamine nucleophilicity [17]. What are the principal properties that a solvent should have to exhibit this remarkable effect? If the aniline bears an additional proton-donating group, can the reaction proceed without a strong proton donor such as HFIP? To answer these questions, we decided to examine the reaction of methyl crotonate (1) as Michael acceptor with anilines bearing an amino-, alkoxy- or hydroxyl group.
2 Results and discussion
The acidity/hydrogen bond donation ability of HFIP seems to stand at the appropriate point where it is sufficient to activate the Michael acceptor and at the same time not acidic enough to deactivate the anilines by protonation. In an effort to understand the role of the solvent in the aza-Michael reaction with weak nucleophiles, we decided to study the effect of protic solvents instead of fluorinated alcohols in the conjugate addition of anilines. Because phenol and HFIP have close pKa values (10.0 for PhOH and 9.3 for HFIP), we assumed that they should exert a similar influence on the reaction course. To test this hypothesis, we reacted 1 with 2-anisidine (2a) under different conditions. The reaction was conducted in alcoholic solvents (MeOH and HFIP) at room temperature and under high pressure (10 kbar) in the presence (or not) of PhOH. As expected, the fluorinated solvent favors the conjugate addition (45%; Table 1, entry 1), whereas no reaction occurs when methanol was used as a solvent (Table 1, entry 2). Interestingly, the addition of even 1 equiv of phenol in MeOH promoted this reaction up to 19% (Table 1, entry 3).
Solvent and additive effect in the aza-Michael addition of 2-methoxyaniline 2a and 2-hydroxyaniline 2b onto methyl crotonate.
| Entry | Aniline | R | Solvent | Additive | Conversion,a (%) |
| 1 | 2a | Me | HFIP | – | 45 |
| 2 | 2a | Me | MeOH | – | 0 |
| 3 | 2a | Me | MeOH | PhOH (1 equiv) | 19 |
| 4 | 2a | Me | MeOH | PhOH (3 equiv) | 84 |
| 5 | 2b | H | HFIP | – | 10 |
| 6 | 2b | H | MeOH | – | 25 |
a Conversion of 1 was calculated from 1H NMR spectrum of the reaction mixture with toluene as an internal standard.
So, the use of another proton donor such as phenol instead of HFIP increases the reaction efficiency under similar reaction conditions (84% vs 45%). To confirm the ability of phenol to activate the Michael acceptor by H-bonding, we recorded IR spectra of the ester 1 in the presence of either HFIP or phenol. A low-frequency shift ν (CO) of 15 cm−1 was observed in both cases assigned to the formation of a hydrogen bond between the carbonyl oxygen and the alcoholic or phenolic proton.
Next, we assumed that if the initial aniline contains a phenolic hydroxy group, the conjugate addition of such hydroxyaniline will take place without any promotor. To confirm this hypothesis, we carried out an experiment with 2-hydroxyaniline (2b). Interestingly, and in contrast to the previous results on the conjugate addition of anilines in HFIP, the 2b (10 times less acidic than HFIP) added to methyl crotonate is better in MeOH (conversion is 25%) than in HFIP (10%) (Table 1, entries 5 and 6). This result is difficult to explain but can be partially due to the low solubility of 2-hydroxyaniline in HFIP at room temperature.
Complementary quantum chemical calculations suggest that 2b plays simultaneously a role of promoter and weak nucleophile (Scheme 2).
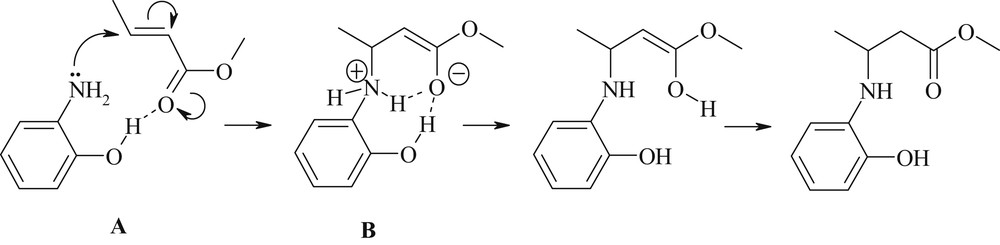
Aza-Michael addition of 2-hydroxyaniline 2b onto methyl crotonate.
Thus, according to density functional theory (DFT) calculations run in the gas phase at the B3LYP/6-311+G** level of theory [18], the complex A displays a strong intermolecular H-bond between the aminophenol hydroxy group and the carbonyl oxygen atom (d[OH⋯OC] = 1.823 Å, δE = −7.2 kcal/mol). At the transition state B corresponding to the addition of the amino group on the Cβ olefinic atom, this intermolecular H-bond strengthens (dH⋯O = 1.667 Å only). The activation barrier for the first reaction step (addition of the primary amine to the CC double bond) is equal to +29.7 kcal/mol for 2b, whereas for 2a it increases to +32.1 kcal/mol. It is likely that in HFIP the fluorous alcohol disrupts this interaction and thus deactivates the process (Table 1, entry 5).
On the basis of these results, we decided to test the reaction of 1 with anilines bearing a second amino group. These reactions were conducted in fluorinated and nonfluorinated alcohols at room temperature and under high pressure. It should be emphasized that high pressure is necessary for the reaction to occur [16]. Thus, in our experiments, when ester 1 (2 equiv) was refluxed with 1,4-diaminobenzene 4a in methanol overnight under atmospheric pressure, only starting materials were recovered.
To our surprise, and in contrast to the previous results obtained for the aza-Michael reaction with primary and secondary anilines, methanol is the best choice to promote the conjugate addition of arylamines 4a–c to Michael acceptor 1 under high-pressure conditions. The conversion of 1 depends slightly on the position of the NH2 group, the more nucleophilic 2- and 4-amino anilines giving, expectedly, the best results. In HFIP, the conversion reached only 10–25% (Table 2). Note that the treatment of 1 with diamine 4a leads to bis-adduct 6a only; monoadduct 5a was never observed.
Addition of phenylene diamines (4a-c) and aniline (4d) onto methyl crotonate.
| Entry | Aniline | Solvent | Conversiona (%) | Product |
| 1 | 4a | MeOH | 90 | 6a |
| 2 | 4a | HFIP | 20 | 6a |
| 4 | 4b | MeOH | 60 | 5b |
| 6 | 4b | HFIP | 25 | 5b |
| 7 | 4c | MeOH | 95 | 5c |
| 8 | 4c | HFIP | 10 | 5c |
| 9 | 4d | MeOH | 12b | 5d |
| 10 | 4d | HFIP | 100 | 5d |
a Conversion of 1 was calculated from the 1H NMR spectrum of the reaction mixture with toluene as an internal standard.
b After 24 h: Ref. [16].
These results led us to the conclusion that the acidity of the aniline amino group is high enough to activate the Michael acceptor 1. To confirm this assumption, we performed an experiment using an excess of aniline. To our delight, when 1 was treated with 4 equiv of aniline 4d (instead of 0.5 equiv as previously) in methanol (instead of HFIP), the target adduct 5d was obtained in very good yield (Table 3, entry 4).
Influence of the amount of aniline on the outcome of the reaction with methyl crotonate under high pressure.
| Entry | Solvent | Aniline (equiv) | Conditions | Conversiona (%) | Reference |
| 1 | HFIP | 0.5 | 14 kbar, 17 h | 100 | [16] |
| 2 | HFIP | 0.5 | 10 kbar, 24 h | 90 | [16] |
| 3 | MeOH | 0.5 | 10 kbar, 24 h | 12 | [16] |
| 4 | THF | 5.0 | 10 kbar, 17 h | 0 | This work |
| 5 | HFIP | 5.0 | 10 kbar, 17 h | 20 | This work |
| 6 | MeOH | 5.0 | 10 kbar, 17 h | 30 | This work |
| 7 | MeOH | 4.0 | 14 kbar, 17 h | 84 | This work |
a Conversion of 1 was measured by 1H NMR of the reaction mixture with toluene as a standard.
In summary, we describe in this article suitable conditions to promote the conjugate nucleophilic addition of functionally substituted aromatic amines to enoates. These preliminary researches show that, contrary to unsubstituted anilines, their analogues bearing OH or NH2 groups are good hydrogen bond donors. In these cases, no expensive fluorinated alcohols are required and the reaction can be carried out in usual protic solvents under very mild conditions. Further works on the chemoselectivity of the hetero-Michael reaction with aromatic amines are in progress.
3 Experimental part
1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded using a Bruker AVANCE 400 MHz (at 400 and 100 MHz, respectively) and Bruker AVANCE 300 MHz (at 300 and 75 MHz, respectively) spectrometers for solution in CDCl3. Chemical shifts (δ) in parts per million are reported using residual chloroform (7.24 for 1H NMR and 77.2 for 13C NMR) as an internal reference. The coupling constants (J) are given in Hertz. The IR spectra were measured using a Perkin–Elmer 16PC FT-IR Instrument. ESI-MS spectra were obtained by direct injection of the sample solution using a Thermo LCQ Advantage Max with methanol as a solvent. High-pressure reactions were performed using a piston-cylinder type apparatus (Ollivaud/Lebas, France) for pressures up to 14 kbar. The silica gel used for flash chromatography was 230–400 mesh. All reagents were of reagents grade and were either used as such or distilled before use.
All reactions under consideration were carried out in an appropriate solvent under exactly the same conditions. The 1H NMR spectra of the reaction mixture were recorded immediately after the end of reaction time without elimination of the solvent. The conversion of initial ester was calculated using toluene signals as the internal standard.
4 General procedure for the reaction of methyl crotonate 1 with substituted anilines 2a,b and 4a–c
The mixture of functionally substituted aniline 2a,b or 4a–c (1 mmol) and 1 (2 mmol) in the corresponding solvent (0.5–1.5 mL) was placed in a Teflon reaction vessel and allowed to stand for 2–17 h under 10–14 kbar at room temperature. After that the pressure was released and the mixture was concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography (silica gel, eluent pentane/diethyl ether, from 90:10 to 50:50). The compounds 3a,b, 5b,c, and 6a–c were obtained according to this procedure. Aminoester 5d was described previously [19].
5 Methyl 3-((2-methoxyphenyl)amino)butanoate (3a) [20]
Oil (66 mg, 30%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ 1.31 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H, CH3C), 2.40 (dd, J = 14.9, 7.6 Hz, 1H, CH2), 2.73 (dd, J = 14.8, 5.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.69 (s, 3H, OMe), 3.84 (s, 3H, CH3OC(O)), 3.91–4.02 (m, 1H, CH), 4.29 (br.s, 1H, NH), 6.64–6.71 (m, 2H, Ar), 6.75–6.81 (m, 1H, Ar), 6.85–6.92 (m, 1H, Ar); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz): δ 20.9 (CH3C), 41.2 (CH2), 45.7 (CH), 51.7 (CH3OC(O)), 55.5 (CH3O), 109.8, 110.6, 116.8, 121.4, 136.7, 147.1 (Ar), 172.4 (CO).
6 Methyl 3-((2-hydroxyphenyl)amino)butanoate (3b)
Oil (146 mg, 70%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ 1.16 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H, CH3C), 2.37 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 2.55 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.61 (s, 3H, CH3O), 3.68–3.80 (m, 1H, CH), 4.50 (br.s, 1H, OH), 6.53–6.78 (m, 4H, Ar); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz): δ 20.7 (CH3C), 41.2 (CH2), 47.3 (CH), 52.0 (CH3O), 115.0, 116.1, 119.9, 121.0, 134.9, 146.1 (CAr), 173.3 (CO). IR (cm−1): ν 1711 (CO), 3385 (NH). HRMS (ESI, m/z) calcd for C11H15NO3 209.1052; found 209.1045.
7 Methyl 3-((3-aminophenyl)amino)butanoate (5b)
Oil (52 mg, 25%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ 1.26 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H, CH3C), 2.41 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 2.66 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.30 (br. s, 3H, NH), 3.68 (s, 3H, CH3O), 3.83–3.96 (m, 1H, CH), 5.95–6.15 (m, 3H, Ar), 6.90–7.00 (m, 1H, Ph); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz): δ 20.8 (CH3C), 40.9 (CH2), 46.1 (CH), 51.8 (CH3O), 100.4, 104.9, 105.4, 130.4, 147.7, 148.0 (CAr), 172.5 (CO). IR (cm−1): ν 1721 (CO), 3359 (NH). HRMS (ESI, m/z) calcd for C11H16N2O2 208.1212; found 208.1221.
8 Methyl 3-((2-aminophenyl)amino)butanoate (5c)
Oil (135 mg, 65%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ 1.28 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 3H, CH3C), 2.46 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 2.66 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.39 (br. s, 3H, NH), 3.70 (s, 3H, CH3O), 3.85–3.96 (m, 1H, CH), 6.68–6.78 (m, 4H, Ar), 7.21–7.30 (m, 2H, Ph); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz): δ 20.8 (CH3C), 41.1 (CH2), 46.2 (CH), 51.7 (CH3O), 114.5, 116.9, 119.7, 120.4, 135.6, 135.7 (CAr), 172.6 (CO). IR (cm−1): ν 1723 (CO), 3339 (NH). HRMS (ESI, m/z) calcd for C11H16N2O2 208.1212; found 208.1222.
9 Dimethyl 3,3′-(1,4-phenylenebis(azanediyl))dibutanoate (5a)
Oil (221 mg, 72%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ 1.23 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 6H, CH3C), 2.38 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2), 2.61 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2), 3.30 (br.s, 2H, NH), 3.66 (s, 6H, CH3O), 3.70–3.80 (m, 2H, CH), 6.56 (s, 4H, Ar); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz): δ 20.9 (CH3C), 40.9 (CH2), 47.6 (CH), 51.7 (CH3O), 116.3, 139.5 (CAr), 172.6 (CO). IR (cm−1): ν 1714 (CO), 3361 (NH). HRMS (ESI, m/z) calcd for C16H24N2O4 308.1736; found 308.1727.
10 Dimethyl 3,3′-(1,3-phenylenebis(azanediyl))dibutanoate (6b)
Oil (77 mg, 25%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ 1.26 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 6H, CH3C), 1.55 (s, 1H, NH), 2.41 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2), 2.66 (dd, J = 15.0, 6.0 Hz, 2H, CH2), 3.65 (s, 1H, NH), 3.68 (s, 6H, CH3O), 3.84–3.96 (m, 2H, CH), 5.80–5.9-(m, 1H, Ar), 5.95–6.05 (m, 2H, Ar), 6.90–7.05 (m, 1H, Ar); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz): δ 20.9 (CH3C), 41.0 (CH2), 46.1 (CH), 51.8 (CH3O), 98.9, 103.9, 130.4, 148.1 (CAr), 172.2 (CO). IR (cm−1): ν 1724 (CO), 3386 (NH). HRMS (ESI, m/z) calcd for C16H24N2O4 308.1736; found 308.1726.
11 Dimethyl 3,3′-(1,2-phenylenebis(azanediyl))dibutanoate (6c)
Oil (31 mg, 10%). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ 1.24–1.30 (m, 7H, CH3C, NH), 2.38–2.50 (m, 2H, CH2), 2.58–2.71 (m, 2H, CH2), 3.60–3.90 (m, 9H, CH3O, CH, NH), 6.65–6.75 (m, 4H, Ar); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz): δ 20.9 (CH3C), 41.3 (CH2), 46.6 (CH), 51.7 (CH3O), 115.5, 120.1, 136.6 (CAr), 172.7 (CO). IR (cm−1): ν 1727 (CO), 3325 (NH). HRMS (ESI, m/z) calcd for C16H24N2O4 308.1736; found 308.1741.
Acknowledgments
A.F. is grateful to the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs for the fellowship (program Metchnikov). The CNRS (PICS 6293) through joint program HP2O, Labex SynOrg (ANR-11-LABX-0029), the Région Normandie, and the ERDF are also thanked for their financial support.