1 Introduction
Copper (II) square planar complexes are intensively investigated for their role in various domains of chemistry as versatile catalysts, in metal-organic semi-conductors, in magnetic materials or in biosystems. In contrast and because of their structural behavior at room temperature in solution, the Cu (I) tetrahedral complexes were of little use until the discovery of Sauvage and McMillin [1] who were able to stabilize the tetrahedral geometry of a copper (I)-diimine complexe using bulky ligands and to prevent a deformation to the formal copper (II) square planar arrangement, responsible for the quenching of luminescence. However, none of the many synthesized homoleptic Cu (I) complexes having a great potential as luminescent probe and electron/energy transfer carrier is able to compete with [Ru(bpy)3]2+ for solar conversion applications. A new generation of molecules with luminescent properties, low-lying long-lived metal-to-ligand-charge-transfer (MLCT) excited states, absorbing in the visible energy domain and rigid enough to prevent distortion of geometry and sub-sequent quenching of the excited state were synthesized [2].
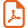
As compared to the huge amount of theoretical studies devoted to Ru(II) complexes, the investigation of the structural and spectral properties of Cu(I)-diimine complexes is still scarce [3]. Due to the size of the molecules and the low degree of symmetry, accurate ab initio calculations are unlikely. Moreover the scan of a large number of molecules is necessary to rationalize the electronic effects on the overall properties of this class of complexes. The present systematic theoretical study, extension of a joint experimental/theoretical investigation devoted to the synthesis, spectral, electrochemical and electronic properties of a series of heteropleptic bis-phenanthroline copper (I) complexes [4], reports the structural and spectral properties obtained by density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT) calculations for [Cu(phen)L1]+ 1, [Cu(Me-phen)L1]+ 2, [Cu(nBu-phen)L1]+ 3, [CuL1L2]+ 4, [Cu(Mes-phen)L2]+ 5, [Cu(Mes-phen)(nBu-phen)]+ 6 and [Cu(MePh-phen)L1]+ 7, with L1 = 2,9-dimesityl-2-(4′-bromophenyl)imidazo[4,5-f][1,10]phenanthroline, L2 = 3,6-di-nbutyl-11-bromodipyrido[3,2-a:2′,3′-c]phenazine, phen = 1,10-phenanthroline, Me-phen = 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline, nBu-phen = 2,9-di-n-butyl-1,10-phenanthroline, Mes-phen = 2,9-dimsityl-1,10-phenanthroline, MePh-phen = 2,9-dimethyl-4,11-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline. Most of the experimental results related to these complexes are published elsewhere [4].
2 Computational details
The geometries of complexes 1 to 7 (Fig. 1) in the 1A electronic ground state have been optimized at the DFT level using the generalized gradient approximation PBE functional [5] with Grimme's dispersion correction, so-called PBE-D and PBE-D3 [6], needed to describe π-stacking interactions.
Molecular structures of the heteroleptic Cu (I) complexes 1 to 7. The numbering corresponding to [4] and Fig. 3 is specified in parenthesis.
Triple-ζ basis sets [7] have been used for all atoms, and the calculations were performed without symmetry constraint in the C1 point group. Only the isomers of lowest energy have been selected for these costly geometry optimizations. Although the choice of PBE-D functional is appropriate for reproducing π-stacking structures, it adds difficulties at describing planarity of floppy systems and tends to curve long ligands. In order to solve related problems of convergence, specific constraints on floppy ligands dihedral angles have been applied to keep them planar. The structures have been calculated with ADF2010.02 quantum chemistry software [8,9].
The theoretical absorption spectra of the complexes depicted in Fig. 1 have been determined by means of TD-DFT method [10] using B3LYP functional [11,12] in vacuum and with solvent corrections according to the integral equation formalism PCM (IEFPCM) model [13] within the linear response scheme. Dunning's correlation consistent basis sets (cc-pVDZ) have been used for hydrogen, bromide and second-row atoms [14], together with a modified Ahlrichs TZV basis set (7s, 6p, 5d) contracted to [6s,3p, 3d] for the Cu atom [15]. A modified version of Gaussian 09 quantum chemistry software [16] has been used for the calculation of the theoretical TD-DFT spectra.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Optimized density functional theory structures
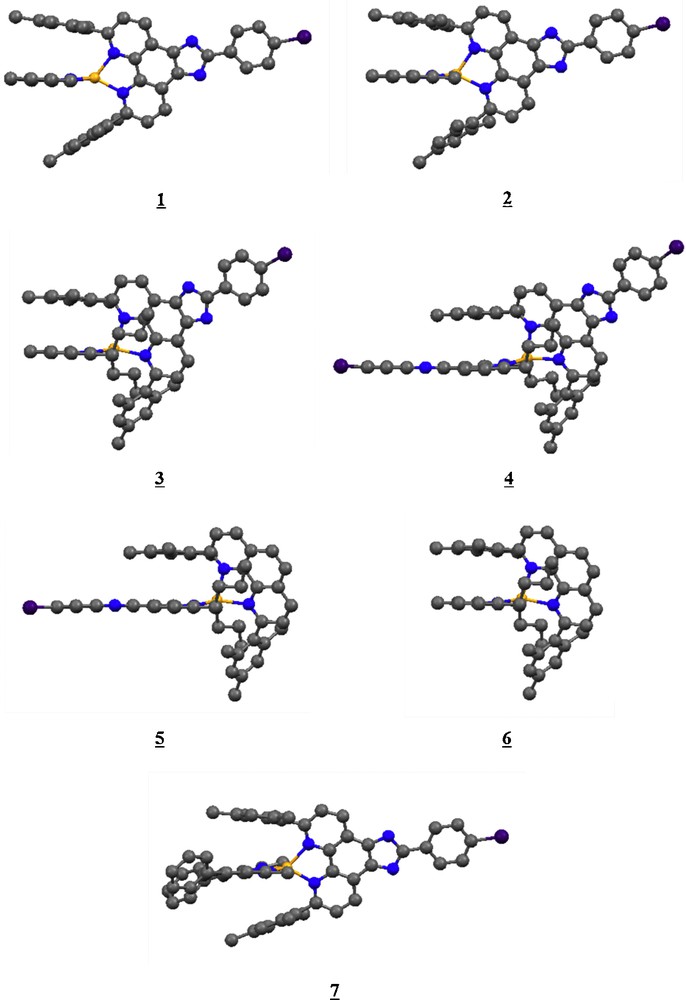
Some important bond lengths and bond angles of the complexes depicted in Fig. 1 are reported in Table 1 and compared to X-ray values when available (complex 5).
Bond lengths (in Å) and angles (in °) of four Cu-N bonds in complex 1 to 7 optimized at PBE-D/TZP level of theory. The parameters of PBE-D3/TZP optimized structures are in parentheses and the X-ray data [4] for complex 5 in square bracket.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| Cu-N4 | 1.996 (2.000) | 2.003 (2.009) | 2.005 (2.009) | 1.999 (2.004) | 2.003 (2.011) [2.009] | 2.011 (2.018) | 2.006 (2.009) |
| Cu-N3 | 2.025 (2.026) | 2.028 (2.033) | 2.060 (2.065) | 2.072 (2.078) | 2.075 (2.082) [2.115] | 2.075 (2.090) | 2.005 (2.007) |
| Cu-N1 | 2.006 (2.008) | 2.020 (2.023) | 2.014 (2.017) | 1.999 (2.006) | 2.008 (2.016) [2.004] | 2.017 (2.031) | 2.019 (2.023) |
| Cu-N2 | 2.023 (2.026) | 2.031 (2.035) | 2.057 (2.057) | 2.068 (2.072) | 2.075 (2.079) [2.124] | 2.071 (2.077) | 2.029 (2.032) |
| N3-Cu-N4 | 83.27 (83.18) | 83.35 (83.61) | 82.65 (82.99) | 82.24 (82.62) | 82.15 (82.48) [81.45] | 82.36 (82.49) | 83.04 (83.39) |
| N1-Cu-N2 | 82.12 (82.47) | 81.88 (82.40) | 82.32 (82.57) | 82.49 (82.86) | 82.26 (82.61) [81.98] | 81.96 (82.11) | 81.94 (82.56) |
| N3-Cu-N1 | 133.08 (132.09) | 131.84 (130.38) | 124.87 (122.95) | 124.52 (124.43) | 124.55 (124.29) [123.38] | 124.32 (123.76) | 135.42 (134.37) |
| N2-Cu-N3 | 109.35 (109.58) | 109.10 (110.45) | 100.42 (104.17) | 96.75 (99.32) | 97.31 (99.29) [95.53] | 98.68 (99.88) | 114.15 (114.62) |
| N1-Cu-N4 | 123.85 (123.25) | 127.58 (126.96) | 142.04 (140.80) | 144.67 (142.84) | 144.47 (142.42) [147.18] | 143.09 (141.62) | 117.00 (117.60) |
| N2-Cu-N4 | 131.24 (132.50) | 127.58 (127.82) | 121.34 (122.13) | 120.10 (120.67) | 120.47 (121.96) [119.68] | 122.21 (123.96) | 133.20 (131.55) |
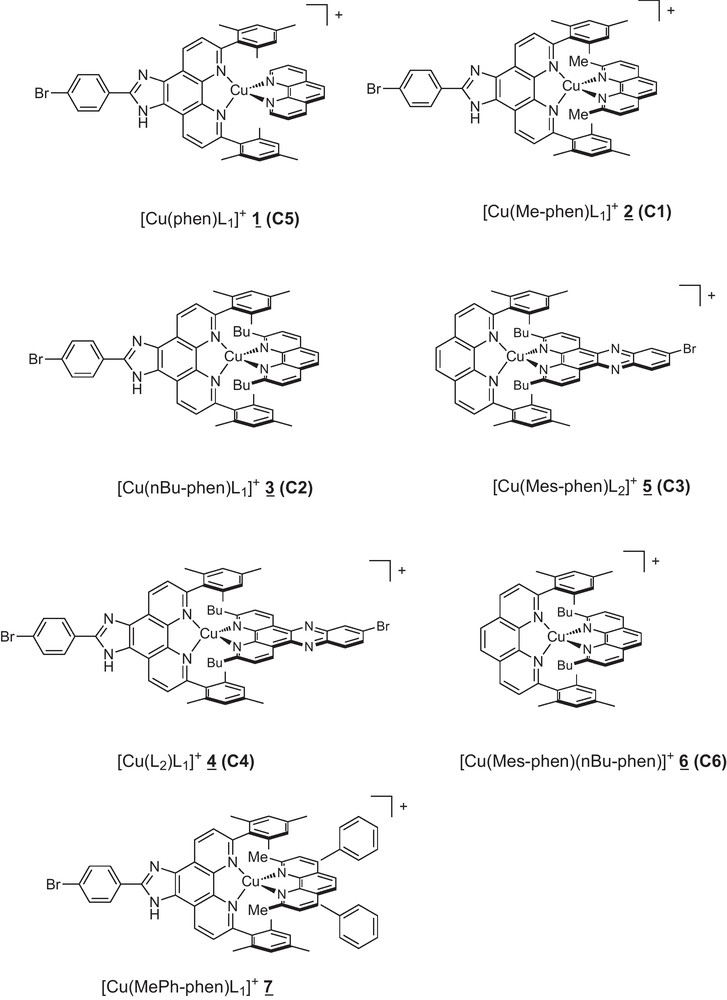
The optimized structures of complexes 1 to 7 are depicted in Fig. 2 (hydrogen atoms are hidden for clarify).
Side view of the density functional theory (PBE-D) optimized structures of Cu (I) complexes 1 to 7.
The complexes 1 to 7 show significant π-stacking interactions between one (3, 4, 5, 6) or two (1, 2, 7) mesityl group(s) and the phenanthroline (substituted) -ligands. The double interaction occurs in symmetric complexes with less bulky ligands. In the other complexes substituted by butyl groups in 2,9 position of the phenantroline, the symmetry is destroyed, leading to a single interaction. Preliminary calculations performed at the DFT (B3LYP) level did not show these important π-stacking interactions that stabilize the structures of this class of heteroleptic complexes.
The main geometrical parameters reported in Table 1, optimized at the DFT (PBE-D) and DFT (PBE-D3) levels, are numbered according to Scheme 1. The only X-ray structure available is that of [Cu(Mes-phen)(nBu-phen)]+ (5). The experimental data are reported in brackets for comparison.
The analysis of the calculated Cu-N bond distances puts in evidence two distinct behaviours depending again on the presence of butyl groups on the phenantroline-like ligands. In complexes 3, 4, 5, 6, we are in presence of two short bond lengths Cu-N4 and Cu-N1 (∼ 2.0 Å) and two long bond lengths Cu-N3 and Cu-N2 (2.055–2.075 Å). This dissymmetry is correlated to the steric hindrance of the butyl groups and the π-stacking interactions in these complexes. In contrast, the optimized Cu-N bond distances in 1, 2 and 7 range from ∼ 2.0 Å to ∼ 2.03 Å with less distorted structures. The DFT (PBE-D) and DFT (PBE-D3) results are very similar for the bond distances as well as for the bond angles. In both cases, the errors with respect to the X-ray data do not exceed 5% on the bond distances and 3% on the bond angles and the main trends are well reproduced by the calculations.
The Kohn-Sham (KS) orbitals corresponding to the structures of complexes 1 and 5 are depicted in Schemes 2 and 3, respectively.
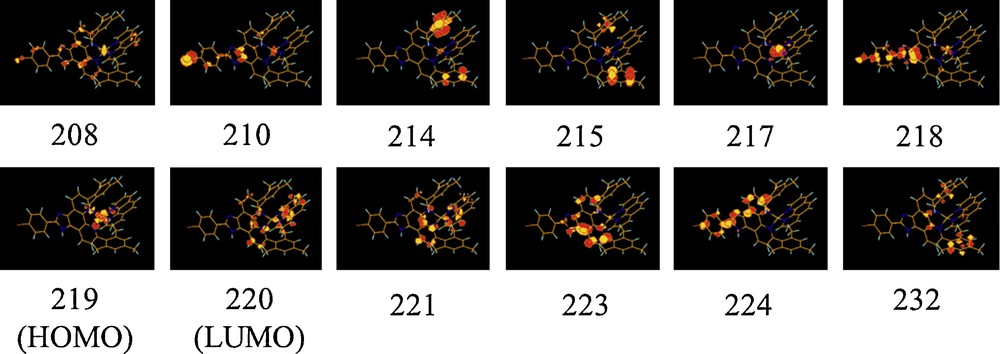
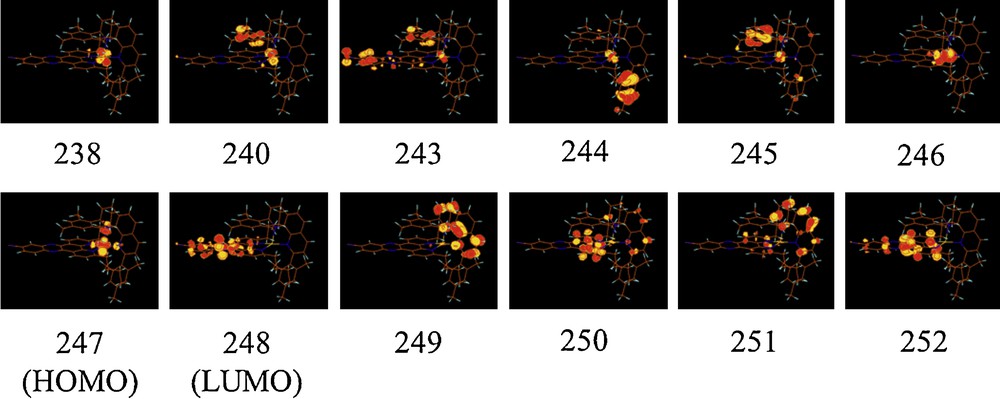
The HOMO corresponds to 3dCu in both complexes whereas the LUMO is localized on the phen ligand in 1 (π*phen) and on the L2 ligand in 5 (π*L2). In complex 5, with a Mes-phen ligand and butyl groups on L2, the HOMO-1 is localized on the Cu atom whereas the HOMO-2 (245) and HOMO-3 (244) are localized separately on the two mesityl groups of L2, reflecting the distorted structure of the complex. In complex 1, with a simple phen ligand, HOMO-1 corresponds to a π* localized on L1 (218) and HOMO-2 is localized on the metal atom. As shown in our previous paper [4], the electronic properties of these complexes are very sensitive to the ligands coordinated to the Cu atom and their substituants.
This is shown in Table 2 where the HOMO-LUMO gaps are reported for complexes 1 to 6. As expected, a small HOMO-LUMO energy gap is observed for complexes 4 and 5 where the LUMO is localized on the strongly π*L2 acceptor ligand. Complexes 1, 2 and 6 have similar HOMO-LUMO gaps whereas complex 3 is characterized by the highest energy gap due to an important destabilization of the HOMO, localized on Bu-phen, not compensated by the small destabilization of the LUMO. These features will have important consequences on the electronic spectroscopy as illustrated in the next section.
HOMO-LUMO orbitals energies (in a.u.) and energy gaps (in eV) of complexes 1 to 6.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| LUMO | ||||||
| −0.165 | −0.164 | −0.090 | −0.177 | −0.183 | −0.167 | |
| HOMO | ||||||
| −0.277 | −0.276 | −0.208 | −0.282 | −0.285 | −0.283 | |
| ΔE | 3.06 | 3.05 | 3.22 | 2.86 | 2.77 | 3.15 |
3.2 Time dependant-density functional theory electronic absorption spectra
The transition energies to the low-lying singlet excited states of the L1 substituted complexes 1, 2, 3 are reported in Table 3 whereas the transition energies to the low-lying singlet states of the L2 substituted complexes 4, 5 and of the complex 6 with mesityl and butyl groups on the two phenanthrolines are reported in Table 4.
Time-dependent/density functional theory (B3LYP) transition energies (in nm) to the low-lying singlet excited states of complexes 1, 2 and 3 and associated oscillator strengths f calculated in vacuum. The main character of the state is given in percentage of each contribution.
| 1 | nma | f | 2 | nma | f | 3 | nm | f | ||||||
| MLCTL1/ 45% | MLCTphen 47% | 578 (581) | 0.05 | MLCTL1 88% | 576 (578) | 0.02 | MLCTphen/ 81% | MLCTL1 12% | 509 | 0.02 | ||||
| MLCTL1/ 58% | MLCTphen 32% | 494 | 0.09 | |||||||||||
| MLCTphen/ 35% | MLCTL1 38% | 463 (461) | 0.12 | MLCTL1/ 47% | MLCTphen 48% | 469 (470) | 0.12 | |||||||
| MLCTL1/ 37% | ILL1 37% | 374 | 0.13 | |||||||||||
| ILL1/ 51% | MLCTL1 23% | 369 (358) | 0.20 | ILL1/ 46% | MLCTL1 36% | 372 (361) | 0.27 | ILL1/ 56% | LLCTphen 12% | 371 | 0.13 | |||
| ILL1 69% | 326 (326) | 0.55 | MLCTphen/ 64% | LLCTphen 15% | 324 | 0.05 | ||||||||
| ILL1/ 29% | LLCTphen 53% | 322 | 0.34 | ILL1 69% | 324 | 0.64 | ||||||||
| ILL1/ 50% | LLCTphen 28% | 322 (327) | 0.44 | MLCTL1/ 22% | ILL1/ 34% | LLCTphen 23% | 323 | 0.06 | ||||||
| LLCTphen/ 36% | ILL1/ 36% | MLCTL1 12% | 319 | 0.06 | ||||||||||
| MLCTL1/ 77% | ILL1 11% | 317 | 0.37 | ILL1/ 56% | MLCTphen 20% | 318 | 0.07 | LLCTphen/ 40% | MLCTL1 25% | 318 | 0.05 | |||
| ILL1 89% | 313 | 0.11 | MLCTL1/ 34% | ILL1 33% | 313 (312) | 0.19 | ILL1// 40% | MLCTL1 14% | LLCTphen 25% | 316 | 0.29 | |||
| MLCTL1/ 46% | ILL1/ 17% | LLCTphen 11% | 307 (308) | 0.14 | ILL1/ 30% | LLCTL1/ 20% | MLCTL1 12% | 307 | 0.04 | |||||
| MLCTL1/ 29% | ILL1/ 25% | LLCTphen 22% | 294 (290) | 0.07 | ILL1 53% | 293 (292) | 0.06 | ILL1 67% | 295 | 0.1 | ||||
| MLCTphen/ 59% | LLCTL1 15% | 283 | 0.05 | |||||||||||
| LLCTL1/ 22% | Lphen/ 20% | IILL1 30% | 281 | 0.04 | LLCTL1/ 58% | MLCTphen 21% | 282 | 0.13 | MLCTL1/ 25% | LLCTL1 24% | 280 | 0.13 | ||
| ILL1/ 47% | MLCTL1 19% | 277 | 0.17 | MLCTL1/ 43% | ILL1 30% | 277 | 0.08 | ILL1 68% | 272 | 0.05 | ||||
| ILL1/ 62% | MLCTL1 15% | 277 | 0.10 | MLCTL1/ 32% | LLCTL1 12% | 272 | 0.06 | ILphen/ 23% | LLCTphen 25% | 272 | 0.04 | |||
| ILL1/ 52% | MLCTL1 30% | 275 | 0.12 | MLCTL1/ 29% | ILL1 29% | 270 | 0.10 | LLCTL1/ | MLCTL1 | 272 | 0.13 | |||
| MLCTL1/ 49% | ILL1 12% | 268 | 0.07 | LLCTphen 61% | 268 | 0.13 | LLCTL1/ 17% | ILL1/ 15% | LLCTphen/ 24% | 271 | 0.13 | |||
| MLCTL1/ 33% | ILphen/ 10% | MLCTphen 10% | 265 | 0.08 | LLCTphen 69% | 267 | 0.08 | MLCTL1 72% | 269 | 0.06 | ||||
| MLCTL1/ 34% | ILL1 34% | 264 | 0.07 |
a The solvent corrected values (IEPCM for CH2Cl2) are given in parenthesis.
Time-dependent/density functional theory (B3LYP) transition energies (in nm) to the low-lying singlet excited states of complexes 4, 5 and 6 and associated oscillator strengths f calculated in vacuum. The main character of the state is given in percentage of each contribution.
| 4 | nm | f | 5 | nm | f | 6 | nm | f | ||||
| MLCTL1/ 55% | MLCTL2 37% | 500 | 0.06 | MLCTMesphen 80% | 494 | 0.04 | MLCTMesphen/MLCTphen 63% 21% | 492 | 0.03 | |||
| MLCTL2 63% | 392 | 0.07 | LLCTL2/ 75% | ILL2 10% | 393 | 0.06 | ||||||
| LLCTL2 74% | 385 | 0.06 | LLCTL2/ 47% | ILL2 13% | 384 | 0.05 | ||||||
| LLCTL2 85% | 382 | 0.04 | ||||||||||
| MLCTL1/ 32% MLCTL2/ 16% | LLCTL2 19% ILL1 17% | 378 | 0.05 | LLCTL2/ 43% | MLCTL2 28% | 378 | 0.04 | |||||
| ILL1 53% | 375 | 0.16 | ||||||||||
| MLCTL1/ 36% | MLCTL2/ 10% | ILL1 10% | 371 | 0.08 | ILL2/ 41% | MLCTL2 19% | 372 | 0.02 | ||||
| MLCTL1/ 40% | LLCTL2/ 16% | ILL2 15% | 354 | 0.05 | ILL2/ 27% | LLCTL2 17% | 357 | 0.1 | MLCTMesphen/ILMesphen 43% 38% | 355 | 0.08 | |
| LLCTL2/ 33% | MLCTL2/ 16% | ILL2 15% | 348 | 0.1 | MLCTMesphen/ 22% ILMesphen 18% | ILL2/ 12% | 349 | 0.02 | ||||
| ILL1/ 40% | LLCTL2 19% | 325 | 0.58 | MLCTMesphen/ILMesphen 44% 30% | 332 | 0.07 | ||||||
| ILL1/ 37% | MLCTL1/ 22% | LLCTL1 15% | 324 | 0.38 | ||||||||
| MLCTL2/ 25% MLCTL1/ 10% | ILL1/ 15% LLCTL1 10% | 323 | 0.11 | |||||||||
| MLCTL1/ 52% | ILL1 25% | 317 | 0.08 | |||||||||
| ILL2/ 29% | MLCTL2/ 36% | LLCTL2 14% | 312 | 0.06 | LLCTL2/ 53% | MLCTL2 19% | 308 | 0.13 | ||||
| MLCTL1/ 36% | ILL1 26% | 303 | 0.12 | MLCTL2/ 55% | LLCTL2 25% | 303 | 0.07 | |||||
| ILL1 69% | 302 | 0.05 | ||||||||||
| MLCTL2/ 54% | ILL2 20% | 300 | 0.06 | |||||||||
| MLCTL2/ 53% | MLCTL1 37% | 297 | 0.05 | |||||||||
| MLCTL1/ 21% | MLCTL2/ 32% | LLCTL2 13% | 295 | 0.44 | MLCTL2/ 36% | LLCTL2 34% | 297 | 0.44 | ||||
| MLCTL1/ 57% | MLCTL2 16% | 294 | 0.22 | MLCTL2/ 55% | LLCTL2 21% | 295 | 0.22 | |||||
| MLCTL2/ 31% MLCTL1/ 12% | ILL2/ 25% LLCTL1 12% | 286 | 0.14 | ILL2 66% | 285 | 0.14 | ||||||
| ILL2/ 23% | ILMesphen/ 26% | LLCTL2 14% | 272 | 0.11 | MLCTMesphen/ILMesphen | 272 | 0.11 | |||||
| MLCTMesphen | 272 | 0.03 | ||||||||||
| LLCTphen/ILphen | 271 | 0.07 | ||||||||||
| ILphen/LLCTphen/ MLCTphen | 271 | 0.26 |
Only the excited states with significant oscillator strengths (greater than 0.05), excepting in case of necessity, and ranging in the UV/vis energy domain between 600 nm and 250 nm are reported in Tables 3 and 4 as well as their character: MLCT, IL or LLCT. The localization of the charge transfer is given by the indices L1 (when CT occurs towards the substituted phen of the L1 ligand) or phen (when CT occurs towards the phen substituted by H in 1, Me in 2 and Bu in 3). The main character of the excited states listed in Tables 3 and 4 are given in percentage.
The theoretical absorption spectra of the complexes 1, 2 and 3 are very similar and the structural deformation of complex 3 due to the presence of butyl ligands is of little influence on the absorption spectroscopy. This is in agreement with the experimental findings [4] (Fig. 3). However, the character of the low-lying states may be slightly different with the occurrence of LLCT states in the lowest part of the spectrum of 3 and a blue shift of the starting absorption at 509 nm (vs. 580 nm for 1 and 2), not observed experimentally and probably due to the strong contribution of the MLCTphen state. The presence of butyl groups seems to induce more charge transfer towards the phen ligand in the lowest as well as in the highest excited states of 3. The absorption of complexes 1 and 2 starts at about 580 nm (vs. 600 nm experimentally), with low-lying MLCT states corresponding to dCu → π*L1/phen excitations showing a major contribution of the charge transfer to L1 and a maximum calculated at about 465 nm (vs. 480 nm experimentally). The solvent corrected values for CH2Cl2 are nearly identical to those in vacuum as illustrated by the data given in parenthesis for some of the important states of 1 and 2. The same trends are observed for complex 3.
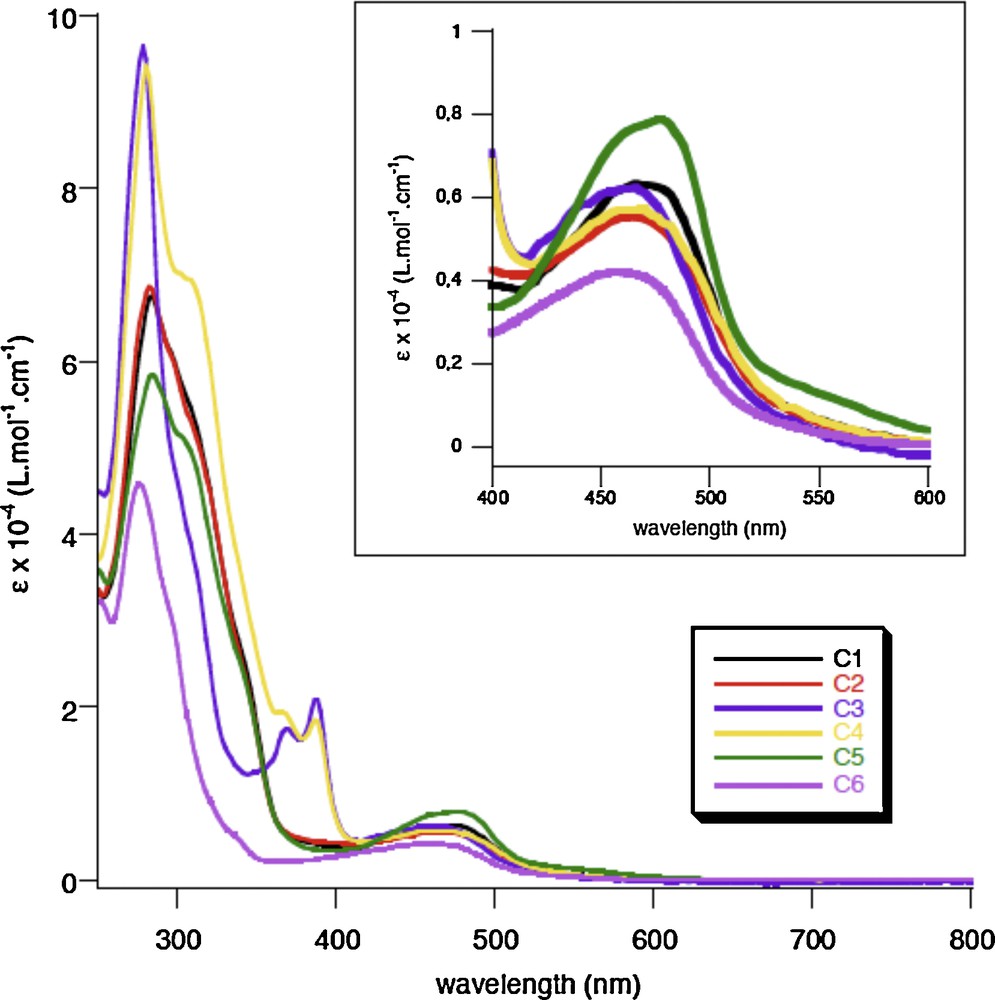
Experimental absorption spectra of complexes 1 to 6 recorded in CH2Cl2 (from [4]). The numbering corresponds to [4] (see Fig. 1 for correspondence).
The near-UV region of the absorption spectra is characterized by the presence of IL states localized on the L1 ligand calculated at 370 nm and 320 nm and characterized by rather large oscillator strengths. They correspond to the absorption at 360 nm and 325 nm observed on the experimental spectrum of 1. The UV region is characterized by a high density of states between 315 nm and 265 nm that contribute to the large band centered at 280 nm experimentally. The most intense peaks possess an important contribution of states localized on L1, either IL or LLCT (πphen →π*L1).
All the calculated TD-DFT excited states with non-zero oscillator strengths have been included in the theoretical spectra represented in Fig. 4.
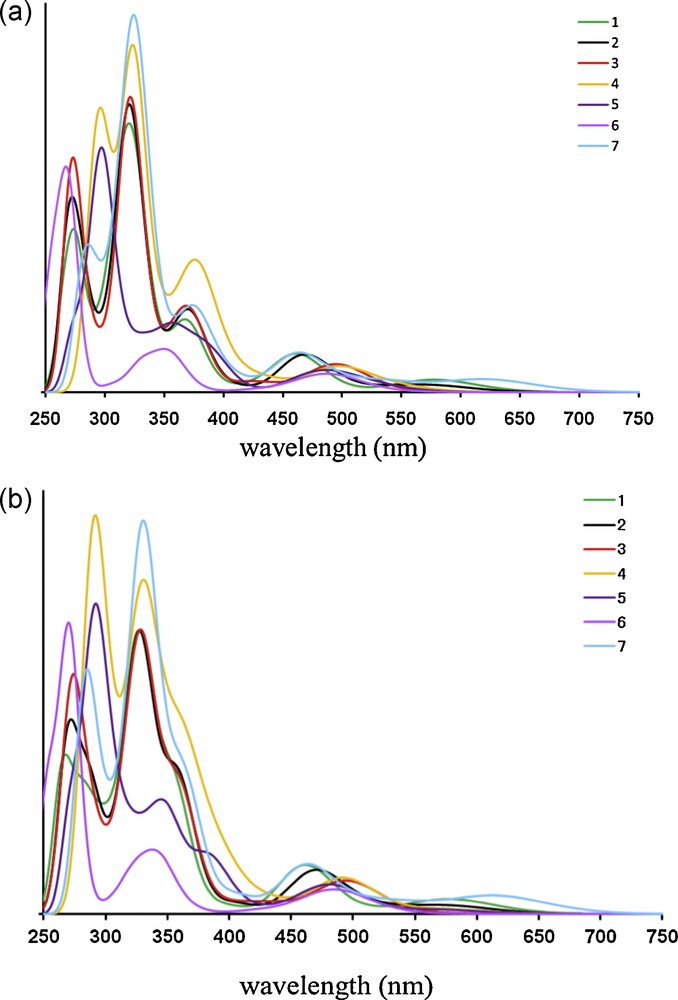
Time-dependent/density functional theory absorption spectra of complexes 1 to 7 without (a) and with (b) solvent correction for CH2Cl2. The calculated spectrum is obtained by convoluting the theoretical line spectrum by Gaussians of 1000 cm−1 full width at half maximum (FWHM).
According to the shape of the calculated absorption spectra of complexes 1, 2 and 3 represented in Fig. 4 and taking into account the relative intensities, the calculations including solvent correction (Fig. 4 (a)) are rather realistic leading to a perfect agreement with the experimental spectra depicted in Fig. 3. The theoretical absorption spectrum of complex 7 with phenyl groups on the Me-subsituted phenanthroline ligand, for which there is no experimental spectrum available, starts at 620 nm and is very similar to the spectrum of complexes 1, 2 and 3 as illustrated in Fig. 4 with a band at 460 nm corresponding to MLCTL1 transitions and at 376 nm with an important ILL1 character. A series of states calculated around 320 nm correspond to MLCT/IL/LLCT states of mixed character similarly to complexes 1 to 3. The band calculated at 307 nm is present as well, like in the theoretical spectra of complexes 1 and 2.
The absorption spectroscopy of complexes 1, 2, 3 and 7 is characterized by low-lying MLCT states with more (3) or less (1,2 and 7) contribution of charge transfer to the phen ligand. It seems that the presence of butyl groups increases the charge transfer to the phen. The character of the excited states and the energetics are not dramatically affected by the structural distortions due to the presence of butyl groups and the nature of the π-stacking interactions which are very weak and do not modify visible/UV energetics. However, the study of nuclear relaxation in the low-lying electronic excited states that is beyond the scope of the present study could change this conclusion.
The transition energies to the low-lying singlet excited states of the second series of Cu (I) heteroleptic complexes 4, 5 and 6 are reported in Table 4, together with their character and associated oscillator strengths. The theoretical spectra of 4 and 5 are very similar in agreement with the experimental finding (Fig. 3) with higher intensities for 4 related to the contribution of IL states localized on L1.
The density of states is more important in 4 than in 5 because of the presence of the two ligands L1 and L2 in 4 that induce large mixing between MLCT and LLCT states. The absorption starts at about 500 nm in both complexes with a MLCT state localized on L1/L2 in 4 and on the mesityl substituted phen in 5. We retrieve the two peaks observed at 390 nm and 370 nm characteristics of these two complexes on the experimental spectra (Fig. 3) and the shoulder at 325 nm only in the spectrum of 4. This shoulder is attributed to a ILL1/LLCTL2 state with 40% of intra-ligand character. Most of the important states in 5 are localized on L2, either MLCT or LLCT whereas important IL/MLCT/LLCT mixing is observed for 4, leading to stronger intensities and higher densities of states. Beyond 300 nm, the absorption spectra of 4 and 5 are nearly identical with strongly absorbing states of similar characters in both molecules.
According to the experimental data (Fig. 3), the absorption spectrum of 6 is less intense than the other spectra and it does not show any peaks at 390, 370 and 325 nm. The UV region is shifted to the blue with respect to 4 and 5. This is confirmed by the theoretical results reported in Table 4 and the theoretical spectra depicted in Fig. 4. The absorption spectrum of 6 is characterized by IL and MLCT states towards the mesityl substituted phen with weak oscillator strengths and an intense peak calculated at 271 nm corresponding to a mixed MLCT/IL/LLCT state localized on the butyl substituted phen ligand.
4 Conclusion
A new series of Cu(I) heteroleptic complexes has been investigated theoretically by means of DFT/TD-DFT calculations with DFT-D functionals for the structural investigation and B3LYP for excited states determination. π-stacking interactions have been put in evidence leading to two classes of structures with more or less distorted geometries. The theoretical absorption spectra are characterized by high density of states of mixed character. Most of the transitions correspond to charge transfer towards L1 (2,9-dimesityl-2-(4′-bromophenyl)imidazo[4,5-f][1,10]phenanthroline) with important contributions of MLCT states. In complex 4 where L1 and L2 (3,6-di-nbutyl-11-bromodipyrido[3,2-a:2′,3′-c]phenazine) are in competition, the lowest band corresponds to a mixed MLCTL1/MLCTL2 state with 55% of MLCTL1. The absorption spectrum of the complex 6, substituted by a phen and a mesityl-phen, differs significantly from the others with a low density of states corresponding to MLCT mainly localized on the mesityl-phen ligand. The theoretical absorption spectra of complexes 1, 2, 3 where the phen ligand is substituted by hydrogen, methyl and butyl, respectively, are very similar and reproduce rather well the experimental spectra. Similarly, the calculations reproduce the two peaks at 370 nm and 390 nm, characteristics of complexes 4 and 5 and observed in the experimental spectra. However, these peaks have not the same origin in both complexes. Where a pronounced MLCT character is found in complex 4, these bands are attributed to mixed states with significant LLCT and IL contributions in 5. This illustrates the complexity of electronic excited states manifold in this class of new molecules.
Acknowledgements
The “Agence nationale de la recherche” (ANR) is gratefully acknowledged for the financial support of this research through the “Programme Blanc” entitled “HeteroCop” referenced ANR-09-BLAN-0183-01. These studies were also supported by the European program COSTD35. The calculations were carried out at the IDRIS and CINES centres (Orsay and Montpellier) through a grant of computer time from the Conseil Scientifique.
CD dedicates this work to Marie-Madeleine Rohmer for 30 years of friendship.