1 Introduction
The increasing demand for biobased materials offering competitive and characteristic properties similar to those of well-established petrochemical analogues is a subject of interest nowadays [1,2]. Among several building blocks, 1,4-3,6-dianhydrohexitols have emerged in the fields of polymers chemistry, owing to a multitude of advantages: biodisponibility, non-toxicity, good resistance and chirality. Although these attractive diols have been employed to produce polyesters [3–5], polyethers [6], polyethersulfones [7,8], polycarbonates [9,10] and so on, their use in the polyamide field remains little described. In fact, the tedious transformation of these diols into their corresponding diamines does not make them attractive. Thiem et al. initiated the synthesis of polyamides based on the three diamino dianhydrohexitols, isosorbide (Is), isomannide (Im), and isoidide (Id), with several diacyl chlorides [11]. They exhibited differences in monomer reactivity, and the best results were obtained with Is and Id analogues. In the same trend, Koning et al. have recently described an elegant synthesis of fully biobased polyamides, starting from the diamino homologue of isoidide and sebacoyl acid [12]. By using solid-state polymerization (SSP), they obtained successfully semi-crystalline materials, as confirmed by CP–MAS NMR studies [13]. In addition to these few works, polyesteramides were also proposed in order to enhance the solubilities and to improve the biocompatibilities of materials for eventual medical purposes [14–16].
Another approach proposed by Loupy et al. consisted in incorporating an aromatic moiety to an Is-based diamine monomer to enhance the Tg of the expected polyamides [17,18].
In continuation of anterior works and contributions in this field, we tried to extend the scope of the synthesis to unprecedented diamines based on Im and Id. These monomers were used to obtain new polyether-amides. We planned to study the effect of the 1,4-3,6-dianhydrohexitols type as well as the nature of the diacylchloride moieties on the inherent viscosities, molecular weights and thermal properties of the resulting polymers. In this context, these polyether-amides were obtained by using a standard method of Nomex synthesis [2]. In order to enhance the biosourced balance composition of these useful materials, sebacoyl chloride was considered in addition to isophtaloyl chloride. The resulting polyether-amides were characterized using different complementary analytical methods (1H and 13C NMR, FTIR, MALDI–ToF mass spectrometry) to determine and confirm all the obtained structure. Viscosimetry and DSC were used in order to study their thermal performances.
2 Experimental part
The inherent viscosities were measured in a [CH2Cl2/TFA = 10/1] mixture with an automated Ubbelohde viscometer thermostated at 20 °C.
The MALDI–ToF mass spectra were recorded with an UltraflexIII, Bruker device, equipped with a smart beam laser®. All the mass spectra were recorded in the reflectron mode with an acceleration voltage of 25 kV. The samples were dissolved in DMSO + TFA solutions, with dithranol as a matrix. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded at 400 and 100 MHz, respectively (Bruker WP 250). The chemical shifts are given in ppm. DSC measurements were conducted from 30 °C to 350 °C at 10 °C/min. Then, the samples were cooled back to 30 °C, after which a second heating scan similar to the first was conducted. The Tg and Tm values were determined from the second DSC heating scan.
2.1 Dinitro compound synthesis
Dianhydrohexitol (10 mmol, 1.46 g), KOH (30 mmol, 1.68 g) 4-fluoronitrobenzene (20 mmol, 2.82 g) and 18 C 6 (10%, 146 mg) were placed in a cylindrical reactor equipped with a mechanical stirrer. The reaction media was warmed gradually to 140–150 °C (depending on dianhydrohexitol) and stirring was maintained during 3 to 4 h. After reaction completion, the crude product was diluted with chloroform and precipitated in cold methanol, affording the dinitrocompound after filtration.
2.2 Diamine synthesis
The process is adapted from the mononitro reduction with a slight modification: the dinitro compound (500 mg) is suspended in EtOH with Pd/C (10%) in two round-bottom necked flasks. The media is warmed to 50 °C then, a hydrazine solution (1 mL in 4 mL of EtOH) is added dropwise during 1 h 30. When addition is completed, the reaction is refluxed for an additional 2 h (TLC control). After completion, the warm crude is filtered on an ice bath and the diamine is recovered as a pure white crystalline solid by precipitation in EtOH.
2.3 Polymer synthesis
Diamine DA (1 mmol, 328 mg) and LiCl (2 mmol, 85 mg) were dissolved in NMP (2 mL). The mixture was cooled at −10 °C and a solution of diacyl chloride (1 mmol in 1.5 mL of NMP) was added dropwise. After completion, the media was warmed to room temperature and stirred magnetically. After 18 h, the reaction medium was precipitated in MeOH and the polymer was filtrated and vacuum dried until the weight is kept constant.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Diamines synthesis
The synthesis of the diamino monomers was optimized compared to the anterior works [17,19]. In fact, the latter could be obtained in gram scale without any chromatographic purification in only two steps. The previous method described for dinitro compound synthesis, which used microwave (MW) irradiation at 170 °C during 30 min. In our context, the first step was carried out in solvent-free conditions and adapted to the classical heating method at 150 °C (Scheme 1). This could be considered as advantageous as a domestic MW was not able to give rise to the desired product, whereas the specially designed monomode MW represent an expensive apparatus, which is not easily accessible.
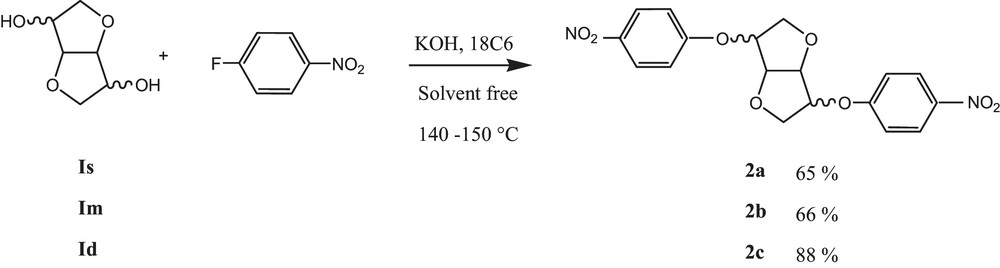
Synthesis of dinitro compounds.
After 4 h, the dinitro compound was recovered by precipitation in MeOH. The latter was engaged in a Pd/C hydrazine-promoted reduction in EtOH [20]. After reaction completion, pure crystalline diamine could be obtained by precipitation and subsequent recrystallisation in EtOH. The process tolerates small impurities contained in non-purified dinitro starting compounds, as mentioned above. This method was extended to the two additional dianhydrohexitols (Im and Id) to obtain unprecedented corresponding diamines (Scheme 2).
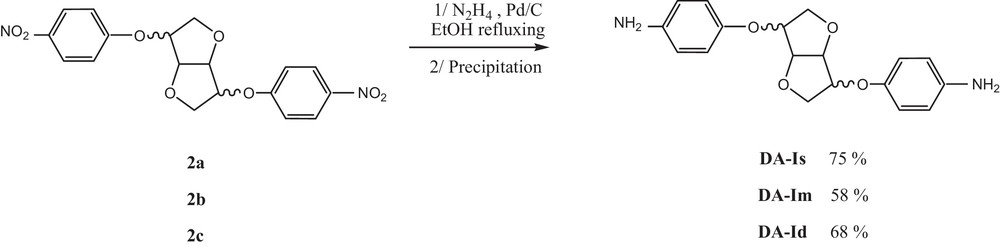
Synthesis of diamine compounds.
After mass confirmation by GC–MS analysis, NMR studies were carried out to confirm structures and highlight the characteristic signal of each dinahydrohexitol type.
3.2 NMR studies
Comparing diamines originating from three dianhydrohexitols prompted us to several findings: due to its two hydroxyls stereochemistry, Is exhibits six signals. In order to identify each signal and proceed to the right attribution, superposition of Im and Id analogues diamine was undertaken. Each characteristic carbon signal was labelled with a specific colour. We reasoned that when the two hydroxyl groups are in exo position (i.e. Id), the residue carbons were represented by carbons labelled 1, 2 and 3. Likewise, in Id analogue where hydroxyl functions are in endo position, the residue carbons are represented by 4, 5 and 6. Superposing them allows us to clearly identify and attribute them in the Is-based diamine (Fig. 1). It clearly appears that the stereochemistry of hydroxyls highly influences the carbons’ behaviour, the latter shifting to higher values in exo configuration. This observation confirms that no epimerisation took place during the synthesis process.
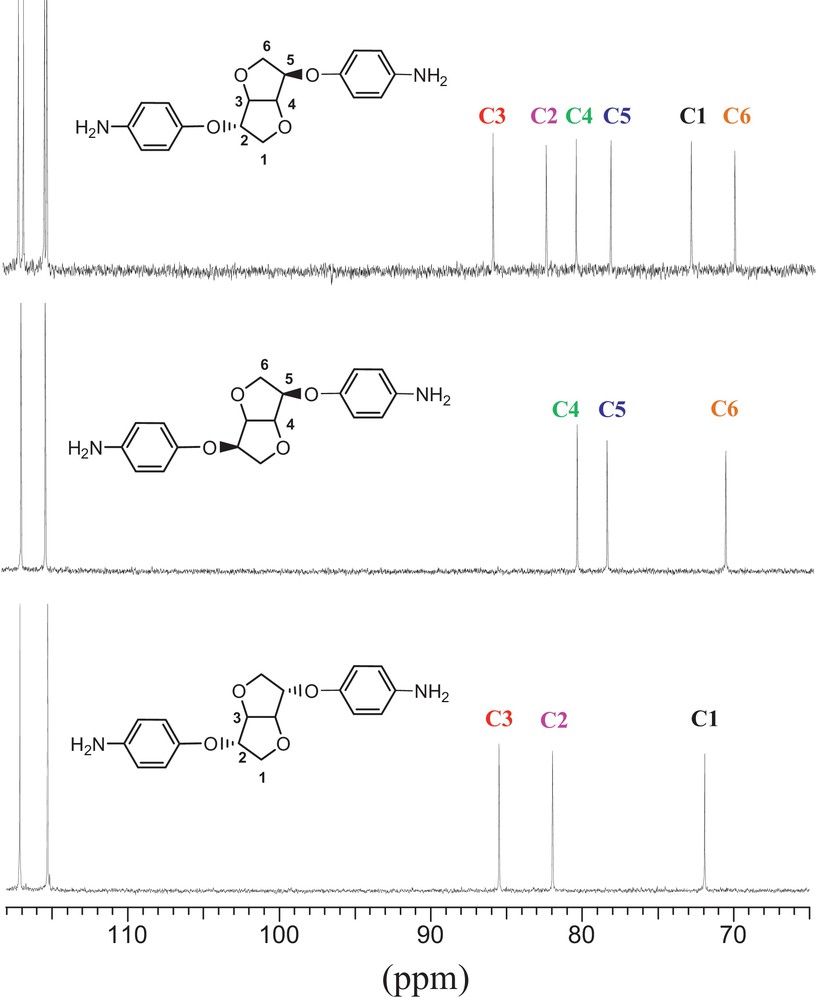
Comparison of 13C NMR spectra of diamine based on 1,4-3,6-dianhydrohexitols (aliphatic zone).
In the aromatic zone, under the influence of the exo/endo alternation of the signals, the carbons (quaternary) directly attached to the hydroxyl functions split into two signals (C 7: 148.1 and 149.3 ppm; Fig. 2). This difference goes by diminishing gradually as the carbon is far from the hydroxyl (C 10: 143.5 and 143.2 ppm; C 8: 117.1 and 117.2 ppm). The superposition with other diamines shows each peak as originating from the corresponding isomer.
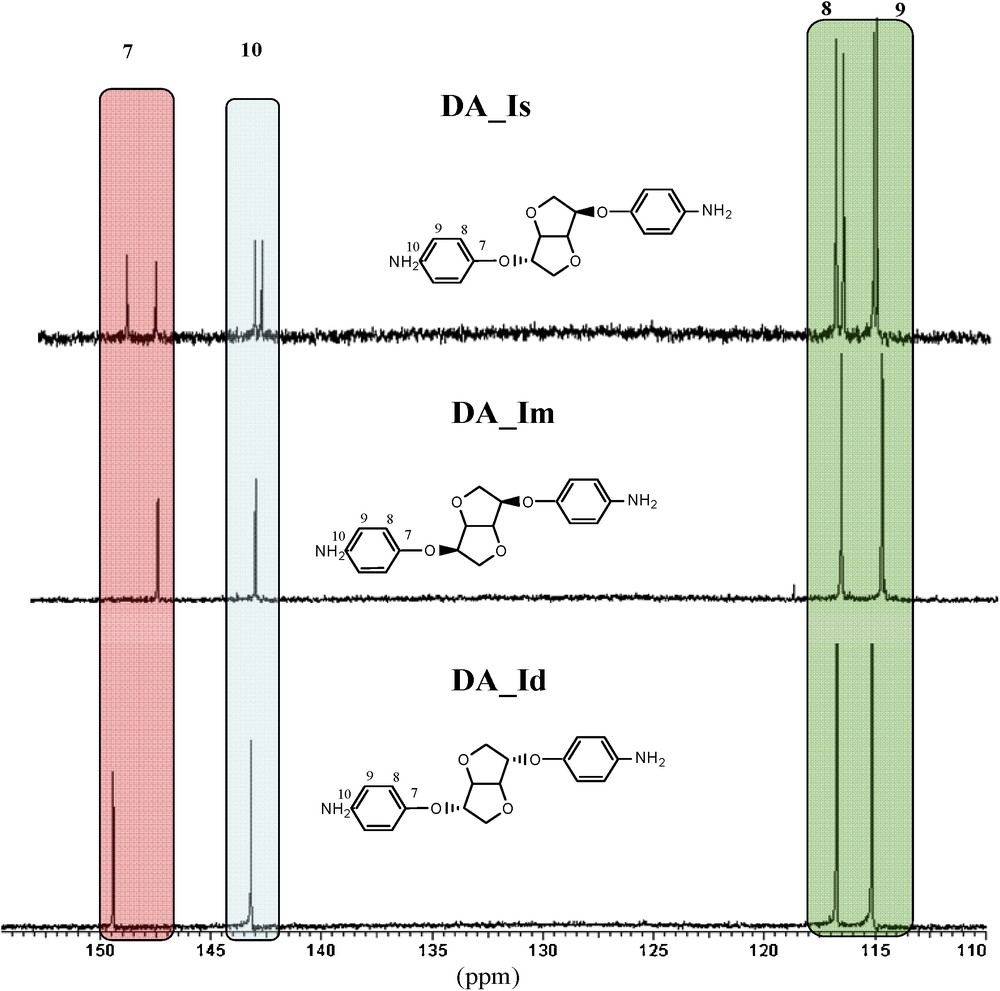
Comparison of 13C NMR spectra of diamines (aromatic zone).
3.3 Polymer synthesis and characterization
The diamine natures as well as the diacyl chloride were varied in order to observe their effect on the properties of the expected polymers.
The method used for the synthesis is derived from Nomex procedures.
First, 1 equiv of LiCl per amine function was used to provide electrophilic assistance and enhance solubility in NMP. After reaction completion at room temperature, the polymers were recovered by precipitation in MeOH in good yields (Scheme 3, Table 1).
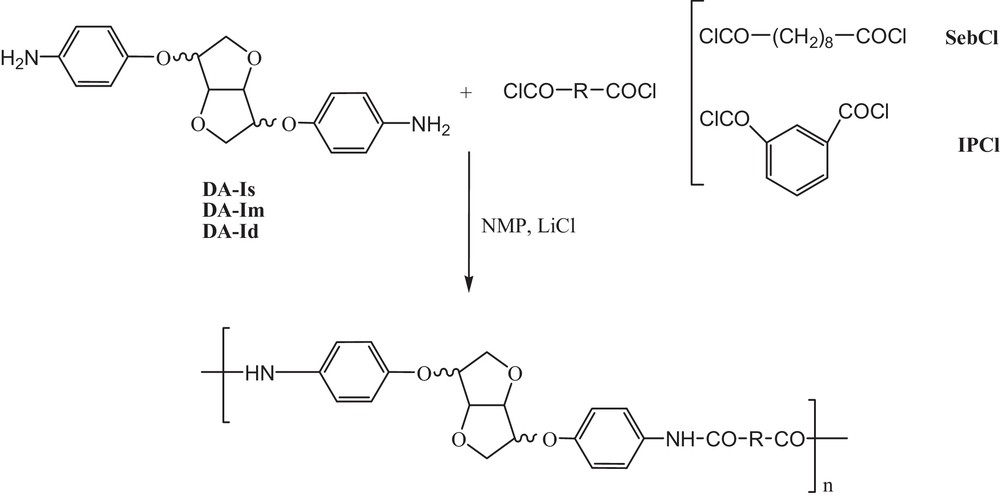
Polymer synthesis.
Polymer results and measurements.
| Entry | Exp. No | Diamines + diacyl chlorides | Yield (%)a | ηinh (dL/g)b | Tg/Tm |
| 1 | PeA_Is_Ip | DA-Is + IPCl | 93 | 0.32 | 217 |
| 2 | PeA_Im_Ip | DA-Im + IPCl | 89 | 0.22 | 201 |
| 3 | PeA_Id_Ip | DA-Id + IPCl | 91 | 0.19 | 210 |
| 4 | PeA_Is _Seb | DA-Is + SebCl | 98 | 0.23 | 129/243 |
| 5 | PeA_Im _Seb | DA-Im + SebCl | 88 | 0.18 | 108/297 |
| 6 | PeA_Id _Sebc | DA-Id + SebCl | 93 | 0.15 | 112/278–289 |
a Precipitation into methanol.
b Measured at 20 oC, with c = 2 g/L in dichloromethane-TFA 95-5
c This product showed two Tm values.
The denomination of monomers and products follows this rule: DA stands for diamines separated by dash and the dianhydrohexitols corresponding isomer, Is for isosorbide, Im for isomannide and Id for isoidide. The corresponding polyether-amides are designed as PeA separated by dash, then the dianhydrohexitol nature and the diacylchlorides abbreviation PeA_Ip for isophtaloyl and PeA_Seb for sebacoyl.
Viscosities and Tg/Tm measurements disclosed in Table 1 and Fig. 3 deserve some comments:
- • viscosity values have been improved compared to anterior works upon the RT synthesis method;
- • considering PeA derived from the same dianhydrohexitol, the diacyl chloride moiety affects the viscosity values, the highest one being obtained for the isophtaloyl core;
- • the highest viscosity was obtained for Is-based PeA (0.32, for Ip; entry 1, and 0.23 for Seb);
- • as expected, Tg values were lower for the Seb moiety than for those with the Ip family, regardless of the dianhydrohexitol moiety;
- • it is worth noting that Seb series revealed semi-crystalline, as shown by DSC experiments;
- • thermal properties of Is-based polymers were interesting (Tg above 210 °C and Tm above 240 °C);
- • the Id-based polyether-amide PeA_Id_Seb showed two Tm values. This phenomenon, already observed for Id-based polyamides, can be explained by the melting of imperfect crystals (first peak), recrystallization upon heating and re-melting of the more perfectly formed crystals (second peak) [21]. The hypothesis of the existence of oligomers, giving rise to heterogeneity, can be considered as well.

DSC thermograms of polyether-amides PeA_Seb and PeA_Ip.
3.4 MALDI–TOF-MS studies
Potential structures that could be obtained are depicted in Fig. 4.
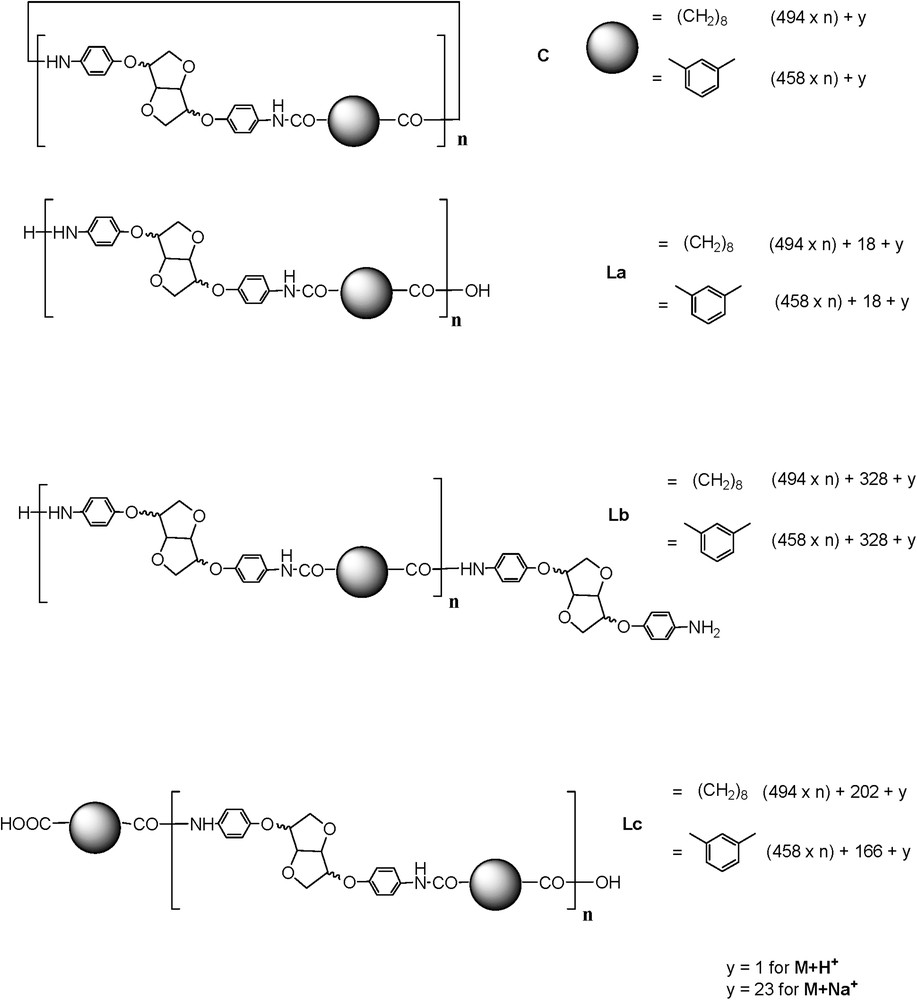
Different potential structures obtained from the polymerisation reaction.
3.4.1 Isophtaloyl_family
The investigation of structure type PeA_Is_Ip (Is moiety) was considered in details. The calculated masses of potential structures are given in Table 2.
PEA_Ip family calculated masses.
| DP | C | La | Lb | Lc | C′ |
| H+ doped | |||||
| 1 | 459.1550 | 477.1656 | 787.2973 | 625.1816 | 607.1711 |
| 2 | 917.3028 | 935.3134 | 1245.4451 | 1083.3294 | 1065.3189 |
| 3 | 1375.4506 | 1393.4612 | 1703.5929 | 1541.4772 | 1523.4666 |
| 4 | 1833.5984 | 1851.6089 | 2161.7407 | 1999.6250 | 1981.6144 |
| 5 | 2291.7462 | 2309.7567 | 2619.8885 | 2457.7728 | 2439.7622 |
| 6 | 2749.8939 | 2767.9045 | 3078.0363 | 2915.9206 | 2897.9100 |
| 7 | 3208.0417 | 3226.0523 | 3536.1840 | 3374.0683 | 3356.0578 |
| 8 | 3666.1895 | 3684.2001 | 3994.3318 | 3832.2162 | 3814.2056 |
| Na+ doped | |||||
| 1 | 481.1370 | 499.1475 | 809.2793 | 647.1636 | 629.1530 |
| 2 | 939.2847 | 957.2953 | 1267.4271 | 1105.3114 | 1087.3008 |
| 3 | 1397.4325 | 1415.4431 | 1725.5749 | 1563.4591 | 1545.4486 |
| 4 | 1855.5803 | 1873.5909 | 2183.7226 | 2021.6069 | 2003.5964 |
| 5 | 2313.7281 | 2331.7387 | 2641.8704 | 2479.7547 | 2461.7441 |
| 6 | 2771.8759 | 2789.8865 | 3100.0182 | 2937.9025 | 2919.8919 |
| 7 | 3230.0237 | 3248.0342 | 3558.1660 | 3396.0503 | 3378.0397 |
| 8 | 3688.1715 | 3706.1821 | 4016.3138 | 3854.1981 | 3836.1875 |
In the spectrum enlargement (900–5000) (Fig. 5), the repeating unit 458 Da revealed the predominant presence of the Lc-type structure accompanied by C and La types. The identification and attribution were very tedious, due to the unusual and predominant formation of [M + H]+ adducts accompanied by classical [M + Na]+ and [M + K]+ (in some cases) ionised adducts [22]. Surprisingly, the same value of the repeating unit revealed the presence of an unexpected structure type, represented by the most intense peak of the [M + H]+ type. The latter could be attributed to a cyclic anhydride-type structure originating probably from Lc dehydration (noted C′, Scheme 4).
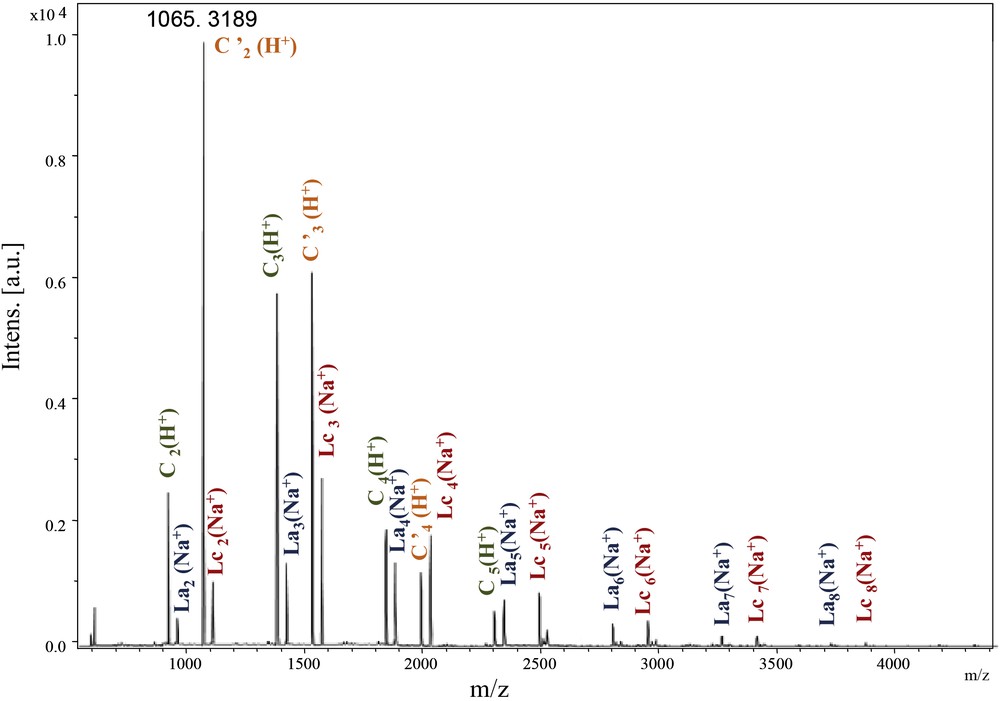
MALDI–ToF spectrum of PeA_Is_Ip (500–4500 Da).
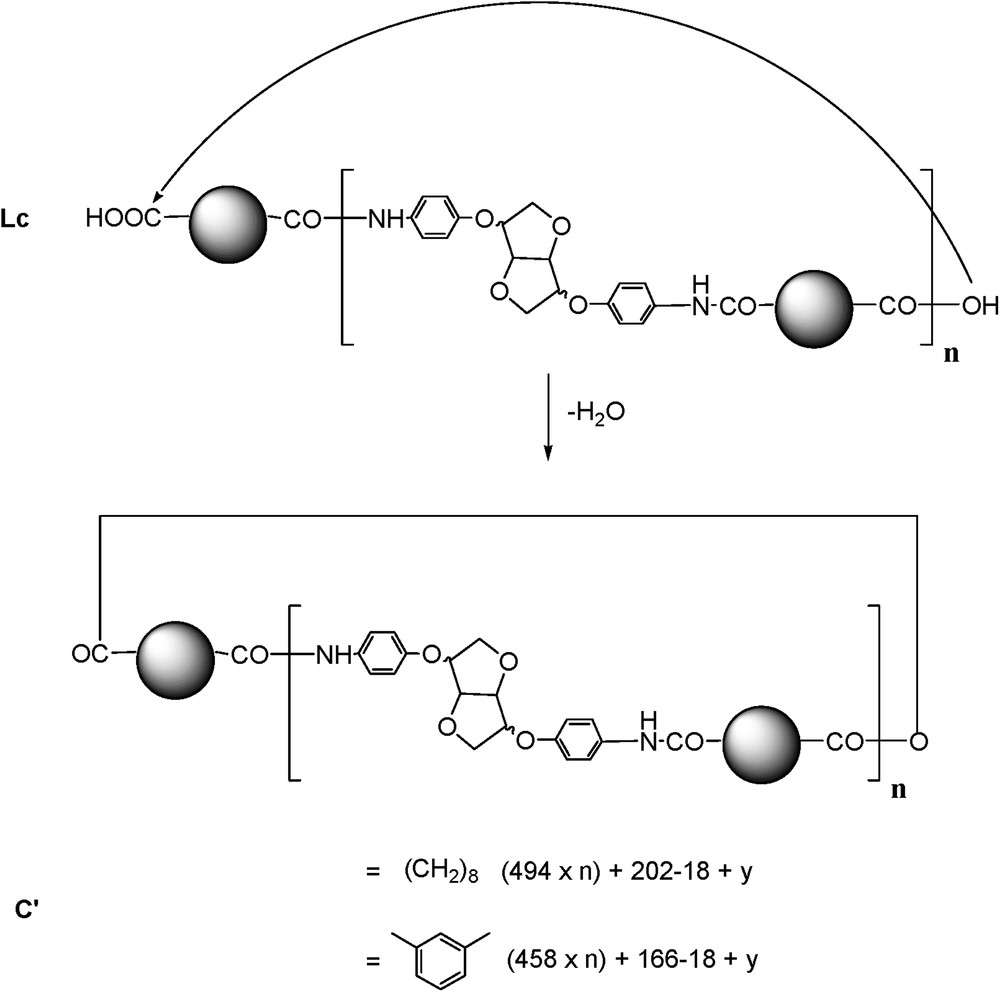
Anhydride-type structure formation.
The same structure types are observed for the other polyamides Ip families originating from Im and Id moieties (Fig. 6). In the latter case, cyclic structures (C and C′) became predominant.
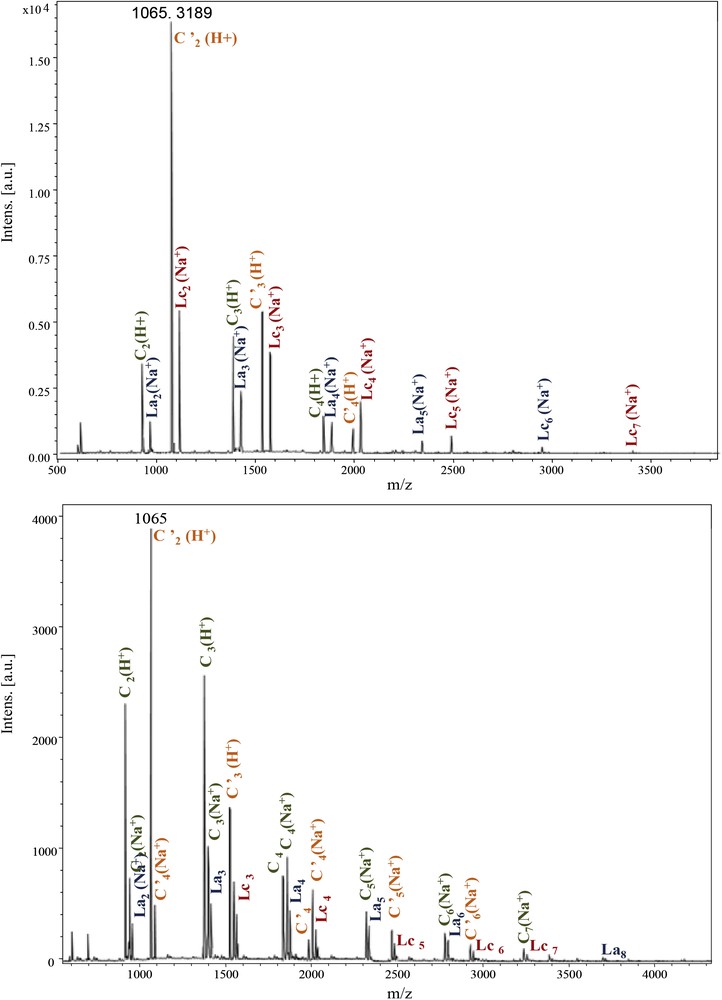
MALDI–ToF spectra of PeA_Im_Ip (500–4000 Da) and PeA_Id_Ip (500–4500 Da).
3.4.2 Sebacoyl family
As for the Ip family, we investigated carefully the PeA_Is_Seb sample (Fig. 7). The calculated masses of the potential structures are depicted in Table 3.
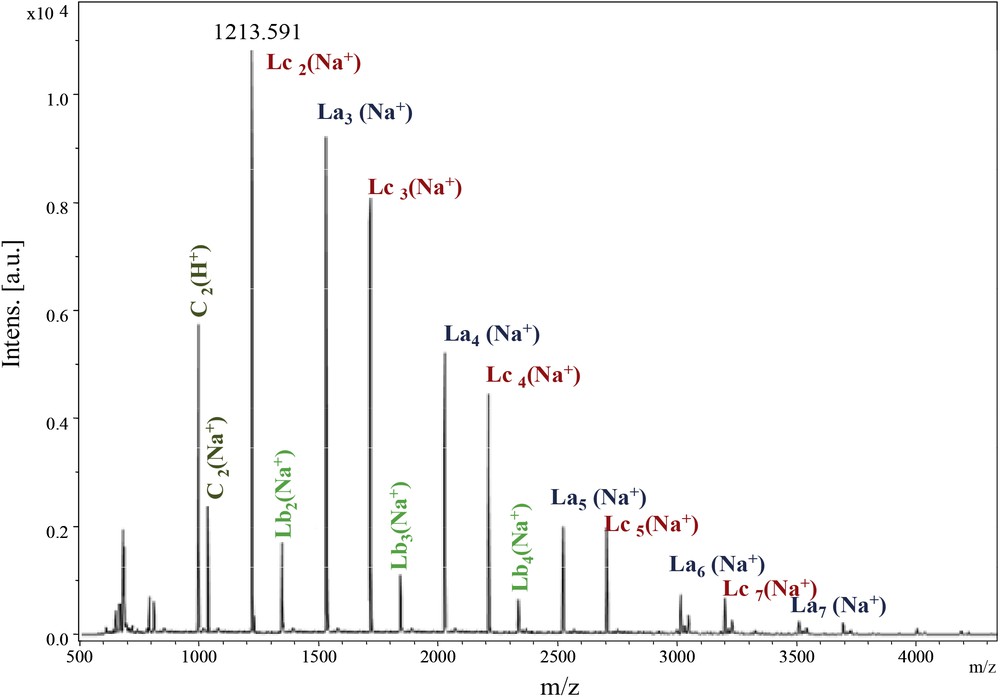
MALDI–ToF spectrum of PeA_Is_Seb (500–4500 Da).
PEA_Seb family calculated masses.
| DP | C | La | Lb | Lc | C′ |
| H+ Doped | |||||
| 1 | 495.2489 | 513.2595 | 823.3912 | 697.3694 | 679.3589 |
| 2 | 989.4906 | 1007.5012 | 1317.6329 | 1191.6111 | 1173.6005 |
| 3 | 1483.7323 | 1501.7429 | 1811.8746 | 1685.8528 | 1667.8422 |
| 4 | 1977.9740 | 1995.9845 | 2306.1163 | 2180.0945 | 2162.0839 |
| 5 | 2472.2157 | 2490.2262 | 2800.3580 | 2674.3362 | 2656.3256 |
| 6 | 2966.4574 | 2984.4679 | 3294.5997 | 3168.5779 | 3150.5673 |
| 7 | 3460.6990 | 3478.7096 | 3788.8413 | 3662.8195 | 3644.8090 |
| 8 | 3954.9407 | 3972.9513 | 4283.0830 | 4157.0612 | 4139.0507 |
| Na+ Doped | |||||
| 1 | 517.2309 | 535.2414 | 845.3732 | 719.3514 | 701.3408 |
| 2 | 1011.4725 | 1029.4831 | 1339.6149 | 1213.5331 | 1195.5825 |
| 3 | 1505.7142 | 1523.7248 | 1833.8565 | 1707.8347 | 1689.8242 |
| 4 | 1999.9559 | 2017.9665 | 2328.0982 | 2202.0764 | 2184.0659 |
| 5 | 2494.1976 | 2512.2082 | 2822.3399 | 2696.3181 | 2678.3076 |
| 6 | 2988.4393 | 3006.4499 | 3316.5816 | 3190.5598 | 3172.5492 |
| 7 | 3482.6810 | 3500.6915 | 3810.8233 | 3684.8015 | 3666.7909 |
| 8 | 3976.9227 | 3994.9332 | 4305.0650 | 4179.0432 | 4161.0326 |
These samples were partially soluble in DMSO in the preparation step, leading to a pronounced signal/noise ratio. The same type of adducts as with the Ip family was observed.
The repeating unit 494 Da revealed the major presence of the Lc-type structure, alternating with the La type. C and Lb were in the minority. The cyclic anhydride-type structure C′, originating from Lc dehydration, is also present, with higher intensities for Im and Id moieties (Fig. 8). For these samples, adducts ionised with K+ were also observed.
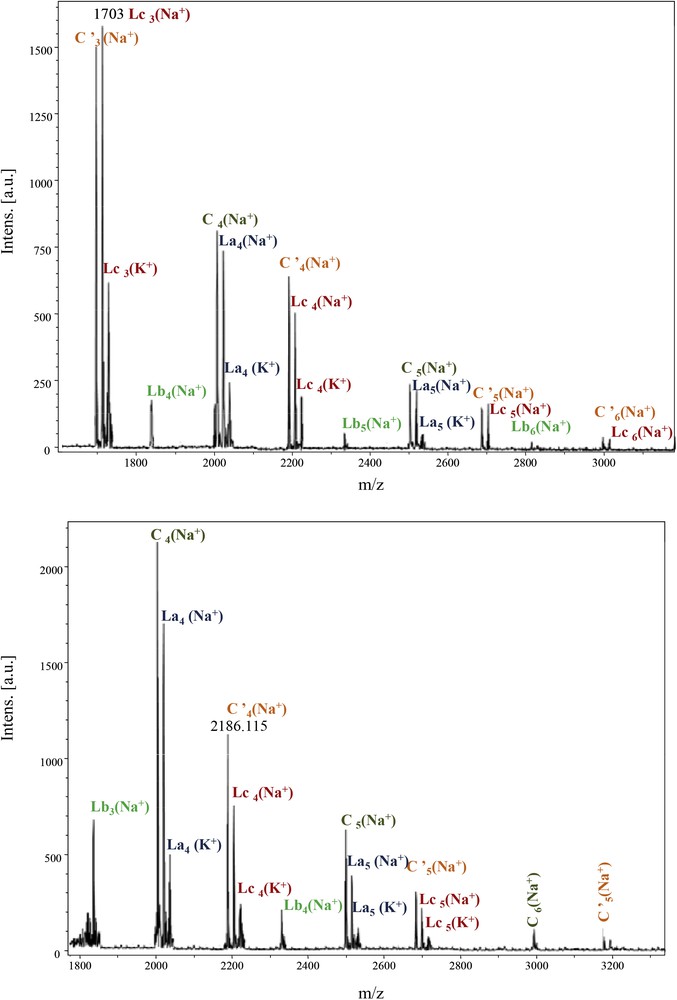
MALDI–ToF spectra of PeA_Im_Seb and PeA_Id_Seb (1800–3500 Da).
3.4.3 NMR studies
NMR investigations allowed us to determine and attribute all signals. Comparing 1H NMR spectra of PeA originating from three dianhydrohexitols in the Seb family prompted us to several findings (Fig. 9):
- • the signal at 9.75 ppm confirms the formation of a new amide bond (–NHCO–);
- • nevertheless, the appearance of a doublet clearly indicates that the starting diamine corresponds to the isosorbide moiety. The enlargement of the area from 6 to 10 ppm shows the same bond as a singlet for polymers starting from the two other isomers. This observation confirms that no epimerisation took place during the synthesis process.
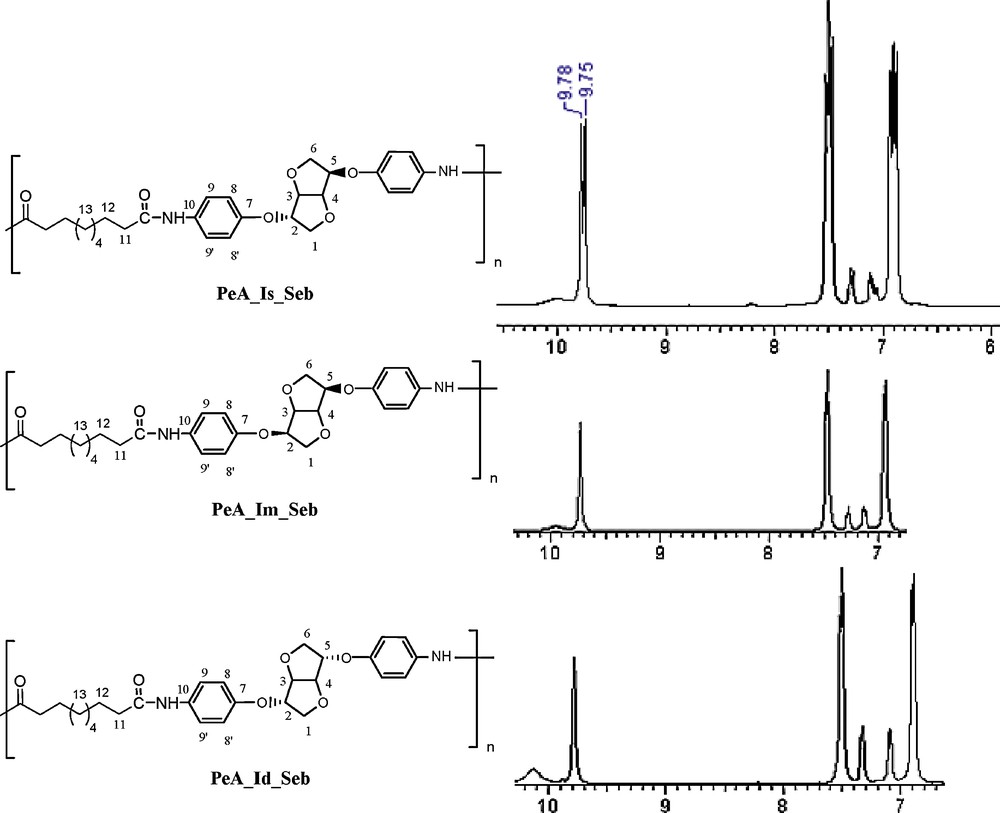
Comparison of 13C NMR spectra from the PeA_Seb family (DMSO D6).
In order to investigate and confirm the predominant existing structures, i.e. Lc, an NMR study of the PeA_Is_Seb sample was considered (Fig. 10).
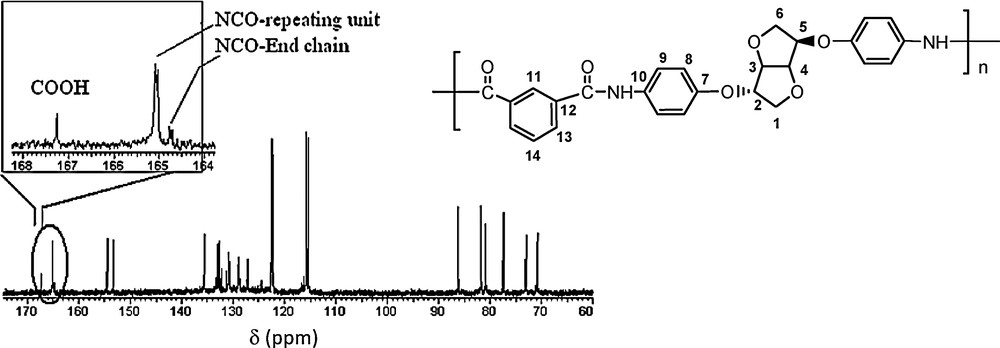
13C NMR spectrum of PeA_Is_Ip (DMSO D6).
The absence of an additional small signal related to the Is moiety in the aliphatic zone confirms the absence of Lb-type structures.
In the aromatic zone, the isophtaloyl typical signals are represented by four carbon types. Additional signals of small intensity related to the isophtalic moiety end-chain confirm the Lc-type structure. The NCO bond signal (165 ppm) exhibits a slight split due to Is stereochemistry. Careful observations in this region show the existence of an additional small intensity signal (164.7 ppm) proper to NCO functions as the split value remains the same. This observation supposes the existence of an end-chain different from the repeating unit, inducing a different behaviour on the terminal NCO function. An additional singlet (167.3 ppm), potentially of carbonyl type, could be attributed to the carboxylic end-chain type, in concordance with the Lc-type structure.
4 Conclusion
In conclusion, we were able to improve the synthesis process of diamines based on 1,4-3,6-dianhydrohexitols and extend the latter to unpublished isomannide and isoidide isomers. The process involved a first solvent-free SNAr step followed by reduction and isolation of the product by crystallization. These diamines were reacted with diacyl chlorides moieties at room temperature in NMP to obtain biosourced polyether-amides. Isophtaloyl and biosourced sebacoyl chlorides were chosen as diacyl chlorides. We investigated the influence of the dianhydrohexitol moieties as well as of the diacyl moieties on the thermal performances and on the structure type of the polyether-amides as well. The first results showed that the best viscosity values were obtained for the isosorbide moiety for both diacyl chlorides, the highest value being obtained with isophtaloyl. The same trend is observed for Tg, as the highest value was observed for PeA_Is_Ip (isosorbide moiety with isophtaloyl chloride). These results are in agreement with economical expectations, isosorbide being the most commercially available diol. It is worth noting that these thermal performances were similar to those obtained in previous polyamide synthesis in high-temperature conditions.
MALDI–ToF mass spectrometry in association with NMR spectroscopy allowed us to identify the nature of the structures obtained and of the end-chain moieties.
5 Supplementary data
5.1 Dinitro compounds description
5.1.1 1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-2,5-di-O-(4-nitrophenyl)-d-sorbitol (2a): 65%
1H NMR: (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 4.03–4,18 (m, 4H, H1 + H6); 4.65–4.66 (d, J = 5 Hz, 1H,H3,), 4.90–4.94 (m, 2H, H2 + H5); 5.08–5.10 (m, 1H, H4.); 7.02 (d, J = 10 Hz,2H, H8,); 7.04 (d, 15 Hz, 2H, H8,); 8.21(d, J = 5 Hz, 2H, H9); 8.23 (d, J = 5 Hz, 2H, H9). 13C NMR: (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 71.8 (C6); 73.3 (C1); 77.9 (C5); 81.6 (C4); 81.9 (C2); 86.2 (C3); 115.1 (C8); 115.2 (C8); 125.9 (C9); 126.1 (C9); 142.2 (C10); 161.8 (C7); 162.8 (C7). ATR–FTIR: δ (cm−1): 744, 849, 1103, 1244, 1331, 1496, 1587; 2874, 3075.
5.1.2 1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-2,5-di-O-(4-nitrophenyl)-d-mannitol (2b): 65%
1H NMR: (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 4.09–4.13 (m, 4H, H1 + H6), 4.88–4.90 (m, 2H, H2 + H5); 4.94–4.95 (m, 2H, H3+ H4). 7.05 (d, J = 5 Hz, 4H, H8,), 8.22 (d, J = 5 Hz, 4H, H9,). 13C NMR: (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 71.6 (C1C6); 77.6 (C2C5); 80.9 (C3C4); 115.1 (C8); 125.9 (C9); 142.1(C10); 162.7 (C7). ATR–FTIR: δ (cm−1): 744, 849, 1103, 1244, 1331, 1496, 1587; 2874, 3075.
5.1.3 1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-2,5-di-O-(4-nitrophenyl)-d-iditol (2c): 88 %
1H NMR: (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 4.13–4.25 (m, 4H, H1 + H6); 4.80 (m, 2H, H3 + H4); 4.94 (m, 2H, H2 + H5); 7.02 (d, J = 10 Hz, 4H, H8); 8.22(d, J = 10 Hz, 4H, H9). 13C NMR:(125 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 72.2 (C1C6); 81.6 (C2C5), 85.7 (C3C4); 115.2 (C8); 126.0 (C9); 142.2 (C10); 161.7 (C7). ATR–FTIR: δ (cm−1): 744, 849, 1103, 1244, 1331, 1496, 1587; 2874, 3075.
5.2 Diamino compounds description
5.2.1 4,4′-(Diamino)-1,4:3,6-dianhydro-2,5-di-O-phenyl-d-sorbitol (DA-Is): 75%
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3 D6): δ (ppm): 3.42 (brs,4H,NH2); 4.11–4.17 (m, 4H,H1 + H6); 4.60–4.69 (m,2H,H3 + H5), 4.71–4.71 (m,1H, H2); 4.86–4.88 (m, 1H, H4); 6.62–6.65 (m,4H, H9); 6.75–6.85 (m,4H, H8). 13C NMR (50 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 69.8 (C6); 72.7 (C1); 77.9 (C5); 80.0 (C4); 82.1 (C2); 85.6 (C3); 114.8 (C9); 114.9 (C9); 116.3 (C8); 116.6 (C8); 142.8 (C10); 143.1 (C10); 147.6 (C7); 149.0 (C7). ATR–FTIR: δ (cm−1): 719, 824, 1094, 1224, 1502, 2896, 3373.
5.2.2 4,4′-(Diamino)-1,4:3,6-dianhydro-2,5-di-O-phenyl-d-mannitol (DA-Im): 58%
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3 D6): δ (ppm): 3.46 (brs,4H,NH2); 3.94–4.12 (m, 2H, H1); 4.15–4.20 (m, 2H, H6); 4.62–4.66 (m, 2H, H2 + H5); 4.74–4.75 (m, 2H, H3 + H4); 6.60–6.65 (m,4H, H9), 6.81–6.86 (m,4H, H8). 13C NMR (50 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 70.3 (CC6); 78.1 (C2C5); 80.0 (C4C3); 114.7 (C9); 116.3 (C8); 142.8 (C10); 149.0 (C7). ATR–FTIR: δ (cm−1): 719, 824, 1094, 1224, 1502, 2896, 3373.
5.2.3 4,4′-(Diamino)-1,4:3,6-dianhydro-2,5-di-O-phenyl-d-iditol (DA-Id): 68%
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3 D6): δ (ppm): 3.43 (brs, 4H,NH2); 4.04–4.05 (d, J = 20 Hz, 4H, H1 + H6,); 4.69–4.72 (t, J = 20 Hz, 2H, H2 + H5,); 4.78(s, 2H, H3 + H4); 6.61–6.65 (m, 4H, H9); 6.74–6.79 (m, 4H, H8). 13C NMR (50 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm): 71.5 (C16); 81.6 (C25); 85.1 (C43); 114.9 (C9); 116.7 (C8); 143.2 (C10); 147.6 (C7). ATR–FTIR: δ (cm−1): 719, 824, 1094, 1224, 1502, 2896, 3373.
5.3 Polyether-amides description
5.3.1 PeA_Is_Ip: 93%
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm): 3.83–3.87 (m, 1H, H1); 3.93–3.96 (m, 1H, H6); 4.03–4.07 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.60 (d, J = 4 Hz, 1H, H3); 4.91(m, 2H, H2 + H5); 5.01 (m,1H, H4); 6.99–7.06 (m, 4H, H9); 7.66–7.76 (m, 5H, H8 + H14); 8.13 (d, J = 7.07 Hz, 2H, H13); 8.55 (s, 1H, H11); 10.4 (s, 2H, NHCO). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm) 70.5 (C6); 72.7 (C1); 77.1 (C5); 80.6 (C4); 81.5 (C2); 85.8 (C3); 115.1 (C8); 115.4 (C8); 121.9 (C9); 122.1 (C9); 126.9 (C14); 128.6 (C13); 130.5 (C12); 132.5 (C10); 132.9 (C10); 135.2 (C11); 153.0(C7); 154.2 (C7); 164.7 (NCO); 164.8 (NCO); 166.9 (COOH). ATR–FTIR: δ (cm−1): 826, 1090, 1229, 1509, 1652, 3295.
5.3.2 PeA_Im_Ip: 89%
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm): 3.81 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.07 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.88 (brs, 4H, H3 + H4, H2 + H5); 7.05 (m, 1H, H9); 7.66–7.76 (m, 5H, H8 + H14); 8.14–8.16 (m, 2H, H13); 8.61 (m, 1H, H11); 10.42 (s, 2H, NHCO). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm) 70.6 (C1C6); 77.0 (C2C5); 80.2 (C3C4); 115.1 (C8); 121.9 (C9); 126.1 (C14); 128.6 (C13); 131.1 (C12); 132.5 (C10); 135.2 (C11); 154.2 (C7); 164.7 (NCO); 166.9 (COOH).
5.3.3 PeA_Id_Ip: 91%
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm): 3.95–3.98 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.08–4.11 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.72 (brs, 2H, H3 + H4); 4.93 (brs, 2H, H2 + H5); 7.02 (d, J = 8.59 Hz, 4H, H9); 7.65–7.70 (m, 1H, H14); 7.78 (d, J = 8.59 Hz, 4H, H8); 8.14 (d, J = 8.59 Hz,2H, H13); 8.60 (s, 1H, H11); 10.45 (s, 2H, NHCO). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm) 71.6 (C1C6); 81.0 (C2C5); 85.3 (C3C4); 115.5 (C8); 122.0 (C9); 126.8 (C14); 128.6 (C13); 130.6 (C12); 133.0 (C10); 135.1 (C11); 152.9 (C7); 164.7 (NCO); 166.9 (COOH).
5.3.4 PeA_Is_Seb: 98%
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm): 1.28 (bsr, 8H, H13); 1.56 (brs, 4H, H12); 2.14–2.27 (m, 4H, H11); 3.76–3.79 (m, 1H, H1); 3.86–3.89 (m, 1H, H6); 3.97–4.00 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.53 (m, 1H, H3); 4.81 (brs, 2H, H2 + H5); 4.92 (brs, 1H, H4); 6.89 (d, J = 8.59 Hz, 2H, H9); 6.90 d, J = 8.34 Hz, 2H, H9); 7.47(d, J = 8.84 Hz, 2H, H8); 7.48 (d, J = 8.84 Hz, 2H, H8); 9.75 (d, J = 13.39 Hz, 2H, NHCO). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm) 25.2 (C13); 33.7 (C12); 36.8 (C11); 70.3 (C6); 72.6 (C1); 77.1 (C2); 80.4 (C4); 81.4 (C5); 85.7 (C3); 115.0 (C8); 115.4 (C8); 120.4 C9); 120.7 (C9); 132.9 (C10); 133.3 (C10); 152.2 (C7); 153.4 (C7); 170.8 (NCO); 174.6 (COOH). ATR–FTIR: δ (cm−1): 825, 969,1090, 1224, 1504, 1653, 2360, 2855, 2924, 3281.
5.3.5 PeA_Im_Seb: 88%
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm): 1.28 (brs, 8H, H13); 1.56 (brs, 4H, H12); 2.24 (m, 4H, H11); 3.70–3.72 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.00 (brs, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.79 (brs, 4H, H2 + H3 + H4 + H5); 6.93 (d, J = 8.08 Hz, 4H, H9); 7.47 (d, J = 8.08 Hz, 4H, H8); 9.72 (s, 1H, NHCO). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm) 25.1 (C13); 33.6 (C12); 36.2 (C11); 70.5 (C1C6); 77.1 (C2C5); 80.1 (C3C4); 115.1 (C8); 120.5 (C9); 132.8 (C10); 153.5 (C7); 170.8 (NCO); 174.1 (COOH).
5.3.6 PeA_Id_Seb: 93%
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm): 1.28 (brs, 8H, H13); 1.56 (brs, 4H, H12); 2.15–2.24 (m, 4H, H11); 3.88–3.92 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.02–4.04 (m, 2H, H1 + H6); 4.65 (m, 2H, H3 + H4); 4.84 (brs, 2H, H2 + H5); 6.89 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, H9); 6.9 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, H9); 7.5 (d, J = 8 Hz, 4H, H8); 9.77 (s, 1H, NHCO). 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO D6): δ (ppm) 25.2(C13); 33.7 (C12); 36.3 (C11); 71.0 (C6C1); 80.9 (C2C5); 85.2 (C3C4); 115.5 (C8); 120.6 (C9); 133.3 (C10); 152.1 (C7); 170.8 (NCO); 173.8 (COOH).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Societé Roquette Frères (Lestrem, France) for a kind gift of isosorbide (isomannide and isoidide) and to the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Research for Financial support. The authors want to thanks all INRAP staff for analysis and helpful discussions and Marie Hangouet (SCA France) for the DSC measurements.


