1. Introduction
Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (APDT) with natural or synthetic photosensitizers seems to be a very promising alternative or an important supplement to classical antibiotic therapy of many localized infections [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]. This bright technique consists of three crucial components: a photosensitizer, molecular oxygen and visible light taken together and leads to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as singlet oxygen 1O2 (Type II photochemical mechanism) or various radical forms (HO∙, O
With these results in mind, we studied photo-bleaching of the well-established 1O2 trap, viz. 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran, using several chlorin PSs with one, two or three iodide ions in OctOH as an appropriate lipid-like environment model [11]. Then, the respective photo-bleaching rates were used to compute the 𝛷𝛥 values and to compare them with the quantities obtained by direct spectroscopic measurements [9].
2. Experimental section
2.1. Reagents
1-Octanol (Panreac, >98%) was dried with 4 Å molecular sieves and distilled under reduced pressure at 353 K. Karl Fisher titration showed that the final water content in OctOH was less than 0.02 wt%. 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran (DPBF) (Sigma-Aldich, >99%) and crystal iodine (Reachem, >99%) were used as supplied.
PSs shown in Figure 1 were synthesized, purified and identified in our laboratory with 1H NMR, MS- and UV-Vis spectra. 1H NMR spectra were registered with the Bruker Avance II spectrometer (300 MHz) or Bruker Avance III spectrometer (500 MHz). CDCl3 or DMSO d6 were used as appropriate solvents and TMS was applied as the internal standard for the 1H NMR measurements. MS-spectra were obtained with the Thermo finnigan LCQ Flut (ESI) instrument and/or MALDI FAB MS-spectrometer Shimadzu AXIMA Confidence with α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHCA) and 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) as a matrix. UV-Vis spectra were obtained at 293 K with the Drawell D8 spectrophotometer in a highly diluted pigment solution ( ∼5–8 μmol).
A detailed description of the synthetic and identification procedures of compounds 1, 2, 5–8 was given earlier [9, 10, 12]. For newly synthesized compounds 3, 4 this information can be found in the Supplementary material file.
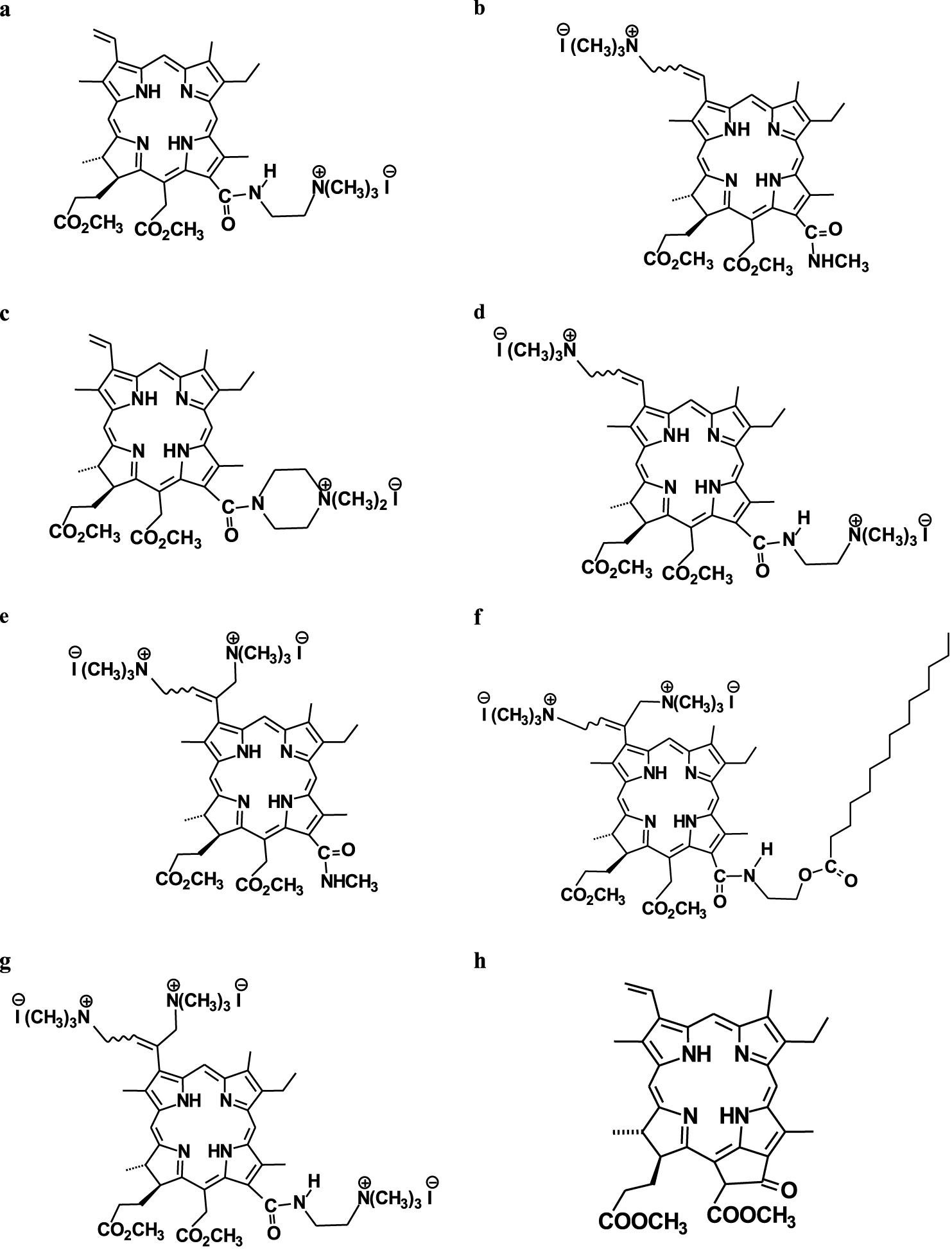
Molecular structures of the PSs studied: (a) 13(1)-N-(2-N′N′N′-trimethylammonioethyl iodide)amide chlorin e6 15(2),17(3)-dimethyl ester 1, (b) 3(2)-(N,N,N-trimethylaminomethyl iodide) chlorin e6 13(1)-N-methylamide 15(2),17(3)-dimethyl ester 2; (c) chlorin e6 13(1)-(4′-N,N-dimethylpiperazinyl iodide)amide 15(2),17(3)-dimethyl ester 3; (d) 3(2)-(N,N,N-trimethylaminomethyl iodide) chlorin e6 13(1)-N′-(2-N′′,N′′,N′′-trimethylammonioethyl iodide)amide 15(2),17(3)-dimethyl ester 4; (e) 3(1),3(2)-bis-(N,N,N-trimethylaminomethyl iodide) chlorin e6 13(1)-N-methylamide 15(2),17(3)-dimethyl ester 5; (f) 3(1),3(2)-bis-(N,N,N-trimethylaminomethyl iodide) chlorin e6 13(1)-N-(2-myristoxyethyl)amide 15(2),17(3)-dimethyl ester 6; (g) 3(1),3(2)-bis-(N,N,N-trimethylaminomethyl iodide) chlorin e6 13(1)-N′-(2-N′′,N′′,N′′-trimethylammonioethyl iodide)amide 15(2),17(3)-dimethyl ester 7; (h) pheophorbide a 17(3)-methyl ester (methylpheophorbide a) 8.
Singlet oxygen quantum yield for methylpheophorbide a (compound 8) and seven chlorin photosensitizers (compounds 1–7) in liquid 1-OctOH
| PS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 0.63 ± 0.05a | 0.63 ± 0.02 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 0.60 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.02 | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 0.77 ± 0.05 | 0.49 ± 0.05 |
| 0.65 ± 0.07b | - | - | - | 0.60 ± 0.06b | 0.53 ± 0.05b | 0.47 ± 0.05b | |
2.2. Determination of singlet oxygen quantum yield
The singlet oxygen quantum yield was determined by the indirect chemical method which was very similar to the technique described elsewhere [13, 14]. In brief, two quartz cuvettes with a 1 cm optical way contained 3 ml of a PS + DPBF or St + DPBF solution with the absorbance of 0.2–0.3 at the Q-band and 0.9–1.2 at 444 nm. The cuvettes were irradiated with a red light diode panel (BIC, Minsk) [9, 10]. This panel emitting between 590 and 720 nm with the maximum at 662 nm provided the light spot of 10 × 10 cm. The power density of red light was chosen to be equal to 3 mW⋅cm−2. At this irradiance a fluence (light dose) of 0.18 J⋅cm−2 was delivered every minute. The monocationic chlorin (see compound 1 in Figure 1) with the known 𝛷𝛥 value equaling to 0.67 [9] was used as an appropriate standard.
DPBF degradation in both cuvettes was monitored spectrophotometrically each minute, and each irradiation session contained usually six-eight measurements. Then, the rate-of-degradation constants kd were evaluated in terms of the first order exponential decay. All the photo-bleaching experiments were repeated from six to eight times. The 𝛷𝛥 values were derived from the following equation:
| (1) |
| (2) |
3. Results and discussion
The PS molecules shown in Figure 1 in their ground state, i.e. singlet electronic state (S0), contain two electrons with the opposite spins located in the most favorable molecular orbital [6]. Absorbance of red light at 660 nm leads to the transfer of the macrocycle to an excited singlet state (S1). The excited PS molecule is capable of intersystem crossing and transition to the long-lived biradical triplet state (T1) with an inverted spin of one electron [4, 6]. Then, the PS molecule in this triplet state may transfer its energy to molecular oxygen, 3O2, which leads to the formation of a reactive singlet oxygen species, 1O2. This so-called Type II process is characteristic of apolar media, while in H-bonded solvents, especially water, some fraction of radical forms is detected [15].
We have recently shown [9] that in many chlorin-type PSs without metal ions in their coordination sphere, the 𝛷𝛥 values range from 0.47 to 0.67 regardless of the macrocycle structure. Hence, the quantum yield of singlet oxygen of a chlorin photosensitizer is within 0.55 ± 0.1 in any weakly polar solvent. This finding is in agreement with chemical intuition and the available literature values [16, 17, 18, 19]. Table 1 shows that for compounds 1–4 and 8 the corresponding quantum yields agree with this estimation. It is interesting to note that the corresponding 𝛷𝛥 values are larger for chlorin PSs (see compounds 1–4) compared to phorbin-type pigments (compound 8). Moreover, for compounds 1, 8 the indirectly obtained quantum yields are seen to be in very good agreement with the previously reported values [9].
However, compounds 5–7 demonstrate significantly higher quantum yields than what could be expected from direct measurements (see Table 1). This difference results from the higher rate of DPBF oxidation that leads to larger kd values (see (1)). Inspection of the solute structures shown in Figure 1 indicates that all three PS molecules (see compounds 5–7) contain two or even three iodine atoms which may be responsible for the higher oxidation rate of the trap. However, compound 4 also contains two iodine atoms but has a “normal” 𝛷𝛥 value (see Table 1). Hence, the close location of ionic groups in compounds 5–7 is much more important for the higher oxidation rate of the trap than their relative number. In fact, two cationic groups occupy opposite positions in compound 4, while they are located in the 3(1),3(2)-bis-(N,N,N-trimethylaminomethylvinyl) iodide fragment in compounds 5–7. This close location seems to be responsible for the higher oxidation rate of DPBF. Another proof comes from our comparative analysis showing that the 𝛷𝛥 values for compounds 5 and 7 are almost identical, although the latter solute contains an additional ionic group (see Figure 1). Thus, the structure of the 3(1),3(2)-bis-(N,N,N-trimethylaminomethylvinyl) iodide fragment with two adjacent ionic groups is responsible for the interaction between iodine and singlet oxygen [5]. The intermediate of this reaction can further decompose to free iodine (I2/I
In principal, both of these processes may lead to the abnormal 𝛷𝛥 values due to faster oxidation of the trap. However, it should be kept in mind that the “extra killing effect” mentioned above takes place in an aqueous medium, where each singlet oxygen molecule interacts with well-hydrated iodide ions [5]. However, all the cationic PSs shown in Figure 1 are weakly dissociated in apolar OctOH, and 1O2 molecules interact with the iodide ion bound to the cationic group of PS.
To shed more light on the trap photobleaching mechanisms in a lipid-like medium, we studied the effect of ammonium iodide addition (∼0.2 mmol/kg) to compound 5 and found that irradiation lead to an increase in the solution absorbance at 365 nm (see Figure S12 in the Supplementary material file). According to the results mentioned above (see [4, 5] and references therein), this phenomenon can be attributed to the formation of molecular iodine in the liquid phase. To check this point, we dissolved an appropriate amount of iodine and NH4I in OctOH and found that the solution spectrum was very similar to the spectrum of compound 5 + NH4I shown in Figure S12. It is apparent that this proves that singlet oxygen interacts with ammonium iodide, which leads to the formation of molecular iodine. We assume that a similar phenomenon occurs in a solution of PSs with a 3(1),3(2)-bis-(N,N,N-trimethylaminomethylvinyl) iodide fragment. This induces faster oxidation of DPBF, which is responsible for the abnormal 𝛷𝛥 values.
4. Conclusions
In summary, our experimental efforts aimed to study singlet oxygen generation by cationic chlorins indicate that PSs with one or two cationic groups occupying opposite positions in the macrocycle have normal 𝛷𝛥 values of 0.6, which is in good agreement with the results of direct measurements. However, PSs with two adjacent cationic groups have a larger quantum yield that reaches 0.8. This phenomenon results from faster trap oxidation due to radical reactions that lead to the formation of molecular iodine.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
AVK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Review and editing, Funding acquisition. PKM: Investigation, Formal analysis. NVK: Synthesis, Investigation. MAK: Methodology, Investigation. NLS: Methodology, Investigation. DBB: Conceptualization, Writing, Review and editing, Funding acquisition. GNK: Methodology, Formal analysis. DVB: Investigation, Synthesis, Writing—review and editing, Funding acquisition.
Conflicts of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project N 21-13-00398).




 CC-BY 4.0
CC-BY 4.0
Vous devez vous connecter pour continuer.
S'authentifier