1 Introduction
Metal–carbon σ-bond is apparently the most important bond in organometallic compounds since so many metal-mediated organic syntheses involve steps of forming and breaking of metal–carbon bonds, and numerous well-known catalytic reactions by metal complexes usually include key intermediates having metal–carbon bonds. Among metal–carbon σ-bond containing compounds, metal-unsaturated hydrocarbyls draw more attention due to their applicability to diverse organic synthesis than metal-saturated hydrocarbyls. We have prepared, from reactions of alkynes with iridium, a variety of metal-unsaturated hydrocarbyls containing (i) three, four and five metal–carbon σ-bonds, (ii) all of sp, sp2 and sp3 carbons bound to one metal, and (iii) nitrogen, phosphorus and arsenic ylide ligands [1–7]. In this account, we summarize our recent works on the formation of iridium–carbon σ-bonds from reactions of alkynes with iridium producing a variety of iridium-unsaturated hydrocarbyls and the formation of new C–C bonds between the neighboring hydrocarbyl ligands to produce interesting unsaturated organic compounds.
2 Iridium-alkynyls
2.1 Oxidative addition of terminal alkynes: hydrido-alkynyl-iridium
Terminal alkynes are oxidatively added to four coordinated iridium(I) to give six coordinated cis-hydrido-alkynyl-iridium(III) (1) that are stable in general (Eq. (1)) [8,9].
Metal-alkynyls have drawn much attention [10–12] since they are probably the key intermediates for metal-mediated oligomerization of alkynes that produces diverse forms of unsaturated oligomeric hydrocarbons such as cross-conjugated poly-olefin [3], poly-enynes [13,14], alkyne polymers [15] and aromatic compounds [14,16]. In the metal-mediated oligomerization of alkynes, metal-hydrido moiety M–H also plays important roles being involved in the insertion step of an alkyne into the M–C bond (M−H + RC≡CH → M−CH=CHR [3]) and the termination step to give products (M(H)R → M + RH). When these hydrido-alkynyl complexes (1) have a labile ligand such as RCN, they show catalytic activity for reactions of alkynes such as oligomerization to give dimeric en-ynes and cyclo-trimerization to give aromatics, and in the presence of H2 hydrogenation of alkynes to give cis-olefins and saturated hydrocarbons [17].
2.2 Alkynylation by substitution of labile ligand in the presence of base
Nitriles coordinated to late transition metals such as iridium(I, III) are so labile that they are readily replaced by alkynyl ligands in reactions of metal with alkynes in the presence of a base such as NEt3 (Eqs. (2)–(4)) [14,18,19]. Complexes 2 are somewhat unique compounds since they have only the unsaturated hydrocarbyl ligands and react with electrophiles to undergo the carbon–carbon bond forming reactions between the alkynyl and allyl ligands to produce conjugated dienes (see Eq. (7) [18]). Complexes 3 and 4 are also interesting compounds since they have three and four Ir–C σ-bonds for each metal and yet they are so stable that they do not undergo any intra-molecular C–C bond forming reactions by themselves unless a strong electrophilic reagent such as H+ is added (see Eq. (8) [4,19]).
Relatively inert ligands such as CO and X– (X = Cl, Br, I) are also effectively replaced with alkynyl ligands by using removing agents, Me3NO and Ag+, respectively (Eqs. (5) and (6)). Only one of the two CO ligands is substituted with an alkynyl group in high yields in the reactions of alkynes in the presence of Me3NO (Eq. (5)) [3] while both of halo ligands are effectively removed by Ag+ and replaced with alkynyl groups in the presence of an amine NEt3 (Eq. (6)) [20].
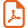
Complexes 5 and 6 are also interesting compounds as they have four Ir–C σ-bonds through the sp2 and sp3 carbons, and undergo the C–C bond forming reactions between the hydrocarbyl ligands in the presence of H+ (see Eqs. (9) and (10)).
2.3 Reactivity of alkynyl ligands
The β-carbon (Ir–C≡CR) of the alkynyl ligands of 2–6 readily reacts with electrophiles (E+) such as H+ and Me+ to make the α-carbon (Ir–C+=CER) of the resulting alkenyl ligand so electrophilic that it reacts with the nucleophilic carbon of a neighboring hydrocarbyl ligand to form a new C–C bond between hydrocarbyl ligands [3,4,12,18]. It has been well-known that the β-carbon of the alkynyl ligand is so nucleophilic that it is readily attacked by electrophiles [21].
Interesting unsaturated organic compounds such as conjugated polyenes (Eq. (7)) [18], polyen-ynes (Eq. (8)) [4], cross-conjugated olefins (Eq. (9)) [3] and cis-olefins (Eq. (10)) [22] may be selectively obtained in high yields.
3 Iridium-alkenyls
3.1 Oxidative coupling of terminal alkynes: iridacyclopentadienes
Terminal alkynes are added to [Ir(NCCH3)(CO)(PPh3)2]+ by oxidative coupling to give stable cis-bis(alkenyl) complexes 7 [23] in high yields and these irida-cyclopentadienes 7 further react with alkynes to give alkyne trimerization products, cis-dien-ynes (linear trimers) and aromatic compounds (cyclotrimers) (Eq. (11)) [4]. Metalla-cyclopentadienes have been known to be obtained from reactions of metals not only with terminal alkynes (RC≡CH) but also substituted alkynes (RC≡CR′) and they draw attentions as key intermediates for the metal-mediated cyclo-trimerization of alkynes to produce aromatic compounds [24,25].
3.2 Apparent insertion of alkynes into Ir–H, –C, –O, –N, –P, –As bonds
3.2.1 Insertion of alkynes into Ir–H and Ir–C bonds
cis-Bis(ethenyl)iridium (8) is produced from the 1,2-insertion reaction of acetylene into the Ir–H bonds of cis-dihydrido complex (7) and further undergoes another insertion of alkynes (1,1-insertion) into Ir–C bond to give another cis-bis(alkenyl) complex (9) (Eq. (12)) [3]. No insertion product, analogues of 8, has been obtained from reactions of 7 with substituted alkynes such as PhC≡CH. Reactions of 7 with excess PhC≡CH, instead, catalytically produce oligomers of PhC≡CH. While complex 8 has been isolated and stable in both solid state and in solution under N2, complex 9 has not been isolated yet but its formation is unambiguously supported by the products obtained from reactions of 8 with excess alkynes (RC≡CH) to give cross-conjugated tri-enes and tetra-enes (Eq. (13)) [3].
Tri-enes (CH2=CH–C(–CH=CH2)=CHR) are exclusively produced from reactions of RC≡CH with [Ir(–CH=CH2)2(CO)2L2]+ obtained by replacing CH3CN of 8 with CO [3]. Complex 8 undergoes the C–C coupling reactions between the two ethenyl ligands to give 1,3-butadiene at elevated temperature or in the presence of alkynes and NEt3 [3].
3.2.2 Insertion of alkynes into Ir–O bond
Acetylene is inserted into the Ir–O bond of the η2-acetato-alkyl-carbonyl complex (10) through the same carbon (i.e. 1,1-insertion) to give the alkyl-carbonyl irida-cycle (11) of η2-vinylacetato ligand (Eq. (14a)) while unknown complex(es) have been obtained from reactions of PhC≡CH with 10. Substituted alkynes (PhC≡CH) could also be inserted into the Ir–O bond only after the two trans ligands (R and CO) to the η2-acetato ligand of 10 are replaced with two alkynyl ligands (Eq. (14b)) [26].
3.2.3 Insertion of alkynes into Ir–N, –P, –As bonds
There have been a number of reports for phosphorus ylide complexes (for example, M–CR=CR′-PPh3) [27–30] while nitrogen and arsenic ylide complexes had been rarely reported except the recent works of ours [19,23]. Apparent insertion of alkynes into the Ir–B (B = NMe3, PPh3, AsPh3) bonds occurs to give iridium complexes of nitrogen, phosphorus and arsenic ylides (Eq. (15)) [19,23,31]. These ylide compounds are prepared from reactions of Ir–NCR complexes with alkynes in the presence of B. Phosphorus ylides are also prepared from reactions of Ir–PPh3 complexes with alkynes in the absence of excess PPh3 in relatively high yields. We recently succeeded in preparing iridium complexes having three hydrocabyl ligands (13 [Ir(CH3)(–CH=CH–NEt3)(–C≡CR)(CO)(PPh3)2]+), each of which is bound to the metal through σ-bond of sp3, sp2 and sp carbon, respectively [22]. Complexes 13 are the first examples of metal complexes having alkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl ligands. It is interesting that nitrogen ylides of conjugated dienes ([trans,cis-Et3N–CH=CH=CHR]+) are separated from the metal by the proton-initiated C–C bond forming reactions between the three sp3 (alkyl), sp2 (alkenyl) and sp (alkynyl) carbons of the three hydrocarbyl ligands of 13 [22].
4 Iridium-carbenes
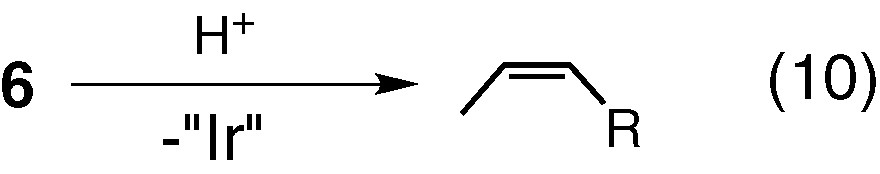
Metal-carbenes (vinylidenes) are frequently found and suggested as the early products during reactions of alkynes with metals [32–34] and Fisher-type metal-carbenes are produced from reactions of alkynes with metals in the presence of alcohols [35,36]. Iridium-alkoxycarbenes (14, 15) are formed from reactions of alkynes in presence of alcohols or yn-ols (Eq. (16)) [6]. Formation of both metal-carbenes 14 and 15 is accompanied by CO insertion into Ir–R bond to provide vacant site for the carbene ligands. Metal vinylidenes (Ir=C=CH2, Ir=C=CH–CH–CH–OH) are the probable initial intermediates that are attacked by the alcoholic oxygen on the carbene carbon to produce the alkoxycarbenes as previously suggested [6]. Reactivity of these iridium-carbenes is currently under investigation.
5 Alkyl-carbonyl-iridium from reactions with alkynes and water
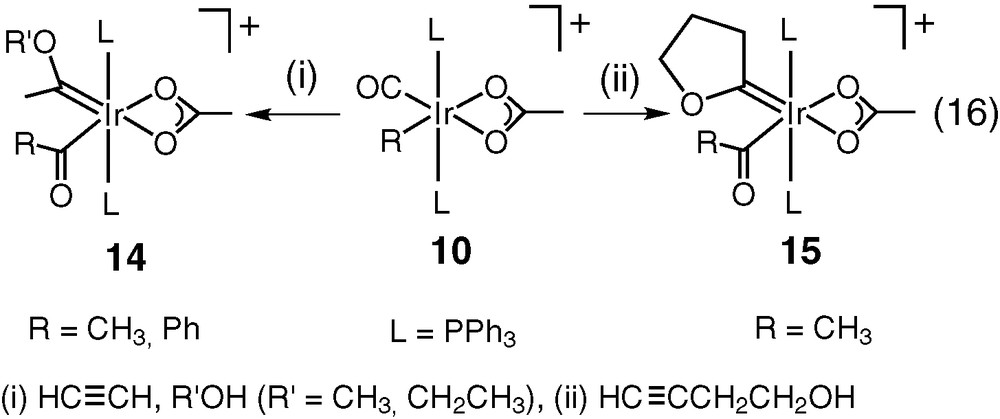
Alkyl-carbonyl complexes, M(–CH2R)(CO) are obtained from reactions of metal with alkynes (RC≡CH) in the presence of H2O [37–40]. Plausible mechanisms involves the attack of H2O on the α-carbon of the alkynyl ligand to give the acyl group (M–C≡CR + H2O → M–C(OH)=CHR → M–COCH2R) followed by the CO de-insertion (M–COCH2R → M(–CH2R)(CO)) [37–40]. We recently observed that a water-soluble η5-Cp*IrCl2(PAr3) (16, Cp* = C5Me5–; PAr3 = P(m-C6H4SO3Na)3) reacts with alkynes in H2O to give water-soluble alkyl-carbonyl-iridium complexes 17 (Eq. (17)) [41].
While no reaction is observed between 16 and olefins such as CH2=CH2 in H2O, the reaction readily occurs to give water-soluble [Cp*(PAr3)Ir(CH3)(CO)]+ when Ag+ is added to the reaction mixture of 16 and CH2=CH2 in H2O to produce in situ [η5-Cp*Ir(PAr3)(OH2)2]2+ [22]. It has not been well understood yet how the elimination of Cl– ligands from 16 makes the reaction with CH2=CH2 to occur while it is not necessary for complex 16 to be reactive with alkynes (Eq. (17)). We found that the water-soluble 16 dissociates Cl– ligand in H2O to some extent while the dissociation of Cl– ligand has not been reported for Cp*IrCl2(Ph3P) that is not water-soluble and does not react with alkynes and olefins at all.
6 Concluding remarks
A variety of hydrocarbyl-iridium complexes such as iridium-alkyls, -alkenyls, -alkynyls and -carbenes can be prepared from reactions with alkynes under appropriate conditions. Various types of conjugated poly-enes and poly-en-ynes can be prepared by the carbon–carbon coupling reactions between neighboring unsaturated hydrocarbyl ligands. Further investigation should be carried out to make these stoichiometric reactions above to occur catalytically.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Korea Research Foundation (KRF) for their financial support of this study through the Basic Science Research Institute program (Grant No. KRF-2003-015-C00332).