1 Introduction
Using radicals is an elegant although demanding strategy to develop highly coupled magnetic molecular systems. The radicals indeed benefit from the versatility of organic chemistry to introduce a welfare of chemical functions but suffer from stability problems. The latter phenomenon is more accurate when going from the nitronyl nitroxide radicals [1] used from the early stage of molecular magnetism to the more recently developed verdazyl radicals [2,3]. Given the strong exchange interaction found in some verdazyl-based systems [4,5] and their ability to coordinate lanthanide ions [6], it is necessary to find solutions to these problems to fully exploit the potential of verdazyl radicals.
A solution to the stability problem is the introduction of isopropyl side chain onto the radical moiety [7]. This bulky group stabilizes the radical and limits π-stacking interaction that usually leads to rather strong antiferromagnetic interactions [8–10].
To test the possibility opened by such radicals, we have synthesized the 1,5-diisopropyl-3-(4′-carboxyphenyl)-6-oxoverdazyl [11]. Along these lines, we describe the reactivity of this radical toward divalent metal ions. The structures of three adducts determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) are detailed, whereas the magnetic properties of the five compounds that were obtained are described.
2 Experimental section
2.1 Synthesis
All chemicals were purchased from Sigma–Aldrich and were used as received.
HIi-Pr verdazyl radicals have been prepared according to the procedure previously reported [11].
[Mg(Ii-Pr)2·2H2O]n·0.35H2O (Ii-Pr–Mg): 0.1 g (0.33 mmol) of verdazyl radical HIi-Pr was dissolved in 15.0 mL of methanol. To this solution was added an excess amount 0.5 g (8.6 mmol) of freshly prepared Mg(OH)2. The reaction mixture was stirred for 30 minutes, filtered, and the solution was allowed to crystallize. These crystals were further recrystallized from ethyl acetate to give homogeneous and pure crystals of Ii-Pr–Mg. The compound was characterized by elemental analysis, IR spectroscopy, and single-crystal XRD. Yield (%) 61, Elemental analyses. Anal. Calcd for C30H40.7MgN8O8.35 (Mr = 671.3): C, 53.68; H, 6.11; N, 16.69. Found: C, 52.57; H, 6.08; N, 16.19. IR (cm−1): 483, 546, 657, 667, 711, 794, 1167, 1230, 1369, 1387, 1410, 1456, 1539, 1558, 1611, 1652, 2982, 3446.
[Mn(Ii-Pr)2(CH3OH)4] (Ii-Pr–Mn): 0.1 g (0.4 mmol) of manganese (II) acetate tetrahydrate was dissolved in 5.0 mL of methanol. To this solution was added a solution of 0.24 g (0.8 mmol) of HIi-Pr in 15.0 mL of methanol. To this reaction mixture was added 20.0 mL of toluene. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred for 3 hours and thereafter was concentrated under reduced pressure. Toluene (20.0 mL) was added to the concentrated solution and stirred for another 3 hours. All of the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and the obtained microcrystalline product was recrystallized from methanol to yield red crystals of Mn(II)-verdazyl compound. These crystals were characterized by elemental analysis, IR spectroscopy, and single-crystal XRD. Yield (%) 57, Anal. Calcd for C34H52N8MnO10 (Mr = 787.32): C, 51.84; H, 6.65; N, 14.22. Found: C, 51.41; H, 6.57; N, 14.33. IR (cm−1): 481, 656, 710, 791, 1168, 1229, 1370, 1387, 1404, 1456, 1545, 1610, 1684, 2978, 3416.
[Zn(Ii-Pr)2(CH3OH)4] (Ii-Pr–Zn): the zinc(II) analogue Ii-Pr–Zn was obtained using the same procedure as for Ii-Pr–Mn but the crystals were not suitable for single-crystal XRD. Yield (%) 48.2, Anal. Calcd for C34H52N8O10Zn (Mr = 796.31): C, 51.16; H, 6.57; N, 14.04. Found: C, 51.27; H, 6.37; N, 14.70. IR(cm−1): 484, 546, 656, 710, 790, 871, 1018, 1128, 1168, 1229, 1301, 1368, 1386, 1557, 1610, 1685, 2934, 2978, 3419.
[Ni(Ii-Pr)2(CH3OH)4] (Ii-Pr–Ni): 0.1 g (0.4 mmol) of nickel (II) acetate tetrahydrate was dissolved in 5.0 mL of methanol. To this solution was added a solution of 0.24 g (0.8 mmol) of HIi-Pr in 15.0 mL of methanol. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred for 20 minutes and allowed to crystallize to yield small crystals of Ii-Pr–Ni. These crystals were characterized by elemental analysis, IR spectroscopy and single-crystal XRD. IR spectrum is given in Annexure. Yield (%) 55, Anal. Calcd for C34H52N8NiO10 (Mr = 790.32): C, 51.59; H, 6.62; N, 14.16. Found: C, 50.49; H, 6.57; N, 14.32. IR (cm−1): 657, 710, 789, 1018, 1168, 1229, 1369, 1387, 1550, 1610, 1685, 2979, 3420.
[Co(Ii-Pr)2(CH3OH)4] (Ii-Pr–Co): the cobalt (II) analogue Ii-Pr–Co was obtained using the same procedure as for Ii-Pr–Ni but the crystals were not suitable for single-crystal XRD. Yield (%) 68, Elemental analyses. Anal. Calcd for C34H52N8O10Co (Mr = 791.31): C, 51.58; H, 6.62; N, 14.15. Found: C, 51.69; H, 6.43; N, 14.24. IR (cm−1): 485, 547, 657, 711, 789, 871, 1018, 1168, 1229, 1369, 1387, 1558, 1610, 1685, 2978, 3420.
2.2 Physical measurements and instrumentation
Elemental analyses were carried out at the Microanalytical Service of the Faculty of Chemistry of the Grenoble University. IR spectra were measured using a Nicolet iS50FTIR spectrometer in KBr.
2.3 Crystallographic structure determination
Crystallographic measurements for compounds Ii-Pr–Mg, Ii-Pr–Mn, Ii-Pr–Ni were carried out using an Oxford-Diffraction Xcalibur E charge-coupled device (CCD) diffractometer equipped with graphite-monochromated Mo Kα radiation. The crystals were placed 40 mm from the CCD detector. The unit cell determination and data integration were carried out using the CrysAlis package of Oxford Diffraction [12]. The structure was solved by direct methods using Olex2 [13] software with the SHELXS [14] structure solution program and refined by full-matrix least-squares on Fo2 with SHELXL-2015 [14]. Atomic displacements for non-hydrogen, nondisordered atoms were refined using an anisotropic model. For Ii-Pr–Mg, which crystallizes in Sohnke C2, space group inversion twinning was checked by the refinement of BASF parameter (the BASF is the refined parameter which indicates the twin component ratio); however, the value of −0.1 (4) for the Flack gave no conclusive answer. In addition, the “Solvent Mask” tool available in Olex2 was used to model the contribution of disordered solvent molecules to structure factors. The hydrogen atoms have been placed by Fourier Difference accounting for the hybridization of the supporting atoms and the possible presence of hydrogen bonds in the case of donor atoms. The molecular plots were obtained using the Olex2 program [13]. The main crystallographic data together with refinement details are summarized in Table 1, whereas the selected bond lengths and angles are presented in Table 2.
Crystallographic data, details of data collection, and structure refinement parameters for the investigated compounds.
| Ii-Pr–Mg | Ii-Pr–Ni | Ii-Pr–Mn | |
| Empirical formula | C30H40.7MgN8O8.35 | C34H52N8NiO10 | C34H52MnN8O10 |
| Formula weight | 671.31 | 791.54 | 787.77 |
| Temperature (K) | 200 | 200 | 293 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | C2 | P21/n | P21/n |
| a (Å) | 27.2230 (10) | 9.1932 (4) | 9.1746 (8) |
| b (Å) | 9.4380 (3) | 14.1686 (5) | 14.4667 (15) |
| c (Å) | 15.4136 (6) | 15.1827 (6) | 15.3873 (8) |
| α(°) | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| β(°) | 104.751 (4) | 94.809 (3) | 93.480 (6) |
| γ(°) | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| V (/Å3) | 3829.7 (2) | 1970.67 (13) | 2038.5 (3) |
| Z | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Dcalc (/mg/mm3) | 1.164 | 1.334 | 1.283 |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.101 | 0.556 | 0.385 |
| Crystal size (/mm3) | 0.10 × 0.10 × 0.35 | 0.10 × 0.15 × 0.20 | 0.05 × 0.15 × 0.40 |
| θmin, θmax (°) | 5.536–50.048 | 3.938–50.052 | 3.868–50.046 |
| Reflections collected | 13,980 | 9548 | 8634 |
| Independent reflections | 6745 [Rint = 0.0359] | 3459 [Rint = 0.0239] | 3582 [Rint = 0.0356] |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 6745/2/465 | 3459/4/247 | 3582/7/235 |
| R1a (I > 2σ(I) | 0.0489 | 0.0348 | 0.0589 |
| wR2b (all data) | 0.0924 | 0.0849 | 0.1537 |
| GOFc | 0.991 | 1.081 | 1.0394 |
| Flack parameter | −0.1 (4) | – | – |
| Δρmax and Δρmin (e/Å3) | 0.29/−0.26 | 0.30/−0.24 | 0.32/−0.38 |
a R1 = Σ||Fo|–|Fc||/Σ|Fo|.
b .
c GOF = {∑[w(Fo2 - Fc2)2] /(n – p)}1/2, where n is the number of reflections and p is the total number of parameters refined.
Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Distance | HaIi-Pr[11] | Ii-Pr–Mg M = Mg | Ii-Pr–Ni M = Ni | Ii-Pr–Mn M = Mn | |
| A | B | ||||
| C1-O1 | 1.326 (2) | 1.249 (4) | 1.256 (4) | 1.261 (2) | 1.262 (4) |
| C1-O2 | 1.210 (2) | 1.263 (6) | 1.252 (6) | 1.252 (2) | 1.247 (4) |
| C1-C2 | 1.491 (2) | 1.487 (5) | 1.498 (5) | 1.512 (3) | 1.506 (4) |
| C2-C3 | 1.387 (2) | 1.409 (5) | 1.377 (5) | 1.383 (3) | 1.386 (4) |
| C3-C4 | 1.378 (2) | 1.382 (5) | 1.398 (5) | 1.386 (3) | 1.373 (4) |
| C4-C5 | 1.393 (2) | 1.394 (5) | 1.389 (5) | 1.388 (3) | 1.378 (3) |
| C5-C6 | 1.391 (2) | 1.400 (5) | 1.381 (5) | 1.389 (3) | 1.383 (4) |
| C5-C8 | 1.488 (2) | 1.477 (5) | 1.486 (5) | 1.486 (3) | 1.484 (4) |
| C6-C7 | 1.381 (2) | 1.384 (6) | 1.387 (5) | 1.383 (3) | 1.386(4) |
| C7-C2 | 1.392 (2) | 1.383(5) | 1.384 (5) | 1.389 (3) | 1.382(3) |
| C8-N3 | 1.333 (2) | 1.324 (5) | 1.325 (5) | 1.326 (2) | 1.340 (4) |
| N3-N2 | 1.367 (2) | 1.365 (4) | 1.363 (4) | 1.368(2) | 1.363 (3) |
| N2-C9 | 1.369 (2) | 1.376 (5) | 1.371 (5) | 1.373 (2) | 1.363 (3) |
| N2-C10 | 1.484 (2) | 1.482 (5) | 1.498 (5) | 1.478 (3) | 1.477 (4) |
| C9-O3 | 1.231 (2) | 1.225 (4) | 1.224 (4) | 1.230 (2) | 1.231 (3) |
| C9-N1 | 1.369 (2) | 1.380 (5) | 1.370 (5) | 1.371 (3) | 1.371 (4) |
| N4-C8 | 1.326 (2) | 1.316 (5) | 1.332 (5) | 1.331 (2) | 1.321 (4) |
| N1-N4 | 1.367 (2) | 1.357 (4) | 1.365 (4) | 1.362 (2) | 1.367 (3) |
| N1-C11 | 1.481 (2) | 1.495 (5) | 1.489 (5) | 1.478 (2) | 1.472 (4) |
| C10-C12 | 1.509 (2) | 1.504 (7) | 1.500 (6) | 1.513 (3) | 1.509 (5) |
| C10-C13 | 1.509 (2) | 1.520 (6) | 1.478 (6) | 1.506 (3) | 1.493 (5) |
| C11-C14 | 1.520 (3) | 1.492 (7) | 1.440 (11) | 1.508 (3) | 1.500 (5) |
| C11-C15 | 1.505 (3) | 1.510 (7) | 1.453 (7) | 1.504 (3) | 1.501 (5) |
| C16-O4 | 1.412 (3) | 1.371 (6) | |||
| C17-O5 | 1.426 (3) | 1.312 (6) | |||
| M1-O1 | 2.199 (3) | 2.035 (3) | 2.0306 (13) | 2.1169 (19) | |
| M1-O2 | 2.139 (3) | 2.027 (3)i | |||
| M1-O4 | 2.0651 (13) | 2.254 (4) | |||
| M1-O5 | 2.0815 (13) | 2.178 (4) | |||
| M1-O1w | 2.025 (4) | ||||
| M1-O2w | 2.0346 (3) |
CCDC-1892270 for Ii-Pr–Mg, CCDC-1892067 for Ii-Pr–Ni, and 1892068 for Ii-Pr–Mn contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this article; these data can be obtained free of charge via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/conts/retrieving.html.
The powder XRD experiment at room temperature was performed on a D8 Advance Bruker AXS diffractometer using a Cu Kα source with an emission current of 36 mA and a voltage of 30 kV. Scans were collected over the 2θ = 5–45 range using a step size of 0.01° and a count time of 0.5 s/step.
2.4 Magnetism studies
Magnetic measurements were carried out on microcrystalline samples with a Quantum Design SQUID magnetometer (MPMS-XL). Variable-temperature (2–300 K) direct current magnetic susceptibility was measured under an applied magnetic field of 0.1 T. All data were corrected for the contribution of the sample holder and diamagnetism of the samples estimated from Pascal's constants [15,16]. The analysis of the magnetic data was carried out by fitting the χT and χ thermal variations including temperature-independent paramagnetism, impurity contribution (ρ), and intermolecular interaction (zJ′) [16–18].
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Synthesis
The chemistry of HIi-Pr with a bivalent metal is explored. Ii-Pr–Mg was obtained by reacting HIi-Pr with an excess of freshly prepared Mg(OH)2 in methanol according to the following reaction:
| Mg(OH)2 + 2HIi-Pr ↔ Mg(Ii-Pr)2 + 2H2O |
After filtration, methanol was evaporated and crystals suitable for XRD were grown from ethyl acetate.
For the 3d bivalent metal ions (Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II)), the starting materials were the hydrates of the metal (II) acetate. The overall reaction toward the final compounds thus appears as a substitution of the acetate ions by the carboxylate moiety of Ii-Pr− according to the following reaction:
| M(Ac)2 + 2HIi-Pr ↔ M(Ii-Pr)2 + 2HAc M(II) = Mn, Co, Ni, Zn |
In the case of Co(II) and Ni(II) (Ii-Pr–Co and Ii-Pr–Ni), a direct substitution of acetic acid in methanol solution was performed. On the contrary, for Mn(II) and Zn(II), it is necessary to displace the equilibrium toward the desired compounds, Ii-Pr–Mn and Ii-Pr–Zn, by a double azeotropic distillation of acetic acid in toluene. This procedure is similar to the one used to vary the nature of the carboxylate in Mn12 derivatives [19]. It should be noted that an analogous synthesis was undertaken starting from iron (II) and copper (II) acetate. Nonetheless, the redox activity of these metal ions toward verdazyl radicals [7,10] has modified the overall reaction scheme and prevented the synthesis of the corresponding analogues. According to X-ray analysis, the magnesium salt contains two coordination molecules of water.
Elemental analysis is in good agreement with the proposed composition, but in the case of Mg salt, some discrepancy may be observed, which probably can be associated with solvent loss before analysis. The IR spectra of all the 3d divalent metal ion derivatives Ii-Pr–M (M = Mn, Co, Ni, Zn; Fig. SI 1) are very similar and markedly different from that of the magnesium (II) derivatives Ii-Pr–Mg (Fig. SI 2). This strongly suggests that the composition and bond repartitions are similar within the Ii-Pr–M (M = Mn, Co, Ni, Zn) series and notably different in Ii-Pr–Mg. Several features in the IR spectra of the synthesized compounds compared with that of the starting radical HIi-Pr can be detailed (Fig. SI 3). First, the fingerprint of the organic part of HIi-Pr is retrieved in all of the five derivatives. On the contrary, significant differences appear in the vibrations associated with the carboxylate moiety of the radical. Upon deprotonation and complexation, the characteristic band of OH vibration is deeply modified because in HIi-Pr the molecules form H-bonded dimers that forced the O-H bond, hence displaced the OH vibration down to 2680–2550 cm−1 whereas the O-H bonds of the water and methanol molecules present in the divalent metal adducts, Ii-Pr–M, vibrate at much higher wavenumbers, for example, 3420 cm−1, indicating the presence of much less efficient H-bonding. Another striking consequence of the coordination is the modification of νas (COO) and νs (COO), respectively, the asymmetrical and symmetrical carboxylate oscillation bands. The difference between the two bands Δν= νas (COO) − νs (COO) takes value from (1680–1404) 282 cm−1 in Ii-Pr–Mn down to (1652–1410) 242 cm−1 when the carboxylate moiety adopts a pseudobidentate coordination (Ii-Pr–Mg). These results indicate that the verdazyl moiety itself shall not be coordinated whereas the carboxylate moiety does. These results must be compared with those obtained by the single-crystal X-ray structural analysis.
3.2 X-ray diffraction
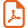
Fig. 1(a) shows the asymmetric unit of Ii-Pr–Mg. Two different modes of coordination of the radical to magnesium (II) are found in Ii-Pr–Mg. They are denoted as A and B. One radical is coordinated to Mg(II) by its carboxylate group in a bidentate κ(O,O′) coordination mode (A). The second radical is coordinated in a μ − 1κ(O);1κ(O′) syn–anti mode (B): one oxygen atom (O1B) is coordinated to Mg1 atom (Mg1-O1B = 2.031 Å) whereas the second oxygen atom of the carboxylate group (O2B) is connected to another, crystallographically equivalent, Mg atom (O2B-Mg1 = 2.037 Å). These bridges between the Mg(II) ions lead to the formation a one-dimensional (1D) coordination polymer (Fig. 1b).
The crystal structure of compound Ii-Pr–Mg. (a) Extended view of the asymmetric part and coordination environment around Mg2+ along with the atom labeling scheme and thermal ellipsoids the 50% probability level. Two radical ligands are denoted as A and B. Symmetry generated fragments are shown with faded colors. Symmetry codes: (i)−0.5 − x, 0.5 + y, −z; (b) fragment of 1D polymer chain, intrachain H-bonds as dashed lines: O1w–H⋯O2A [O1w–H 0.86 Å, H⋯O2A 1.91 Å, O1w⋯O2A (−x, +0.5, y − 0.5, −z) 2.758 Å, ∠ O1w–H⋯O2A 160.0°], O2w–H⋯O1A [O2w–H 0.85 Å, H⋯O1A 1.84 Å, O2w⋯O1A (−x, +0.5, y + 0.5, −z) 2.685 Å, ∠ O2wHO1A 177.2°]; (c) coordination polyhedron of Mg(II); (d) crystal packing viewed along the b axis; and (e) closer view at π–π stacking between two B radical ligands.
The coordination sphere of the metal ion is completed by two water molecules leading to a highly distorted octahedral environment (Fig. 1c). The two intrachain hydrogen bonds between the coordinated water molecules and the bidentate radical further reinforce the 1D chain. Fig. 1(d) shows the crystal packing of the coordinated polymer. There is no π-stacking between the molecules of bidentate chelating radicals A. On the contrary, there are some π–π interactions between bridging ligands B. Fig. 1e shows that the stacking is far from being perfect because of both the bulkiness of the isopropyl groups borne by the verdazyl moieties and to the coordinated magnesium (II) ions onto the carboxylate groups. Centroid-to-centroid distance is of 3.911 and 5.613 (Å) for phenyl–verdazyl and verdazyl–verdazyl pairs, respectively, and angle between two stacked molecules equal to 18.7°(2).
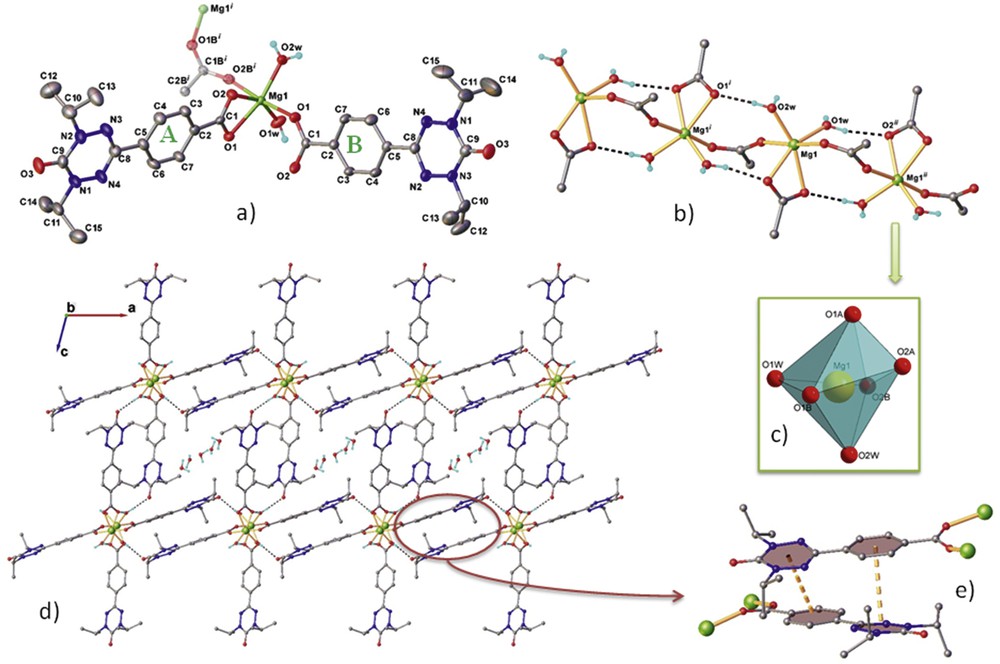
Thermal variations of χT product for Ii-Pr–M (M = Mn, Co, Ni, and Zn). Solid lines represent the best fits according to the model given in the text.
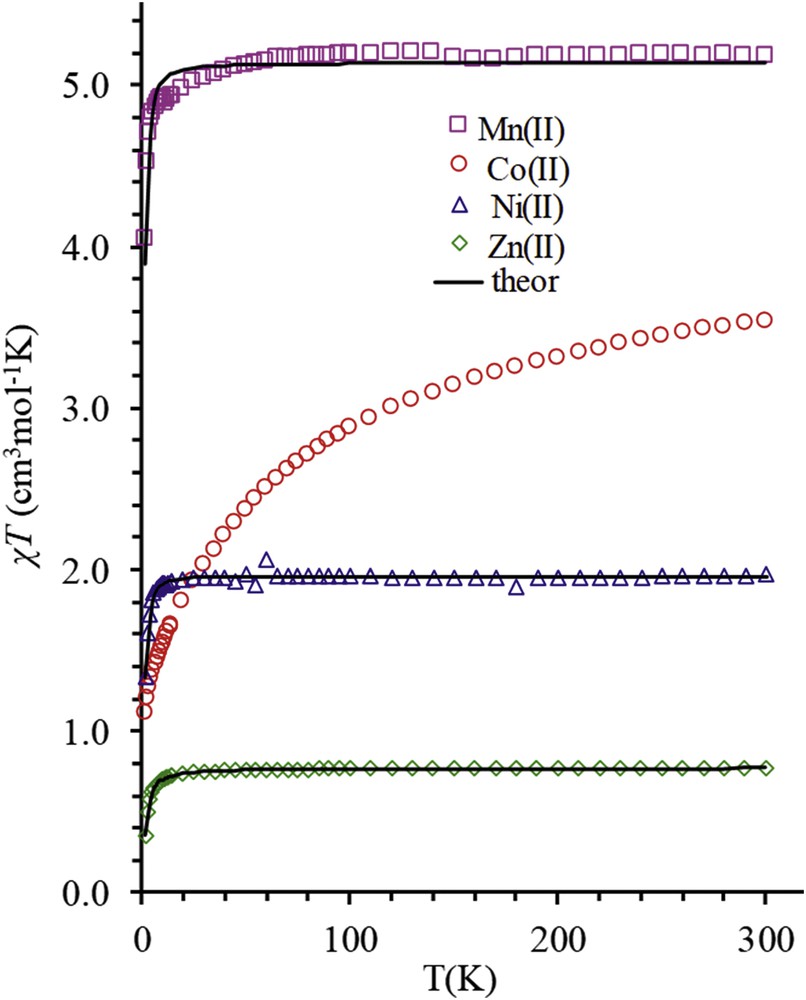
Ii-Pr–Mn and Ii-Pr–Ni are isostructural (Table 1). The structure of the latter is presented in detail in Fig. 2. This compound is formed of isolated mononuclear complexes. In the complex, the nickel (II) ion is coordinated by four methanol molecules and two radicals (Fig. 2a). The two radicals are coordinated to the metal ion by the carboxylate group in a monodentate mode. The second oxygen atoms of the two carboxylate groups (O2) are engaged in an intramolecular hydrogen bond with the hydrogen atoms (H4) of two coordinated methanol molecules. The two remaining methanol ligands form additional hydrogen bonds with oxygen atoms of the carbonyl groups of a verdazyl ring (Fig. 2b). The intermolecular interactions between the neighboring complexes are reinforced by π-stacking between the organic parts of the radicals arranged in a head-to-tail configuration (Fig. 2b). Centroid-to-centroid distance is of 3.940 for phenyl–verdazyl and 6.069 (Å) verdazyl–verdazyl pairs, respectively. These two intermolecular interactions lead to the formation of well-isolated 1D chain of complexes, which propagate along the c-axis (Fig. 2c and d).
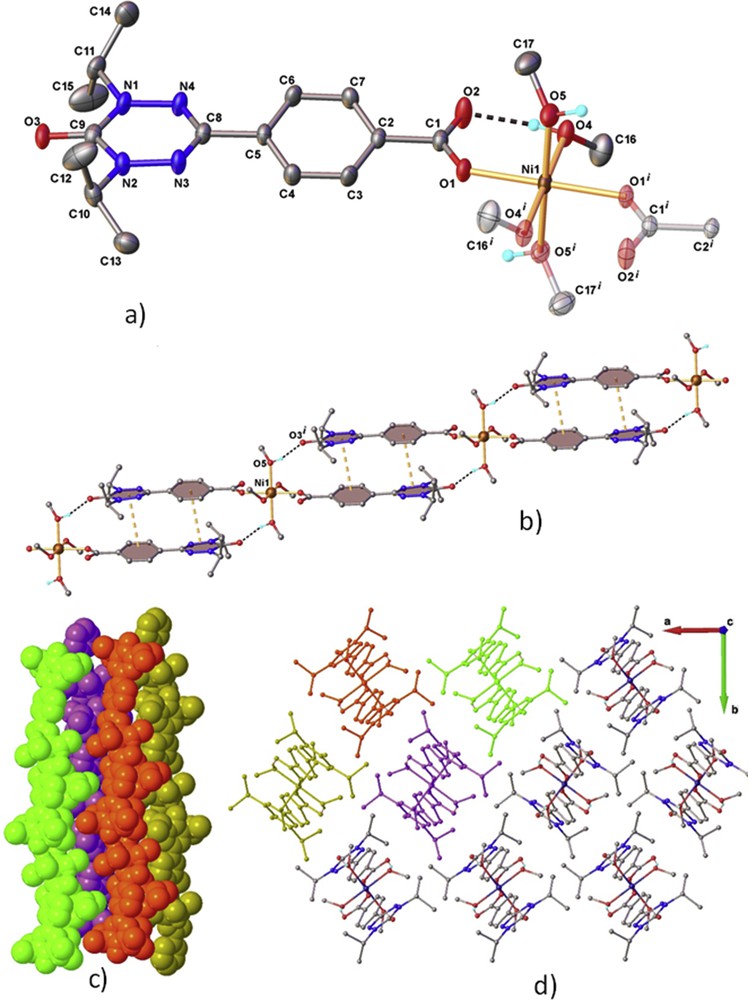
Crystal structure of Ii-Pr–Ni.A) Extended view of the asymmetric part and coordination environment around Ni2+ along with the atom labeling scheme and thermal ellipsoids the 50% probability level. Symmetry generated fragments are shown with faded colors. Symmetry codes: (i)1 − x, 1 − y, −z; (b) the supramolecular chain of π–π stacking and hydrogen bonds: O4-H⋯O2 [O4-H 0.85 Å, H⋯O2 1.76 Å, O4⋯O2 2.589 (2), ∠O4HO2 165.1°, O5-H⋯O3 [O5-H 0.84 Å, H⋯O3 1.90 Å, O5⋯O3(x, y, −1 + z) 2.722 (2), ∠O5HO3 164.3°; (c) and (d) the packing of 1D discrete chains along the c axis.
The structure of the mononuclear complexes observed in Ii-Pr–Mn and Ii-Pr–Ni is very similar to that of the [M(OOCCH3)2(H2O)4] [20] supporting the substitution scenario proposed for the reaction. On the basis of the similarity of the IR spectra of Ii-Pr–Mn, Ii-Pr–Co, Ii-Pr–Ni, and Ii-Pr–Zn, as well and on the powder XRD (see Supplementary Information), this scenario should hold for Ii-Pr–Co and Ii-Pr–Zn.
3.3 Magnetic properties
Fig. 3 shows the temperature variation of magnetic susceptibility of Ii-Pr–Mg. The χMT product is worth 0.72 cm3 mol−1 K at room temperature. This is close to the value expected for the sum of two noninteracting radicals (0.75 cm3 mol−1 K for g = 2.00). Upon cooling, the χMT product decreases continuously with an increasing rate when the temperature is decreased. This evolution indicates that the exchange interactions between the two spin bearers are dominated by antiferromagnetic interactions.
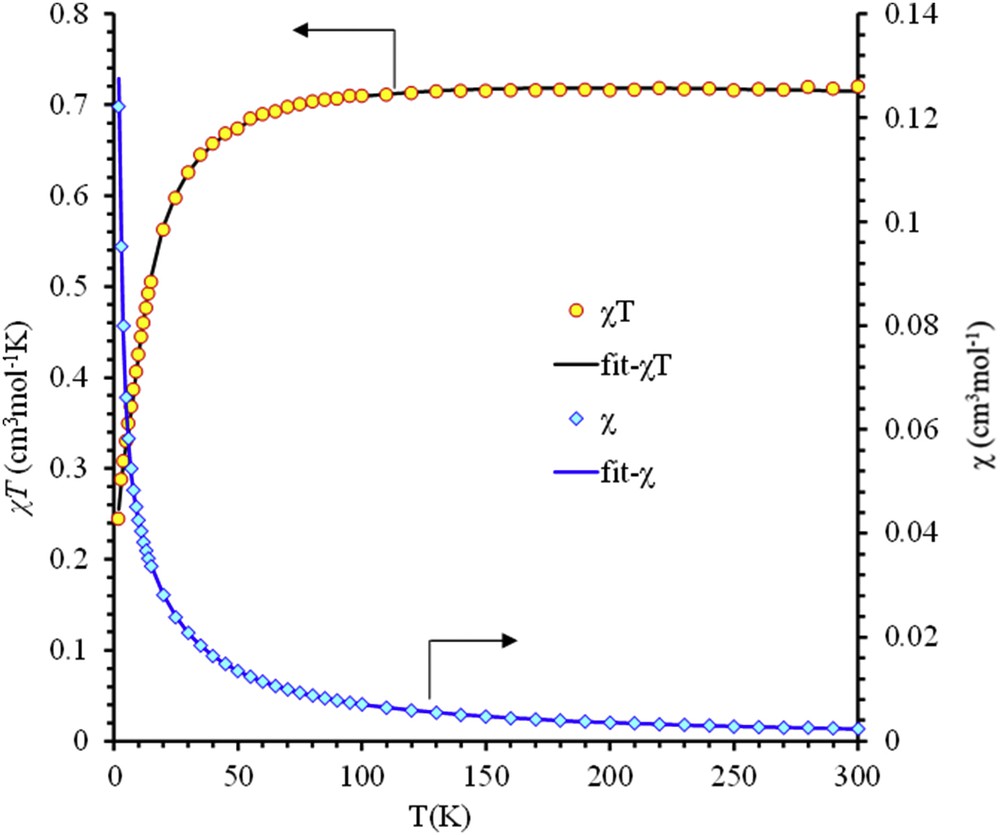
Thermal variations of χM and χMT of Ii-Pr–Mg. Solid lines represent the best fit according to the model given in the text.
With this diamagnetic metal ion, exchange interaction should mainly originate from π–π interactions between the radicals. Following the structure analysis of Ii-Pr–Mg (Fig. 1), such interactions exist between radicals labeled B whereas the A radicals are not coupled. Accordingly, the magnetic susceptibility is fitted using the following equation:
From fitting the value of antiferromagnetic coupling constant was found to be J = −17.56 cm−1 and g = 1.96 (2). The low value of the g factor, as compared with the one expected for an organic radical, is probably due to the presence of a diamagnetic amorphous impurity. The constant of intermolecular interaction is −0.68 (1) cm−1.
The thermal variations of χT product for the series of 3d series compounds Ii-Pr–M (M = Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Zn(II)) is presented in Fig. 4. The values at the room temperature are consistent with theoretical value expected for two independent radical and one bivalent metal ion. Upon cooling, the χT products undergo a monotonous decrease. For Ii-Pr–Mn, Ii-Pr–Ni, and Ii-Pr–Zn, this temperature dependence suggests the presence of antiferromagnetic interaction whereas the much marked evolution for Ii-Pr–Co is a characteristic trademark of the strong spin orbital contribution of the octahedral Co(II) ion. Given that the radical is coordinated through its carboxylate, hence the long distance between the radical and the metal ion, and the similarity of the structure (Fig. 2) and thermal dependence of the χT products (Fig. 4) for Ii-Pr–Mn, Ii-Pr–Ni, and Ii-Pr–Zn, it clearly appears that the exchange interaction mainly originates from the π-stacking of the verdazyl moieties (Fig. 2b). Accordingly, the magnetic susceptibility data for Ii-Pr–M (M = Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Zn(II)) can be written as
Characteristic parameters for the series Ii-Pr–M (M = Mg, Mn, Co, Ni, Zn) extracted from the fit of the magnetic data.
| Ii-Pr–M | χT (300 K) (exp) | SM | gR | gMet | J | R | ZFS |
| Mg(II) | 0 | 1.960 (2) | – | −17.6 (2) | 3 × 10−4 | ||
| Zn(II) | 0.771 | 0 | 2.030 (1) | – | −2.40 (2) | 6.6 × 10−6 | |
| Ni(II) | 1.968 | 1 | 2.0 (fix) | 2.20 (3) | −1.98 (8) | 1.5 × 10−2 | D=−4.37 (3), |
| Co(II) | 3.539 | 3/2 | – | – | – | – | |
| Mn(II) | 5.179 | 5/2 | 2.0 (fix) | 2.003 (7) | −2.2 (4) | 8 × 10−3 |
The values obtained for the exchange interaction parameter of the π-stacked radicals all along the Ii-Pr–M (M = Mn, Co, Ni, Zn) series fall below −2.4 cm−1. They are in line with the value found for one of the polymorphs of HIi-Pr [11] where a comparable highly head-to-tail arrangement with large verdazyl–verdazyl distances known to provoke a dramatic decrease in the exchange interaction [7] was found because of the steric hindrance imposed by the isopropyl side chains of the verdazyl moiety.
4 Conclusion
The reactions of 1,5-diisopropyl-3-(4′-carboxyphenyl)-6-oxoverdazyl with divalent metal ions have led to a series of 5 compounds. Two common features appear from the analysis of the single-crystal XRD. First, the coordination to the metal ions occurs through the carboxylate moiety rather than the verdazyl one. In turn, for the Ii-Pr–M (M = Mn, Co, Ni, Zn) series where HIi-Pr was reacted with the acetate of the divalent metal ion, the reaction appears as a mere carboxylate exchange as previously observed for Mn12 derivatives [19]. This statement confirms the difficulty for the verdazyl moiety to act as a monodentate ligand. Second, in all of the compounds, the π-stacking is deeply influenced by the bulky isopropyl side chains: the head-to-tail arrangement is preferred, the two interacting π-systems are not really parallel and the centroid–centroid distance between the verdazyl moieties is dramatically increased. The consequence of this structural organization onto the magnetic properties is straightforward: because of the coordination by the carboxylate group, the exchange interaction between the radical and paramagnetic metal ions is negligible, whereas the verdazyl–verdazyl interaction mediated by the π–π interactions is severely reduced.