1 Introduction
Analysis of the prevalence of urolithiasis in the last decades reveals an increase of calcium oxalate stones worldwide [1–6]. Depending on the number of water molecules present in the crystalline structure, calcium oxalate stones are related to hyperoxaluria or hypercalciuria [7–9]. More precisely, kidney stones made of whewellite (calcium oxalate monohydrate or COM, CaC2O4·H2O) are induced by hyperoxaluria which can be intermittent and moderate (Ia), due to low urine output and stasis (Ib, and Id) or heavy hyperoxaluria as a result of gut absorption (Ie) or of genetic origin in primary hyperoxalurias (Ic) [10–17]. In a previous investigation [18,19], we provide evidence that each whewellite subtype namely Ia, Ib, Ic, Id and Ie is associated with a peculiar crystallite morphology. The other crystalline form, i.e. weddellite (calcium oxalate dihydrate or COD, CaC2O4·(2 + x)H2O), is induced by hypercalciuria. For such kidney stones, subtypes, IIa, IIb and IIc, also exist.
Crystalline conversion from weddellite to whewellite introduces a contradiction between Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra which indicate the presence of whewellite and the fact that bipyramid crystallites, a morphology specific of weddellite, can be observed. It constitutes thus a major problem for the clinicians as hyperoxaluria and hypercalciuria are associated with very different aetiologies and treatments. In the present contribution, we would like to understand more deeply this crystalline conversion, its relationship with the IR absorption spectrum. To do that, a set of kidney stones including ones which display unconventional IR absorption spectra have been selected. On these pathological concretions [20–29], FTIR measurements [30,31] have been completed by observations using a last generation scanning electron microscope [32], measurements on a neutron diffractometer [18,33–35] as well as 3D and 2D cross-section visualisations derived from μComputed Tomography measurements have been considered [36–42]. These characterization techniques will allow us to assess the structural parameters at micrometre and nanometre scales of these pathological concretions [20–29].
2 Material and methods
A set of 13 kidney stones first examined under a stereomicroscope for recording their main morphological characteristics and second analysed by FTIR spectroscopy [30,31] have been selected for the study (Table 1). Infrared data were collected between 4000 and 400 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1. The FTIR spectra show characteristic absorption bands of the whewellite phase.
Morphology and chemical composition as given by FTIR spectroscopy of the set of samples selected for this investigation.
| Sample | Morphology | FTIR analysis |
| N68096 | Ia | 100%COM |
| N68214 | Ia | 100%COM |
| N55348 | Ia | 100%COM |
| N52350 | Ia | 100%COM |
| N68102 | Ia | 96%COM + 2%CA + 2%PROT |
| N68074 | Ia + IIb | 65%COM + 30%COD + 3%CA + 2%PROT |
| N68140 | Ia + IIb | 64%COM + 28%COD + 4%CA + 3%PROT + 1%MPS |
| N68258 | Ia + IIb | 80%COM + 15%COD + 3%CA + 2%PROT |
| N57404 | Ia + IVa + IIb | 49%COM + 17%CA + 16%COD + 10%ACCP + 6%MAP + 2%PROT |
| N52299 | Id | 100%COM |
| N69923 | Ie | 87%COM + 7%CA + 4%PROT + 2%MPS |
| N68076 | IIb | 52%COM + 40%COD + 5%CA + 3%Br |
| N68097 | IIb | 80%COM + 11%COD + 6%CA + 3%PROT |
| N68285 | IIb | 56%COD + 35%COM + 7%CA + 2%PROT |
| N68114 | IIb + Ia | 50%COM + 45%COD + 3%CA + 2%PROT |
| N68231 | IIb + IVb | 36%COM + 26%COD + 25%CA + 10%WK + 3%PROT |
| N68316 | IIb + IVa + Ib | 60%COM + 21%CA + 15%COD + 4%PROT |
| N68351 | IIb + IVa | 36%COD + 32%CA + 28%COM + 4%PROT |
| N11566 | IIba | 70%COM + 25%COD + 5%WK |
| N56070 | IIba | 83%COD + 10%COM + 4%CA + 3%PROT |
| N58795 | IIb | 65%COD + 19%COM + 13%CA + 3%PROT |
| N63539 | IIb | 70%COD + 15%COM + 7%CA + 7%PROT + 1%ACCP |
| N68683 | IIb | 63%COM + 26%COD + 8%CA + 3%PROT |
| N71212 | IIba | 74%COD + 20%COM + 4%CA + 2%PROT |
| N7118 | IIba | 65%COM + 20%COD + 8%WK + 4%CA + 3%PROT |
a Presence of large crystals of COD.
Observations through a last generation Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM) for characterization of the samples at the mesoscopic scale have been performed [32]. Such apparatus offers the opportunity to investigate nonconductive materials without any conductive coating and permits thus a direct observation causing no damage for the sample. A set of observations have been performed with a gaseous secondary electron detector at a low accelerating voltage (under 2 kV).
Neutron diffraction patterns were collected on the G4.1 diffractometer [43] at Laboratoire Léon Brillouin [44] at room temperature. This powder diffractometer is equipped with a vertical focussing pyrolytic graphite monochromator and an 800-cell multidetector covering an 80° 2θ range (step 0.1° between two cells). Neutron diffraction diagrams were collected using a wavelength of 2.4226 Å, with an acquisition time of a few hours on samples. Data analysis was done using the FullProf program [45]. Details regarding the data analysis procedure can be obtained elsewhere [18,33–35].
For non-destructive three-dimensional (3D) scanning, a set of kidney stones were selected and analysed with a Quantum FX (Micro-CT Caliper PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA [46]) tomography system, equipped with a 90 kV/20 W maximum power unipolar microfocus (5 μm focal spot) X-ray tube and a high-contrast digital array detector DXR250 with a 10 μm3 voxel, 5000 × 5000 μm pixel size used. The μCT scan was performed for 3 min at 90 kV and 180 μA acceleration voltage and X-ray tube current, respectively. The DICOM III data frames were subsequently analysed using OsiriX imaging software (64 bits, 3.7.1 version). The scans resulted in reconstructed 3D data sets with a voxel-size of 9.92 μm3 jointive slices.
3 Results and discussion
Whewellite and weddellite stones may be easily distinguished by very different morphological characteristics as shown in Fig. 1.

Macroscopic observations of COM and COD kidney stones. A and B: type Ia COM stone (A = surface; B = section) – C and D: type IIa COD stone (C = surface; D = section).
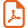
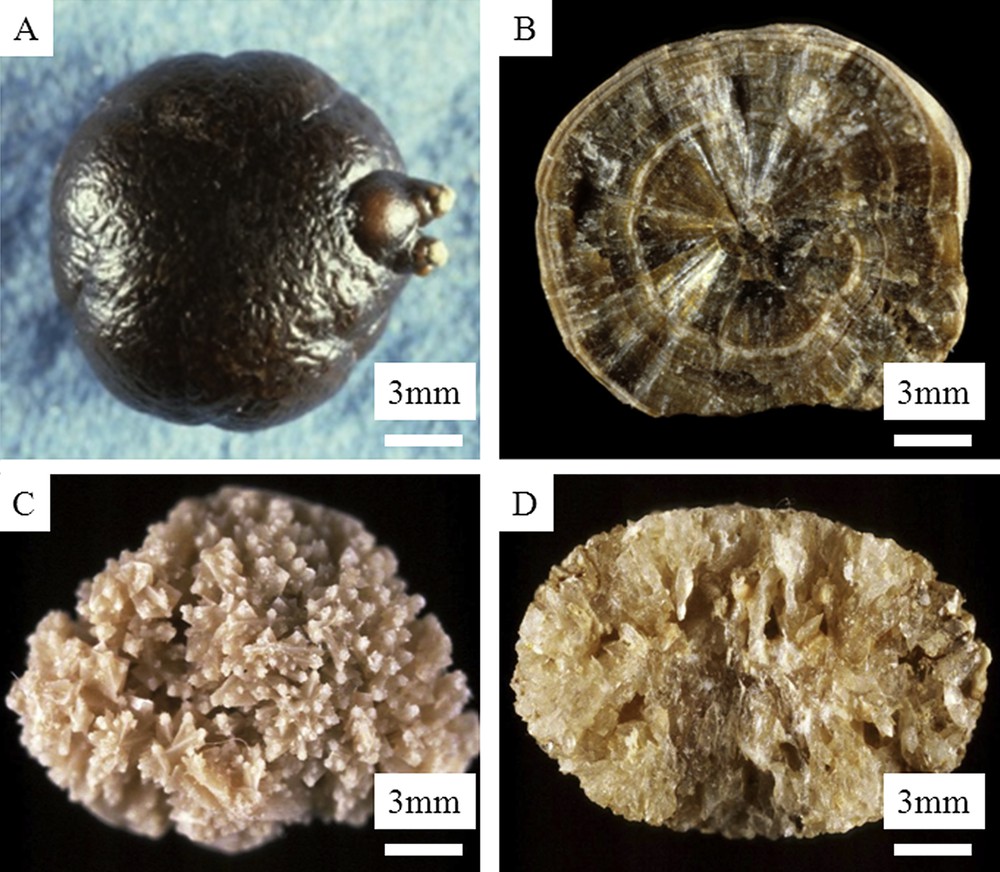
In some cases, COM and COD crystals are clearly formed independently, with well separated areas of calculi containing either COM or COD (Fig. 2).
Macroscopic observations of mixed COD + COM stones: A = surface – B = section. Arrows correspond to COM areas.
However, in a number of cases, the two crystalline forms appear less clearly separated and even COM seems to be the result of crystalline conversion from COD to COM as whewellite is the thermodynamically stable form of calcium oxalate. In such cases, the stone morphology is also suggestive for such a transformation (Fig. 3).

Macroscopic observations of mixed COM + COD kidney stones. A to D examples of crystalline conversion from COD to COM in calcium oxalate stones. A and C = surface; B and D = section.
Since the first set of publications [47–50] dedicated to calcium oxalate compounds, numerous studies of these compounds were performed by different groups who have addressed more deeply the crystallographic structures [51–59]. In fact, we can distinguish at least two communities for which calcium oxalate constitutes an important matter, urologists [60–66] and botanists [67–71]. The fact that calcium oxalate is at the core of a major public health problem explains the dynamism of such research [72–81].
Regarding their crystallographic structure, the three calcium oxalate forms (whewellite, weddellite and caoxite, CaC2O4·3H2O) can be viewed as edge-shared CaO8 polyhedra that constitute the linkage between oxalate ions [(C2O4)2−] [51–59]. On the basis of this structural polyhedron model, whewellite, weddellite and caoxite are composed of sheets, chains and dimers, respectively [51–59]. While the crystallographic structure of whewellite and caoxite display a sheet structure consisting of Ca2+ ions and oxalate ions, it is definitely not the case of the weddellite one [51–59]. According to V. Tazzoli and C. Domeneghetti [55], such a structural similarity between whewellite and caoxite allows a direct transformation of caoxite into whewellite without an intermediate weddellite stage [55]. More precisely, during the dehydration process, interlayered water molecules in caoxite lead to intralayered water molecules of the crystal structure of whewellite. It should be noted that a precise examination of the crystallographic structure of weddellite indicates the existence of a channel in which free (extra framework) water molecules occur in two alternative and very close positions. Taking into account this structural specificity, the maximum water content is 2.5 [55].
Thanks to their very different crystallographic structures [51–59] whewellite, the most stable as given by thermodynamic and weddellite compounds, can be easily distinguished using either vibrational spectroscopies such as IR [82,83] or Raman [84] spectroscopy, diffraction techniques [85,86] or microtomography [87]. Recent breakthroughs in theoretical chemistry allow a precise assignation of the IR absorption bands. In our cases, all these theoretical values for the IR absorption bands, namely position as well as intensity, have been obtained using geometry optimizations based on an ab initio plane-wave pseudopotential approach as implemented in VASP [88,89]. The Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof functional [90,91] has been chosen to perform the periodic DFT calculations with an accuracy on the overall convergence tested elsewhere [92–95]. The valence electrons are treated explicitly and their interactions with the ionic cores are described by the Projector Augmented-Wave method [96,97], which allows us to use a low energy cut off equal to 500 eV for the plane-wave basis. The gamma point is used in the Brillouin-zone integration. The positions of all the atoms in the super cell are relaxed until the total energy differences decrease below 10−4 eV. The atom positions as well as the unit cell have been relaxed. From these results one can conclude that the vibrational bands were well attributed, besides the 517 cm−1 peak and bands in the region of 790–750 cm−1, which are attributed to the C–C stretching mode and a mixing of COO wagging/stretching + water rocking, respectively. The vibrations implicating Ca2+ ions are expected to appear at much lower wave numbers (below 320 cm−1). Regarding the contribution of water molecules to the IR absorption spectrum, experimentally the bands in the range of 3500–3200 cm−1 are attributed to its symmetric and asymmetric stretch, whereas the strong peaks around 1620 cm−1 and the weak band at 661 cm−1 are assigned to its bending and wagging modes [98–100]. The bands at 1664, 1316, 780 and 517 cm−1 are due to σa(CO), σs(CO), δ (O–CO) and σ (Ca–O).
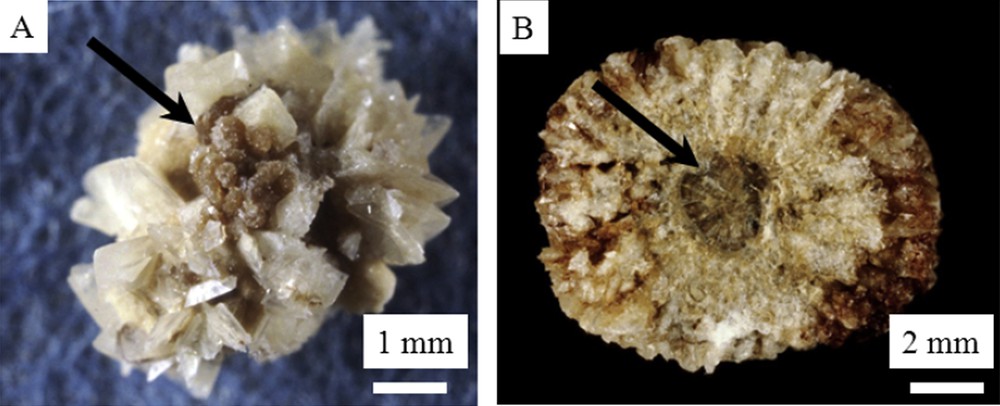
At the hospital, crystalline conversion between whewellite and weddellite is suspected through morphological characteristics of calculi in both surface and section, and also by a modification of the IR absorption bands. Pure weddellite or whewellite calculi exhibit a very different infrared spectrum as shown in Fig. 4.
FTIR spectra of pure COM (black) and COD (red).
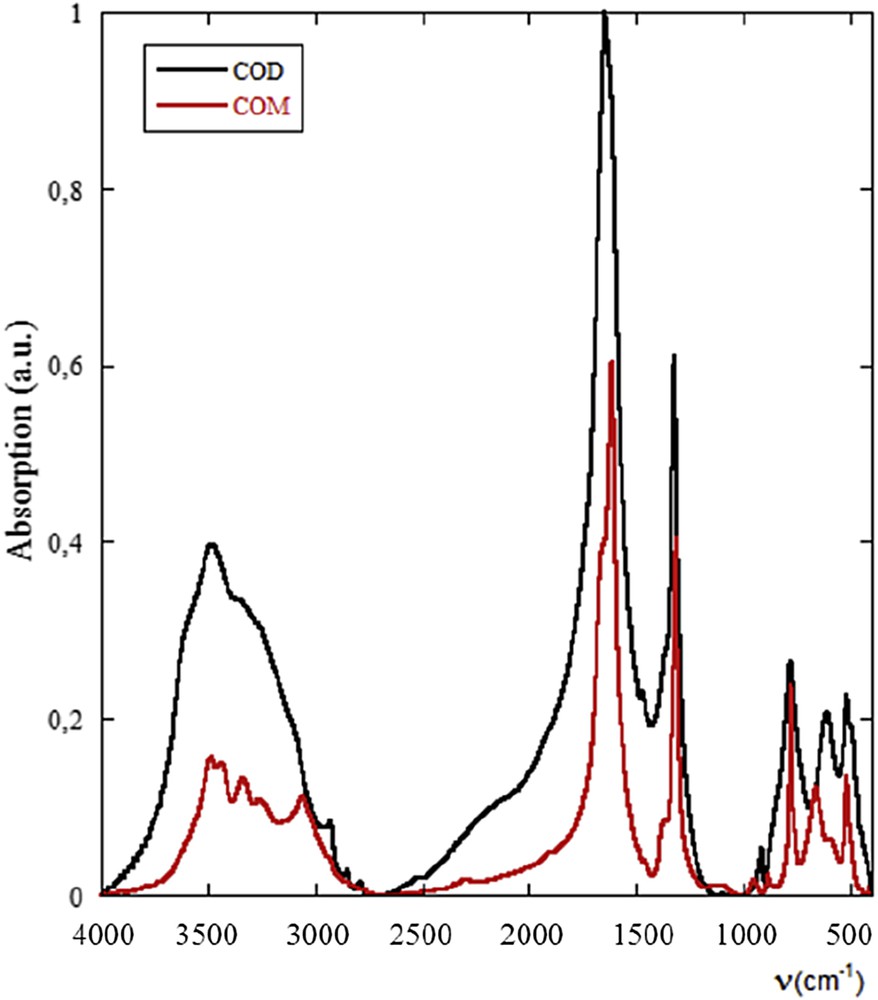
In Fig. 5, it is clearly seen that if the IR absorption bands of the whewellite compounds are well identified, the morphology as well as the position of the σa(CO) absorption band (1618 cm−1 for COM and 1640 cm−1 for COD) are significantly different.
FTIR spectra of whewellite corresponding to a chemical conversion from weddellite. Crystalline conversion affects significantly the intensity and the shape of the IR absorption band (see the inset). IR absorption bands of unusual (a and b), usual (c) and synthetic (d) whewellite.
At this point, it is worth to underline that SEM observations allow us to compare the usual morphology of the weddellite bipyramidal crystallite [53,101–103] displaying surface without defects (Fig. 6a) and the ones corresponding to the kidney stone N68097 (Fig. 6b–e). As we can see, a bipyramidal morphology exists with large structural defects and observations at higher magnification indicate that these defects follow the crystallographic axis. In the literature, different studies have been dedicated to the partial dissolution of the calcium oxalate crystals observed in water, in the presence of EDTA (ethylene diamino tetracetate) [104–109] or an extract of green tea [110]. For example, P. Vijaya et al. [109] have found that whewellite with a monoclinic structure is the more favoured polymorph in the presence of EDTA. In the case of calcium oxalate dihydrate crystals, corrosion figures, in the form of etch square pits, can be present at the surface [29,111]. The striking point of these observations is given by the fact that the main component of the chemical composition of this kidney stone as determined by FTIR is whewellite indicating thus a strong conversion of the initial weddellite bipyramide. Moreover, we may understand the fact that part of the weddellite bipyramide crystal disappears if we consider the volume of the unit cell of the two calcium oxalates. The loss of more than one water molecule in the structure (from whewellite CaC2O4·H2O to weddellite CaC2O4·(2 + x)H2O) is done along a significant decrease of the volume of the unit cell (V (Å3) is equal to 878.2 for whewellite, while V (Å3) is equal to 1125 for weddellite).
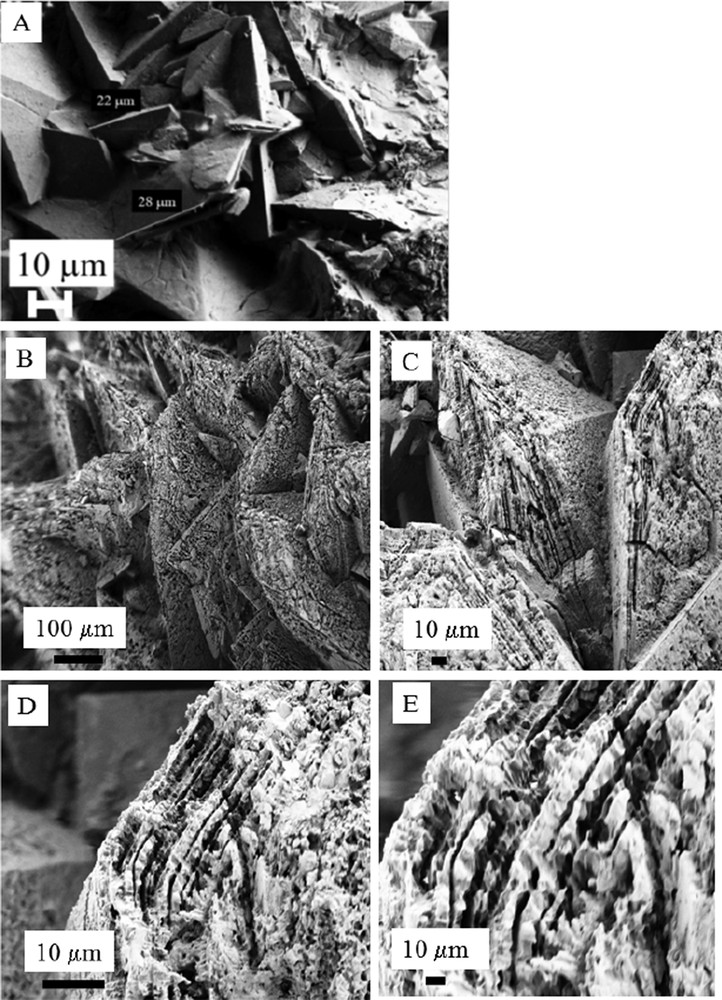
A: SEM observations showing weddellite crystallites displaying their usual bipyramidal morphologies without alteration at their surface; B, C, D, E: SEM observations obtained for the kidney stone N68097.
Several publications have demonstrated that precious information can also be obtained through X-ray tomography [36–42]. In order to show the opportunities given by X-ray tomography, a set of samples (N69923, N11566, N56070, N57404, N58795, N68683, N71212, and N7118) have been investigated through a double-blind trial. At the macroscopic scale, microtomography observations (Figs. 7–9) are able to distinguish between different structures which correspond to very different pathologies. For Fig. 7, structures corresponding to Ia kidney stones are associated with intermittent and moderate hyperoxaluria of dietary origin while in Fig. 8 the loose globular structure results from high levels of urine oxalate concentration related to an increase of oxalate absorption in patients who suffer from inflammatory bowel diseases that have required ileal resection. Finally, in Fig. 9, the stone is mainly composed of COD crystals and is related to hypercalciuric states. The interest of microtomography is that, thanks to the penetration of hard X-rays, the determination of the different structures can be performed in the bulk without any alterations of the 3D structure of the kidney stones. Such an approach is a very first step toward similar experiments performed in vivo.
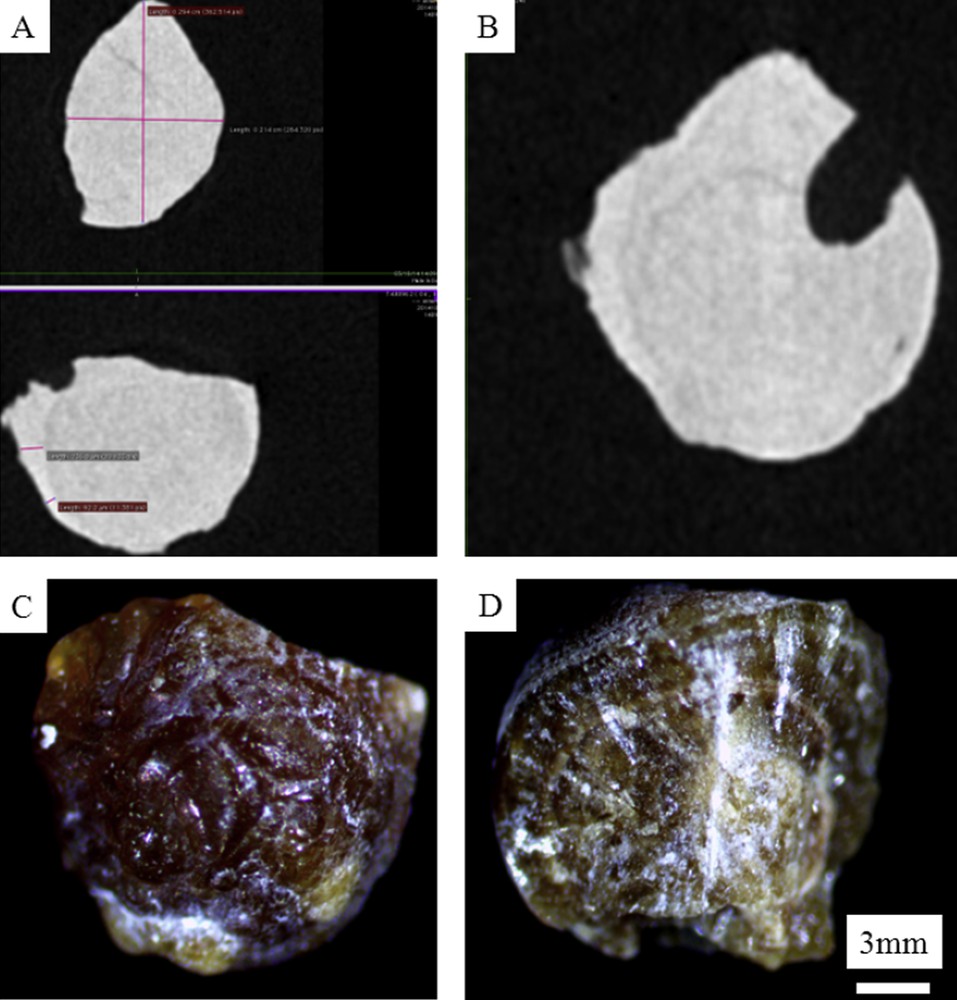
Microtomography observations (A and B) revealing a concentric organisation inside the N68102 kidney stone in line with the fact that this kidney stone belongs to the morphological type Ia as observed in Fig. 7C (surface) and 7D (section).
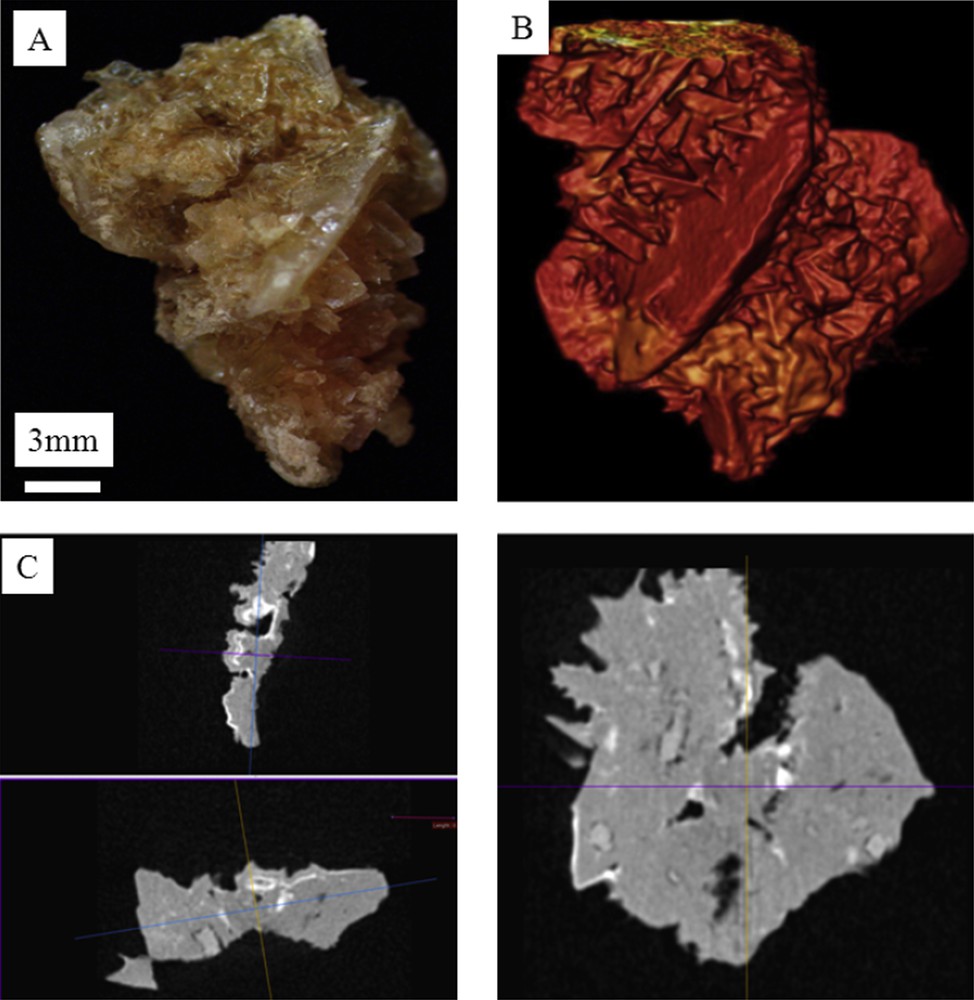
A: Macroscopic observations of N69923 COM kidney stone. B: Colorized 3D microtomography of the stone. C: Different views of 3D microtomography observations revealing a globular organisation inside the N69923 kidney stone in line with the fact that this kidney stone belongs to the morphological type Ie, associated with enteric hyperoxaluria.
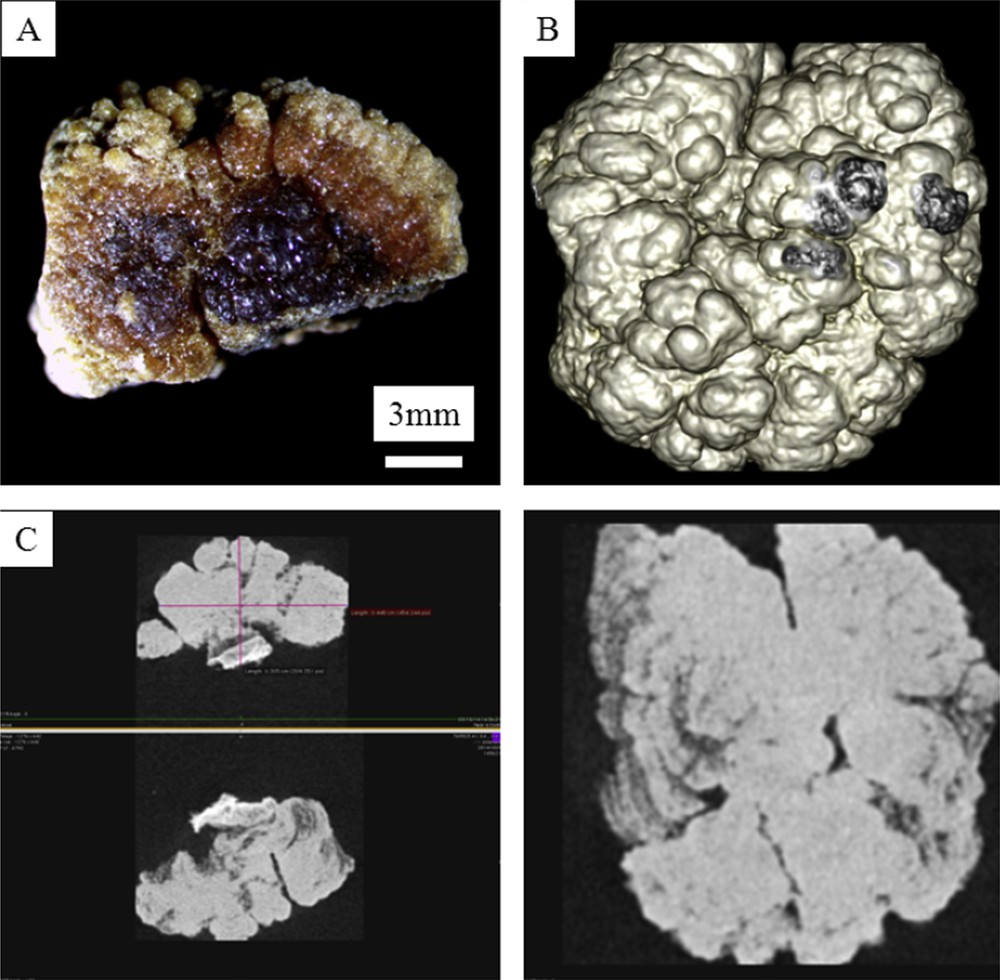
A: Macroscopic observations of N56070 COD kidney stone. B: Colorized 3D microtomography of the COM kidney stone. C: Different views of 3D microtomography observations revealing the absence of concentric layers inside the stone in line with the fact that this kidney stone belongs to the morphological type II. Of note, small whitish deposits dispersed within the section correspond to carbapatite deposits inside the stone.
Observations of all the μCT measurements show clearly that such an approach is able to point out the presence of bipyramide morphologies even in the bulk. Thus, structural characteristics with significant clinical information can be obtained using μX-ray tomography.
Information at the nanometre scale can be gathered using X-ray or neutron diffraction techniques [112–116]. At this point, we would like to recall the definition of nanocrystals and crystallites as defined by Van Meerssche and Feneau-Dupont [117] in order to describe the hierarchical structure of these pathological concretions. Crystallites (measuring typically some tens of micrometres) are made up of a collection of nanocrystals (measuring typically some hundreds of nanometres). Such characterization tools can be considered as a non-destructive microscope seeing inside matter. We have already used this technique in the case of calcium oxalate, cystine, struvite and uric acid kidney stones [18,33–35]. In Fig. 10, a set of Neutron Powder Diffraction (NPD) diagrams have been plotted. For some kidney stones, the signal to noise ratio was enough to analyse the data through the FullProf program. Such an approach leads to the knowledge of the apparent mean size of the coherently diffracting crystals from the observed broadened Bragg peaks of the NPD stone diagrams taking into account the instrumental resolution function of the neutron diffractometer. The FullProf program thus provided a value of this mean size (80 nm) with its standard deviation. Fig. 11 is an example of the diffraction pattern at room temperature of the N68097 kidney stone. Although the background level was high, owing to the hydrogen content of this biological sample, the high quality of the diagram allowed for a complete Rietveld-type refinement with an excellent RBragg factor (16.83). We used the crystallographic model that we have already published [18]. We found that the structural parameters (a, b, c and β) did not differ significantly from the values obtained previously. The significant difference we have between the experimental data and its numerical simulations (red arrows on Fig. 11) comes from the presence of weddellite (Fig. 12).
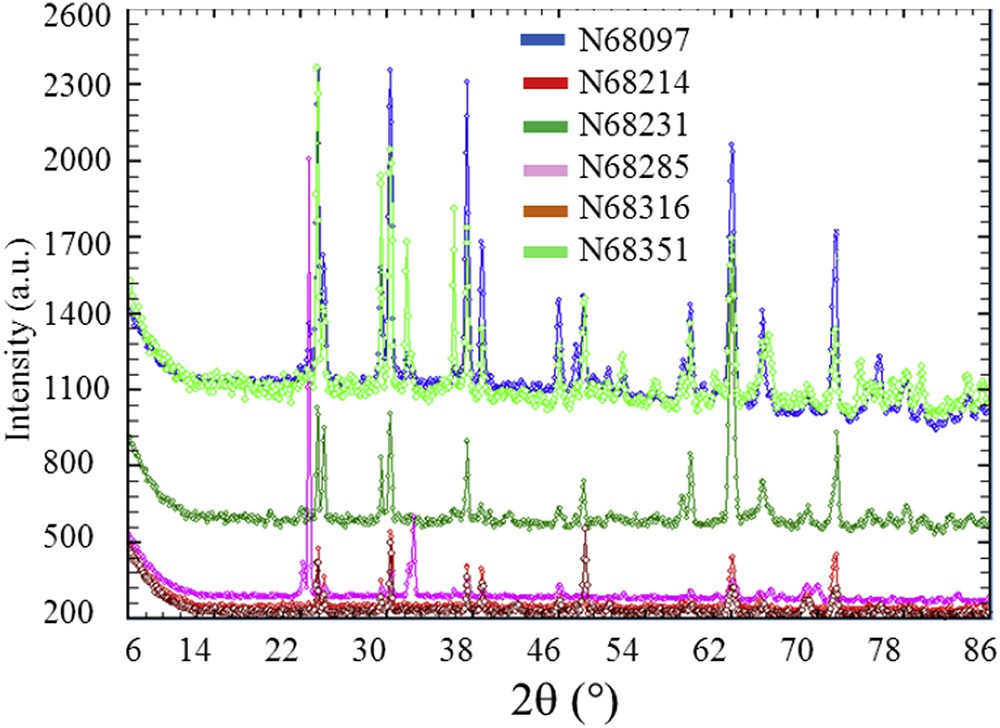
NPD diagrams of a set of kidney stones (N68097, N68214, N68231, N68285, N68316, and N68351). The fact that the quantity of samples as viewed by the neutron beam is not constant from one sample to another explained the variation intensity of the background.
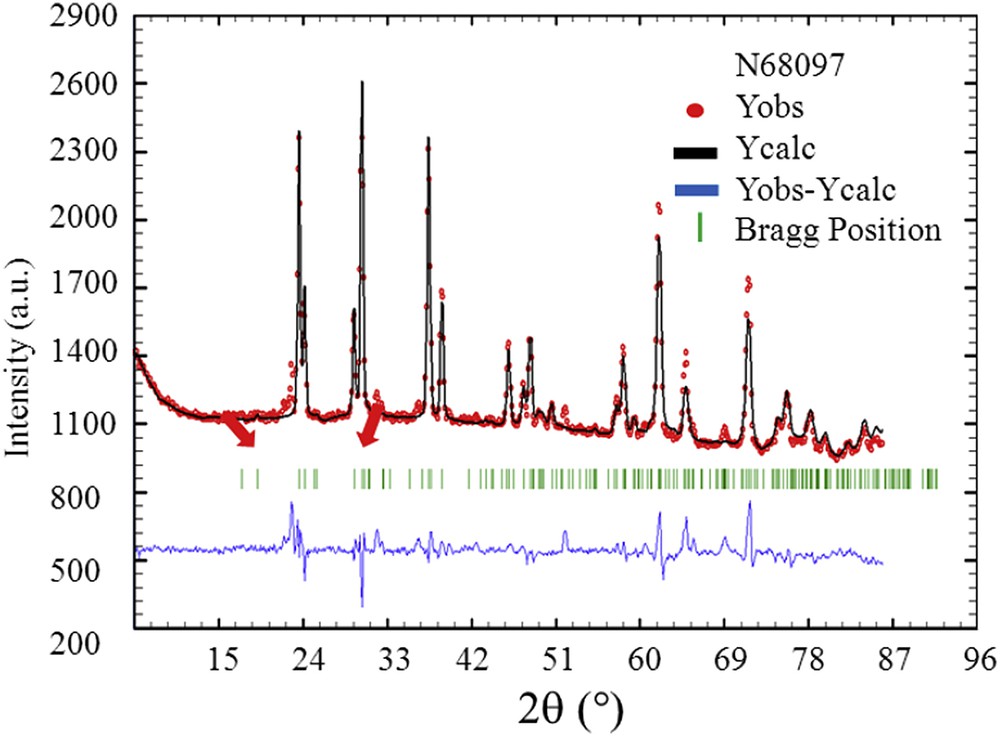
Typical final observed (Yobs in red), calculated (Ycalc) and difference profiles (Yobs-Ycalc in blue) of the NPD diagram of the N68097 kidney stone. Tick marks (Bragg position in green) below the profiles indicate the peak positions of allowed Bragg reflections for whewellite.
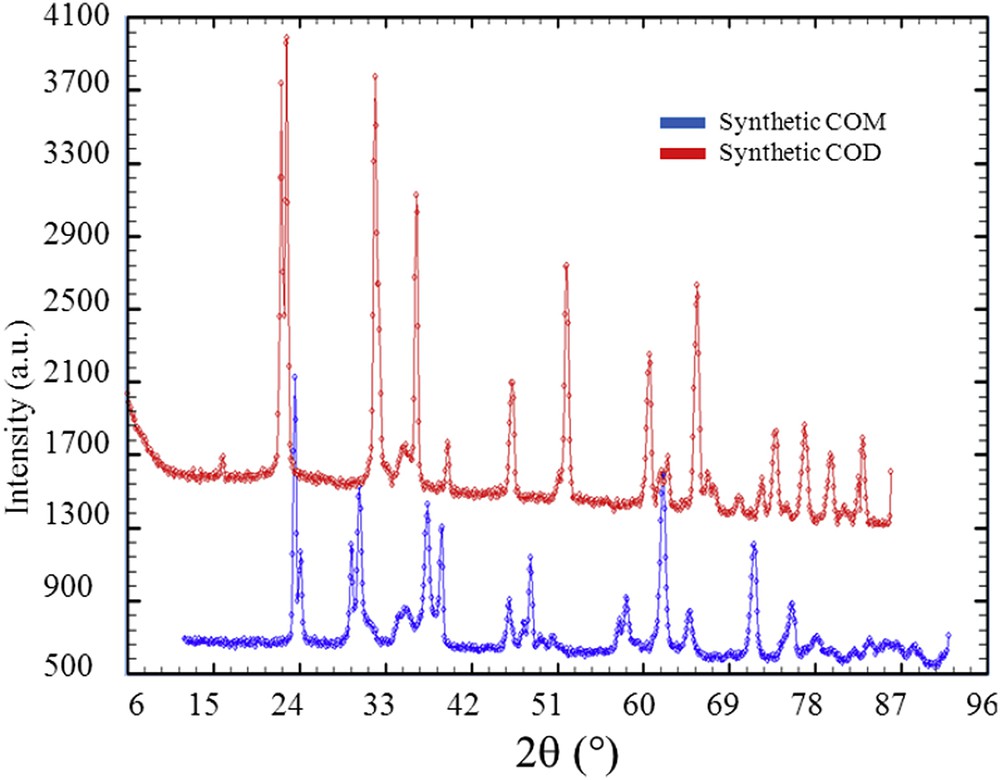
NPD diagrams collected for synthetic weddellite and whewellite.
As a conclusion of these experiments related to the conversion process of weddellite into whewellite, whewellite kidney stones for which IR spectra are not usual, are associated to classical NPD diagrams. As underlined by A. Millan [118], whewellite presents an enantiotropic transformation between 38 and 45 °C. The high-temperature structure belongs to space group I2/m with an unit cell: a = 9.978 Å, b = 7.295 Å, c = 6.292 Å, β = 107.07°. The low-temperature structure belongs to space group P21/n, and it has a double unit cell with dimensions: a = 9.9763 Å, b = 14.5884 Å, c = 6.2913 Å, β = 107.05°. This transformation is only distortional, and it hardly affects the bond network [118]. Nevertheless, these two crystallographic structures are associated to different NPD diagrams (Fig. 13). Thus, the presence of the other polymorph could affect the NPD of kidney stones which is not observed in the KS studied.
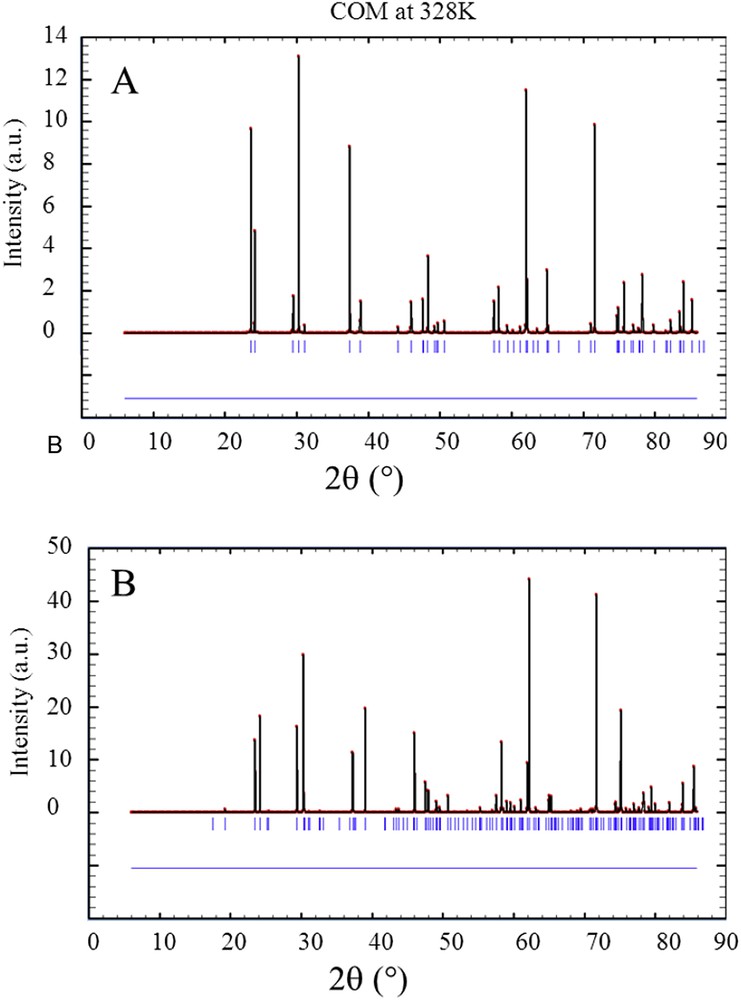
NPD diagrams calculated for the two polymorphs of whewellite which coexist at room temperature. On (A) our model and on (B) the other polymorph.
In order to assess this contradiction, the very same NPD diagrams but different FTIR spectra, an analogy can be drawn with Ca phosphate apatite [119–123]. For this chemical compound, the presence of amorphous Ca phosphate apatite induces a modification of the IR absorption spectrum (Fig. 14) and is not detected for neutron diffraction.
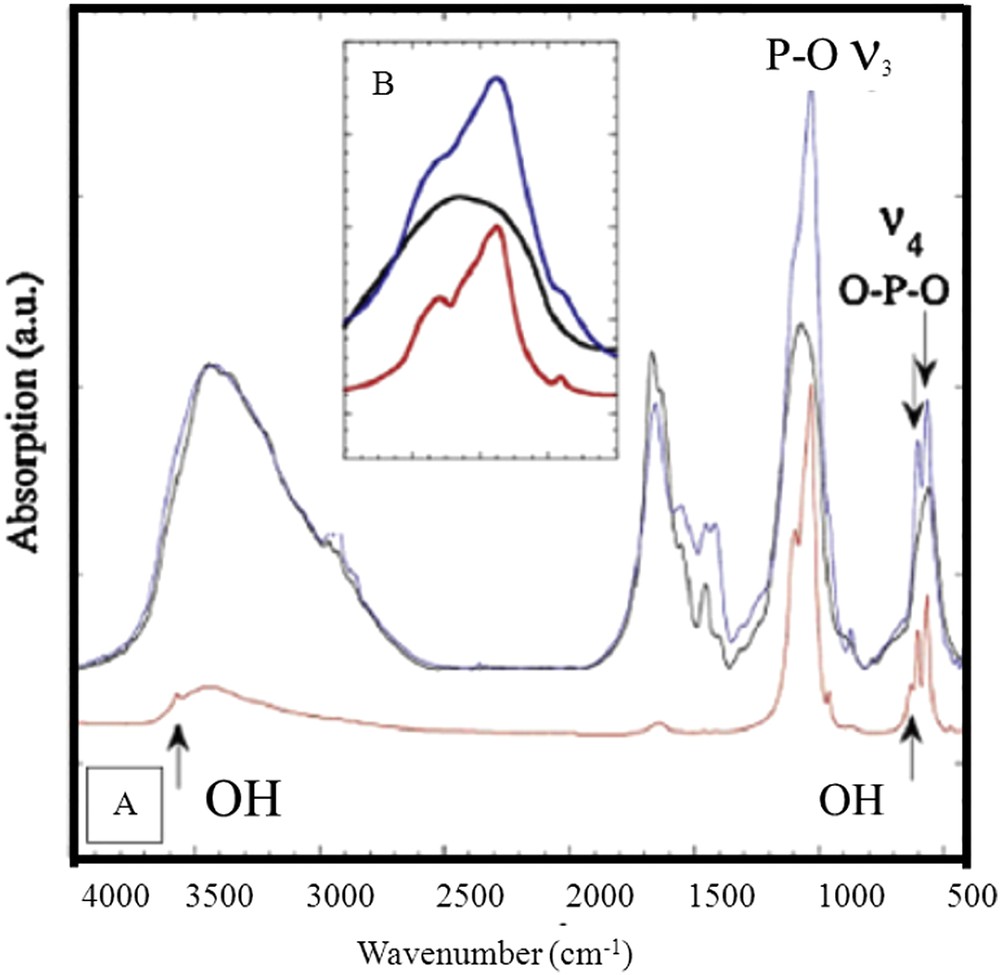
FT-IR absorption spectra of the compounds used here as references (in red, hydroxy apatite (HAP); in blue, carbapatite (CA); in black, amorphous carbonated calcium phosphate (ACCP). Inset: ν3 PO4 vibration.
A simple hypothesis to explain our results is thus given by the existence of an amorphous whewellite. Indeed, this chemical phase has been recently synthetized [124]. At this point, we can underline the fact why such amorphous calcium oxalate has been synthetized only recently. One explanation may come from the choice of precursors. Among numerous publications dedicated to the synthesis of whewellite (see in Table 2 selected examples), if different kinds of precursors have been used, most of the syntheses of calcium oxalate crystals are based on mixing CaCl2 and Na2C2O4 solutions. Using (CH3)2C2O4 was a different way which could explain why amorphous calcium oxalate has been successfully synthetized. In the case of kidney stones, such amorphous whewellite could be present as a result of COD conversion at the surface of whewellite crystals or coexisting with whewellite crystals. Only another set of experiments based on X-ray absorption and NMR could assess precisely the localisation of the amorphous whewellite versus crystalline whewellite.
Precursors used for the synthesis of whewellite crystals.
| Ca | Oxalate | References |
| CaCl2·2H2O | (CH3)2C2O4 | M. Hajir et al., 2014 [124] |
| Calcium chloride (CaCl2) | Sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4) | R. Zauner et al., 2000 [125], J. Yu et al., 2005 [126], S.-P. Deng et al., 2006 [127], M. Liang et al., 2009 [128], Z. Chen et al., 2010 [110], X. Wei et al., 2012 [129], K. Pitt et al., 2012 [130], K.P. Aggarwal et al., 2013 [131], C. Conti et al., 2014 [85]. |
| CaCl2·2H2O or CaCl2 | (COOH)2·2H2O | G. Wiedemann et al., 1988 [132] |
| H2C2O4 | J.W. Kurutz et al., 2003 [133], K. Niimi et al., 2012 [134], P. Vijaya et al., 2012 [109], K. Akhtar et al., 2013 [135]. | |
| K2C2O4 | D. Jauregui-Zuniga et al., 2005 [136], Rabinovich et al., 2008 [137], Y. Xiu-Qiong et al., 2012 [138], S. Zhang et al., 2012 [139]. | |
| Na2C2O4 | T. Jung et al., 2005 [140] | |
| Na2C2O4, H2C2O4, | A. Millan, 2001 [118] | |
| H2C2O4, Na2C2O4, K2C2O4 | J.-M. Ouyang et al., 2005 [141] | |
| Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | Sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4) | B. Grohe et al., 2012 [142] |
| Oxalic acid (H2C2O4) | P. Thanasekaran et al., 2012 [143] | |
| Sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4) | B.P.H. Chana et al., 2012 [103] | |
| Sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4) | E.C. Arvaniti et al., 2010 [144] |
4 Conclusion
In this investigation, a set of kidney stones containing whewellite and associated to a particular FTIR spectrum have been considered. The complete set of data including FE-SEM observations at the mesoscopic scale, NPD experiments to assess their crystallographic structure at the nanometre scale and 3D and 2D cross-section visualisations evaluated from the μCT measurements indicate the presence of amorphous whewellite. This structural possibility is quite similar to what is observed for calcium phosphate apatite. Moreover, stable amorphous whewellite has recently been synthetized [69].
Such improvement in the structural description of calcium oxalate compounds is of major importance for clinicians. According to the results presented in the paper, NPD and μCT measurements do not show the presence of amorphous whewellite contrary to FTIR and FE-SEM observations. These results imply that the quantity of amorphous calcium oxalate is quite low. Finally, such improvement in the structural description of calcium oxalate compounds is of major importance for clinicians. The presence of amorphous whewellite leads to hypercalciuria-related and not to hyperoxaluria-related stones, while crystalline whewellite is highly suggestive for hyperoxaluric states.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Laboratoire Léon-Brillouin for beam time allocation.