Three successive generations of iron(III) porphyrins have been developed during the last twenty years as oxidation catalysts mimicking cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenases 〚1–6〛. Some iron meso-tetraarylporphyrins bearing electron-withdrawing substituents on the meso-aryl rings and/or on the β-pyrrole positions are very efficient catalysts for alkene epoxidation and alkane hydroxylation by single oxygen atom donors, including the readily available and particularly interesting oxidant, H2O2 〚4, 7–11〛. More recently, non-heme iron complexes that were developed as mimics of non-heme iron containing monooxygenases, have also been found to act as good catalysts for the epoxidation or cis-dihydroxylation of alkenes, and for the hydroxylation of alkanes by H2O2 (for recent articles, see for instance refs 〚12–17〛). Cytochrome P450-dependent and non-heme iron-containing monooxygenases also catalyse the selective hydroxylation of aromatic compounds 〚18〛. However, very few model systems, based either on iron porphyrins or on non-heme iron complexes, have been described so far for the selective hydroxylation of aromatic compounds 〚1–6〛. The most efficient ones used H2O2 as oxygen atom donor in the presence of catalytic amounts of an iron porphyrin bearing electron-withdrawing β-substituents 〚9, 11, 19, 20〛. Thus, quite recently, a study of the hydroxylation of anisole and ethoxybenzene by H2O2 in the presence of various iron porphyrins, Fe(TDCPNxP)Cl, that derive from Fe〚TDCPP = meso-tetra-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)porphyrin〛Cl, by introducing x β-NO2 substituents (1 ≤ x ≤ 8) on the tetrapyrrole ring, has shown that the best catalyst for those reactions was Fe〚TDCPN5P = meso-tetra-(2,6-dichlorophenyl) β-penta nitroporphyrin〛Cl 〚20〛.
In the course of a comparison of the catalytic properties of iron porphyrins and non-heme iron complexes in the oxidation of hydrocarbons by H2O2, we recently found that the previously described non porphyrin iron complex, Fe(TPAA = tris-〚N-(2-pyridylmethyl)-2-aminoethyl〛amine)(ClO4)2 (Fig. 1) 〚21〛, was a poor catalyst for alkene epoxidation and alkane hydroxylation, but a quite efficient catalyst for hydroxylation of aromatic compounds. This preliminary communication describes these results and compares the catalytic properties of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 and Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl.
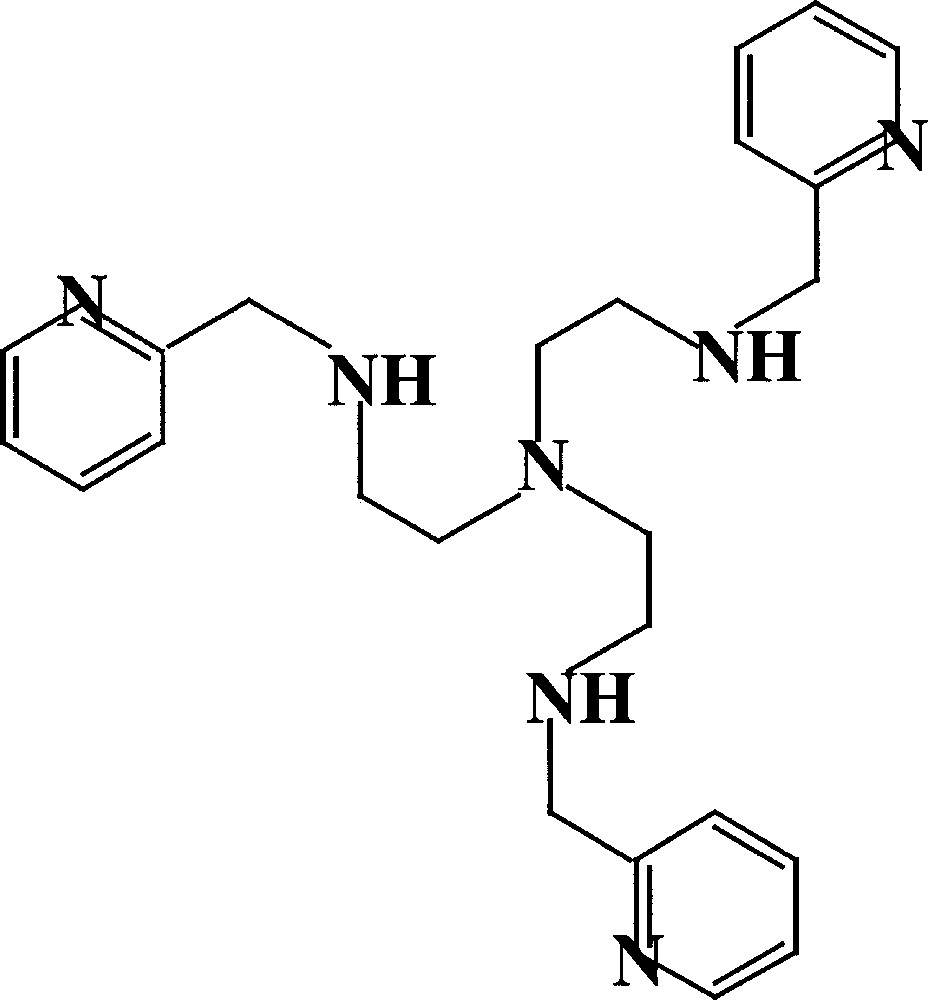
Formula of the TPAA ligand.
As previously reported 〚20〛, Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl is an efficient catalyst for the epoxidation of cyclooctene by H2O2. The epoxide yield (based on cyclooctene) is 90% when using conditions of conversion of this alkene (catalyst: H2O2: cyclooctene molar ratio = 1:300:100 in CH2Cl2/CH3CN 1:1) 〚20〛, and 50% (based on H2O2) when using cyclooctene in excess relative to H2O2 (catalyst: H2O2: cyclooctene = 1:40:800) (Table 1).
Comparison between Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 and Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl as oxidation catalysts by H2O2a.
| Substrate | Catalyst | Products (yields %)c | ||
| Epoxide | ||||
| Cyclooctene | Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 6 | ||
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | 50 | |||
| Epoxide | 3-ol | 3-one | ||
| Cyclohexene | Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 3 | 8 | 6 |
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | 19 | 7 | 4 | |
| cis-epoxide | trans-epoxide | PhCHO | ||
| Cis-stilbene | Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 1 | 1 | 16 |
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | 26 | 2 | < 1 | |
| Adamantane | 1-ol | 2-ol | 2-one | |
| Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 11 | 4 | < 1 | |
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | 26 | 9 | 1 | |
| o-OH | p-OH | phenol | ||
| Anisoleb | Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 26 | 27 | 3 |
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | 14 | 3 | 7 |
a Conditions: catalyst/H2O2/substrate molar ratio = 1:40:800 in CH2Cl2/CH3CN (1:1) for 2 h at 20 °C, except for cis-stilbene and adamantane, for which 1:10:100 and 1:40:300 molar ratios were used; 〚catalyst〛 = 2mM. 3-ol and 3-one products from cyclohexene denote cyclohexen-3-ol and cyclohexen-3-one ; 1-ol, 2-ol and 2-one were used in the case of adamantane for adamantan-1-ol, -2-ol and -2-one respectively.
b Conditions used in the case of anisole: catalyst/H2O2/anisole molar ratio = 1:20:3000 in CH3CN/H2O (90:10) for 2 h at 20 °C; o-OH and p-OH denote ortho- and para-methoxyphenol.
c Yields are based on starting H2O2. Oxidation of cyclohexene was performed under anaerobic conditions (under Ar). It is noteworthy that, for the oxidation of all the other substrates by H2O2, almost identical results were obtained under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
This means that under the latter conditions of substrate in excess, 50% of H2O2 consumed is used for the transfer of an oxygen atom to cyclooctene. At the opposite, Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 is a bad catalyst for this reaction as it leads to a very low epoxide yield under identical conditions (6%, Table 1). This weak ability of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 to act as an epoxidation catalyst is further shown with cyclohexene as substrate, the main reaction observed being an allylic hydroxylation with formation of cyclohexen-3-ol and cyclohexen-3-one (14% of products deriving from this allylic hydroxylation to be compared with only 3% epoxide). In the same manner, the Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2-catalysed oxidation of cis-stilbene only leads to a very low yield of epoxides in a non stereoselective manner, whereas the main product, benzaldehyde, is derived from the oxidative cleavage of the double bond (Table 1). On the contrary, the Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl-catalysed oxidation of those alkenes by H2O2 always leads to the corresponding epoxide as a major product. Moreover, the Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl-catalysed epoxidation of cis-stilbene gives the cis-epoxide as a very major product (Table 1).
Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 is also a bad catalyst for adamantane hydroxylation by H2O2 with a total 15% yield (11% adamantan-1-ol and 4% adamantan-2-ol) which is markedly lower than that obtained in the case of Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl (35%, Table 1). However, surprisingly, Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 appears to be a quite efficient catalyst for the hydroxylation of anisole by H2O2, with a total yield of 53% (26% of ortho-hydroxyanisole and 27% of para-hydroxyanisole). Under identical conditions, Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl, which is the best catalyst of the Fe(TDCPNxP)Cl series for this hydroxylation 〚20〛, gives a markedly lower total yield (17%, Table 1). This particular efficiency of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 for catalysing the hydroxylation of the aromatic ring of anisole is further shown by the relatively low yield of the competing reaction, the oxidative demethylation of anisole leading to phenol. In fact, the aromatic hydroxylation/oxidative demethylation ratio is 17.7 in the case of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 instead of 2.4 with Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl.
The properties of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 and Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl were then compared towards the hydroxylation of several aromatic compounds by H2O2. Table 2 shows that, for all these substrates, Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 was a markedly better catalyst than Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl. This is true for toluene and ethylbenzene, with a total yield of alkylphenols of 17 and 24% respectively when using Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2, whereas their yield is of 5 and 8% with Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl. Once again, the efficiency of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 as a catalyst for the hydroxylation of aromatic rings is further shown, when comparing the relative importance of the competing reaction, which is generally favoured in the oxidation of alkylbenzenes, the oxidation at the benzylic position 〚22〛. The aromatic hydroxylation/benzylic oxidation ratio is 17 and 2.2 in the case of the Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2-catalysed oxidations of toluene and ethylbenzene respectively, instead of 1.7 and 0.3 for the corresponding Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl-catalysed reactions. In that regard, it is noteworthy that simple iron complexes, such as Fe(TDCPP)Cl and Fe(acac = acetylacetonate)3, exclusively lead to benzylic oxidation products from oxidation of ethylbenzene under identical conditions.
Oxidation of various aromatic compounds by H2O2 in the presence of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 or Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl as catalystsa.
| Substrate | Catalyst | Products (yields %) | ||||
| o-OH | m-OH | p-OH | PhCH2OH | PhCHO | ||
| Toluene | Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 8 | 2 | 7 | < 1 | 1 |
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | 2 | < 1 | 2 | < 1 | 3 | |
| o-OH | m-OH | p-OH | PhCHOHMe | PhCOMe | ||
| Ethylbenzene | Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 9 | 4 | 11 | 4 | 7 |
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | 3 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 17 | |
| phenol | ||||||
| Benzene | Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 22 | ||||
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | 1 | |||||
| o-OH | p-OH | |||||
| Chlorobenzene | Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 | 6 | 7 | |||
| Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl | < 1 | < 1 |
Finally, Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 was also found to be able to catalyse the hydroxylation of less electron-rich and much less reactive aromatic compounds. Thus, benzene is transformed to phenol with a 22% yield, and chlorobenzene to ortho- and para-chlorophenol with a 13% total yield. Under identical conditions, Fe(TDCPN5P)Cl only leads to very low hydroxylation yields (<2%) (Table 2).
The aforementioned results show the peculiar behaviour of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 in the oxidation of hydrocarbons by H2O2; it is a poor catalyst for alkene epoxidation and alkane hydroxylation and a surprisingly efficient catalyst for the hydroxylation of aromatic compounds. In fact, not only Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 leads to the formation of phenols from the corresponding arenes in yields between 13 (for the less reactive substrate, chlorobenzene) to 53% (for anisole), but it leads also to unexpected chemoselectivities in favour of the hydroxylation of aromatic rings over oxidative demethylation in the case of anisole and benzylic hydroxylation in the case of alkylbenzenes (Table 2).
The mechanistic basis of this original behaviour is presently unknown. It could be related to an original, intrinsic reactivity of the active oxygen species derived from the reaction of Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 with H2O2, which would be more reactive towards aromatic rings than towards OCH3 and benzylic C–H bonds, and not too reactive towards the phenol products under the used conditions (great excess of arene substrates relative to H2O2). This relatively small importance of further oxidations of the phenol products under the used conditions (arene:H2O2 molar ratio of 150 in general) is illustrated by experiments performed on anisole and ethylbenzene, in which 20 equivalents of H2O2 (relative to Fe(TPAA)(ClO4) 2) were further added to the reaction media at the end of the first reaction. In fact, this second addition of H2O2 led to almost identical yields of the phenol products as the first one, indicating that there was no significant oxidation of the phenol products in these reactions performed in the presence of a large excess of an arene substrate. The mechanism of the Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2-catalyzed oxidation of arenes is currently under study in order to determine the nature of the active oxygen species involved. Preliminary results showed us that other previously reported polypyridine iron complexes, such as Fe〚TPA = tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine〛 〚CH3CN〛2(ClO4)2 or Fe〚MEP = N,N’-dimethyl-N,N’-bis(2-pyridylmethyl)-ethane, 1,2-diamine〛Cl2 〚13, 14〛, also catalyse the hydroxylation of aromatic compounds by H2O2, however with a markedly lower efficiency. The chemio- and regio-selectivities of these reactions catalysed by Fe(TPAA)(ClO4)2 and other polypyridine iron complexes are very much dependent on the nature of the polypyridine ligand, which suggests that iron-containing species play a key role in the control of these oxidations.



